1 2nd Department of Radiology, Medical School, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, 11527 Athens, Greece
2 Physics Department, School of Applied Mathematical and Physical Sciences, National Technical University of Athens, 15780 Zografou, Athens, Greece
3 Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Laboratory of Biology, Medical School, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, 11527 Athens, Greece
4 Paediatric Cardiology and Adult with Congenital Heart Disease Department, Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center, 17674 Athens, Greece
5 Department of Medical Physics, Medical School, National and Kapodistrian University, 11527 Athens, Greece
6 Department of Sciences, Hellenic Open University, 26335 Patra, Greece
7 DNA Damage Laboratory, Department of Physics, School of Applied Mathematical and Physical Sciences, Zografou Campus, National Technical University of Athens (NTUA), 15780 Athens, Greece
Academic Editor: Taeg Kyu Kwon
Abstract
Background: Ferredoxin reductase (FDXR) has already been reported as a
promising biomarker for estimating radiation doses in radiotherapy. This study
aimed to investigate the responsiveness of FDXR on pediatric population exposed
to ionizing radiation (X-rays) during pediatric interventional cardiology (IC)
procedures. Patients and Methods: Peripheral blood was collected by
venipuncture from 24 pediatric donors before and 24 hours after the IC procedure.
To estimate the effective dose, demographic data and Air Kerma-Area Product
(P
Keywords
- FDXR gene
- ionizing radiation
- pediatric interventional cardiology
During the last two decades, the number of pediatric interventional cardiology (IC) procedures has shown a significant increase due to the advances in digital fluoroscopy systems and the development of smaller and more flexible catheters [1]. Although IC procedures are minimally invasive, they are associated with exposure to ionizing radiation, raising serious concerns, especially for the pediatric population. According to UNSCEAR, children appear to have increased radiosensitivity than adults for specific cancer types, including leukemia, thyroid, skin, breast, and brain cancer [2]. In addition, pediatric patients with complex heart disease often need multiple x-ray examinations during their life, receiving thus high cumulative radiation doses [3]. To minimize the risk of radiation-induced cancer, optimization of radiation doses and accurate dosimetric approaches are essential.
Accurate dosimetry should consider not only the exposure parameters but also the patient’s somatometric and biological characteristics. Recently, many advanced methods have been developed to combine physical dosimetry with biodosimetry [4]. The hybrid dosimetry aimed to provide a more accurate calculation of the delivered dose and, therefore, a more precise estimation of cancer risk.
Biomarkers of ionizing radiation exposure can effectively be used for
biodosimetry. One of the most prominent biomarkers for the evaluation of
radiation-induced biological effects is the protein
Large scale studies have been performed by utilizing quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), microarrays or nCounter analysis systems to probe radiation responsive genes [11, 12, 13, 14]. Among them, the gene Ferredoxin Reductase (FDXR) has been demonstrated as the only gene which is expressed differentially in cells after their exposure to anti-cancer drugs [15, 16] and is also sensitizes cells to oxidative stress-induced apoptosis [17]. However, only a few studies have been reported to reflect the effect of ionizing radiation on the transcriptional response of FDXR [18, 19]. This gene encodes a mitochondrial flavoprotein that initiates electron transport for cytochromes P450 receiving electrons from NADPH. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for the FDXR gene. FDXR has recently emerged as one of the most accurate genes for medium-to-high dose estimation due to its dose-dependent transcriptional up-regulation [19]. In 2017, O’Brien et al. [19] identified for the first time FDXR transcriptional up-regulation in human blood 24 hr after patients’ exposure to high (radiotherapy) as well as low (CT, IC procedures) radiation doses. The results of the study were encouraging, showing that FDXR can be rendered a promising unique biomarker for radiation dose estimation over a wide range of exposures (ranging from mGy to Gy). In 2019, Palumbo et al. [20] found that adverse effects of radiotherapy such as dermatitis radiation, pain, pruritus and fatigue were associated with significant FDXR expression change in irradiated patients.
The current study aimed to examine for the first time, to our knowledge, the responsiveness of FDXR using qPCR analysis on the radiosensitive pediatric population exposed to ionizing radiation during IC procedures.
3 mL of peripheral blood was collected by venipuncture from the pediatric donors before and 24 hours after the IC procedure. All the blood collections were carried out after approval by the Ethics Committee of the Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center. The blood samples were kept in EDTA tubes for 2–3 hours and stored at –20 °C until further analysis.
The study enrolled a total of 24 pediatric patients (0–18 years) who underwent diagnostic and therapeutic IC procedures, including radiofrequency catheter ablations (RFA) (n = 12) for the treatment of supraventricular tachycardia, atria septal defect (ASD) closure (n = 5), diagnostic cardiac catheterizations (n = 3), balloon valvuloplasty (n = 2) and balloon angioplasty (n = 2).
