1 Department of Histology and Cell Pathology in Zabrze, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Zabrze, Medical University of Silesia in Katowice, 40-055 Katowice, Poland
2 Departmentof Descriptive and Topographic Anatomy, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Zabrze, Medical University od Silesia, 40-055 Katowice, Poland
3 Department of Pathology, Pomeranian Medical University, 71-344 Szczecin, Poland
4 Autophagy Research Center, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, 7134845794 Shiraz, Iran
5 Linkocare Life Sciences AM, 583-30 Linkoping, Sweden
Abstract
Background: The Apoptotic protease activating factor 1 (Apaf-1)
protein, as one of the factors involved in the activation of the mitochondrial
apoptotic pathway, plays an important role in cancer biology. Apaf-1 expression
in tumour cells has been shown to be downregulated, with significant implications
for tumour progression. Hence, we investigated the expression of Apaf-1 protein
in the Polish population of patients with colon adenocarcinoma without any
therapy prior to radical surgery. Moreover, we assessed the relation between
Apaf-1 protein expression and the clinicopathological factors. The prognostic
activity of this protein was analyzed in relation to 5-year survival of patients.
In order to show the localization of Apaf-1 protein at the cellular level, the
immunogold labelling method was used. Methods: The study was conducted
using the colon tissue material from patients with histopathologically confirmed
colon adenocarcinoma. Immunohistochemical expression of Apaf-1 protein was
performed using Apaf-1 antibody at dilution 1:600. The associations between the
immunohistochemistry (IHC) expression of Apaf-1 and clinical parameters were
analyzed using the Chi
Keywords
- immunohistochemistry
- prognostic marker
- 5-year survival rate
- colon adenocarcinoma
- apoptosis
- immunogold labelling
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common cancers of the gastrointestinal tract with approximately 90% of histopathological diagnoses being colorectal adenocarcinoma (COAD) [1]. Factors that significantly influence the development of this type of malignancy include lifestyle, e.g., obesity, prolonged and frequent smoking, alcohol consumption and a diet low in fibre but rich in red meat. Other risk factors include the presence of chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), inadequate exposure to sunlight, including vitamin D3 deficiency, and genetically determined changes leading to colonic mucosal cell dysplasia [2, 3, 4]. It should also be noted that CRC is a highly invasive type of cancer and shows a high level of heterogeneity. This in turn raises many questions and concerns regarding the timely diagnosis and treatment of patients. The 5-year survival rate applies to approximately 60–95% of patients with early-stage disease but drops significantly (approximately 35%) with the presence of lymph node metastases [5, 6, 7]. Hence there is a need for early diagnosis, which would certainly improve patient survival.
Apoptotic protease activating factor 1 (Apaf-1) is a protein with multiple domains in its structure, including a caspase recruitment domain (CARD), a nucleotide-binding domain and an oligomerization domain (NOD). A WD-40 repeat region (WDR) is also present in the Apaf-1 protein framework [8]. The released cytochrome C associates with a single Apaf-1 molecule within the WD40 domain to generate a heptameric apoptosome, ultimately leading to caspase activation [9, 10]. As Apaf-1 is known to be a key molecule during the activation of mitochondrial apoptosis pathway apoptosis, and changes in its expression may contribute to many diseases including cancer [11, 12]. Therefore, a detailed understanding of the function and regulation of Apaf-1 may influence the development of new better anti-cancer therapies.
Zlobec et al. [13, 14] revealed that in Canadian patients Apaf-1 is a marker of tumour progression in MMR- proficient colorectal cancer and an independent adverse prognostic factor in MLH1-negative colorectal cancer. Nevertheless, we have little data on Apaf-1 protein expression in patients suffering from colon adenocarcinoma, especially in the European population. With this in mind, we decided to investigate the expression of Apaf-1 protein in the Polish population of patients with colon adenocarcinoma without any therapy prior to radical surgery. Moreover, we also investigated the association between Apaf-1 protein expression and the clinicopathological factors of colon adenocarcinoma patients. The prognostic activity of this protein was analyzed in relation to 5-year survival of patients. It should be pointed out that our study is the first that assessed the correlation between immunohistochemical expression of Apaf-1 and Proliferative Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) in the population of patients with colon adenocarcinoma. Yang et al. [15] revealed that PCNA expression has been found to correlate with the degree of malignancy, vascular infiltration, distant metastasis and survival. This antigen has been described as a biomarker of colorectal adenocarcinoma [16]. Nevertheless, the relationship between Apaf-1 and PCNA in colon adenocarcinoma has not yet been assessed.
Tissue colon material collected from the patients undergoing colon resection at the Municipal Hospital in Jaworzno between January 2014 and December 2015 with histopathologically confirmed colon adenocarcinoma was used for the study. Patients who received preoperative radiotherapy or chemotherapy, patients with distant metastasis, patients undergoing resection from tumour recurrence, patients with adenocarcinoma in the setting of inflammatory bowel disease and patients with histopathologically confirmed subtype other than adenocarcinoma were excluded from the study. Based on an established protocol, histopathological sections containing tumour fragments and adjacent tissue sections without tumour lesions were taken from each surgical specimen. The collected samples were fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin blocks. In the next step, the paraffin blocks were cut and sections were routinely stained with hematoxylin-eosin staining (H&E) to confirm the histopathological diagnosis. Sections containing tissue margins were also assessed. If tumour cells were found, the material was excluded from the study. To determine whether Apaf-1 protein had prognostic significance, patients were followed up for 5 years to estimate the 5-year survival rate.
