1 Department of Gastroenterology, The 960th Hospital of the PLA, 250000 Jinan, Shandong, China
2 Liver Research Unit, Medica Sur Clinic & Foundation and Faculty of Medicine, National Autonomous University of Mexico, 14050 Mexico City, Mexico
3 Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command (formerly General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area), 110840 Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Abstract
Stem cell therapy offers a promising avenue for advanced liver disease cases as an alternative to liver transplantation. Clinical studies are underway to explore the potential of stem cells from various sources in treating different liver diseases. However, due to the variability among current studies, further validation is needed to ensure the safety and effectiveness of stem cell therapy. To establish a strong foundation for optimal stem cell therapy applications, selection of suitable stem cell sources, standardization of transplantation protocols, and patient criteria are vital. This review comprehensively examines existing literature on stem cell sources, transplantation methods, and patient selection. Additionally, we discuss novel strategies, including stem cell preconditioning, cell-free therapy, genetic modification of stem cells, and the use of liver organoids, addressing the limitations of current stem cell therapies. Nevertheless, these innovative approaches require further validation.
Keywords
- stem cells
- liver diseases
- regenerative medicine
- organoids
- clinical trials
While the liver can regenerate, injuries from various causes can lead to conditions like liver cirrhosis, hepatic failure, or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), accounting for 3.5% of global mortality [1]. Liver transplantation is a life-saving option for acute liver failure or end-stage liver disease. However, the growing gap between donors and recipients necessitates alternative therapies. Stem cell-based therapy emerges as a promising approach due to limitations of hepatocyte transplantation, such as limited proliferation and availability [2].
Stem cells possess self-renewal and differentiation abilities. Embryonic stem cells (ESC), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are potential sources for liver regeneration. Numerous clinical studies have explored stem cell therapy for liver diseases in the past 20 years, going beyond end-stage liver disease treatment [3, 4, 5]. However, study heterogeneity challenges widespread clinical application. Our aim is to discuss patient inclusion criteria, transplanted stem cell types, transplantation methods, and therapeutic effect assessment from existing studies.
This will present an alternative viewpoint on enhancing the safety and effectiveness of stem cell therapy for liver ailments. Additionally, cell-based therapeutics encounter several constraints, including limited access to viable cells, inadequate potential for successful implantation, and susceptibility to immune rejection [6]. Even with extensively investigated and widely utilized MSCs, concerns about undesirable differentiation, iatrogenic tumorigenicity, cellular rejection, emboli formation, infusion toxicity, and infection transmission persist [7, 8]. As a result, preparatory regimens [9], three-dimensional (3D) culture systems [10], and cell-free products [6] are gaining recognition as emerging domains within stem cell therapy, providing potential solutions to these challenges. We also examine these novel strategies and the potential challenges linked with these advancing areas.
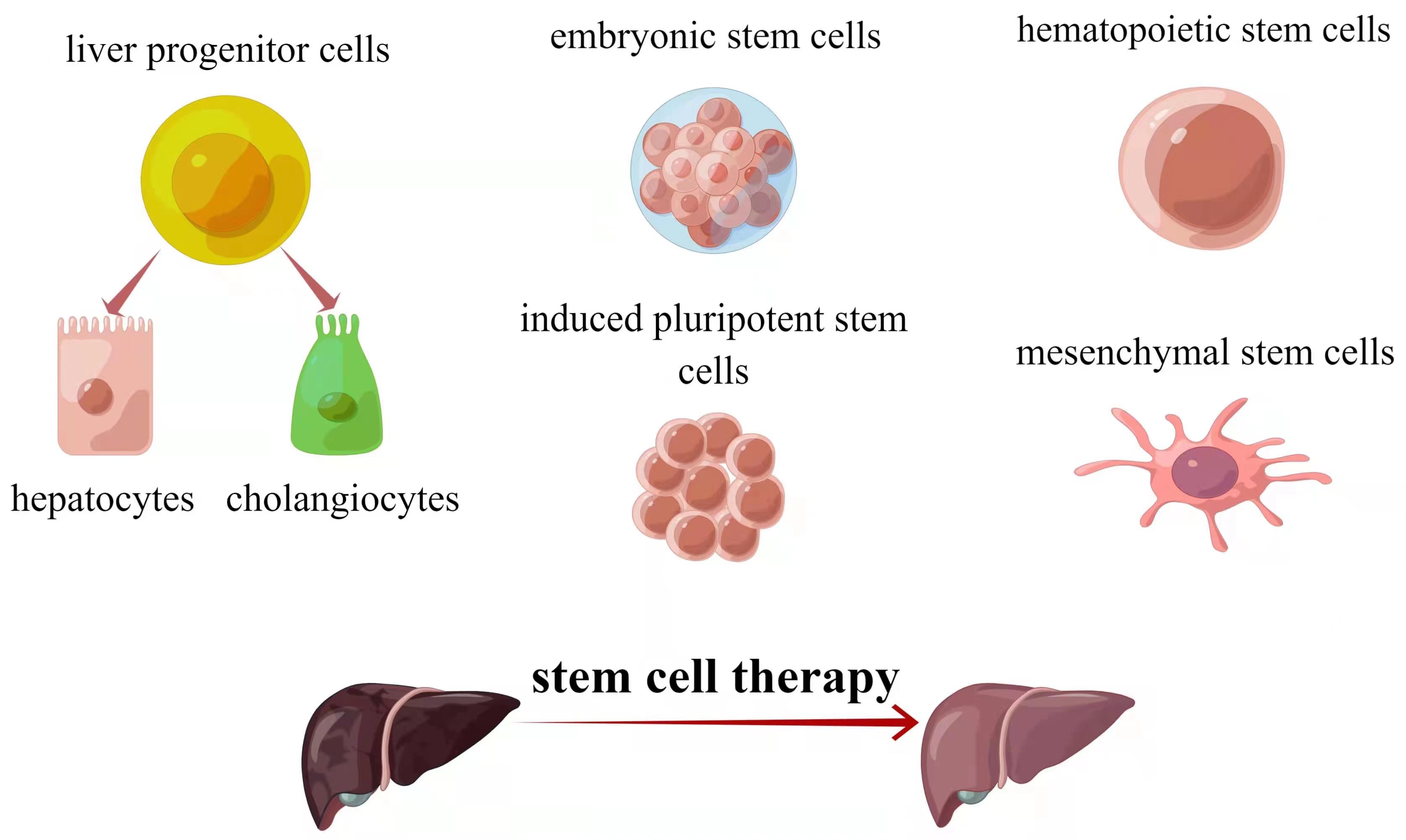
Cell-based treatments show promise as alternatives to transplantation or artificial liver support. Three stem cell types—hepatocytes, intrahepatic stem cells, and extrahepatic stem cells—have been identified for liver regeneration [11] (Fig. 1). Hepatocyte transplantation started in 1992 and is effective against metabolic liver diseases [12, 13]. Challenges include limited functional cells and hepatocyte susceptibility to cryopreservation damage [12, 13]. Stem cells offer potential solutions due to differentiation and proliferation capabilities. Intrahepatic stem cells, called liver progenitor cells (LPCs), can become both cholangiocytes and hepatocytes [14]. Extrahepatic stem cells like embryonic stem cells (ESCs), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and adult stem cells (ASCs) are explored. Each type has merits and limitations. Table 1 summarizes stem cell types for liver regeneration.