IC procedures were carried out by two experienced pediatric interventional
cardiologists in a single center. RFA procedures were performed in a digital
fluoroscopy system integrated with a nonfluoroscopic 3D mapping system (Artis
Zee multi-purpose, Siemens Healthineers, Germany). The rest of the IC procedures
were implemented using a digital biplane fluoroscopy system (Artis Zee, Siemens
Healthineers, Germany). Both fluoroscopy systems had a 1.5 mm Al inherent filter
and 0.6 mm Al added filter. Copper filters were also used to reduce the entrance
skin dose (0.1–0.9 mm Cu). Demographic data were recorded, and Air Kerma-Area
Product (P
The effective dose was calculated from P
where ED is the effective dose (mSv), P
According to the manufacturer’s instructions, total RNA extraction was performed
using TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Reverse transcription was
performed using the PrimeScript First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (TaKaRa). The
reaction conditions were 37 °C for 30 min and 85 °C for 5 s.
The reaction was performed on Thermal Cycler (Kyratec Super Cycler). Quantitative
PCR was conducted on an ABI Prism 7000 apparatus (Applied Biosystems, Foster
City, CA, USA). Each cDNA sample was mixed with specific primer sets and PCR
master mix (KAPA SYBR FAST qPCR Kit). The levels of genes expression were
normalized by subtracting the threshold PCR cycle (Ct) value of the GAPDH RNA
internal control (found not to vary across samples- data not shown) from that of
the GOI (gene of interest) (
The relative quantification (RQ) of GOI in irradiated blood samples compared to
the non-irradiated blood samples was determined by the
2
Primers used were:
FDXRF: 5’- GTCCGTCTGAGTGGGACTTT -3’
FDXRR: 5’- GAGGAGAGACGCTGGAAGAG -3’
GAPDHF: 5’- CATCTCTGCCCCCTCTGCTG -3’
GAPDHR: 5’- GCCTGCTTCACCACCTTGTTG -3’
The data were transformed to the log2 scale. The normality of data was examined using the Shapiro Wilk test. The independent t-test was performed to evaluate the statistical significance in FDXR expression between male and female patients.
Patients’ demographic characteristics, P
| Patient | Gender (F/M) | Age (Years) | BW (kg) | P |
Effective dose (mSv) | FDXR Fold regulation |
| 1 | M | 9.8 | 31.2 | 0.19 | 0.057 | 2.64 |
| 2 | F | 13.4 | 47.5 | 2.82 | 0.551 | –1.32 |
| 3 | M | 8.4 | 26.7 | 1.29 | 0.447 | –1.71 |
| 4 | M | 14.0 | 51.2 | 2.00 | 0.363 | –2.00 |
| 5 | F | 16.0 | 53.9 | 0.16 | 0.028 | 2.46 |
| 6 | F | 10.4 | 33.0 | 2.73 | 0.769 | 1.10 |
| 7 | M | 16.9 | 61.2 | 52.79 | 8.004 | –1.21 |
| 8 | M | 1.5 | 10.9 | 0.52 | 0.445 | 2.22 |
