1 University of Medicine and Pharmacy “Carol Davila”, 020021 Bucharest, Romania
2 National Teaching Center for Children’s Neurorehabilitation “Dr. Nicolae Robanescu”, 041408 Bucharest, Romania
3 Teaching Emergency Hospital “Bagdasar-Arseni”, 041915 Bucharest, Romania
4 Clinical Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology “Filantropia”, 011132 Bucharest, Romania
†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: Amedeo Amedei
Abstract
Introduction: Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a progressive
neurological disease with autosomal recessive transmission that affects motor
neurons, causing their loss and resulting in muscle waste and motor deficiency.
Nusinersen, the first SMN2 pre-mRNA targeted therapy approved by the Food and
Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency, has demonstrated high
efficacy in improving motor function, as well as respiratory and nutritional
statuses. Materials and Methods: We observed 55 patients
(children/adolescents) diagnosed with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), who received
nusinersen therapy. To investigate the benefits of physical therapy on
rehabilitation outcomes, we compared the motor evolution of patients who received
nusinersen and performed daily physical therapy (study group) to those of the
control group, who received only nusinersen therapy. Results: Motor
skill improvements were statistically significantly (p
Keywords
- spinal muscular atrophy
- nusinersen
- physical therapy
- neuromuscular disorder
- motor functioning
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a neurodegenerative progressive disease [1] with autosomal recessive inheritance [2]. It affects motor neurons [3] in the anterior medullar horn and brainstem, thus contributing to their apoptosis, leading to muscle waste [4]. The consequent motor deficiencies are predominantly axial as well as involving the shoulder and pelvic girdles. It is the second most common genetic disease after cystic fibrosis [5] and it is also known to be a leading cause of infant mortality [6].
The disease substrate is the insufficient level of “Survival Motor Neuron” (SMN) protein [7], caused by the presence of homozygous [8] or compound heterozygous deletions or deleterious point mutations in the SMN1 gene [9]. This gene encodes approximately 90% [10] of the total SMN protein. The SMN2 gene is very similar to SMN1 [11] and differs from it only by two bases in exon 7 [12]. As a result of this difference, SMN2 only encodes 10% [13] of the functional SMN protein.
SMA can be functionally classified into five types [14] based on the age of onset and the achieved motor milestones: 0, I, II, III, and IV [15].
Type 0 [16] has an onset before birth and survival is less than 6 months. It’s considered the most rare form of SMA (accounting for less than 1% of all cases) and manifests itself during pregnancy and is defined by the absence of fetal movements. Children with this disease are never able to sit or control their heads and they have significant muscle weakness and hypotonia as well as facial diplegia, contractures, a lack of responsiveness to stimuli, dysphagia and breathing insufficiency. The presence of congenital heart abnormalities is also common in a high majority of these patients. Death occurs before the age of six months, and in some cases, it occurs within the first few weeks of life [17, 18].
Type I (also called Werdnig-Hoffmann disease [19]) occurs during early infancy (before the age of 6 months) [20], being the most frequent type of SMA (almost 60% of all the cases) [21, 22]. The disease is also called SMA with infantile onset. This group of patients is very hypotonic, with predominantly proximal muscle weakness, weak cry, breathing insufficiency or abdominal breathing, difficulties in suckling or swallowing, tongue fasciculations and a high risk of aspiration pneumonia; these patients never acquire sitting, and in the absence of assisted ventilation, they die within the first two years of life due to breathing insufficiency [17, 18, 23].
Type II (Dubowitz disease [19]) has an onset after 6 months of age [15] and represents approximately 30% of all SMA patients [24]. Patients gain the ability to sit, but they never achieve orthostatic posture nor are they able to walk unassisted. Proximal muscular weakness, swallowing difficulty, tongue fasciculations, and respiratory insufficiency are more common in this group [18]. In most cases, the face and ocular muscles are not engaged. The life expectancy is increased as compared to patients who have type 0 or type I SMA, because these patients can live to maturity without treatment [23].
