1 Department of Abodominal Oncology, West China Hospital, West China Medical School, Sichuan University, 610041 Chengdu, Sichuan, China
2 Department of Gastroentology, West China Hospital, West China Medical School, Sichuan University, 610041 Chengdu, Sichuan, China
3 West China Stomatological Hospital, Sichuan University, 610041 Chengdu, Sichuan, China
4 Department of Radiation Oncology, Hainan General Hospital (Hainan Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University), 570311 Haikou, Hainan, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: François Chevalier
Abstract
Locally advanced rectal cancer (RC) is treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) followed by radical surgery. Currently, organ-sparing approaches and/or “watch-and-wait” strategies other than unnecessary surgery have been suggested as the best option for patients who achieve complete regression after neoadjuvant treatment. However, patients respond differently to nCRT, hence the urgent need for effective methods to predict whether individual rectal cancer patients could benefit from this treatment. In this review, we summarize the biomarkers reported to be potential predictors of the therapeutic response of RC to nCRT. Biomarkers that are associated with genes, ribonucleic acid (RNA) and proteins are summarized and described first, followed by other types including immune and tumour microenvironment-related biomarkers, imaging biomarkers, microbiome-associated biomarkers, and blood-based biomarkers.
Keywords
- rectal cancer
- biomarker
- neoadjuvant chemoradiation
- response
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is identified as the third most common malignancy worldwide and the second most common cause of cancer-related deaths [1]. Rectal cancer (RC) accounts for approximately 30% of CRC and has worse clinical outcomes than colon cancer [2]. Chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery is the current standard of care for locally advanced RC. To maximally resect the tumour, preserve the sphincter and improve local control, surgery is usually performed after a 6–8 week period of chemoradiotherapy and according to the principles of total mesorectal excision (TME) [3, 4]. However, TME has been associated with high postoperative morbidity and mortality rates. In addition, TME-associated bowel, urinary and sexual dysfunctions result in poor long-term quality of life in these patients [2, 3]. Therefore, more personalized and less invasive multimodal treatment strategies are urgently needed for RC patients. New strategies have received much attention in recent years, but regrettably there is a ceiling effect (approximately 20% of cases) on achieving a pathologic complete response (pCR). According to previous reports, the pCR rate of RC patients at the time of surgery is in the range of only 8% to 20%. Up to 40% of RC patients are resistant to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT), with some experiencing a progression of disease and others showing a slight regression to stable disease [3, 4, 5]. Clearly, different responses to nCRT contribute to varying clinical outcomes, including disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) [2, 3]. Organ preservation with no immediate surgery, otherwise referred to as the “watch-and-wait” strategy, is currently suggested as the preferred management for RC patients who have shown an adequate response [2]. In contrast, patients who are resistant to nCRT need more successful treatment strategies at an early stage. Although radiation therapy has been widely used for various tumours, little progress has been made in predicting treatment outcomes following radiation. The inability to accurately predict treatment outcome has also limited the use of personalized therapy at an individual level [6]. It is clearly desirable to have the ability to accurately determine treatment outcomes before the start of treatment, to identify individuals who would benefit most from nCRT, to know what dose should be given, and to know whether the therapeutic response could be improved by combining with other molecular-targeted strategies.
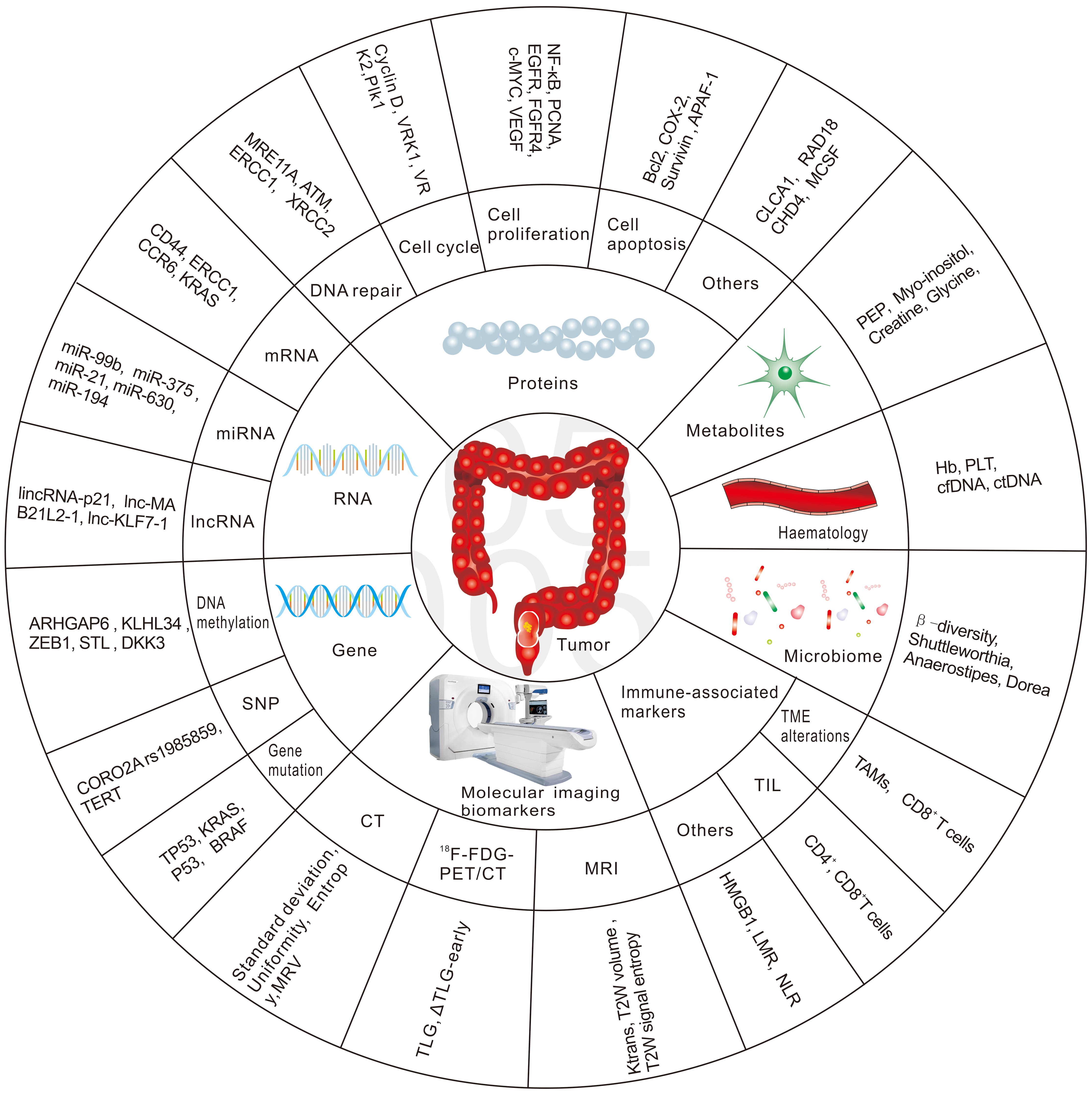
Hence, there is an urgent need to identify biomarkers that predict patient response to nCRT in the early phase, to develop alternative treatment strategies for non-responders and thus reduce the toxicity from ineffective nCRT, and to provide appropriate alternative treatments in a timely manner. The future management of RC patients is likely to be highly individualized, with a more rigorous treatment approach for high-risk patients and more flexible treatment principles for good responders. This review will focus on potential biomarkers to predict the response to radiation-based neoadjuvant therapy in patients with RC. We have summarized the most common biomarkers in Fig. 1.