Paraffin-embedded tissue blocks with formalin-fixed colon adenocarcinoma specimens and resected margins were cut into 4-m-thick sections, fixed on Polysine slides and deparaffinized in xylene and rehydrated through a graded series of alcohol. To retrieve the antigenicity, the tissue sections were treated with microwaves in a 10 mM citrate buffer (pH 6.0) for 8 min each. Subsequently, sections were incubated with antibody to Apaf-1 (Zytomed Systems. polyclonal antibody. order no. 501395. final dilution 1:600, Berlin, Germany) and Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) (GeneTex. polyclonal antibody. Cat. No. GTX100539, final dilution 1:600, Irvine, CA, USA). For visualization of protein expression, the sections were treated with Bright Vision detected system and Permanent AP Red Kit (Zytomed, Cat. No. ZUCC001-125, Berlin, Germany). Mayer’s haematoxylin was used to counterstain the nuclei). In addition, the Expression of Apaf-1 and PCNA was studied in sections of healthy mucosa from patients undergoing screening colonoscopy with no inflammatory or cancerous lesions. The scoring of Apaf-1 and PCNA expression was based on both the intensity and frequency of immunohistochemical reaction determining the presence of Apaf-1 and PCNA. The intensity was graded as follows: 0, no signals; 1, weak; 2, moderate; and 3, strong staining. The frequency of positive tumour cells was determined semiquantitatively by assessing the whole section, and each sample was scored on a scale of 0 to 4: 0, negative; 1, positive staining in 10–25% cells, 2, 26–50% cells; 3, 51–75% cells; and 4, 76–100% cells. A total score of 0–12 was finally calculated and graded as; I, score 0–1; II, 2–4; III, 5–8; IV, 9–12. Grade I was considered negative; and grades II, III and IV were positive. Grades I and II represented no or weak staining (low expression), and grades III and IV represented strong staining (strong expression). The evaluation was carried out by two independent pathologists. Differences were again assessed until consensus was obtained.
The associations between the IHC expression of Apaf-1 and clinical parameters
were analyzed statistically with Statistica 9.1 (Software, StatSoft, Cracow,
Poland). All the quantitative variables were described as medians and ranges. The
Chi
All figures in this manuscript were generated by the use of Xara Designer Pro X 18 (ProX 18, MAGIX Software GmbH, Berlin, Germany).
For the study with the use of immunogold labelling methods, the tissue samples
were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 2
hours at room temperature and then washed several times in PBS. After washing,
the specimens were dehydrated in a graded ethanol series and infiltrated in a 2:1
(v:v) ethanol/LR White mixture and 1:2 (v:v) for 30 min each on ice. Afterwards,
the samples were infiltrated in pure LR White. Ultra-thin sections (70 nm) were
cut with a RMC Boeckeler Power Tomo PC ultramicrotome with a diamond knife
(45°; Diatom AG, Biel, Switzerland). Ultrasections were mounted on
200-mesh nickel grids coated with Formvar and immunolabelled. Sections on the
grids were preincubated first for 30 minutes by floating on drops of 50 mM
NH
The patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
| N (number of cases) | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Females | 58 | 47.93 |
| Males | 63 | 52.07 | |
| Age [years] | 47 | 38.84 | |
| 61–75 years | 36 | 29.75 | |
| 38 | 31.45 | ||
| M |
65.89 | ||
| Me [Q1–Q3] | 64 [55–78] | ||
| Min–Max | 33–89 | ||
| Grade of histological differentiation | G1 | 20 | 16.53 |
| G2 | 64 | 52.89 | |
| G3 | 37 | 30.58 | |
| Depth of invasion | T1 | 11 | 9.09 |
| T2 | 14 | 11.57 | |
| T3 | 75 | 61.98 | |
| T4 | 21 | 17.36 | |
| Regional LymphNode involvement | N0 | 49 | 40.49 |
| N1 | 43 | 35.54 | |
| N2 | 29 | 23.97 | |
| Location of tumour | Right sided tumours | 64 | 52.89 |
| Left sided tumours | 57 | 47.11 | |
| Angioinwasion | No | 26 | 21.49 |
| Yes | 95 | 78.51 | |
| PCNA expression | Low | 33 | 27.27 |
| High | 88 | 72.73 | |
| Staging | I | 18 | 14.88 |
| II | 34 | 28.10 | |
| III | 69 | 57.02 | |
The colon adenocarcinoma specimens belonged to 63 men and 58 women (mean age: 64; range: 55–78 years). Tumours were located in the proximal part of the colonin64 (52.89%) cases and in the distal part of the colon in 57 (47.11%). Three levels of histological differentiation were used to classify the grading as follows: G1, 20 cases (16.53%), G2, 64 cases (52.89%) and G3, 37 (30.58%).
A positive immunohistochemical reaction determining the expression of Apaf-1 protein was found in cancerous tissues and surgical margins of colon adenocarcinoma patients (Fig. 1).
