1 Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Clinical Medical College, Jining Medical University, 272000 Jining, Shandong, China
2 Jining Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases, 272000 Jining, Shandong, China
3 Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, 250012 Jinan, Shandong, China
Abstract
Background: Doxorubicin (DOX) is an effective broad-spectrum antitumor
drug, but its clinical application is limited due to the side effects of cardiac
damage. Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) is a significant active component of
Astragalus membranaceus that exerts cardioprotective effects through
various pathways. However, whether AS-IV exerts protective effects against
DOX-induced myocardial injury by regulating the pyroptosis is still unknown and
is investigated in this study. Methods: The myocardial injury model was
constructed by intraperitoneal injection of DOX, and AS-IV was administered via
oral gavage to explore its specific protective mechanism. Cardiac function and
cardiac injury indicators, including lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), cardiac
troponin I (cTnI), creatine kinase isoenzyme (CK-MB), and brain natriuretic
peptide (BNP), and histopathology of the cardiomyocytes were assessed 4 weeks
post DOX challenge. Serum levels of IL-1
Keywords
- Astragalus membranaceus
- doxorubicin
- pyroptosis
- Nrf-2/HO-1
- cardiac dysfunction
- cardioprotection
Doxorubicin (DOX) is an effective antitumor drug that is used to treat a variety of cancers, including solid organ tumors and hematologic malignancies [1, 2, 3, 4]. DOX kills cancer cells mainly through the inhibition of DNA synthesis, interference with topoisomerase II activity, and induction of oxidative stress [5, 6, 7]. However, despite its antitumor effects, DOX is associated with causing undesired cell death in healthy tissues and cells [8, 9]. The side effects of DOX, particularly its dose-dependent cardiotoxicity, can lead to heart failure, which greatly limits its clinical application [10]. In the past decades, multiple studies have clarified the pathogenesis of DOX-induced cardiac dysfunction, especially cell death, which plays an important role in DOX-induced myocardial injury, including autophagy, apoptosis, and necrosis [11, 12]. In recent years, it has been reported that pyroptosis is involved in cardiomyocyte death and cardiac dysfunction induced by DOX. However, its underlying regulatory mechanism has not been fully investigated [13]. Therefore, further exploration of the specific mechanisms by which DOX causes cardiomyocyte death could help to mitigate its cardiotoxic effects.
Pyroptosis is caspase-dependent inflammatory programmed cell
death with inflammasome activation being a key process in the development of
pyroptosis [14]. Among these, nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3)
inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis is the most important pathway involved in the
pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases [15]. NLRP3 can be activated by external
stimuli and interact with apoptosis-associated speck-like protein (ASC). After
activation by NLRP3, ASC recruits cysteine protease caspase-1 (pro-caspase-1) to
form the NLRP3 inflammasome, which leads to the activation of caspase-1 to form
cleaved caspase-1 [16]. Subsequently, cleaved caspase-1 cleaves full length
gasdermin D (GSDMD-FL) to produce an N-terminal activated product (GSDMD-N),
leading to the conversion of IL-1
Although some drugs, such as dexrazoxane, can be used as cardioprotective agents and have been found to reduce DOX-induced myocardial damage. However, they have a potential risk of secondary malignancies [20]. Additionally, some traditional drugs for heart disease, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and beta-blockers, have not been clearly proven to protect against DOX-induced myocardial injury, and these drugs also have also been reported to exhibit adverse effects [20]; hence it is necessary to explore drugs with few side effects to improve DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. Compared with traditional compound drugs, natural drugs have the advantages of fewer adverse effects, less long-term toxicity, and variable bioavailability [21]. Modern research has found that herbal medicines exert a polypharmacological action and can effectively prevent and treat cardiovascular diseases [22]. Astragalus membranaceus is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine which is widely used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases due to its effects of invigorating and promoting yang, diffusing edema, and detoxifying muscles [23]. AS-IV is a key active ingredient extracted from Astragalus membranaceus and is involved in various pharmacological properties including antioxidant activity, inhibition of apoptosis, inhibition of fibrosis, and immune modulation [24]. Among these, its cardioprotective effects are the most important. It has been reported that AS-IV alleviates heart failure by improving myocardial energy metabolism [25, 26]. Our previous studies also suggested that AS-IV has a protective effect against myocardial fibrosis and reverse ventricular hypertrophy [27]. Currently, new studies have found that AS-IV has significant anti-inflammatory effects [28, 29]. AS-IV attenuates pulmonary toxicity and cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. However, there is a paucity of knowledge as to whether AS-IV protects cardiac function by inhibiting pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes. Considering that there is no specific drug for DOX-induced myocardial injury, this study explores whether AS-IV, a traditional Chinese medicine with low side effects, has a good curative effect, and aims to investigate its possible mechanism and regulatory pathway.
Specific pathogen free (SPF) healthy male C57BL/6 mice (n =
40, weight 22
The cardiac function of mice was assessed after 4 weeks. Mice from the four groups were anesthetized with 1–2% isoflurane (1349003, Sigma-Aldrich (Shanghai) Trading Co.Ltd., Shanghai, China), and transthoracic echocardiography was performed using an animal-specific ultrasound imaging system with a 40 MHz transducer (M9Vet, Mindray, Shenzhen, China). Mice were placed supine and fixed on a board, the parasternal long axis was taken, and M-mode images were obtained at the inferior border of the mitral papillary muscle. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), left ventricular fractional shortening (LVFS), left ventricular internal dimension at end-diastole (LVIDd), and left ventricular internal dimension at end-systole (LVIDs) were measured and calculated to evaluate cardiac function.
Blood samples were collected from the carotid artery after over-anesthesia.
Serum was obtained after centrifugation of whole blood. According to the
instructions of each kit, ELISA was performed to detect the serum concentration
of the heart failure marker brain natriuretic peptide (BNP, E-EL-M0204c,
Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China), the myocardial injury markers
lactate dehydrogenase (LDH, 12239, MEIMIAN Industrial Co.,
Ltd., Yancheng, China), creatine kinase isoenzyme (CK-MB, E-EL-M0355c, Elabscience
Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China), cardiac troponin I (cTnI, E-EL-M1203c,
Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China), the inflammatory markers
IL-1
Mice were sacrificed after 4 weeks of DOX and AS-IV treatment. The heart of each
mouse was removed and the weight was recorded. Cardiac tissue was rinsed with
phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for at least 48
h, and embedded in paraffin. The slices were cut into 5
Fresh myocardial tissue was dissected into small pieces of approximately 1
mm
To determine the expression of NLRP3, caspase-1, and GSDMD in the heart, immunohistochemical analysis was performed using anti-NLRP3 (GB11300, Servicebio, Wuha, China), anti-caspase-1 (sc-56036, Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX, USA), and anti-GSDMD (sc-81868, Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX, USA) antibodies as previously described [33]. Briefly, after dewaxing and antigen repair, the paraffin sections were placed in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 25 min at RT. The sections were subsequently incubated with primary antibodies overnight (16–18 h) at 4 °C and secondary antibodies at RT for 50 min. The sections were stained with diaminobenzidine (G1211, Servicebio, Wuha, China) and hematoxylin (G1004, Servicebio, Wuha, China). After sufficient drying, the slides were photographed and evaluated using the ImageJ software.
Heart tissues were fully dissolved in RIPA buffer (P0013B,
Beyotime, Shanghai, China) containing protease inhibitor (P1045, Beyotime,
Shanghai, China) and phosphatase inhibitor (P1045, Beyotime, Shanghai, China).