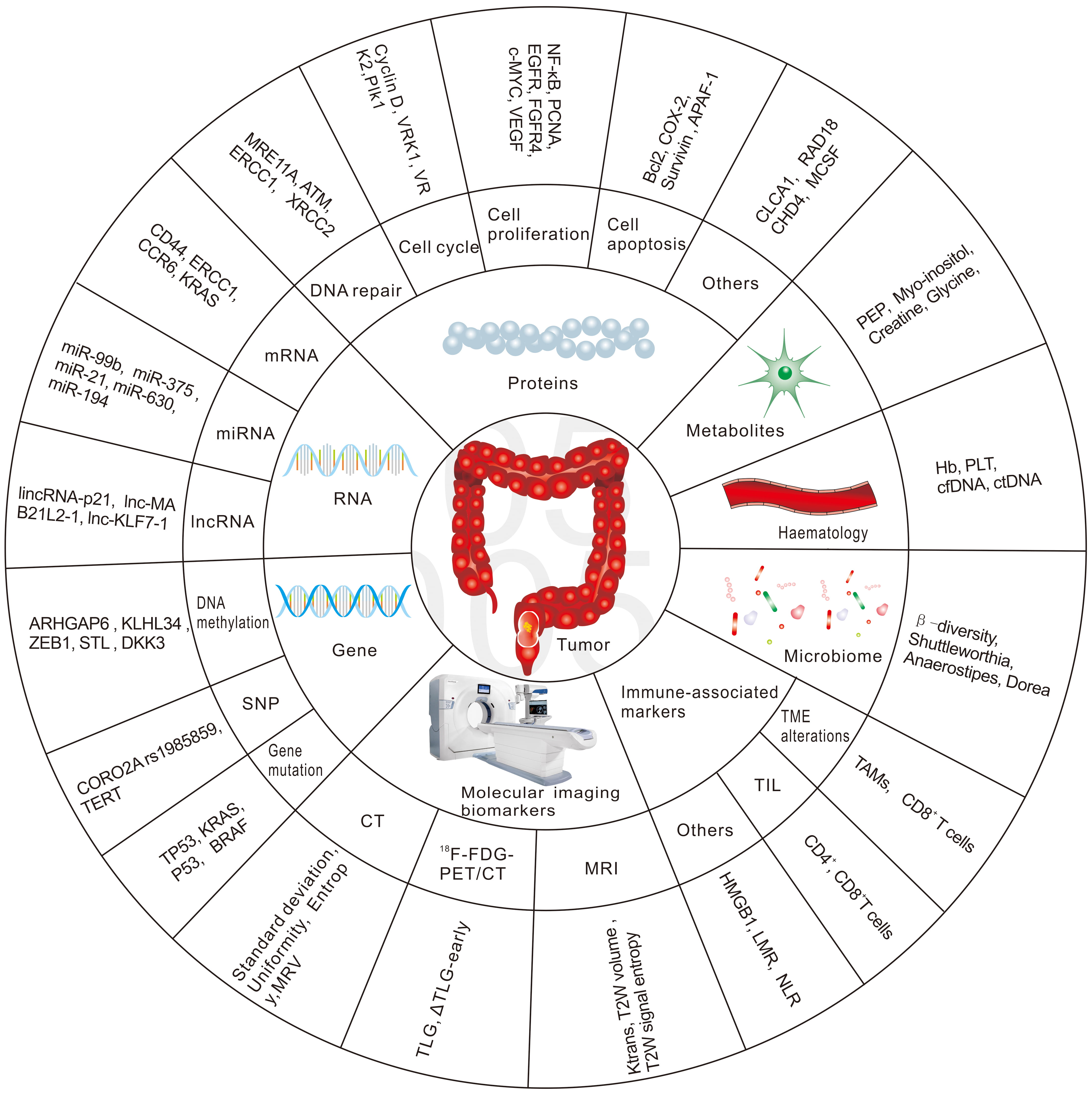 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.The most common biomarkers in predicting response to nCRT in RC.
Previous reports have shown that the gold standard for evaluating the extent of tumour regression after nCRT is histopathological assessment of the surgically resected tumour and lymph node samples. However, these assessment criteria vary in different countries and centres, and scholars have yet to reach agreement on the best assessment method. With regard to the evaluation of nCRT response, the American Joint Commission on Cancer (AJCC) [7], Dworak/Rodel [8], Mandard [9], Becker [10], Ryan [11], and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) [12] are currently the most commonly used tumour regression grading (TRG) systems [13, 14]. These are described in Table 1 (Ref. [7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]).
| Grading system | Grading | Description | Reference No. |
| American Joint Commission on Cancer (AJCC) | 0 | No residual cancer (complete regression) | [7] |
| 1 | single cells or small groups of cells | ||
| 2 | residual cancer with the desmoplastic response | ||
| 3 | minimal evidence of tumour response | ||
| Dworak/Rodel scoring system | 0 | No regression | [8] |
| 1 | Dominant tumour mass with fibrosis and/or vasculopathy | ||
| 2 | Dominantly fibrosis with few cancer cells or groups | ||
| 3 | few scattered cancer cells on | ||
| fibrosis background | |||
| 4 | No tumour cells, only fibrotic mass (complete regression) | ||
| Mandard scoring system | 1 | No residual cancer (complete regression) | [9] |
| 2 | Rare residual cancer cells | ||
| 3 | Predominantly fibrosis, but increase of residual cancer cells | ||
| 4 | Residual cancer outgrowing fibrosis | ||
| 5 | Absent of regressive changes | ||
| Becker classification | 1a | No residual tumour cells | [10] |
| 1b | |||
| 2 | 10–50% residual tumour cells | ||
| 3 | |||
| Ryan | 1 | No or rare residual of cancer cells (complete regression) | [11] |
| 2 | Residual cancer cells with predominant fibrosis | ||
| 3 | No fibrosis and/or with extensive residual cancer cells | ||
| Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center | 1 | complete regression | [12] |
| 2 | 86%–99% of tumour remission | ||
| 3 |
DeoxyriboNucleic acid (DNA) is an extremely important biomolecule that stores genetic information used to determine the formation of different cells, tissues and the whole organism [15]. The main mechanism of action of chemoradiotherapy is by damaging the cellular DNA [4]. Various DNA repair mechanisms are stimulated in DNA-damaged cells to arrest the cell cycle and allow repair enzymes to identify and repair the aberrant nucleotides, thus keeping the genome in good condition. Over time, irreparable damage can occur if the damaging events inside the cell and the activity of DNA repair machinery become unbalanced. This can be seen in the radiation therapy process, which finally leads to cell apoptosis. Previous studies have provided substantial evidence that some genetic characteristics are potential predictors of the therapeutic response to nCRT.