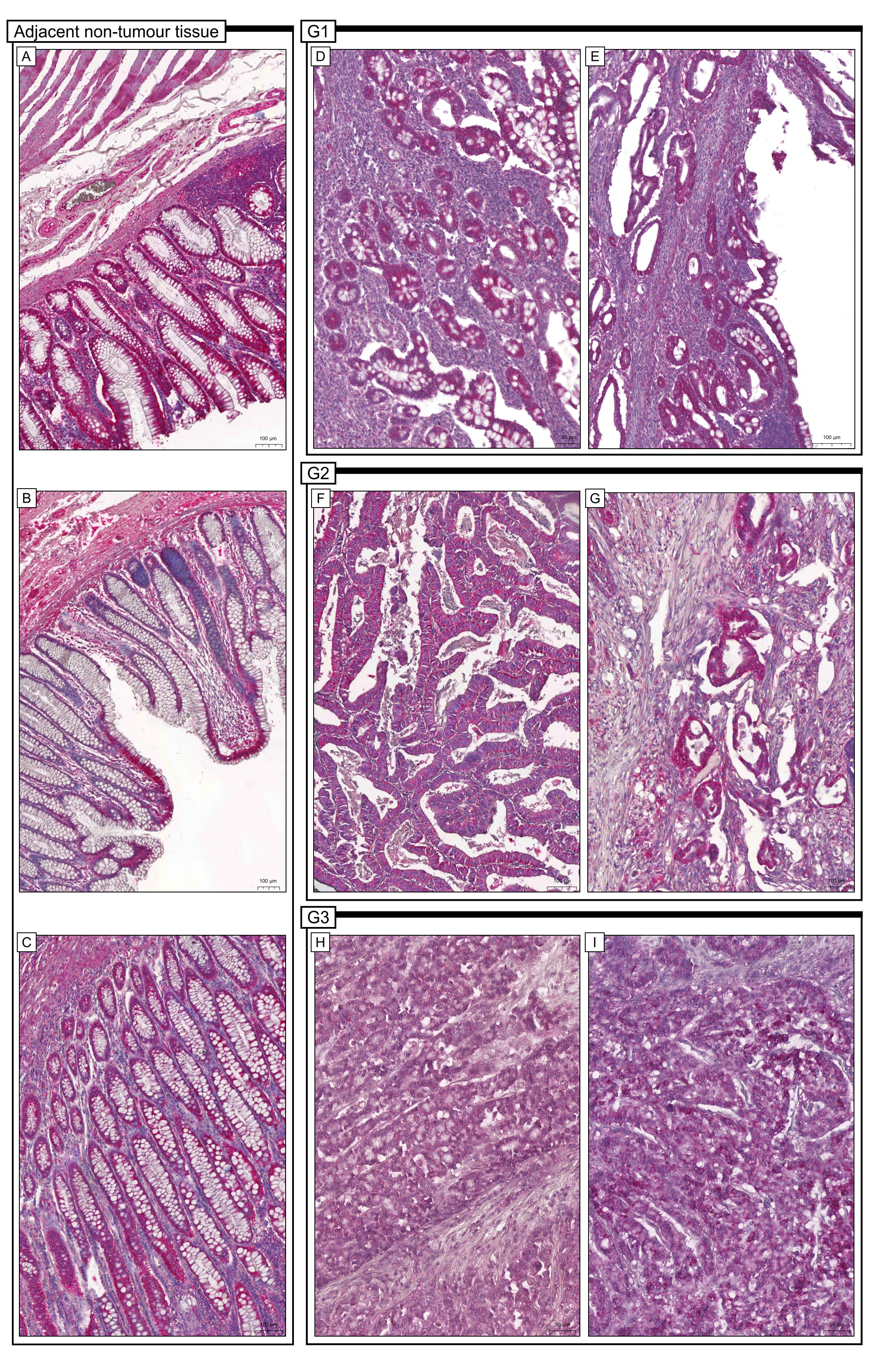 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Representative microphotographs of immunohistochemical
expression of Apaf-1 (Apaf-1 antibody at dilution: 1:600) in colon adenocarcinoma
tissue (G1, G2, G3) and tissue margins with no cancerous lesions (adjacent
non-tumour tissue). (A,B,C-magnification
It should be noted that in the vast majority of patients, the expression in cancer tissue was determined to be low. The cytoplasmic or membranous expression was detected in cancer cells and stromal cells. In contrast, expression in surgical margins and healthy colon mucosa was described as strong. In healthy colon mucosa, the expression was detected in glandular cells and in infiltrating cells of lamina propria.
39 (33.23%) samples of colon adenocarcinoma specimens had strong Apaf-1 protein
expression whereas a low level of immunoreactivity was observed in 82 samples
(67.77%). The high expression of Apaf-1 was inversely related to histological
grade of the tumour (p = 0.001, Chi
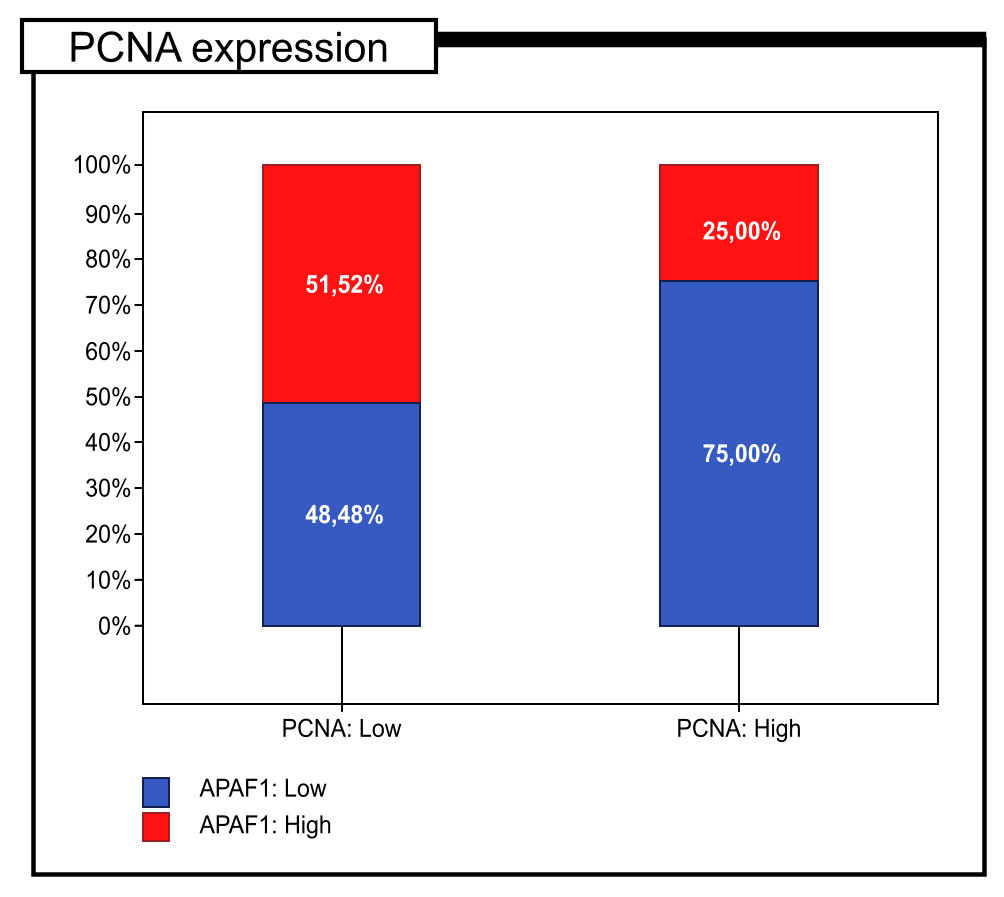 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Percentage of immunohistochemical expression of PCNA defined as high and low expression in colon adenocarcinoma patients (n = 121).
