1 National Demonstration Center for Experimental General Medicine Education, Xianning Medical College, Hubei University of Science and Technology, 437100 Xianning, Hubei, China
2 School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xianning Medical College, Hubei University of Science and Technology, 437100 Xianning, Hubei, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: Accumulative evidence suggests that pyroptosis plays a key role in mediating angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced cardiac remodeling However, the potential role of pyroptosis-related transcription factor (TF)-microRNA (miRNA)-gene regulatory networks in mediating Ang II-associated cardiac remodeling remains largely unknown. Therefore, we identified the pyroptosis-related hub genes and constructed a transcription factor (TF)-miRNA-target gene regulatory network using bioinformatic tools to elucidate the pathogenesis of Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling. Methods: The pyroptosis-related differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified from the cardiac remodeling-related dataset GSE47420. Gene ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis, and protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis were performed to identify the pyroptosis-related hub DEGs. A TF-miRNA-target gene network was constructed and further validated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) in animal experiments. The correlation between the pyroptosis-related hub DEGs and cardiac remodeling was evaluated using comparative toxicogenomics database. The drug-gene interaction analysis was performed to identify potential drugs that target the pyroptosis-related hub DEGs. Results: A total of 32 pyroptosis-related DEGs were identified and enriched in the inflammation-related pathways by KEGG analysis. 13 of the 32 pyroptosis-related DEGs were identified as hub DEGs. Furthermore, a TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network containing 16 TFs, 6 miRNAs, and 5 hub target genes was constructed. The five pyroptosis-related hub target genes (DDX3X, ELAVL1, YWHAZ, STAT3, and EED) were identified as crucial cardiac remodeling-related genes using the comparative toxicogenomics database (CTD) database. Five drugs including celecoxib were identified as potential drugs for the treatment of cardiac remodeling. Finally, the expression levels of two top-ranked TF-miRNA-target genes axis were verified by qRT-PCR in mice with Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling and found to be generally consistent with the microarray results. Conclusions: This study constructed a pyroptosis-related TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network for Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling. Five pyroptosis-related genes (DDX3X, ELAVL1, YWHAZ, STAT3, and EED) can be considered the core genes associated with pyrotposis-related cardiac remodeling. The findings of this study provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms of Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling and may serve as potential biomarkers or therapeutic targets for Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling.
Keywords
- cardiac remodeling
- angiotensin II
- pyroptosis
- microRNA
- inflammation
Cardiac remodeling, a pathological process that is characterized by
cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, apoptosis, and interstitial fibrosis, is often found
in many cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, myocardial infarction,
valvular heart disease, and diabetes, and has been regarded as an
independent risk factor for the development of heart failure [1, 2]. A variety of
neurohumoral factors such as angiotensin II (Ang II) and transforming growth
factor-
Accumulative evidence suggests that pyroptosis, a type of programmed cell death
associated with inflammation, may play a key role in mediating Ang II-induced
cardiac remodeling [5]. Pyroptosis, an inflammatory form of programmed cell
death, is driven by the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor
protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation. The activated NLRP3 inflammasome
consequently activates caspase-1 to cleave the pro-IL-1
microRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous single-stranded non-coding RNAs consisting of approximately 22 nucleotides. They regulate various target genes at the post-transcriptional level either by cleaving mRNA or by translational repression or mRNA decay. Recent studies suggest that the dysregulation of various miRNAs such as miR-21 and miR-208a may play a key role in the pathogenesis of cardiac remodeling [10, 11, 12]. The miRNAs such as miR-133a-3p and miR-92b-3p reportedly mediate Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte remodeling through regulation of pyroptosis [13, 14]. Additionally, the transcription factors (TFs) upstream of miRNAs have been reported to regulate cardiac remodeling through their interaction with miRNAs [15, 16]. Integrated bioinformatics analysis of mRNA and miRNA expression profiles can provide novel insights into the research of the mechanisms underlying various diseases such as cancers [17], Alzheimer’s disease [18], and cardiac remodeling [19]. However, the potential role of pyroptosis-related TF-miRNA-gene regulatory networks in mediating Ang II-associated cardiac remodeling remains to be systematically explored.
Therefore, in this study, we analyzed the transcriptome signatures of heart tissues from a microarray dataset (GSE47420) of Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling in the BALB/c background mice to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between Ang II-infused mice and saline-infused control mice. These DEGs were intersected with the pyroptosis-related genes from the GeneCards database to obtain pyroptosis-related DEGs. The hub genes derived from these pyroptosis-related DEGs were identified by integrating gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses and protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis. Furthermore, the upstream miRNAs that target the pyroptosis-related hub DEGs were predicted and intersected with the differentially expressed miRNAs (DE-miRNAs) in the dataset GSE69559 to obtain the overlapping DE-miRNAs. The potential transcription factors (TFs) that regulate these overlapping DE-miRNAs were predicted and intersected with the total DEGs in GSE47420 to obtain the overlapping differentially expressed TFs (DE-TFs). Finally, a pyroptosis-related TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network was constructed to show the potential molecular mechanisms of Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling. Some key components in this network were validated in mice with Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling. The finding of the study may provide new insights into the mechanism and therapeutic targets of cardiac remodeling.
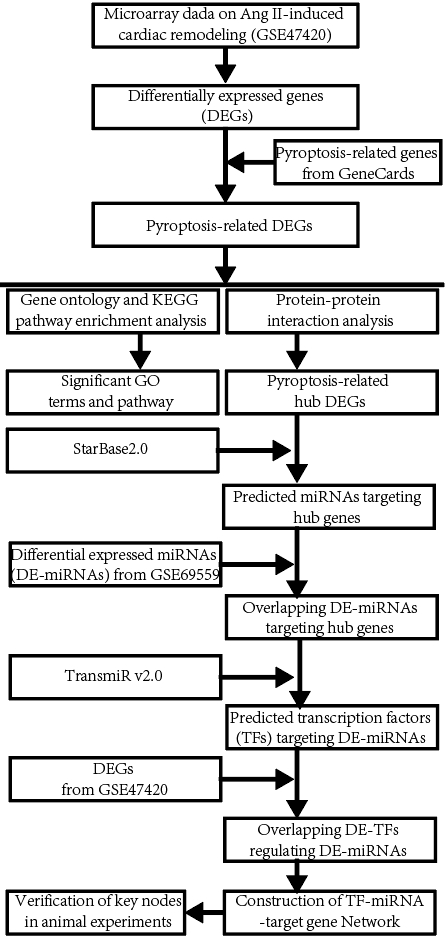
The workflow diagram of the present study was shown in Fig. 1.
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.The workflow diagram of the present study. miRNA, microRNA; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
The Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) was searched to obtain the gene expression datasets by using the search terms ((cardiac hypertrophy OR cardiac remodeling OR cardiac fibrosis) AND angiotensin II). The obtained datasets were filtered according to the following inclusion criteria: (i) the organism was filtered by “mus musculus”; (ii) the study type was “Expression profiling by array”; (iii) mRNA expression profiles derived from the samples from both the Ang II-infused mice (cardiac remodeling) and the saline-infused mice (control); (iv) the raw data of the series matrix file(s) should be provided for reanalysis. Datasets that did not meet the aforementioned criteria were excluded. After careful review and comparison, the gene expression dataset GSE47420 was downloaded from the GEO database for subsequent analysis. GSE47420 was processed based on the GPL6887 platforms and contained heart samples of 3 Balb/C mice with Ang II-infused cardiac remodeling and 3 age-matched control mice [20]. Before analysis, these data were normalized using R’s limma package (R version 4.2.2 and limma version 3.54.0, Bell Labs, Lucent Technologies, Murray Hill, NJ, USA).
We first used GEO2R (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/geo2r/) to identify the
differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the Ang II-infused mice (cardiac
remodeling) and the saline-infused mice (control) in GSE47420. GEO2R (version 1, National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda, MD, USA) is an
interactive web tool that allows for comparison between two groups of Samples
from normalized GEO datasets. The Benjamini and Hochberg false discovery rate
(FDR) method was used in GEO2R to adjust the p-value to reduce false
positivity. Then the significant DEGs between the Ang II and control groups were
obtained based on the following inclusion criteria: a threshold of adjusted
p
The pyroptosis-related genes were downloaded from the GeneCards database (https://www.genecards.org/). The GeneCards database is a searchable, integrative database that can be used to integrate gene-centric data from approximately 150 web sources, including genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, genetic, clinical, and functional information. Pyroptosis-related genes were intersected with the total DEGs in GSE47420 to obtain the pyroptosis-related DEGs. Venn diagram and heatmaps of pyroptosis-related DEGs were visualized by TBtools.
The online biological tool Metascape
(https://metascape.org/gp/index.html#/main/step1) was used to perform Gene
Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway
enrichment analysis of pyroptosis-related DEGs in GSE47420 [22]. GO enrichment
analysis included biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular
function (MF). The adjusted p value
In order to investigate the mechanism of interaction among the pyroptosis-related DEGs in Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling, a PPI network was constructed by the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins (STRING) online database (http://stringdb.org/) and then visualized using Cytoscape v3.8.2 software (https://cytoscape.org/). The Cytohubba plug-in of Cytoscape software was used to screen out the top 15 key genes with high connectivity in this PPI network using the Maximal Clique Centrality (MCC) method. Pyroptosis-related hub genes were identified by using multiple algorithms including the MCC, Maximum Neighborhood Component (MNC), and Degree, and those genes ranked in the top 15 in at least three types of algorithms were considered to be hub genes for Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling.
