1 Laboratório de Genética Animal e Humana, Departamento de Genética, Ecologia e Evolução, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (UFMG), 31270-901 Belo Horizonte, Brazil
2 Centro das Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde, Universidade Federal do Oeste da Bahia (UFOB), 47810-047 Barreiras, Brazil
3 Centro de Pesquisas em Doenças Inflamatórias (CRID), Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto, Departamento de Farmacologia, Universidade de São Paulo (FMRP), 14049-900 Ribeirão Preto, Brazil
4 Laboratório de Bioquímica e Biologia Molecular, Instituto de Biotecnologia, Universidade Federal de Uberlândia (UFU), 38402-045 Uberlândia, Brazil
5 Biotério Central, Departamento de Medicina Veterinária, Universidade Federal de Lavras (UFLA), 37200-000 Lavras, Brazil
Abstract
Background: The motivations for and effects of ethanol consumption vary considerably among individuals, and as such, a significant proportion of the population is prone to substance abuse and its negative consequences in the physical, social, and psychological spheres. In a biological context, the characterization of these phenotypes provides clues for understanding the neurological complexity associated with ethanol abuse behavior. Therefore, the objective of this research was to characterize four ethanol preference phenotypes described in zebrafish: Light, Heavy, Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement. Methods: To do this, we evaluated the telomere length, mtDNA copy number using real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR), and the activity of these antioxidant enzymes: catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) in the brain, and the interactions between these biomarkers. Changes observed in these parameters were associated with ethanol consumption and alcohol abuse. Results: The Heavy, Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement phenotypes showed ethanol preference. This was particularly the case with the Inflexible phenotype, which was the group with the greatest ethanol preference. These three phenotypes showed telomere shortening as well as high SOD/CAT and/or GPx activities, while the Heavy phenotype also showed an increase in the mtDNA copy number. However, the Light phenotype, containing individuals without ethanol preference, did not demonstrate any changes in the analyzed parameters even after being exposed to the drug. Additionally, the PCA analysis showed a tendency to cluster the Light and Control groups differently from the other ethanol preference phenotypes. There was also a negative correlation between the results of the relative telomere length and SOD and CAT activity, providing further evidence of the biological relationship between these parameters. Conclusions: Our results showed differential molecular and biochemistry patterns in individuals with ethanol preference, suggesting that the molecular and biochemical basis of alcohol abuse behavior extends beyond its harmful physiological effects, but rather is correlated with preference phenotypes.
Keywords
- telomeres
- antioxidant enzymes
- mtDNA
- zebrafish
- ethanol preference
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a chronic condition with behavioral, physiologic, and socioeconomic aspects, characterized by compulsive alcohol intake [1]. In humans, there are varying established patterns of alcohol consumption: light drinking, heavy drinking, and AUD [2, 3]. Animal models have been developed to better understand the mechanisms of ethanol abuse influencing voluntary ethanol intake [4, 5, 6] as well as ethanol preference phenotypes [7, 8]. In the context of alcohol abuse, vulnerability to alcohol dependence is associated with biological, psychological, social, and environmental conditions. Evidence suggests that genomic instability and cell disorders, mainly related to telomere shortening, mitochondrial dysfunction, and alterations in the antioxidant system, are parameters associated with alcohol abuse [9, 10, 11, 12].
Aside from its role in accelerating physiological aging, alcohol abuse has been proposed as one of the factors responsible for telomere shortening, which may be a bidirectional relationship [13, 14, 15]. In a behavioral study, Kang et al. (2017) [10] suggested that impulsive election of alcohol consumption is associated with shorter telomere length. Other studies have also suggested that telomere shortening is associated with behavioral changes [16] and risk factors, such as exposure to stress and adversity in childhood, which are also linked with mental illness [17, 18, 19].
Telomere shortening is related to mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage [20, 21, 22]. Mitochondrial dysfunctions cause telomere shortening, while telomere damage can lead to biosynthesis reprogramming, mitochondrial dysfunctions, and increased oxidative stress [23]. Shortening telomeres below a certain critical length limits cell proliferation; and consequently has implications for oncogenesis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, liver cirrhosis, mental/cognitive disorders, depression, and drug abuse [24, 25, 26, 27, 28].
Mitochondria dysfunction is related to ethanol abuse and is heavily involved in the generation of oxidative stress [29], as it produces indiscriminate amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that may lead to oxidative cell damage [30]. In cellular respiration, mitochondria consume large amounts of molecular oxygen and contribute significantly to the production of ROS, and, at the same time, they are the main targets of oxidative damage [31]. The number of mitochondria may vary according to the cell energy demand, or in response to stressful conditions [32, 33]. The levels of antioxidants and pro-oxidants may play a role in this adjustment mechanism of mitochondrial mass or the number of mitochondrial DNA copies (mtDNA) in the cells [34]. Measurement of mtDNA content using real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) has been proposed as a method of identifying biomarkers in mitochondrial dysfunction studies [35]. Associated with behavior alterations, higher mtDNA copy numbers have been seen in individuals with major depression, depressive disorders, and anxiety [33]. High mtDNA copy numbers have also been found in the blood of people with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma associated with smoking and smokeless tobacco, betel quid chewing, and alcohol consumption [36].
Ethanol abuse promotes alterations in antioxidant enzyme activities, such as catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase, that contribute to oxidative stress, cellular disturbances, and damage [37, 38, 39]. The balance between ROS production and antioxidant defenses determines the degree of cellular oxidative stress [40]. Oxidative stress is also associated with ethanol-induced aggressive and suicidal behavior, and neuropsychiatric disorders such as Alzheimer’s, schizophrenia, depression, anxiety, and drug/alcohol abuse [41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46]. In the brain, oxidative stress induced by alcohol abuse is related to behavioral changes associated with addiction [47].
Mitochondrial dysfunction leads to increased mitochondrial biogenesis and produces indiscriminate amounts of ROS, which can cause oxidative cell damage, such as telomere shortening [48], causing a cyclic effect involving telomeric shortening, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. With this in mind, we aimed to evaluate these parameters in a behavioral change context using an ethanol preference protocol.
Many research models have been used to study the effects of alcohol abuse, often aiming to identify the molecular patterns related to changes in behavior and loss of control over ethanol consumption [49, 50, 51]. Research models that are based on behavioral studies and define ethanol preference suggest differential individual responses, indicating phenotypic distinctions in ethanol preference [7, 8].
