1 Science and Math Program, Asian University for Women, 4000 Chattogram, Bangladesh
2 Department of Clinical and Molecular Sciences, Università Politecnica Delle Marche, 60126 Ancona, Italy
3 Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Division of Reproductive Sciences & Women’s Health Research, Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Fibrotic disorders are defined by accumulating excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) components, especially collagens, in various organs, leading to tissue scarring and organ dysfunction. These conditions are associated with significant challenges in the healthcare system because of their progressive nature and limited treatment options. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules (approximately 22 nucleotides) that modulate gene expression by selectively targeting mRNAs for degradation or translational repression. MiRNAs have recently been identified as potential targets for therapeutic developments in fibrotic disorders. They play vital roles in inducing fibrotic phenotype by regulating fibroblast activation and ECM remodeling. Multiple strategies for targeting specific miRNAs in fibrotic disorders have been explored, including antisense oligonucleotides, small molecule modulators, and natural compounds. This review discussed the role of miRNAs in different fibrotic disorders, including cardiac fibrosis, liver fibrosis, kidney fibrosis, lung fibrosis, dermal fibrosis, and primary myelofibrosis, with recent advances in developing miRNA-based therapeutics.
Keywords
- microRNA
- fibrotic disorders
- cardiac fibrosis
- liver fibrosis
- kidney fibrosis
- lung fibrosis
- dermal fibrosis
- primary myelofibrosis
- miRNA therapeutic
- natural compounds
Fibrosis is defined by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, especially collagens, and loss of cellular homeostasis. The highly progressive nature of fibrosis is associated with the loss of tissue architecture and organ function [1, 2]. Current data suggests the major role that fibrosis plays in a wide range of diseases, including scleroderma, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, myelofibrosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), systemic sclerosis, liver cirrhosis, progressive kidney disease, cystic fibrosis, cardiac fibrosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), and cancer [2, 3]. There are around 4968 fibrosis cases per 100000 individuals annually [4]. Fibrosis has been reported to be associated with up to 45% of all deaths in industrialized nations [5]. These conditions are associated with a significant burden in global healthcare systems because of their progressive nature and limited treatment options.
Fibrosis is a complex process influenced by a combination of various molecular
factors, including transforming growth factor-
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the role of miRNAs in fibrotic diseases, with a particular focus on their potential as therapeutic targets for future therapeutics. Particularly, we discuss: (1) the functional roles of miRNAs in the fibrosis process, (2) the role of miRNAs in various fibrotic diseases, including cardiac, liver, kidney, lung, dermal, and primary myelofibrosis, and (3) the recent advances in developing miRNA-based therapeutics for fibrotic diseases.
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the role of miRNAs in fibrotic diseases and explores potential therapeutic approaches. An extensive literature search has been performed until May 2023 using electronic databases such as PubMed and Google Scholar. Review articles were used as a source to identify additional articles relevant to miRNA and fibrosis. Only articles published in English have been included in this review. The search strategy involved using the following keywords: “fibrosis”, “fibrotic disorders”, “fibrotic diseases”, “extracellular matrix”, “wound healing”, “microRNA or miRNA”, “cardiac fibrosis”, “liver fibrosis”, “kidney fibrosis”, “lung fibrosis”, “dermal fibrosis”, “primary myelofibrosis,”, “miRNA therapeutic”, “miRNA inhibitor”, “natural compounds”, “antisense oligonucleotides”, “antagomirs”, “carvedilol”, “ivabradine”, “nebivolol”, “astragaloside IV”, “baicalin”, “berberine”, “celastrol”, “corilagin”, “EGCG”, “quercetin”, “resveratrol”, “tanshinone IIA”, and “ursolic acid”.
MiRNAs are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules that are evolutionarily conserved [12]. They are transcribed from specific DNA regions and exhibit a broad spectrum of functions. The primary role of miRNA is to pair with mRNA molecules that contain a complementary sequence, resulting in the downregulation of their expression. A single miRNA molecule can target multiple mRNA molecules, thereby regulating numerous cellular pathways [13]. MiRNA biogenesis is complex and regulated by several mechanisms facilitated by transportation, RISC (RNA-induced silencing complex) biding, miRNA decay, and processing performed by Drosha and Dicer enzymes (Fig. 1).
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.The biogenesis steps of microRNAs (miRNAs). The miRNA biogenesis involves several steps, including transcription, pri-miRNA processing, export to the cytoplasm, dicer processing, strand selection, and target recognition and regulation. After several sequential process, the pre-miRNA is recognized in the cytoplasm, and cleaved by Dicer, and miRNA duplex is generated. In the final step, the guide strand of the miRNA duplex is preferentially selected and loaded onto an argonaute (AGO) protein within the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The miRNA-loaded RISC complex recognizes target mRNA molecules through base pairing, usually resulting in mRNA degradation or translational repression. Figure created with biorender.com. GTP, Guanosine triphosphate; mRNA, messenger RNA.
The process of miRNA biogenesis begins with specific miRNA genes in the DNA, which can be transcribed as individual miRNAs or as part of polycistronic transcripts [14]. In addition to being transcribed as individual miRNAs or polycistronic transcripts, miRNA genes can also be found within introns or UTRs of protein-encoding genes [15].
Typically, the transcription of a miRNA gene occurs through RNA polymerase III,
which produces primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) transcripts. These pri-miRNA transcripts
then undergo capping and polyadenylation. They undergo a processing step mediated
by the microprocessor complex, which converts them into pre-miRNAs (precursor
miRNAs) [16, 17]. The microprocessor complex consists of at least two essential
proteins: Drosha, a ribonuclease III enzyme, and DGCR8 (DiGeorge syndrome
critical region 8), a dsRNA binding protein, along with some less studied
components such as DDX5 (DEAD-box RNA helicases p68) and DDX17 (p72) [18, 19].
These two proteins work together to process pri-miRNA into pre-miRNA during the
miRNA biogenesis pathway. The microprocessor identifies distinct motifs in the
primary miRNA and cuts it at the stem of the classic hairpin loop formation,
creating a 5
MiRNAs have been studied in various biological processes, including fibrosis. Understanding the interaction between miRNAs and ECM accumulation is crucial for tissue remodeling, wound healing, and fibrosis. The ECM microenvironment is a complex network of macromolecules that provides structural support to cells and tissues, serving as a physical barrier between cells and their surroundings [28, 29]. ECM consists of diverse proteins, including collagens, fibronectin, laminins, and proteoglycans, maintaining tissue integrity and function [30]. Dysregulation of ECM remodeling and excessive deposition can result in the development of fibrotic conditions [31].