| 9 | M | 13.1 | 46.2 | 0.85 | 0.171 | 2.28 |
| 10 | F | 11.5 | 31.0 | 11.23 | 3.361 | 2.32 |
| 11 | M | 12.9 | 45.4 | 6.71 | 1.372 | 1.89 |
| 12 | M | 17.8 | 66.7 | 1.71 | 0.237 | 1.32 |
| 13 | M | 8.2 | 22.0 | 1.41 | 0.595 | 1.46 |
| 14 | F | 13.6 | 48.1 | 2.85 | 0.550 | –1.41 |
| 15 | F | 17.5 | 55.7 | 37.39 | 6.229 | 4.00 |
| 16 | F | 12.5 | 40.0 | 5.57 | 1.292 | 1.26 |
| 17 | F | 0.5 | 7.3 | 0.99 | 1.262 | 3.25 |
| 18 | F | 9.5 | 31.0 | 0.40 | 0.120 | –1.31 |
| 19 | F | 13.7 | 48.4 | 0.01 | 0.002 | 1.57 |
| 20 | M | 12.5 | 43.2 | 1.69 | 0.363 | 1.10 |
| 21 | F | 17.0 | 60.0 | 9.13 | 1.413 | 4.20 |
| 22 | M | 12.6 | 59.0 | 11.64 | 1.830 | –1.54 |
| 23 | M | 16.5 | 63.0 | 13.22 | 1.947 | 3.48 |
| 24 | M | 0.8 | 7.1 | 2.28 | 2.980 | 1.96 |
| F/M, Female/Male; BW, Body Weight; P | ||||||
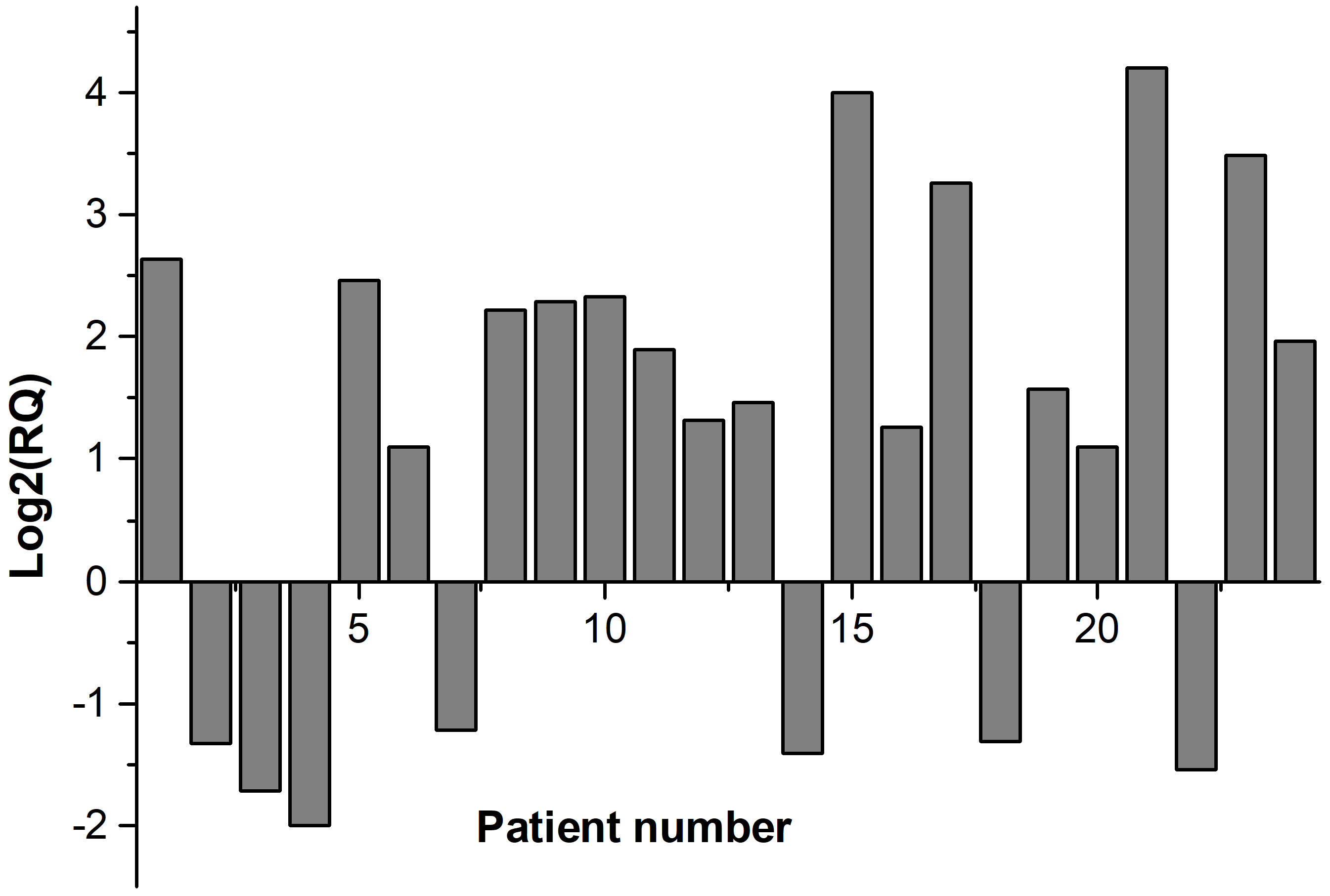
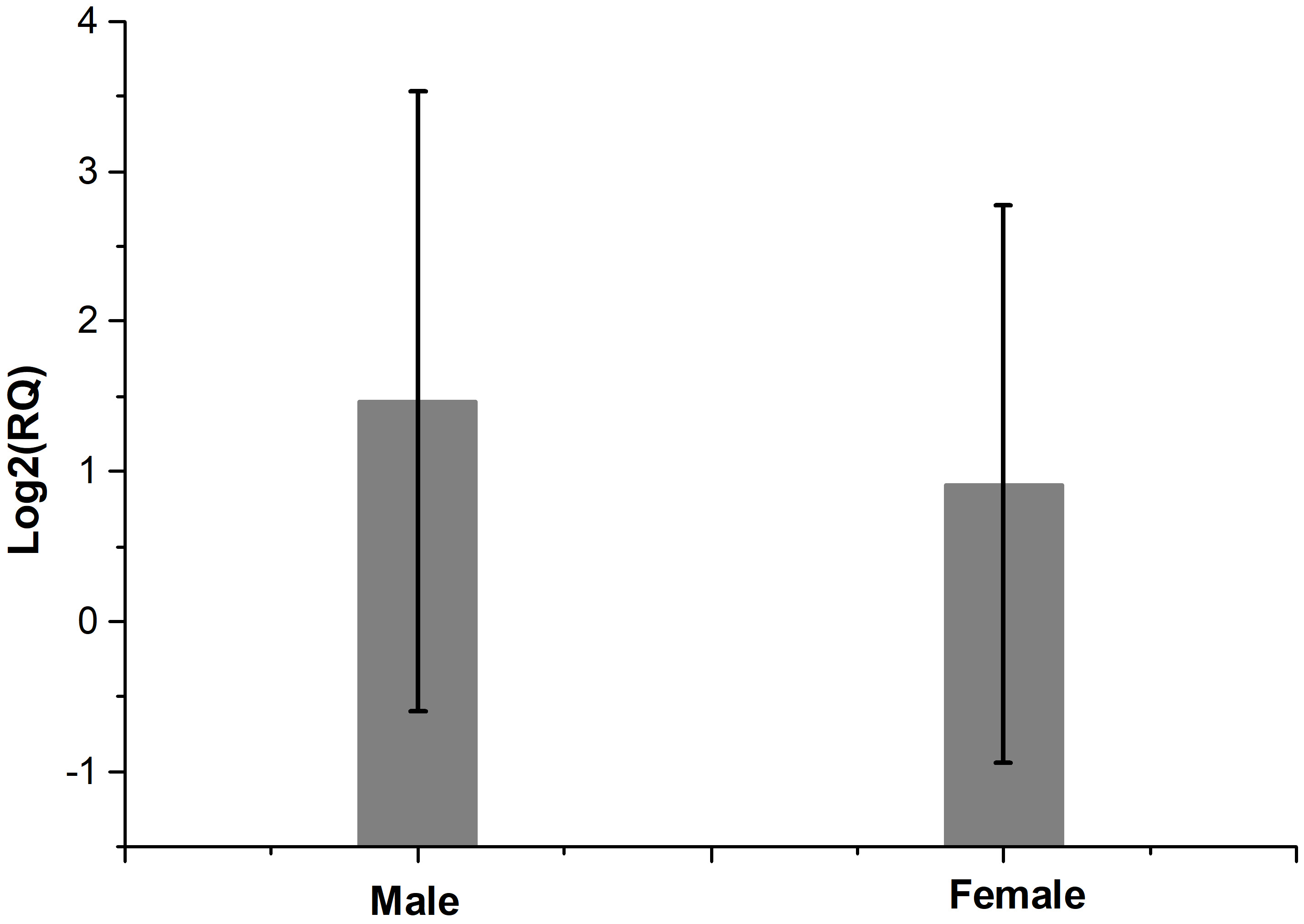
Fig. 1 shows the fold regulation of FDXR for each patient where Log2 (RQ) was used. Up-regulation of FDXR was observed in 17 patients (positive values) and down-regulation of FDXR in 7 patients (negative values) 24 hr after irradiation. The relative expression of FDXR considering patients’ gender is presented in Fig. 2. Comparing the FDXR expression in female and male patients, no statistically significant difference was observed (p = 0.499).
