1 Department of Gynecology, Medical Center, University of Leipzig, 04103 Leipzig, Germany
Academic Editor: Stergios Boussios
Abstract
Background: Disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) in bone marrow aspirates of patients with primary breast cancer may serve as independent prognostic markers associated with impaired survival. Due to limited therapy options and high risk of recurrence particularly, women diagnosed with the aggressive triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) require personalized treatment choices. Genetic profiling of circulating cell-free tumor DNA (ctDNA) might help to find individual treatment options and to monitor disease course. Methods: Here we report the case of a 66-year-old patient with TNBC. She received neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) that had to be interrupted due to intolerance. Surgical resection of the residual tumor resulted in pathologic complete response (pCR), though. Results: Bone marrow aspiration during surgery revealed an unusual high number of DTCs and thus elevated risk for recurrence. Analysis of pre-surgical blood and urine samples revealed the presence of plasma-derived and urinary ctDNA after NACT and indicated poor prognosis. Subsequent targeted sequencing showed that pathogenic variants occurred in urinary and plasma-derived ctDNA emphasizing the potential of liquid biopsy usage for early detection of relapse. Despite the detection of residual molecular disease after NACT, the presented patient reached pCR and could benefit from standard treatment until present. Conclusions: In this case, liquid biopsy based biomarkers did not necessarily correlate to clinical outcome. Further, ctDNA analysis did not reveal approved therapeutic options to target the identified pathogenic variants. Adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment was applied based on the positive DTC status and may improve the patients’ prognosis. Further investigations are required to identify TNBC patients at risk for recurrence.
Keywords
- breast cancer
- TNBC
- disseminated tumor cells
- bisphosphonates
- liquid biopsy
- circulating cell-free tumor DNA
Despite successful treatment of the primary tumor, about 30% of breast cancer patients suffer from recurrence. One reason might be hematogenous spread during early disease stages when isolated tumor cells disseminate from the primary tumor site. They enter the lymphatic system and the blood stream and travel to distant organs like liver or lung where they are able to seed metastases. They also disseminate into the bone marrow where they can become dormant and seed so-called “micro-metastases”. In this steady state, they are “sleeping” which means they have a slow proliferation rate and hence cannot be eliminated by chemotherapy. They might “wake up” at later stages of the disease to re-circulate into the blood stream and cause recurrence. Disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) in the bone marrow aspirates of patients with primary breast cancer may serve as independent prognostic markers associated with impaired survival. However, the adjuvant intake of bisphosphonates was shown to have an apoptotic effect on DTCs and to decrease the risk of bone metastases thus, providing an overall survival benefit [1, 2, 3].
Breast cancer is a very heterogeneous disease and can be classified into distinct molecular subtypes. The most aggressive subtype is triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), which is hormone-receptor negative (neither ER nor PR) and HER2 negative. The majority of TNBCs are of high grade and show a high proliferation rate. Patients usually receive chemotherapy but have an increased risk of recurrence and poor prognosis [4]. Particularly patients that do not achieve pathological complete remission (pCR) after chemotherapy might require targeted treatment approaches.
Among TNBC, a variety of subgroups has been identified including high cellular proliferation, increased immunological infiltration, basal-like and mesenchymal phenotype as well as deficiency in homologous recombination, which was partly associated with loss of BRCA1 or BRCA2 function. Genetic profiling of TNBC revealed potential options for tailored therapy strategies such as modified chemotherapy approaches targeting the DNA damage response, angiogenesis inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors, or even anti-androgens, which are currently under investigation in various phase I to III clinical studies [5, 6, 7, 8]. At diagnosis, TNBC patients and patients with hereditary disease (about 20% of the breast cancer patients) receive multi-germline gene panel testing for risk assessment. Strictly speaking, therapeutic decisions are based on histopathological profiles from an initial tissue sample and germline mutation profiles that were received from an initial blood sample. During therapy, however, the genetic tumor profile might change [9], meaning that distinct somatic mutations such as targetable driver mutations might become functionally neutral passenger mutations. Consequently, treatment efficacy might be affected ultimately leading to resistance. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) was postulated to be shed by all tumor sites, even micro-metastases, and could enable early detection of recurrence as well as identification of somatic molecular alterations during treatment courses that might be relevant for targeted therapy options [10].
