1 Laboratory of Transmembrane Signaling, Institute of Biophysics and Biomedical Engineering, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, 1113 Sofia, Bulgaria
2 Institute of Biology and Immunology of Reproduction “Acad. Kiril Bratanov'', Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, 1113 Sofia, Bulgaria
Abstract
Background: Common butterbur (Petasites hybridus L.)
is a traditional medicinal plant with numerous therapeutic properties among which
is its recently uncovered anti-tumor activity. The present study aims to examine
the activity of a standardized Bulgarian Petasites hybridus L. root
extract, containing the active ingredients petasins, on the human breast cancer
cell line MDA-MB-231 and non-cancerous MCF-10A cells. Specifically, we examined
cell death, oxidative stress, and nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
- Petasites hybridus L.
- petasins
- apoptosis
- oxidative stress
- NF-κB
- anticancer effects
Despite current progress in cancer treatment, breast cancer death rates continue to increase each year in women worldwide [1]. The severe toxicity and multidrug resistance (MDR) of conventional chemotherapeutics remain significant challenges in the treatment of this disease. Hence, efforts need to focus on finding effective treatment strategies with minimized side effects on healthy cells and tissues. A number of investigations regarding the use of natural products and herbal extracts as anti-tumor therapeutics have increased in the last years due to favorable safety profiles and the possibility for long-term patient treatment.
The common butterbur (Petasites hybridus L.) is a medicinal plant of the Asteraceae family and has been used in traditional medicine for the treatment of a wide variety of medical conditions, including migraine, hypertension, bronchial asthma, and allergic rhinitis. This herb is primarily distributed in Europe, as well as in some regions of North America and Asia [2, 3, 4]. Different parts of the plant contain bioactive compounds with anti-inflammatory, spasmolytic, and antioxidant properties. The therapeutic effects of butterbur are principally due to secondary metabolites, primarily sesquiterpenes known as petasins, which are esters of petasol and angelic acid [5, 6]. The concentration of petasins and their derivatives, specifically isopetasin, neopetasin, S-petasin, iso-S-petasin, neo-S-petasin, varies but is generally higher in the plant’s rhizomes and roots. In addition to sesquiterpene esters, the rhizome and roots also contain toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs). For this reason, extracts prepared from the plant for medicinal use must be free of PAs [2, 6]. At present, the petasins are commercially available as dietary supplements for the prevention and treatment of migraine and allergic rhinitis [7, 8, 9]. It has been proposed that the mechanisms by which petasins exert anti-migraine and antiallergic effects are mediated by their anti-inflammatory activity and inhibition of leukotriene synthesis. However, calcium channel blockage by petasins stems from their spasmolytic potential and may also explain their anti-migraine action [10, 11]. Although the exact modes of action of butterbur’s compounds remain elusive, their efficacy and favorable tolerance have been extensively documented [7, 8, 10]. In addition, petasins have shown efficacy against cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and urogenital disorders and might be beneficial for the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases as well [2, 11].
Recently, it was demonstrated that petasins and their derivates, isolated from different Petasites species, also exert anti-tumor activity. In vitro and some in vivo studies have shown strong antiproliferative activities of these bioactive substances towards various types of human cancers [12, 13, 14, 15, 16]. A new benzofuran derivative isolated from P. hybridus roots showed moderate inhibitory activity on human breast cancer MCF-7 cell proliferation [17, 18]. Guo et al. [12] found that S-petasin from Petasites japonicus inhibited proliferation and migration of the human melanoma cell line A375, and induced apoptosis activating the tumor suppressor p53. Similarly, significant anti-tumor effects of petasin have been reported when different colorectal cancer cell lines were used. Furthermore, the authors of this study have also confirmed these effects in a murine colorectal tumor model showing reduced tumor growth. Moreover, findings suggested that petasin inhibited the Akt/mTOR signaling axis [13]. Another study revealed that exposure to S-petasin and iso-S-petasin isolated from common butterbur elicits high cytotoxicity and apoptotic cell death responses through caspase activation and cytochrome c release in prostate cancer cells [14]. Further, isopetasin and S-isopetasin extracted from Petasites formosanus have been shown to act as MDR inhibitors by targeting P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and suppressing the proliferation of multidrug-resistant cancer cells [15]. Our previous findings indicate that standardized Petasites hybridus L. root extract, with the active ingredient petasin and its derivatives, showed a selective cytotoxic effect towards non-invasive MCF-7 and highly invasive MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. These studies documented that MDA-MB-231 cells display an approximate two-fold higher sensitivity to this root extract [16]. However, the mechanisms that underlie the anti-breast cancer activities of sesquiterpene esters remain to be elucidated.