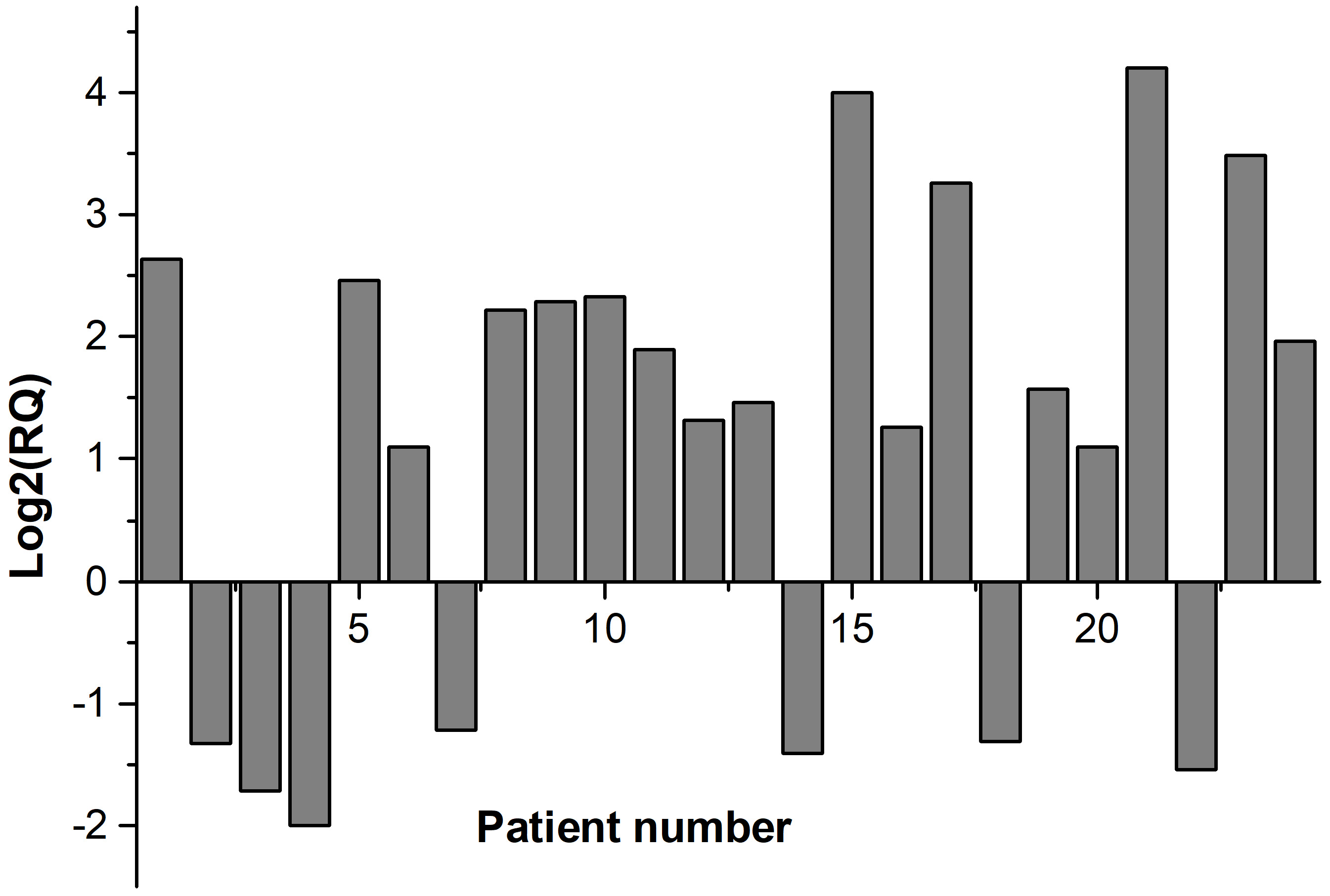 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Relative expression of FDXR gene for each patient.
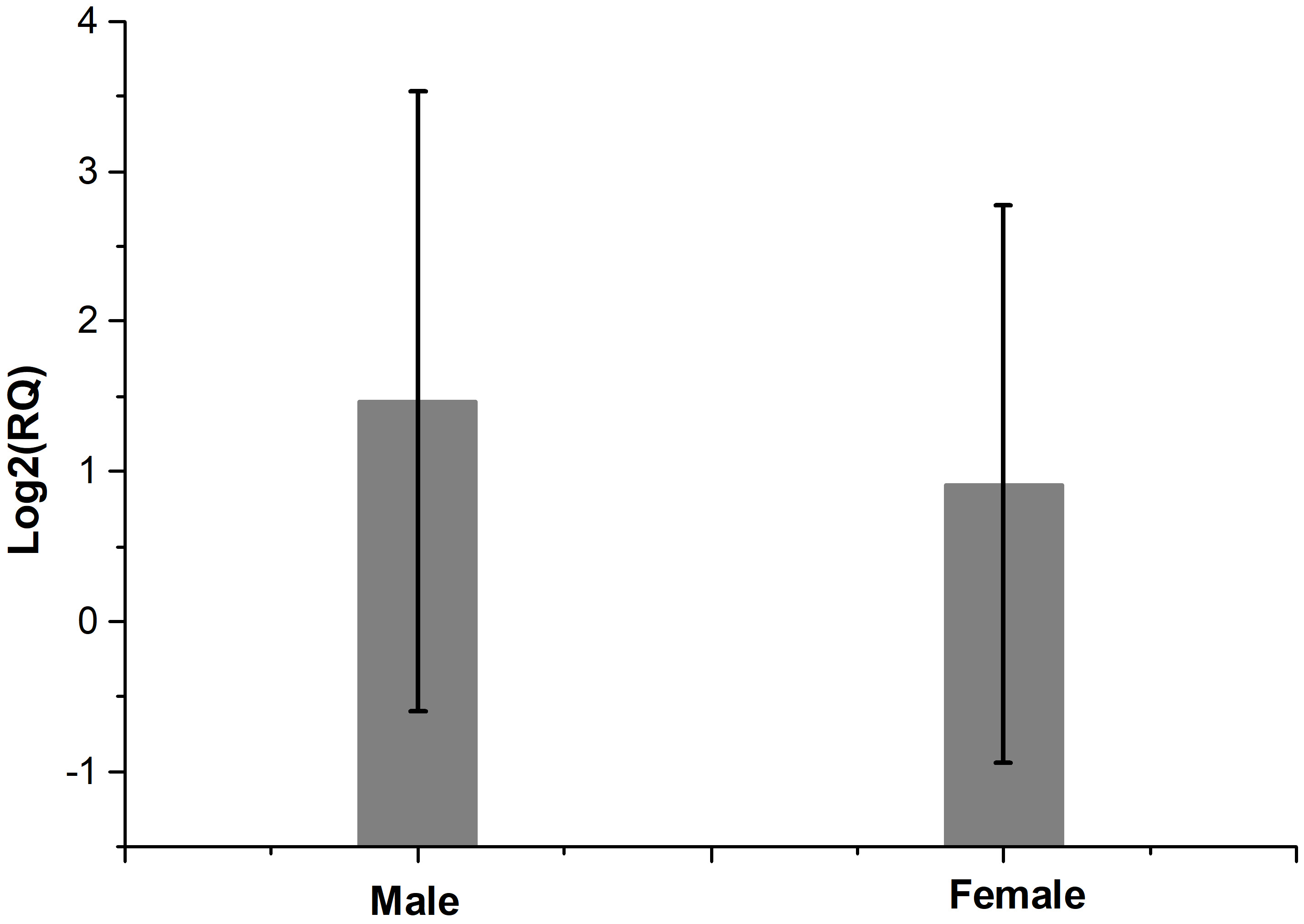 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.The relative expression of FDXR after irradiation comparing patients’ gender. There is no