To investigate the interaction between the upstream miRNAs and the pyroptosis-related hub genes, the upstream miRNAs that regulate the pyroptosis-related hub genes were predicted using the online StarBase v2.0 dataset based on one/multiple target-predicting programs (TargetScan, PicTar, RNA22, PITA, miRanda, and mirSVR) [24]. Subsequently, the predicted miRNAs were intersected with the differentially expressed miRNA (DE-miRNAs) in the dataset GSE69559 to obtain the pyroptosis-related DE-miRNAs. In GSE69559, the DE-miRNAs derived from the heart samples from both the Ang II-infused mice (cardiac remodeling) and the saline-infused mice (control), and there were three miRNAs upregulated and nineteen miRNAs downregulated [25], as shown in Supplementary Table 1. The obtained overlapping DE-miRNAs were filtered according to the following inclusion criteria: the upregulated DE-miRNAs in GSE69559 target the downregulated pyroptosis-related DEGs in GSE47420, whilst the downregulated DE-miRNAs target the upregulated pyroptosis-related DEGs. Subsequently, the miRNA-target gene pairs were constructed based on the potential interaction between the DE-miRNAs and their corresponding target genes. A miRNA-target gene interaction sub-network was visualized using Cytoscape software.
To investigate the interaction between the upstream transcription factors (TFs) and the pyroptosis-related DE-miRNAs, the upstream TFs that regulate the pyroptosis-related DE-miRNAs were predicted using the online TransmiR v2.0 dataset [26]. Currently, TransmiR v2.0 contains 3730 literature-curated TF-miRNA regulations, which cover ~623 TFs, ~785 miRNAs, 19 organisms, and 1349 publications. Subsequently, the predicted upstream TFs were intersected with the total DEGs in GSE47420 to obtain the differentially expressed TFs (DE-TFs). The TF-miRNA pairs were constructed based on the potential interaction between the DE-TFs and their corresponding target miRNAs. The predicted interaction between the DE-TFs and miRNAs by TransmiR2.0 includes four action types: regulation, activation, repression, and feedback. The obtained TF-miRNA pairs were filtered according to the following inclusion criteria: the TF-miRNA pair whose action type is activation or repression must be differentially expressed in terms of transcript expression in GSE47420 and GSE69559 in the same or opposite directions. A TF-miRNA interaction sub-network was visualized using Cytoscape software.
A TF-miRNA-target gene Interaction Network in Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling was constructed based on the TF-miRNA pairs and the miRNA-target gene pairs. The integrated TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network was visualized by Cytoscape software. The integrated TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network was filtered according to the following inclusion criteria: the miRNA-target gene pairs that had no predicted regulatory TFs will be discarded.
The correlation between the target genes and cardiac remodeling was evaluated by the online platform CTD (https://ctdbase.org/), scored, and visualized as bar graphs.
To screen potential drugs targeting cardiac remodeling, the identified target genes in our regulatory network were introduced into the Drug-Gene Interaction Database (DGIdb, https://dgidb.genome.wustl.edu/) as drug targets to search for potential drugs that target them. Those drugs that show well-known interaction types with the identified target genes were considered potential drugs for the treatment of cardiac remodeling.