The aim of this study was to reveal the role of Bulgarian Petasites hybridus L. root extract on the induction of apoptosis, necrosis, oxidative stress, and NF-
A standardized butterbur powered extract containing a minimum of 15% petasins manufactured by Rumex Ltd., Sofia, Bulgaria (batch #321010) was used. The lipophilic extract was prepared from the subterranean portion of the plant, formally known as the radix petasitidis, from Bulgarian populations of Petasites hybridus L. These plant portions were extracted by maceration in ethanol, followed by liquid-liquid extraction with a more selective extractant. The crude extract was subjected to a final treatment in an aqueous medium pH value
To prepare samples for High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis of petasins, the mobile phase was used as a solvent. Analysis was performed on HPLC system Waters Alliance e2695 Separations Module with 4-channel degasser, Quaternary HPLC Pump, Autosampler with 100 µL loop, column thermostat and UV-VIS detector Waters 2998 PDA (Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA). The analysis was performed on a Venusil XBP C 18 column (250 mm
For biochemical assays, the powdered extract was dissolved in fresh cell culture medium containing 2% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) which was used as a solvent. The solution was filtered using 0.45 µm syringe filter prior to use. The final concentration of DMSO in the samples with different concentrations of Petasites extract was approximately 1%, which was shown to be completely non-toxic [16].
The human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 and the non-transformed mammary epithelial cell line (MCF-10A) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). The MDA-MB-231 cell line was cultured in complete Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), L-glutamine (2 mM) and Penicillin (100 U/mL)/Streptomycin (100 µg/mL)/Amphotericin B (0.25 µg/mL). The MCF-10A cell line was cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium/Nutrient Mixture F-12 (Sigma-Aldrich, USA), additionally supplemented with insulin (10 µg/mL), hydrocortisone (500 µg/mL), hEGF (20 ng/mL) and cholera toxin (20 ng/mL). Both cell lines were cultured in 37 °C and 5% CO
Human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and non-cancerous MCF-10A cells were plated in 100 mm petri dishes and T-25 flasks at a density of 5
To evaluate the alterations in the redox balance and the occurrence of oxidative stress, the levels of glutathione (GSH) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were quantitatively estimated using cell lysates. The levels of GSH were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Cat. No MBS161025, MyBioSource, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm using a plate reader (Tecan Infinite F200 PRO (Tecan Austria GmbH, Salzburg, Austria)). MDA was measured colorimetrically by a thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TB ARS) assay (Cat. No 10009055, Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 530 nm using a plate reader (Tecan Infinite F200 PRO (Tecan Austria GmbH)).
The quantification of the p105 subunit of human NF-
All data in this study were analyzed using GraphPad Prism version 5.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). Values are expressed as the mean
The principal active substances in Petasites hybridus L. are esters of 3-isomeric sesquiterpene alcohols, specifically petasole, iso-petasole and neopetasole. Active substances also include six sesquiterpene esters, specifically petasin and its isomers iso-petasin and neopetasin, and the methylthio derivative of petasin, s-petasin and its isomers iso-s-petasin and neo-s-petasin [6]. HPLC analysis of the investigated extract from the subterranean parts of P. hybridus (Fig. 1) show the presence of all six main sesquiterpene components with neopetasin, petasin and s-petasin being the dominate compounds in this extract.
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.HPLC analysis of sesquiterpene esters isolated from standardized 15% petasin Petasites hybridus L. root extract. The graph shows the concentration of the principal sesquiterpene esters in the extract expressed in mg/g. This equals the total amount of 15% petasins isolated from the powdered Petasites hybridus L. extract. Neopetasin, petasin and s-petasin are presented in relatively higher quantities when compared to the other identified sesquiterpene esters.