After examination of protein concentrations using a BCA kit (P0010, Beyotime,
Shanghai, China), 30
All data are expressed as the mean
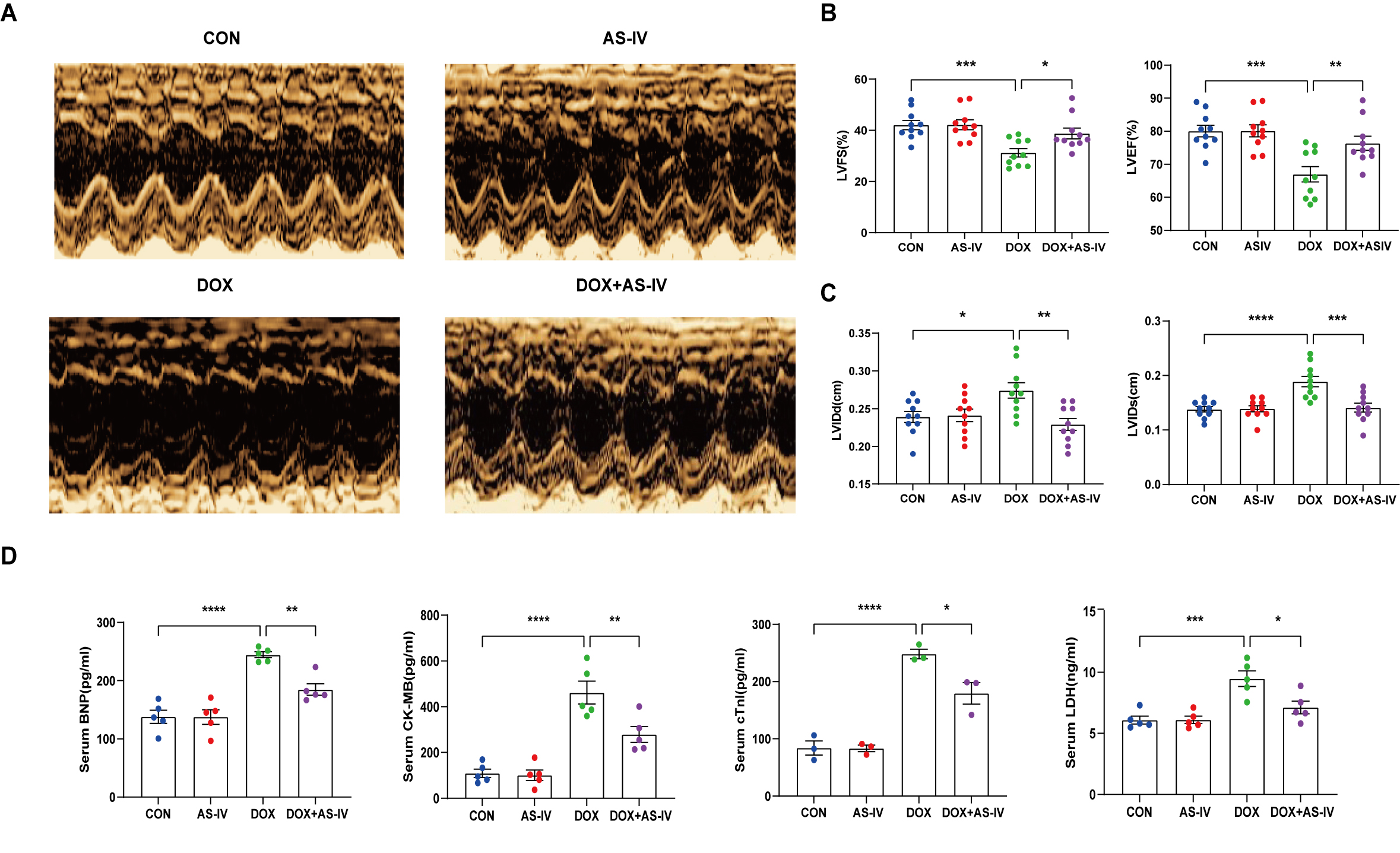
To investigate the cardioprotective effects of AS-IV, DOX-treated mice were subsequently treated with AS-IV. After 4 weeks of intervention, transthoracic echocardiography was performed to evaluate cardiac structure and function in the four groups of mice (Fig. 1A). Our data indicated that intraperitoneal injection of DOX caused cardiac dysfunction, as evidenced by reduced LVEF and LVFS, compared with that in the control group. However, LVEF and LVFS significantly improved in mice treated with AS-IV (Fig. 1B). In terms of heart structure, LVIDd and LVIDs were increased in the DOX group compared to the control group, and LVIDd and LVIDs were lower in the AS-IV-treated mice than in the DOX-treated mice (Fig. 1C). To further evaluate the effects of DOX and AS-IV on cardiac function, we measured serum BNP, CK-MB, cTnI, and LDH levels, which are classical biomarkers of cardiac injury. As shown in Fig. 1D, the serum levels of BNP, CK-MB, cTnI, and LDH of the mice in the DOX group were significantly higher than those in the control group. Compared with the model group, the serum concentrations of these heart injury markers were reduced in the AS-IV-treated group. The results indicate that AS-IV alone does not alter cardiac function but can improve DOX-induced cardiac dysfunction.
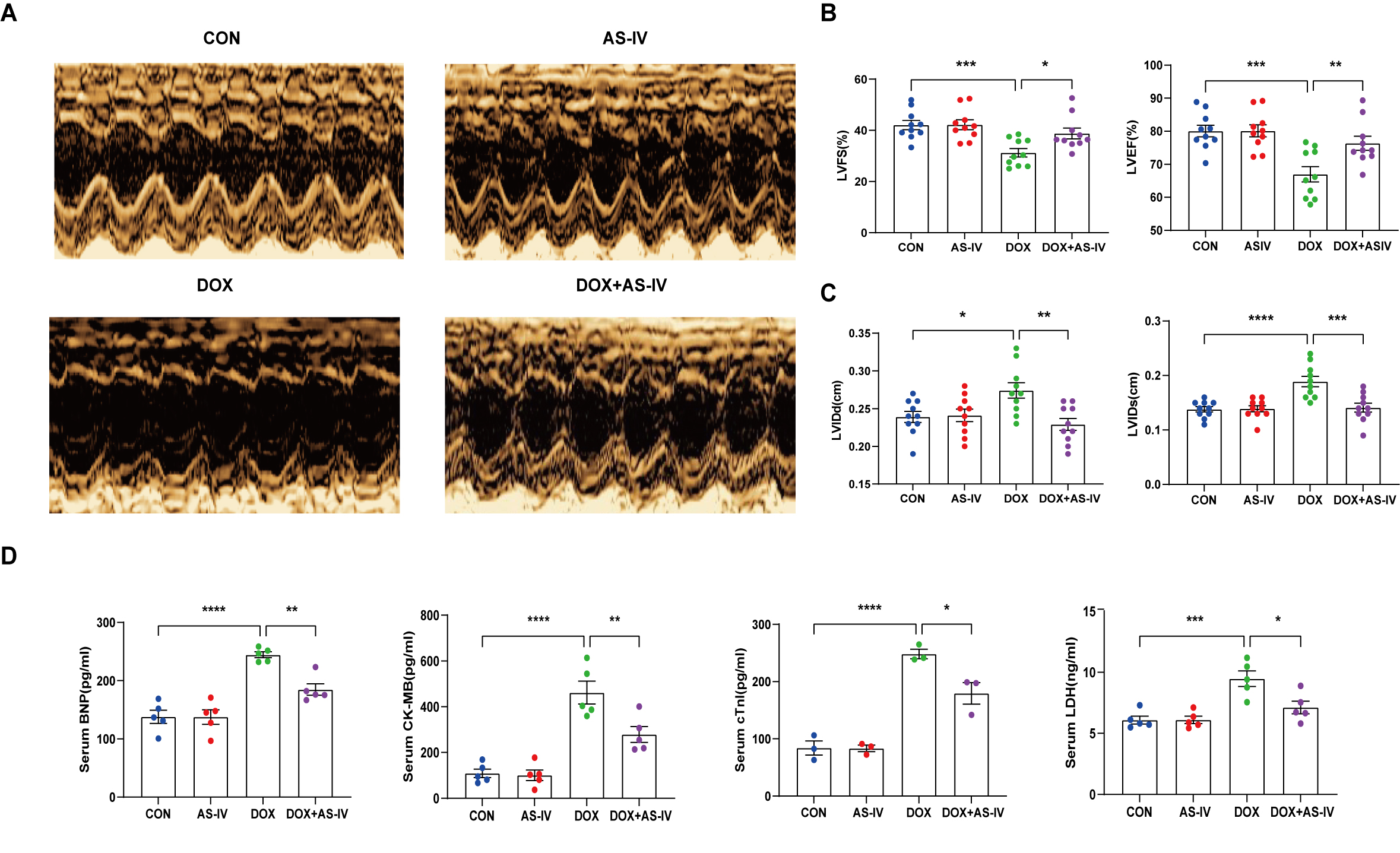 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.AS-IV attenuates DOX-induced cardiac
dysfunction. (A) Representative M-mode images of echocardiograms of experimental
animals in each group. (B) Quantitative analysis of left ventricular fractional
shortening (LVFS) and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). (C) Quantitative
analysis of left ventricular internal dimension at end-diastole (LVIDd) and left
ventricular internal dimension at end-systole (LVIDs). (D) Quantitative analysis
of serum concentration of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), creatine kinase
isoenzyme (CK-MB), cardiac troponin I (cTnI) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).