To deepen the understanding of the relationship between behavioral phenotypes and molecular modulations related to ethanol preference, we established a protocol using zebrafish (Danio rerio) based on the Conditioned Place Preference test (CPP). We describe four phenotypes corresponding to ethanol preference in juvenile zebrafish (Light, Heavy, Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement) and found differential gene regulation in these groups associated with ethanol abuse (drd1, drd2, grin1a, gria2a, gabbr1b, and lrrk2) [7]. Ethanol-seeking behavior is complex; as established in the literature, it is related to telomere shortening and is associated with oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. As these parameters have their own modulatory mechanisms, we aimed to establish ethanol preference phenotypes in adult zebrafish and evaluate the mentioned parameters in the brains of these animals (i.e., telomere shortening, antioxidant enzyme activity, and mtDNA copy number) to further examine the relationship between these parameters and ethanol preference phenotypes.
Two independent experiments were carried out using the protocol described by
Paiva for juveniles [7], however, adults were used in this study. For Experiment
1, we used 85 wild-type, shortfin zebrafish (Danio rerio) of
heterogeneous backgrounds and both sexes, which were obtained from Ecofish (Minas
Gerais, Brazil). Animals were 4–5 months old and presented an average weight of
0.39 grams. For Experiment 2, we used 140 wild-type adult zebrafish obtained from
the Aquatic Animal Housing of Universidade Federal de Lavras (Minas Gerais,
Brazil); all fish in this group were the same age and presented an average weight
of 0.387 grams. Animals were housed in an automated system for both experiments
(Rack Hydrus, model ZEB-40-Alesco) using polycarbonate aquariums with 2.5 L
capacity (11.5
The two experiments were conducted according to the protocol described by Paiva and colleagues [7], as shown in Fig. 1 (Ref. [7]). In Experiment 1, 75 animals were used to define the ethanol preference phenotypes and 10 were used for the control group, which experienced no drug exposure. For Experiment 2, 120 animals were used to define ethanol preference phenotypes and 20 animals were designated as the control group. Animals were individualized and acclimated for seven days before the beginning of the experiment, during which they were kept in the rack (ALESCO® Indústria e Comércio Ltda, Campinas, SP, Brazil).
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Experimental design. After an adaptation period, the CPP test was performed on day 1 considering the established protocol: First, Basal Preference was determined, followed by ethanol conditioning. On the day 2, the Post-conditioning Preference test was perfomed. Lastly, After-withdrawal Preference was determined on day 17 (Modified from Paiva et al. [7] (2020)).
To determine ethanol preference phenotypes, we used the protocol described [7].
5 L (30
Determining the basal (B) preference – Individualized animals were transferred to the experimental tanks and recorded for 10 min to determine basal preference. Basal (B) preference was defined as the side that the animal spent more time on.
Conditioned exposure to the ethanol – Following B preference determination, animals were placed in the conditioning tank, on the opposite side to the Basal Preference. These tanks had the same dimensions as the ones used for the preference test, with the same environmental clues but with a sealed central glass divider, preventing the animal from accessing the other side. On the least-preferred side, each animal was exposed to 1% ethanol (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) for 20 minutes. Then, they were removed from that compartment and left in a beaker with water for 5 minutes to remove the ethanol excess. Next, they were placed in the compartment corresponding to the preferred side in B, without ethanol, for 20 minutes. After conditioning on both sides, the animals were taken back to the maintenance tanks. Both the water and the ethanol solution were exchanged between each animal.
Determining Post-Conditioning (PC) preference – PC preference was determined following the same procedures described in the B preference. This evaluation was performed 24 hours after the ethanol conditioning.
Determining preference After Withdrawal (AW) – Following PC preference determination, the animals were kept in the maintenance tanks for 16 days, when the AW preference was established according to the procedures previously described for B and PC preference.
To establish the individual ethanol preference, 10 min of video recording was used. The initial 2 min of filming were disregarded and the following 5 min of recording videos were analyzed using the software EthoVision XT 12 (Noldus, Wageningen, Netherlands). In the software program, both sides of the tank were defined so that the preferencce results were expressed according to the time spent on the opposite side of B Preference (i.e., the side on wich they were exposed to the ethanol). A hypothetical value of 50.1% was used to determine statistical differences in the percentages of time spent on the conditioning side. Values outside the threshold were considered to be an aversion to ethanol. Animals exhibiting freezing behavior were excluded.
After the AW test, the animals were euthanized with an overdose of the anesthetic benzocaine (ethyl p-aminobenzoate, 250 mg/L) [53]. The brains of animals from Experiment 1 were dissected, immersed in a phosphate-buffered saline solution (PBS), frozen, and stored at –80 °C for RNA extraction. Animals of each phenotype and the control group from Experiment 2 were randomly divided for antioxidant enzyme activities or molecular analysis. Brains were collected and stored as described in Experiment 1.
Total mRNA was extracted using ReliaPrep™ RNA Miniprep Systems (Promega, Fitchburg, MA, USA) according to manufacturer instructions. Quantification was performed with a DeNovix DS-11 (DeNovix, Delaware, Wilmington, DE, USA).
Primers were designed as described [5]; the sequences used are available in Supplementary Table 1. For each sample in Experiment 1, 800 ng of total mRNA was used for reverse transcription with oligo (dT20), primers (Prodimol Biotecnologia, Belo Horizonte, Brazil), dNTP mix (10 mM), Reaction Buffer 5X (Thermo Fisher Scientific, São Paulo, Brazil), Ribolock RNase Inhibitor (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and Revertaid® Reverse Transcriptase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, São Paulo, Brazil) according to manufacturer instructions. Target gene transcripts were quantified with qPCR using the CFX 96TM Real-Time system (BioRad) and Kapa SYBR Fast qPCR Kit Master Mix (Kapa Biosystems, São Paulo, Brazil). The amplification was performed according to the following protocol: 95 °C for 3 min, 40 cycles at 95 °C for 3 s and 60 °C for 20 s. A negative control without a sample (NTC) was tested in all reactions. The qPCR data were analyzed with the Ct delta-delta method. For normalization, the reference genes eef1a1a (eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha 1a) and rpl13 (ribosomal protein L13) were used, as seen in previous studies [54, 55, 56]. The algorithms BestKeeper and Genorm [57, 58] were used to confirm the stability of the reference genes. The relative amount of transcripts was calculated as described [59].