It is well recognized that genomic copy number can change during the cell life
cycle. For example, the amplification of oncogenes, the deletion of tumour
suppressor genes, or some other rearrangements may result in alterations to gene
transcription [15]. Chromosomal instability, which includes the amplification and
deletion of chromosomal segments or entire chromosomes, is a common feature of
most CRCs. In an exploratory study, Molinari et al. [16] analysed
alterations of chromosomal copy number and found that non-responders had a
specific alteration profile. These included more frequent changes at the 18q23,
17p13-12, 13q31-34, 13q12, 10p14-13, 16p13, 8q23-24, 7p22-21, 7q21, 7q36, 3q29
and 2q21 chromosomal regions. Insights into the profile of chromosomal
alterations could thus provide helpful information in predicting the response to
nCRT, leading to an optimized strategy for RC. Chen et al. [17] also
reported that chromosomal copy number alterations (CNAs) were associated with the
response to nCRT. In their prospective phase II study, they revealed that non-pCR
patients showed more frequent loss of chromosomal region 15q11.1-q26.3
(p
Various molecular pathways are involved in the development of CRC, of which DNA
methylation is an important pathway. Although the development of RC has been
widely studied, methylation profiling is seldom explored for its ability to
predict response to nCRT. Molinari et al. [20] first analysed
methylation profiles in biopsy samples from normal individuals and from RC
patients and evaluated whether these could be used to predict nCRT. Only TIMP3
methylation status showed a significant difference within the four TRG classes
(p
Global genomics research into single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) variations
and the initial stages of human genomic haplotype mapping both contributed to the
discovery of cancer-promoting genes. This led to the identification of specific
molecular characteristics as potential biomarkers to predict therapy response and
prognosis [25]. Several studies have reported that polymorphisms in DNA repair
genes are associated with the sensitivity of cancer patients to nCRT. For
example, several groups investigated the potential association between
thymidylate synthase (TS) polymorphisms and the response of RC to nCRT, but no
consensus has been reached [26, 27, 28]. A meta-analysis was conducted by Yang
et al. [27] to determine whether TS polymorphisms could predict the
response to nCRT in RC. They found that patients with the TS 2R/3R genotype
showed a positive response and that patients with the 2R/3R or 2R/2R genotype
could benefit more from nCRT than patients with other genotypes. However, both
the 1494del6 and the 5’-untranslated region expression allele polymorphisms
showed little predictive value. Lamas et al. [28] collected blood
samples from 93 stage II-III RC patients and determined their genotypes for TS,
excision repair cross-complementing group 1 (ERCC1) and X-ray cross-complementing
group 1 (XRCC1). An overall tumour response rate of 47.3% was observed, and the
authors found that XRCC1 G/G carriers were more likely to show a better response
than G/A carriers (odds ratio (OR) 4.18; 95% confidence interval (CI):
1.62–10.74, p = 0.003). In addition, higher expression of TS linked to
the 3G/3G, 3C/3G and 2R/3G genotypes was associated with a better treatment
response rate than lower expression genotypes (OR= 2.65; 95% CI: 1.10–6.39,
p = 0.02) [28]. Kim et al. [29] found 9 SNPs that were
associated with nCRT response. In particular, the reference allele (C) of the SNP
CORO2A rs1985859 was more likely to be associated with a positive response than
the substitution allele (T) (p = 0.01). In clinical analysis, the SNP
FAM101A rs7955740 showed no relation to radiosensitivity, but dysfunction of
FAM101A in RC cells in vitro was closely associated with early phase
apoptosis and colony formation. Sebio et al. [30] analysed polymorphisms
in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and its ligands, TS, and DNA repair
genes in 84 patients with stages II-III RC who underwent nCRT. They found the
rs11615 C
Studies have suggested that RC patients with or without p53 mutations respond differently to neoadjuvant radiation-based therapy. Whether p53 mutation is a reliable biomarker to predict therapeutic response to nCRT remains controversial [35, 36], with early studies reporting that it did not predict response to radiotherapy [35]. A meta-analysis published in 2012 showed that patients with wild-type p53 or with low expression levels of p53 protein were more likely to show pCR when treated with nCRT (poor response: RR = 0.85; 95% CI: 0.75–0.96; p = 0.007; good response: RR = 1.30; 95% CI: 1.14–1.49; p = 0.001; complete response RR = 1.65; 95% CI: 1.19–2.30; p = 0.003) [36]. Duldulao et al. [37] screened for TP53 and KRAS mutations in pre-treatment tumour biopsies and in paired normal surgical tissue from 148 stage II–III RC patients treated with nCRT. They concluded that mutations in TP53 and in different KRAS codons could influence the response to nCRT. For example, wild-type KRAS patients were more likely to show pCR than those with any KRAS mutation (p = 0.006), while KRAS codon 13 mutations were negatively associated with pCR (p = 0.03). Nevertheless, the role of KRAS mutation in predicting the response to nCRT is still controversial [38]. TP53 mutation was reported to be associated with radioresistance, while patients with both TP53 and KRAS mutations were more likely to show less response to nCRT and to suffer lymph node metastasis [39, 40]. Jiang et al. [41] analysed the genes of RC patients who underwent nCRT and found that BRAF and SMAD4 mutations were associated with positive response to chemoradiotherapy and better prognosis. Some researchers have attempted to construct models of predictive genotype signatures (PGS) to predict nCRT responses in RC. Xiao et al. [25] recently built a PGS model, based on target sequencing of 15 genes, whose predictive value was proved better than that of any clinical factor. Predictive models that contain multiple gene characteristics could therefore assist in the more accurate selection of patients who might benefit from nCRT, thus facilitating the personalization of treatment strategies.
Messenger RNA (mRNA), transcribed from a strand of template DNA, is a class of single-stranded RNA that carries genetic information to guide protein synthesis, thus gene alterations caused by nCRT can change the expression profiles of mRNA. These may in turn also be potential biomarkers for predicting therapeutic outcomes in RC. Some newly reported mRNA-associated biomarkers are listed in Table 2 (Ref. [42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50]).
| Sample type | No. of samples | Treatment | Methods | Response assessment | Predictive biomarker | Performance | Main function | Reference no. |
| Pre-nCRT biopsy | 123 | Ncrt (leucovorin and 5-FU and radiotherapy) | RT-PCR | Rodel scoring: responder: grade 3–4 | CD44 | p = 0.030 | cell adhesion | [42] |
| Non-responder: grade 1–2 | ||||||||
| Pre-nCRT biopsy | 86 | nCRT (FOLFOX-4 and radiotherapy) | immunohistochemistry | AJCC/UICC | ERCC1 | p |
DNA damage repair | [43] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 12 | nCRT | RNA sequencing and IHC | Mandard scoring standard pCR: TRG 1 | CCR6 | p = 0.004 | chemokine receptor | [44] |
| Pre- and post nCRT biopsy | 83 | nCRT | IHC | Dworak scoring | RAD18 | p |
an E3 ubiquitin‐linked enzyme | [45] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 172 | nCRT (5-FU and radiotherapy) | IHC | Dworak scoring | CHD4 | p = 0.001 | DNA-binding, DNA repair | [46] |
| Pre-nCRT and Pre-surgery blood | 30 | nCRT (5-FU/capecitabin and radiotherapy) | CISH | Not mentioned | TS | p = 0.001 | DNA synthesis | [47] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 184 | nCRT (capecitabin or 5-FU + leucovorin and radiotherapy) | NanoString nCounter gene | Criteria from the Korean Society of Pathologists | ITGA7, FZD9, MMP3 HRAS, MECOM, NKD1, PRKCB, | AUC: 0.846 | a multi-gene mRNA-based biomarker model | [48] |
| expression assay | and PIK3CD | |||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 120 | nCRT (radiotherapy and 5-FU with leucovorin or xeloda only) | RT-PCR | Mandard scoring responder: grade 1–2 | p53, p21, Ki67, CD133 | AUC 0.922 (95% CI: 0.841−0.999) | a predictive model | [49] |
| Non-responder: grade 3–5 | ||||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 33 | nCRT (5-FU and radiotherapy) | RT-qPCR | AJCC | COASY | AUC 0.827 | a mitochondrial bi-functional enzyme | [50] |
| Abbreviations: nCRT, neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy; RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction; AJCC/UICC, American Joint Commission on Cancer/International Union Against Cancer; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; ERCC1, excision repair cross-complementing group 1; IHC, immunohistochemistry; CCR6, C-C motif chemokine receptor 6; CHD4, chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 4; CISH, chromogenic in-situ hybridization; TS, thymidylate synthase; COASY, CoA Synthase; RT-qPCR, real time quantitative-polymerase chain reaction. | ||||||||
Huh et al. [42] analysed pre-nCRT biopsies of RC patients to determine
the predictive value of 13 tissue biomarkers: nuclear factor-kappa B, survivin,
proliferating cell nuclear antigen, TS, p53, vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF), matrix metalloproteinase-9, matrix metalloproteinase-2, cluster of
differentiation 44 (CD44), CD133, thymidine phosphorylase, cyclooxygenase-2 and
BCL2-associated X protein. These authors concluded that only CD44 mRNA expression
was significantly predictive of therapeutic response (OR = 4.69, p =
0.030), even though it also correlated with expression of the other 12 markers
(all p
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a kind of short, single-stranded, non-coding RNA, which can regulate gene expression and physiological processes [13, 14]. Owing to their stability in serum, plasma, and other biofluids, miRNAs have been suggested as promising biomarkers for disease diagnosis, for predicting certain treatment responses, and for estimating the prognosis of various types of cancers [14]. Ionizing radiation can regulate the expression of miRNAs, while in turn the spectrum of diverse miRNAs can also affect the radiosensitivity of tumour cells and ultimately their response to radiation [52]. The biological functions of miRNAs have been widely investigated, in particular the potential as predictive biomarkers because of their peculiar features [53, 54].