statistically significant difference between female and male patients (p = 0.499).
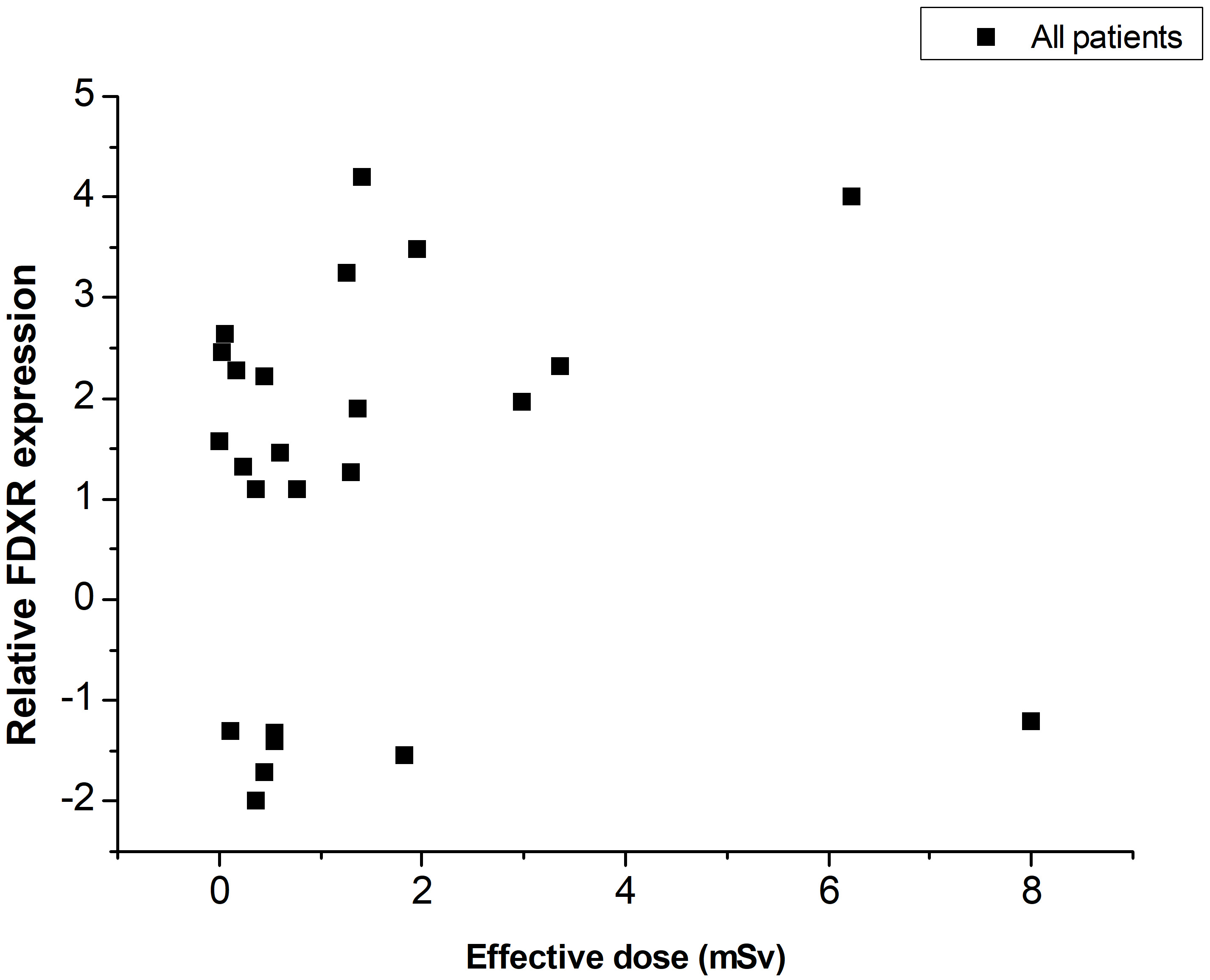
Based on Table 1, the relative expression of FDXR in periphery blood was presented graphically as a function of the effective dose of each pediatric patient (Fig. 3). In all patients, an FDXR gene expression