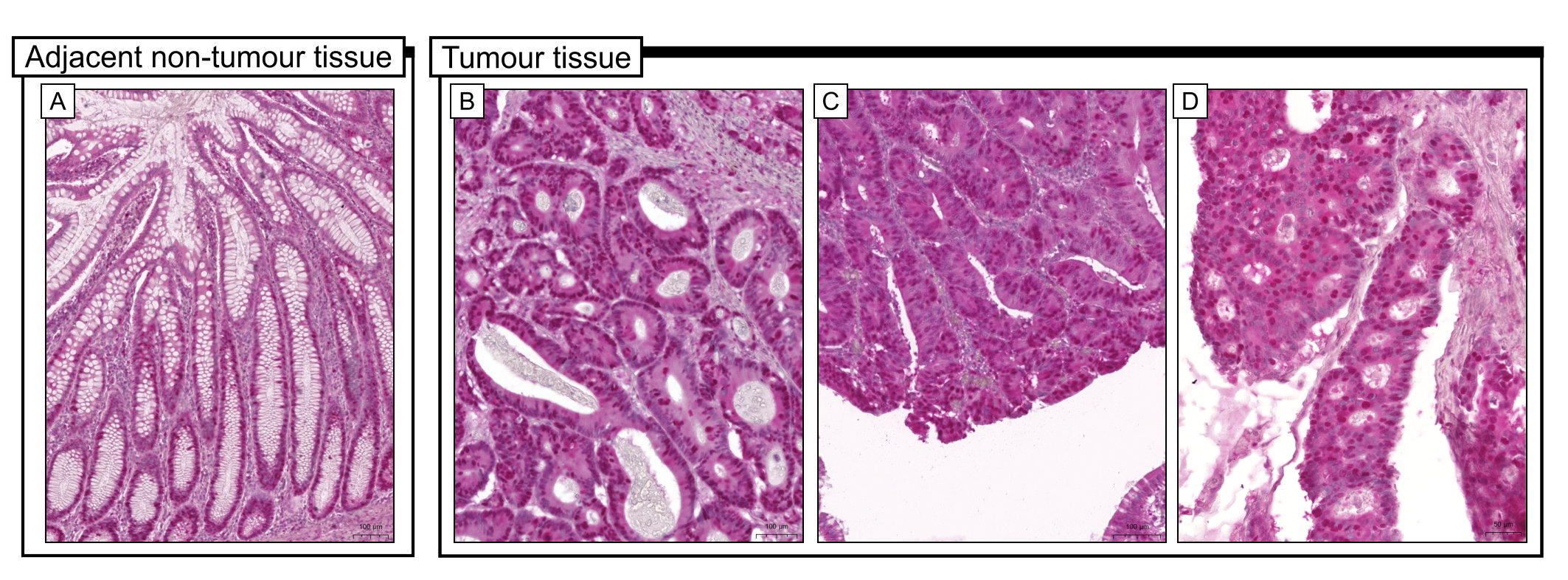 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Representative microphotographs of immunohistochemical
expression of PCNA (dilution 1:600) in colon adenocarcinoma tissue
(B-magnification
| The immunoexpression level of Apaf-1 | Statistical analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||||
| PCNA expression | Low | 16 | (48.48%) | 17 | (51.52%) | Chi |
p = 0.005 |
| High | 66 | (75.00%) | 22 | (25.00%) | R = –0.253 | p = 0.005 | |
It should be pointed out that Apaf-1 protein expression was markedly correlated
with age (p = 0.015, Chi
| The immune expression level of Apaf-1 | Statistical analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | |||||
| Age [Years] | 37 | (78.72%) | 10 | (21.28%) | Chi | |
| 61–75 years | 26 | (72.22%) | 10 | (27.78%) | p = 0.015 | |
| 19 | (50.00%) | 19 | (50.00%) | df = 2 | ||
| Gender | Females | 41 | (70.69%) | 17 | (29.31%) | Chi |
| Males | 41 | (65.08%) | 22 | (34.92%) | p = 0.509 | |
| df = 1 | ||||||
| Grade of histological differentiation | G1 | 3 | (15.00%) | 17 | (85.00%) | Chi |
| G2 | 46 | (71.88%) | 18 | (28.13%) | p | |
| G3 | 33 | (89.19%) | 4 | (10.81%) | df = 2 | |
| Depth of invasion | T1 | 1 | (9.09%) | 10 | (90.91%) | Chi |
| T2 | 9 | (64.29%) | 5 | (35.71%) | p | |
| T3 | 56 | (74.67%) | 19 | (25.33%) | df = 3 | |
| T4 | 16 | (76.19%) | 5 | (23.81%) | ||
| Regional Lymph Node involvement | N0 | 30 | (61.22%) | 19 | (38.78%) | Chi |
| N1 | 29 | (67.44%) | 14 | (32.56%) | p = 0.255 | |
| N2 | 23 | (79.31%) | 6 | (20.69%) | df = 2 | |
| Angioinwasion | No | 8 | (30.77%) | 18 | (69.23%) | Chi |
| Yes | 74 | (77.89%) | 21 | (22.11%) | p | |
| df = 1 | ||||||