Type III, also called Kugelberg-Welander disease [19], can be observed after the first year of life, sometimes even in adolescence, and progresses in a varied manner. Some individuals have been wheelchair-bound since childhood, while others may walk independently until adulthood. All patients learn to walk, but proximal muscle weakness, which predominantly affects the lower limbs, causes frequent falls and makes it difficult to climb stairs, eventually leading to loss of ambulation [17]. These patients’ life expectancy is normal [23]. Type IV occurs in adulthood, usually beyond the age of 30. Patients are able to mantain their mobility throughout their lives. Their life expectancy is considered normal [17, 23].
A systematic review of the SMA symptoms in children is shown in Table 1 (Ref. [16, 17, 18, 23, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29]).
| SMA 0 [16, 17, 18] | SMA I [25, 26, 27] | SMA II [17, 23] | SMA III [23, 27, 28] |
| reduced fetal movements | generalized hypotonia, but more severe axially | generalized hypotonia, but more severe axially | proximal motor deficit |
| severe generalized hypotonia | muscle weakness | muscle weakness | frequent falls |
| contractures | “Floppy infant” aspect | sitting position possible, but generating chest deformities and scoliosis due to hypotonia | difficulty in climbing stairs |
| facial palsy | motor impairment: not able to sit, sometimes absence of head control | motor impairment: not able to walk independently, even though they might stand or walk with assistance | Gowers’ sign [29] present |
| swallowing disorder | in evolution, contractures might appear | in evolution, contractures might appear | gradual ambulation loss |
| respiratory failure | weak cry | in evolution, may present swallowing difficulties | tongue fasciculations |
| facial palsy | paradoxical breathing and hypoventilation | in evolution, may present ventilation difficulties | deep tendon areflexia |
| congenital heart disease | inefficient cough | in evolution, inefficient cough | normal life expectancy |
| deep tendon areflexia | swallowing difficulties | tongue fasciculations | |
| death before 6 months | tongue fasciculations | deep tendon areflexia | |
| deep tendon areflexia | death in adulthood | ||
| death before 2 years |
There are currently three therapies approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [30] and the European Medicine Agency (EMA) [31]. These three promising therapies consist of either targeting of SMN2 gene pre-m-RNA (nusinersen [32] and risdiplam [33]) or gene therapy (GT) using an AAV-modified healthy SMN1 gene [34].
Nusinersen [35] is the first SMN2 pre-mRNA targeted therapy approved (December 2016 in the United States of America and May 2017 in Europe) [36, 37]. It consists of modified antisense oligonucleotides [38] targeted to bind to the intronic splice silencer located on intron 7 of SMN-2 pre-messenger RNA. This in turn promotes exon 7 inclusion at the SMN2 messenger RNA level [35]. Thus, a complete and functional SMN protein is obtained. Nusinersen is given to patients of all ages via intrathecal administration, with the first four loading doses given in the first two months of treatment, followed by one injection every four months for life [39, 40].
Nusinersen demonstrated a high level of efficacy in improving motor function [41, 42]. Several studies have shown that nusinersen improves patients’ respiratory [43] and nutritional [43] statuses. Hospitalization time was reduced with no severe specific adverse reactions post-administration. Rare possible adverse reactions are mainly those associated with lumbar punctures (i.e., headache, vomiting, fever, low back pain, etc.) [40, 44].
For a better outcome, it is mandatory to administer as soon as possible [45] — ideally prior to the onset of symptoms, any of the 3 approved modifying disease drugs–nusinersen [46], onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi [47] or risdiplam [48]. Besides these treatments, it is critical to follow correct and comprehensive standards of care [49, 50], one of them being physical therapy (PT) [21, 51].
One of the SMA PT goals is to maintain a proper posture [52] and to improve motor functionality. Trunk and limb orthoses, as well as other advanced assistive-rehabilitative devices, such as mobile/mechatronic apparatuses [53] for increasing independence, may be beneficial depending on the individual patient’s requirements.