change was noticed 24 hours after exposure to ionizing radiation. However, no correlation was observed between FDXR expression and effective dose.
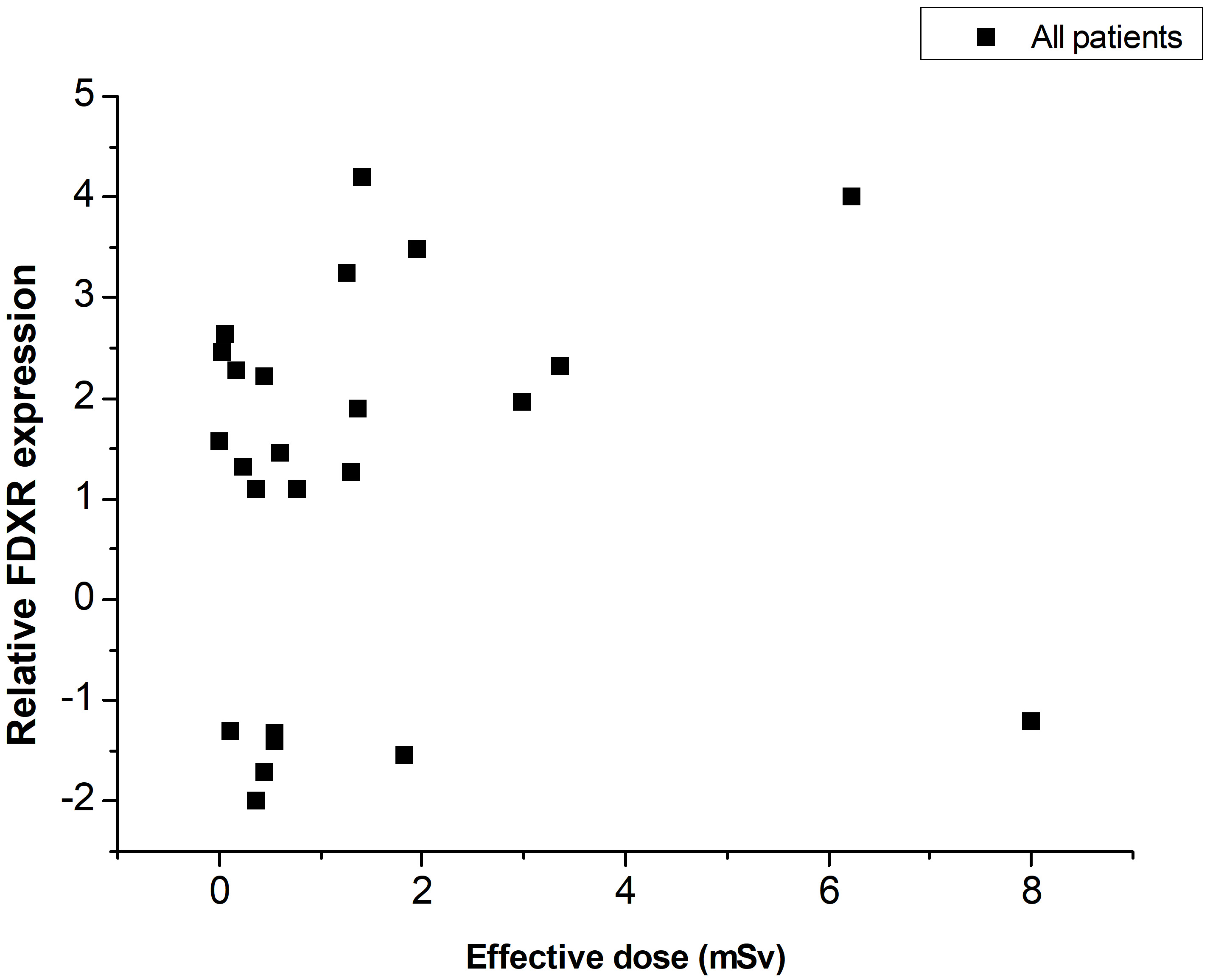 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.FDXR relative expression change versus effective dose for all pediatric patients.