DNA was extracted from tissue samples from Experiment 2 using Direct-Zol DNA (Zymo Research São Paulo, Brazil) according to manufacturer instructions, allowing extraction of DNA free of contaminants. The quantification was performed on the DeNovix DS-11 (DeNovix, Delaware, USA).
64 ng of DNA were used to perform the qPCR using the CFX 96TM Real-Time system (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA) and QuantiNova SYBR Green RT-PCR Kit (Qiagen, São Paulo, Brazil). PCR amplification was performed using the following protocol: 95 °C for 15 minutes, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 seconds and 54 °C for 2 minutes. The negative control, without the template DNA, was tested in all reactions. Analysis of real-time PCR data was calculated with the Ct delta-delta method using a reference gene (rps11 (ribosomal protein S11)) for normalization. For telomere length, we used the primer sequences: 5′GGTTTTTGAGGGTGAGGGTGAGGGTGAGGGTGAGGGT3′ (forward primer) and 5′TCCCGACTATCCCTATCCCTATCCCTATCCCTATCCCTA3′ (reverse primer) [60]. For rps11, we used the sequences: 5′CTCTGACGACACTGCCTTATG3′ (forward primer) and 5′GAAGATGGTGGGCTGTTTCT3′ (reverse primer) [This study].
For mitochondrial DNA copy number analyses, 10 ng of DNA were used to perform the qPCR, using the CFX 96TM Real-Time system (BioRad) and QuantiNova SYBR Green RT-PCR Kit (Qiagen, São Paulo, Brazil). PCR amplification was performed according to the following protocol: 95 °C for 2 minutes, followed by 40 cycles at 95 °C for 5 seconds and 60 °C for 10 seconds. The negative control, without the template DNA, was tested in all reactions. Analysis of real-time PCR data was performed with the Ct delta-delta method using a nuclear reference gene (rps11 (ribosomal protein S11)) for normalization. Primers were designed considering the sequence of mitochondrial cox1 and atp6 genes, and were synthesized by IDT (Integrated DNA Technologies); the sequences are listed in Table 1.
| Target | Gene description | Primer forward (5′-3′) | Primer reverse (5′-3′) | Amplicon - pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rps11 | Ribosomal protein S11 | CTCTGACGACACTGCCTTATG | GAAGATGGTGGGCTGTTTCT | 205 |
| cox1 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I | ACCAGGATTCGGCATTATCTC | CTCGGGTGTCTACATCCATTC | 164 |
| atp6 | ATP synthase 6 | CCTTATCCTCGTTGCCATACTT | GTTTGTGAATCGTCCAGTCAATC | 115 |
Tissue homogenization – Tissue samples were homogenized in 200
uL of phosphate homogenization buffer (pH 7.4) on ice. The homogenate was
centrifuged at 800
Total antioxidant capacity – Total antioxidant capacity was evaluated using the ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) method [61]. Superoxide Dismutase – SOD activity (U/ug protein) was assessed by inhibiting autoxidation of pyrogallol by SOD present in the tissue samples [62]. Catalase – CAT activity (U/mg protein) was determined with the method described by Aebi [63]. Glutathione Peroxidase – GPx activity (U/mg protein) GPx test is a method that consists of recording the decrease in NADPH [64].
All data were analyzed for normality with the Shapiro-Wilk test. A one-sample
t-test (GraphPad Prism version 7 (GraphPad Software, Boston, MA)) was performed to determine the
preference, considering the hypothetical threshold of 50.1%. A one-way ANOVA
test (GraphPad Prism version 7) was used to analyze molecular data and
antioxidant enzyme activity. Pearson’s correlation coefficients (GraphPad Prism
version 7) were calculated to evaluate the association between telomere length,
mtDNA copy number, and antioxidant enzyme activities. The results were expressed
as the mean and standard error of the mean (
Animals from Experiments 1 and 2 subjected to the CPP test were classified into four phenotypes according to their preference for the ethanol: (1) Light – animals without ethanol preference (B, PC, and AW); (2) Heavy – animals with ethanol preference in PC; (3) Inflexible – animals that preferred the conditioning side in both PC and AW; and (4) Negative Reinforcement – animals with ethanol preference in AW (Table 2). In Experiment 2, 14 animals showed freezing behavior and were excluded from phenotype analysis. The behavior measures are given in Supplementary Fig. 1.
| Phenotype | Description | Exp1 | Exp2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | n | ||
| Light | No ethanol prefence | 20 | 27 |
| Heavy | Ethanol preference in PC preference test | 20 | 32 |
| Inflexible | Ethanol preference in PC and AW preference tests | 20 | 24 |
| Negative Reinforcement | Ethanol preference in AW preference test | 15 | 23 |
PC, Post-Conditioned Preference; AW, After Withdrawal Preference.
To validate the protocol described by Paiva et al. [7] in juveniles, we performed an analysis of the transcripts of ethanol target receptors in adult zebrafish brains from Experiment 1. These results are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2.