Maintaining the range of motion [54] and increasing muscle strength [27] are necessary for achieving better mobility [51] and functionality as it can be objectified on the Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale Extended (HFMSE) [55, 56]. Walking assistance and other activities of daily living should be encouraged for these patients, to improve their quality of life [57, 58, 59].
The abstract of a preliminary version of this study, with a less thorough approach, was presented at the National Congress of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine and Balneology in 2020 [60].
This study aims to objectify better outcome in SMA patients that receive nusinersen treatment and physical therapy.
We included in this retrospective observational study 55 SMA patients (29 females and 26 males), aged 0–17 years: 20 type I, 26 type II and 9 type III patients.
All patients were diagnosed by paediatric neurologists and treated by the multidisciplinary team from the National Teaching Center for Children’s Neuro-psychomotor rehabilitation “Dr. Nicolae Robanescu” (NTCCNNR). SMA diagnosis was completed by genetic lab tests that confirmed exon 7 (+/-exon 8) homozygous deletion and the presence of 2 copies of SMN2 for patients with types I and II, and 3 copies of SMN2 for type III SMA patients.
All patients’ parents signed the informed consent and the study has been approved by the local committee of ethics from NTCCNNR (Registration No 5028/06.03.2021).
For uniformity in care, all patients/parents were informed about the standards of care and have been taught how to apply them correctly, being thoroughly observed in this matter.
Unfortunately, not all of them could benefit from daily PT, due to their home locations, far from any facility or professional health care. Therefore, we could divide all 55 patients into 2 groups: those who received daily PT in addition to nusinersen treatment (named PT-N group) and those who received only nusinersen, with PT less than 1 session/week, PT (N group). There were thus 39 patients (20 females and 19 males) in the PT-N group and 16 patients (9 females and 7 males) in the N group.
Inclusion Criteria (for the PT-N group):
SMA genetic confirmation of SMN1 gene homozygous deletion;
Symptomatic SMA type I, II, or III;
Nusinersen initiated in our clinic (thus all tests were performed by the same physical therapists, for uniformity in evaluation);
PT at least 5 times per week.
Exclusion Criteria (patients thus included in N group):
PT less than 1 session/week;
Patients who had spine surgery and needed a prolonged bed-side period.
The patients were evaluated by licensed physical therapists with pediatric SMA experience. The assessment was performed between October 2018 and June 2021 at the NTCCNNR. The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Infant Test of Neuromuscular Disorders - CHOP INTEND [61] was performed in SMA type I patients, while HFMSE [55, 56] in type II and III patients. The evaluations were carried out prior to starting nusinersen, six months after initiation, and one year after initiation, respectively.
Our working hypothesis was that PT-N group patients have better results in CHOP and HFMSE score than N group patients.
Statistical calculations were performed using Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) for preparing the data and SPSS 24.0 version for Windows (IBM Inc., Chicago, USA) for the analysis itself. We applied t test after checking data normality distribution with the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test (KS) [62, 63, 64]. The Paired-Samples T-test [63, 65, 66] and Mann–Whitney Test [67] were used to assess differences within and between groups, respectively, effect size. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant and the confidence level was 95%, with related intervals afferent to the respective calculated averages [68, 69].
According to SMA type, the percent yields for the evolution of the CHOP/HFMSE scores were calculated. The percent yield is the ratio of the actual yield (the actual improvement in motor development after PT) to the theoretical yield (the maximum possible value of motor development), multiplied by 100. Therefore, T1 compares the initial scores (before starting nusinersen) to the ones obtained 6 months later (from nusinersen initiation) and T2 compares the initial scores to those achieved 12 months after nusinersen initiation in both groups.
Patients with SMA types I and II had 2 copies of SMN2, while those with type III had 3 copies.
The evolution of motor function for the two groups (PT-N group and N group, respectively) is shown in Fig. 1 (we used CHOP for type I patients and HFMSE for type II and type III patients):
The calculated yield for CHOP/HFMSE score evolution after T1 is shown in Table 2.