| Localisation | Right sided tumours | 42 | (65.63%) | 22 | (34.38%) | Chi |
| Left sided tumours | 40 | (70.18%) | 17 | (29.82%) | p = 0.593 | |
| df = 1 | ||||||
| Staging | I | 6 | (33.33%) | 12 | (66.67%) | Chi |
| II | 25 | (73.53%) | 9 | (26.47%) | p = 0.003 | |
| III | 51 | (73.91%) | 18 | (26.09%) | df = 3 | |
The prognostic significance of Apaf-1 expression in colon adenocarcinoma
patients was analyzed in relation to 5-year survival rate. All samples were
assessed by Kaplan-Meier survival curves. The 5-year survival rate was
significantly higher in the group of patients where high Apaf-1 expression was
found (log-rank, p
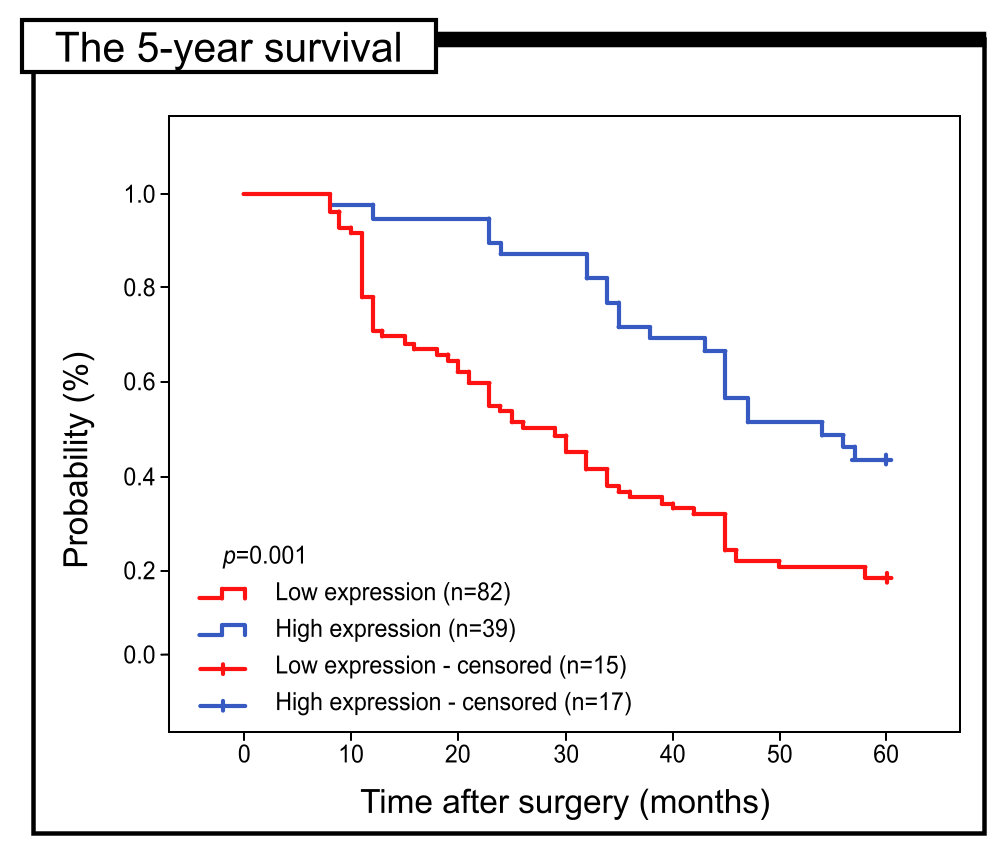 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Kaplan-Meier curves of univariate analysis date (log-rank test) showing the 5-year survival rate for patients with high versus low Apaf-1 expression.
Additionally, the value of Apaf-1 expression in the context of the 5-year survival rate was evaluated in patients’ subgroups stratified by PCNA expression, grade of histological differentiation, depth of invasion and lymph node involvement. The expression of Apaf-1 was strongly associated with the 5-year survival rate of patients with a high level of PCNA expression. The patients with a high level of this antigen and low level of Apaf-1 expression has significantly lower 5-year survival rate (log rank test, p = 0.012). Interestingly, in the group of patients without lymph node involvement and with low level of Apaf-1 expression, the 5-year survival rate was also reduced (log rank test, p = 0.002). Similar results have been obtained in patients with T3/T4 depth of invasion (log rank test, p = 0.003) and low levels of Apaf-1 immunohistochemical reaction (Fig. 5).