For telomere length analysis, we used a qPCR protocol [60]. As shown in Fig. 2,
there was evidence of telomere shortening (F (4.28) = 5.601) in the Heavy,
Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement groups compared to the Light group
(p
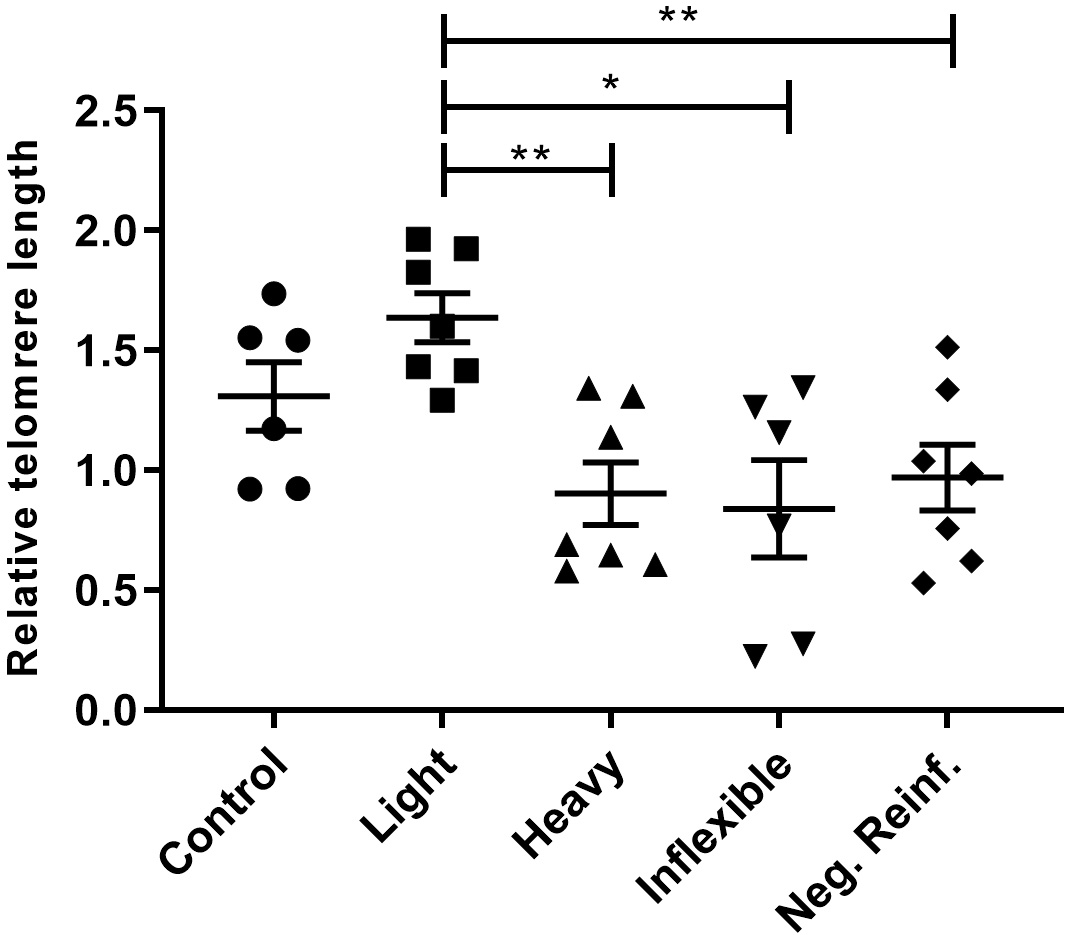 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Relative telomere length in brains of adult zebrafish submitted
to CPP testing and distinguished by phenotypes of ethanol preference. One-way
ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s post hoc test. Data are expressed as the mean and
standard error of the mean (
The mtDNA copy number was analyzed by qPCR, with a focus on the amplification of
two mitochondrial genes: atp6 and cox1. As shown in Fig. 3, an
increased mtDNA copy number (atp6 and cox1) (F (4.30) = 5.981;
F (4.31) = 3.892) was observed in the Heavy phenotype compared to the control
(p
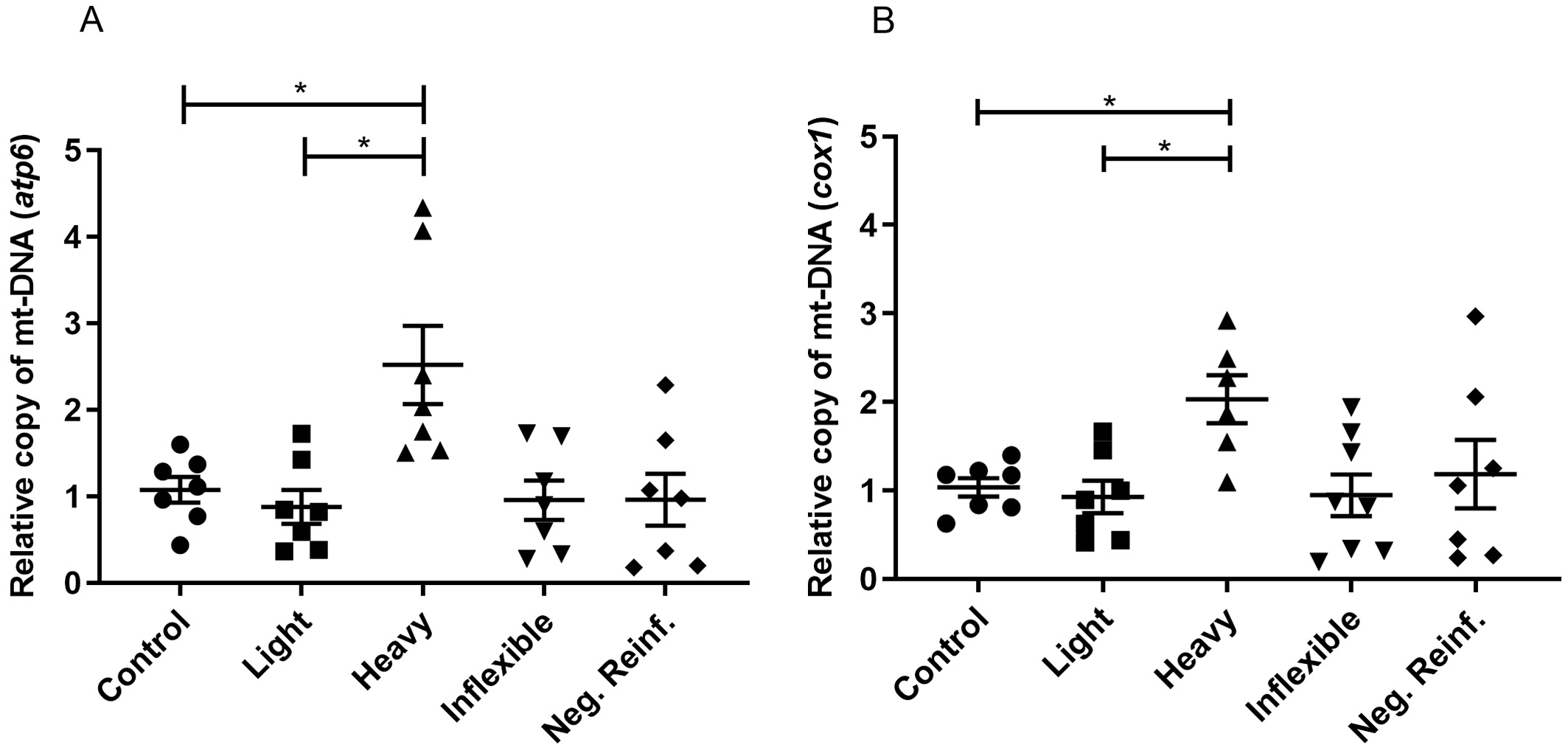 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Relative mtDNA copy number in brains of adult zebrafish
submitted to CPP testing and distinguished by ethanol preference phenotypes. (A)
Results for atp6. (B) Results for cox1. One-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s post
hoc test. Data are expressed as the mean and standard error of the mean (
For the analysis of antioxidant status, evaluations of the total antioxidant potential were performed using the FRAP method in animal brains from Experiment 2. As seen in Fig. 4A (F (4.25) = 7.084), there was a decrease in the total antioxidant capacity for the Heavy (p = 0.0016), Inflexible (p = 0.0167), and Negative Reinforcement (p = 0.0028) phenotypes compared to the Light group.
