1 Department of Ophthalmology, Shanghai General Hospital (Shanghai First People’s Hospital), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 200080 Shanghai, China
2 National Clinical Research Center for Eye Diseases, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Ocular Fundus Diseases, Shanghai Engineering Center for Visual Science and Photomedicine, Shanghai Engineering Center for Precise Diagnosis and Treatment of Eye Diseases, 200080 Shanghai, China
Academic Editors: Shikun He and Graham Pawelec
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the progression of neovascular remodeling and
subretinal fibrosis in neovascular age-related macular degeneration (NVAMD) after
anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy. Methods: Twenty
eyes from 20 patients with subretinal fibrosis complicating NVAMD were
retrospectively reviewed. All patients complied with at least three consecutive
monthly intravitreal treatments and final follow-up visit at 12 months after the
initial anti-VEGF treatment of aflibercept or ranibizumab. Using optical
coherence tomography angiography (OCTA), the central macular thickness (CMT),
microvascular density in the superficial capillary plexus (SCP), deep capillary
plexus (DCP), choroidal neovascularization (CNV) lesions, as well as subretinal
fibrotic lesions were compared between baseline and final visit.
Results: The mean number for anti-VEGF injections was 4.40
Keywords
- neovascular age-related macular degeneration
- choroidal neovascularization
- anti-VEGF
- neovascular remodeling
- subretinal fibrosis
Neovascular age-related macular degeneration (NVAMD), which represents late stage of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is the leading cause of irreversible vision loss and blindness in the elderly. The prevalence of AMD increases with age and approximately 30% of patients progress to late stage [1]. The estimated number of elders suffering with AMD worldwide is expected to more than double from 2.07 to 5.44 million by 2050 [2]. Currently, intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy has become the first-line therapy for the treatment of NVAMD, and this therapy has significant benefits for patients. However, some patients with NVAMD suffer from either incomplete response or are resistant to anti-VEGF therapy, and in these cases anti-VEGF treatment fails to prevent progressive vision loss. Thus, it is of great urgency to understand pathological changes during NVAMD progression that are linked to incomplete response to anti-VEGF therapy, and to develop additive, or alternative treatments, for NVAMD to protect visual function in these patients.
NVAMD is principally characterized by pathologic macular choroidal neovascularization (CNV). This neovascularization originates from the choroid and extends into the subretinal space, disrupting Bruch’s membrane and stretching into the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) [3]. With CNV progression, neovascularization undergoes remodeling from a neovascular membrane to a variably mixed tissue with both active and inactive choroidal fibrovascular tissues which ultimately culminates into a fibrotic scar. As our understanding of NVAMD grows, the term of CNV is not appropriate as newly obtained knowledge, especially that obtained using optical coherence tomography (OCT), has led the field to adopt the new terminology of macular neovascularization (MNV) to define the various types of CNV observed in AMD patients. During disease progression, photoreceptors and RPE are gradually destroyed and this is accompanied with neovascular remodeling and subretinal fibrosis progression.
Subretinal fibrosis often progresses at late stage of NVAMD, contributing to local permanent photoreceptor degeneration and irreversible and profound vision loss in patients with NVAMD [4]. However, the association between subretinal fibrosis and neovascular remodeling is still unclear during NVAMD progression, and this remains a challenge for ophthalmologists treating NVAMD with anti-VEGF agents. Thus, it is of importance to elucidate the mechanisms responsible for incomplete response or resistance to anti-VEGF therapy.
It remains a challenge to study subretinal fibrosis associated with anti-VEGF therapy, and an especial challenge is to define a biomarker for subretinal fibrosis in patients with NVAMD. Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) allows simultaneous noninvasive detection of microstructural changes and microvascular flow in the retina and choroid [5]. This study aims to investigate the microstructural and neovascular characteristics of NVAMD complicating subretinal fibrosis by using OCTA, and explore the association between neovascular remodeling and subretinal fibrosis.