Each specific tissue cell type possesses a particular combination of ECM components that influence mechanical properties and organization of cells. Specialized proteins, such as the integrin families of trans-membrane receptors, regulate cell adhesion to the ECM. Cell adhesion is essential for cell proliferation and survival and, more generally, for developing the typical architecture constitutive of healthy tissues. Structural changes in the ECM are strongly associated with disease development and progression [29]. Along with its structural role, ECM steers cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. When triggered by specific signals, growth factors and cytokines stored in the ECM are released, stimulating proper cellular responses toward cell growth, differentiation, adhesion, and migration. It is the substrate for fibroblast activation and differentiation into myofibroblasts, the primary effector cells in fibrotic tissue formation [32].
The ECM maintains tissue integrity by undergoing quantitative and qualitative remodeling mediated by specific enzymes in particular glycosidases and MMPs [32, 33]. Altered ECM composition encompasses either excessive matrix degradation, as in osteoarthritis, or its abnormal production and accumulation, leading to tissue scarring and impaired organ function, both hallmarks of fibrosis [32]. This unbalanced process disrupts the regular cell-matrix interactions, leading to stiffening, decreased perfusion, and hypoxia, further promoting cell injury and fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation [34]. Surprisingly, the ECM translationally contributes to pathological gene expression, thus promoting the establishment of a positive feedback loop of self-amplifying fibroblast activation and augmented tissue fibrosis, culminating in disease progression [35].
Some of the most investigated pro-fibrotic regulators are the TGF-
Similarly, miR-21 influences the upregulation of other types of ECM proteins
[44, 45, 46], while miR-30 influences the downregulation of genes involved in ECM
degradation [47]. MiR-155 is upregulated in fibrotic disorders, promoting ECM
production by targeting the TGF-
MiRNA dysregulation can significantly impact fibrosis-related key cellular processes, including fibroblast activation and ECM remodeling [55, 56]. Studies have shown different patterns of miRNA expression in multiple fibrotic disorders, including cardiac fibrosis, liver fibrosis, kidney fibrosis, lung fibrosis, and dermal fibrosis, as well as primary myelofibrosis (Fig. 2).
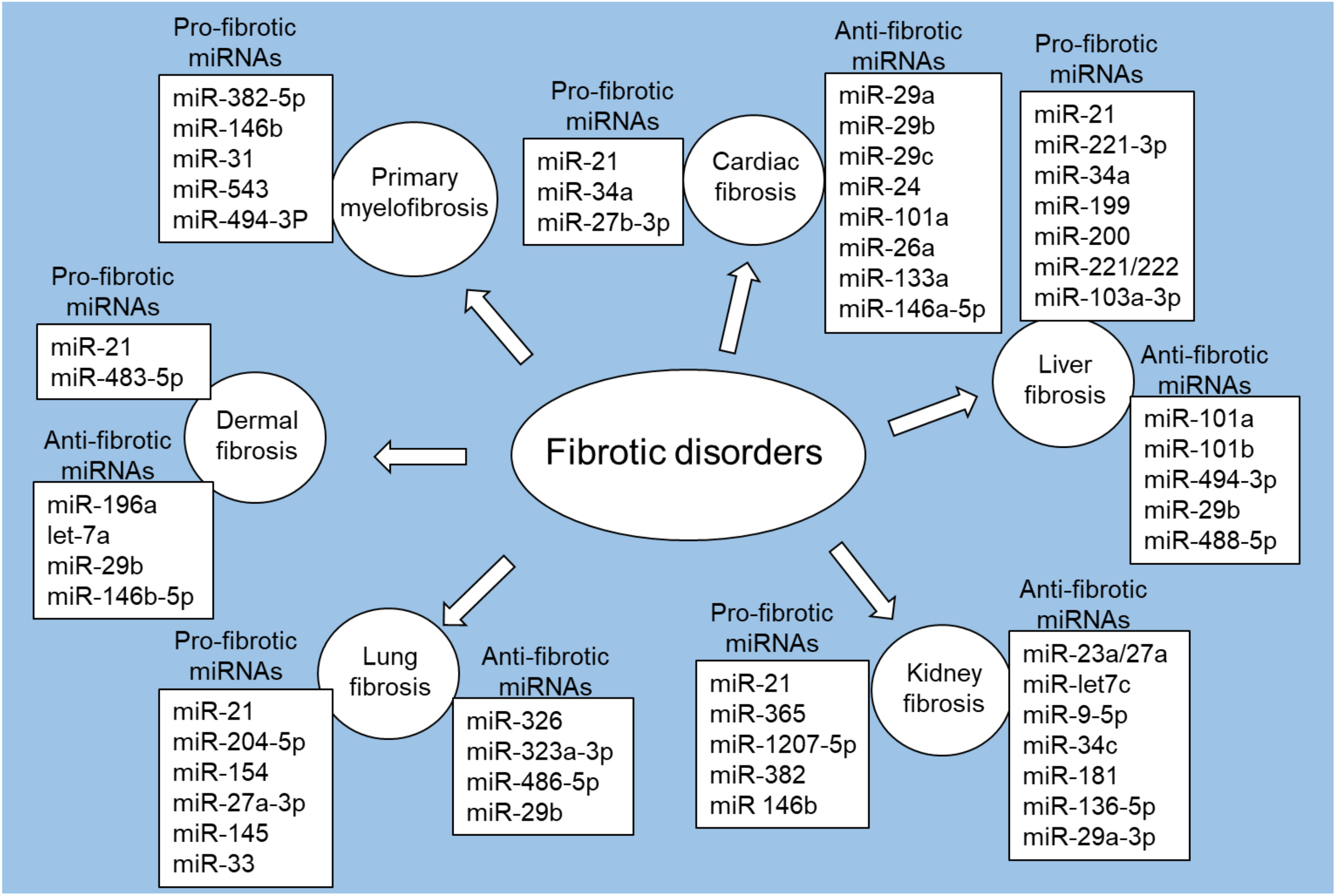 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Pro-fibrotic and anti-fibrotic miRNAs in fibrotic disorders. Figure created with biorender.com.
Cardiac fibrosis is defined by the excessive buildup of ECM components in the heart that leads to the rigidity and impaired function of the cardiac tissue [57]. The development of cardiac fibrosis can be influenced by various risk factors, including diabetes, aging, genetic factors, alcohol abuse, hypertension (high blood pressure), coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction (heart attack), heart failure, and SLE and rheumatoid arthritis [58, 59]. Emerging data suggest that miRNAs play an important role in developing and progressing cardiac fibrosis [9].