CON, mice treated with an equal volume of saline. AS-IV, mice treated with 40
mg/kg AS-IV. DOX, mice treated with 2 mg/kg BW doxorubicin every other day with a
cumulative dosage of 28 mg/kg. DOX + AS-IV, mice treated with doxorubicin and
AS-IV. Data are shown as mean
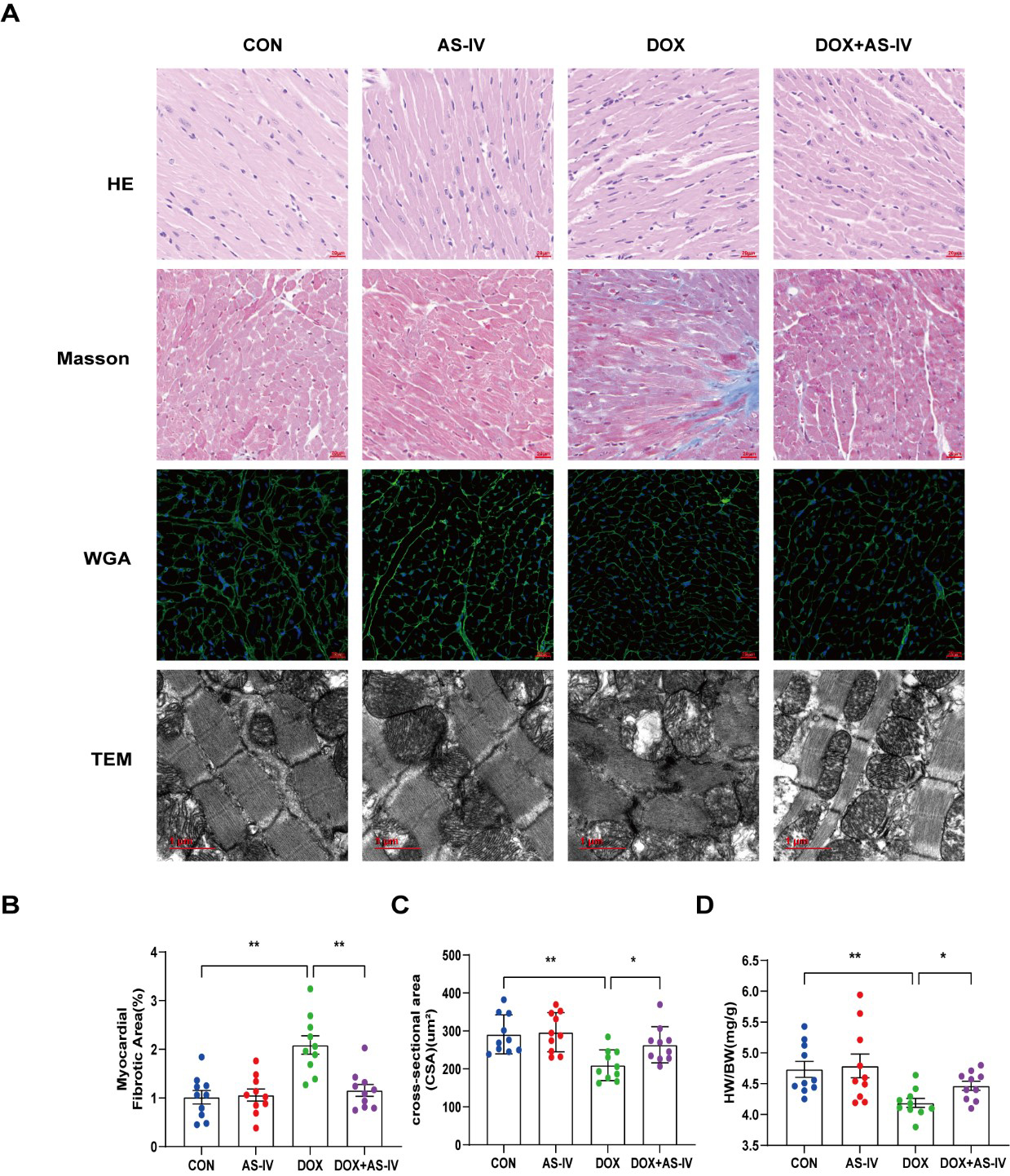
Histological examinations were then performed to examine the microstructural abnormalities of mice in the four groups. HE staining showed that myocardial fibers in the control group were neatly and tightly arranged, with distinct nuclei, while myocardial tissue in the DOX group was disorganized. However, treatment with AS-IV effectively improved the histopathological features of the myocardial tissue (Fig. 2A). Masson-stained collagen was significantly increased in the DOX group compared to that in the other groups (Fig. 2B). In addition, WGA staining showed that the mean area of cardiomyocytes in the DOX-induced myocardial injury group was significantly lower than that in the control group, and AS-IV treatment increased the area of cardiomyocytes (Fig. 2C), which was consistent with the ratio of heart weight to body weight (HW/BW) (Fig. 2D). TEM was conducted