To confirm and extend our previous findings demonstrating selective cytotoxicity and activation of apoptosis in breast cancer cells after exposure to Petasites hybridus L. root extract [16], cell death was further analyzed by Annexin V-APC/PI double stain flow cytometry. The stages of apoptosis and necrosis were monitored after treatment of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and non-cancerous MCF-10A cells with different concentrations of the root extract of Bulgarian Petasites hybridus L. for 72 h. These concentrations correspond to the IC
The two cell lines were treated with the same increasing concentrations of the root extract of Petasites hybridus L., specifically, 260.4 µg/mL, 520.8 µg/mL and 781.2 µg/mL [16] and we monitored the toxic effect in cancer and non-cancer cells. In MDA-MB-231 cells, the percentage of early apoptotic cells, Annexin V-APC positive/ PI- negative, was lower (4.41
 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Quantification of apoptosis in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and non-transformed MCF-10A cells by standardized Petasites hybridus L. root extract. (A) and (B) Representative flow cytometry plots of apoptosis/necrosis in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-10A cells, respectively. Cells were treated for 72 h with 260.4 µg/mL (IC
The population of necrotic cells, Annexin V-APC negative/PI positive, remained relatively low in both cell lines (2.51
Oxidative stress is a potent inducer of apoptotic cell death [22]. In addition, several plant-derived bioactive compounds have been found to exert pro-oxidant activity resulting in increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) and selectively inducing cell death in cancer cells due to their excess ROS [23, 24]. To test whether late apoptosis in breast cancer cells detected after treatment with Petasites hybridus L. extract was associated with an induction of oxidative stress, GSH and MDA were quantitatively measured as biomarkers of oxidative stress response. The reduced form of glutathione (GSH) is a major cellular antioxidant that neutralizes various forms of ROS, such as superoxide anion (O
As shown in Fig. 3A, ELISA analysis determined that cellular GSH levels were significantly decreased in a concentration-dependent manner in MDA-MB-231 cells in the presence of increasing doses (IC
 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.The effect of standardized Petasites hybridus L. root extract on GSH levels in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and non-cancerous MCF-10A cells. (A) and (B) GSH levels expressed as ng GSH/mg protein in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-10A after 72 h of treatment with 260.4 µg/mL (IC
To verify whether diminished GSH levels in MDA-MB-231 cells after exposure to Petasites hybridus L. root extract were related to a redox imbalance and induction of oxidative stress, the levels of MDA were also analyzed. As shown in Fig. 4A, MDA levels were slightly increased after exposure to the IC
 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.The effect of standardized Petasites hybridus L. root extract on MDA levels in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-10A cells. (A) and (B) MDA levels expressed as nmol MDA/mg protein in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-10A after treatment of both cell lines for 72 h with 260.4 µg/mL (IC