This study is a retrospective cohort study (ClinicalTrials.gov number,
https://www.chictr.org.cn,ChiCTR2000038911), and complies with the tenets of the
Declaration of Helsinki. Twenty patients diagnosed as NVAMD with subretinal
fibrosis were selected for this study. Each of these patients was treated with
intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy in the Department of Ophthalmology, Shanghai
General Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University, between February 1,
2019, and June 31, 2020. All patients were treated with at least three
consecutive monthly intravitreal injections of either aflibercept or ranibizumab.
The treatment was administered pro re nata (PRN) according to the
patient’s condition. Guideline criteria for anti-VEGF retreatment included either
a persistent increase of subretinal fluid under the macula or macular cystoid
edema compared with the previous visit, an increase thickening of more than 50
The inclusion criteria for patients in this study were: (A) Active macular CNV;
(B) Subretinal fibrovascular membrane secondary to NVAMD; and (C) Best-corrected
visual acuity (BCVA) of 20/400 or better. The BCVA was calculated as the
logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution (logMAR). The exclusion criteria
were: (A) Apparent media opacification; (B) Other vitreoretinal diseases, such as
vitreous hemorrhage, diabetic retinopathy, and retinal vein occlusion; (C) High
myopia defined as spherical equivalent refraction
All participants underwent a thorough ophthalmologic examination. Baseline characteristics of participants with NVAMD were recorded, including age, sex, BCVA, intraocular pressure (IOP), anterior segment evaluation using a slit-lamp biomicroscope, fundus examination, and OCTA imaging at baseline and 1 week after intravitreal treatment.
Retinal structure and microvasculature were imaged using the OCT system (RTVue
XR, Optovue Inc., Fremont, CA, USA), and data analysis was obtained by using the
manufacturer’s AngioVue software (Version 2017.1.0.155, Optovue Inc., Fremont,
CA, USA). Angiography scans covered an area of 3
En face images of the superficial capillary plexus (SCP), deep capillary plexus (DCP), and total capillary plexus (TCP) were measured automatically by the OCTA segmentation software. The central macular thickness (CMT) was defined as the distance between the internal limiting membrane (ILM) and the interface between the photoreceptor outer segments and RPE. The boundaries of different capillary plexuses were manually adjusted and improved to avoid imprecise segmentation. The signal-to-noise ratio of blood flow detection was refined by split-spectrum processing of the OCT signal. The x-fast and y-fast scans were registered and analyzed by the contained software in the case of the motion artifacts [7].
Data were analyzed using SPSS 22.0 software (IBM Corp., Chicago, IL, USA).
Patient characteristics were presented as counts for categorical data and as mean
Twenty eyes from 20 NVAMD patients with subretinal fibrosis were retrospectively
reviewed in this study and baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. The
participants included 11 females and 9 males, and the average age was 71.15
| Characteristics | Baseline | Final visit | p value | |
| Eyes (No.) | 20 | - | - | |
| Right/left eyes | 7/13 | - | - | |
| Sex (male/female) | 9/11 | - | - | |
| Mean ages (years old) | 71.15 |
- | - | |
| Anti-VEGF reagents | ||||
| Aflibercept (No.) | - | 15 | - | |
| Ranibizumab (No.) | - | 5 | - | |
| Injection numbers (No.) | - | 4.40 |
- | |
| BCVA (logMAR) | 1.07 |
1.05 |
0.69 | |
| CMT ( |
434.95 |
365.15 |
0.02* | |
| Data are shown as number or mean | ||||
There was no significant difference for the capillary densities in SCP, DCP, and TCP measured between baseline and final visit using OCTA (p = 0.12, 0.16 and 0.72, respectively) (Table 2). As for fovea and parafovea, there was also no significant change in vascular densities measured at baseline and final visit (Table 2).