to further detect the effects of DOX and AS-IV on the ultrastructure of the cardiomyocytes. In the absence of DOX, mitochondria were arranged normally in organized sarcomeres. However, in the DOX-treated group, mitochondrial damage was observed and was characterized by swelling and vacuolization as well as disarrangement of myofilaments, the disappearance of the H-band, reduced ridge lysis, and widened Z-rays. Fewer injuries were observed after AS-IV administration (Fig. 2A). These results demonstrate that AS-IV attenuates myocardial fibrosis and mitochondrial damage.
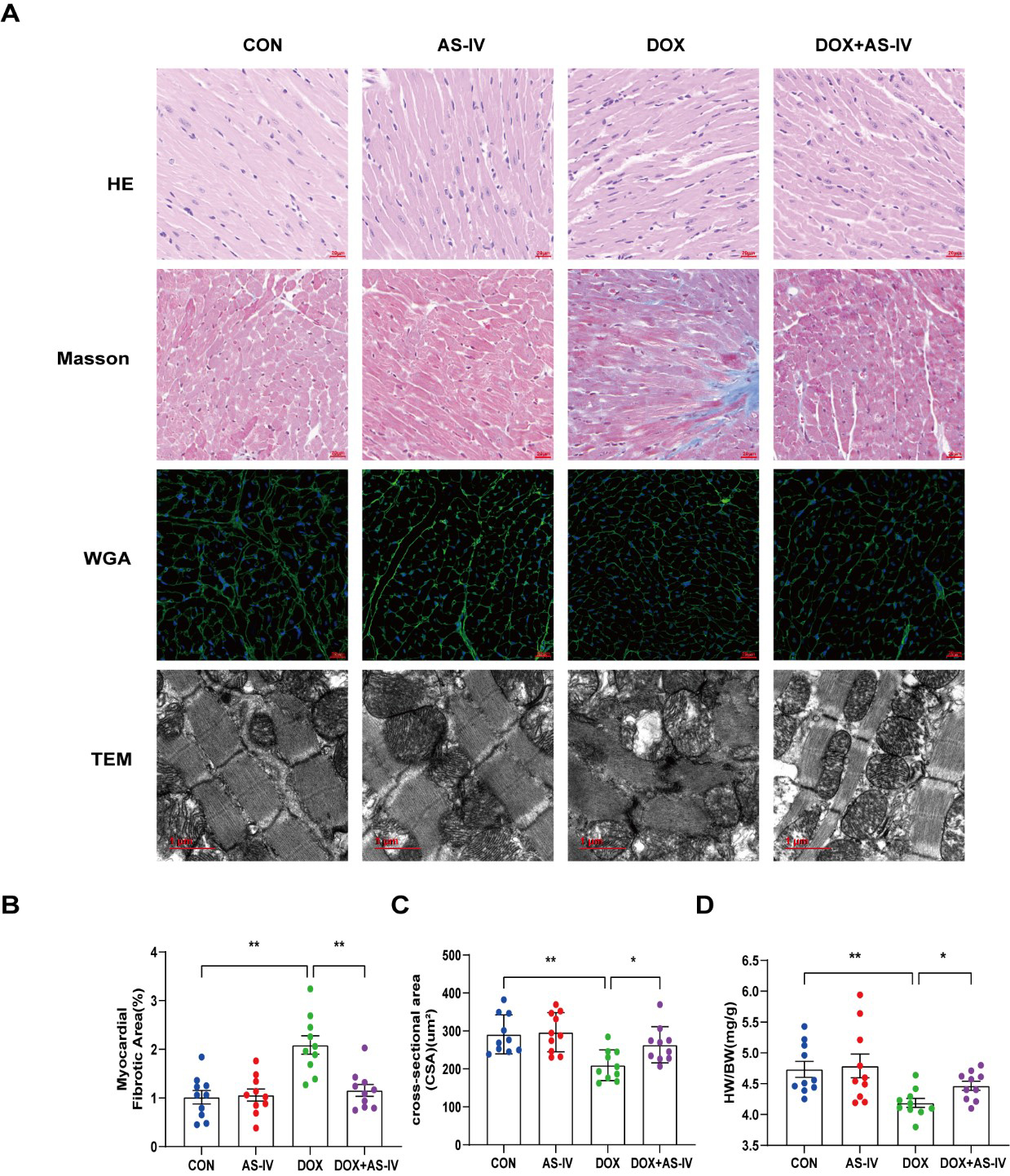 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.AS-IV ameliorated DOX-induced myocardial remodeling and
myocardial injuries. (A) Representative images of HE (magnification,
400
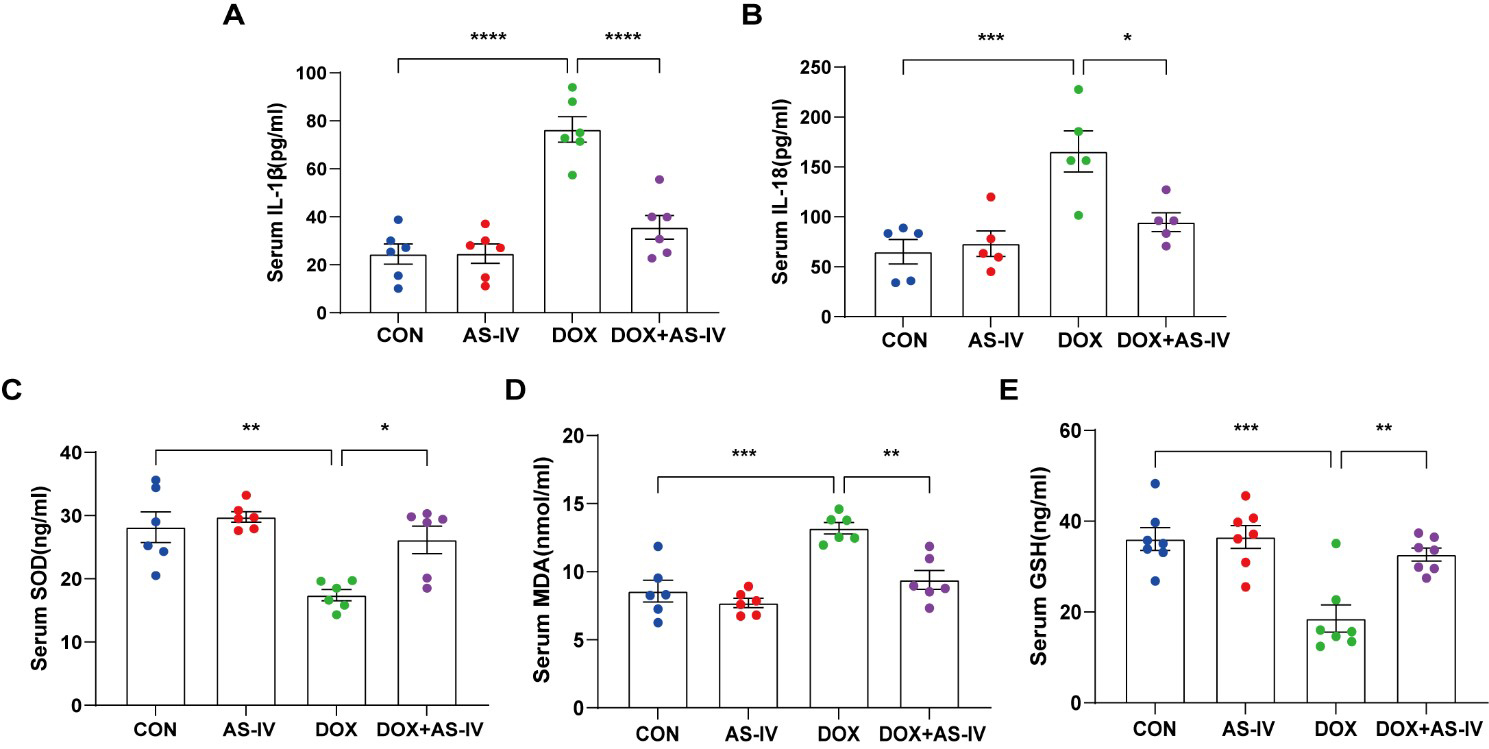
As the activation of inflammasomes and release of inflammatory factors are
important in the process of pyroptosis and the fact that oxidative stress can
cause pyroptosis [34], we measured the levels of serum IL-1
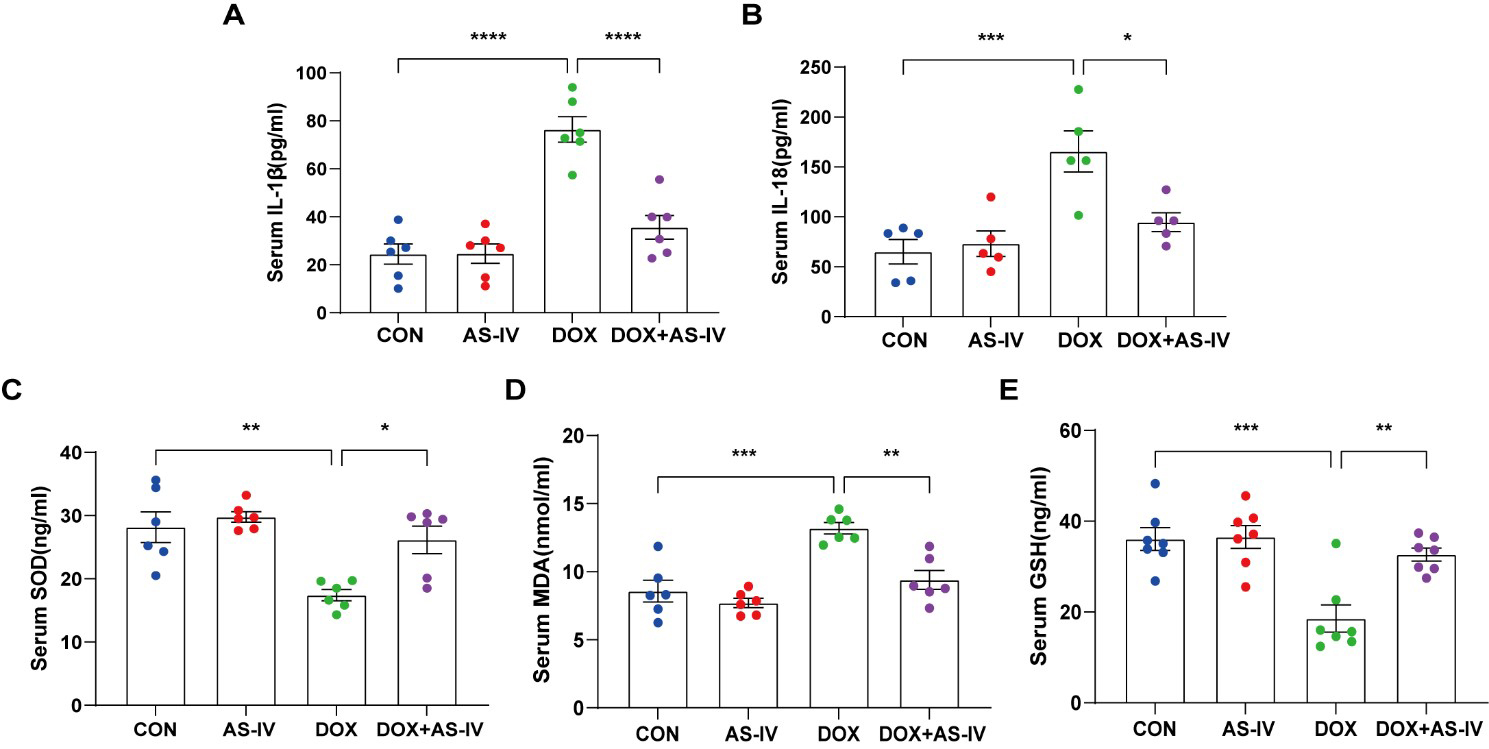 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.AS-IV ameliorated the release of DOX-induced serum inflammatory