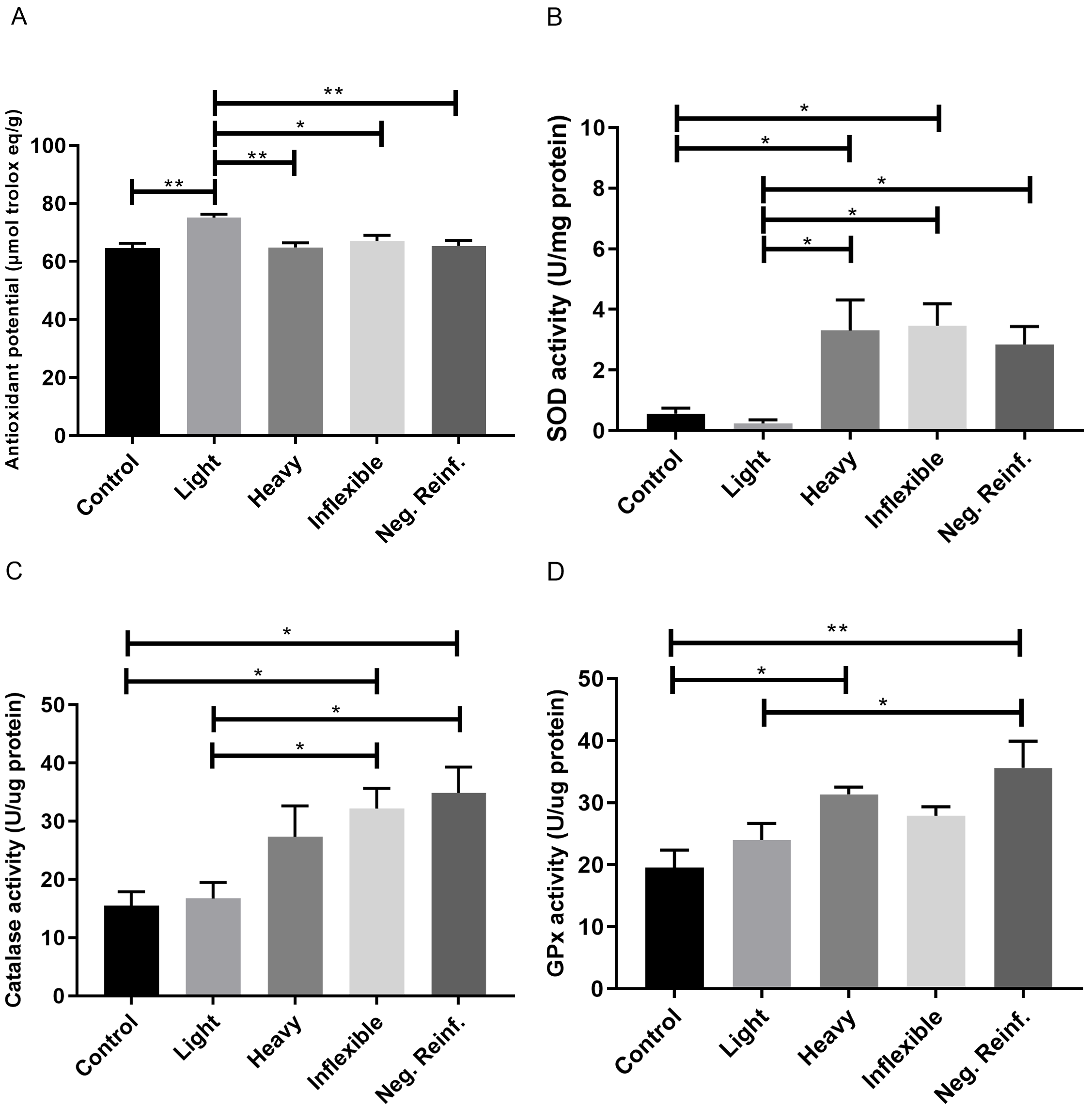 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Biochemistry analysis of brains of adult zebrafish submitted to
CPP testing and distinguished by ethanol preference phenotypes. (A) Total
antioxidant potential by the FRAP method. (B) SOD activity. (C) Catalase
activity. (D) GPx activity. One-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s post hoc test.
Data are expressed as the mean and standard error of the mean (
The experiments also showed a significant increase in SOD activity in brains (F (4.24) = 5.716) from the Heavy, Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement groups (Fig. 4B) compared to the Light phenotype (p = 0.0084; p = 0.0055; p = 0.0269, respectively), as well as in Heavy and Inflexible groups compared to the control group (p = 0.0266; p = 0.0182).
CAT activity (F(4.25) = 5.275) was higher in the Inflexible and Negative Reinforcement groups compared to both the control (p = 0.0176; p = 0.055) and the Light group (p = 0.0298; p = 0.0096) (Fig. 4C).
An increase in GPx activity (F(4.23) = 5.102) was evidenced in the Heavy group compared to the control (p = 0.0436) and Negative Reinforcement compared to both the control (p = 0.0036) and Light group (p = 0.0485) (Fig. 4D).
PCA analysis of the variance of the preference data and the molecular and biochemistry parameters analyzed corroborated the grouping of the animals into two dimensions (Fig. 5). First, determined by telomere length (TL), there is the control group and Light phenotype, which showed higher TL measurements. Second, there is clustering by the ethanol preference phenotypes according to CAT, SOD, and GPx results, meaning that these individuals showed increased enzyme activity. The Heavy phenotype was better explained by the mtDNA copy number.