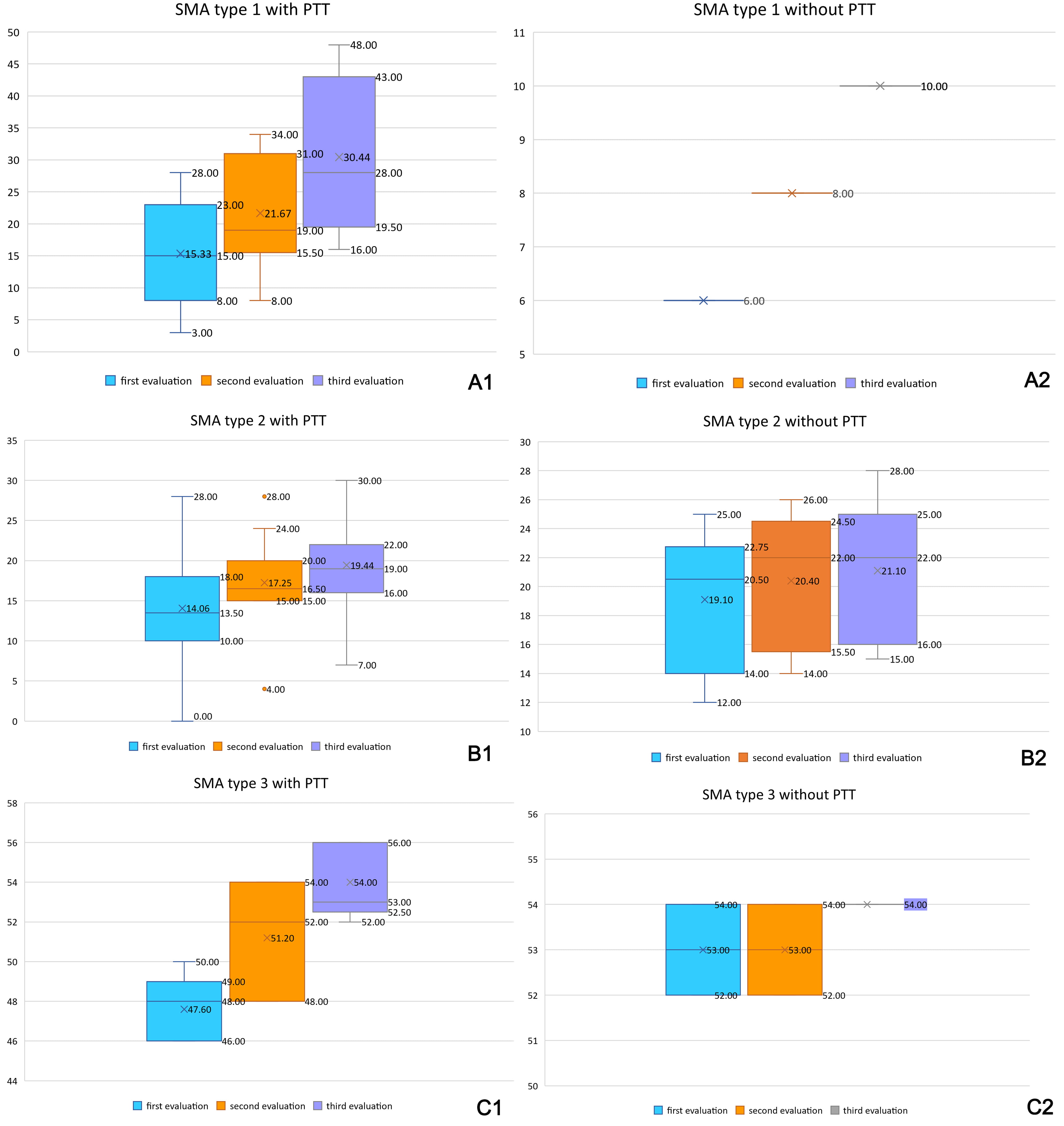 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Motor function evolution during treatment, for SMA type I, II, and III, for PT-N and N groups. Legend: ■, first evaluation; ■, second evaluation; ■, third evaluation. A1, PT-N group, SMA type I; A2, N group SMA type I; B1, PT-N group, SMA type II; B2, N group SMA type II; C1, PT-N group, SMA type III; C2, N group SMA type III.