As reviewed in previous studies, various miRNAs have been investigated as
predictive biomarkers of nCRT response, including miR-95, miR-99a, miR-99,
let-7e, let-7c, miR-765, miR-720, miR-630, miR-622, miR-671-5p, miR-519c-3p,
miR-590-5p, miR-1274b, miR-561, miR-490, miR-483-5p, miR-451a, miR-450a,
miR-450b-5p, miR-21, miR-205-5p, miR-200c, miR-215, miR-345, miR-29b-2,
miR-21-5p, miR-196b, miR-1909, miR-190b, miR-1471, miR-125-b1, miR-1183,
miR-188-5p, miR-153, miR-16, miR-1246, miR-1290-3p, miR-130a, miR-1224-5p,
miR-135b, miR-145, miR-125b and miR-125a-3p [13, 52, 54, 55]. Table 3 (Ref.
[53, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62]) summarized Some newly discovered miRNA-related biomarkers. Millino
et al. [56] analysed gene expression and miRNA levels in biopsies of RC
patients and found that the expression levels of 29 miRNAs and 256 genes were
different between responders (R) and non-responders (NR). In particular, only the
NR patients who had low levels of a single transcript, RAB5B, appeared to express
miR-630. Moreover, 8 transcripts (BCL2L13, NRG, ITGA2, MYO1B, GTSE1, KLF7, TRAM1
and TMEM188) were strong predictors of nCRT response. In another study, Angelo
et al. [53] found that miR-194 was significantly upregulated in
responders (p = 0.016) and may be a predictive biomarker of response to
nCRT. Campayo et al. [57] tested a nCRT-response signature in which
miR-483-5p, let-7e, miR-375, let-7b, miR-328, miR-183, miR-99b and miR-21 were
included in the preliminary screening. After validation, they found that the
levels of miR-99b, miR-375 and miR-21 could predict the response to nCRT. After
combining miR-375, miR-21 and miR-99b, they were able to predict the response to
nCRT in RC. Baek et al. [58] analysed the serum samples and biopsy
specimens from patients with RC before nCRT and found that overexpression of
miR-199a-5p, miR-199b-5p and miR-199a/b-3p were associated with better
therapeutic outcomes to nCRT. These workers also reported that exosomal
miR-199b-5p was associated with the response to Ncrt. Notably, Machackova
et al. [59] reported that 69 miRNAs were differentially expressed
between non-responders (TRG 4, 5) and responders (TRG1, 2), with 21 miRNAs being
overexpressed and 48 miRNAs expressed at low levels. A significantly higher level
of miR-487a-3p expression was confirmed in non-responders (AUC = 0.766,
p
| Sample type | No. of samples | Treatment | Methods | Response assessment | Endpoint | Predictive biomarker | Performance | Reference no. |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 38 | nCRT | RT-qPCR and ISH | Mandard scoring | responsiveness | miR-194 | p = 0.016 | [53] |
| responder: grade 1–2 non-responder grade 3–5 | ||||||||
| Pre- and post-CRT biopsy | 59 | nCRT(5-FU or capecitabine |
one-color microarray technique | Mandard scoring | responsiveness | miR-630 | Not reported | [56] |
| responder: grade 1–2 non-responder grade 3–5 | ||||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 96 | nCRT (5-FU and radiotherapy) | Recover All Total Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit | Dworak classification | responsiveness | miR-99b, miR-375 and miR-21 | AUC 0.736 (0.62,0.85) | [57] |
| p = 0.00043 sensitivity 60% specificity 82.9% | ||||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy and serum | 65 biopsies and 89 serum samples | nCRT (capecitabine or 5-FU+leucovorin and radiotherapy) | RT-qPCR | Rodel scoring | responsiveness | miR-199b-5p | p = 0.0397 | [58] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 87 | nCRT (5-FU and radiotherapy) | small RNA sequencing and qPCR | Mandard scoring | responsiveness | miR-487a-3p | p |
[59] |
| responder: grade 1–2 non-responder grade 3–5 | ||||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 185 | Ncrt (5-FU and radiotherapy) | RT-PCR | Ryan classification | responsiveness | miR-199b | p = 0.004 | [60] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 121 | Ncrt (5-FU and radiotherapy) | Recover All Total Nucleic Acid | Ryan classification | responsiveness | miR-19b | p |
[61] |
| Isolation Kit | ||||||||
| Pre-CRT plasma specimens | 106 | Ncrt (5-FU or capecitabine and radiotherapy) | RT-qPCR | Mandard scoring | pCR | miRNAs: miR-33a-5p, miR-30e-5p, miR-210-3p, miR-130a-5p, miR-214-3p, miR-320a, miR-338-3p, and miR-1260a | 0.82 (0.67,0.92) sensitivity 77% | [62] |
| responder: grade 1–2 non-responder grade 3–5 | specificity 73% | |||||||
| Abbreviations: nCRT, neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy; RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction; ISH, in-situ hybridization; RT-qPCR, real time quantitative-polymerase chain reaction; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil. | ||||||||
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) is a special
type of RNA that is
Small nuclear ribonucleic acids (snRNAs) and small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are short, non-protein-coding RNAs with complicated functions. These include guiding ribose methylation of ribosomal RNA and pseudouridylation of small nuclear RNAs at targeted nucleotide residues. Previous studies have reported that snRNAs and snoRNAs contribute to tumour development by stimulating cell proliferation, cell invasion and cell migration, as well as by inhibiting the apoptosis of RC cells [70]. It was previously reported that some types of snoRNAs, such as SNORD14E, SNORD67, SNORD12C, and SNORD17, can provide useful prognostic information on colon cancer [71]. However, the value of snRNAs and snoRNAs in predicting the response to chemoradiotherapy needs further exploration in prospective studies.