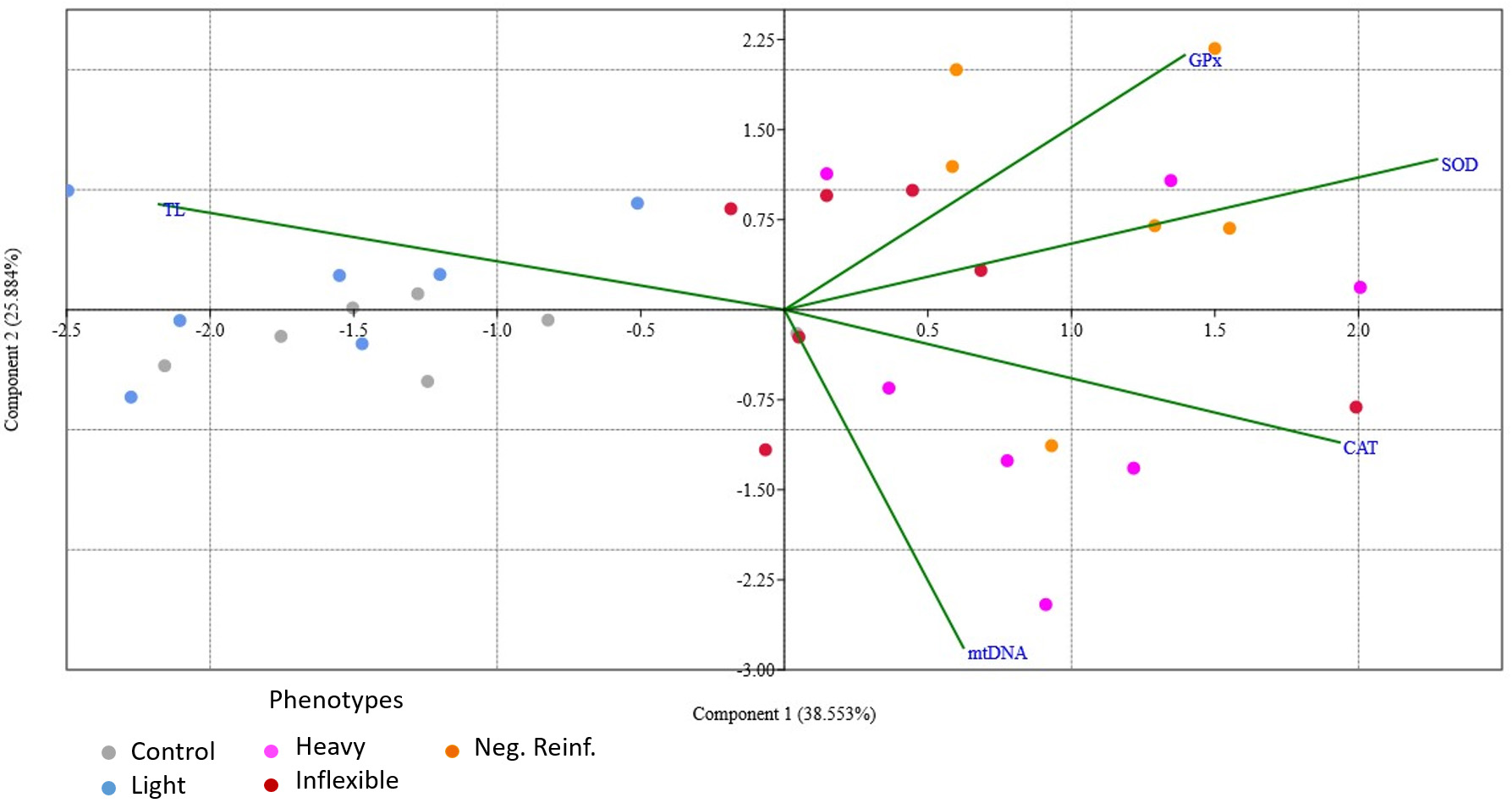 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Distribution of the control and preference data and its relationship to the molecular and biochemistry parameters that were analyzed (TL, mtDNA, CAT, SOD, and GPx). Colors indicate the control and four phenotype groupings (Light, Heavy, Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement). Arrows indicate the parameters analyzed. The proximity of phenotypes to each line indicate which parameters are related to the variance of data in each phenotypic category. TL, telomere length; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA copy number; CAT, catalase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase.
The results of Pearson’s Correlation (r) are shown in Fig. 6. Based on the p-values obtained for this analysis, there was a negative correlation when comparing telomere length and CAT activity (p = 0.039) (Fig. 6A) or telomere length and SOD (p = 0.004) activity (Fig. 6B). In this case, we observed an increase in CAT and SOD enzyme activity related the telomere shortening. There was no correlation for the other parameters analyzed.
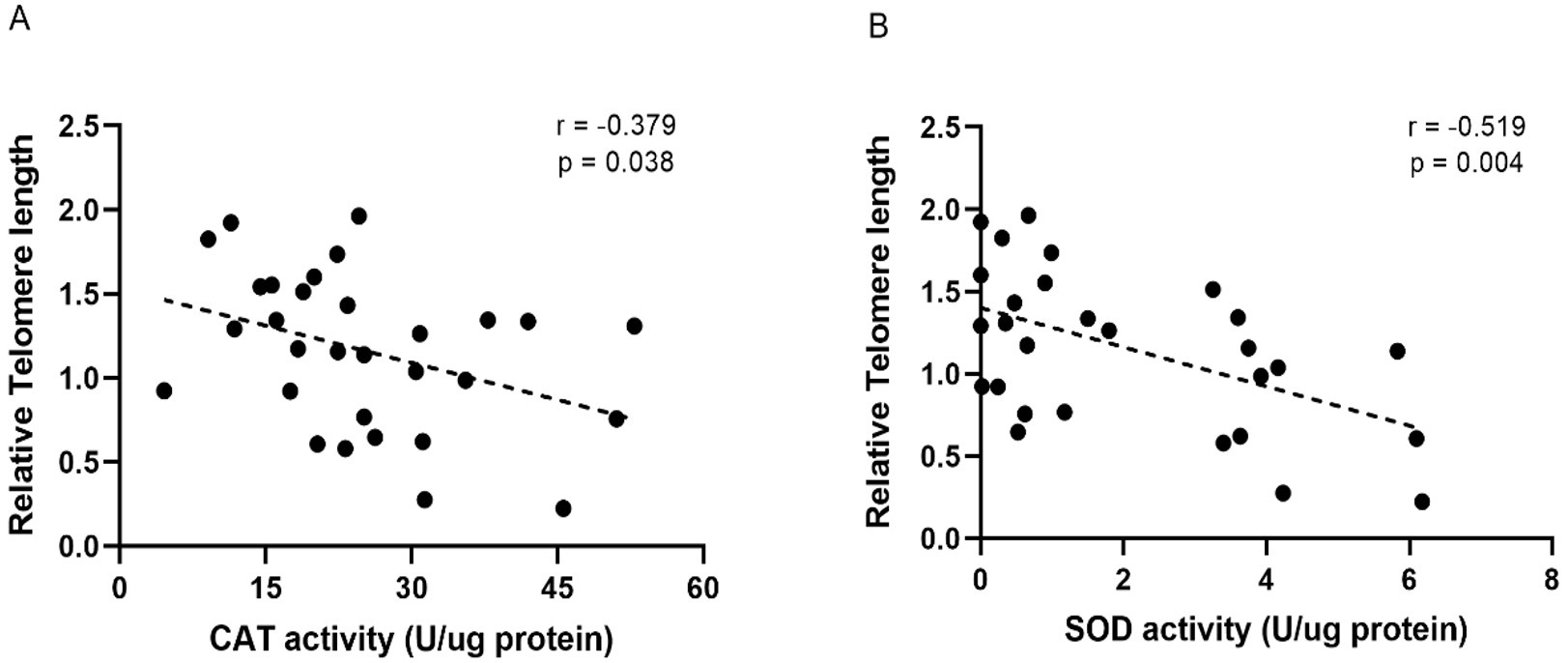 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.Correlation between telomere length and the results for enzyme activity levels for (A) CAT; and (B) SOD. There is a tendency for higher enzyme activity associated with lower telomere length and this relationship is approximately linear, as indicated by the dotted line. Coefficients (r) were calculated by Pearson’s correlation model. CAT, catalase; SOD, superoxide dismutase.