Here we report the case of a 66-year-old, post-menopausal, non-smoking patient with a body mass index (BMI) of 25.4 that was referred by her gynecologist with a nodule in the right breast (Table 1). In January 2020, mammography screening in our outpatient unit revealed a lesion in the right breast with a size of 2 cm, which was also detectable per ultrasound. Ultrasound guided core needle biopsy of the right breast and subsequent histological staining revealed breast cancer with the triple-negative molecular subtype, grade 3 and a Ki-67 proliferation rate of 60%. No visceral or bone manifestation was found in the staging computer tomogram. Tumor staging revealed cT1c cN0 cM0. She had a history of various comorbidities including hypertension and allergic bronchial asthma. Further, she had undergone thyroid resection and hysterectomy without adnexa. Germline testing based on a blood sample using the TruRisk gene panel including ATM, BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CDH1, CHEK2, PALB2, RAD51C, RAD51D, TP53, PTEN showed no mutations or variants. Analysis of somatic mutations in the tumor tissue is not part of the clinical routine in breast cancer patients, yet. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) with 4 cycles Epirubicin and Cyclophosphamide was conducted in a biweekly regime. After the first cycle, dose was reduced to 80%. Subsequently, treatment with Paclitaxel/Carboplatin was initiated weekly for 12 cycles. However, in May 2020, after only 5 cycles, therapy was interrupted due to intolerance. In June 2020 lumpectomy and lymph node dissection was scheduled to remove the residual tumor mass. After agreeing and signing a written informed consent in accordance with the requirements of our institution’s board of ethics (internal reference number: No. 216/18-ek), blood and urine was sampled prior surgery and bone marrow aspirates were collected from the anterior iliac crest during surgery. Histopathological analysis confirmed that the patient reached pathological complete remission: ypT0 ypN0 (0/1sn) R0 G3.
| Age at diagnosis | 66 years |
| BMI | 25.4 |
| Non-smoking | |
| Comorbididies (treatment) | Hypertension (candesartan, betablockers) |
| Allergic asthma (none) | |
| Thyroid resection (L-thyroxine) | |
| Hysterectomy (1996) | |
| Menopausal status | post menopausal (since hysterectomy) |
| Histology | ductal |
| Ki-67-proliferation rate | 60% |
| Grade | 3 |
| Tumor size | 2 cm |
| Nodal status | N0 |
| BRCA1/2 gemline mutation | none |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | epirubicin/cyclophosphamide 4 cycles biweekly |
| paclitaxel/carboplatin 12 cycles weekly | |