Among the miRNAs associated with pro-fibrotic effects, miR-21 and miR-34 have
received significant attention. MiR-21 is upregulated in cardiac fibrosis and is
associated with fibroblast activation, collagen synthesis, and ECM remodeling
[60, 61]. In a mouse model of pressure-overload-induced cardiac disease, specific
inhibition of miR-21 resulted in reduced interstitial fibrosis and cardiac
dysfunction mediated by the ERK/MAPK signaling cascade [62]. Similarly, in
chronic Chagas disease cardiomyopathy (CCC), where intense cardiac fibrosis and
inflammation occur, silencing miR-21 through locked nucleic acid
(LNA)-anti-miR-21 inhibitor led to a significant reduction in cardiac fibrosis in
Trypanosoma cruzi-infected mice [61]. The upregulation of miR-21 was
associated with elevated content of collagens in cardiac fibroblasts, and its
increase in collagen content was partially mediated by the downregulation of
TGF-
In a mouse model of transverse aortic constriction (TAC)-induced cardiac hypertrophy, miR-27b-3p showed elevated expression, and miR-27b-knockout mice exhibited remarkably attenuated cardiac hypertrophy, inflammation, and fibrosis. Analysis of the transcriptome revealed that miR-27b deletion significantly reduced TAC-induced cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and inflammatory genes. Interestingly, miR-27b-3p directly targets the fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1), and the administration of rFGF1 decreased fibrosis and cardiac hypertrophy in TAC-models [65].
Several miRNAs, including miR-29, miR-24, miR-101a, miR-26a, and miR-133a, have
exhibited antifibrotic effects in various studies [41, 66, 67, 68, 69]. The antifibrotic
properties of the miR-29 family (such as miR-29a, miR-29b, and miR-29c) have been
extensively investigated in cardiac fibrosis [41, 70, 71]. The lower expression
levels of miRNAs were detected in the myocardial region adjacent to the infarct,
and their down-regulation was linked to increased expression of collagens [41].
In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that down-regulation of
miR-29 was associated with increased collagen expression levels, while
overexpression of miR-29 decreased collagen expression levels in fibroblasts
[41]. Additionally, the down-regulation of miR-29a was accompanied by
up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) in cardiac
fibrosis tissues, and overexpression of miR-29a reduced cardiac fibrosis and
fibroblast proliferation by targeting the VEGF-A/MAPK signaling pathway [70].
Furthermore, overexpression of miR-29b decreased angiotensin II-induced cardiac
fibrosis, partly by inhibiting the TGF-
MiR-24 was downregulated in heart tissue from subjects with myocardial
infarction [66]. The overexpression of miR-24 improved heart function, decreased
fibrosis, and reduced the differentiation and migration of cardiac fibroblasts
[66]. The overexpression of miR-24 also reduced TGF-
The antifibrotic properties of miR-101a have been reported in cardiac fibrosis
[67]. The downregulation of miR-101a/b was observed in the peri-infarct area of
rats four weeks after coronary artery ligation [67]. Overexpression of miR-101a
in rats with chronic myocardial infarction was associated with improved cardiac
performance and reduced interstitial fibrosis [67]. Moreover, overexpression of
miR-101a/b decreased the proliferation and collagen secretion in rat neonatal
cardiac fibroblasts by targeting c-Fos and TGF-
A systematic review of miRNAs in cardiac fibrosis and aortic stenosis showed
that miR-133a is associated with increased left ventricular mass regression
post-surgery, whereas in the aortic valve, the downregulation of miR-665,
miR-602, and miR-939, but the upregulation of miR-193b and miR-214 [74]. Several
researchers have recently uncovered an extensive crosstalk between the
TGF-
Isoproterenol (ISO) is recognized for its propensity to elevate levels of
proinflammatory cytokines, thereby inducing cardiac fibrosis through the
upregulation of MMPs expression in cardiac fibroblasts. A study exploring
ISO-induced cardiac fibrosis observed a notable decreased levels of miR-146a-5p
in both ISO-treated rat cardiac tissue and ISO-induced cardiac fibroblasts [76].
On the other hand, the expression levels of FGF2, Col-1, and
In a study investigating myocardial infarction in rats, miR-133a levels were
found to be lower in cardiac fibrosis [69]. Upregulation of miR-133a in rats with
myocardial infarction significantly increased cardiac function and decreased
collagen content, accompanied by reduced expression levels of fibrotic factors,
such as TGF-
Liver fibrosis may develop due to liver damage, resulting in excessive deposition of ECM proteins in the liver tissue [90]. The major causes of liver fibrosis include chronic injury, local inflammation, viral infection, and oxidative stress [91].
A number of miRNAs have been reported in liver fibrosis, with distinct roles in either promoting or inhibiting the fibrotic process [92]. Among them, miR-21 has been extensively studied in liver fibrosis and is known to be upregulated in fibrotic liver tissues [93]. Notably, several studies have shown that a major feature of hepatic fibrosis is the extensive activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) [94], and the upregulation of miR-21 contributed to fibrogenesis by activating HSCs and increasing ECM secretion [95]. A miRNA profiling study identified a significant dysregulation of miR-451a, miR-142-5p, let-7f-5p, and miR-378a-3p upon in vitro activation of HSCs [96]. These miRNAs were upregulated in extracellular vesicles, indicating their potential as promising biomarkers for liver fibrosis. Another study by Tsay et al. [97] focused on miR-221-3p in hepatocytes as a therapeutic target for liver fibrosis. They found that blocking miR-221-3p in hepatocytes promoted the recovery of liver function and accelerated the resolution of ECM deposition [97]. This effect was attributed to the post-transcriptional regulation of GNAI2 by miR-221-3p, leading to reduced CCL2 secretion [97]. The reduction in CCL2 secretion may be associated with the mitigating effect of miRNA-221-3p on liver fibrosis.
In a study by Tu et al. [92], the impact of miR-101a and miR-101b on
the TGF-
The antifibrotic effect of miR-29b in liver fibrosis has been reported by Wang
and colleagues [100]. Human and mouse fibrotic liver tissues and primary HSCs
showed significant downregulation of miRNA-29b expression [100]. The
overexpression of miR-29b prevented CCL4-induced liver fibrosis in mice [100].
This protective effect was mediated by the downregulation of
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a leading global cause of chronic liver diseases. Many HCV-infected individuals progress from mild symptoms of acute infection to chronic infection, which can advance to a late-stage condition denoted cirrhosis and characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with nodules and scar tissue resulting from long-term liver damage. In some cases, irreversible cirrhosis can ultimately lead to developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [105]. It has been shown that plasma levels of several miRNAs are deregulated in the various stages of liver fibrosis. Some of them were able to differentiate patients among early/late cirrhotic stage and HCC, such as circulatory miR-221 and miR-542 [105], miR-484, miR-524, miR-615 and miR-628 expression profiling in HCV mediated HCC [106], and lastly miR-650, 552-3p, 676-3p, 512-5p and 147b [107].