Alcohol abuse is a complex human condition, with the great challenge currently being understanding the mechanisms that lead to loss of control over ethanol consumption, which causes harm to individuals in physical, mental, and social capacities. While there is evidence of different patterns of behavior, few studies have described phenotypic distinctions in animal models. Our research characterized four phenotypes in juvenile zebrafish (20 days post fertilization (dpf)) as Light, Heavy, Inflexible, or Negative Reinforcement according to their behavior, and identified transcriptional dysregulation of genes associated with addiction-like phenotypes (drd1, drd2, grin1a, gria2a, gabbr1b, and lrrk2) [7]. In this study, we were also able to validate the protocol in adult zebrafish by identifying the same patterns in these ethanol target receptors and identifying the same ethanol preference phenotypes.
As described, our protocol defines four phenotypes of ethanol preference resulting from acute ethanol exposure over 20 minutes and encompasses 16 days, from ethanol conditioning to euthanasia and tissue collection. Animals were grouped into the four phenotypes based on the behavioral response to ethanol in a CPP test. Our results demonstrate the effect triggered by acute ethanol exposure regarding phenotypic distinction, considering this effect over time.
As for ethanol preference in adult zebrafish, telomere shortening was evidenced in the Heavy, Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement groups. These phenotypes showed ethanol preference in the CPP test; particularly for the Inflexible group, which preferred the ethanol side in both PC and AW tests. Shorter telomeres were found in a study of early stress associated with anxiety and substance use disorders in humans [33]. Our results show the same pattern of telomere shortening in the brains of ethanol preference phenotypes. Our results also demonstrated a differential cellular response in telomere shortening regarding ethanol preference. One consideration for our experiment is the phenotypic definition using heterogenetic animals. Individual differences in telomere length are associated with individual differences in behavior, suggesting a possible relationship between telomere length and higher impulsivity regarding choices between delayed rewards, higher propensity to take risky decisions, higher probability of smoking, higher alcohol consumption, higher stress reactivity, and more neurotic and pessimistic personality types [16]. Previous research has also shown an association between telomere shortening and biobehavioral symptoms [66], such as depression [28], stress [67], and violence [68].
Our results support that telomere shortening in ethanol preference phenotypes is a characteristic of these behaviors. However, Bateson and Nettle [16] present different perspectives on the cause-and-effect relationship between telomere shortening and behavior. They claim that there are two main hypotheses: either telomere shortening makes individuals more prone to a certain behavior, or some habits trigger cellular events that promote telomere shortening. Chronic ethanol abuse is related to this latter process, as continuous consumption of alcohol promotes functional cell disturbances related to genomic instability [15, 69]. Our research model considers an acute form of ethanol exposure, finding evidence of shortened telomeres in the brain of animals with an ethanol preference; however, we did not find evidence of this phenomenon in animals of the Light phenotype compared to the control. There was no difference between the Light and the control groups in all analyses that we performed, and, in regard to relative telomere length, the control animals could belong to any of the ethanol preference phenotypes. This opens the possibility that these results characterize a predisposition to ethanol preference, or, possibly, that ethanol triggers specific responses in individuals with ethanol-seeking behavior. As they are related to telomere shortening, alterations in the mtDNA copy number and increased activity of the main enzymes of the antioxidant system were also evaluated in the same phenotypes.
Mitochondria play an important role in the context of oxidative stress, which is related to drug addiction [70] and can be induced by ethanol [29, 71]. Alterations in the mtDNA copy number have been proposed as a biomarker of mitochondrial dysfunction [72]. In such a case, mitochondrial genome to nuclear genome ratio (Mt/N) values would increase as a result of increased mitochondrial biogenesis [35]. Previous studies of chronic alcohol abuse do not seem to have found differences in the mtDNA copy number of alcoholic individuals [73, 74]. However, higher mtDNA copy numbers associated with telomere shortening were evidenced in a study of early stress associated with anxiety and substance use disorders [33]. In the context of ethanol preference, we found an increased mtDNA copy number, as well telomere shortening, in the Heavy phenotype.
We also found an increase in antioxidant enzyme activities in the brains of the ethanol preference phenotypes. Studies that indicate an increase in antioxidant enzyme activities is probably a compensatory regulatory response to oxidative stress [75, 76, 77], such as ethanol exposure [78, 79]. Furthermore, antioxidant enzymes play an important role in behavioral contexts, mainly related to ethanol abuse [80]. Evidence suggests that, during oxidative stress, ROS generation can function as a signal to the nucleus to limit cell proliferation, using telomere shortening to sense damage in the mitochondria [48]. During oxidative stress, the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) component of telomerase has been shown to translocate to the mitochondria [81, 82], suggesting that TERT may protect mitochondrial function indirectly by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis [30]. In the Heavy phenotype group, we found evidence of increased mtDNA copy numbers and elevated antioxidant enzyme activities, as well telomere shortening. The Inflexible and Negative Reinforcement phenotypes showed telomere shortening and increased antioxidant enzyme activities.