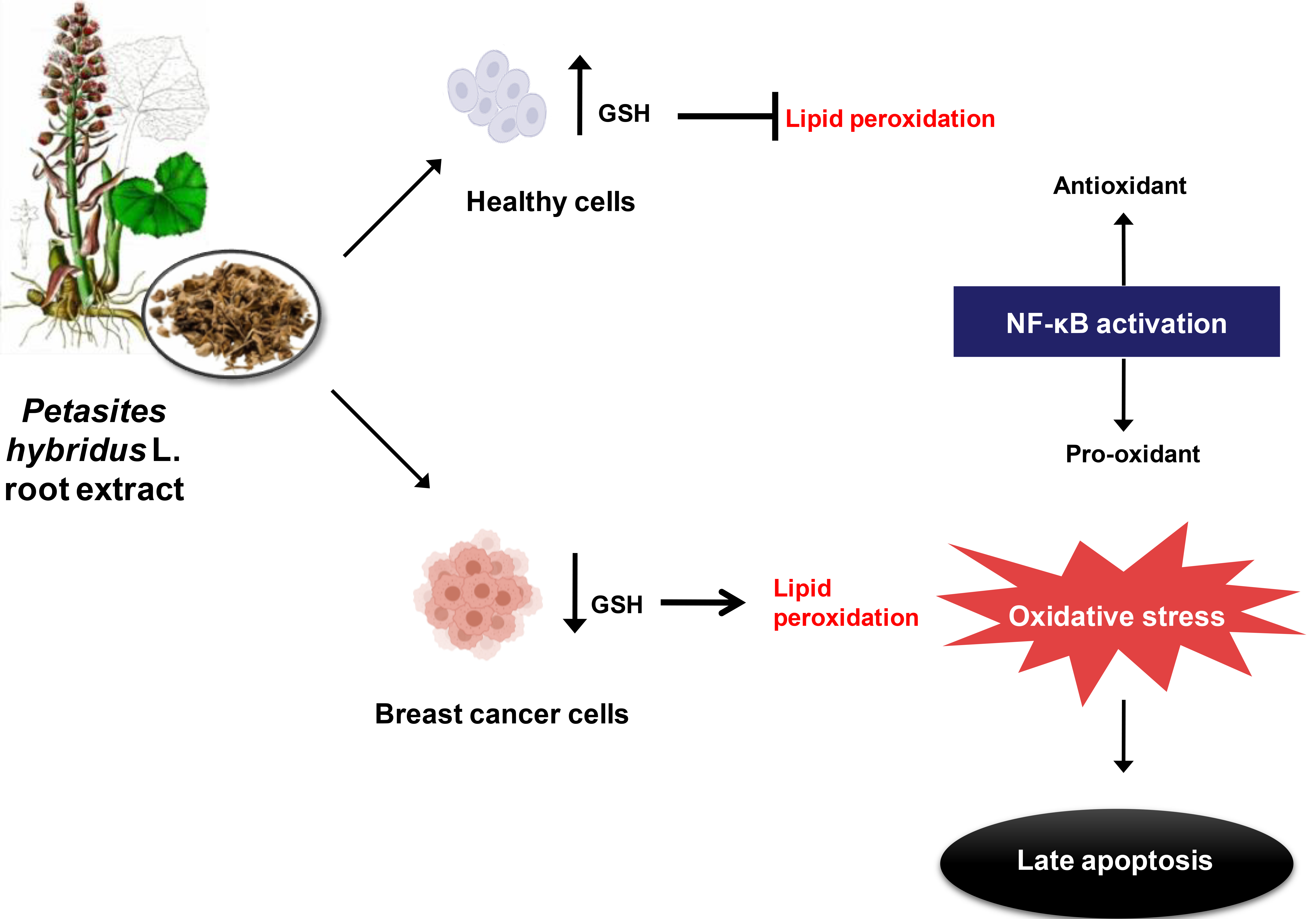
In sum, results obtained indicate that Petasites hybridus L. root extract acts as pro-oxidant, inducing oxidative stress specifically in MDA-MB-231 cells. In contrast, in non-cancerous MCF10A cells oxidative stress is alleviated due, in part, to a compensatory increase in the GSH antioxidant defense system. Therefore, these findings suggest that butterbur extract triggers a late apoptotic response in human breast cancer cells as result of oxidative stress, and this response is accompanied by increased lipid peroxidation and GSH depletion.
To further investigate the link between nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-
 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.The effect of standardized Petasites hybridus L. root extract on NF-
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of death among women worldwide and, despite recent advances in breast cancer therapy, the mortality rate continues to rise [1]. Thus, new alternative approaches, with non or low-toxic treatment regimens, need to be developed. One principal therapeutic strategy is targeting apoptosis specifically within cancer cells and without harming normal cell function [35]. Apoptosis is a tightly coordinated process which is essential for the development and homeostasis of multicellular organisms. This type of regulated cell death efficiently eliminates harmful, damaged and malignantly-transformed cells [20, 21]. In contrast to necrotic cell death, apoptosis does not cause inflammation in surrounding tissues, this feature makes induction of apoptosis in tumor cells a preferential cell response in cancer therapy. However, most currently used chemotherapeutics are highly toxic and induce apoptosis in both tumor and healthy cells causing systemic cellular injury.
Many plants and their bioactive compounds have long been the subject of study due to their multiple therapeutic properties. Such properties may make these compounds useful for the prevention and treatment of various diseases. Excluding toxic plant alkaloids that are currently used in cancer chemotherapy, the interest in herbal plant products with anti-proliferative activity and tolerability to normal cells has dramatically increased in recent years. A growing body of evidence indicates that different plant-derived compounds such as polyphenols, flavonoids, phytosterols, and terpenoids (sesquiterpenes), exert anti-tumor effects through modulating diverse signaling pathways associated with cancer cell growth and invasiveness and, primarily, selectively inducing apoptosis [36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41]. We previously demonstrated selective cytotoxic effects and morphological changes associates with apoptosis in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells after exposure to a standardized root extract of the medicinal plant Petasites hybridus L. with active sesquiterpenes termed petasins [16]. Common butterbur and its bioactive components are well-studied for treatment of migraine and other disorders, but their potential anti-tumor activity remains poorly investigated and available literature on this topic are quite limited [9].