Kidney fibrosis, also known as renal fibrosis, is defined by the excessive deposition of ECM components, such as collagens, in the kidney tissue. It is a common feature of various chronic kidney diseases (CKD). Diabetes and high blood pressure stand as the predominant causes of CKD. Recent studies have suggested the substantial role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis of kidney fibrosis [89].
Zarjou et al. [108] identified a dynamic miRNA signature associated
with renal fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Among the
altered miRNAs, miR-21 showed the maximum increase in UUO kidneys, and its
upregulation in renal tubular epithelial cells was stimulated by TGF-
In a diabetic nephropathy rat model induced by streptozotocin, upregulation of
miR-365 was observed in renal tissues, and similar elevated expression of miR-365
was reported in high glucose-treated HK-2 cells [110]. Silencing miR-365 was
associated with the accumulation of ECM components and inflammatory cytokines,
suggesting its inhibitory effect on renal fibrosis [110]. Alvarez et al.
[111] reported that miR-1207-5p, a PVT1 (plasmacytoma variant translocation
1)-derived miRNA, is highly expressed in kidney cells and is increased by glucose
and TGF-
Other miRNAs, such as miR-23a/27a [112], miR-let7c [113], miR-9-5p [114], miR-34c [115], miR‑181 [116], miR-136-5p [117], miR-29a-3p [118], miR-382 [119] and miR‑146b [120] have also been reported in kidney fibrosis.
MiR-23a and miR-27a, located together in a gene cluster, regulate proteins
involved in muscle atrophy. Zhang et al. [112] explored the role of
miR-23a/27a in reducing muscle atrophy and renal fibrosis. They demonstrated that
miR-23a/27a could reduce muscle loss and kidney fibrosis. Injection of
miR-23a/27a into the muscle of diabetic mice was associated with reduced fibrosis
in the kidneys and downregulated fibrotic proteins [112]. In experimental
studies, the administration of miR-let7c-modified mesenchymal stem cells improved
kidney injury associated with UUO by decreasing Col-4
MiR-9-5p exhibited a protective effect against renal fibrosis in a mouse model
of UUO [114]. This protective effect was partially mediated through the
downregulation of profibrotic proteins, reduction in the number of infiltrating
monocytes/macrophages, mitigation of tubular epithelial cell injury, and the
inhibition of TGF-
It has been shown that noncoding RNA activated by DNA damage (NORAD) can
activate the TGF-
Lung fibrosis, also known as pulmonary fibrosis (PF), is a pathological condition characterized by the excessive and abnormal deposition of fibrous tissue in the lungs [121]. A number of studies demonstrated the differential expressions of miRNAs and their role in lung fibrosis [122].
Zhou et al. [123] investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the
role of miR-21 in PF. They found that inhibition of miR-21 was associated with
reduced levels of ECM proteins in a mouse model of PF induced by bleomycin and in
human pulmonary fibroblasts treated with TGF-
A study by Das et al. [125] utilized a combination of computational
analysis, laboratory experiments, and animal models to explore miRNAs involved in
TGF-
The miR-33 family, encoded within the introns of sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP) genes, serves as pivotal regulators of sterol and FA metabolism. miR-33 plays a central role in modulating the immunometabolic response of macrophages, facilitating mitochondrial biogenesis, enhancing FA oxidation, and promoting cholesterol efflux [128]. Elevated levels of miR-33 have been found in bronchoalveolar lavage cells obtained from individuals with IPF when compared to healthy controls. Interestingly, the pharmacological inhibition of miR-33 in macrophages through the administration of anti-miR-33 peptide nucleic acids (PNA-33) effectively mitigates fibrotic processes in various in vivo and ex vivo models of PF in both mice and humans [128].
Decreased levels of miR-29b in human peripheral blood from IPF patients were
associated with increased mortality [129]. Notably, in animal models, miR-29
mimic MRG-201 systemic delivery reduced fibrosis, and the next-generation miR-29
mimic, with improved chemical stability, downregulated profibrotic genes with
lower doses than the original compound and was well tolerated without adverse
effects observed [129]. MiR-29, renamed as miR-29a-3p according to the new
nomenclature, appears to be involved in lung inflammation and PF induced by
neodymium oxide (Nd
Exosomes, nanovesicles released by almost all cell types, represent fundamental mediators of cell-cell communication and are emerging as essential elements in regulating several diseases through carrying condition-specific miRNAs. This feature represents a potential mechanism to be investigated for developing novel therapeutics [131]. In PF exosomes carry fibrotic mediators and multiple differentially expressed miRNAs were detected in exosomes from plasma and lung tissue of patients with PF compared with controls, such as let-7d-5p, miR-103-3p, miR-27b-3p, miR-30a-5p, miR-125b-5p, miR-128-3p, miR-21-5p, miR-100-5p, miR-140-3p, and miR-374b-5p [131]. Finally, alterations in the composition of the lung microbiota have a apparent impact on the development of lung fibrosis. Recent investigations have indentified disparities in lung microbiota composition among healthy individuals, those afflicted with IPF, and individuals experiencing acute exacerbation-IPF [132]. Several studies have started investigating the relationship between immune response modulation, lung microbiota dynamics, exosome-mediated miRNA regulation, and preserving pulmonary homeostasis. These inquiries may explore the relationships among these elements and their collective influence on the development of PF [132].
To summarize, the above studies highlighted the role of specific miRNAs, including miR-21, miR-204-5p, miR-154, miR-27a-3p, miR-145, miR-326, miR-323a-3p, miR-486-5p, miR-33 and miR-29b in lung fibrosis.
Dermal fibrosis is defined by the excessive accumulation of fibrous connective tissue in the skin, leading to the affected area’s thickening, hardening, and stiffening. Dermal fibrosis may occur when the normal balance of ECM production and remodeling in the skin is disturbed. Several conditions, including keloids, hypertrophic scars, scleroderma or systemic sclerosis (SSc), and graft versus host disease, are associated with the presence of skin fibrosis. Many studies have demonstrated the differential expression of several miRNAs in skin fibrosis.
In a recent study by Jafarinejad-Farsangi et al. [133], the expression
patterns of miR-29a and miR-21, two miRNAs with opposing effects on collagen
production in fibroblasts, were examined in SSc patients and healthy controls.
The study found that miR-21 was upregulated, while miR-29a was downregulated in
SSc and TGF-
Honda et al. [136] found that miR-196a was found to be lower in SSc
fibroblasts, both in vitro and in vivo, and its expression was
restored by inhibition of TGF-
In the study by Gallant-Behm et al. [138], the pharmacodynamic activity of a miR-29b mimic (remlarsen) was examined for its therapeutic potential in fibrotic conditions. The miR-29 mimic effectively regulated the expression levels of collagens. In a clinical trial, miR-29 mimic demonstrated the ability to suppress collagen expression and prevent fibroplasia in skin wounds [138]. This result suggests that miR-29b mimic could be a promising therapeutic approach for preventing fibrotic scarring and cutaneous fibrosis.