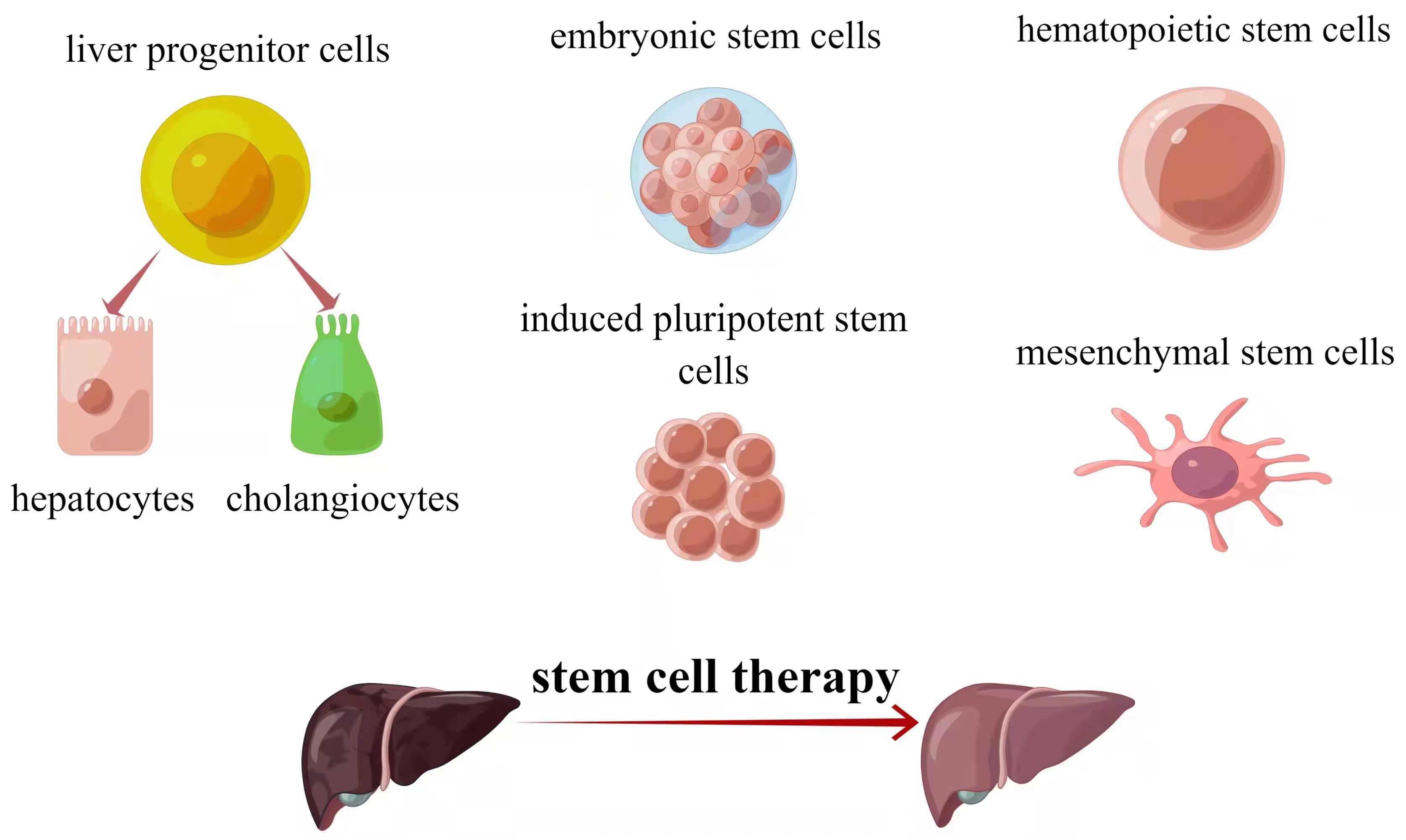 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.The major sources of stem cells for liver diseases therapy. Source: https://www.figdraw.com/static/index.html#/paint_user_home. ID: ASAUU3233f.
| Cell sources | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| LPCs | ·Self-renewal capacity | ·Non-directed differentiation into myofibroblasts |
| ·Bi-potentiality of differentiating into hepatocytes and cholangiocytes | ||
| ESCs | ·Pluripotent differentiation potential | ·Tumorigenic risk |
| ·Potential value for disease modeling, tissue engineering, and drug metabolism | ·Ethical issues | |
| iPSCs | ·Pluripotent differentiation potential | ·Without functionally mature properties |
| ·Free from ethical controversies | ·Limited efficiency in engraftment | |
| ·Solvation of histocompatibility issues | ·Tumorigenic and teratogenicity risks | |
| HSCs | ·Wide spread sources | ·Uncertainty for efficacy and safety |
| ·Autologous and allogeneic infusion | ||
| ·Direct hepatocyte differentiation and indirect microenvironmental modulation | ||
| MSCs | ·Widely and easily accessible | ·Heterogeneous populations from different donors |
| ·Multiple differentiation and extensive expansion | ·Limited ability to proliferate | |
| ·Hypoimmunogenic feature | ·Challenges for the long-term maintenance of genomic stability | |
| ·Autologous and allogeneic infusion |
LPCs, liver progenitor cells; ESCs, embryonic stem cells; iPSCs, induced pluripotent stem cells; HSCs, hematopoietic stem cells; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells.