| Characteristics | Baseline | Final visit | p value | |
| SCP | ||||
| Fovea | 16.48 |
15.98 |
0.65 | |
| Parafovea | 43.14 |
41.63 |
0.15 | |
| Whole | 40.55 |
38.78 |
0.12 | |
| DCP | ||||
| Fovea | 27.23 |
25.39 |
0.30 | |
| Parafovea | 44.37 |
47.83 |
0.06 | |
| Whole | 42.93 |
45.15 |
0.16 | |
| TCP | 83.48 |
84.07 |
0.72 | |
| Data are shown as mean | ||||
Fig. 1 shows serial OCTA en face images of neovascular remodeling in the outer retina and choriocapillaris layer after anti-VEGF treatment in NVAMD patients during 12-month follow-up. CNV lesions were partly decreased in response to anti-VEGF treatment, however, during 12-month follow-up, we observed a trend for CNV recurrence with morphological changes in those NVAMD patients with subretinal fibrosis (Fig. 1A–F). These findings indicate neovascular remodeling during the development of NVAMD even with anti-VEGF treatment.
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.OCTA en face images of a 69-year-old female patient with NVAMD in right eye showing an incomplete response to anti-VEGF treatment during 12-month follow-up (A–F). The area of the macular CNV lesion decreased in size after three consecutive monthly anti-VEGF injections (A–C). Images taken at baseline (A), one week after the 1st anti-VEGF injection (B), and one week after the 3rd anti-VEGF injection (C) are shown. The size of the macular CNV lesion increased again at six months during the follow-up period (D), one week after the 4th anti-VEGF injection (E), and 12 months at final visit (F). The thin green line at the center of each en face OCTA frame indicates the location in cross-sectional OCTA.
Using OCTA, subretinal fibrosis was revealed as compact, hyperreflective lesions
with variable degrees of the degeneration of both the RPE and photoreceptors.
Subretinal fibrosis was associated with a perfused and abnormal neovascular
network in the outer retina and the choriocapillaris layer. Fig. 2 illustrates
the development and progression of subretinal fibrosis, which was associated with