In the SSc primary skin fibroblasts, Zhou et al. [139] reported the
overexpression of miR-146b levels. In a recent study by Fujisawa et al.
[140], the antifibrotic properties of miR-146b-5p were investigated in skin
wounds. They found that basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) upregulated
miR-146b-5p, and its target gene PDGFR
Primary myelofibrosis, also called chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis, is a relatively uncommon and chronic hematological disorder belonging to the group of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Primary myelofibrosis is a type of blood cancer defined by the formation of fibrous tissue in the bone marrow. The progressive fibrosis in the bone marrow disturbs the normal production of blood cells and is associated with anemia, thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), and abnormal levels of white blood cells. Numerous studies have identified distinct miRNA expression patterns and their functional roles in dermal fibrosis.
Rossi et al. [141] identified that the upregulation of miR-382-5p in
CD34+ cells was associated with the downregulation of superoxide dismutase 2
(SOD2), resulting in the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and
oxidative DNA damage. Additionally, TGF-
Aberrant regulation of several miRNAs, including miR-10b-5p, miR-19b-3p,
miR-29a-3p, miR-379-5p, and miR-543 was observed in both primary myelofibrosis
granulocytes and CD34+ cells, along with consistent downregulation of a
microRNA-offset RNAs (moRNAs) called 3
Collectively, it is apparent that multiple miRNAs, including miR-382-5p, miR-146b, miR-31, miR-128-2, miR-543, and miR-494-3p could potentially contribute to the development and progression of primary myelofibrosis. Consequently, targeting and modulating the expression levels and functions of these specific miRNAs could present promising therapeutic approaches for primary myelofibrosis.
MiRNAs exert their regulatory influence upon an extensive array of target genes. Table 1 (Ref. [41, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 76, 78, 79, 92, 93, 94, 95, 97, 98, 100, 108, 110, 111, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137, 138, 139, 140, 145]) provides a comprehensive view of major miRNA targets involved in fibrotic diseases. Several compounds have been assessed for their potential to target and modulate miRNA expression in fibrotic diseases (Table 2, Ref. [62, 77, 109, 147, 148, 149, 150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159, 160, 161, 162, 163, 164, 165, 166, 167, 168, 169, 170, 171, 172]). These include antisense oligonucleotides, small molecule modulators, and natural compounds.
| MiRNA species | MiRNA expression in fibrotic disorders | MiRNA targets |
| let-7a | ↓let-7a (dermal fibrosis) [137]. | Col 1 [137]. |
| miR-let7c | ↓miR-let7c (kidney fibrosis) [113]. | Collagen Iv |
| miR-9-5p | miR-9-5p (kidney fibrosis) [114]. | Profibrotic factors (i.e., ACTA2, COL1A1, FN1) [114]. |
| miR-21 | ↑miR-21 (cardiac fibrosis, liver fibrosis, kidney fibrosis, lung fibrosis, dermal fibrosis) [63, 93, 108, 123, 133]. | Collagen [63, 133], ECM secretion [95], PPAR |
| miR-24 | ↓miR-24 (cardiac fibrosis) [66]. | TGF- |
| miR-26a | ↓miR-26a (cardiac fibrosis) [68]. | CTGF, Smad4, EZH2/p21 pathway [68]. |
| miR-27b-3p | ↑miR-27b-3p (cardiac fibrosis) [65]. | FGF1 [65]. |
| miR-29a | ↓miR-29a (dermal fibrosis, cardiac fibrosis, kidney fibrosis) [41, 118, 133]. | Collagen [41, 133], MMP-2 [118]. VEGF-A/MAPK [70]. |
| miR-29b | ↓miR-29b (dermal fibrosis, cardiac fibrosis, liver fibrosis) [41, 100, 138]. | Collagens [41, 138], TGF- |
| miR-29c | ↓miR-29c (cardiac fibrosis) [41]. | Collagen [41]. |
| miR-34a | ↑miR-34a (cardiac fibrosis) [64]. | TGF- |
| miR-34c | ↑miR-34c (kidney fibrosis) [115]. | CTGF, |
| miR-101a/b | ↓miR-101a/b (cardiac fibrosis, liver fibrosis) [67, 92]. | Collagen secretion, c-Fos and TGF- |
| miR-133 | ↓miR-133a (cardiac fibrosis) [69], ↓miR-133 (cardiac fibrosis) [78]. | TGF- |
| miR-136-5p | ↓miR-136-5p (kidney fibrosis) [117]. | TGF- |
| miR-146a-5p | ↓miR-146a-5p [76]. | FGF2, Col-1, and |
| miR-146b-5p | ↑miR-146b-5p (dermal fibrosis) [139]. | PDGFR |
| miR‑181 | ↓miR‑181 (kidney fibrosis) [116]. | |
| miR-196a | ↓miR-196a (dermal fibrosis) [136]. | Col 1 [136]. |
| miR-204-5p | ↑miR-204-5p (lung fibrosis) [124]. | AP1S2 [124]. |
| miR-221-3p | ↑miR-221-3p (liver fibrosis) [97]. | GNAI2, CCL2 [97]. |
| miR-323a-3p | ↓miR-323a-3p (lung fibrosis) [126]. | TGF- |
| miR-326 | ↓miR-326 (lung fibrosis) [125]. | TGF- |
| miR-365 | ↑miR-365 (kidney fibrosis) [110]. | ECM components and inflammatory cytokines [110]. |
| miR-483-5p | ↑miR-483-5p (dermal fibrosis) [135]. | Col4A1 and Col4A2, Col1A2, |
| miR-486-5p | ↓miR-486-5p (lung fibrosis) [127]. | SMAD2 [127]. |
| miR-488-5p | ↓miR-488-5p (liver fibrosis) [94]. | TET3 [94]. |
| miR-494-3p | ↓miR-494-3p (liver fibrosis) [98], ↑miR-494-3p (primary myelofibrosis) [145]. | |
| miR-1207-5p | ↑miR-1207-5p (kidney fibrosis) [111]. | TGF- |
| Therapeutic agent | Fibrotic disorders | Targeted miRNAs | Function | |
| Antisense oligonucleotides | Antagomirs | Cardiac fibrosis | ↓miR-34 | LNA-antimiR-34 (8-mer) decreased cardiac fibrosis, by targeting miR-34 [147]. |
| ↓miR-21 | The inhibition of miR-21 was associated with the attenuation of cardiac dysfunction and interstitial fibrosis [62]. | |||
| Kidney fibrosis | ↓miR-21 | Anti-miR-21 was associated with reduction of kidney fibrosis after injury [109]. | ||
| MiRNA mimics | Liver fibrosis | ↑miRNA-200a | MiR-200a-mimic can regulate the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and fibrosis [148]. | |
| Carvedilol | Cardiac fibrosis | ↑miR-133 | Carvedilol treatment upregulated miR-133a expression, which was associated with reduced fibrosis and improved cardiac function of rat model [77]. | |
| ↑miR-29b | Carvedilol showed cardioprotective effects against myocardial fibrosis by upregulating miR-29b expression [149]. | |||
| Carvedilol showed cytoprotective effects against cardiomyocyte apoptosis by upregulating miR-133 expression [150]. | ||||
| Liver fibrosis | ↑miR-200a | Carvedilol decreased liver fibrosis and improved liver function in rats treated with CCl4 by upregulating circulating miR-200a [151]. | ||
| Ivabradine | Cardiac fibrosis | ↑miRNA-133a | Ivabradine reduced cardiac fibroblast activation and myocardial fibrosis by upregulation of miRNA-133a [152]. | |