Proteins are the most sophisticated and crucial biomacromolecules in the human body and are the ultimate product of gene expression. Previous studies have reported that epigenetic and/or genomic mutations, as well as alterations in the transcription process can result in changes to protein expression. The level and spectrum of certain proteins might therefore indicate vital signs of the internal environment and of some diseases. Moreover, alterations in protein expression could be used as potential markers of the response to cancer treatment. Researchers have therefore explored the ability of proteins to predict the response to specific treatments. By using prior knowledge of genes and transcriptomics, it has been revealed that some proteins are linked to the radiosensitivity of RC and to clinical outcomes. Usually, researchers focus on a single protein or protein panel in which the expression level can be assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) or western blot (WB) analysis of biopsy tissues or serum samples, respectively.
Certain proteins with predictive potential are involved in the process of DNA
repair. These include meiotic recombination 11 homolog A, ataxia telangiectasia
mutated (ATM), proliferating cell nuclear antigen-associated factor 15 (Paf15),
ERCC1, X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 2 (XRCC2), and cell cycle
proteins such as cyclin D, vaccinia-related kinase-1 and -2, and polo-like kinase
1 (Plk1). Other proteins contribute to cell proliferation, including nuclear
factor-
| Sample type | No. of samples | Treatment | Methods | Response assessment | Predictive biomarker | Performance | Main function | Reference no. |
| Pre- and post-nCRT biopsy | 23 | nCRT (capecitabine and radiotherapy) | IHC | Dworack scoring Responder Grade 4 | Ku70/80 | p |
DNA repair, apoptosis regulator | [73] |
| partial responder Grade 1–3 | ||||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 62 | nCRT | RNA sequencing and RT-PCR | Mandard scoring | PSMB8 | p = 0.001 | cell metabolism, immune modulation | [74] |
| responder: grade 1–2 non-responder grade 3–5 | ||||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 172 | nCRT (5-FU and radiotherapy) | IHC | Dworack scoring | CLCA1 | p = 0.042 | ion transporter, regulating | [75] |
| chloride conductance | ||||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 74 | nCRT (5FU or FOLFOX and radiotherapy) | IHC | Ryan classification | DEK | p = 0.023 | DNA damage repair | [76] |
| Pre- and post-nCRT biopsy | 152 | (capecitabine or CapOX or FOLFOX or 5-FU and radiotherapy) | IHC and WB | AJCC scoring responder: grade 0–1 | TACC 3 | p = 0.001 | cell proliferation | [77] |
| non-responder: grade 2–3 | ||||||||
| Pre- and post-nCRT biopsy | 256 | (FOLFOX or CapOX and radiotherapy) | IHC | AJCC scoring | FOXK1, FOXK2 | AUC = 0.80, p |
cell proliferation, myogenic differentiation | [78] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 172 | nCRT (5-FU and radiotherapy) | IHC and WB | Dworak/Rodel scoring | BMI1 | p = 0.001 | cell proliferation, tumourigenesis | [79] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 110 | radiotherapy | IHC and WB | not mentioned | SGK1 | p = 0.0325 | transcription regulation,cell metabolism, cell differentiation | [80] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 156 | nCRT (capecitabine or 5-FU plus leucovorin and radiotherapy) | nCounter Pan-Cancer Pathway Panel | Mandard scoring | IL12A, GNA11, | specificity 79.4% | / | [81] |
| FGFR3, H3F3A, SPRY2, IL2RB, SGK2, NKD1 | accuracy 81.0% sensitivity 82.3% | |||||||
| responder: grade 1–2 non-responder grade 3–5 | and IL1R1 | |||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 186 | nCRT | RT-qPCR and WB | AJCC scoring | VSTM2L | p = 0.03 | uncharacterized function | [82] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 95 | nCRT (5-FU and radiotherapy) | IHC | Mandard scoring | CXCR4 and COX2 | OR = 4.47; | chemokine receptor; tumourigenesis | [83] |
| CR: grade 1 non-CR: grade 2–4 | 95% CI: 1.15–17.4; OR = 3.21; 95% CI: 1.14–9.09, respectively | |||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 35 | nCRT (5-FU plus leucovorin and radiotherapy) | RT-qPCR | Mandard scoring | SMAD7 | p = 0.014 | signaling cascade regulation; tumouriogenesis | [84] |
| responder: grade 1–2 non-responder grade 3–4 | ||||||||
| Abbreviations: nCRT, neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy; IHC, immunohistochemistry; RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction; AJCC, American Joint Commission on Cancer; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; FOLFOX, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin; CLCA1, chloride channel accessory 1; TACC 3, transforming acidic coiled-coil protein-3; BMI1, B-cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion site 1; VSTM2L, V-set and transmembrane domain containing 2 like; CXCR4, CXC chemokine receptor 4; SGK1, serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1. | ||||||||
Pucci et al. [73] reported that aberrant Ku70, Ku80 and sClusterin (a
partner of Ku70) expression were significantly associated with radioresistance
and may form a potential “cluster” of predictive factors for nCRT response in
patients with RC. Another study examined differential gene expression between RC
and normal tissue and identified 8 genes with a
The forkhead box (FOX) family members FOXK1 and FOXK2 participate in cell
proliferation and carcinogenesis. Recently, Zhang et al. [78] evaluated
the expression of these proteins in RC and their ability to predict nCRT
responses. They found that lower levels of FOXK1 and FOXK2 expression were
detected in patients with pCR (p
High expression levels for the V-set and transmembrane domain-containing 2 like
protein in RC have been associated with the therapeutic results of nCRT
(p = 0.030). These proteins are thought to contribute to
radio-resistance in an IL-4-mediated signalling pathway by downregulating
Metabolites are generated by various types of biochemical reactions in the body and also participate in the pathophysiological process of tumourigenesis and progression. Recent work in laboratory medicine has applied metabolomics for the classification of tumours and for the evaluation of treatment response, recurrence and prognosis. This has allowed metabolomics to produce biomarkers in various fields [87]. Early studies showed that serum concentrations of phosphoenolpyruvic acid, hypoxanthine, myo-inositol, creatine, and glycine were potential metabolic biomarkers for predicting response to CRT and prognosis in RC [88, 89]. A prospective cohort study (NCT03149978) by Jia et al. [87] found that RC patients who underwent nCRT could be discriminated between responders and non-responders by conducting metabolomic analyses of their serum. Potential responders could be identified using 15 differentially expressed metabolites. These results suggest that complete resection for all patients is not required in order to achieve the desired clinical and therapeutic outcomes. Using proper evaluation, potential non-responders could avoid unnecessary nCRT and oncologists could directly advise patients for whom surgery is the preferred option. Tomàs et al. [90] recently conducted a study of RC patients to identify biomarkers related to energy metabolism and to circulating levels of paraoxonase-1 that are able to predict nCRT responses. A low pre-nCRT level of plasma valine was associated with pCR (AUC = 0.826), while low concentrations of succinate were associated with relapse (AUC = 0.833). The content of serum exosomes has the potential to predict responses to neoadjuvant radiotherapy in RC. Recent work detected 129 metabolites in the plasma and exosomes, of which 23 differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) were present at significantly different levels between responders and non-responders. The exosome levels of pentadecanoic acid and of sucrose were higher in poor responders. Proteome components of serum-derived exosomes are also promising biomarkers, and the combination of proteomic and metabolomic biomarkers is likely to be a fruitful area of investigation [91].