In this study, an Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling in mice was used to analyze and compare the expression of key hub DEGs, DE-miRNAs, and DE-TFs. The animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Use and Care Committee at the Hubei University of Science and Technology and followed the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (8th Ed., National Research Council, National Academy Press, Washington, DC, 2011). 12 healthy C57BL/6 male mice (8-week-old, 20–25 g), purchased from the Center for Disease Control of Hubei Province (Wuhan, China), were randomly assigned to two groups (n = 6 per group): the control group and the Ang II group. All animals were subcutaneously implanted with osmotic pumps (ALZET Model 2004, Durect Corporation, Cupertino, CA, USA.) to continuously infuse Ang II (1.5 mg/kg per day for 2 weeks, Ang II group) or equal volumes of PBS (vehicle, pH 7.2, control group) as described previously [27].
Mouse body weights were obtained before the animals were euthanized. At the end of the study, all the animals were killed by cervical dislocation, and the hearts were quickly dissected and weighed to calculate the ratio of heart weight to body weight (HW/BW, mg/kg). Heart tissues were quickly harvested, frozen, and stored at –80 °C until assays of gene expression analyses, or embedded in 4% paraformaldehyde for wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) staining.
Average CSA was measured by WGA staining. Left ventricular tissues were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned into 5-µm slices. After being deparaffinized and rehydrated according to the usual procedure, tissue sections were stained with an Alexa Fluor 488–conjugated WGA (20 µg/mL, Sigma-Aldrich) at 4 °C overnight to visualize cell membranes and DAPI for 15 min to stain cell nuclei. The average CSA from approximately 200 cells per slide was measured from the image captured with the fluorescence microscope and analyzed by Image-Pro Plus 5.0 software (Media Cybernetics, Inc., Silver Spring, MD, USA).
The total RNA was extracted from left ventricular tissues using TRIzol Reagent
(cat. no. 15596018, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to
the manufacturer’s instructions. For mRNA detection of DEAD-Box Helicase 3
X-Linked (DDX3X), Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase
activation protein zeta (YWHAZ, also named 14-3-3
| Gene | GenBank accession | Forward and reverse primers (5 |
Product length | |
| GAPDH | F | NM_001289726.2 | 5 |
258 bp |
| R | 5 | |||
| DDX3X | F | NM_010028.3 | 5 |
122 bp |
| R | 5 | |||
| YWHAZ | F | XM_054361185.1 | 5 |
162 bp |
| R | 5 | |||
| CEBPB | F | NM_001287738.1 | 5 |
130 bp |
| R | 5 | |||
| BCL11B | F | XM_006516116.4 | 5 |
292 bp |
| R | 5 | |||
| ANP | F | NM_008725.3 | 5 |
90 bp |
| R | 5 | |||
| F | XM_036158456.1 | 5 |
185 bp | |
| R | 5 | |||
| U6 | F | 5 |
||
| R | 5 | |||
| miR-16-5p | F | 5 |
||
| miR-22-3p | F | 5 |
||
| Universal reverse primer for miRNAs | 5 |
|||
F, Forward; R, Reverse.
For quantitative real-time PCR of miRNAs, total RNA was reversed-transcribed to
cDNA by a TaqMan miRNA reverse transcription kit (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA)
using specific stem-loop primers. After single-stranded cDNA was synthesized,
quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) amplifications were performed using an
iCycleriQ Real-Time Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA). Primer
sequences used for miR-16-5p, miR-22-3p, and U6 were listed in Table 1. PCR
amplification protocol consisted of initial denaturation at 94 °C for
5 min followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 10 s, annealing
at 55 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 30 s. Data were
calculated by the 2
All data were presented as mean
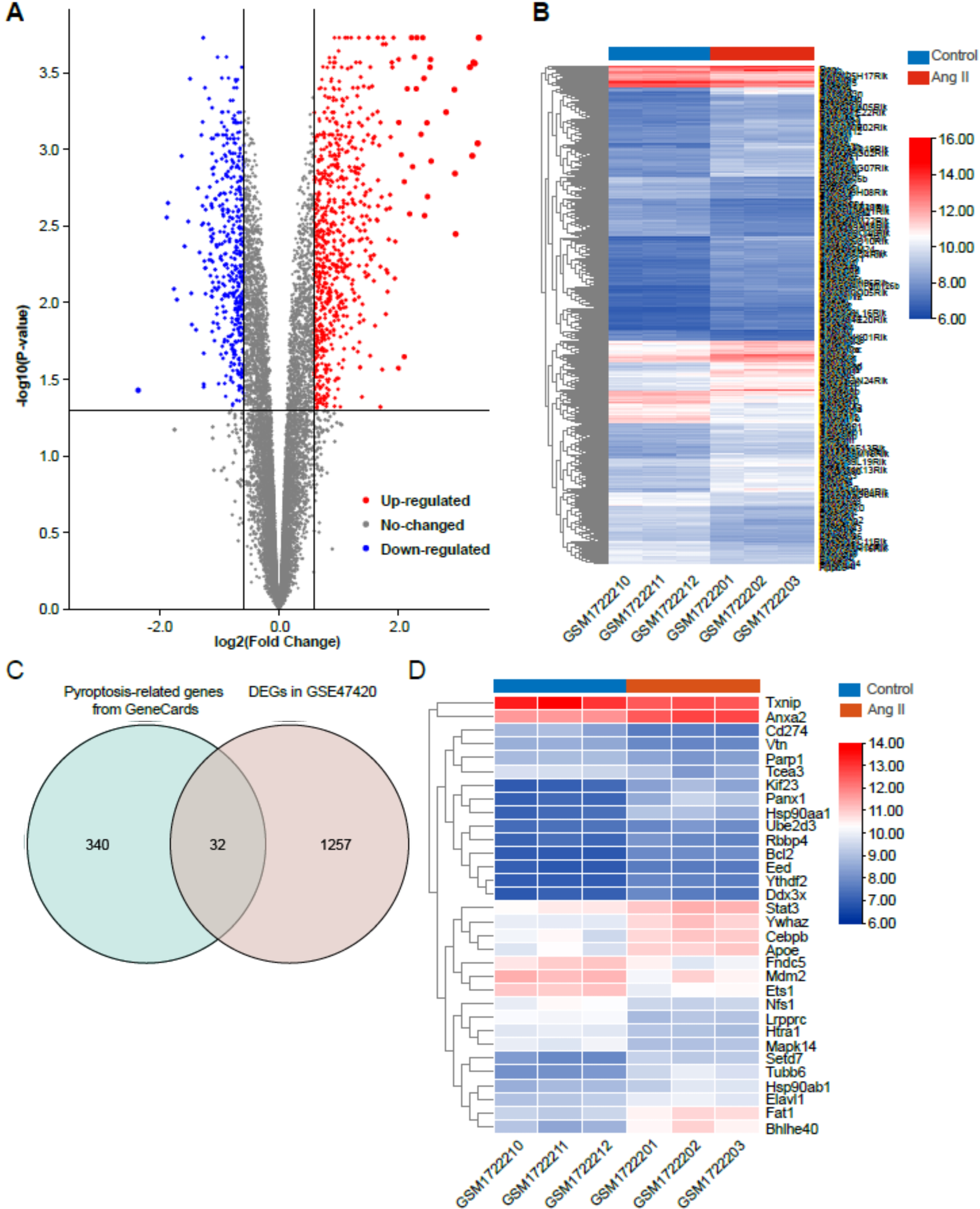
The dataset GSE47420 contained the expression data of mRNA transcripts from the
Ang II-infused mice and the control mice. The online GEO2R tool was used to
identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the two groups. Based
on the inclusion criteria (adjusted p