neovascular remodeling during the 12-month follow-up. With anti-VEGF treatment
CNV density was decreased (Fig. 2A–C), leaving the vessels with a large-caliber
feeder artery such as trunk micro-vessels, which were possibly mature vessels,
and the intraretinal fluid was completely absorbed (Fig. 2D–F). Some of the fine
vessels, such as capillary tufts, at the edges of fibrovascular membrane
regressed gradually after anti-VEGF treatment (Fig. 2G–I). The relative density
of CNV lesions were decreased by 19.12% (n = 20, p = 0.01) when
baseline and the 12-month follow-up values were compared (Fig. 3A). However,
progression of subretinal fibrosis was evident during the follow-up period (Fig. 2D–E) and the relative density of the subretinal fibrosis was approximately 1.21
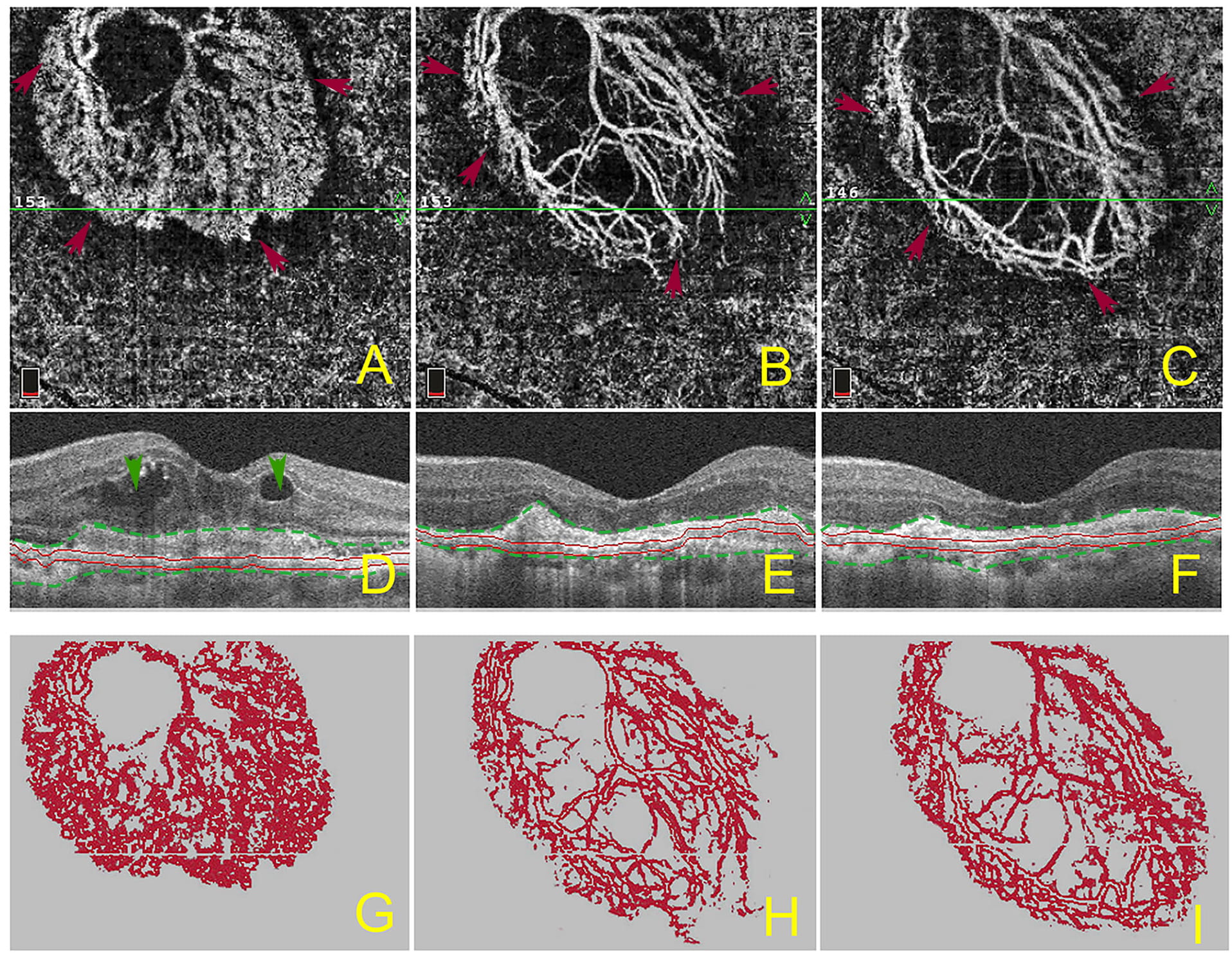 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Morphologic changes of macular CNV and progression of subretinal fibrosis before and after anti-VEGF treatment. The OCTA en face image (A–C) and corresponding B-scan (D–F) show the morphological changes of macular CNV lesions and progression of subretinal hyperreflective materials before, and after, anti-VEGF treatment. The OCTA en face image (A) and B-scan (D) show the macular CNV lesion and subretinal fibrosis at baseline. The OCTA en face image (B) and B-scan (E) show the macular CNV lesion and subretinal hyperreflective materials after 3 consecutive anti-VEGF injections. The OCTA en face image (C) and B-scan (F) show the macular CNV lesion and subretinal hyperreflective materials at the final 12-month follow-up timepoint. The images of G–I present the subtracted, colorized neovascular network, as perceived in the segmentation corresponding to the fibrotic lesion. Red arrows depict the boundaries of macular CNV (A–C), green arrows show the intraretinal fluids (D), green lines show the boundaries of subretinal hyperreflective materials mainly containing fibrosis and exudations (D–F).