factors and oxidative stress levels. (A–E) Quantitative analysis of serum
concentration of IL-1
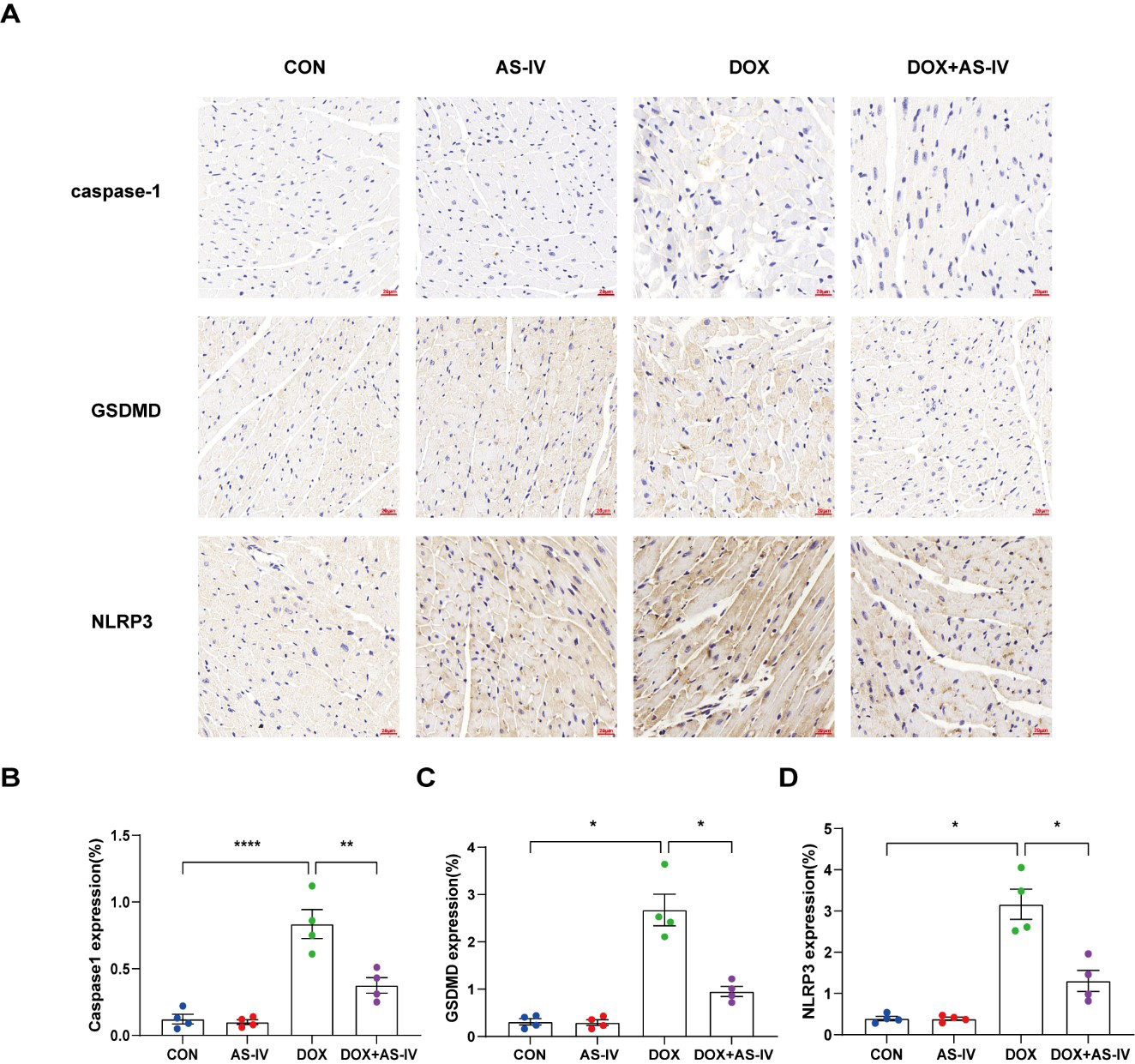
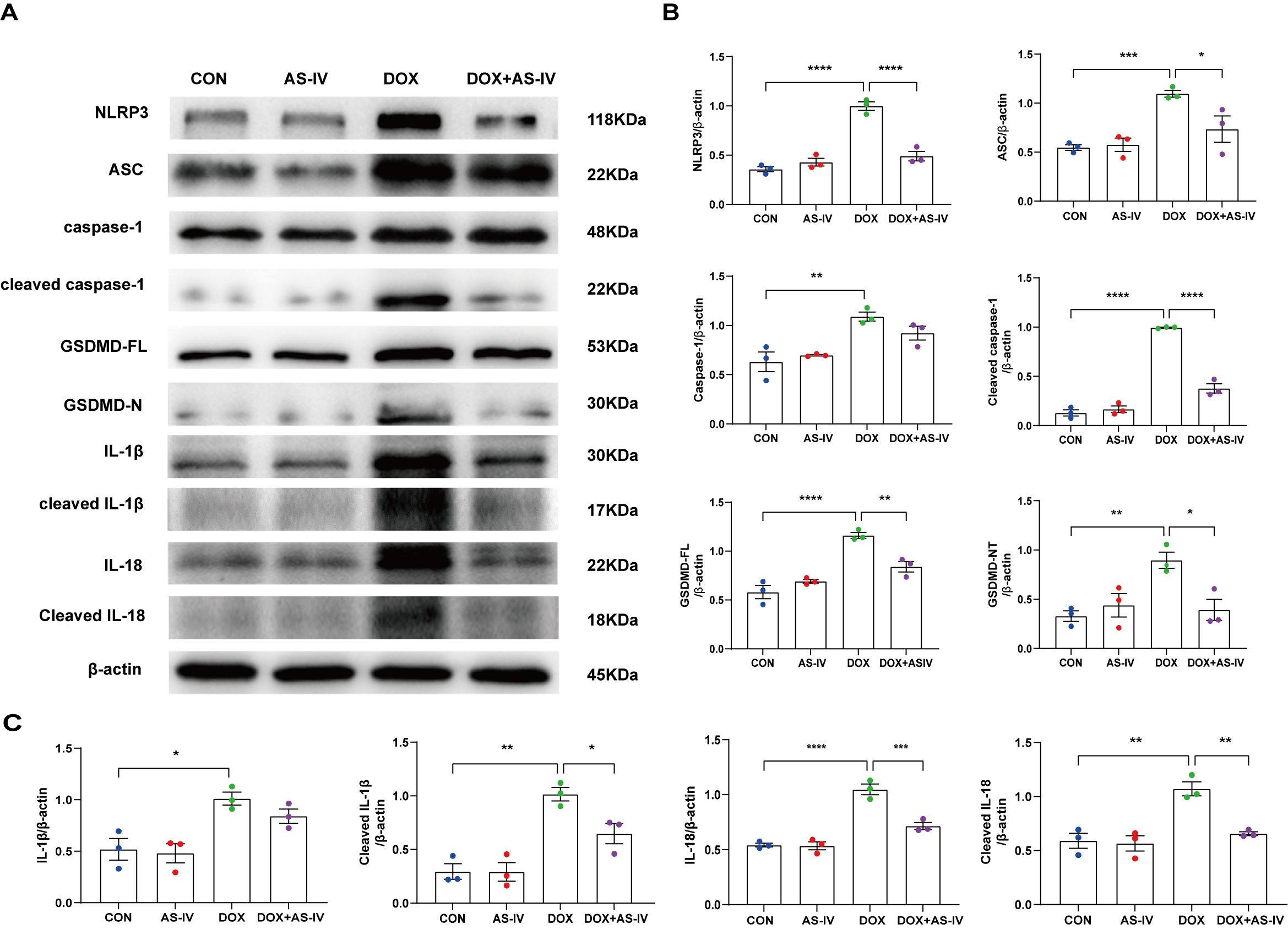
To further investigate whether AS-IV alleviates myocardial injury by inhibiting
DOX-induced myocardial pyroptosis, we first examined the expression of
pyroptosis-related proteins in myocardial tissue using immunohistochemistry (Fig. 4A). Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis showed that the expression of
pyroptosis-related proteins NLRP3, caspase-1, and GSDMD dramatically increased
after DOX treatment, and subsequent treatment with AS-IV markedly attenuated the
expression of these markers (Fig. 4B–D). In addition, the protective role of
AS-IV was confirmed using immunoblotting (Fig. 5A). As shown in Fig. 5B,C, DOX
significantly upregulated the expression of NLRP3 and ASC and activated the
cleavage of caspase-1, GSDMD-FL, IL-1
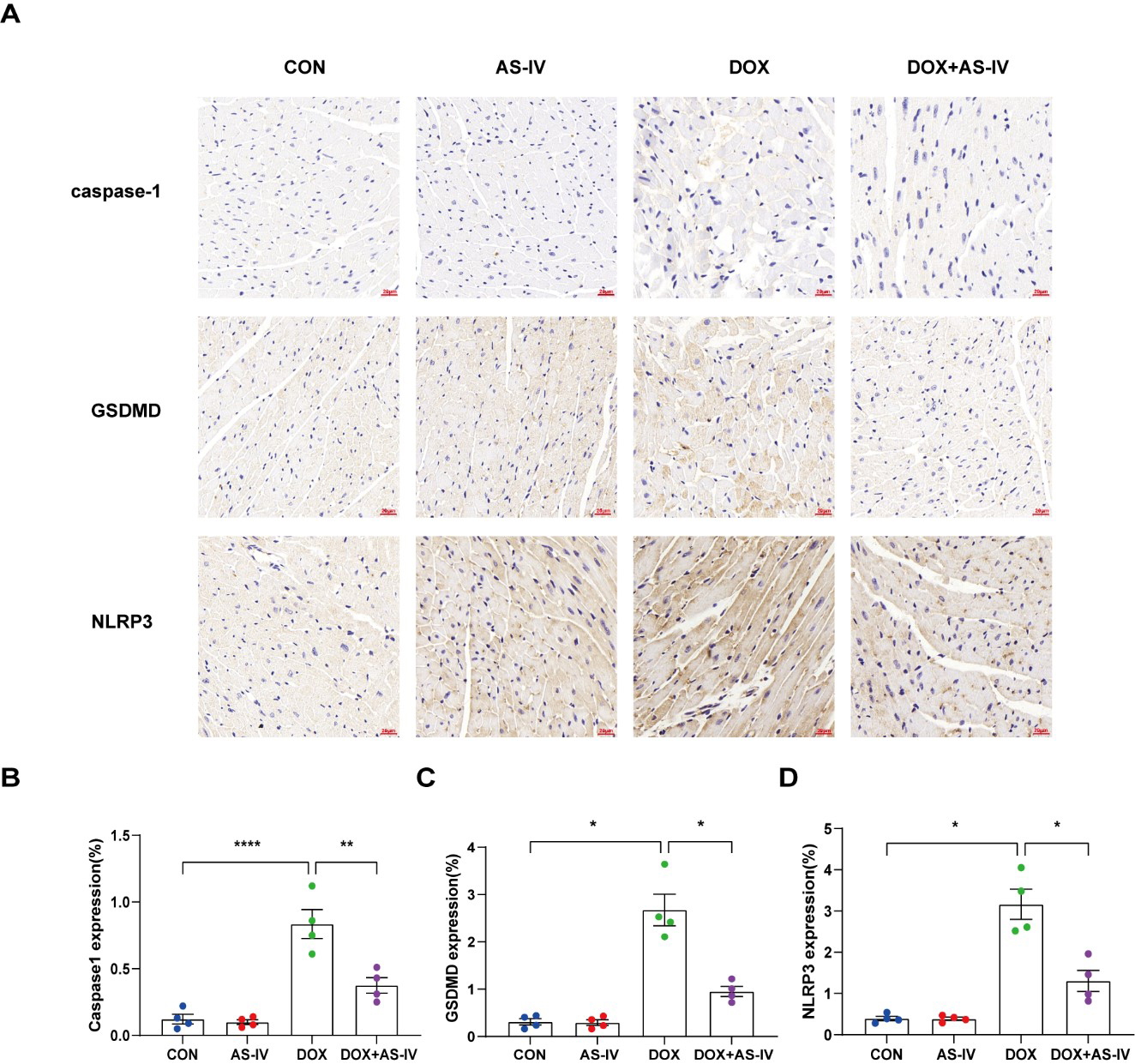 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.AS-IV attenuates the expression of pyroptosis proteins in
myocardial tissue. (A) Representative immunohistochemical images of the four