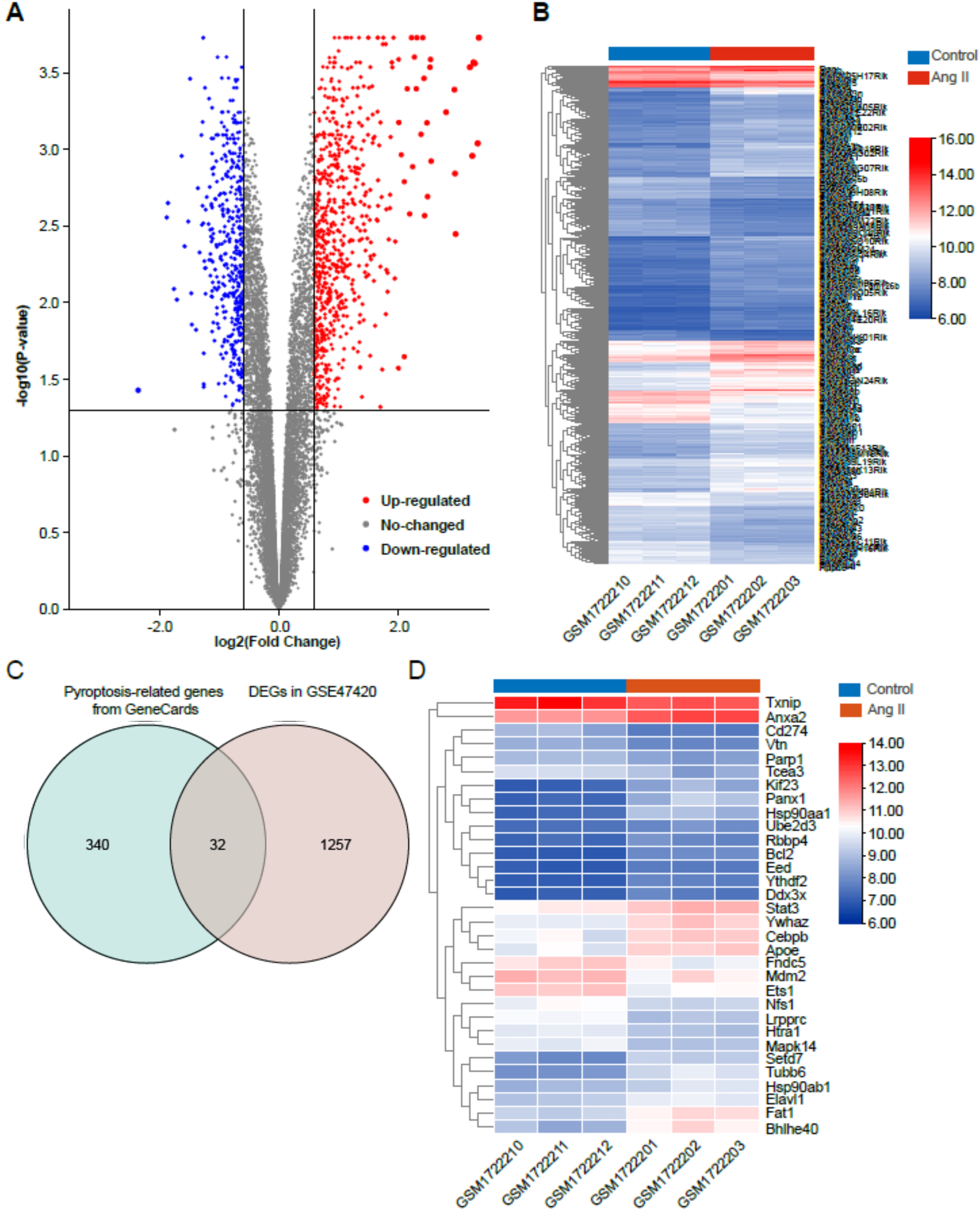 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Identification of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling. (A) Volcano plot of total DEGs in GSE47420 associated with Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling. (B) Heatmap of total DEGs in GSE47420. (C) Venn diagram demonstrating the intersection between total DEGs in GSE47420 and pyroptosis-related genes from GeneCards. (D) Heatmap of 32 pyroptosis-related DEGs in GSE47420. The red arrow indicated pyroptosis-related DEGs, blue arrows indicated downregulated pyroptosis-related DEGs.
| Gene.symbol | adj.p.Val | Log2FC | Changes |
| PANX1 | 0.002407 | 1.86 | upregulated |
| BHLHE40 | 0.002458 | 1.8 | upregulated |
| HSP90AA1 | 0.000939 | 1.68 | upregulated |
| TUBB6 | 0.000847 | 1.58 | upregulated |
| KIF23 | 0.00236 | 1.51 | upregulated |
| FAT1 | 0.001434 | 1.33 | upregulated |
| SETD7 | 0.001388 | 1.27 | upregulated |
| YWHAZ | 0.001502 | 1.05 | upregulated |
| APOE | 0.010959 | 1.03 | upregulated |
| ANXA2 | 0.001055 | 1.01 | upregulated |
| BCL2 | 0.000186 | 1.01 | upregulated |
| CEBPB | 0.031187 | 0.97 | upregulated |
| HSP90AB1 | 0.020592 | 0.8 | upregulated |
| YTHDF2 | 0.000789 | 0.76 | upregulated |
| ELAVL1 | 0.002938 | 0.747 | upregulated |
| STAT3 | 0.008507 | 0.733 | upregulated |
| RBBP4 | 0.012685 | 0.68 | upregulated |
| DDX3X | 0.012976 | 0.643 | upregulated |
| EED | 0.000802 | 0.64 | upregulated |
| UBE2D3 | 0.010028 | 0.617 | upregulated |
| PARP1 | 0.004678 | –0.61 | downregulated |
| NFS1 | 0.008993 | –0.757 | downregulated |
| VTN | 0.000477 | –0.77 | downregulated |
| TXNIP | 0.027727 | –0.773 | downregulated |
| MDM2 | 0.045637 | –0.773 | downregulated |
| FNDC5 | 0.046852 | –0.777 | downregulated |
| HTRA1 | 0.000847 | –0.817 | downregulated |
| ETS1 | 0.006617 | –0.843 | downregulated |
| MAPK14 | 0.001443 | –0.887 | downregulated |
| TCEA3 | 0.033629 | –0.91 | downregulated |
| CD274 | 0.005412 | –1.11 | downregulated |
| LRPPRC | 0.000534 | –1.12 | downregulated |
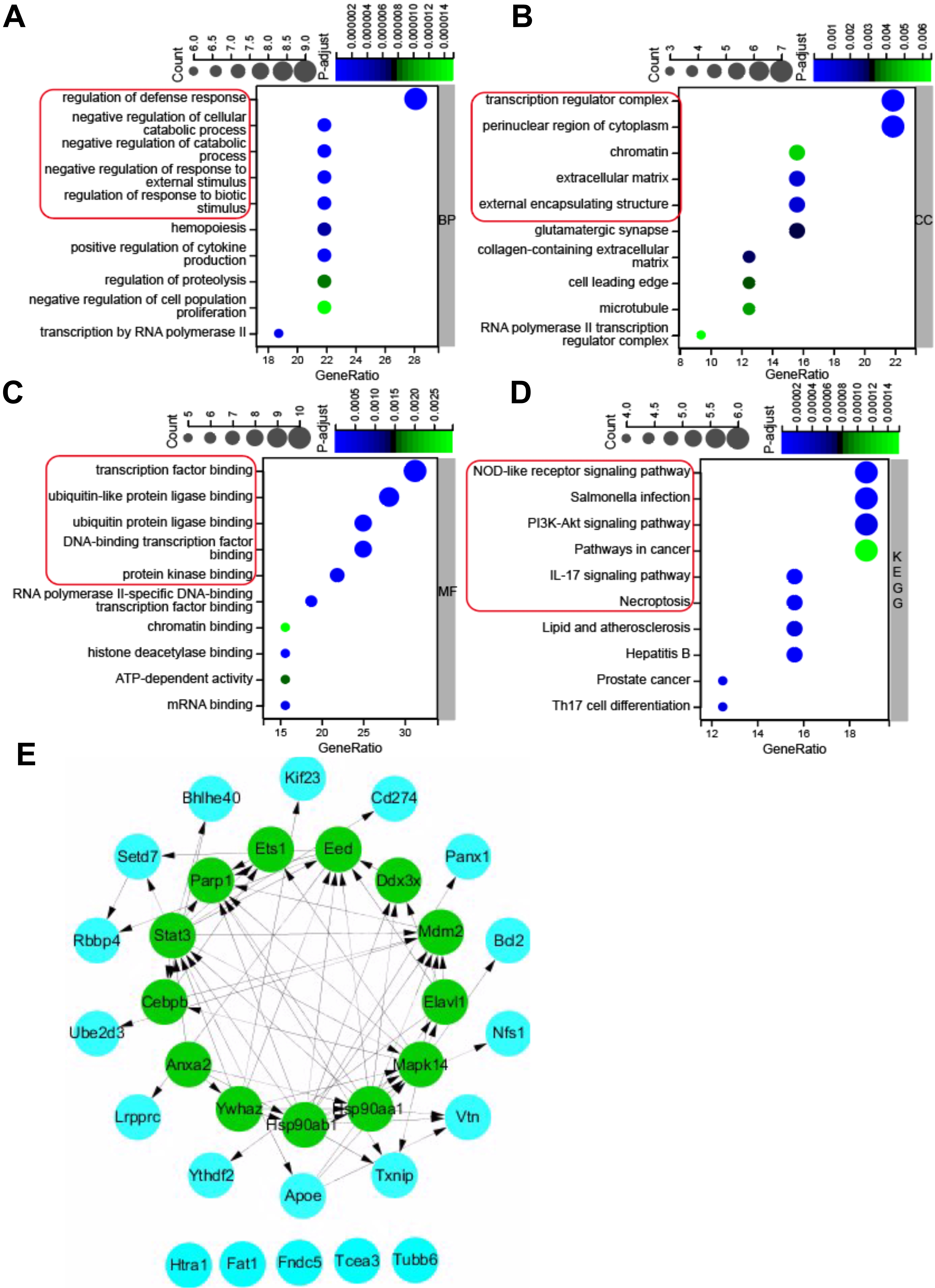
Gene ontology (GO) annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis were used to
deduce the function of the 32 pyroptosis-related DEGs. The results of GO and KEGG
enrichment analyses were shown in Fig. 3. For the BP category of GO enrichment,
the pyroptosis-related DEGs were mainly enriched in regulation of defense
response, negative regulation of cellular catabolic process, negative regulation
of catabolic process, negative regulation of response to external stimulus,
regulation of response to biotic stimulus, etc. (Fig. 3A). The pyroptosis-related
DEGs were enriched in the CC category of GO analysis such as transcription
regulator complex, perinuclear region of cytoplasm, chromatin, extracellular
matrix, and external encapsulating structure (Fig. 3B), and MF category of GO
analysis such as transcription factor binding, ubiquitin-like protein ligase
binding, ubiquitin protein ligase binding, DNA binding transcription factor
binding, and protein kinase binding (Fig. 3C). KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
revealed that the pyroptosis-related DEGs were enriched in NOD-like receptor
signaling pathway, salmonella infection, PI
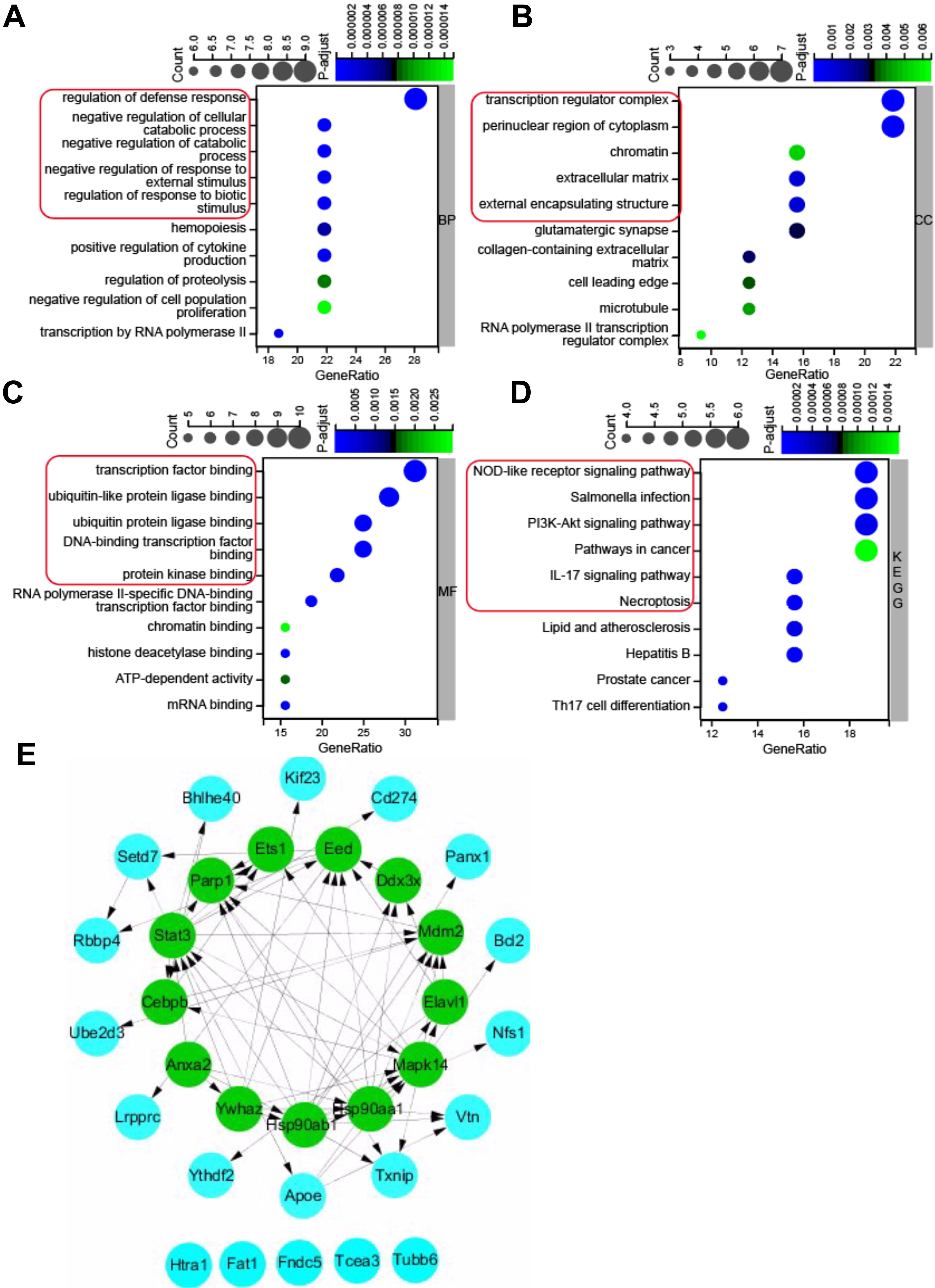 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.GO (Gene Ontology) and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of 32 pyroptosis-related DEGs, and PPI network. (A) Top 10 GO terms for biological process (BP). (B) Top 10 GO terms for cellular component (CC). (C) Top 10 GO terms for molecular function (MF). (D) Top 10 KEGG pathways. (E) PPI networks visualized using Cytoscape software and hub genes. Red round rectangles indicated representative GO enrichment and KEGG pathway enrichment terms. GO, gene ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; DEGs, differentially expressed genes; PPI, protein-protein interaction.
To further investigate the protein-protein interaction (PPI), the 32
pyroptosis-related DEGs were introduced into the String database to construct a
PPI network with the cut-off criterion of confidence score