It has been suggested that radiotherapy could stimulate the immune response process in a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP)-mediated manner, thus making it more efficient than chemotherapy. Non-irradiated tumour sites can sometimes also obtain a therapeutic response in what is known as the abscopal effect [92, 93]. Hence, radiation may enhance the body’s immune response through the initiation of immunogenic cell death (ICD), exposure of DAMPs, increased tumour-associated antigens (TAAS), and the recruitment of priming T lymphocytes and myeloid cells. This has also been considered to represent an in situ vaccination [34]. Substantial evidence indicates the tumour microenvironment is a vital factor and a reliable marker for predicting the response to certain treatments, the progression of tumours, and the clinical outcome of patients [94]. Thanks to rapid advances in next-generation sequencing technology over the past decade, the relationship between tumour microenvironment, immune regulation-associated biomarkers, and the response to chemoradiotherapy have all been areas of active investigation. The recently reported immune-associated biomarkers were listed in Table 5 (Ref. [95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103]).
| Sample type | No. of samples | Treatment | Methods | Response assessment | Endpoint | Predictive biomarkers | Performance | Reference no. |
| Pre- and post-CRT biopsy | 62 | nCRT (5-FU and radiotherapy) | IHC | Dworak scoring | responsiveness | CD8+ TILs, CD4+ TILs and MDSC-TILs | p = 0.022, p = 0.022 and p = 0.005, respectively | [95] |
| responder: grade 3–4 non-responder grade 0–2 | ||||||||
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 55 | nCRT | IHC | Ryan classification | responsiveness | CD3+ TILs | p = 0.01 | [96] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 117 | nCRT (FOLFOX or 5-FU and radiotherapy) | IHC and quantitative digital | Ryan classification CR grade 0–1 non-CR grade 2–3 | pCR | CD8+ T-cell density | p = 0.001 | [97] |
| image analysis | ||||||||
| Pre- and post- CRT biopsy | 67 | nCRT (5-FU and radiotherapy) | IHC and RT-PCR | Dworak scoring responder: grade 3–4 partial responder: grade 2 non-responder grade 1 | responsiveness | TCR diversity index and CD8+ TIL density | p = 0.049, and p |
[98] |
| Pre- and post- CRT biopsy and blood | 25 | nCRT (capecitabine and radiotherapy) | Flow Cytometry Analysis | Ryan classification | responsiveness | HLA DR−/CD33+/CD16−/CD11b+ MDSC | / | [99] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 50 | nCRT (capecitabine and radiotherapy and/or CAPOX) | IHC | mrTRG | responsiveness | B cell infiltration | p = 0.047 | [100] |
| Pre-CRT blood | 295 | nCRT | Chemoluminescence sequential immunometric | Not mentioned | responsiveness | IL-8 | p |
[101] |
| assay | ||||||||
| Pre- and post- CRT blood | 35 | nCRT (5-FU and radiotherapy) | Procarta polystyrene bead-based multiplex immunoassay | The Japanese Classification of Colorectal Carcinoma | responsiveness | IL-6, sCD40L, CCL-5 | / | [102] |
| Pre-CRT biopsy | 267 | nCRT | IHC | Dworak scoring good responder: grade 3–4 | pCR | LCR and N × M value | p = 0.016 and p = 0.005, respectively | [103] |
| Abbreviations: nCRT, neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy; IHC, immunohistochemistry;
RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction; 5-FU,5-fluorouracil;
CD8, cluster of differentiation 8; CD4, cluster of differentiation 4; TILs,
tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes; FOLFOX, 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and
oxaliplatin; pCR, pathologic complete response; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor
cells; TCR, T-cell receptor; mrTRG, magnetic resonance tumour regression grade;
IL-8, interleukin-8; IL-6, interleukin-6; Scd40l, soluble CD40-ligand; CCL-5,
chemokine ligand-5; LCR, lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio; N | ||||||||
The tumour microenvironment is composed of stromal fibroblasts, endothelial
cells, immune cells and an array of bio-macromolecules in the surrounding tissues
and inside the tumour cells. Increasing evidence shows that radiation can alter
the tumour microenvironment according to the tumour histology, anatomic site, and
various other clinical characteristics [104]. Kamran et al. [6]
demonstrated that radiation could alter the tumour microenvironment. They
analysed post-CRT tumour biopsy samples and observed significantly more CD8
Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are an important component of the body’s
primary immune response and have a major influence on the progression and
survival of tumours, including the response to radiotherapy and chemotherapy
[108]. Previous studies have shown that tumour in situ immune cell
infiltration markedly influences the clinical outcome of patients with solid
tumours [92]. Since chemoradiotherapy is known to induce cell death and
immunogenic potential in CRCs, several studies have examined immune infiltration
as a predictor of response to nCRT in patients with RC. Teng et al. [95]
performed immunohistochemistry of CD33, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein
4 (CTLA-4), programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1), CD11b, forkhead box protein
3 (FOXP3), CD4, CD56 and CD8 in pre-treatment biopsy specimens and in post-nCRT
surgical tissue samples of RC patients. CD4
Programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is a kind of transmembrane protein which is
related to the inhibition of the immune system. The expression of PD-L1 was
reported to be associated with therapeutic results of nCRT in RC. Chen et
al. evaluated the density of CD8
High mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1) is a kind of damage-associated
molecular pattern which is caused by radiation-associated ICD and that HMGB1 has
a vital influence on antigen-specific, T-cell-mediated tumour immunity. Previous
studies have reported that radiotherapy contributes to ICD, thus strengthening
the radiation-mediated tumouricidal effect [93]. Huang et al. [110]
reported that higher PD-1
In addition to the above-mentioned immune-related biomarkers for predicting
response to nCRT in RC, others that have received attention include CD133, COX-2,
CD56
The regulation of immunity is complex, with many researchers investigating the connection between circulating bio-macromolecules and the immune system. Once validated, serum biomarkers could be more applicable clinically than biopsy biomarkers due to their non-invasive characteristics.
A prospective study analysed 9 biomarkers (25-OH-vitamin D, osteopontin, CA IX,
IL-6, IL-8, CRP, LDH, CA19-9 and CEA) of RC patients who underwent CRT. The
authors found that IL-8 (OR 0.94, p = 0.036) and CEA (OR= 0.97,
p = 0.029) were significant predictors of response [101]. The levels of
C-C motif chemokine ligand-5, TNF-
Many blood-based cellular and secreted bio-macromolecules have been studied over the past few years thanks to technical advances in the minimally invasive method of liquid biopsy. Several of these molecules have been reported as biomarkers that provide real-time and comprehensive information on tumour diagnosis, staging, progression, and even on the tumour micro- and macro-environment [119]. These biomarkers could also be used to predict the clinical response to specific therapies, therapy-related side-effects, and prognosis, thus improving the decision-making process [119]. Importantly, blood samples can be readily obtained before, during, and after nCRT. Additionally, the assessment of tumour biomarkers is not disturbed by the process of blood collecting. Therefore, haematological markers of therapeutic response and prognosis are now widely studied in clinical oncology.
Haemoglobin is a kind protein responsible for carrying oxygen in higher
organisms. The role of hemoglobin in predicting response of certain therapeutic
strategies has been widely investigated. McGrane et al. [120] analysed
blood samples from 273 patients with RC and treated with nCRT. They found that a
hemoglobin level of
Lymphocytes are extremely sensitive to radiation. Radiation therapy therefore
leads to exhaustion of lymphocytes in the hematopoietic system, with radiation
doses of
Circulating tumour cells (CTCs) are released into the bloodstream by primary
tumours which then could metastasize to distant organ sites. Moreover, CTCs are a
minimally invasive and preferred alternative to tumour biopsy [14, 119]. The
clinical utility of CTCs in RC has been widely investigated. Most studies have
confirmed that a high level of CTC counts correlates with poor prognosis [119].