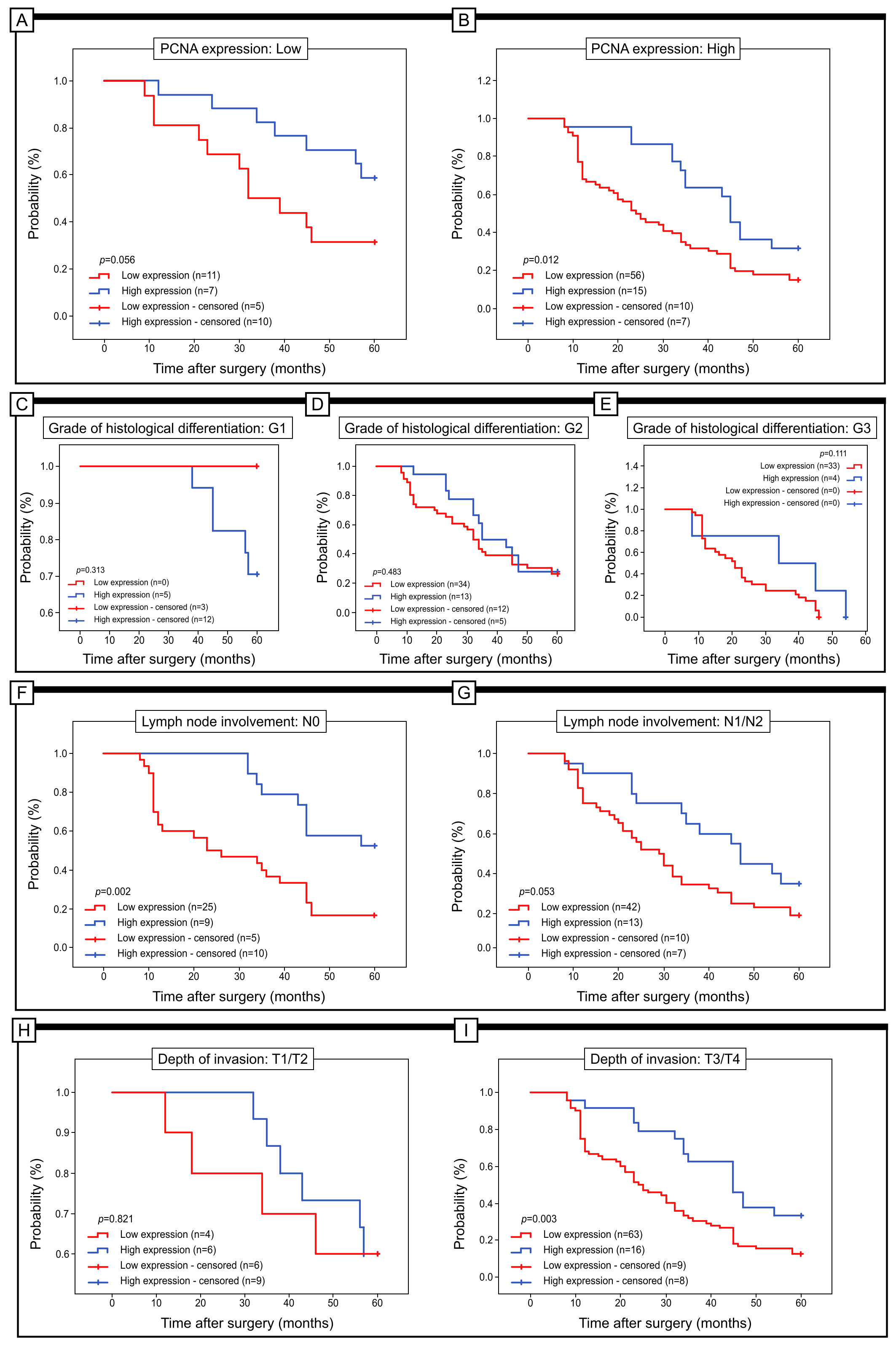 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Kaplan-Meier curves of univariate analysis date (log-rank test) of patients with high versus low level of Apaf-1 immunoreactivity. (A,B) 5-year survivaval of patients with low (A) and high (B) PCNA expression. (C,D,E) 5-year survival rate of patients with tumour at G1 (A), G2 (B) and G3 (C). (F,G) 5-year survivaval of patients without lymph node involvement (F) and with lymph node involvement (G). (H,I) 5-year survivaval of patients with T1/T2 (H) and with T3/T4 depth of invasion (I).
Univariate Cox regression analyses revealed that Apaf-1 protein level, the grade of histological differentiation, and depth of invasion are significant prognostic factors. However, multivariate analysis showed that Apaf-1 cannot be considered an independent indicator associated with the 5-year survival rate in patients with colon adenocarcinoma. Additionally, the multivariate analysis showed that only one clinicopathological factor should be considered an independent prognostic marker. In our group of patients, this factor was associated with the grade of histological differentiation (Table 4).
| Prognostic parameter | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| Gender | 1.088 | 0.718–1.651 | 0.690 | – | – | – |
| Age | 1.006 | 0.991–1.021 | 0.408 | – | – | – |
| Grade | 2.907 | 2.062–4.097 | 2.402 | 1.596–3.614 | ||
| Depth of invasion | 1.824 | 1.367–2.434 | 1.265 | 0.899–1.780 | 0.177 | |
| Regional Lymph Node involvement | 1.202 | 0.924–1.563 | 0.171 | – | – | – |
| Angioinwasion | 3.598 | 1.855–6.981 | 1.097 | 0.500–2.406 | 0.818 | |
| Localisation | 1.166 | 0.769–1.768 | 0.469 | – | – | – |
| PCNA expression | 2.061 | 1.226–3.465 | 0.006 | 1.461 | 0.794–2.690 | 0.223 |
| Staging | 1.357 | 1.018–1.808 | 0.037 | 0.866 | 0.592–1.269 | 0.461 |
HR, hazard ratio.