| Gene.symbol | MCC | MNC | Degree |
| STAT3 | 241 | 13 | 28 |
| HSP90AB1 | 232 | 11 | 26 |
| HSP90AA1 | 224 | 10 | 20 |
| MAPK14 | 175 | 11 | 24 |
| PARP1 | 156 | 8 | 16 |
| MDM2 | 129 | 7 | 16 |
| YWHAZ | 73 | 6 | 14 |
| EED | 61 | 9 | 20 |
| ANXA2 | 24 | 4 | 8 |
| CEBPB | 14 | 5 | 10 |
| ETS1 | 12 | 4 | 8 |
| DDX3X | 8 | 4 | 8 |
| ELAVL1 | 7 | 3 | 12 |
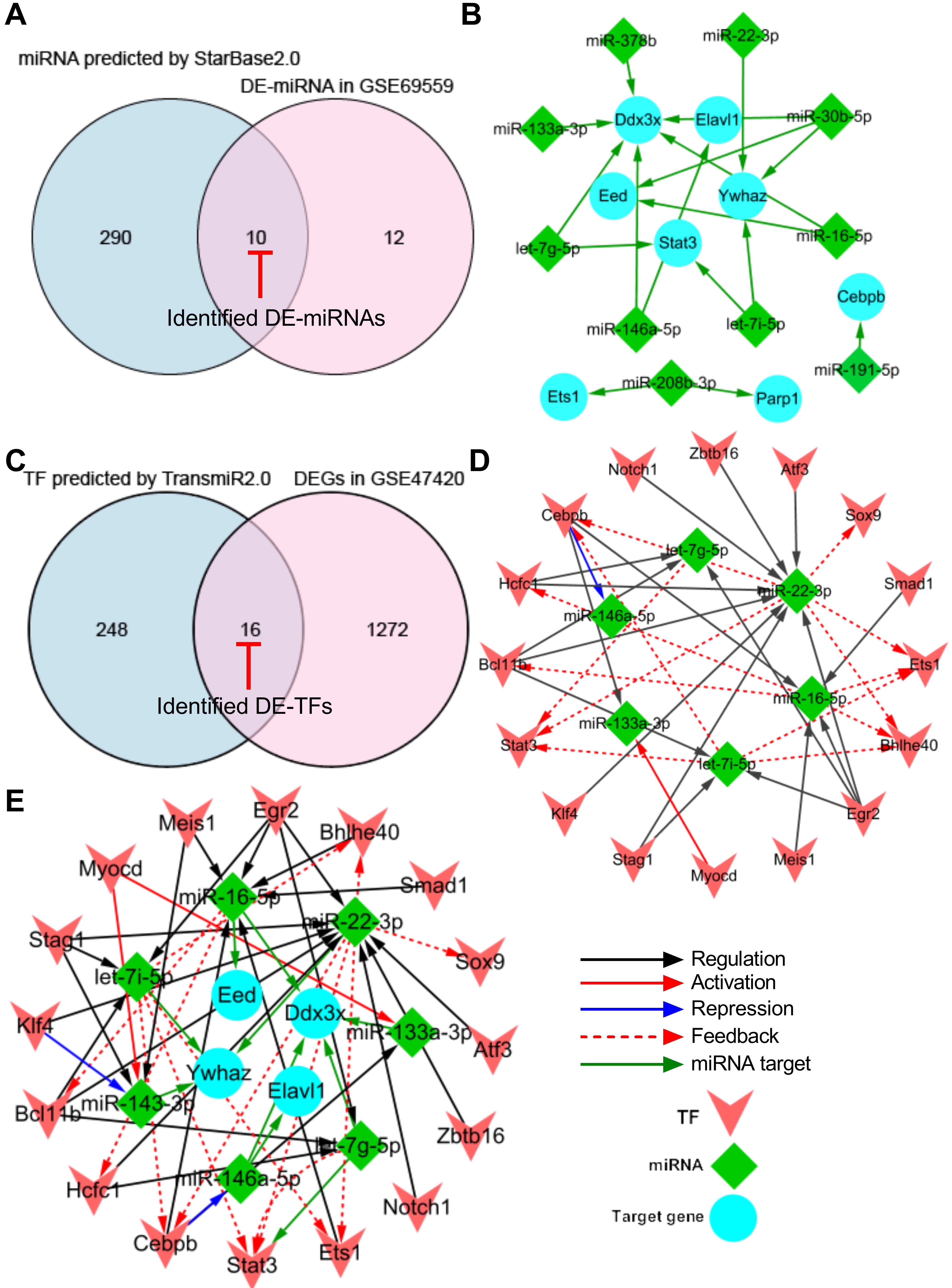
To generate a miRNA-target gene network, the 13 pyroptosis-related hub DEGs were introduced into the online StarBase v2.0 dataset to predict the upstream miRNAs that target these hub DEGs. A total of 300 miRNAs were predicted using the StarBase v2.0 dataset based on one/multiple target-predicting programs (TargetScan, PicTar, RNA22, PITA, miRanda, and mirSVR). Subsequently, the predicted 300 miRNAs were intersected with the 22 differentially expressed miRNAs (DE-miRNAs) in GSE69559 to obtain 10 overlapping pyroptosis-related DE-miRNAs (Fig. 4A, Table 4). In these overlapping DE-miRNAs, miR-208b-3p was upregulated in GSE69559, whilst the other nine miRNAs were downregulated. The upregulated miR-208b-3p was predicted to target two pyroptosis-related hub DEGs, PARP1 and ETS1. The downregulated miR-191-5p was predicted to target upregulated CEBPB. The other eight upregulated miRNAs (let-7g-5p, let-7i-5p, miR-133a-3p, miR-146a-5p, miR-16-5p, miR-22-3p, miR-30b-5p, miR-378b) were predicted to target five pyroptosis-related hub DEGs (DDX3X, ELAVL1, YWHAZ, STAT3, EED). These detailed miRNA-target gene regulatory pairs were outlined in Table 4. Subsequently, the miRNA-target gene pairs were integrated to generate a miRNA-target gene sub-network and visualized using Cytoscape software (Fig. 4B). Three unrelated miRNA-target gene pairs (miR-208b-3p-PARP1, miR-208b-3p-ETS1, miR-191-5p-CEBPB) were eliminated in further analysis. Thus, the miRNA-target gene sub-network eventually contained eight DE-miRNAs, five target DEGs related to pyroptosis, and fourteen interactions between the DE-miRNAs and the target DEGs.
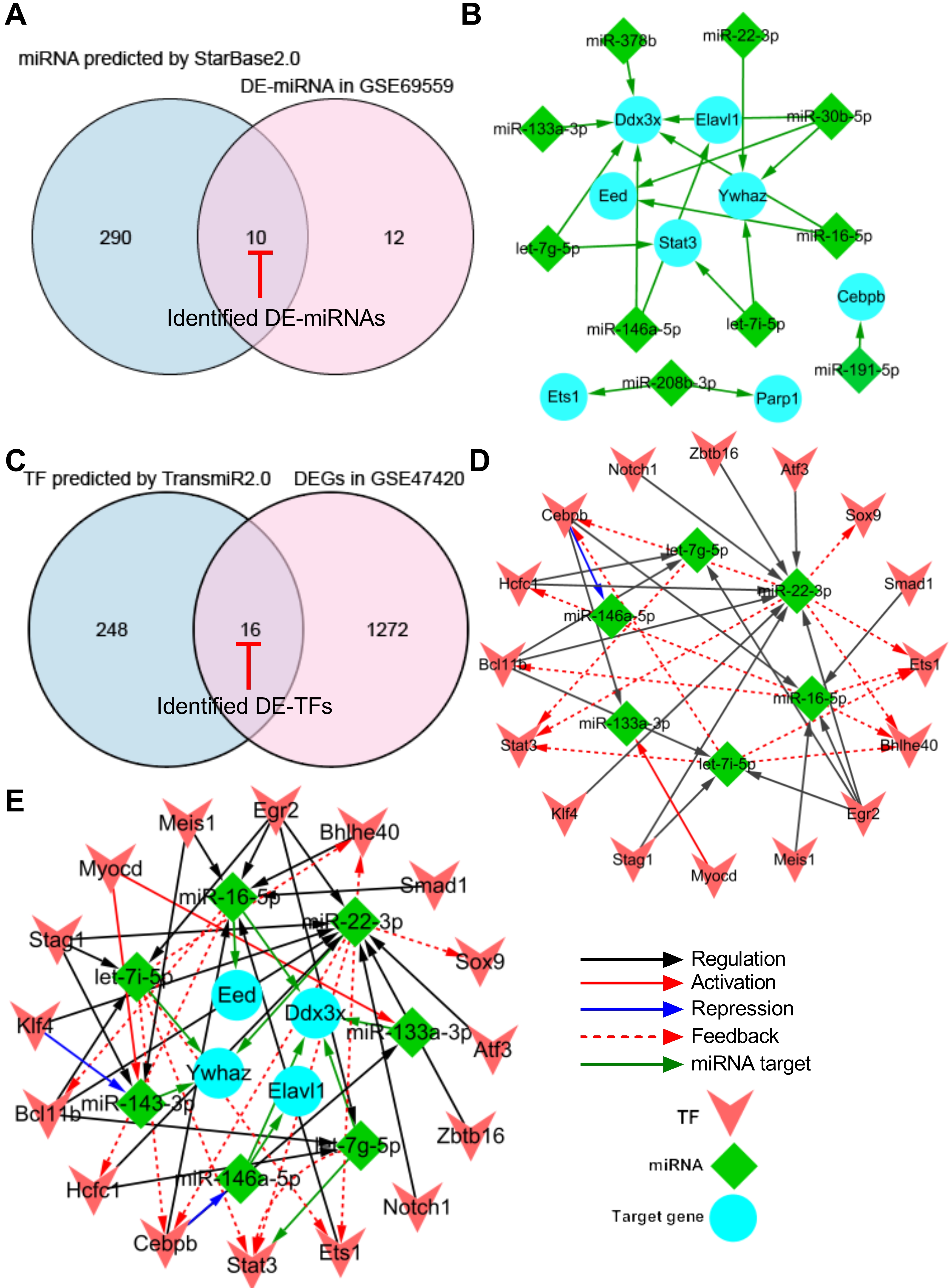 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Construction of TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network. (A) Venn diagram demonstrating the intersection between total DE-miRNAs in GSE69559 and the predicted miRNAs by StarBase2.0. (B) miRNA-target gene sub-network. (C) Venn diagram demonstrating the intersection between total DEGs in GSE47420 and the predicted TFs by TransmiR2.0. (D) TF-miRNA sub-network. (E) TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network. Blue nodes indicate the target genes that were targeted by miRNAs, green nodes indicate the miRNAs and pink nodes indicate the TFs. Red-capped lines indicated overlapping differentially expressed miRNAs (DE-miRNAs) and TFs (DE-TFs). TF, transcription factor; miRNA, microRNA; DE-miRNA, differentially expressed microRNA; DEG, differentially expressed gene.
| DE-miRNAs | Changes in GSE69559 | Hub DEGs | Changes in GSE47420 |
| miR-208b-3p | upregulated | PARP1 | downregulated |
| miR-208b-3p | upregulated | ETS1 | downregulated |
| miR-191-5p | downregulated | CEBPB | upregulated |
| miR-146a-5p | downregulated | DDX3X | upregulated |
| miR-146a-5p | downregulated | ELAVL1 | upregulated |
| let-7i-5p | downregulated | YWHAZ | upregulated |
| let-7i-5p | downregulated | STAT3 | upregulated |
| miR-16-5p | downregulated | DDX3X | upregulated |
| miR-16-5p | downregulated | EED | upregulated |
| miR-30b-5p | downregulated | DDX3X | upregulated |
| miR-30b-5p | downregulated | EED | upregulated |
| miR-30b-5p | downregulated | YWHAZ | upregulated |
| miR-22-3p | downregulated | YWHAZ | upregulated |
| miR-378b | downregulated | DDX3X | upregulated |
| miR-133a-3p | downregulated | DDX3X | upregulated |
| let-7g-5p | downregulated | STAT3 | upregulated |
| let-7g-5p | downregulated | DDX3X | upregulated |
DE-miRNA, differentially expressed miRNA.