When integrated with tumour characteristics, CTC counts could be used as a
substitute for primary tumour cells. Previous research demonstrated that
cytokeratin 20-positive CTCs were predictors of the response to nCRT in RC
patients [129]. Troncarelli et al. [47] reported that TS expression was
completely absent in CTCs from patients with a pCR (p = 0.001). In
contrast, CTCs from 83% of non-responders expressed TS (p
It has been hypothesized that cell-free DNA (cfDNA) results from cell lysis caused by apoptosis or necrosis of cells [14]. In a study of 34 RC patients, Sun et al. [130] analysed cfDNA for the methylation status of the O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter region and to screen for KRAS mutations. They concluded that MGMT promoter methylation status, the 400-/100-bp DNA ratio, and the 400-base pair DNA concentration in the baseline cfDNA were helpful for predicting the response to nCRT. Schou et al. [131] analysed cfDNA in plasma samples of RC patients treated with nCRT and surgery. These authors concluded that cfDNA had the potential to improve pre- and post-nCRT risk assessment and thus promote the development of personalized therapy in RC.
Circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) represents 0.01%–10% of the total cfDNA and has become a promising biomarker in various types of cancers [118]. Numerous studies have shown the value of ctDNA genomic alterations or ctDNA concentrations in tumour diagnosis, monitoring of treatment response and of resistance, selection of targeted therapy, and the detection of residual disease [119, 132, 133].
A Japanese study investigated the clinical utility of ctDNA to predict nCRT
responses and post-operative recurrence in RC patients. ctDNA levels at baseline
and after nCRT were found to be significantly different (p = 0.0003).
The authors concluded that the change in ctDNA was independently associated with
pCR (p = 0.0276) [132]. A prospective multicentre Chinese trial further
explored the value of ctDNA for monitoring tumour burden, predicting nCRT
response, and predicting survival. Zhou et al. [134] found that baseline
ctDNA levels were strongly associated with positive nCRT responses and that MFS
was closely related to the median variant allele frequency (VAF) of mutations in
the baseline ctDNA (HR 1.27, p
Computed tomography (CT) is extremely important for diagnosing and staging
cancers and for evaluating the efficacy of certain therapeutic strategies. Over
the past few years, researchers have been exploring the role of CT imaging in
determining the prognosis of RC and for predicting the response to nCRT. A
retrospective study (n = 95) analysed the texture features of pre-nCRT CT images,
including standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis, uniformity and entropy. Chee
et al. [135] concluded that features of homogeneous textures were
associated with better nCRT responses. Other studies have also suggested that
kurtosis and fractal dimension (FD) are potential CT-derived biomarkers for
predicting nCRT responses [136, 137]. Perfusion CT imaging was also investigated
in a prospective study of RC treated with nCRT. The results showed that hot-spot
blood volume and a decline in hot-spot permeability were significant predictors
of pCR outcome (p
F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography
(18F-FDG-PET/CT) is a helpful imaging tool used extensively in clinical oncology
for disease diagnosis, staging, evaluation of therapeutic efficacy, diagnosis of
relapse, identification of the underlying lesion, and long-term follow-up.
Researchers have explored FDG-PET/CT-derived imaging markers for predicting the
response of RC patients to nCRT by studying pre- and post-CRT radiological
characteristics and correlating them with the response to nCRT. The most
challenging aspect was to choose the best parameter for semi-quantitative
analysis to assess response so that it could be used as a predictive biomarker.
Previous studies in patients with RC have shown that changes in the standard
uptake value (
Using baseline FDG-PET/CT and metric learning (ML), Wu et al. [143] built a novel artificial intelligence (AI) model to predict the response to nCRT in 236 newly diagnosed RC patients. ML determines the dissimilarity or similarity between objects in an AI-mediated manner based on a distance metric. The authors found that the model had a preferable accuracy, specificity and sensitivity in predicting therapeutic response of nCRT. Using the AI-mediated ML model, baseline FDG-PET/CT images were concluded to be robust biomarkers for predicting nCRT responses in RC. The AI-based ML model is non-invasive and may allow significant progress in personalized, precision therapy.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is also a helpful imaging tool used extensively in clinical oncology which has several desirable characteristics, particularly its exceptional resolution and contrast definition between the lesions and surrounding tissues. These have contributed to wide application of MRI in the disease setting, including the evaluation of response to nCRT in RC [55, 144]. Although the alterations in tumour morphology occur later than other changes at the molecular and biological levels, MRI can still accurately assess tumour characteristics. The potential role of MRI in predicting response to nCRT in RC has been thoroughly investigated.
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) has been employed extensively to obtain functional imaging. This can in turn be used to provide useful information on vascular and tissue permeability. Kim et al. [145] reported that a decrease in the tumour perfusion parameter (Ktrans) was significantly associated with good response to nCRT in RC (p = 0.0007). In contrast, none of the other parameters examined were effective at predicting the efficacy of nCRT [145]. Ciolina et al. [146] confirmed that pre-Ktrans predicted response to therapy, while wash-out and Kep measured before nCRT correlated with RC grading.
Diffusion-weighted MRI (DW-MRI) detects water proton mobility in tissues to
provide information on microscopic structures. This technique has also been
applied to monitor treatment and to predict nCRT response in RC. The apparent
diffusion coefficient (ADC) in DW-MRI is a useful instrument for quantitative
analysis owing to its various characteristics, including cellularity, tumour
proliferation, tumour necrosis, tumour grade, extracellular space tortuosity and
tissue organization [55]. However, the use of ADC as a predictive biomarker of
nCRT response has been controversial, as discussed elsewhere [55, 144]. A
prospective study showed that texture features of RC on T2-weighted (T2w)
magnetic resonance images were potential imaging biomarkers for the clinical
outcome of nCRT. The authors found that pre-treatment medium texture-scale
quantified as kurtosis, mid-treatment kurtosis without filtration, and changes of
kurtosis in the pre-treatment and mid-treatment images differed significantly
between the PR+NR and pCR patient groups (p = 0.045, 0.038, and 0.01,
respectively). In particular, the ROC value in pre-treatment kurtosis was
significantly higher than all other parameters (0.907, p
Recently, a multivariable model incorporating mrT stage and quantitative parameters from baseline MRI, including T2w volume and T2w signal entropy, was used to distinguish responders from non-responders prior to nCRT in RC [149]. The combination of T2-weighted MRI volumetry, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), and 18F-FDG PET/CT obtained before CRT and before surgery was useful for predicting therapeutic results in RC [150]. Furthermore, quantitative imaging outperformed molecular markers for the prediction of response to nCRT. These findings may help physicians in selecting the most appropriate patients for organ preservation in RC cases.
Radiomics, which converts digital images into quantitative data, is based on the concept that radiological images are comprised of data that reflects underlying pathophysiology. Advances in science and technology have allowed the extraction of large amounts of quantitative data from tomographic images (CT, MR or PET images). The end goal of radiomics is to generate imaging biomarkers as decision support tools for clinical practice [151]. The implementation of radiomics has progressed rapidly as our understanding of tumour biology has improved. This has in turn contributed to the introduction of precision medicine. Recently, several studies evaluated the potential role of radiomics as a biomarker for predicting tumour responses in RC.