| Surgery | lumpectomy and lymph node dissection |
| Pathologic response | complete remission |
| DTC status | positive |
| DTC count | 85/4 million cells |
| Adjuvant therapy | Clodronate daily for 2 years |
| local radio therapy 50.05 Gy |
After density gradient centrifugation cell suspensions were transferred onto
glass slides (1
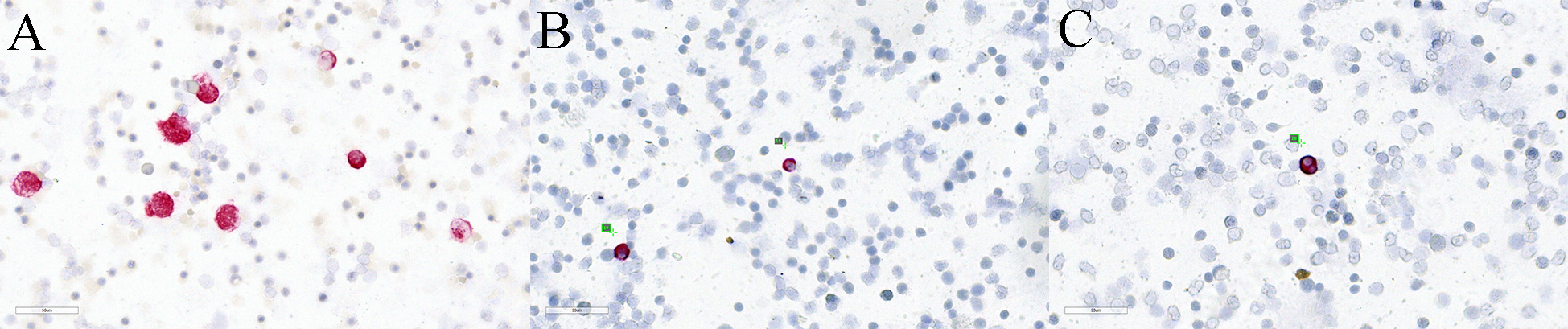
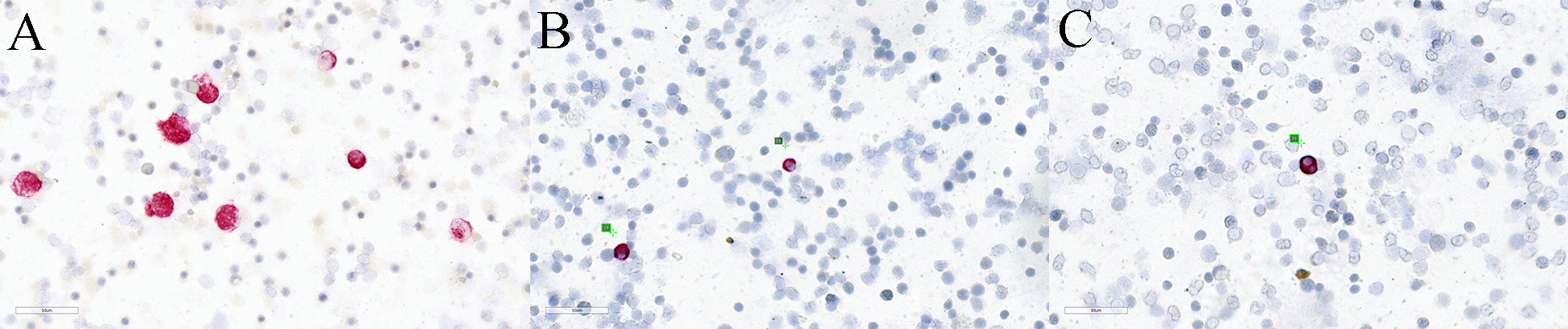 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Detection of Pan-CK positive cells in bone marrow. (A) Positive control consisting of bone marrow cells mixed with epithelial CK-expressing HCT116 colon cancer cells. (B,C) DTCs in bone marrow sample of the reported patient.
The blood and urine samples were obtained one day prior surgery and processed
within 4 hours after collection. We successfully adapted the manufacturer’s
instructions to yield increased concentrations of extracted plasma-derived and
urinary cell-free DNA (QIAamp MinElute ccfDNA Kit, QIAGEN). After quality control
of cell-free DNA fragments, matched samples were applied to library preparation
and target enrichment with a commercially available diagnostic breast cancer
specific 93-gene panel service (QIAGEN). Libraries were analyzed by paired-end
sequencing on a NextSeq550 (Illumina Inc.) instrument followed by bioinformatical
analysis with QIAGEN Biomedical Genomics Workbench and subsequent interpretation
of variants using QCI Interpret Translational Software (QIAGEN). In the patient,
109 somatic breast-cancer related genetic alterations (VAF
Based on the positive DTC status and the post-menopausal status, adjuvant bisphosphonate intake was recommended at an oral dose of Clodronate 1040 mg/day for a period of two years to improve the patients’ prognosis. Clodronate is indicated for the management of osteolytic lesions, hypercalcaemia and bone pain associated with skeletal metastases in patients with carcinoma of the breast or multiple myeloma. Usually, clodronic acid is a well-tolerated drug with minimal adverse events. The most common reported adverse events are gastrointestinal disorders such as diarrhoea, which is usually mild and occurs more commonly with higher doses. In this case, the patient suffered from gastrointestinal disorders within the first month of treatment and disrupted the Clodronate intake for four weeks before she decided to continue. Treatment regime was proceeded according to AGO guidelines administering local radiotherapy on the right breast at a dose of 50.05 Gy until September 2020.
After occurrence of a BI-RADS 4 lesion in June 2021, a core needle biopsy was obtained. Histopathological staining revealed a chronic inflammation in keloid tissue without malignancy.