To generate a TF-miRNA network, the eight DE-miRNAs that targeted five pyroptosis-related hub DEGs in the miRNA-target gene sub-network were introduced into the online TransmiR v2.0 dataset to predict the upstream TFs that interact with these DE-miRNAs. A total of 265 TFs were predicted to interact with the eight DE-miRNAs. Subsequently, the predicted 265 TFs were intersected with the total DEGs in GSE47420 to obtain 16 overlapping differentially expressed TFs (DE-TFs) (Fig. 4C, Table 5). Subsequently, the TF-miRNA pairs were constructed based on the potential interaction between the overlapping DE-TFs and their corresponding target DE-miRNAs. The TF-miRNA pairs were integrated to generate a TF-miRNA sub-network and visualized using Cytoscape software. The TF-miRNA sub-network eventually contained sixteen DE-TFs, six DE-miRNAs, and thirty-five interactions between the DE-TFs and their target DE-miRNAs (Fig. 4D).
| DE-TFs | Changes in GSE47420 | DE-miRNAs | Changes in GSE69559 | Interaction types |
| EGR2 | upregulated | let-7i-5p | downregulated | regulation |
| STAG1 | upregulated | let-7i-5p | downregulated | regulation |
| BCL11B | downregulated | let-7i-5p | downregulated | regulation |
| STAT3 | upregulated | let-7i-5p | downregulated | feedback |
| BHLHE40 | upregulated | let-7i-5p | downregulated | feedback |
| ETS1 | downregulated | let-7i-5p | downregulated | feedback |
| CEBPB | upregulated | let-7i-5p | downregulated | feedback |
| HCFC1 | upregulated | miR-16-5p | downregulated | feedback |
| EGR2 | upregulated | miR-16-5p | downregulated | regulation |
| BCL11B | downregulated | miR-16-5p | downregulated | feedback |
| BHLHE40 | upregulated | miR-16-5p | downregulated | feedback |
| ETS1 | downregulated | miR-16-5p | downregulated | feedback |
| SMAD1 | upregulated | miR-16-5p | downregulated | regulation |
| CEBPB | upregulated | miR-16-5p | downregulated | regulation |
| MEIS1 | downregulated | miR-16-5p | downregulated | regulation |
| SOX9 | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | feedback |
| HCFC1 | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | regulation |
| ATF3 | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | regulation |
| EGR2 | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | regulation |
| STAG1 | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | regulation |
| BCL11B | downregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | regulation |
| STAT3 | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | feedback |
| BHLHE40 | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | feedback |
| ETS1 | downregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | feedback |
| ZBTB16 | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | regulation |
| NOTCH1 | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | regulation |
| CEBPB | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | feedback |
| KLF4 | upregulated | miR-22-3p | downregulated | regulation |
| HCFC1 | upregulated | let-7g-5p | downregulated | regulation |
| EGR2 | upregulated | let-7g-5p | downregulated | regulation |
| BCL11B | downregulated | let-7g-5p | downregulated | regulation |
| STAT3 | upregulated | let-7g-5p | downregulated | feedback |
| CEBPB | upregulated | mir-146a-5p | downregulated | repression |
| MYOCD | downregulated | miR-133a-3p | downregulated | activation |
| CEBPB | upregulated | miR-133a-3p | downregulated | regulation |
Finally, the miRNA-target gene sub-network and the TF-miRNA sub-network were merged using the network merge operation of Cytoscape to build a TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network (Fig. 4E). The TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network was composed of 26 nodes, 49 edges, and two types of regulatory relationships, including the TF-miRNA and miRNA-target gene actions.
In addition, the topological properties of the regulatory network were analyzed with the NetworkAnalyzer plugin in the Cytoscape. The top-ranked four key target genes, miRNAs, and TFs with high degrees were listed in Table 6. To ensure the rationality of the finding, the expression of the top-ranked CEBPB-miR-16-5p-DDX3X and BCL11B-miR-22-3p-YWHAZ regulatory axes were further verified in the following animal experiments using qRT-PCR.
| Gene.symbol | Attribution | Average shortest path length | Betweenness centrality | Closeness centrality | Degree |
| miR-22-3p | miRNA | 1.68 | 0.487497 | 0.595238 | 14 |
| miR-16-5p | miRNA | 2 | 0.310992 | 0.5 | 10 |
| let-7i-5p | miRNA | 2.16 | 0.094541 | 0.462963 | 8 |