In order to show the localization of Apaf-1 protein at the cellular level of colon adenocarcinoma tissue, the immunogold labelling method was used (Fig. 6). The black electron-dense granules formed by immunohistochemical reaction indicating the presence of Apaf-1 protein were found both in cancer cells and in cells of colon epithelium in control samples. The small gold particles conjugated to the anti-Apaf-1 antibody were dispersed in the cytoplasm in vicinity of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi Apparatus. Moreover, black electron-dense granules were found in mitochondria. Interestingly, in the control samples, the gold granules associated with the Apaf-1 antibody were detected within the endoplasmic reticulum and small vesicles, especially in the apical part of cells (Fig. 6).
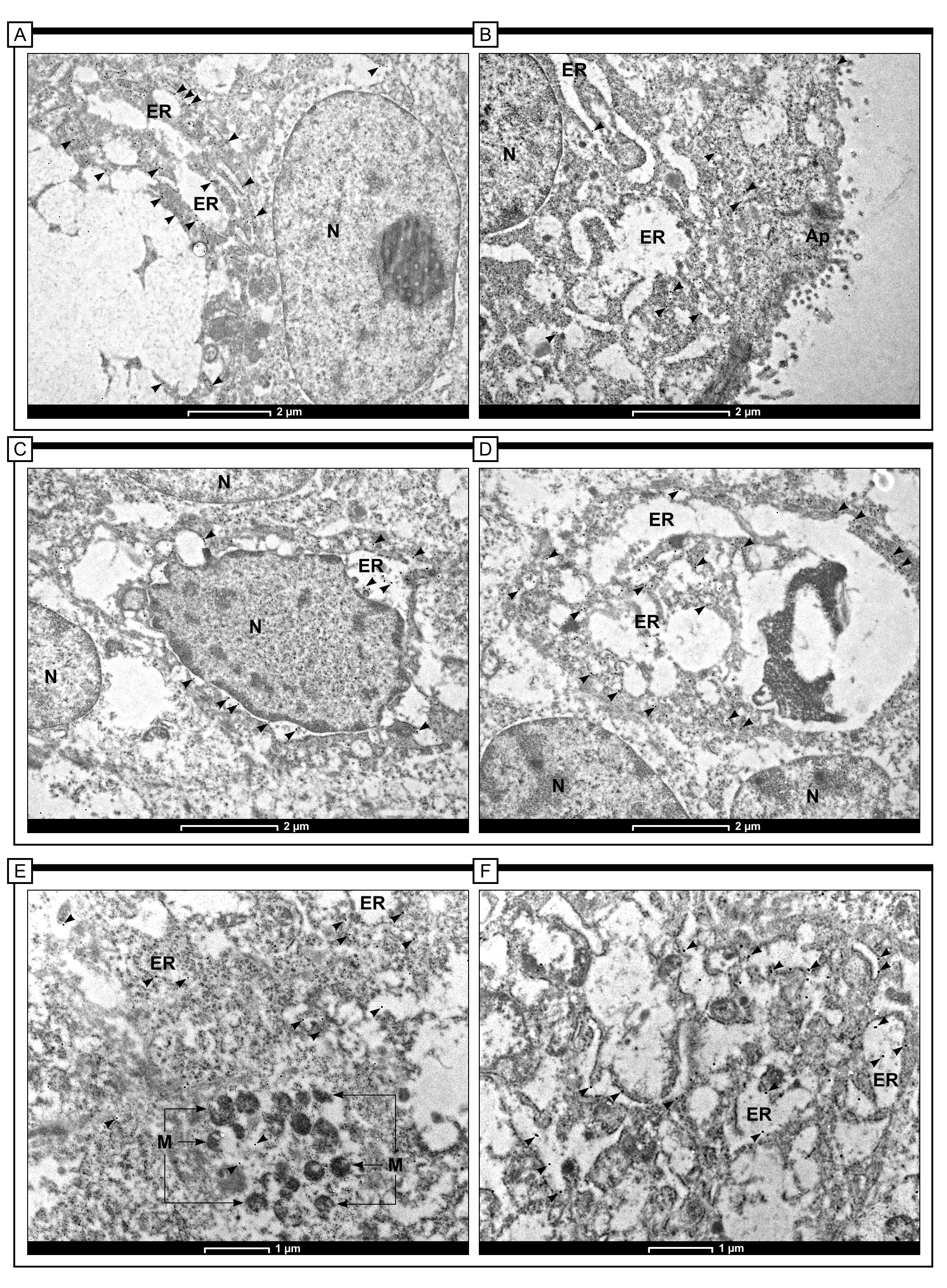 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.Immunogold labeling of Apaf-1 protein in colon adenocarcinoma
tissue in control cells (A-magnification
Apoptosis is a process that is critical to the systemic homeostasis of
multicellular organisms. Considering that Apaf-1 is a focal molecule during
activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, deregulation of its expression is
unavoidably implicated in human diseases, including cancer [17, 18, 19]. Inactivation
of the Apaf-1 gene is implicated in disease progression and
chemoresistance of some malignancies [20]. Unfortunately, little is known about
the prognostic significance of the Apaf-1 protein in patients with colon
adenocarcinoma, especially in the European population. Paik et al. [21]
have shown that specimens of primary colorectal adenocarcinomas and around 88%
of metastatic lesions exhibited impairment in Apaf-1 expression. This could
suggest that impairment of Apaf-1 expression is implicated in the malignant
transformation from adenoma to adenocarcinoma, particularly during the later
stage of colorectal carcinogenesis. In addition, the lower expression of Apaf-1
in samples with metastatic lesions compared to primary colorectal adenocarcinoma
would suggest that loss of Apaf-1 expression may promote metastasis. Moreover, a
study of allelic imbalance of the Apaf-1 locus in colorectal cancer revealed that
allelic imbalance of the Apaf-1 locus on 12q23 was absent in adenoma tissue, but
was commonly noted in adenocarcinoma and metastatic tumour tissue. What is more,
mRNA levels were markedly reduced, which was consistent with their allelic
imbalance [22]. Results of our study demonstrated that expression of Apaf-1 in
colon cancerous tissue was lower than that observed in normal tissue margin or
healthy colon tissue. Moreover, by the use of the immunogold labelling method, we
have confirmed the Apaf-1 presence in the cytoplasm of tumour cells, mostly in
the vicinity of membranous organelles including the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi
Apparatus and mitochondria. The presence of Apaf-1 protein was also observed in
normal cells of non-tumour colonic mucosa. Our study revealed that approximately
32% of colon adenocarcinoma specimens demonstrated strong Apaf-1 protein
expression, while low levels of immunoreactivity were found in 68% of cases.