| yield 1 (T1–T0) | PT-N group | N group | ||||||
| N | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | N | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | |
| SMA type I CHOP | 18 | 13.62% | 4.17% | 21.05% | 2 | 3.45% | 3.45% | 3.45% |
| SMA type II HFMSE | 16 | 5.86% | 0.00% | 10.53% | 10 | 2.81% | 0.00% | 4.55% |
| SMA type III HFMSE | 5 | 19.83% | 10.00% | 33.33% | 4 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| Legend: Yield represents the ratio of the actual improvement in motor
development, in a selected period, to the theoretical yield, quantified by the
difference between two consecutive evaluations (yield 1 represents the difference
between T1 and T0 motor score evaluations).
T0, first evaluation, right before nusinersen intiation; T1, second evaluation, six months after nusinersen initiation. | ||||||||
At T1, for the PT-N group: CHOP yield for SMA type I patients was between 4.17% and 21.05%, mean value 13.62%, HFMSE for SMA type II was between 0 and 10.53%, mean value 5.86%, while HFMSE for SMA type III patients was between 10% and 33.33%, mean value 19.83%. For the N group: CHOP yield for SMA type I patients was 3.45%, HFMSE for SMA type II was between 0 and 4.55%, mean value 2.81%, while HFMSE for SMA type III patients was 0.00%. The evolution of scores for the two groups (PT-N group and, respectively, N group) after T2 is shown in Table 3.
| yield 2 (T2–T0) | PT-N group | N group | ||||||
| N | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | N | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | |
| SMA type I CHOP | 18 | 33.22% | 15.38% | 55.56% | 2 | 6.90% | 6.90% | 6.90% |
| SMA type II HFMSE | 16 | 10.16% | 5.26% | 12.96% | 10 | 4.35% | 0.00% | 7.41% |
| SMA type III HFMSE | 5 | 34.28% | 12.50% | 44.44% | 4 | 7.15% | 0.00% | 14.29% |
| Legend: Yield represents the ratio of the actual improvement in motor
development, in a selected period, to the theoretical yield, quantified by the
difference between two consecutive evaluations (yield 2 represents the difference
between T2 and T0 motor score evaluations).
T0, first evaluation, right before nusinersen intiation; T2, third evaluation, twelve months after nusinersen initiation. | ||||||||
At T2, for the PT-N group: CHOP yield for SMA type I patients was between 15.38% and 55.56%, mean value 33.22%, HFMSE for SMA type II was between 5.26 and 12.96%, mean value 10.16%, while HFMSE for SMA type III patients was between 12.5% and 44.44%, mean value 34.28%. For the N group: CHOP yield for SMA type I patients was 6.90%, HFMSE for SMA type II was between 0 and 7.41%, mean value 4.35%, while HFMSE for SMA type III patients was between 0 and 14.29%, mean value 7.15%.
As shown in the tables above, we obtained higher yields for SMA type I patients, evaluated using CHOP, than for SMA type II patients, for whom HFMSE was performed.
At the same time, we observed that the PT-N group yields were significantly higher than those obtained in the N group, as shown in Fig. 2 (we used CHOP for type I patients and HFMSE for type II and type III patients).