| let-7g-5p | miRNA | 2.4 | 0.042357 | 0.416667 | 6 |
| CEBPB | TF | 1.84 | 0.23825 | 0.543478 | 5 |
| BCL11B | TF | 2.08 | 0.045789 | 0.480769 | 4 |
| EGR2 | TF | 2.08 | 0.045789 | 0.480769 | 4 |
| STAT3 | TF | 2.4 | 0.015264 | 0.416667 | 4 |
| DDX3X | Target gene | 2.48 | 0.080709 | 0.403226 | 4 |
| YWHAZ | Target gene | 2.56 | 0.002708 | 0.390625 | 2 |
| ELAVL1 | Target gene | 3.52 | 0 | 0.284091 | 1 |
| EED | Target gene | 2.96 | 0 | 0.337838 | 1 |
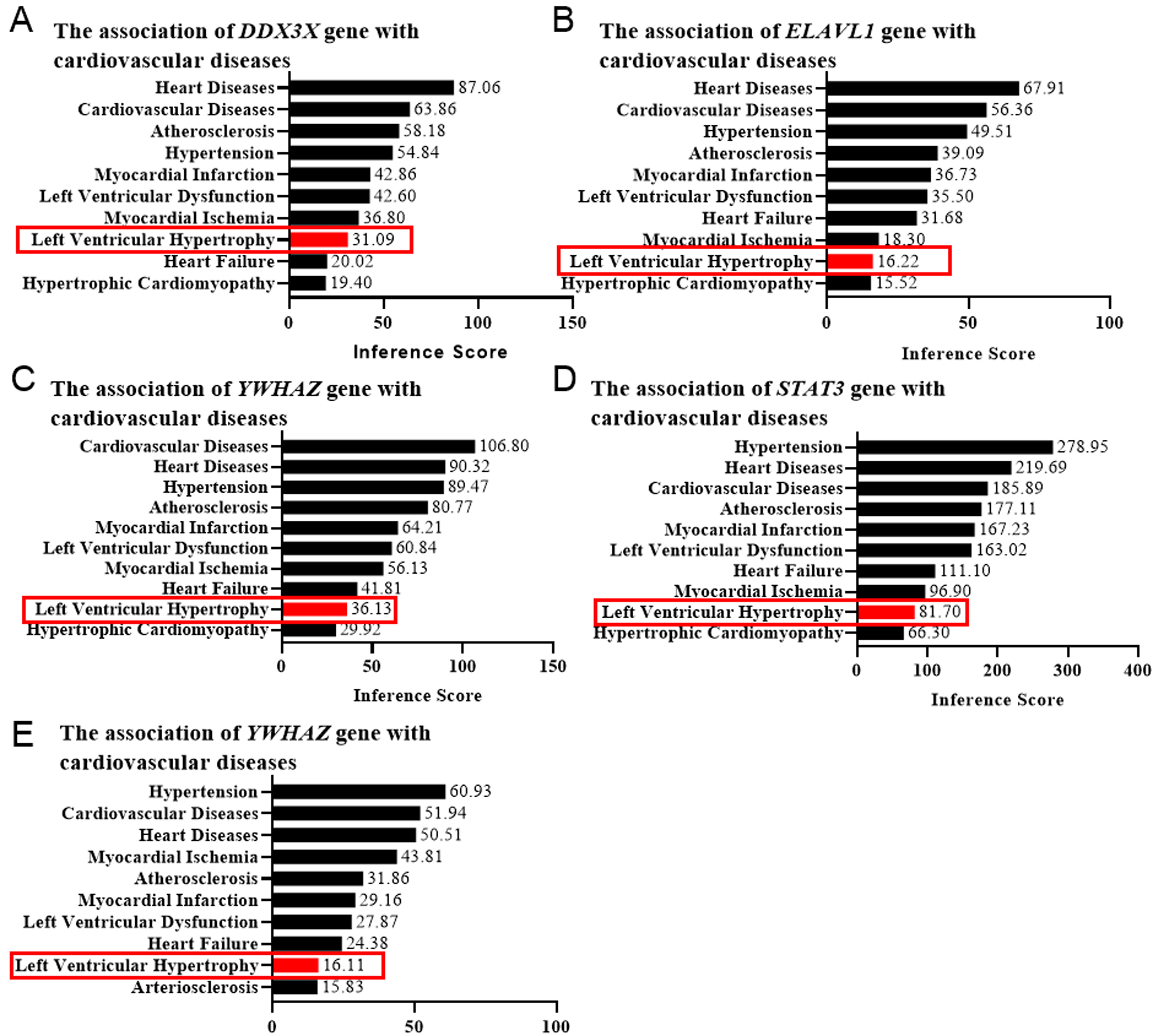
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a characteristic component of left
ventricular remodeling. To confirm the functional roles of the target genes in
cardiac remodeling, we employed the CTD database to confirm their correlation
with cardiovascular diseases via evaluating the LVH score. The genes with an LVH
score
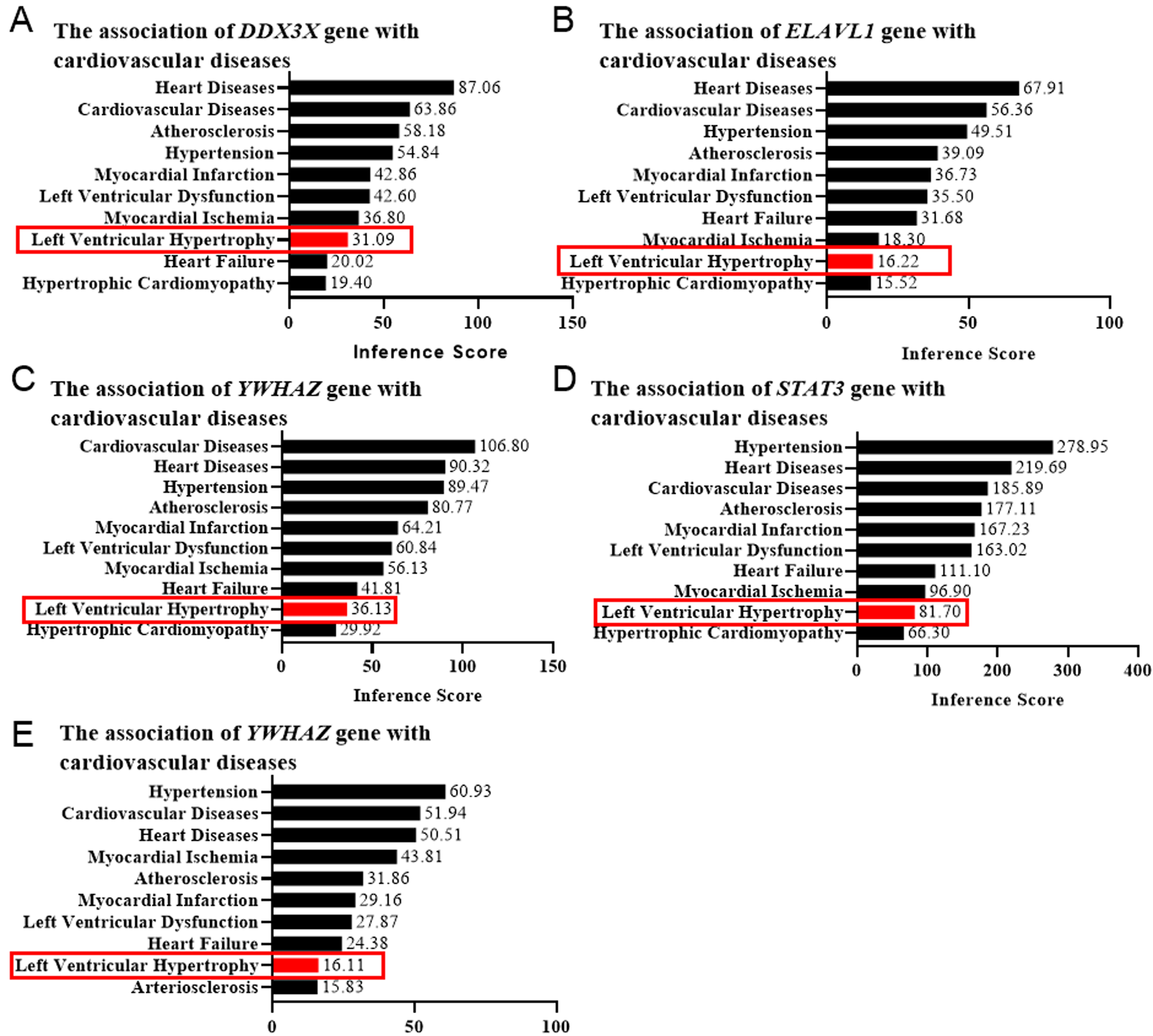 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) score determined by the CTD database. The correlation between the genesis of LVH and DDX3X (A), ELAVL1 (B), YWHAZ (C), STAT3 (D), and EED (E) was evaluated by the online platform Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD), scored, and shown as bar graphs. Red rectangles indicated the LVH scores.
To explore the interrelationship between the central genetic aspects of cardiac remodeling and the available drugs, the drug-target gene interaction network was predicted using the DGIdb database. As shown in Table 7 (Ref.[29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40]), 26 drugs targeting 3 hub genes (ELAVL1, STAT3, and EED) were identified. Except for 5 known types, most drug-gene interaction types were unknown. The 5 known interaction types were all inhibitory for ELAVL1 and STAT3. The 5 drugs (dehydromutactin, celecoxib, Azd-1480, ochromycinone, and cosmomycin C) with inhibitory effects on ELAVL1 and STAT3 were considered as potential drugs for the treatment of cardiac remodeling. STAT3 was screened for a wide range of relationships with multiple drugs, which may provide potential targets for the treatment and prognosis of cardiac remodeling.
| Drug | Target gene | Interaction type | Reference |
| Dehydromutactin | ELAVL1 | inhibitor | [29] |
| Androstanolone | ELAVL1 | unknown | [30] |
| Chembl578504 | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Niclosamide | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Celecoxib | STAT3 | inhibitor | [31] |
| Azd-1480 | STAT3 | inhibitor | [32, 33] |
| Ouabain | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Bardoxolone Methyl | STAT3 | unknown | [34] |
| Ciglitazone | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Cucurbitacin B | STAT3 | unknown | [35] |
| Chembl1687979 | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Chembl2062862 | STAT3 | unknown | [36] |
| Chembl2062863 | STAT3 | unknown | [36] |
| Cucurbitacin E | STAT3 | unknown | [35] |
| Pyrimethamine | STAT3 | unknown | [37] |
| Ochromycinone | STAT3 | inhibitor | [38] |
| Chembl2062869 | STAT3 | unknown | [36] |
| Atiprimod | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Golotimod | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Digitoxin | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Acitretin | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Chembl2062868 | STAT3 | unknown | [36] |
| Cosmomycin C | STAT3 | inhibitor | [39] |
| Digoxin | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Chembl530664 | STAT3 | unknown | |
| Astemizole | EED | unknown | [40] |
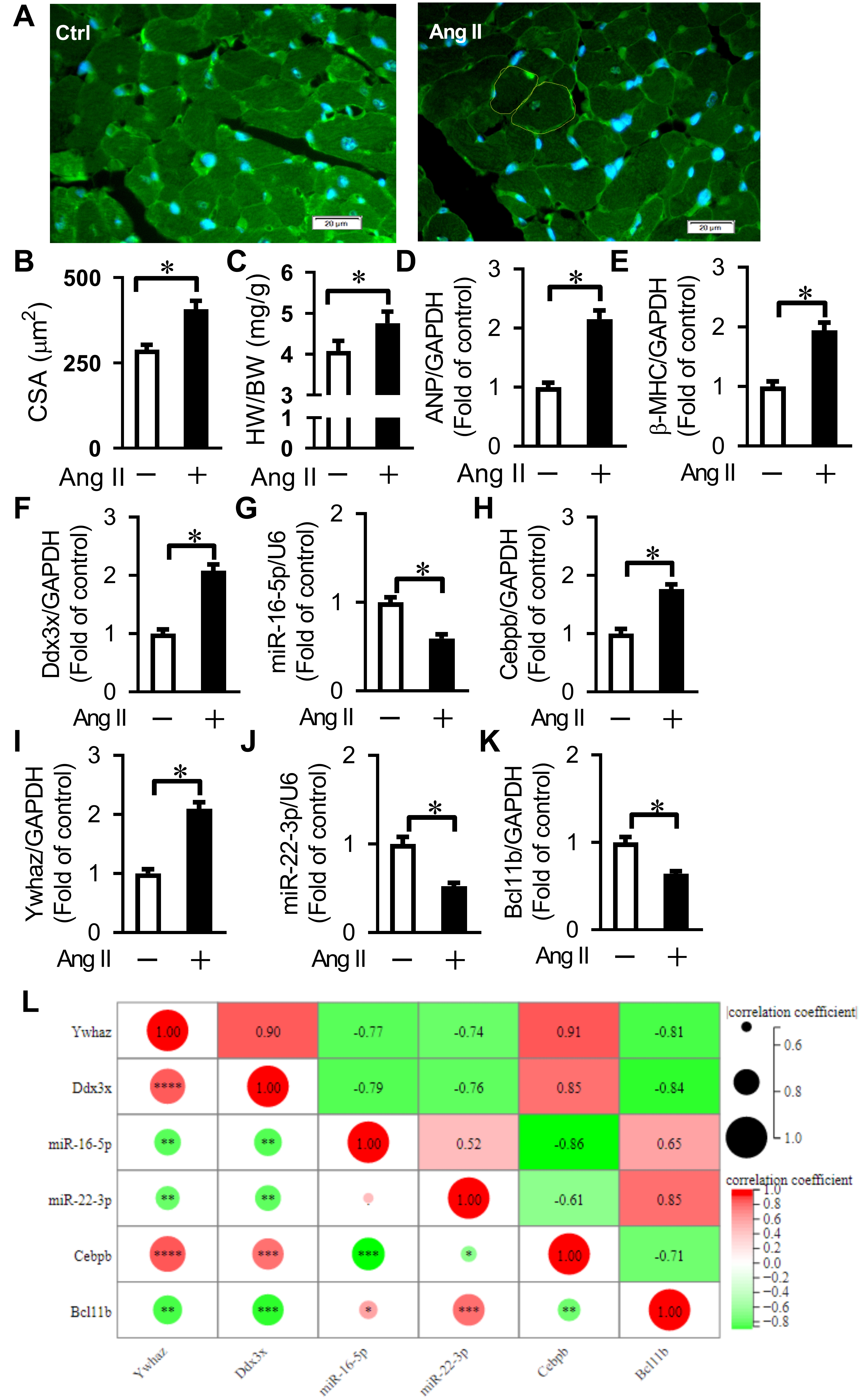
To validate the key nodes and regulatory relationship in cardiac remodeling,
qRT-PCR was used to analyze the expression of the core
CEBPB-miR-16-5p-DDX3X and
BCL11B-miR-22-3p-YWHAZ regulatory axes in an Ang II-induced
cardiac remodeling in mice. In this study, the 8-week-old C57BL/6 male mice were
subcutaneously implanted with osmotic pumps to continuously infuse Ang II (1.5
mg/kg per day for 2 weeks) to establish an Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling, as
evidenced by the elevated ratios of heart weight to body weight (HW/BW),
increased average CSA, and enhanced mRNA expression of hypertrophic genes (ANP,
 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.Verification of key differentially expressed genes
related to Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling and pyroptosis. (A) Representative
WGA staining for cross-sectional area (CSA) measurement. Bars = 20 µm. (B)
Quantification of cardiomyocyte CSA. Averaged data results from 20 fields per
heart. (C) Quantification of the ratio of heart weight to body weight (HW/BW).