One study explored the clinical and pre-nCRT multi-parameter MRI features of 186 RC patients in order to develop and validate a radiomics model for predicting therapeutic response. Cui et al. [152] concluded that their pre-treatment radiomics-based model was of great value for predicting pCR and could potentially guide the selection of patients for a “watch-and-wait” policy. Another study showed that MRI and FDG-PET radiomics features could serve as potential biomarkers. A logistic regression model comprised of six second-order texture features (one from T2w MRI: T2w correlation and five from PET: metabolic volume, glycolytic volume, PET 10th percentile, PET homogeneity, PET contrast) gave the best results for predicting nCRT responses in RC patients (AUC = 0.86) [153]. By comprehensively analysing pre- and post-nCRT MRI data, Liu et al. [154] developed a radiomics model that showed excellent performance and could be employed as a non-invasive and individualized tool to predict cases of pCR in patients treated with nCRT. An international multicentre study of RC patients who underwent nCRT and total mesorectal excision showed that pre-treatment, MRI-based radiomics of RC and/or the characteristics of the surrounding mesorectal compartment were able to predict TRG, the neoadjuvant rectal (NAR) score, and pCR. Both the mesorectal compartment and tumour provided useful and authentic information on therapeutic response and prognosis [155]. More recently, elevated heterogeneity in skewness maps of baseline tumours in T2w-based radiomics has been shown to correlate with nCRT responses [156].
Variation in the collection and analysis of imaging data has impeded the clinical use of imaging biomarkers. Hence, standard and independent software is urgently needed to acquire original data and to further analyse the post-processing data. The primary obstacles with regard to radiomics are the optimal collection and combination of diverse multimodal data sources in a quantitative fashion, the variety of radiomic features, unbalanced datasets, and having few observations. Moreover, the study populations are usually small and limited to single institutions, and the reproducibility of techniques has seldom been investigated. Consequently, the usefulness of the above imaging biomarkers requires further validation and larger prospective studies are warranted before applying these biomarkers as predictive factors in clinical trials.
The microbiome is a complicated ecosystem that includes viruses, protozoa,
fungi, bacteria and other microbes within the body. The disequilibrium of
commensal microbes is thought to contribute to the genesis of cancers and has
also been linked to treatment response and survival of different cancer types
[157]. For example, a high level of Fusobacterium nucleatum was found to
be associated with mutational characteristics in colorectal cancer [158]. Serna
et al. [159] reported that pre-nCRT F. nucleatum levels were
not reliable for predicting a pCR to nCRT, but the persistence of F.
nucleatum post-nCRT was associated with a high relapse rate in RC. Jang
et al. [160] further explored the predictive value of the gut microbiome
for response to preoperative nCRT. These authors found a significant difference
in
Recently, a prospective study explored the value of the gut microbiome for predicting the nCRT response. Yi et al. [162] reported that nCRT was associated with significant alterations in the microbiome, including a large increase in Streptococcus spp. and Lactobacillus and a decrease in pathogens associated with RC. They also found the microbiota of baseline samples varied between non-responders and responders. In the responders, Anaerostipes, Dorea and Roseburia, which contribute to the production of butyrate, were overrepresented, whereas non-responders were rich in Fusobacterium and Coriobacteriaceae. The relationship between intestinal microbiota and radiotherapy warrants further investigation of a possible role for the microbiome in predicting the therapeutic efficacy of nCRT, and to evaluate the possibility of modifying the gut microbiome before nCRT. The transplantation of fecal microbiota to improve therapeutic efficacy should also be further investigated.
The identification and validation of specific and sensitive molecular biomarkers to select patients who may obtain a clinical benefit from nCRT is a research-intensive process. Although previous studies have shown some progress with the discovery of many potentially interesting biomarkers, several limitations still exist. First, clinical variations in the radiation dose, in the interval between nCRT and surgery, in the chemotherapy regimen used, and in the evaluation criteria may lead to different results between studies. Second, the majority of previous studies evaluated only one type of biomarker (e.g., gene alteration, RNA, protein) and did not use a holistic approach. Moreover, the lack of validation studies of potential biomarkers requires further large-scale prospective studies. Although most RC patients routinely receive nCRT as the main therapeutic strategy, they do not gain equal benefit from this treatment. Robust and confirmed predictive biomarkers should help to select RC patients who benefit the most from nCRT, thus ensuring the best and most appropriate treatment for each patient. Taking a “watch and wait” strategy could avoid high-morbidity surgery, prolong the surgery interval, and avoid the unnecessary side-effects of ineffective chemoradiotherapy. Further exploration of predictive biomarkers is necessary to identify new chemo-radiosensitizing targets and to provide further evidence in support of combined radiation-based therapy and immunotherapy.
RC, rectal cancer; nCRT, neoadjuvant chemoradiotherap; CRC, Colorectal cancer;
TME, total mesorectal excision; pCR, pathologic complete response; DFS,
disease-free survival; OS, overall survival; TRGs, tumor regression grading
systems; MSKCC, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center; DNA, Deoxyribonucleic
acid; aCGH, array Comparative Genomic Hybridization; CNAs, chromosomal copy
number alterations; CRT, chemoradiotherap; CRBP1, cellular retinol-binding protein
1; SNPs, Single-nucleotide polymorphisms; TS, thymidylate synthase; pCRT,
preoperative chemoradiotherap; XRCC1, X-ray cross-complementing group 1; RR,
relative risk; OR, odds ratio; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; CR,
complete response; PFS, progression-free survival; FPR1, formyl peptide receptor
1; AUC, area under the curve; mRNA, messenger RNA; TERT, telomerase reverse
transcriptase; CTCs, circulating tumor cells; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth
factor; RT-PCR, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction; AJCC/UICC,
American Joint Commission on Cancer/International Union Against Cancer; 5-FU,
5-fluorouracil; ERCC1, excision repair cross-complementing group 1; IHC,
immunohistochemistry; CCR6, C-C motif chemokine receptor 6; CHD4, chromodomain
helicase DNA-binding protein 4; CISH, chromogenic in-situ hybridization; COASY,
CoA Synthase; RT-qPCR, real time quantitative- polymerase chain reaction; miRNAs,
microRNAs; lncRNA, long noncoding RNA; XRCC2, X-ray repair cross-complementing
protein 2; ERCC1, excision repair cross-complementing group 1; ATM, ataxia
telangiectasia mutated; MRE11, meiotic recombination 11 homolog A; PCNA,
proliferating cell nuclear antigen; FGFR4, fibroblast growth factor receptor 4;
CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; CA19-9, carbohydrate antigen 19-9; FOLFOX,
5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin; CLCA1, chloride channel accessory 1;
TACC 3, transforming acidic coiled-coil protein-3; BMI1, B-cell-specific Moloney
murine leukemia virus insertion site 1; VSTM2L, V-set and transmembrane domain
containing 2 like; CXCR4, CXC chemokine receptor 4; SGK1, serum and
glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1; DAMPs, damage associated molecular patterns;
TAAS, tumour-associated antigens; TAM, tumor-associated macrophages; TILs,
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes; PD-L1, programmed death ligand-1; HMGB1, high
mobility group box protein 1; ICD, immunogenic cell death; CD8, cluster of
differentiation 8; CD4, cluster of differentiation 4; FOLFOX, 5-fluorouracil,
leucovorin, and oxaliplatin; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; TCR, T-cell
receptor; mrTRG, magnetic resonance tumor regression grade; IL-8, interleukin-8;
IL-6, interleukin-6; Scd40l, soluble CD40-ligand; CCL-5, chemokine ligand-5; LCR,
lymphocyte-to-C-reactive protein ratio; N
ZL (Zhaojun Li) and ZL (Zhengyin Liao) contributed to the conception and idea of this article. YC, BY and MC contributed to the literature search. YC and BY wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
The authors would like to thank MC for kind help.
This study received funding from the PostDoctor Research Project, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (2021HXBH023), the Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province of China (21YYJC2782), and Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province (821QN394).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.