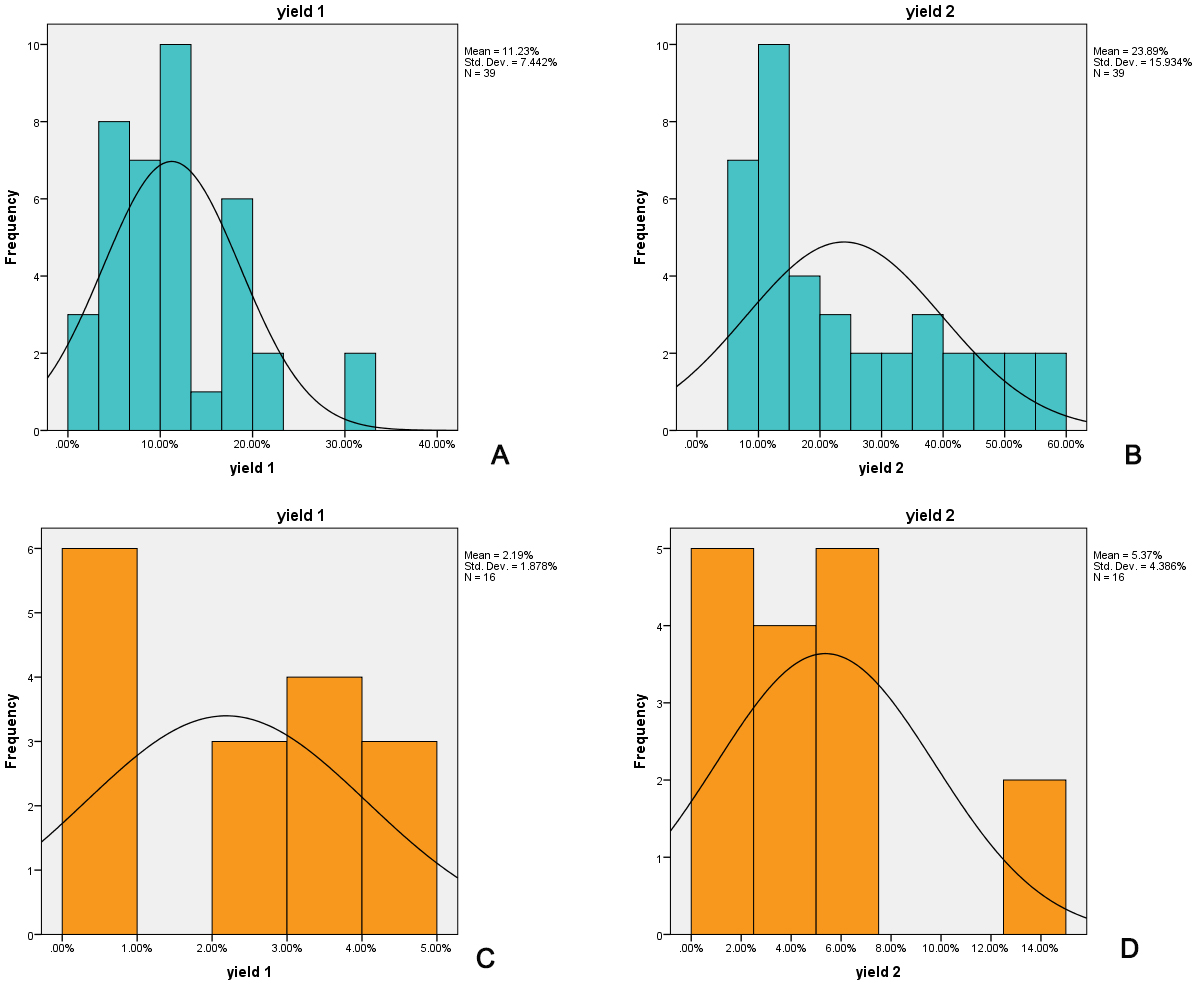 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Yield frequency distribution in PT-N group (A–after T1, B–after T2) and in N group (C–after T1, D–after T2). Legend: yield 1 (after T1) and yield 2 (after T2) for ■ PT-N group and ■ N group.
In order to compare the means of both assessments of the same patients, we used the Paired-Samples T-test. This was possible as the data “normality” condition was satisfied, Kolmogorov–Smirnov producing asymptotic significances higher than 0.2.
At 6 months after nusinersen initiation, the calculated yield for the PT-N group
was 11.23
| Paired Samples Statistics | |||||
| Mean | N | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | ||
| Pair 1 | yield 1 | 11.23% | 39 | 7.44% | 1.19% |
| yield 2 | 23.89% | 39 | 15.93% | 2.55% | |
| Legend: Yield represents the ratio of the actual improvement in motor
development, in a selected period, to the theoretical yield, quantified by the
difference between two consecutive evaluations (yield 1 represents the difference
between T1 and T0 motor score evaluations, yield 2 represents the difference
between T2 and T0 motor score evaluations).