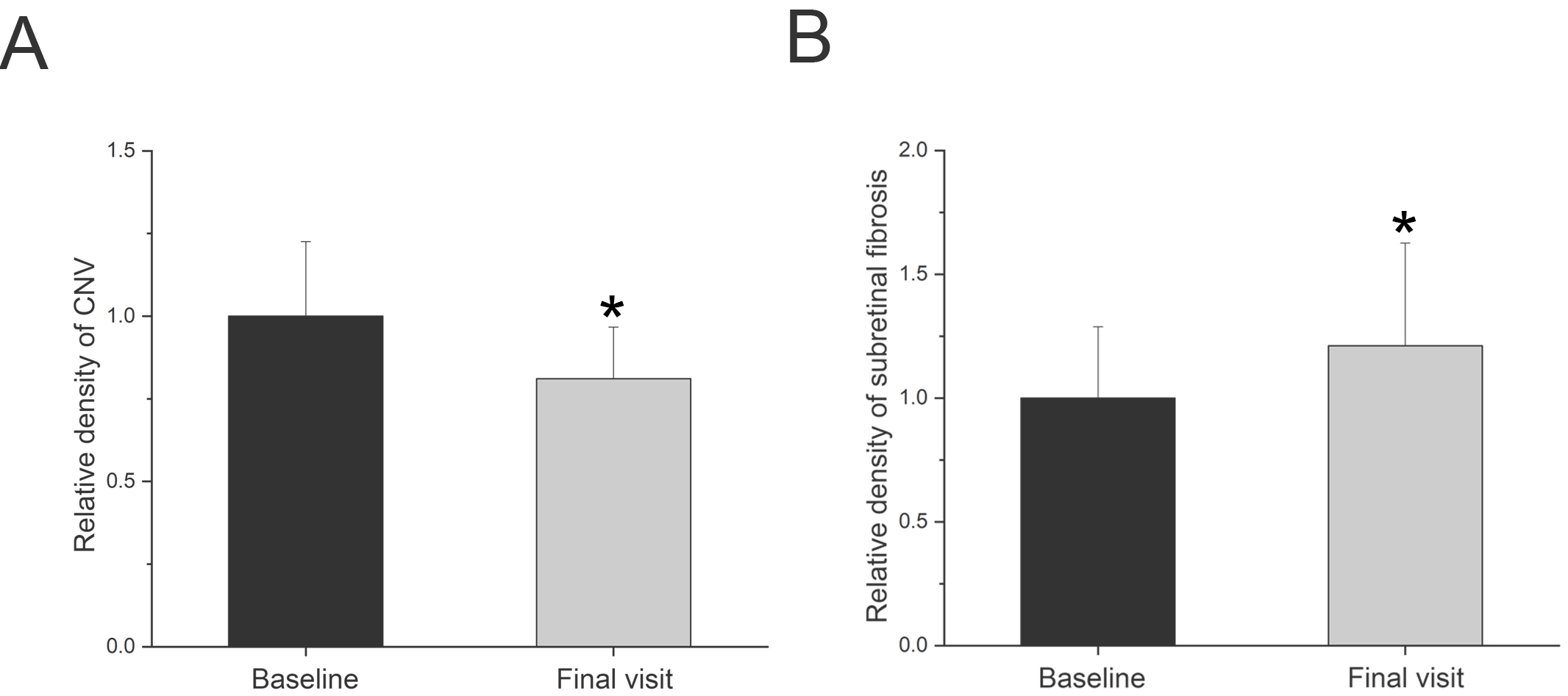 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Comparison of the relative density of CNV (A) and
subretinal fibrosis (B) between the baseline and final follow-up visit. The data
are expressed as mean
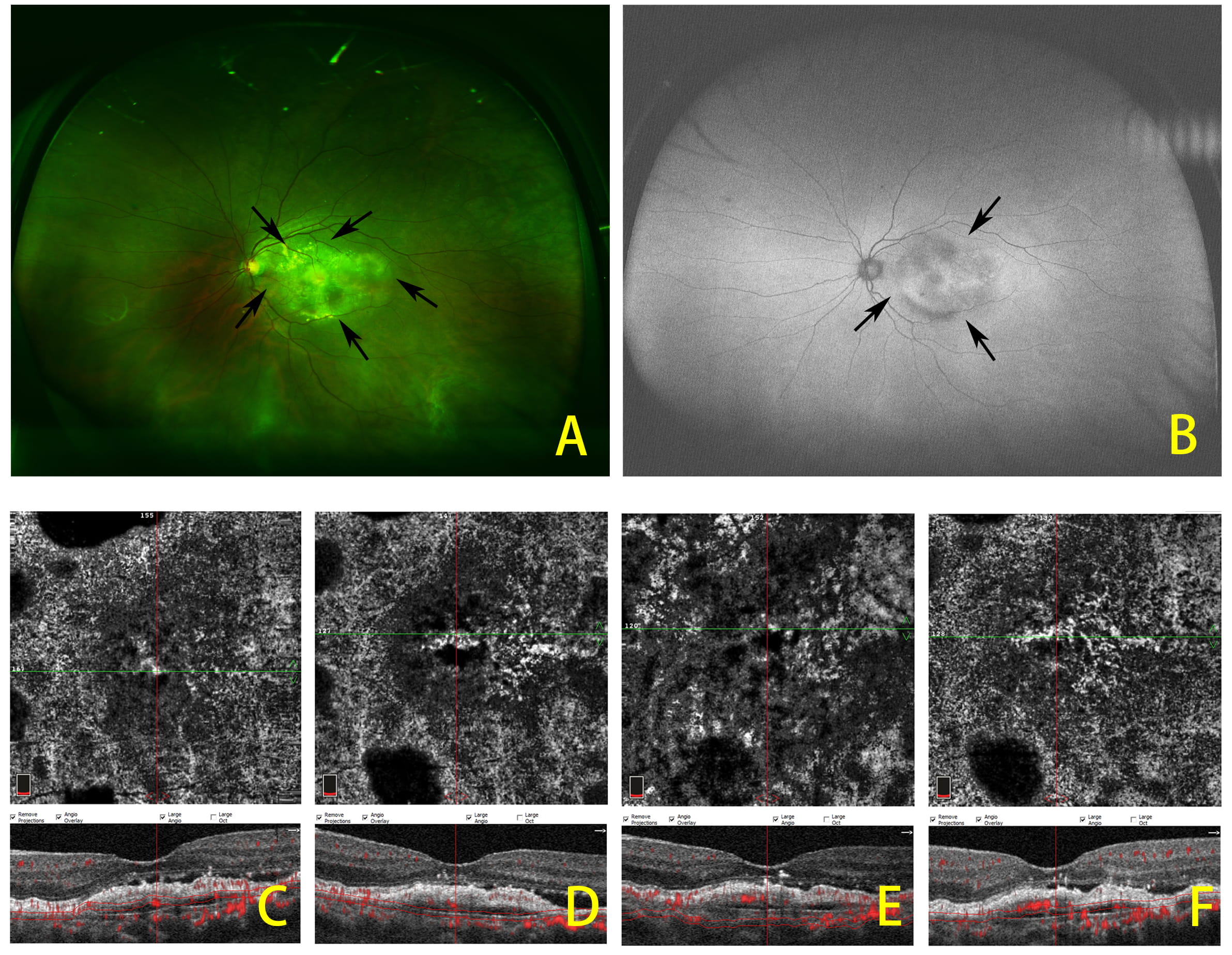 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Representative widefield fundus images of neovascular age-related macular degeneration with subretinal fibrosis and the progression of subretinal fibrosis after anti-VEGF treatment. (A) Fundus color images of subretinal fibrosis showing elevated mound of whitish or yellowish subretinal deposition of aberrant connective tissue at, or near, the fovea. (B) Fundus autofluorescence of the same patient with subretinal fibrosis. OCTA images showing subretinal fibrosis at baseline and after 3 consecutive anti-VEGF injections are given (C–F). Arrows indicate the edge of lesion.