Following the results of our previous work [16] which determined that the triple negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 displayed almost twice the sensitivity to common butterbur extract when compared to the MCF-7 cell line, in the present study we confirmed that standardized Bulgarian Petasites hybridus L. root extract triggered apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells after 72 hours of treatment. Moreover, Annexin V/PI flow cytometry showed that breast cancer cells were committed to late stages of apoptosis, whereas parallel treatment of non-cancerous MCF-10A cells displayed an early apoptotic response. Late stages of apoptosis are characterized by the formation of apoptotic bodies through a process dependent on activation of a class of proteases termed caspases. Caspase activation, in turn, commits the cell to a process of irreversible programmed cell death. In contrast, early apoptosis is a reversible process as studies have determined that early apoptotic cells can fully recover after the elimination of early apoptotic inducers [42, 43]. Moreover, the phagocytosis of early apoptotic cells trigger the processes of regeneration and angiogenesis at sites of tissue injury suggesting that early apoptotic cell uptake is anti-inflammatory in nature and induces a tolerogenic response [44]. Meanwhile, neither MDA-MB-231 nor MCF-10A cells underwent necrosis after exposure to various doses of the extract, indicating that common butterbur selectively kills breast cancer cells through activation of programmed cell death. Other studies showed induction of late stages of apoptosis via different biological mechanisms when various cancer cells were exposed to purified petasin or its derivates [12, 13, 14, 15]. Based on the findings outlined in this study, we propose that the pronounced pro-apoptotic effect of Petasites hybridus L. root extract on metastatic MDA-MB-231 is due to the presence of petasins.
A possible mechanism by which Petasites hybridus L. root extract induces apoptosis in cancer cells could be through increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Under normal physiological conditions, ROS play an essential role in cellular metabolism and homeostasis. ROS levels are strictly regulated by the endogenous antioxidant defense system which principally comprised of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione (GSH). Excessive ROS formation impairs redox homeostasis and leads to the occurrence of oxidative stress which is harmful to cellular macromolecules such as proteins, lipids, and DNA [45, 46]. Typically, cancer cells display increased levels of ROS and, in order to maintain the redox homeostasis, they upregulate antioxidant defense systems. Several studies have demonstrated that ROS can induce cell proliferation [47], resistance to apoptosis [48], increased angiogenesis [49], and invasion and metastasis [50]. However, a further increase in ROS above certain thresholds stemming from either endogenous or exogenous sources disturbs redox balance in tumor cells resulting in oxidative stress [51, 52]. Oxidative stress may trigger apoptosis by activating the apoptosome protein complex which initiates the caspase cascade resulting in activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway [46]. It should be noted that pro-oxidant agents can increase cellular levels of ROS to cytotoxic levels, and thus this type of agent may induce selective killing of cancer cells and therefore be therapeutically useful [23]. Abdelfatah et al. [15] previously documented that sesquiterpenes from Petasites formosanus act as ROS generators and can trigger a predominantly late apoptotic response in multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Additionally, several other lines of evidence demonstrated that different plant-derived compounds selectively induce apoptosis in cancer cells by driving ROS accumulation and further promoting oxidative stress [53]. Beyond their antioxidant capacities, in certain circumstances, various plant-derived products can exhibit a pro-oxidant role [54, 55]. Accordingly, we showed that the standardized Petasites hybridus L. root extract disturbs the redox balance in MDA-MB-231 and promotes a state of oxidative stress as marked by enhanced MDA levels and depleted GSH levels. MDA, a common marker of oxidative stress, is an end-product of ROS and fatty acid interaction and results in lipid peroxidation and cell membrane damage [26]. GSH depletion is also indicative of oxidative stress [25] as this is the most abundant non-protein intracellular thiol and is commonly present in high (1–10 mM) concentrations. Reduced GSH abundance can have potential application as a marker for various human diseases [56].
The findings outlined in this study are consistent with previous literature regarding the selective pro-oxidant properties of other terpenoids and their ability to activate oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in cultured human cancer cells [21, 22, 57]. In addition, the pro-apoptotic transcription factor NF-
Studies conducted in rats have indicated increased NF-
Based on all these findings, which are in line with our study and that a pro-apoptotic role for NF-
In conclusion, our findings indicate that the Bulgarian standardized Petasites hybridus L. root extract induces oxidative stress and promotes a strong apoptotic response most likely, at least in part, as a result of elevated NF-
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conceptualization — RT and LM; Methodology — VU; Software — IG; Validation — SA, TO and IG; Formal analysis — TO; Investigation — SA; Resources — TO; Data curation — IG; Writing—original draft preparation — SA; writing—review and editing — RT; Visualization — IG; Supervision — RT; Project administration — LM; Funding acquisition — LM. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
This research was funded by the National Science Fund of Bulgaria, grant number KII-06-H21/12/2018.
This research was funded by BSF, grant number KII-06-H21/12/2018 and The APC was funded by KII-06-H21/12/2018.
Given her role as Guest Editor, Rumiana Tzoneva had no involvement in the peer-review of this article and has no access to information regarding its peer-review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to Amedeo Amedei. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.