High Apaf-1 expression was inversely related to the histological grade of the
tumour (p = 0.001, Chi
The multivariate analysis revealed that expression of Apaf-1 in colorectal cancer tissue showed no prognostic significance in terms of 5-year survival time. In the studied group of patients, only the parameter of histological differentiation shows prognostic value. However, the obtained findings indicate that patients with a high level of Apaf-1 protein expression confirmed by immunohistochemistry have significantly longer survival times and the large majority of them achieve a 5-year survival time, which, in the context of clinical oncology, may be important. In addition, when patients are stratified according to clinical parameters, e.g., PCNA expression, the expression of Apaf-1 can have a prognostic value in the context of 5-year survival. Patients with high Apaf-1 expression and high PCNA expression had a statistically better survival time (median overall survival 44 vs. 29.50 in patients with low Apaf-1 and high PCNA). Our study is the first which demonstrated that patients with tumours at the G1 stage and characterized by a strong level of Apaf-1 immunoreactivity had a relatively higher 5-year survival rate in comparison to patients with low expression of this protein. Moreover, in patients with tumours characterized by T3/T4 depth of invasion, the expression of Apaf-1 was also enhanced. These results may indicate that Apaf-1 plays an important role in colon adenocarcinoma progression and may be an identification biomarker for patients with a more aggressive form of this malignancy.
As numerous studies have shown, colon adenocarcinoma is not the only cancer type
to have reduced expression of Apaf-1 protein. Lukosiute-Urbonieniehas shown that
in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) downregulation of Apaf-1 expression
was detected both at mRNA and protein levels [24]. Decreased level of Apaf-1 was
also found in serum samples of patients [25]. In breast adenocarcinoma, Apaf-1
expression was downregulated at both the transcriptional and posttranslational
levels [26]. Wang et al. [27] showed that the low expression level of
Apaf-1 in breast cancer patients was probably related to the hypermethylation
process. In contrast, Lauber et al. [28] identified cleavage of Apaf-1 in
cytosolic extracts of Jurkat or MCF-7 cells after incubation with cytochrome
c/dATP or caspase, suggesting another potential mechanism for reduced Apaf-1
levels in breast cancer. In addition, Fang et al. [29] showed that
increased miR-937 expression has the effect of reducing Apaf-1 protein levels
through binding to the Apaf-1-3
Based on the results obtained in the Cox regression model, Apaf-1 has been identified as a protein connected with the reduced 5-year survival rate in the univariate analysis. The multivariate analysis revealed that only the grade of histological differentiation might be considered a prognostic factor. However, we can conclude that Apaf-1 expression is positively correlated with reduced survival of colon adenocarcinoma patients.
Nevertheless, our study has some limitations that need to be mentioned. The size of the studied group of patients was limited and the patients came from a single hospital, which may introduce selection bias into the study. Future studies should be conducted to increase the sample size in multicentre studies. A large number of patients will also allow the parameter of RAS gene mutations to be addressed. Moreover, the prognostic activity of Apaf-1 should be investigated in the context of Disease Free Survival, especially in relation to chemotherapy that depends on apoptosis and in vivo tests to understand the mechanism of action of the Apaf-1 factor during the development of colon adenocarcinomas. It would be interesting also to know the mRNA levels of PCNA and Apaf-1 in colon adenocarcinoma tissue versus normal adjacent tissue.
The data used to support the findings of this research are available upon request.
MB-Z designed the research study. MB-Z, AP and NM performed the research. MB-Z and MK provided help and advice on raising funds on research. MB-Z and EG analyzed the data. MM drafted the figures. MB-Z and MŁ wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Academy of Physical Education in Katowice (Resolution no. 1/2013 aproved on 21 November 2013).
I would like to express my big gratitude to Prof. Bogna Drozdzowska from Department of Pathomorphology for allowing us to scan the histopathological preparations and Dr Paweł Ziora for his skill technical assistance.
This research was funded by a grant from the Medical University of Silesia (no.PCN-1-153/N/0/O).
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Prof. Łos’es role in the compay is dedicated to the development of specific cellular elements within artificial corneas; it has nothing to do with the research area presented in our paper.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.






