1 School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 410208 Changsha, Hunan, China
2 School of Pharmacy, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 410208 Changsha, Hunan, China
3 Teaching and Research Section of Traditional Chinese Medicine Surgery, The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 410021 Changsha, Hunan, China
4 College of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 410208 Changsha, Hunan, China
5 Department of Internal Medicine, College of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 410208 Changsha, Hunan, China
6 Oncology Department, The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 410021 Changsha, Hunan, China
7 Medical School, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 410208 Changsha, Hunan, China
Academic Editors: Antonio Barbieri and Francesca Bruzzese
Abstract
Background: The key active component(s) in an anti-tumor preparation
used in traditional Chinese medicine, Xihuang Pills, remains unclear.
Methods: We used a network pharmacology analysis to construct a
component-disease-target network diagram and used this to determine quercetin as
a critical active ingredient in Xihuang Pills. Subsequently, human hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) cell lines, H22 and HepG2 cells, were treated with quercetin, and
BALB/c mice were injected with H22 cells and
treated with different concentrations of quercetin. Tumor volume and weight were
determined in these mice with and without quercetin administration. Immune and
pro-inflammatory factors were measured using Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
(ELISA). Macrophage polarization was assessed by western blot and flow cytometry.
Finally, PD-L1, autophagy-related proteins, and the NF-
Keywords
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- Xihuang Pills
- quercetin
- autophagy
- macrophage
- NF-kB
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common malignancy that accounts for 90% of liver tumors and is considered a global health burden [1]. Current treatment methods mainly include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy [2], but these treatments are only effective for 30–40% of patients. The dilemma of poor prognosis, drug resistance, and low 5-year survival rate remains [3]; therefore, it is urgent to investigate new treatment strategies for HCC.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is rich in bioactive components, and TCM is widely used to treat various cancers with few side effects [4]. Xihuang Pills are an anti-cancer TCM made of Commiphora myrrha Engl, Moschus, Boswellia carterii Birdwood and Bos taurus domesticus Gmelin [5]. The anti-tumor activity of Xihuang Pills are multiple in nature and include inhibiting the growth and invasion of tumor cells and tumor stem cells, preventing tumor invasion and metastasis, and regulating the immunosuppressive microenvironment [6, 7]. Previous studies have shown that Boswellia carterii Birdw and Commiphoramyrrha Engl in Xihuang Pills can play an anti-HCC role by regulating tumor angiogenesis through EGFR-activated PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways [8]. Nonetheless, how Xihuang Pills play a regulatory role in HCC patients is still unclear.
The mechanisms by which TCM treat diseases are complex, as they often contain complex components and target multiple aspects of the disease. Network pharmacology, an important tool in traditional Chinese medicine research, can comprehensively analyze the targets, components, and diseases of multiple drugs [9]. PI3K/Akt/mTOR-related proteins were identified as potential Xihuang Pills-related targets of prostate cancer using network pharmacology as well as other experimental approaches [10]. In previous studies, the target strategy of Xihuang Pills for the treatment of liver cancer has been explored based on network pharmacology [11]. However, the active ingredients in Xihuang Pills for the treatment of HCC have not been determined.
Autophagy, a process of degrading cellular material, is closely related to tumor
development and TCM therapy [12, 13]. Autophagy mediates the development of HCC
via the NF-
This study explored the active ingredients of Xihuang Pills and the targeted regulation of HCC through network pharmacology analysis. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments also demonstrated that quercetin, the active ingredient of Xihuang Pills, could synergistically inhibit HCC-related inflammation, autophagy, and macrophage polarization. These results may provide new insights into the disease treatment of HCC by Xihuang Pills.