| Nebivolol | Cardiac fibrosis | ↑miR-27a | In a rodent model of hypertension, nebivolol attenuated left ventricular hypertrophy, fibrosis, and functional deterioration, at least in part, by regulating miR-27a and miR-29a [153]. | |
| ↑miR-29a | ||||
| Astragaloside IV | Kidney fibrosis | ↓miR-21 | Astragaloside IV improved renal function and fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting miR-21 [154]. | |
| Baicalin | Kidney fibrosis | ↑miRNA-124 | Baicalin attenuated renal fibrosis in human kidney cells by upregulation of miRNA-124 [155]. | |
| ↑miR-3595 | Baicalin showed anti-fibrotic effects in HSCs involved in liver fibrosis by induction of miR-3595 expression [156]. | |||
| Lung fibrosis | ↓miR-21 | Baicalein showed antifibrotic effects on bleomycin-induced PF and decreased miR-21 [157]. | ||
| Baicalein reduced differentiation of human lung fibroblasts by inhibiting the expression of miR-21 [158]. | ||||
| Berberine | Liver fibrosis | ↑miR-30a-5p | Berberine inhibited autophagy in activated HSCs through upregulation of miR-30a-5p, leading to HSCs apoptosis and improvement of liver fibrosis in mice [159]. | |
| Celastrol | Cardiac fibrosis | ↓miR-21 | Celastrol attenuated cardiac fibrosis and improved cardiac function in a mouse model of myocardial fibrosis by inhibition of the miR-21 [160]. | |
| Corilagin | Liver fibrosis | ↓miR-21 | Corilagin reduced miR-21 expression and CCl4-induced liver fibrosis of rats [161]. | |
| EGCG | Liver fibrosis | ↑miR-221 | In in vitro and in vivo models of hepatic fibrosis, EGCG effectively inhibited osteopontin (OPN)-dependent injury and fibrosis by upregulation of miR-221 [162]. | |
| Quercetin | Cardiac fibrosis | ↓miR-223-3p | Quercetin inhibited the expression of miR-223-3p, and activated the autophagy pathway, which was associated with reduction in myocardial fibrosis and improvement in atrial remodeling [163]. | |
| Kidney fibrosis | ↓miR-21 | Quercetin showed anti-fibrotic effects against renal fibrosis, at least in part, by inhibition of miR-21 [164]. | ||
| Resveratrol | Cardiac fibrosis | ↓miR-17 | Resveratrol inhibited the proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts and collagen secretion induced by TGF- | |
| Liver fibrosis | ↑miR-20a | Resveratrol alleviated liver fibrosis by inducing autophagy and activating the miR-20a-mediated PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [166]. | ||
| ↓miR-21 | Resveratrol showed protective effects against bile duct ligation-induced liver fibrosis and injury, inhibiting the TGF | |||
| ↓miR-190a-5p | Resveratrol alleviated liver fibrosis by inhibiting miR-190a-5p [168]–, and protected against thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis by attenuating miR-155 expression [169]. | |||
| ↓miR-155 | ||||
| Lung fibrosis | Resveratrol attenuated bleomycin-induced PF by downregulating miR-21 [170]. | |||
| Tanshinone IIA | Cardiac fibrosis | ↑miR-133 | Tanshinone IIA protected neonatal cardiomyocytes from hypoxia-induced apoptosis, at least in part, by upregulation of miR-133 expression [171]. | |
| Ursolic acid | Cardiac fibrosis | ↓miR-21 | Ursolic acid attenuated myocardial fibrosis and pathological cardiac hypertrophy in mice, by inhibition of the miR-21/ERK signaling pathway [172]. | |
EGCG, Epigallocatechin-3-gallate; PF, Pulmonary fibrosis.
Antisense oligonucleotides are synthetic molecules formulated to inhibit or mimic the activity of specific miRNA. Indeed, based on the canonical processes of miRNA biogenesis and RNA interference, two distinct categories of miRNA-based antisense oligonucleotides have been formulated: antagomiRs and miRNA mimics.
AntagomiRs, also called antimiRs or blockmiRs, constitutively inhibit the activity of a specific miRNA target with high specificity and are mainly used for loss-of-function investigations [173]. In particular, antagomiRs are synthesized in the form of single-stranded oligonucleotides that exhibit complementarity to the guide strands of endogenous miRNAs or pre-miRNA sequences. Chemical modifications enhance antagomiR stability and prevent degradation. When delivered in the cytoplasm, they are engaged in homologous binding with the target miRNAs, thus blocking their interaction with the AGO2 protein and loading into the RISC complex. Consequently, antagomiRs impede mRNA degradation or the repression of translation induced by miRNAs [173].
Cardiac fibrosis: Bernardo et al. [147] examined the therapeutic capacity of inhibiting the miR-34 family in mice with preexisting pathological cardiac remodeling and dysfunction triggered by myocardial infarction or pressure overload. They utilized an LNA-modified antimiR called LNA-antimiR-34 to inhibit the miR-34 family. The results showed that LNA-antimiR-34 effectively silenced all three miR-34 family members in both cardiac stress models and contributed to the attenuation of cardiac remodeling, atrial enlargement, and improved outcomes. Interestingly, no benefit was observed in the myocardial infarction model when miR-34a alone was hindered through LNA-antimiR-34a (15-mer) [147]. However, inhibition of the whole miR-34 family with LNA-antimiR-34 (8-mer) offered substantial therapeutic effects in terms of systolic function improvement, decreased lung congestion, minimized cardiac fibrosis, enhanced angiogenesis, increased Akt activity, decreased atrial natriuretic peptide gene expression, and maintained sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase gene expression in mice subjected to pressure overload [147]. Additionally, the enhanced outcomes in the LNA-antimiR-34 (8-mer)-treated mice were linked to the upregulation of several direct miR-34 targets, including VEGF, vinculin, protein O-fucosyltranferase 1, Notch1, and semaphorin 4b [147]. These data suggest the potential of silencing the whole miR-34 family as an intervention approach to protect against pathological cardiac remodeling and improve cardiac function. In a study by Thum et al. [62], antagomirs were utilized to silence miR-21 in a mouse model of pressure-overload-induced heart disease. The researchers were able to attenuate cardiac dysfunction and decrease interstitial fibrosis by blocking miR-21 [62], showing that antagomirs can be used to treat cardiovascular disease by altering miRNA activity.