T0, first evaluation, right before nusinersen intiation; T1, second evaluation, six months after nusinersen initiation; T2, third evaluation, twelve months after nusinersen initiation. | |||||
| Paired Samples Correlations | ||||
| N | Correlation | Sig. | ||
| Pair 1 | yield 1 & yield 2 | 39 | 0.802 | 0.000 |
| Legend: Yield represents the ratio of the actual improvement in motor
development, in a selected period, to the theoretical yield, quantified by the
difference between two consecutive evaluations (yield 1 represents the difference
between T1 and T0 motor score evaluations, yield 2 represents the difference
between T2 and T0 motor score evaluations).
T0, first evaluation, right before nusinersen intiation; T1, second evaluation, six months after nusinersen initiation; T2, third evaluation, twelve months after nusinersen initiation. | ||||
Based on the means of the two yields and the t-value direction (Table 6), we can
conclude that there is a statistically significant (p
| Paired Samples Test | |||||||||
| Paired Differences | t | df | Sig. (2-tailed) | ||||||
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference | ||||||
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Pair 1 | yield 1 & yield 2 | –12.66% | 10.91% | 1.75% | –16.20% | –9.12% | –7.25 | 38 | 0.000 |
| Legend: Yield represents the ratio of the actual improvement in motor
development, in a selected period, to the theoretical yield, quantified by the
difference between two consecutive evaluations (yield 1 represents the difference
between T1 and T0 motor score evaluations, yield 2 represents the difference
between T2 and T0 motor score evaluations).
T0, first evaluation, right before nusinersen intiation; T1, second evaluation, six months after nusinersen initiation; T2, third evaluation, twelve months after nusinersen initiation. t (38) = –7.25; p | |||||||||
At 6 months after nusinersen initiation, the calculated yield for N group was
2.19
| Paired Samples Statistics | |||||
| Mean | N | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | ||
| Pair 1 | yield 1 | 2.19% | 16 | 1.88% | 0.47% |
| yield 2 | 5.37% | 16 | 4.39% | 1.10% | |
| Legend: Yield represents the ratio of the actual improvement in motor
development, in a selected period, to the theoretical yield, quantified by the
difference between two consecutive evaluations (yield 1 represents the difference
between T1 and T0 motor score evaluations, yield 2 represents the difference
between T2 and T0 motor score evaluations).
T0, first evaluation, right before nusinersen intiation; T1, second evaluation, six months after nusinersen initiation; T2, third evaluation, twelve months after nusinersen initiation. | |||||
| Paired Samples Correlations | ||||
| N | Correlation | Sig. | ||
| Pair 1 | yield 1 & yield 2 | 16 | 0.024 | 0.929 |
| Legend: Yield represents the ratio of the actual improvement in motor development, in a selected period, to the theoretical yield, quantified by the difference between two consecutive evaluations (yield 1 represents the difference between T1 and T0 motor score evaluations, yield 2 represents the difference between T2 and T0 motor score evaluations). T0, first evaluation, right before nusinersen intiation; T1, second evaluation, six months after nusinersen initiation; T2, third evaluation, twelve months after nusinersen initiation. | ||||
Due to the means of the two yields and the direction of the t-value (Table 9),
we can conclude that there was a statistically significant improvement in the
health condition of N group patients at 12 months after nusinersen initiation,
from 2.19
| Paired Samples Test | |||||||||
| Paired Differences | t | df | Sig. (2-tailed) | ||||||
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference | ||||||
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Pair 1 | yield 1 & yield 2 | –3.18% | 4.73% | 1.18% | –5.70% | –0.66% | –2.70 | 15 | 0.017 |
| Legend: Yield represents the ratio of the actual improvement in motor
development, in a selected period, to the theoretical yield, quantified by the
difference between two consecutive evaluations (yield 1 represents the difference
between T1 and T0 motor score evaluations, yield 2 represents the difference
between T2 and T0 motor score evaluations).