The research first retrieved the compounds of Bos taurus domesticus Gmelin, Boswellia carterii Birdw, and Commiphora myrrha Engl
through the TCMSP database [20], and the compounds in Moschus were
obtained from the herb [21] and batman databases [22]. Oral bioavailability (OB)
of
We evaluated the core components of Xihuang Pills via UPLC-MS using the Shimadzu
Prominence UPLC system (SCIEX, ExionLC AD) coupled with the QTRAP MS (SCIEX,
QTRAP 5500). The flow rate, the injection tray temperature, and the column
temperature was 0.3 mL/min, 4 ℃, and 40 ℃, respectively. The column used was a
Waters HSS T3 column (100
H22 and HepG2 cell lines were purchased from Procell Life Science & Technology
Co., Ltd (Wuhan, China). The H22 and HepG2 cell lines were cultured in 1640
medium (Sigma, Saint Louis, R8758, USA) and Dulbecco’s minimum essential medium (DMEM) (Sigma,
D5796, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, Grand Island, 10099141, USA),
respectively. The cells were divided into four groups: a control group, a
low-dose group, a medium-dose group, and a high-dose group [29], which were
treated with quercetin (MedChemExpress, New Jersey, HY-18085, China) at concentrations of 0,
25
After digestion, H22 and HepG2 were counted and divided into four groups. Each
well was seeded with 500
Matrigel (354262, Becton Dickenson, Franklin Lakes) was diluted and placed in the upper chamber
and medium containing 10% FBS was placed in the lower chamber. HepG2 cells were
treated with different concentrations of quercetin for 72 h, digested into single
cells, and then resuspended at 2
The cells (H22 and HepG2) were collected and stained with 5
Approximately 5
The cells (H22 and HepG2) and tissue were washed twice with PBS, and the protein
supernatant was obtained by lysing with RIPA buffer and clearing the lysate by
centrifugation. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to the
polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane. Then, the membranes were blocked with
5% nonfat milk for 90 min. The membrane was incubated with primary antibodies to
MMP-2, MMP-9, CD86, CD206, PD-L1, LC3, P62, I
A total of 32 four weeks old male BALB/c mice were purchased from Hunan SJA
Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd. (Changsha, China). Animals were given free access to
water and food under standard animal rearing conditions (temperature 25
Tumor tissues were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. The sections were deparaffinized and stained according to instructions provided with the Hematoxylin-Eosin (H&E) staining kit (Abiowell, Changsha, China). The sections were observed and photographed under a light microscope.
First, peripheral blood samples and tumor tissue homogenates were prepared.
Subsequently, the concentration of granulocyte-macrophage (GM-CSF, KE10015) and
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF, KE10025) in cancer tissue
homogenates, and TNF-
After resuspending the cells, CD86 antibody (eBioscience, San Diego, 12-0862-82, USA) and CD206 antibody (eBioscience, 12-0114-82, USA) were added and incubated with the cells in the dark for 30 min. The cells were subsequently resuspended with PBS, filtered through a nylon mesh, and analyzed by a flow cytometry (Beckman, USA).