LPCs, also known as oval cells in rodents, were initially identified in rat livers in 1937 [15]. In healthy adult livers, LPCs are scarce and dormant, residing in the Canal of Hering, serving as their stem cell niche. However, during severe or chronic liver injury that disrupts homeostatic hepatocyte proliferation, LPCs activate and differentiate into biliary cells and hepatocytes, contributing to liver regeneration [16]. The self-renewal capacity and bi-potentiality of LPCs make them a promising avenue for stem cell-based regenerative therapy. A notable case documented the administration of adult liver stem cells (LSCs) through two infusions to a 3-year-old girl with ornithine carbamoyltransferase (OTC) deficiency [17]. Interestingly, the recipient’s liver exhibited repopulation by the transplanted donor cells, suggesting the viability of LSC transplantation in OTC patients. Conversely, some studies contend that LPC accumulation in the ductular reaction could signal liver disease severity, as LPCs might differentiate into myofibroblasts [18]. Thus, investigating niche-specific modulators governing LPC committed differentiation into specific cell types, such as cholangiocytes or hepatocytes, is crucial. Several ongoing preclinical studies aim to achieve this [19, 20].
ESCs and iPSCs are pluripotent cells with the remarkable capacity to generate diverse body cells. ESCs are derived from the inner mass of blastocyst stage embryos, allowing spontaneous differentiation into various cell lineages, including hepatic endoderm [21]. Animal experiments have shown hepatocyte-like cells (HLCs) derived from ESCs as potential resources for tissue engineering, disease modeling, and drug metabolism, offering alternative therapeutic avenues. However, ethical concerns and the risk of tumorigenesis currently prevent clinical applications of ESCs and their derivatives [22].
IPSCs possess pluripotent properties like ESCs and hold an ethical advantage [23]. Pioneering work by Takahashi et al. [24] and Yu et al. [25] reported successful generation of iPSCs from adult human cells in 2007. iPSCs have since been widely used in disease modeling, cell therapy, and drug metabolism studies. Under specific conditions, iPSCs can differentiate into specific cell types [25]. In 2009, iPSCs were induced into hepatic cells [26], referred to as iPSC-derived hepatocyte-like cells (iPSC-HLCs). Ongoing efforts optimize reprogramming factors for high-quality iPSC-HLCs without genome modification [27, 28]. IPSCs overcome the histocompatibility issues through two known strategies: the generation of a bank comprising HLA homozygous iPSCs and their derived cells [29], and by the generation of universal donor iPSCs engineered with overexpressing CD47 gene while simultaneously suppressing the expression of HLA I/II genes [30]. All these significant advancements in reprogramming technologies present promising prospects for the application of iPSCs in the curative treatment of liver diseases.
However, it should be noted that several “bottleneck” problems hinder the clinical application of iPSCs. First, fully functional hepatocytes from iPSCs remain a challenge [31]. Second, iPSC-HLC engraftment into injured livers is limited [32]. Importantly, iPSCs’ unlimited proliferation and genomic instability pose risks of tumor and teratoma formation [33, 34]. iPSCs’ hepatic disease treatment is still in the preclinical stage.
ASCs, also termed somatic stem cells, reside in specific organs and have limited multi-differentiation capacity, generating specific mature cells for tissue homeostasis [35]. ASCs play a pivotal role in tissue repair and regeneration due to microenvironment signals [36]. Two major ASC populations are HSCs and MSCs, available from allogeneic or autologous sources [36].
HSCs can transdifferentiate into hepatocytes [37, 38] and regulate the liver microenvironment, recruiting cells to injury sites and aiding repair [39]. Currently, HSCs used for treating liver disease can originate from various sources, such as umbilical cord blood, peripheral blood, and bone marrow (BM). In 2005, Am et al. [40] made a significant discovery by demonstrating that portal infusion of BM-HSCs promoted liver regeneration. Meta-analyses and long-term follow-ups confirm autologous HSC transplantation’s efficacy in decompensated cirrhosis [41, 42]. Nevertheless, a phase II multi-arm, open-label, randomized, controlled trial (RCT) unveiled that infusions of autologous HSCs had no discernible impact on fibrosis, disease severity, or quality of life in individuals with compensated cirrhosis. Surprisingly, this treatment was linked with an increased incidence of severe side effects, including encephalopathy or ascites [43]. Hence, the effectiveness and safety of HSCs necessitate further substantiation through rigorous RCTs. Furthermore, novel approaches such as cytokine therapies utilizing bone marrow (BM) stimulation [43] and gene-modified HSCs [44] might advance the clinical applications of HSCs.
MSCs are extensively examined and employed in stem cell-based therapy for addressing liver ailments. MSCs therapy demonstrates notable safety and tolerability, as indicated by numerous clinical trials targeting liver diseases, with no notable risk of adverse outcomes. Notably, MSCs possess several advantages and distinctive features [31, 45, 46, 47]. Primarily, MSCs are widely and conveniently attainable from multiple sources. Thus far, MSCs sourced from umbilical cord blood, umbilical cord, BM, and adipose tissue have been employed for treating end-stage liver diseases encompassing cirrhosis, liver transplantation-related complications, or liver failure [31]. Additionally, MSCs exhibit an exceptional ability for substantial in vitro expansion, facilitating rapid scalability to meet in vivo therapeutic requirements [45]. Thirdly, owing to their hypoimmunogenic attribute, allogeneic MSCs can be utilized without the necessity of supplementary immunosuppressant therapy [46]. Furthermore, MSCs can be cryopreserved with a low risk of viral infection [31]. Despite their notable plasticity to differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells, the therapeutic potential of MSCs primarily stems from their immunomodulatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic properties [47]. Despite these merits, none of the MSC-based products has received approval for liver disease treatment primarily due to unresolved technological challenges. For instance, MSCs exhibit limited proliferative capacity, and MSCs obtained from distinct donors may exhibit variations in their attributes. Additionally, prolonged MSC culturing might lead to phenotypic changes and genetic drift [48]. Consequently, the utilization of primed or genetically-modified MSCs, or cell-free therapy, emerges as a potential strategy for therapeutic interventions [48].