T0, first evaluation, right before nusinersen intiation; T1, second evaluation, six months after nusinersen initiation; T2, third evaluation, twelve months after nusinersen initiation. t (15) = –3.18; p | |||||||||
Compared to the N group, patients in the PT-N group had statistically
significant (p
Further research is needed to explain the differences in the evolution of type I and type II patients in the PT-N group, as well as the reason why the first have greater improvements. At this moment, we assume it is due to motor neuron loss and chronic denervation in patients with type II that started treatment long after they were diagnosed (as a consequence of the lack of treatment until 2018 - in Romania). However, the human factor should be considered, too. It is obvious that, despite all our measures for uniformity in care, SMA type I patients benefit from more intervention tools and methods.
The limitation of our study consists in lack of SMN2 sequencing’s evaluation in each individual participant. This could provide greater insight into why some patients have a better outcome than others, despite the fact that they are all following the same standards of care.
Nusinersen has been shown to stabilize and improve motor status in children with SMA, slowing and even stopping the disease progression [70], as seen also in our study–patients had motor improvement. It is important to preserve the largest possible number of motor neurons, thus starting the treatment as soon as possible [45, 46, 71], in order to provide the best outcome.
However, the administration of nusinersen alone is not expected to provide the best outcome in symptomatic SMA patients. In addition to therapy, it is critical that the standards of care [50] be followed completely and correctly.
Correction of posture, reduced stiffness, increased range of motion and muscle strengthening are all benefits provided by PT methods, with better results for those who use them on a regular basis, as we discovered in our study. As patients can perform more movements, this obviously results in a better quality of life, proving that PT is an important tool in SMA treatment.
Therefore, we strongly encourage regular PT sessions (at least 5 times a week–depending on the general health status of the patient) for all SMA patients, especially those with sudden onset of disease and early treatment, as they have the greatest potential for better recovery, thus boosting rehabilitation of motor functions.
Nusinersen treatment proved to be efficient in SMA patients, as all treated patients improved their motor scores. It is well known that early treatment provides a better outcome [45, 46]. Nevertheless, in order to establish if a correlation between the genetic substrates of the patients that had a better evolution than the others exists, even if the same standards of care and treatment were applied, further studies should be considered to overcome actual limits (i.e., lack of SMN2 sequencing’s evaluation).
In order to achieve better motor results, we can conclude that physical therapy is strongly recommended. The use of nusinersen therapy, in conjunction with physical therapy, can result in a more favorable motor outcome.
Therefore, physical therapy, as part of the standards of care in SMA, should be recommended as one of the important and essential tools in SMA treatment.
All authors had specific but overall equal contributions in achieving this article. AM, ESS, CS, MCL, GO, LP and CD designed the research study. AM, CS, MCL, GO, LP and CD have been involved in the development of methodology. AM, CS, MCL and CD contributed to validation. AM, CS, MCL, GO, CD and VD analyzed the data. AM, MCL and LP have been involved in conducting a research and investigation process. AM, ESS, CS, MCL, GO, CD and VD provided research resources. AM, MCL and LP have been responsible for data curation. AM, ESS, CS, MCL, CD and VD made substantial contributions to original draft preparation. GO and LP provided help on review and editing. All authors contributed to visualization. AM, CS, MCL, GO, LP and CD supervised the entire study. AM administrated the project. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of National Teaching Center for Children’s Neurorehabilitation “Dr. Nicolae Robanescu” (protocol code 5028, date of approval 03/06/2021).
We thank our patients and their parents for the support and care. We bring gratitude to the entire multidisciplinary team from NTCCNNR, especially to the physical therapists that sustained our work by the periodic evaluations. Special thanks go to those who made possible our knowledge in SMA standards of care. Last, but not least, we thank our families for their unconditioned support.
This research received no external funding.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.