groups. (B–D) Quantitative analysis of caspase-1, GSDMD and NLRP3. N = 4, data
are shown as mean
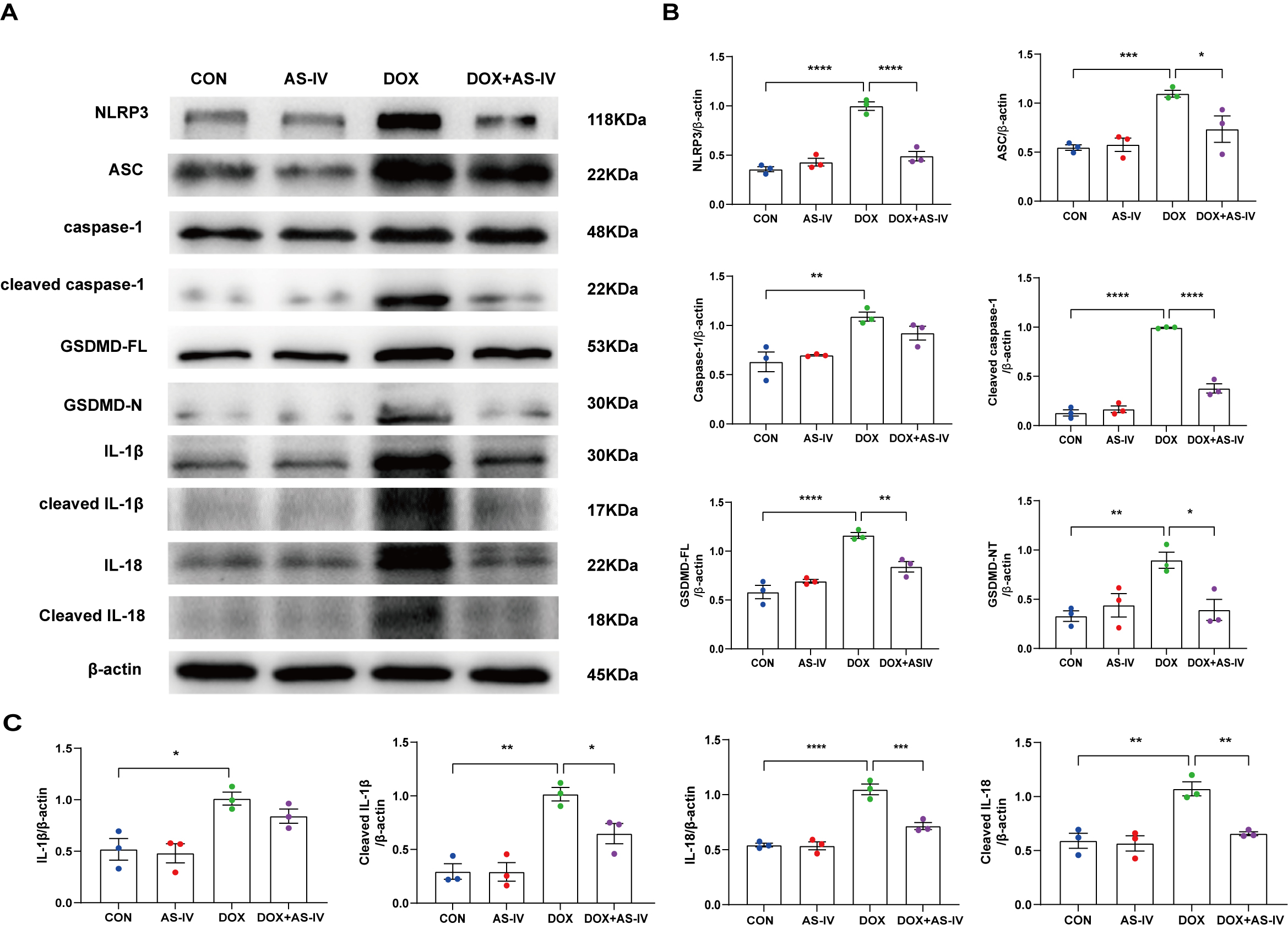 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.AS-IV inhibits the expression of DOX-induced
pyroptosis-associated proteins. (A) Representative images of western blot from
cardiac tissue following DOX and AS-IV treatments. (B,C) Quantitative analysis of
NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1, cleaved caspase-1, GSDMD-FL (full length gasdermin D),
GSDMD-N (activated gsdmd), IL-1
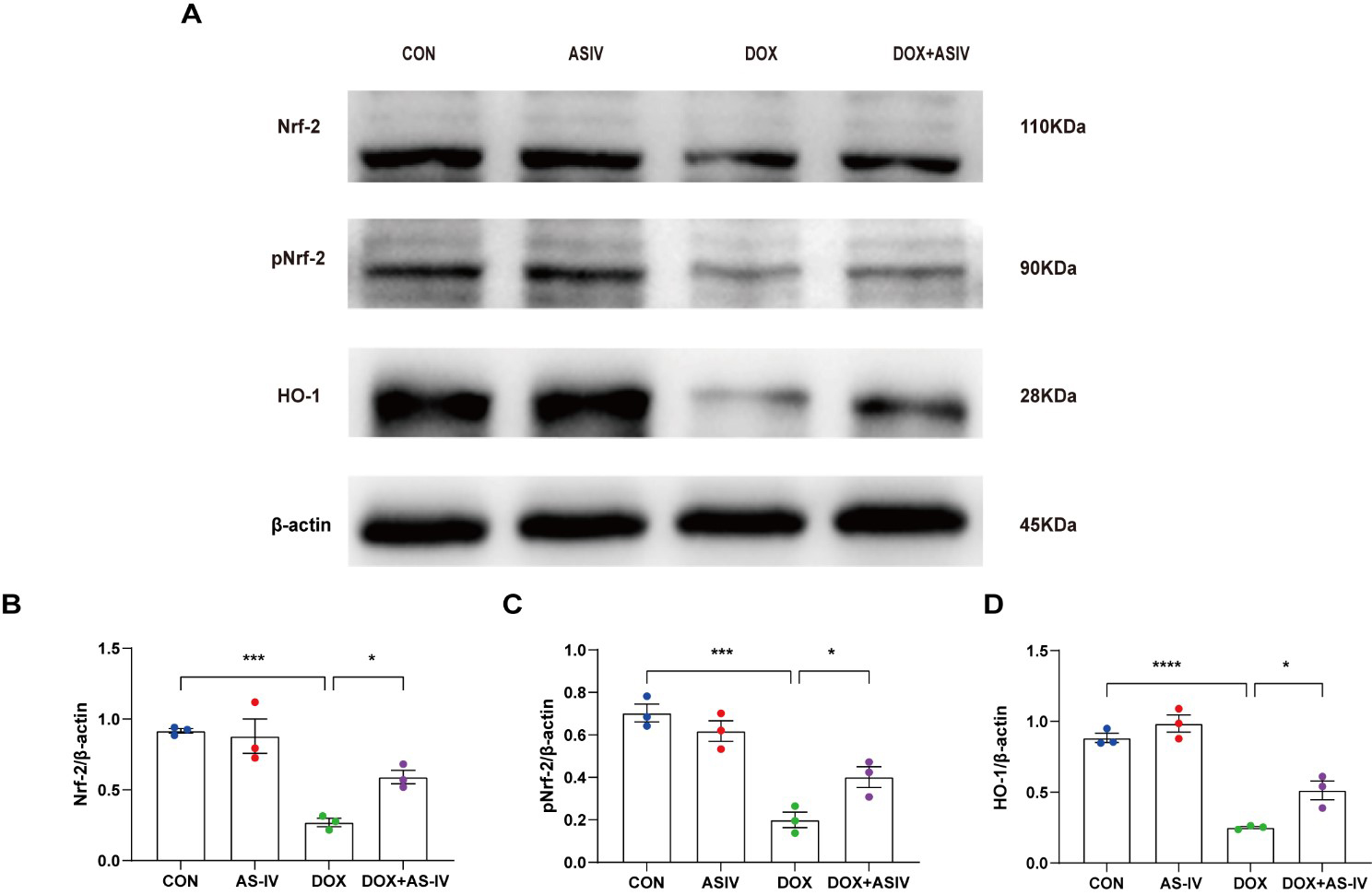
The Nrf-2 signaling pathway has been found to have a potential protective effect on neuronal, vascular endothelial, and cardiac myocyte injury caused by pyroptosis [35, 36, 37]. To further explore the possible regulatory pathways of pyroptosis, we examined the expression of Nrf-2, pNrf-2 and HO-1 (Fig. 6A). Western blotting results in Fig. 6 reveal a reduced expression of Nrf-2, pNrf-2, and HO-1 in the DOX-treated group. AS-IV activates Nrf-2 to phosphorylate it and increases the expression of HO-1. The remaining two western blots images can be found in the supplemental file.