FDXR gene has been demonstrated as an essential target of p53-dependent apoptosis. It is a critical gene for p53-dependent tumour suppression via iron regulatory protein 2 (IRP2) [22]. In the past few years, FDXR gene expression has been reported as a biomarker for radiation exposure in blood. FDXR has shown a remarkable radiosensitivity over a wide range of doses used in radiology (fluoroscopically guided procedures, CT) and radiotherapy (head, neck, lung, prostate, endometrial and Total Body Irradiation). Indeed, a linear correlation was observed between the gene expression and the radiation doses delivered during radiotherapy, which are in the order of Gy [19].
Our result indicated that for the low-level exposures in pediatric IC procedures (ranging from 0.002 mSv to 8.004 mSv), the FDXR gene expression varied randomly with the effective dose. Up-regulation in FDXR expression was observed in 17 patients and down-regulation in 7 patients. Indicatively, the patient who received the effective dose of 0.45 mSv produced a 2-fold increase in FDXR at 24 hr, almost the same with the patient who received 0.17 mSv. The pediatric patient who received the highest effective dose of 8 mSv presented a 1.21-fold down-regulation in FDXR expression. A 1.10-fold up-regulation was observed for the effective dose of 0.769 mSv.
Several confounding factors have been proved to affect the gene expression, including anti-inflammatory therapy [23], simulated bacterial infections [19] and drugs [16, 17, 24]. According to studies, down-regulation of FDXR expression has been noticed at low or high concentrations of Lipopolysaccharides used to mimic a bacterial infection [19, 21] and curcumin used as an anti-inflammatory agent [19]. Treatment with 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU), a frequent antitumor drug, induced a 1.64-fold up-regulation in FDXR expression tumors and a 1.13-fold in normal tissues [24]. A 1.88-fold change of FDXR expression was associated with dermatitis radiation in blood patients treated with a fractionated RT dose of 1 Gy and experienced a several grade (G3) toxicity, while a 1.44-fold change was observed in patients with moderate grade toxicity (G2) [20]. According to Human Protein Atlas [25], there is a substantial variation of gene expression in different tissues and the existence of many variants which can alter final protein levels. Moreover, published studies have shown that the FDXR up-regulation depends on the volume of the body exposed and the time after the exposure with a peak of expression around 8–9 hours after irradiation [26]. Therefore, FDXR gene expression changes are not only radiation-induced but also seem to be associated with an underlying disease or the personalized clinical profile of each patient.
FDXR showed to be sensitive to radiation exposure levels used in pediatric IC procedures. However, the current study indicated that for effective doses between 0.002 mSv and 8.004 mSv, FDXR expression changed randomly with effective dose. Accordingly, no correlation was observed between the gene expression and the effective doses. Further studies on a larger cohort of pediatric patients are required to thoroughly investigate the potential of FDXR gene expression as a biomarker for radiation exposure in pediatric imaging. The possible dependence of FDXR expression on drugs and the patient’s medical history should also be examined.
Conceptualization—EPE; writing - original draft preparation—AP, ES and HK; writing - review and editing—EPE, MG, AGG, and IS; Acquisition data—PA, SA, GB, SR IP; Analysis and interpretation of data—PA, ES, AP, HK. All authors read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
All the blood collections were carried out after approval by the Ethics Committee of the Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center.
Not applicable.
This research received no external funding.
The authors declare no conflict of interest. AGG is serving as one of the Editorial Board members/Guest editors of this journal. We declare that AGG had no involvement in the peer review of this article and has no access to information regarding its peer review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to Taeg Kyu Kwon.
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.