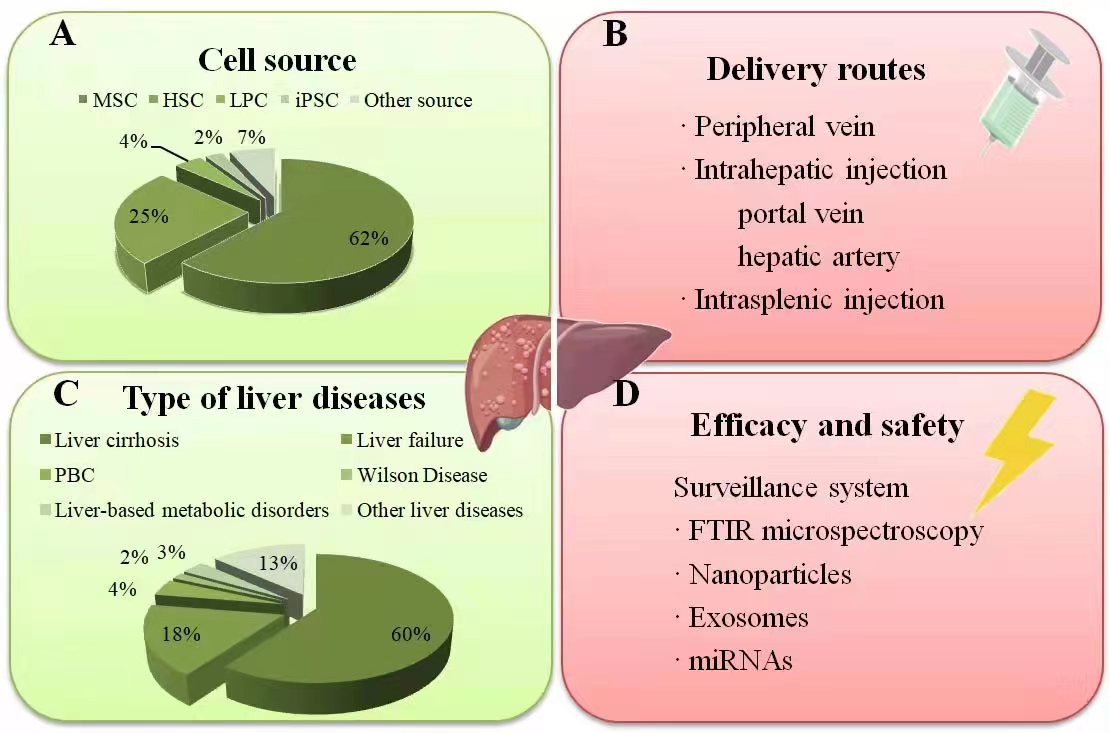
As of June 21, 2022, Clinicaltrials.gov lists 120 clinical studies using stem cells for liver disease treatment, primarily focusing on acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and decompensated cirrhosis. Stem cells also exhibit therapeutic roles in other liver conditions, including metabolic disorders, autoimmune disorders, and genetically linked diseases (Fig. 2).
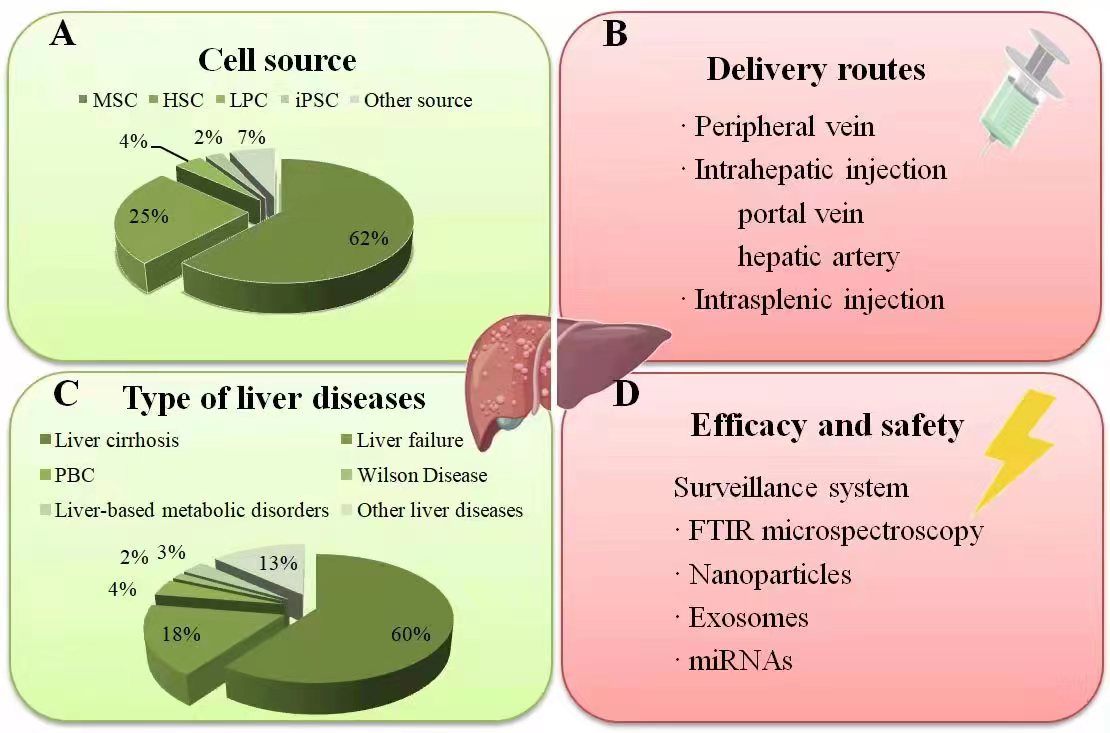 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Summary of current clinical studies on stem cell therapy in liver diseases. (A) The percentage of different stem cell types applied in clinical liver therapy: MSCs have been the most frequently employed type, followed by HSCs. (B) The injection route was mainly via the peripheral vein, followed by the hepatic artery and portal vein, while only a minority through intrasplenic injection. (C) The percentage of various liver diseases treated with stem cell transplantation. (D) The surveillance systems for monitoring the efficacy and safety correlated to the stem cell engraftment in liver diseases. Source: https://www.figdraw.com/static/index.html#/paint_user_home. ID: WWYPO622b0. PBC, primary biliary cholangitis; FTIR, fourier-transform infrared.