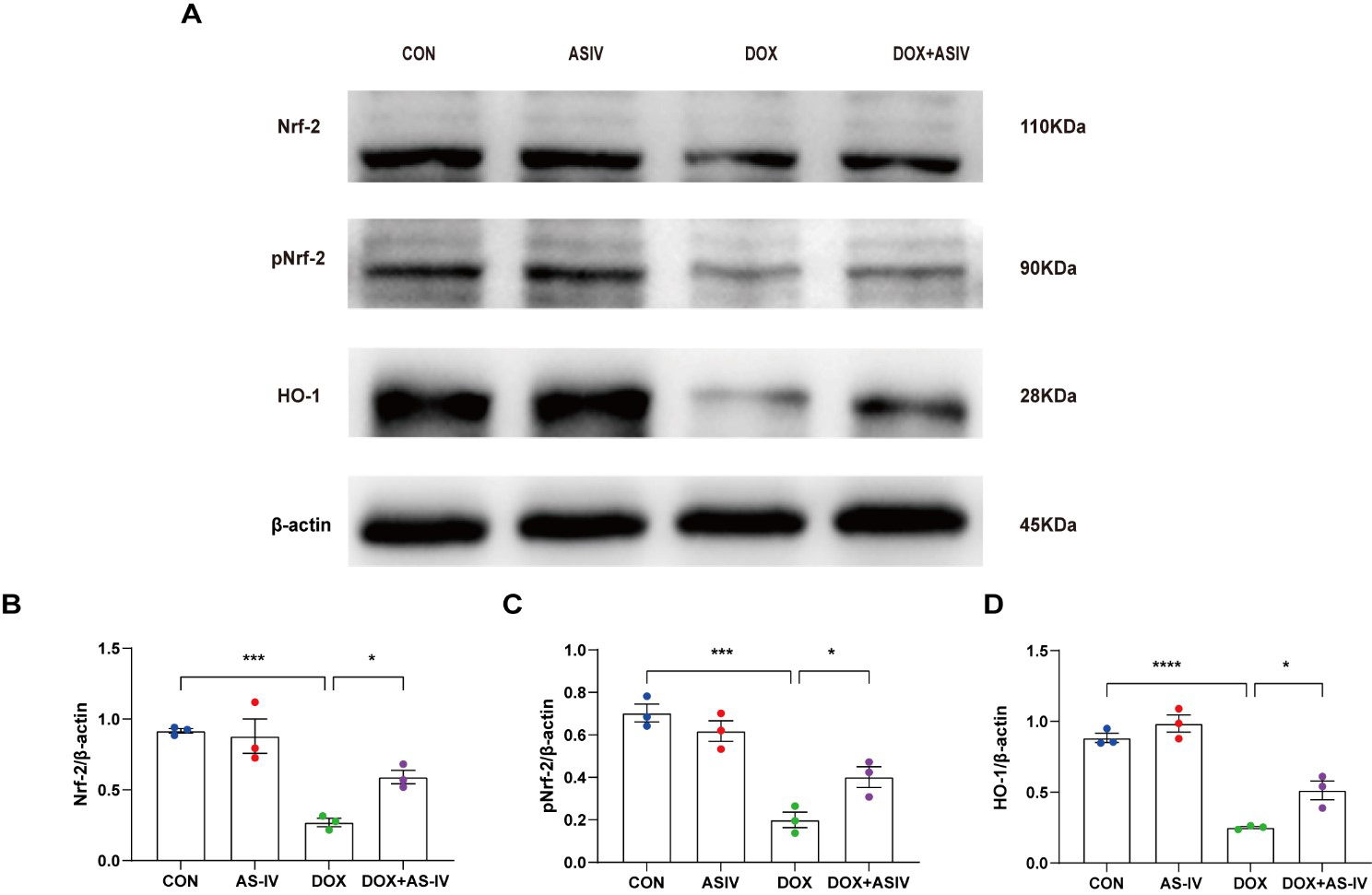 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.AS-IV inhibits DOX-induced pyroptosis by activating the
Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway. (A) Representative images of western blot analysis
of cardiac tissue following DOX and AS-IV treatments. (B–D) Quantitative
analysis of Nrf-2, pNrf-2 and HO-1. N = 3, data are shown as mean
Our findings establish that AS-IV activates the Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway and inhibits cardiomyocyte pyroptosis, and highlights the protective effect of AS-IV against DOX-induced myocardial injury. First, we confirmed the cardiotoxic effects of DOX, as evidenced by the reduced ejection fraction, increased myocardial fibrosis, and elevated serum markers of cardiac injury. Second, we demonstrated that AS-IV restored the deleterious effects of DOX by inhibiting NLRP3-related pyroptosis. Third, we found the activated Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway to be the potential mechanism underlying the protective effects of AS-IV in reducing DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. These findings indicate the potential therapeutic implication of AS-IV in inhibiting pyroptosis and ameliorating DOX-related cardiac complications.
DOX is a widely used anti-cancer drug but has limited clinical applications due to its deleterious effect on multiple organs, particularly the heart. Previous studies have shown that oxidative stress and apoptosis are involved in DOX-induced cardiomyopathy [38, 39, 40]. Moreover, excessive inflammatory responses have been demonstrated to play vital roles in DOX-induced multiple organ damage, and inhibition of the inflammatory response could potentially alleviate the possibility of organ injuries [41, 42]. Inflammasomes are polyprotein complexes that induce both inflammation and pyroptosis. Studies have provided insights into the activation and regulation of inflammasome complexes, including NLRP1, NLRP3, NLR family CARD domain-containing 4 (NLRC4), and pyrin [43]. Recent evidence has demonstrated that DOX can cause cardiotoxicity by activating NLRP1 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis [44]. It has also been shown that NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis plays an important role in the pathogenesis of DOX-induced non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy, and inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome significantly attenuates DOX-induced cardiotoxicity in mice [17, 45]. Our study also showed that DOX increases myocardial NLRP3 inflammasome-associated pyroptosis and inflammation, as evidenced by the increased expression of related proteins. These studies confirm that inflammation-related pyroptosis is a key pathogenic mechanism of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity.
Radix astragali (RA), a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, is widely used in the treatment of cardiovascular, respiratory, and liver diseases as well as immune disorders [46]. Huangqi injection is derived from RA and is widely used in the clinical treatment of patients with chronic heart failure [47, 48]. Astragalus polysaccharide, another extract of RA, has been shown to improve the quality of life of cancer patients and reduce side effects [49, 50]. AS-IV is the most critical active ingredient of RA. In the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, AS-IV is used as a quality control indicator for RA, whereas the European Pharmacopoeia also specifically considered using AS-IV for testing the quality of RA [51]. Previous studies have shown that AS-IV reduces endothelial damage and cardiac dysfunction induced by elevated levels of blood glucose, lipids, inflammatory markers, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and apoptosis [52, 53, 54, 55]. Consistently, we also found that AS-IV increased the ejection fraction, reversed ventricular remodeling, and improved cardiac function in mice after the DOX challenge. Moreover, it has been found that AS-IV attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and PM2.5-induced pulmonary toxicity by inhibiting pyroptosis [56, 57, 58], suggesting its role in regulating pyroptosis. Therefore, we investigated the role and mechanisms underlying pyroptosis, stimulated by AS-IV, in protecting against DOX-induced myocardial injuries. Notably, this study found that AS-IV inhibits the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome-related pyroptotic proteins after the DOX challenge. The present study further clarifies the role and mechanisms by which AS-IV ameliorates DOX-induced myocardial injury by attenuating myocardial pyroptosis.
ROS has been found to play an important role in NLRP3 inflammasome activation [59, 60, 61]. Oxidative stress, as the upstream signal of NLRP3 inflammasome activation, can up-regulate the expression of NLRP3, pro-caspase-1, and ASC and promote the assembly of the NLRP3 inflammasome, which in turn causes pyroptosis [34]. Nrf-2 is an important redox transcription factor that can improve the oxidative stress status of the body and maintain the redox balance of cells by regulating the production of antioxidant enzymes [62]. Phosphorylation of Nrf2 has been shown to play a key role in antioxidant stress, inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome [63, 64]. HO-1 is regulated by Nrf-2 and is the rate-limiting step that catalyzes the oxidative degradation of heme, during which it is converted to bilirubin, and plays a key role in inflammation [65]. Moreover, it was found that the activation of Nrf-2 could attenuate the classical pyroptosis pathway involved in oxidative stress [37, 66]. Our previous study also found that AS-IV can promote Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling to reduce pressure overload-induced heart failure [27]. In this study, DOX reduced the expression of Nrf2, pNrf2 and HO-1, which was reversed by AS-IV treatment. Thus, we suggest that AS-IV ameliorates DOX-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting pyroptosis via activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. However, other regulatory pathways for DOX-induced pyroptosis may exist; therefore, additional genetic modifications of mice or in vitro experiments are needed to verify the specific mechanism by which AS-IV inhibits DOX-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis.