We analyzed the antioxidant status in the brain of ethanol preference phenotypes, considering total antioxidant potential and SOD, CAT, and GPx activities. These enzymes are associated with antioxidant defense and repair mechanisms against oxidative stress. Our study showed increased activity of antioxidant enzymes in the Heavy, Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement phenotypes. Using the FRAP method, we observed a decrease in the total antioxidant potential in the brain in all ethanol preference phenotypes. The Heavy phenotype showed increased SOD and GPx activities, the Inflexible phenotype showed increased activity of SOD and CAT, and the Negative Reinforcement phenotype demonstrated increases in SOD, CAT, and GPx. Our results are in agreement with other studies that have demonstrated a relationship between the imbalance of antioxidant enzyme activities and behavioral patterns associated with ethanol abuse [37, 38, 39] and alcohol preference in mice [44].
We found increases in SOD activity in the brains of all alcohol-preferring phenotypes. The same pattern of high SOD activity in the hippocampus was found in studies with adolescent male rats acutely exposed to ethanol [83], brains from chronic alcoholics [84], and serums of alcohol-dependent patients [37]. These findings reinforce the relationship between antioxidant enzyme imbalance and profiles of ethanol-seeking behavior.
In our study, GPx activity was higher in the Heavy and Negative Reinforcement phenotypes. Similarly, Wu et al. [85] observed increased GPx activity in alcohol use disorders (AUD) patients and suggested that GPx levels may be an AUD state biomarker.
Previous studies have investigated the role of CAT in ethanol intake, as, in the
brain, CAT oxidizes ethanol in acetaldehyde, which has been proposed to be a
mediator of some behavioral effects produced by ethanol [86]. Additionally, our
results demonstrate a possible association between high CAT activity and ethanol
preference. As shown earlier, our study found increased activity of CAT in the
Inflexible and Negative Reinforcement phenotypes. Aragon [87] suggests that
cerebral CAT may be involved in the regulation of animal affinity for ethanol
consumption. Another study showed lower ingestion of ethanol in rats treated with
a CAT blocker [88], further supporting the importance of this enzyme in ethanol
consumption. Interestingly, in a study of ethanol-induced conditioned place
preference (CPP) in mice, Font et al. [89] suggested that the
catalase–H
We present genomic and antioxidant status alterations related to telomere shortening, mtDNA copy number, and antioxidant status in the brains of adult zebrafish submitted to a CPP test, distinguishing between phenotypes according to ethanol preference. All the animals with ethanol preference (Heavy, Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement phenotypes) showed telomere shortening. The Heavy phenotype also showed decreased antioxidant potential, as well as increased activity of SOD and GPx. This phenotype also demonstrated an increased mtDNA copy number. The Inflexible phenotype showed a lower antioxidant potential and high activities of SOD and CAT. A decreased antioxidant potential was found in the Negative Reinforcement phenotype, in addition to increased activities of SOD, CAT, and GPx.
The three cited phenotypes correspond to animals who showed ethanol preference in at least one phase of CPP testing. On the other hand, the Light group was the only phenotype to not show ethanol preference. While the animals in this phenotype were exposed to ethanol, they did not show any changes in telomere shortening, mtDNA copy number, or antioxidant status. Considering the heterogenetic characteristics of the animals used in our experiment and the previously discussed evidence of a relationship between genomic instability, antioxidant status dysfunction, increased mitochondria biogenesis, and voluntary ethanol consumption, we further suggest an association between telomere shortening, mitochondria dysfunction, and antioxidant imbalance and the ethanol preference phenotypes described here. Supporting this, a PCA analysis grouped the Light and control groups by telomere length, while the three ethanol preference phenotypes (Heavy, Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement) were associated with antioxidant enzyme activity. A Pearson’s Correlation showed a negative correlation between telomere length and SOD and CAT activities, reinforcing the premise that telomere shortening is associated with an imbalance of the antioxidant system; we demonstrate this correlation for the first time in ethanol preference phenotypes based on acute ethanol exposure.
In conclusion, our results show an association between genomic vulnerability and antioxidant status alterations related to ethanol preference phenotypes (Heavy, Inflexible, and Negative Reinforcement), elucidating individual responses associated with cellular instability and behavior. Using a model that is easy to develop, has low maintenance costs, and shows results highly similar to those found in murine models and human studies, we have shown that there are differential responses of relative telomere shortening, mitochondrial biogenesis, and antioxidant enzymes activity among ethanol preference phenotypes. This study suggests that behavior modulation goes beyond a physiological response, and involves previously existing patterns of individual characteristics, triggered by ethanol exposure. While our results provide important information on ethanol preference phenotypes, this is also a new model for ethanol-induced behavior studies, and further research is needed for a thorough understanding of these phenotypes.
This study has no dataset.
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The CPP test was performed by IBM and IMP. Material preparation and data collection were performed by IBM and IMP. Molecular analysis was performed by IBM, BMS, and REMJ. Biochemistry analysis was performed by IBM and RRF. The first draft of the manuscript was written by IBM, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. FSE and LDSM commented on previous versions of the manuscript. ALBG contributed with conceptualization, project administration, resources, funding acquisition, supervision, writing - review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
All fish were kept following welfare parameters for the species and protocols were conducted according to the rules of the Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals (Comitê de Ética no Uso de Animais) at the Federal University of Minas Gerais, Minas Gerais, Brazil (Protocol number 64/2016).
Not applicable.
This work was supported by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES - Nº AUXPE 1970/2016), foundation of Ministério da Educação (MEC); Pró-Reitoria de Pesquisa from the Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (PRPQ - UFMG), Brazil; Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG: APQ-01213-21) Pró-reitoria de Pós-Graduação e Pesquisa (PROPGP) from the Universidade Federal do Oeste da Bahia (Edital nº 06/2021 - PROPGP/UFOB). FSE was supported by INCT - TeraNano (CNPq 465669 /2014-0) and scholarship grants were received from FAPEMIG (PPM-00503-18) and CNPq (PQ – 312812/2021-3).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at https://doi.org/10.31083/j.fbl2804073.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.