Incomplete response to anti-VEGF therapy presents a serious challenge for NVAMD patients even after regular, ongoing anti-VEGF treatment for 1 year [8, 9]. However, the detailed mechanism(s) of anti-VEGF resistance and suboptimal vision recovery are not definitively established. Our findings demonstrated that the development of neovascular remodeling and progressive subretinal fibrosis were associated with most cases of incomplete response to anti-VEGF therapy and worse visual outcome in NVAMD.
NVAMD patients have a high frequency of complicating progressive subretinal fibrosis. It was reported that fibrotic scars occur in approximately 24.7% of all eyes in the Comparison of AMD Treatment Trial (CATT) clinical trial [10], regardless of anti-VEGF treatment regimen. Using a fundus biomicroscope, subretinal fibrosis was defined as an elevated mound of whitish or yellowish subretinal deposition of aberrant connective tissue at or near the fovea (Fig. 4) [11]. Using OCTA, subretinal fibrosis is evident as dense hyperreflective thickening bands, typically in the subretinal or sub-RPE space. These features of subretinal fibrosis are associated with both active and inactive fibrotic choroidal neovascular remodeling networks [12], and their exact location and characteristics in the choroid and outer retina could be observed by B-scans and en face measurements using OCTA [13, 14]. Therefore, OCTA allows for exploration of the correlation of imaging and pathology findings in NVAMD patients with subretinal fibrosis and neovascular remodeling, especially for those with incomplete response to anti-VEGF therapy. It is meaningful to investigate the detailed mechanisms of anti-VEGF resistance and explore the sensitive biomarkers to predict clinical outcomes after anti-VEGF treatment.
In this study, a significant decrease of maximal CMT values from baseline to the final follow-up was observed after anti-VEGF treatment; however, BCVA did not improve significantly during the 12-month follow-up period (Table 1). Several confounding factors could explain visual outcomes in eyes with subretinal fibrosis. Such factors include subretinal fibrosis leading to photoreceptor degeneration and RPE disruption [15], the size of CNV lesion being generally larger with subretinal fibrosis at baseline than that observed in those without subretinal fibrosis [16], and photoreceptor synaptic dysfunction developing in the neurosensory retina overlying a CNV lesion caused by infiltrating blood-derived macrophages or retinal microglia and regulated by Müller cell activation [17, 18].
The morphology of macular CNV has usually been represented as central trunk micro-vessels with peripheral capillary tufts using en face projection images. According to its morphological characteristics, macular CNV could be divided into two main types, arteriolar CNV lesions and capillary CNV lesions [8]. In contrast to capillary CNV, which is highly responsive to anti-VEGF therapy, arteriolar CNV most frequently shows suboptimal response to anti-VEGF therapy. Arteriolar CNV is the type most commonly observed in our studies showing incomplete response to anti-VEGF treatments. With anti-VEGF treatment, fine vessels, such as capillary tufts, at the edges of CNV lesions regressed gradually, leaving the trunk micro-vessels which may represent mature vessels and mark arteriolar CNV type with morphological changes (Figs. 1,2). Arteriolar CNV is characterized by high blood flow through large-caliber feeder arteries, many branching arterioles, and terminal vascular anastomotic loops. Such structures may exhibit persistent disease activity despite anti-VEGF therapy [8]. In agreement with these principles, our preliminary results showed that, in NVAMD patients with arteriolar type CNV lesions, the capillary components were reduced by anti-VEGF therapeutics. In contrast, arteriolar components were resistant to anti-VEGF treatment and displayed neovascular remodeling during the treatment.
It has been reported that formation of arteriolar CNV occurs via neovascular remodeling. The blood-derived macrophage to myofibroblast transition contributes to subretinal fibrosis. Macrophages infiltrate the incipient CNV lesion, recruiting bone marrow-derived mesenchymal precursor cells (MPCs) from the circulation, and subsequently activating MPCs to differentiate into vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and myofibroblasts. Myofibroblasts are major cellular components leading to pathogenic fibrosis, driving the progression of CNV with arterialization and perivascular fibrosis [19, 20]. Therefore, incomplete response to anti-VEGF treatment in NVAMD may be associated with neovascular remodeling and progressive fibrosis which requires alternative adjuvant therapeutic approaches [9].