Kidney fibrosis: Studies utilizing anti-miR-21 oligonucleotides have offered proof of their efficacy and specificity in animal models of kidney diseases [109, 174]. Chau et al. [109] reported that inhibition of miR-21 through complementary oligonucleotides in mice was associated with reduced kidney fibrosis after injury. These data highlight that targeting miR-21 through anti-miR-21 would be an effective therapeutic approach in preventing kidney fibrosis.
MiRNA mimics consist of dsRNA oligonucleotides spanning 20–22 nucleotides in length. These mimics of endogenous miRNAs emulate the duplex structures generated by DICER, making them suited for interaction with AGO2 and incorporation into RISCs and ready for translational repression activities. An essential attribute of miRNA mimics lies in their capacity to concurrently target multiple mRNA molecules, thus potentially downregulating and upregulating a range of proteins.
Liver fibrosis: In hepatic cells, the nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a vital transcription factor responsible for inducing a protective effect from oxidative stress through the expression of numerous detoxifying enzymes, including glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), NQO1 (NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase 1), and glucuronosyl transferases. Nrf2 activation depends on the Keap1 (Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1) adaptor protein, a direct target of miRNA-200a [148]. Functional studies based on miR-200a-mimic highlighted that this miRNA regulates the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in HSCs and fibrosis, and interestingly, the epigenetic therapy can restore Keap1 expression triggered by miRNA-200a, therefore restoring the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant pathway in liver fibrosis [148]. MiR-122 is a conserved liver-specific miRNA essential for maintaining liver homeostasis through regulating various functions such as glucose, iron homeostasis, lipid and cholesterol metabolism, and infection of HCV [175]. It has been shown that miR-122 expression is downregulated in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients and in a subset of HCC patients. MiR-122 is a miRNA showing therapeutic potential both as an anti-mir against HCV infection and as a mimic in combating various liver diseases, including fibrosis, cirrhosis, and HCC. MiR-122 represents the first miRNA to have undergone efficacious clinical trials among HCV-infected patients [175].
Carvedilol is a medication classified as a member of the drugs known as
Cardiac fibrosis: Carvedilol therapy upregulated miR-133a expression in a study on rats with myocardial infarction-induced cardiac fibrosis, which was connected to decreased fibrosis and enhanced cardiac function [77]. Another study found that carvedilol prevented myocardial fibrosis by increasing miR-29b expression and inhibiting Smad3 activation, which resulted in the downregulation of fibrotic markers [149]. Furthermore, carvedilol showed cytoprotective effects against cardiomyocyte apoptosis by enhancing the expression of miR-133 and suppressing caspase-9-mediated apoptotic pathways, ameliorating impaired cardiac function and protecting against oxidative stress-induced damage [150]. These reports propose that carvedilol is helpful in heart fibrosis via modulating miRNA expression and inhibiting fibrotic pathways.
Liver fibrosis: Carvedilol was reported to enhance circulating miR-200a
expression, decreasing liver fibrosis and improving liver function in rats
treated with CCl4 [151]. This effect was linked to the upregulation of SMAD7 gene
expression and protein content, resulting in the minimization of the
pro-fibrogenic marker TGF-
Ivabradine is a therapeutic compound that belongs to a class of drugs called hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel blockers. Ivabradine targets and blocks the HCN channels in the sinoatrial node, lowering the heart rate without remarkably affecting other cardiovascular parameters.
Cardiac fibrosis: In mouse models of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), high-dose ivabradine ameliorated diastolic cardiac function in HFpEF and enhanced both diastolic and systolic function and ventricular tachycardia incidence in HFrEF, while decreasing cardiac fibroblast activation and myocardial fibrosis [152]. The overexpression of miRNA-133a, which targets CTGF and Col-1, may contribute to ivabradine’s protective effects [152].
Nebivolol is a medication belonging to the class of drugs known as beta-blockers, essentially used for treating hypertension and heart failure. Nebivolol acts by inhibiting the effects of certain hormones, such as adrenaline, on the heart and blood vessels, reducing heart rate and blood pressure.
Cardiac fibrosis: In a rodent model of hypertension, nebivolol, a
selective
Astragaloside IV is a natural compound derived from the root of Astragalus membranaceus, a traditional Chinese medicinal herb.
Kidney fibrosis: Astragaloside IV was found to improve renal function
and fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease by hindering the overexpression of
miR-21, which triggers podocyte dedifferentiation and mesangial cell activation
[154]. Astragaloside IV exerted its effects by suppressing the
Baicalein is a flavonoid chemical found naturally in the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis, commonly known as Chinese skullcap. It is a yellow crystalline powder used in traditional Chinese medicine for generations.
Liver fibrosis: Zhang et al. [155] examined the potential of
baicalin in attenuating renal fibrosis in human kidney cells. Baicalin therapy
lowered renal fibrosis and damage, as seen by better kidney function and a drop
in the expression of fibrotic markers [155]. This result was achieved by the
overexpression of miRNA-124, which targeted toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and
blocked the TLR4/NF-
Lung fibrosis: Baicalein was assessed for its effects on
bleomycin-induced PF [157]. The results showed that baicalein lowered fibrotic
markers, improved antioxidant activity, alleviated inflammation, reduced miR-21
levels, and blocked the TGF-
Berberine is a natural compound found in different plants, including Coptis chinensis (goldenseal), Phellodendron amurense (Amur cork tree), and Berberis species (such as barberry). It has been used in traditional Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine for centuries.
Liver fibrosis: According to a study on liver fibrosis, berberine inhibited autophagy by upregulating miR-30a-5p, leading to HSCs apoptosis and improving liver fibrosis in mice [159]. These data suggest that berberine may be an effective therapeutic agent for liver fibrosis by targeting autophagy and triggering HSCs apoptosis.
Celastrol is a natural bioactive compound found in the root of the Tripterygium wilfordii plant, also known as the thunder god vine. It has been used in Chinese medicine for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Cardiac fibrosis: In a mouse model of myocardial fibrosis, celastrol attenuated cardiac fibrosis and improved cardiac function [160]. Celastrol’s positive effects have been linked to the suppression of the miR-21/ERK signaling pathway [160], indicating its potential as an intervention for preventing myocardial fibrosis.