Liver cirrhosis represents an advanced stage in the progression of diverse chronic liver ailments. When the liver sustains injury from factors such as hepatitis B/C infections, alcohol misuse, lipid accumulation, and exposure to noxious substances, activated hepatic stellate cells generate excessive collagen and matrix proteins, culminating in liver fibrosis [49]. While early-stage fibrosis holds potential for reversibility, cirrhosis, conversely, tends to be irreversible. Multiple prospective mechanisms of stem cell therapy have been posited for liver cirrhosis treatment. These encompass direct differentiation of stem cells into functional hepatocytes, suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation combined with induction of their apoptosis, modulation of inflammatory microenvironments via paracrine effects, and release of trophic agents to spur regeneration of existing hepatocytes [50, 51]. A meta-analysis indicated that MSCs can enhance clinical status and laboratory indicators in individuals with liver cirrhosis. This suggests that stem cell therapy could be an effective and secure choice, particularly within the initial six months of cirrhosis treatment [52]. However, prudent interpretation of current findings is essential, considering that certain studies lacked comparison groups and only conducted short-term follow-up assessments. Additionally, it must be acknowledged that stem cell applications are not devoid of risks. For instance, intraliver injection of stem cells might lead to hepatorenal syndrome, a severe and life-threatening complication [53]. Moreover, a substantial-scale RCT demonstrated that cirrhotic patients might encounter infusion-related adverse effects without significant therapeutic gains from HSCs infusion [43]. Furthermore, discerning which patients are most likely to benefit from stem cell transplantation is crucial. The efficacy of stem cell therapy is postulated to potentially vary based on the root cause of cirrhosis [54]. In accordance with this, extensive controlled trials have furnished evidence supporting the adoption of MSCs transplantation as a viable intervention to ameliorate liver function in viral-induced cirrhosis [55] and alcoholic cirrhosis [56]. Nonetheless, a pilot study excluding patients with viral-associated cirrhosis did not observe the sought-after therapeutic effect of MSCs treatment on liver cirrhosis [57]. In light of existing literature, cirrhosis cases categorized as Child-Pugh class C, aged below 60 years, and either planning liver transplantation or employing it adjunctively alongside standard medications are considered suitable candidates for stem cell therapy. Conversely, patients with advanced cirrhosis-associated complications like recurrent variceal bleeding, moderate-severe hepatic encephalopathy, bleeding tendencies, HCC, ongoing infections, or hepatic/portal/splenic thrombosis are deemed inappropriate for stem cell transplantation [58]. Nevertheless, the optimal stem cell type, ideal transplantation route, along with suitable injection frequency and cell dosage necessitate further elucidation through substantial-scale RCTs.
Liver failure is a life-threatening syndrome featuring ascites, jaundice, hemorrhagic tendency, and hepatic encephalopathy, with high mortality [59]. It is classified into acute liver failure (ALF), ACLF in chronic liver disease, and chronic liver failure (CLF). Hepatocyte loss underpins liver failure [60], making ACLF another priority area for stem cell research. MSCs’ anti-inflammatory effects make them promising for ACLF treatment [61]. RCT systematic reviews and meta-analyses demonstrate MSC therapy’s efficacy in improving liver function, albumin, coagulation, or MELD score in ACLF and cirrhosis cases [61]. Subgroup analysis shows short-term survival benefits with stem cell therapy in ACLF [62]. Most MSC clinical trials are in phase I or II [61]. Human liver organoid advancements, including integration with organs-on-a-chip perfusion, hold promise for functional liver organoids in ACLF [63].
AILD encompasses a range of chronic liver diseases marked by immune dysfunction, including primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), and autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) [64]. AILD patients often have limited treatment options and a poor prognosis, particularly those who inadequately respond to initial medical treatment. In such cases, stem cell therapy stands as a potentially effective alternative treatment for AILD [65].
Currently, clinical studies primarily target PBC. An initial study enrolled
seven PBC cases with incomplete response to ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). These
patients received monthly infusions of cultured umbilical cord-derived MSCs
(0.5
For AIH and PSC, stem cell therapy’s application is limited to animal models and case reports, underscoring the need for further experimental and clinical studies to ascertain efficacy and safety [3, 67].
WD is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder marked by ATP7B deficiency, a copper (Cu)-transporting ATPase mainly expressed in liver cells. This deficiency leads to Cu accumulation, causing hepatic, neurologic, and psychiatric symptoms of varying severity. Lifelong treatment usually maintains copper balance in WD patients. However, current pharmacotherapy is not curative and has severe side effects. Liver transplantation also faces donor shortages and challenges in neurologically uncontrolled patients. Therefore, stem cell therapy explores potential treatment to restore hepatobiliary copper excretion and alter WD progression [68].
Currently, only one RCT compared BM-MSC transplantation plus penicillamine with penicillamine alone in 60 WD patients [4, 68]. Penicillamine, a chelator balancing copper intake and excretion, has serious side effects and cannot cure WD [68]. Interestingly, the study showed BM-MSCs combined with penicillamine positively affected WD-related liver fibrosis, with few adverse reactions from MSC treatment. Yet, the study did not measure serum copper and ceruloplasmin level changes, important indicators of MSC efficacy in copper removal. Additionally, developing an integrated cell/gene therapy to restore ATP7B levels without extra genetic modification and optimizing protocols for stem cell delivery and liver-specific targeting for proliferation and differentiation remain in preclinical stages [4].
Stem cell therapy holds promise as a treatment option for liver-based metabolic disorders. Studies have indicated that transplanting a hepatocyte mass equivalent to around 1/10 of the patient’s liver is sufficient to normalize enzyme deficiencies [4].
Inborn errors of liver metabolism encompass a group of disorders marked by a deficiency in a single enzyme involved in various metabolic pathways. These deficiencies lead to impaired liver function and dysfunction in distant organs. These conditions typically manifest during the neonatal period. The two most notable disorders within inborn errors of liver metabolism are Crigler-Najjar (CN) syndrome and urea cycle defects (UCD). Presently, no effective treatment is available for these disorders, resulting in approximately 10–50% of affected children requiring liver transplantation. Stem cells have the potential to restore liver enzyme activities in affected individuals. In line with this, the safety and efficacy of heterologous human adult LPCs (HHALPCs) were preliminarily confirmed in a phase I/II, multi-arm, open-label, prospective study involving 14 UCD and 6 CN pediatric patients [69]. A subsequent phase II clinical study is underway to further explore the use of HHALPCs. Notably, HHALPCs were administered via intraportal infusion; however, clinicians need to be vigilant about the possible risk of portal vein thrombus formation. Another partially randomized phase I/II study involving 6 CNs and 5 UCDs revealed that the combination of heparin and bivalirudin exhibited high safety and could limit thrombogenesis caused by MSCs infusion to subclinical signs. This approach indicates significant progress in inhibiting the procoagulant activity of MSCs during transplantation [70].