(D,E) Expression of ANP and
Since the changing trend of most predicted key nodes in our animal experiments was similar to that in the microarray analysis in GSE47420 and GSE69559, our results revealed that the relationships between the predicted miRNAs and their target genes or the corresponding TFs in the TF-miRNA-target gene network were reliable.
It is believed that there is a significant relationship between miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks and cardiovascular diseases [41, 42]. The dysregulation of the miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in the cardiovascular system contributes to a variety of cardiovascular diseases, such as cardiac atherogenesis [43], cardiac infarction [44], heart failure [45], and diabetic cardiomyopathy [46]. Although many studies have intensively suggested that dysregulations of miRNAs and their downstream target genes expression levels are closely associated with the development of cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis [47, 48, 49], a comprehensive pyroptosis-related transcription factor (TF)-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in cardiac remodeling has still not been created up to now.
In the present study, we first conducted a differential expression analysis using miRNA and mRNA datasets from the GEO database to identify the pyroptosis-related DEGs that were associated with Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling and the upstream miRNAs that target the hub pyroptosis-related DEGs. In the mRNA dataset GSE47420, a total of 32 DEGs were identified as pyroptosis-related DEGs Functional enrichment analysis revealed that these pyroptosis-related DEGs were involved in the biological processes related to the regulation of defense response, negative regulation of catabolic process, negative regulation of response to external stimulus, regulation of response to biotic stimulus, etc. Recently, several lines of data have suggested that innate immune responses can be activated in ischemic heart disease [50] and cardiomyocytes can be a significant source of innate immune responses. Sustained activation of the innate immune system is believed to frequently trigger maladaptive inflammatory responses that contribute to cardiovascular remodeling and dysfunction [51, 52]. Additionally, KEGG pathway enrichment analysis revealed that these pyroptosis-related DEGs were enriched in some inflammation-related pathways such as the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, IL-17 signaling pathway, etc. NOD-like receptor subtypes such as NLRP3 and nucleotide-binding oligomerization containing protein 1 (NOD1) have been recently implicated in the progression of several cardiovascular diseases (e.g., atherosclerosis and heart failure) [52]. IL-17 enhances cardiac ventricular remodeling in ischemic heart failure [53], whereas ablation of IL-17 alleviated cardiac interstitial fibrosis and improved cardiac function in diabetic mice [54]. These results partly explained the potential role of these pyroptosis-related DEGs in the pathogenesis of Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling.
Then, through integrating DE-TFs, DE-miRNAs, and target genes of DE-miRNAs, five
hub pyroptosis-related DEGs (DDX3X, ELAVL1, YWHAZ,
STAT3, and EED) were identified as the pyroptosis-related core
target genes in our TF-miRNA-target gene network. The five target genes have been
identified to be upregulated in Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling in GSE47420 and
were associated with cardiovascular diseases in previous studies. DDX3X
exhibits a protective role in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in H9c2
cardiomyocytes [55]. ELAVL1, also known as HuR, is upregulated in
failing human hearts [56]. Activation of HuR promotes cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
[57]. Conversely, cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of HuR reportedly reduces left
ventricular hypertrophy and fibrosis in a transverse aortic constriction (TAC)
model of pressure overload-induced hypertrophy [56]. YWHAZ, also known
as 14-3-3
Next, through integrating DE-TFs, DE-miRNAs, and target genes of DE-miRNAs, six miRNAs (let-7g-5p, let-7i-5p, miR-133a-3p, miR-146a-5p, miR-16-5p, and miR-22-3p) eventually were identified as key DE-miRNAs in the TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network to target the five pyroptosis-related core target genes (DDX3X, ELAVL1, YWHAZ, STAT3, and EED) in Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling. The six DE-miRNAs have been identified to be downregulated in Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling in GSE69559. Previous studies have shown that most of the expression patterns of the six key DE-miRNAs that we screened were identical to our analytic results. For example, let-7i-5p was significantly downregulated in mice with Ang II-induced cardiac fibrosis [25]. Delivery of let-7i-5p to the mice significantly inhibited Ang II-induced cardiac inflammation and fibrosis in a dose-dependent manner. miR-133a-3p expression was downregulated in Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy [13]. Conversely, miR-133a-3p overexpression could attenuate Ang II-induced pyroptosis and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. miR-146a-5p expression was downregulated in isoproterenol (ISO)-treated rat heart tissue and ISO-induced cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) [64]. miR-16-5p expression was markedly decreased in pressure overload-induced myocardial hypertrophy and Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy [65]. miR-22-3p downregulation was found in Ang II-treated cardiac fibroblasts [66]. miR-22-3p overexpression was demonstrated to suppress fibrogenesis in Ang II-treated cardiac fibroblasts [66, 67]. In the present study, the potential roles of let-7g-5p, let-7i-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-16-5p, and miR-22-3p in regulating pyroptosis-associated cardiac remodeling were reported for the first time. Further study is needed to understand the precise roles of let-7g-5p, let-7i-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-16-5p, and miR-22-3p in Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling.
Previous studies have suggested that miRNA expression can be regulated by the upstream transcription factors (TFs) in cardiac remodeling [15, 16, 68]. Therefore, in the present study, the TFs that can potentially regulate DE-miRNAs were predicted, and a total of 16 predicted TFs that target the aforementioned six key DE-miRNAs were identified as differentially expressed TFs (DE-TFs) in the dataset GSE47420. Among the six key DE-miRNAs, miR-16-5p and miR-22-3p were predicted to be regulated by a majority of identified DE-TFs. According to the topological score in the TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network, the six top-ranked DE-TFs were selected as the key TFs, including one downregulated TF (BCL11B) and five upregulated TFs (CEBPB, EGR2, STAT3, HCFC1, BHLHE40). Among these dysregulated TFs, EGR2 was predicted to regulate four miRNAs (let-7i-5p, miR-16-5p, let-7g-5p, miR-22-3p). Other four transcription factors (CEBPB, HCFC1, BCL11B, BHLHE40) were predicted to regulate one or more miRNAs and be feedback regulated by one or two miRNAs. Most of the expression patterns of the six screened key DE-TFs had been previously reported to be identical to our analytic results from the GSE47420. For example, CEBPB was found to be upregulated and mediate phenylephrine (PE)-induced pathological cardiac hypertrophy [69]. CEBPB knockdown could attenuate PE-induced hypertrophic responses [70], whereas CEBPB overexpression abrogated the beneficial effect of atorvastatin on Ang II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, suggesting a possible role of CEBPB in mediating Ang II-induced cardiac hypertrophy [71]. EGR2 was differentially expressed in pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy [72]. BHLHE40, also known as DEC1 (Differentiated embryonic chondrocyte gene1), was significantly upregulated in Ang II-stimulated atrial cardiomyocytes and atrial tissues in mice, and Cardiac-specific knockdown of BHLHE40 significantly ameliorated Ang II-induced atrial fibrosis and inflammation [73]. BHLHE40 deficiency also protected the heart from fibrosis, and inflammation in a mouse model of pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy [74]. In the present study, qRT-PCR was used to verify the expression of the core CEBPB-miR-16-5p-DDX3X and BCL11B-miR-22-3p-YWHAZ regulatory axes in a mice model of Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling. Our results confirmed that the TF-miRNA-target gene network presented here was reliable. More experiments about the roles of these predicted TFs in cardiac remodeling need to be further investigated in the future.
Although we for the first time investigated the potential TF-miRNA–target gene regulatory network in Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling by integrating multiple microarray datasets from the GEO platform, there were several limitations existing in the present study. Firstly, the sample size of the GEO dataset included in this study is not big enough, only containing 6 tissue samples. Secondly, construction of these miRNA-target gene pairs and TF-miRNA pairs in the regulatory network was only based on predictions from public databases and lacking experimental validation of these pairs in this study. Thirdly, we did not perform in vitro and in vivo function experiments on these miRNA-mRNA regulatory pathways in cardiac remodeling.
Future investigations with more tissue samples and corresponding experimental validations in vivo and in vitro are still needed to validate our in silico analysis. Additionally, the clinical relevance of this study is not clear and requires further studies.
In conclusion, we constructed a pyroptosis-related TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network related to Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling, which was joined by 16 key TFs, 6 key miRNAs, and 5 key target genes. The five pyroptosis-related hub target genes (DDX3X, ELAVL1, YWHAZ, STAT3, and EED) were identified to be crucial cardiac remodeling-related genes using the comparative toxicogenomics database (CTD) and proposed to represent potential therapeutic targets. Five drugs (dehydromutactin, celecoxib, Azd-1480, ochromycinone, and cosmomycin C) with inhibitory effects on ELAVL1 and STAT3 were identified as potential drugs for the treatment of cardiac remodeling. The identified key DE-miRNAs and DE-TFs in our regulatory network were associated with Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling. Combined with experimental validation and bioinformatics analysis, our findings suggest that the pyroptosis-related TF-miRNA-target gene regulatory network may be involved in Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling and may be a potential therapeutic target of Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling.
The datasets analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The URLs to all datasets used in this study as follows: GSE47420 dataset: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE47420; GSE69559 dataset: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE69559.
LY and ML designed the study. TH, LL, and LH analyzed the data. TH and JD performed the experiments. LY and ML contributed to the writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript.
The Animal Research Ethic Committee of Hubei University of Science and Technology, China approved this study (approval number: 2021-01-104).
Not applicable.
This research was funded by the Special Fund of Hubei Science & Technology University for Hubei Province Key Laboratory on Diabetes Mellitus (grant no. 2019-20XZ02) and the Key Clinical Specialty Discipline Construction Program (grant no. LCZX201514).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at https://doi.org/10.31083/j.fbl2811293.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.