Corilagin is a natural compound derived from diverse medicinal plants, including Phyllanthus spp., Terminalia spp., and Geranium spp.
Liver fibrosis: Corilagin was reported to lower miR-21 expression and
inhibit the TGF-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is a natural compound in green tea (Camellia sinensis). It is famous for its antioxidant properties.
Liver fibrosis: Arffa et al. [162] have shown that EGCG lowered osteopontin (OPN) expression in HSCs. EGCG substantially prevented OPN-dependent injury and fibrosis in both in vitro and in vivo models of hepatic fibrosis, indicating its promise as a protective agent in liver injury [162]. The mechanism involves the upregulation of miR-221 [162].
Quercetin is a flavonoid, a plant pigment and natural compound found in many fruits, vegetables, and grains. It belongs to a class of flavonoids known as flavonols and is famous for its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Quercetin is commonly found in apples, berries, onions, citrus fruits, grapes, and green leafy vegetables.
Cardiac fibrosis: Hu et al. [163] examined the potential mechanism of quercetin in preventing myocardial fibrosis and improving myocardial remodeling in atrial fibrillation. The findings showed that quercetin decreased the expression levels of miR-223-3p, enhanced the expression levels of FOXO3, and activated the autophagy pathway, significantly reducing myocardial fibrosis and improving atrial remodeling [163]. These results indicate that quercetin may have therapeutic potency for atrial fibrillation by modulating the miR-223-3p/FOXO3 axis and enhancing autophagy.
Kidney fibrosis: The effects of quercetin treatment on renal tubular
epithelial cells were examined [164]. Quercetin partially inhibited fibrosis in
the cells induced by TGF-
Resveratrol is a natural compound derived from diverse plants, including grapes, berries, and peanuts. Resveratrol is well known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. It has received much interest because of its possible health advantages and medicinal properties.
Cardiac fibrosis: Zhang et al. [165] discovered that resveratrol suppressed cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen secretion caused by TGF-1, a crucial profibrogenic factor in myocardial fibrosis. Resveratrol’s inhibitory action was mediated via the downregulation of miR-17 and regulation of Smad7 expression [165], indicating a possible molecular basis for resveratrol’s anti-fibrotic characteristics in myocardial fibrosis.
Liver fibrosis: Numerous studies have examined the therapeutic efficacy
of resveratrol in liver fibrosis. Zhu et al. [166] reported that
resveratrol alleviates liver fibrosis by triggering autophagy and activating the
miR-20a-mediated PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Another study by ShamsEldeen
et al. [167] reported the protective effects of resveratrol against bile
duct ligation-induced liver fibrosis and injury, which was mediated by inhibiting
the TGF
Lung fibrosis: Wang explored the molecular mechanism of resveratrol in regulating PF [170]. The researchers revealed that resveratrol reversed the elevated levels of miR-21 produced by pulmonary fibrosis, relieved PF symptoms, and blocked TGF-1/Smad pathway activation in a rat model of PF induced by bleomycin. In vitro, miR-21 inhibited resveratrol’s beneficial effects on TGF-induced collagen deposition and the production of fibrosis-related proteins [170]. According to the findings, resveratrol reduces bleomycin-induced PF by modulating miR-21 via the MAPK/AP-1 pathways.
Tanshinone IIA is a natural bioactive compound found in the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza, a traditional Chinese herb known as Danshen. It is a lipid-soluble substance and belongs to the class of diterpenes called tanshinones. Tanshinone IIA has been thoroughly examined for its pharmacological activities, particularly its potential benefits in cardiovascular health.
Cardiac fibrosis: Tanshinone IIA was found to protect neonatal cardiomyocytes from hypoxia-induced apoptosis [171]. The protective effects were linked to the elevated expression of miR-133 and activation of the ERK1/2 pathway [171], indicating a possible mechanism by which tanshinone IIA exhibits cardioprotective properties.
Ursolic acid is a natural compound found in diverse plants, including apple peels, rosemary, and holy basil. It belongs to a class of triterpenoids known for their pharmacological properties.
Cardiac fibrosis: Ursolic acid has been found to alleviate myocardial fibrosis and pathological cardiac hypertrophy in mice [172]. The underlying mechanism of these effects indicates the involvement of inhibition of the miR-21/ERK signaling pathway [172]. These data propose that ursolic acid may possess therapeutic promise for treating myocardial fibrosis and cardiac-related complications.
The potential therapeutic benefits of targeting specific miRNAs involved in fibrosis are increasingly evident. Antisense oligonucleotides, antagomirs, small molecule modulators, and natural compounds have become prominent viable strategies for controlling the actions of pro-fibrotic or anti-fibrotic miRNAs. These strategies suggest various alternatives for developing therapeutic drugs to tackle fibrotic disorders.
Recent research shows that miRNAs play a critical role in fibrosis development and progression. Fibrosis is associated with numerous diseases, including cardiac, liver, kidney, lung, dermal, and primary myelofibrosis, and miRNAs have been reported to govern essential pathways and molecules involved in these diseases. Notably, different miRNAs can promote or inhibit fibrosis, suggesting they may be used as therapeutic targets. Numerous strategies for targeting specific miRNAs in fibrotic disorders have been explored, including antisense oligonucleotides, small molecule modulators, and natural compounds. Different compounds, including LNA-antimiR-34, anti-miR-21, carvedilol, ivabradine, and nebivolol, as well as celastrol quercetin, resveratrol, tanshinone IIA, and ursolic acid, have been assessed for the treatment of cardiac fibrosis. Natural compounds, including baicalein, corilagin, EGCG, and resveratrol, have revealed promising results in liver fibrosis. In kidney fibrosis, anti-miR-21 and natural compounds such as astragaloside IV and quercetin have been studied, while natural compounds, including baicalein and resveratrol, have been accessed for lung fibrosis. Despite the potential of these compounds to target fibrotic conditions, further research is needed for a complete understanding of their mechanisms and the development of effective miRNA-based treatments for the diseases. The complex nature of fibrotic disorders suggests that miRNA-based treatment may be complemented by other treatments, particularly natural compounds, to offer a more comprehensive and synergistic approach to treating fibrotic diseases.
MSI designed the study. AM, MK, LM, MMA, AKMMM, and MSI performed the search and analyzed the data. AM, MK, LM, MMA, AKMMM, and MSI wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This research received no external funding.
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Given the role as Guest Editor, Most Mauluda Akhtar and Md Soriful Islam had no involvement in the peer-review of this article and has no access to information regarding its peer-review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to Esteban C. Gabazza.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.