Various routes of stem cell therapy are accessible, such as peripheral vein administration, intrahepatic injection (via the hepatic artery or portal vein), and intrasplenic injection [71]. Peripheral intravenous infusion remains prominent due to its easy administration and reduced trauma [72]. However, it is crucial to note that this systemic delivery approach might lead to excessive cell accumulation in the lungs, a phenomenon potentially mitigated by immune cells [72]. On the other hand, hepatic arterial infusion, the second most common transplantation pathway, is believed to be substantially effective compared to the peripheral vein. This is attributed to mitigating cell attrition in circulation while promoting cell homing to the damaged liver [62]. However, this invasive procedure carries the risk of thrombosis and portal hypertensive hemorrhage [62]. Intraportal injection is a viable alternative to intrahepatic injection, enabling faster engraftment and preventing off-target accumulation [73]. Yet, before selecting this route, the patient’s condition and potential risks, like portal vein thrombosis, should be thoroughly evaluated [54]. Intrasplenic injection, while technically simpler than intrahepatic, brings additional complications requiring careful consideration [74].
The optimal quantity and frequency of transplanted stem cells remain uncertain in the current literature. In most clinical trials, stem cell transplantation is based on patients’ body weight, which seems to be a rational approach [54]. Regarding the frequency of stem cell therapy for chronic liver disease, consensus is lacking. Some studies suggest that multiple infusions enhance and sustain efficacy [75], while others indicate no significant difference between two injections and a single injection [56]. Recent meta-analyses suggest that multiple injections reduce mortality rates and MELD scores advantageously, while a single injection benefits improving albumin (ALB) and total bilirubin (TBIL) levels [62, 76]. Furthermore, some researchers propose that extending the interval between initial and subsequent injections could potentially enhance the long-term therapeutic efficacy of stem cell treatment [54, 62].
Stem cells represent a significant resource for liver regeneration, with an increasing body of studies investigating their application in treating liver diseases of diverse origins, as discussed earlier. However, many of these studies are non-randomized controlled trials (non-RCTs) with limited sample sizes. Even in the case of RCTs, the quality of evidence is compromised due to inadequate sample sizes and relatively short follow-up durations. Consequently, the empirical medical evidence assessing the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy for liver diseases remains largely restricted. In a meta-analysis encompassing 24 RCTs (from inception up to March 16, 2020) [62], stem cell therapy was found to be safe and effective for chronic liver diseases. This treatment led to improved liver function and short-term survival rates compared to conventional treatments, particularly for ACLF patients. Moreover, no severe side effects or deaths were directly attributed to stem cell therapy, and most reported adverse events resolved spontaneously. This comprehensive overview [62] of stem cell therapy was intended to provide consolidated evidence concerning the quality of clinical effect reporting. While these findings undoubtedly hold value in informing clinical practice and guiding future research, the presence of notable heterogeneity and bias risk among current studies necessitates more high-quality, large-scale clinical trials with extended follow-up periods to substantiate the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy.