Although the patient reached pCR, analysis of plasma-derived and urinary ctDNA
indicated minimal residual disease after NACT. However, disease-monitoring using
serial ctDNA testing is not part of the clinical routine, yet. Notably, the
mutational profile gained from the patients’ liquid biopsy might indicate an
alternative route towards personalized treatment. In this case, somatic mutations
in ctDNA might mirror the tumor characteristics after systemic neoadjuvant
therapy but before surgical resection. However, therapeutic decisions based on
somatic variants from body fluids such as blood and urine were not approved, yet.
Further, the patient reached pCR despite NACT was interrupted and up to now,
The presented case indicated a medical need for personalized treatment of breast cancer patients beyond standard therapy, particularly of the triple-negative subtype, as well as the potential use of non-invasive, serial monitoring tools. After diagnosis, the described patient received NACT, which was discontinued due to intolerance after 4 cycles Epirubicin and Cyclophosphamide and 5 of 12 cycles Paclitaxel/Carboplatin. Surgical resection and histopathological analyses of the removed residual tumor mass confirmed that the patient reached pCR. However, analysis of the bone marrow revealed a positive DTC status and hence an elevated risk for recurrence. The number of detected DTCs was 85 cells among 4 million bone marrow cells and hence unusually high, keeping in mind that 1–10 DTCs per 1 million immunocytes were reported to be average [11]. Subsequently, adjuvant treatment with bisphosphonates, which might eradicate micro-metastasis from the bone marrow and improve prognosis, was applied. Although the patient suffered from gastrointestinal disorders, she continued the treatment. An alternative therapy choice might be Densusomab, a human antibody against the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB (RANK) ligand, a protein essential for osteoclast differentiation, activity and survival. However, its role in the prevention of breast cancer recurrence is still under investigation in clinical trials such as the GeparX phase III prospective randomized trial [12].
Looking at the DTC status it might be highly likely that the patient is going to suffer from recurrence, although she reached pCR. At the time being there is no standardized clinical test to stratify patients at elevated risk for recurrence based on their DTC profile at primary diagnosis and therapeutic strategies are still controversially discussed. Already in 1998, a study by Diel et al. [1] showed that primary breast cancer patients treated with Clodronate had a significantly improved prognosis in terms of overall survival. Later on they reported that patients could significantly benefit from Clodronate intake even 10 years after surgery [2]. However, little is known concerning the DTC status and prognosis among various molecular breast cancer subtypes. The international PADDY study which included pooled data from more than 10,000 patients with early invasive breast cancer treated at 11 centers discovered that a positive DTC status was associated with the luminal B subtype and decreased survival [13]. Further studies are required to identify patients at high risk for recurrence based on the molecular subtypes.
Noteworthy, the presented patient underwent multi-gene panel testing for risk assessment. The applied TruRisk germline test (including ATM, BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRIP1, CDH1, CHEK2, PALB2, RAD51C, RAD51D, TP53, PTEN mutations) was based on an initial blood sample, but it turned out negative. Therefore, targeted treatment approaches such as modified chemotherapy targeting the DNA damage response, angiogenesis inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors, or even anti-androgens were not appropriate.
One option to find alternative treatment choices might be analysis of somatic mutations in the primary tumor tissue obtained during core needle biopsy at diagnosis, which is not part of clinical routine, though. Participation in recruiting clinical trials might permit access to novel treatment such as Olaparib or Talazoparib, which might be an option for the presented patient based on the somatic BRCA mutations if these would be detectable in the tumor tissue. Clinically relevant mutations are often not detected in the primary tumor, though. Clonal selection might take place during treatment courses and could cause the occurrence of targetable mutations that were not detectable in the primary tumor tissue, which, however, might be detected in ctDNA.
One promising approach to identify tumor specific alterations in ctDNA might be targeted sequencing of cancer-related mutations in the primary tumor tissue and verifying them in ctDNA at baseline. Common and reliable methods for mutational analysis are digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) or the more comprehensive next generation sequencing (NGS). Many studies compared mutational profiles in plasma-derived ctDNA at baseline, matched tissue samples from breast cancer patients and found good correlations [14].
Interestingly, in patients with early stage TNBC such as the presented case, simply the presence of ctDNA after NACT, was reported to be predictive for recurrence [15, 16]. Further, serial ctDNA monitoring in blood samples from TNBC patients indicated worse relapse-free survival if ctDNA was detected at the end of NACT [17]. The clearance of ctDNA after NACT was described to be associated with improved survival whereas patients who failed to clear ctDNA had inferior distant disease-free recurrence survival [18].