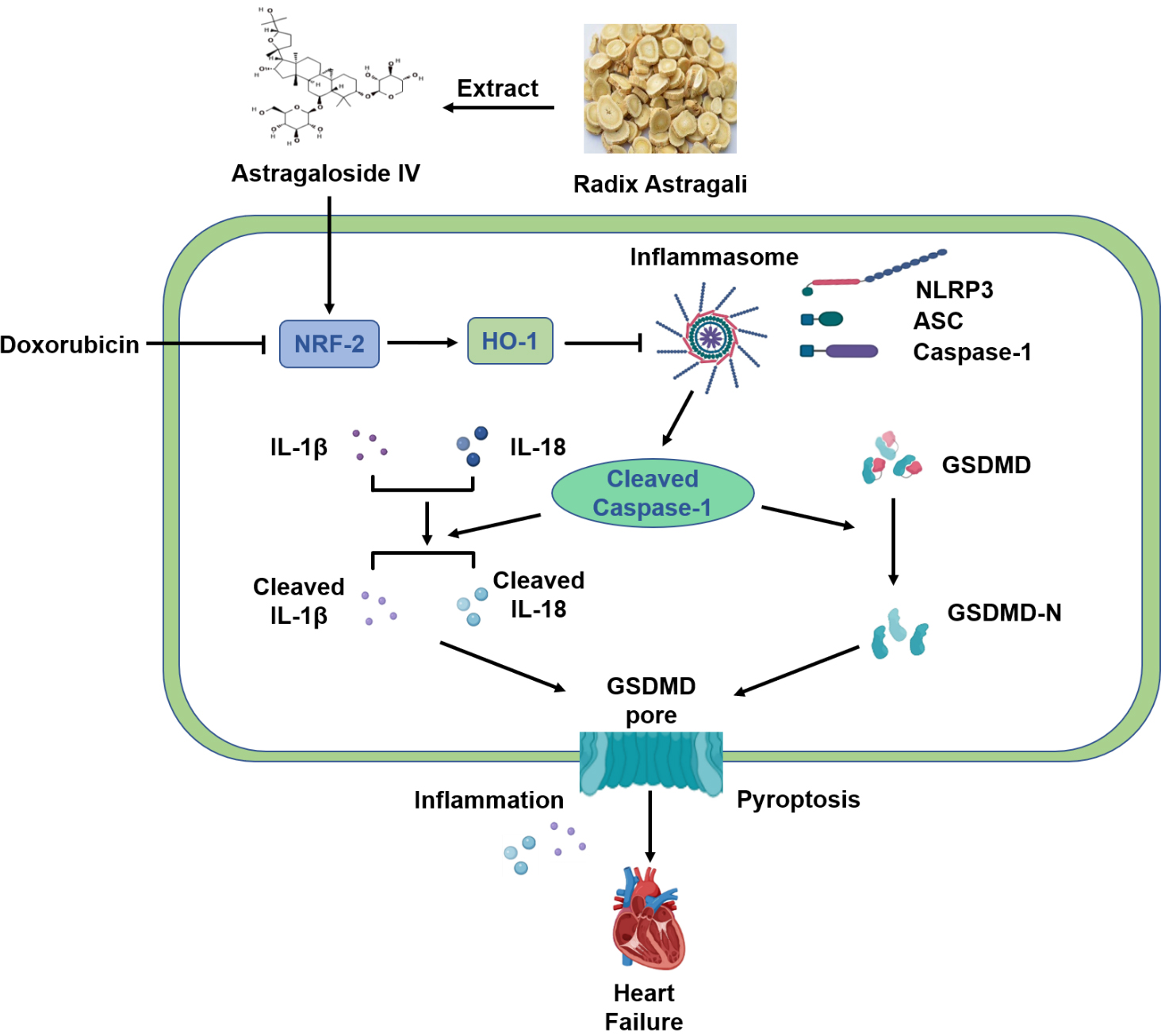
In conclusion, our results suggest that AS-IV exerts a protective effect against DOX-induced myocardial injury by activating the Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway and by inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis (Fig. 7). These results provide evidence for AS-IV to be employed as a potential clinical therapeutic agent for mitigating DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. However, further research using positive controls or gene knockout mice will provide better evidences for verifying the specific mechanisms of the Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway in the protective role of AS-IV in suppressing DOX-induced pyroptosis.
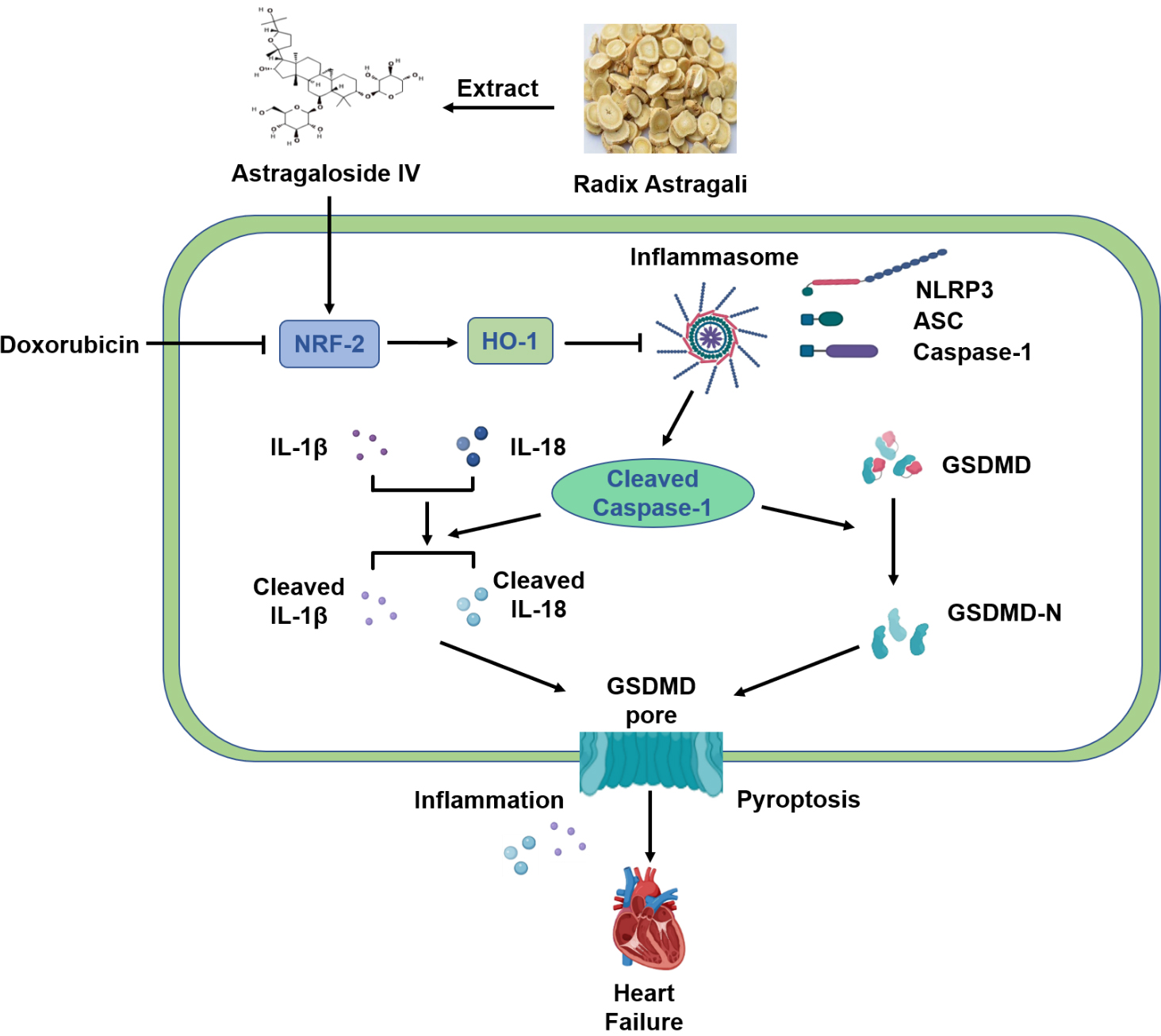 Fig. 7.
Fig. 7.Schematic diagram of protective mechanism of AS-IV against
DOX-induced myocardial injury in mice. AS-IV is extracted from Radix astragali.
DOX inhibits the expression of Nrf-2 and HO-1, which activates the assembly of
NLRP3 inflammasome, leading to the cleavage of Caspase-1. Increased cleaved
Caspase-1 then cleaves the inflammatory factors IL-1
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
CS, JZ and XW conceived and designed this study. XC performed animal administration, echocardiographic examination, ELISA, and western blot data acquisition. CT and ZZ contributed to histological and immunofluorescent data acquisition. XC contributed to the figures and statistical analysis. XC wrote the manuscript. YQ, RM, XD and YZ conducted part of the western blot and data analysis. CS contributed to the revision of this manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The experiments were conducted in accordance with the principles approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University (Permission number: 2021C104). All animal procedures conformed to the US of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. All animals were carefully handled and euthanized during the study.
Not applicable.
This study was supported by Shandong Province Medical and health Science and Technology Development Program (2019WS364), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 82000269), Jining City Science and Technology Key Research and Development Program (2018SMNS006), Research Fund for Academician Lin He New Medicine (JYHL2018FMS02) and Jining City Science and Technology Key Research and Development Program (2021YXNS069).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at https://doi.org/10.31083/j.fbl2803045.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.