Another limitation arises from the lack of an effective surveillance system for evaluating the efficacy related to stem cell engraftment in liver diseases [77]. To understand and scrutinize the function and fate of stem cells, several techniques are under investigation for monitoring transplanted stem cells and analyzing their differentiation, infiltration, and redistribution. Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) microspectroscopy can differentiate stem cells from differentiated cells in humans [78]. By comparing various macromolecular compositions in conventional blood and histological analyses, principal component analysis (PCA) applied to liver tissue spectra can discern stem cell therapy-induced regeneration in liver injury [79]. However, the objective signature detected by FTIR microspectroscopy has only been validated in rat models. Nanoparticles show promise for long-term stem cell tracking with high effectiveness and sensitivity [80] without altering cell function [81]. Nevertheless, their poor biodegradability requires consideration of chronic toxic effects and long-term adverse events. Similarly, the biotoxicity of exosomes has been reported in the context of disseminating toxic factors and inducing cell apoptosis [81]. Recently, the association between microRNAs (miRNAs) and stem cell self-renewal and differentiation has gained prominence [82]. This has sparked interest in exploring miRNA profiling as a tool for assessing the efficacy of stem cell transplantation and its therapeutic impact on liver diseases. Given that miRNAs are non-toxic to cells and serve as specific, rapidly responsive biomarkers for liver diseases [83, 84], they could potentially indicate the effectiveness of stem cell treatments on liver diseases. For instance, miR-122 levels in the liver have been found to increase within the CCl4-mediated acute liver injury mice model but decrease following stem cell therapy [85]. However, additional clinical studies are warranted to substantiate the pivotal role of miRNAs in evaluating stem cell efficacy and validating its effectiveness on the target tissue.
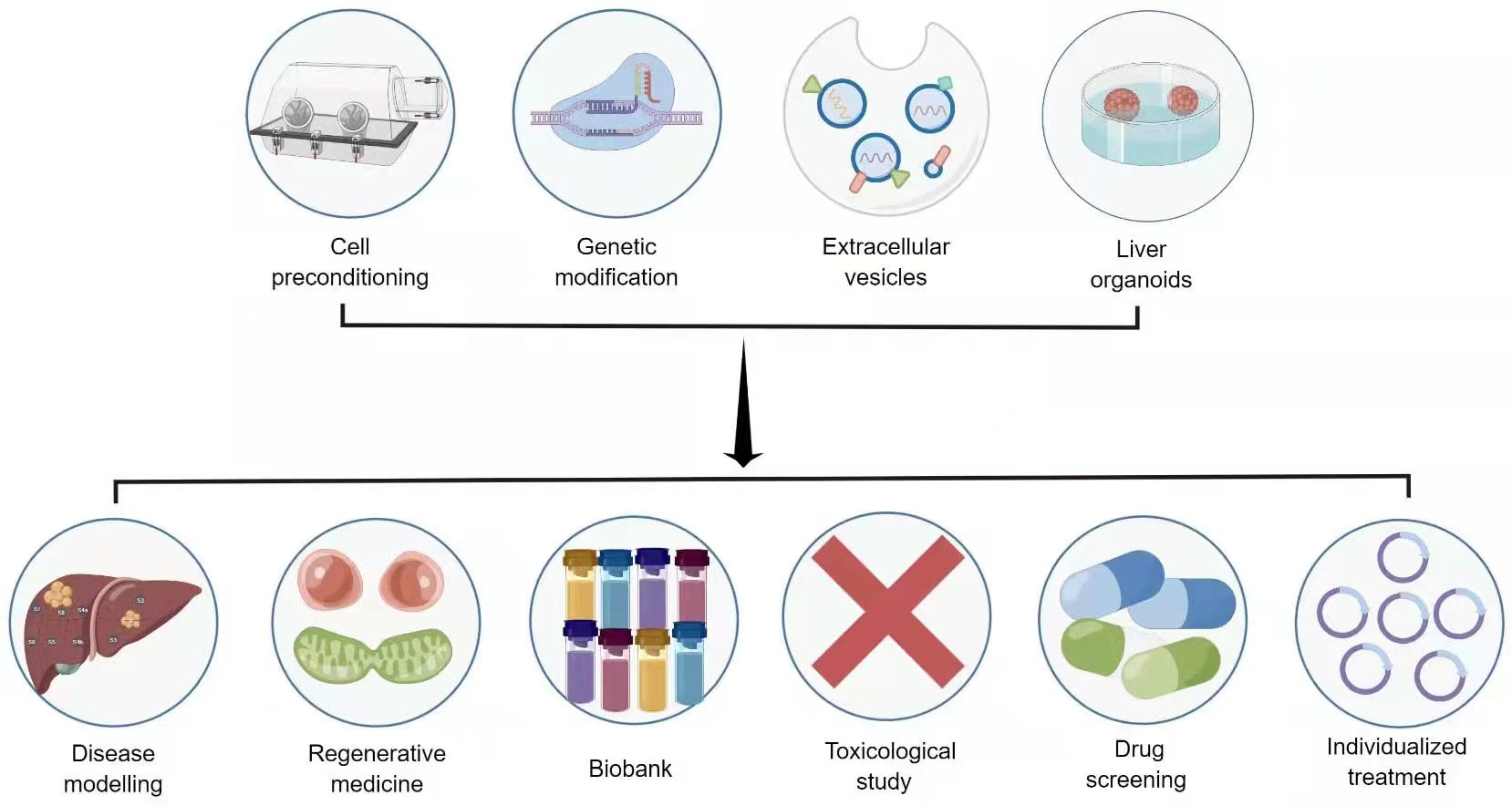
While stem cell therapy holds transformative potential in liver regenerative medicine, several complex issues need resolution before its clinical translational application. These challenges encompass poor cell viability, inadequate intercellular communication, limited differentiation, suboptimal migration, and low extracellular matrix (ECM) generation [54, 61]. Consequently, biomedical techniques designed to enhance stem cell efficacy are under rigorous investigation. These include preconditioning, stem cell-derived exosomes, genetic modification, and three-dimensional culture [6, 9, 10] (Fig. 3).
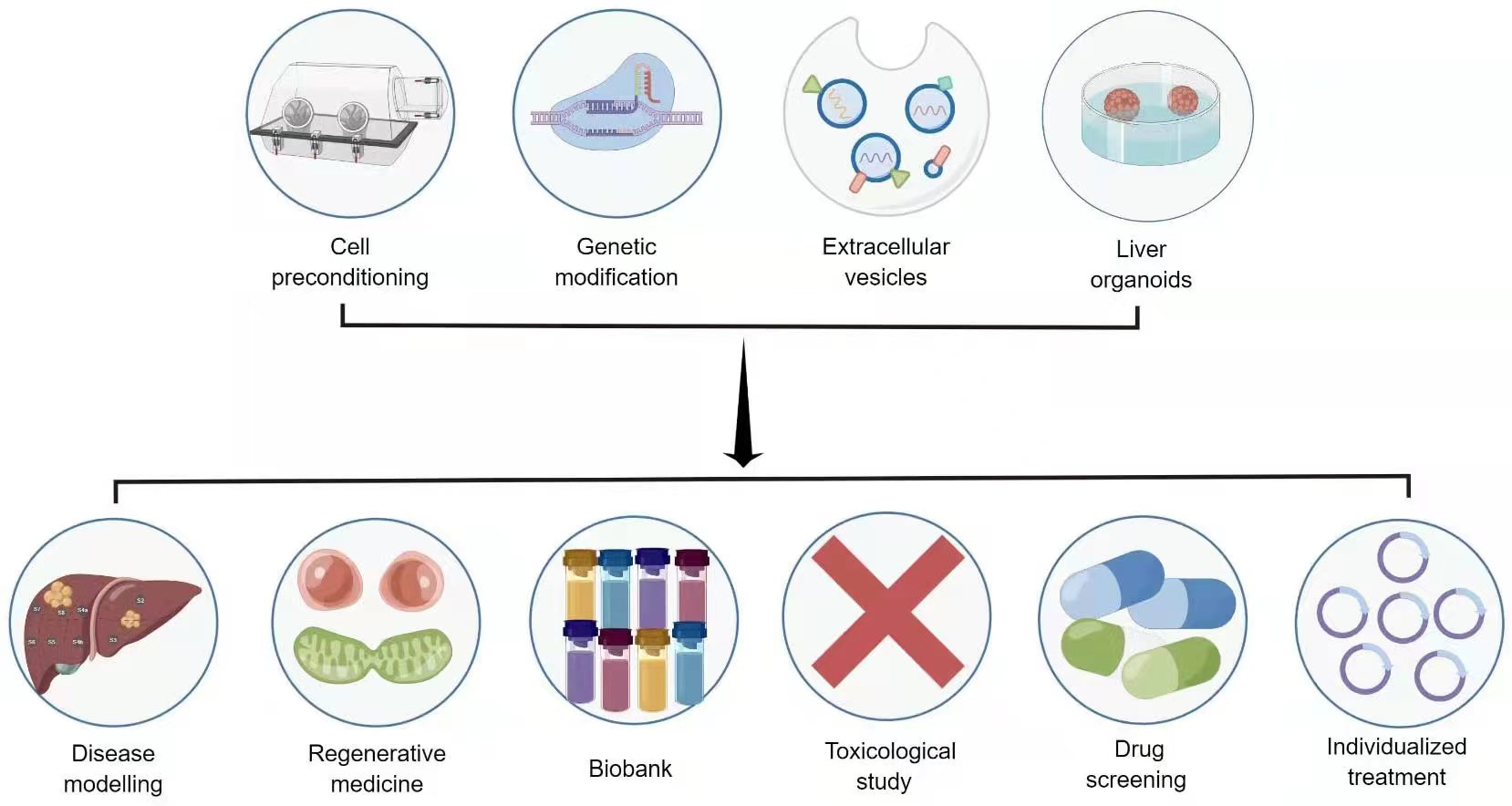 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Novel strategies and application prospects for stem cell therapy in liver diseases. Source: https://www.figdraw.com/static/index.html#/paint_user_home. ID: APORA14382.