There are several studies related to ocular fibrovascular diseases other than NVAMD. It was reported that the shift in the balance of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and VEGF, as scored by the ratio of CTGF/VEGF in vitreous samples after bevacizumab treatment was associated with an angiofibrotic switch in proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) [21]. In PDR patients, vitreous CTGF correlated positively, while VEGF correlated negatively with the degree of vitreoretinal fibrosis. Further, intravitreal bevacizumab administration caused increased fibrosis in these patients by increasing the ratio of CTGF/VEGF. However, other studies showed conflicting results concerning fibrosis progression after anti-VEGF treatments. One study showed intravitreal bevacizumab reduced the vitreous levels of VEGF but had no significant effect on the levels of CTGF in patients with diabetic traction retinal detachment [22]. Another study reported that anti-VEGF treatment suppressed vitreous VEGF levels but did not significantly alter VEGF or CTGF in diabetic membranes. This finding may be explained by the high baseline levels of fibrosis commonly seen in PDR [23]. Since the ratio of CTGF/VEGF in ocular fluids such as aqueous humor or vitreous body might serve as a strong predictor of vitreoretinal fibrosis, it is of great importance to monitor the ratio of CTGF/VEGF in ocular fluids during repeated intravitreal anti-VEGF treatments in patients with NVAMD.
Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) has been implicated in playing an important role in the pathophysiology of both angiogenesis and fibrosis in a variety of tissue and organ systems, including the retina [24]. The anti-FGF2 neutralizing aptamer, RBM-007, was studied both in mouse and rat models, and results demonstrated that FGF2-induced angiogenesis could be inhibited by RBM-007. Moreover, laser-induced CNV and CNV complicated with fibrosis were also inhibited by RBM-007. Pharmacokinetic studies of RBM-007 in the rabbit vitreous showed relatively long-lasting effects that are better than those observed with other approved anti-VEGF drugs [24, 25]. The anti-angiogenic and anti-fibrosis dual action properties of RBM-007 hold promise as an additive, or alternative, therapy to anti-VEGF therapy for NVAMD [26].
Limitations of the present study include the relatively small number of patients enrolled in the study, lack of NVAMD patients without subretinal fibrosis as the control, and the relatively short-term observation and follow-up periods. Therefore, larger study samples from multi-center studies are needed to clarify the progression of subretinal fibrosis from incipient NVAMD with long-term follow-up after anti-VEGF treatments. Furthermore, the study was not designed to identify potentially different effects of aflibercept and ranibizumab on subretinal fibrosis. Novel therapeutic strategies preventing the development of subretinal fibrosis and subsequent neovascular remodeling might improve long-term visual outcome in patients with NVAMD.
AMD is the leading cause of legal blindness in elderly people, that causes severe deterioration of vision and ultimately blindness. NVAMD is responsible for the majority of cases of severe visual loss in eyes with AMD. Subretinal fibrosis complicating NVAMD remains a major obstacle for the management of NVAMD. The introduction of anti- VEGF drugs has revolutionized the treatment of NVAMD, which have been recommended as the first-line treatment for NVAMD. However, long-term anti-VEGF therapy may result in fibrovascular transformation of CNV, including neovascular remodeling and subretinal fibrosis. The progression of neovascular remodeling and subretinal fibrosis may serve as biomarkers to predict incomplete response to anti-VEGF therapy in patients with NVAMD. Thus, novel therapies targeting neovascular remodeling and subretinal fibrosis might provide an adjunctive or alternative strategy in treatment of NVAMD and other fibrovascular diseases.
JW—Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Writing — original draft. JZ—Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Resources, Writing — review & editing, Supervision.
The study approved by the Clinical Research Ethical Committee of Shanghai General Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China (Permits No. 2020KY205-2).
Not applicable.
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (82171062).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.