Our targeted NGS approach, using a breast cancer specific gene-panel, revealed 5 respective 7 pathogenic mutations in plasma-derived and urinary ctDNA, respectively. We found pathogenic variants of CHEK2, PTEN and NF1 in both body fluids. NF1 mutations have been reported in 2.2% (7/313) of TNBC samples analyzed in the Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer (COSMIC, May 2020). Loss of neurofibromin function may result in increased signaling through the Ras pathway and downstream MAPK and mTOR pathways. Tumors bearing NF1 inactivating mutations may therefore be sensitive to mTOR inhibitors and MAPK pathway inhibitors, such as MEK inhibitors [19].
PTEN loss or inactivating mutation may lead to increased activation of the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Hence, inhibitors of this pathway may be relevant in a
tumor with loss or mutation of PTEN [20, 21]. The mTOR inhibitors Everolimus and
Temsirolimus have been approved by the FDA, EMA and PMDA for use in some
indications, and clinical trials of these and other mTOR inhibitors as well as
inhibitors of PI3K and Akt are currently underway in multiple tumor types [22, 23]. Several MEK inhibitors are under clinical investigation, including
Trametinib, Cobimetinib and Binimetinib, which have been approved by several
governing agencies for certain indications [24, 25, 26, 27]. For the variant NF1 splice
site 2325+3A
Further, CHEK2 encodes the tumor suppressor, checkpoint kinase 2 (Chk2), a serine/threonine kinase that plays an important role in cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage [28]. There are currently no approved therapies targeting inactivating alterations in CHEK2. However, depletion of CHEK2 has been reported to increase sensitivity to PARP inhibitors in preclinical models and PARP inhibitors are in clinical trials in cancers with DNA repair deficiencies, including CHEK2 alterations [29]. CHEK2 mutations have been reported in less than 1% (1/303) of TNBC samples analyzed in COSMIC (May 2020). For CHEK2 (T476M) no therapies were approved for TNBC, yet. In other indications, Olaparib, Rucaparib, Niraparib and Talazoparib are approved based on somatic alterations. In breast cancer, these agents are approved only for patients harboring germline BRCA mutations [30].
Liquid biopsy analysis after NACT certainly bears great potential to identify TNBC patients at increased risk for recurrence and might help to find individual treatment options. This case strengthened the hypothesis that ctDNA might be useful to guide adjuvant treatment and to detect recurrence at the molecular level before clinical symptoms occur. In comparison to tissue analysis at primary diagnosis, longitudinal liquid biopsy testing at frequent intervals might offer an assembly of genetic tumor profiles displaying the real-time tumor status throughout the disease course including all potential tumor sites shedding ctDNA and hence, taking tumor heterogeneity into consideration. However, the presented case showed that it is not prime time for ctDNA guided therapeutic consequences, yet. The detected molecular residual disease, which was associated with elevated risk for relapse, did not correlate to the clinico-pathological parameters. Although the presented patient had detectable ctDNA and even pathogenic variants in both pre-surgical plasma and urine samples after NACT, she reached pCR and could benefit from standard adjuvant treatment and Clodronate.
For now, this case rather confirms that pCR appears to remain the most important prognostic factor in TNBC and those patients can benefit from improved outcome if they do not display tumor cells by histopathological staining after NACT [31, 32, 33].
BA initiated sample acquisition and collected clinical data. HH performed ctDNA analysis and interpretation. IN analyzed DTC data. IN wrote the manuscript. BA finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The presented patient gave written consen to be enrolled in a study approved by the local ethics board at University of Leipzig. Internal reference number: No. 216/18-ek.
We would like to thank Annekathrin Hoehn for her continuous support and her great pathological expertise. We also thank Anne Kreklau for clarifying case related matters. Further, we thank Kathleen Ried for sharing her extraordinary cytological knowledge, Regina Scherling for the excellent DTC staining procedure and Carola Koschke for the intense engagement concerning sample acquisition. We acknowledge that the paper was funded by the Open Access Publishing Fund of Leipzig University supported by the German Research Foundation within the program Open Access Publication Funding.
This research received no external funding and was financed by interal means. The publication was funded by the Open Access Publishing Fund of Leipzig University supported by the German Research Foundation within the program Open Access Publication Funding.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.