The limited beneficial impact of stem cells primarily results from the hostile environment of damaged tissues, which is unfavorable for transplantation. Various physical, pharmacological, and biological preconditioning strategies are commonly employed for the clinical application of stem cells. These strategies enhance cell tolerance and the potential for tissue regeneration by inducing conditions resembling the damaged tissue microenvironment [86]. In addition to known pharmacological effects, cell preconditioning also influences various molecular pathways associated with cell growth, migration, survival, angiogenesis, differentiation, immunomodulation, and paracrine effects [9]. Several techniques have been suggested for cell preconditioning. These encompass hypoxia and inducers that involve biological molecules and mediators like metabolic byproducts, cytokines, growth-related agents, lipopolysaccharide, heat shock proteins, specific medications, as well as physical stimulants such as dynamic compression, cyclic hydrostatic pressure, electrical and optical stimulation, and sonic waves. Additionally, acidosis and serum deprivation are also utilized [9, 87].
Encouraging outcomes from cellular preconditioning for stem cell therapy in liver ailments have garnered support from animal investigations. Specifically, antioxidant preconditioning notably enhances the effectiveness of MSCs for reinstating liver function. This enhancement occurs through an augmentation of the hepatic engraftment effect, subsequently leading to a reduction in oxidative harm within a liver fibrosis model [88]. Pharmacological substances like eugenol and rapamycin have displayed an ability to amplify the self-renewal, migratory, immunoregulatory, anti-inflammatory, and proliferative capacities of MSCs in controlled settings, significantly heightening their efficiency in simulated hepatic injuries [89, 90]. Furthermore, exposure to inflammatory cytokines can reinforce the therapeutic attributes of MSCs for addressing inflammatory liver conditions [91]. Nevertheless, owing to variances among cell types and injury microenvironments, available data are currently inadequate for identifying the most suitable preconditioning regimen for clinical application. To attain more substantial advantages and regenerative potential, exploring novel preconditioning stimuli and protocols, along with integrating various hypoxic preconditioning approaches alongside agents like exosomes and pharmacological compounds, stands as a promising albeit formidable pursuit [92].
Genetically altered stem cells present an additional impactful strategy to amplify the therapeutic impact of stem cells. The genetic modification of stem cells can be achieved through specific vectors, cell-specific promoters, antisense inhibition, the Cre/Lox P system, small interfering RNA (siRNA), or microRNA technology. On one side, the elevation of target gene expression within stem cells can enhance the discharge of particular regenerative factors [93], like c-Met, CXCR4, IGF-1, and CCR2 [54, 94]. These factors hold a pivotal role in regulating cell survival, engraftment, homing effectiveness, and therapeutic capability [95]. Conversely, the curbing of gene expression through targeted RNA degradation using microRNAs and other noncoding RNAs can shield stem cells from immune rejection and hinder the activation of hepatic stellate cells [58, 96]. Additionally, the CRISPR/Cas9 system, which enables tailored genome editing, is lately being employed in stem cell engineering and regenerative medicine [97]. While genetically modified stem cells can consistently and effectively deliver cytokines, a comprehensive safety evaluation is imperative before implementing these technologies in clinical contexts [54, 87].
Cell-free therapy has emerged as an innovative strategy aimed at addressing challenges linked with cell-based approaches, such as tumorigenicity and immunogenicity [98]. In this novel therapeutic approach, extracellular vesicles (EVs), particularly those derived from MSCs or iPSCs, have garnered considerable attention [6].
The fundamental mechanisms of MSC-based therapy largely involve paracrine effects, and in this context, EVs have emerged as significant mediators. EVs play a crucial role in regulating intercellular communication and immunomodulation by carrying cytosolic and membranous proteins, lipids, mRNAs, miRNAs, siRNAs, and lncRNAs [6, 98]. Notably, MSC-EVs predominantly accumulate in the liver after intravenous administration [6, 98], sparking interest in investigating MSC-EVs for liver diseases instead of MSCs.
In preclinical studies, MSC-EVs have demonstrated therapeutic effects in various liver conditions, including metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), AIH, ALF, liver fibrosis, and hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury [99]. Beyond modulating immune balance, MSC-EVs also regulate hepatocyte autophagy, apoptosis, and metabolic homeostasis.
Compared to stem cells, cell-free therapy offers several advantages, such as a smaller size, easier procurement, more stable preservation, and reduced risk of immunological reactions and carcinogenesis [99]. However, the clinical application of EVs encounters substantial challenges due to their limited lifespan, notable heterogeneity, and diverse secreted proteins [99].
Liver organoids, with the capability to replace damaged liver tissue and restore impaired liver functions, are anticipated as the next frontier in regenerative medicine [100]. Conventional 2D monolayer culture models inadequately replicate the transcriptional, physiological, and structural attributes present in vivo. An advanced 3D culture system can mimic the in vivo environment, and the resultant organoids hold promise for disease modeling, organ regeneration, and drug testing [101]. Currently, liver organoids find application in modeling liver cancer, steatohepatitis, hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, HBV-associated HCC, and drug-induced liver injuries [102, 103]. The foundation for liver organoid development primarily rests on iPSCs, and co-culturing of mesenchymal and endothelial cells has been a focal point in organoid research [104, 105]. Recent findings indicate that vascularized organoid liver buds could serve as potential organoid transplants for end-stage liver disease cases [106]. However, numerous challenges remain [106]: refinement of differentiation protocols to achieve enhanced cell maturation and representation of specific liver cell types; development of innovative bioengineering techniques to ensure consistent composition and functionality of liver organoids; and creation of enhanced synthetic biomaterials to establish an animal-free culture system suitable for regenerative medicine. Advanced bioengineering strategies, including biomaterial scaffolds, microfluidic systems, 3D perfusable chip systems, and 3D bioprinting integrated with organoid culture, are expected to elevate liver differentiation efficiency and enhance the functional maturity of liver organoids [107].
Based on the existing preclinical and clinical investigations, stem cell therapy emerges as a plausible alternative for addressing liver diseases. However, due to the limited and diverse nature of present data, more exploration into the underlying therapeutic mechanisms and comprehensive RCTs is imperative. This effort will facilitate the identification of optimal stem cell types, appropriate dosage and injection frequency, and suitable administration routes. Acknowledging the inherent constraints of stem cell therapy, advancements in stem cell preconditioning, genetically engineered stem cells, cell-free therapy, and liver organoids may herald a new era in liver regeneration.
XSQ and XFL contributed to conceptualization and visualization. JW, WBL and QL wrote the first draft of the manuscript. JW, WBL, NMS, XSQ, and XFL contributed to acquiring, analyzing, and interpreting data from the reviewed literature. All authors contributed to manuscript revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81900467) and Shandong Medical and Health Science and Technology Project (202103031040).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.