GraphPad 8.0 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, California, USA) was
used for statistical analysis, and three independent experimental data points
were expressed as mean
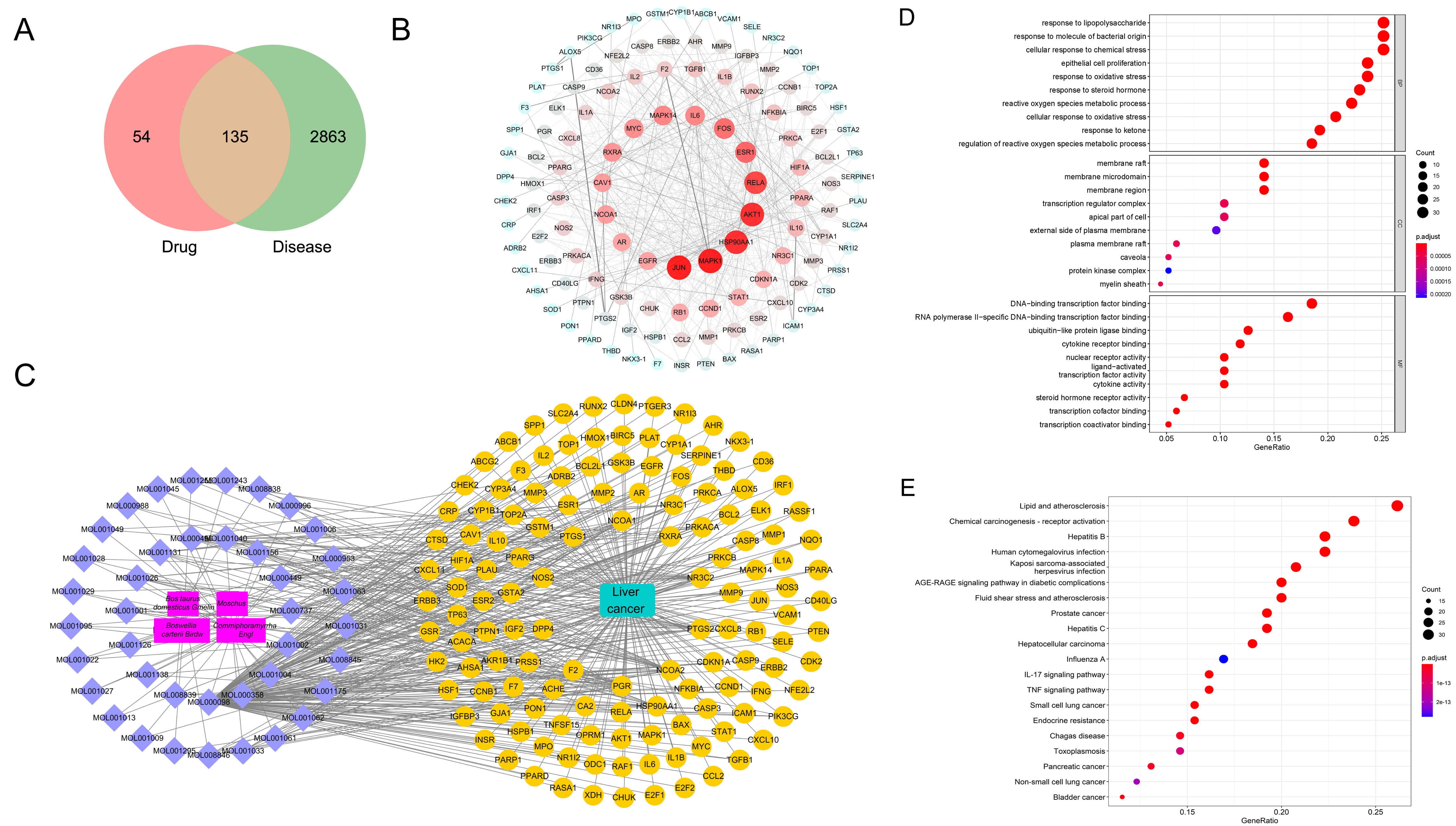
189 potential drug targets and 2998 liver cancer-related genes were acquired through database screening and 135 common targets were obtained (Fig. 1A). JUN, MAPK1, HSP90AA1, and AKT1 could be found to be highly correlated targets in the PPI network (Fig. 1B). Through the network diagram of ingredients/diseases/targets (Fig. 1C), we observed a complex interaction relationship among components, such as Bos taurus domesticus Gmelin, Moschus, Commiphora myrrha Engl and Boswellia carterii Birdw, liver cancer, and corresponding targets. These common targets were principally enriched in responses to lipopolysaccharide, responses to molecules of bacterial origin, cellular responses to chemical stress, epithelial cell proliferation, responses to oxidative stress, lipid and atherosclerosis, chemical carcinogenesis-receptor activation, hepatitis B, human cytogenetic infection, Kaposi sarcoma-associated, herpesvirus infection and other processes (Fig. 1D,E).
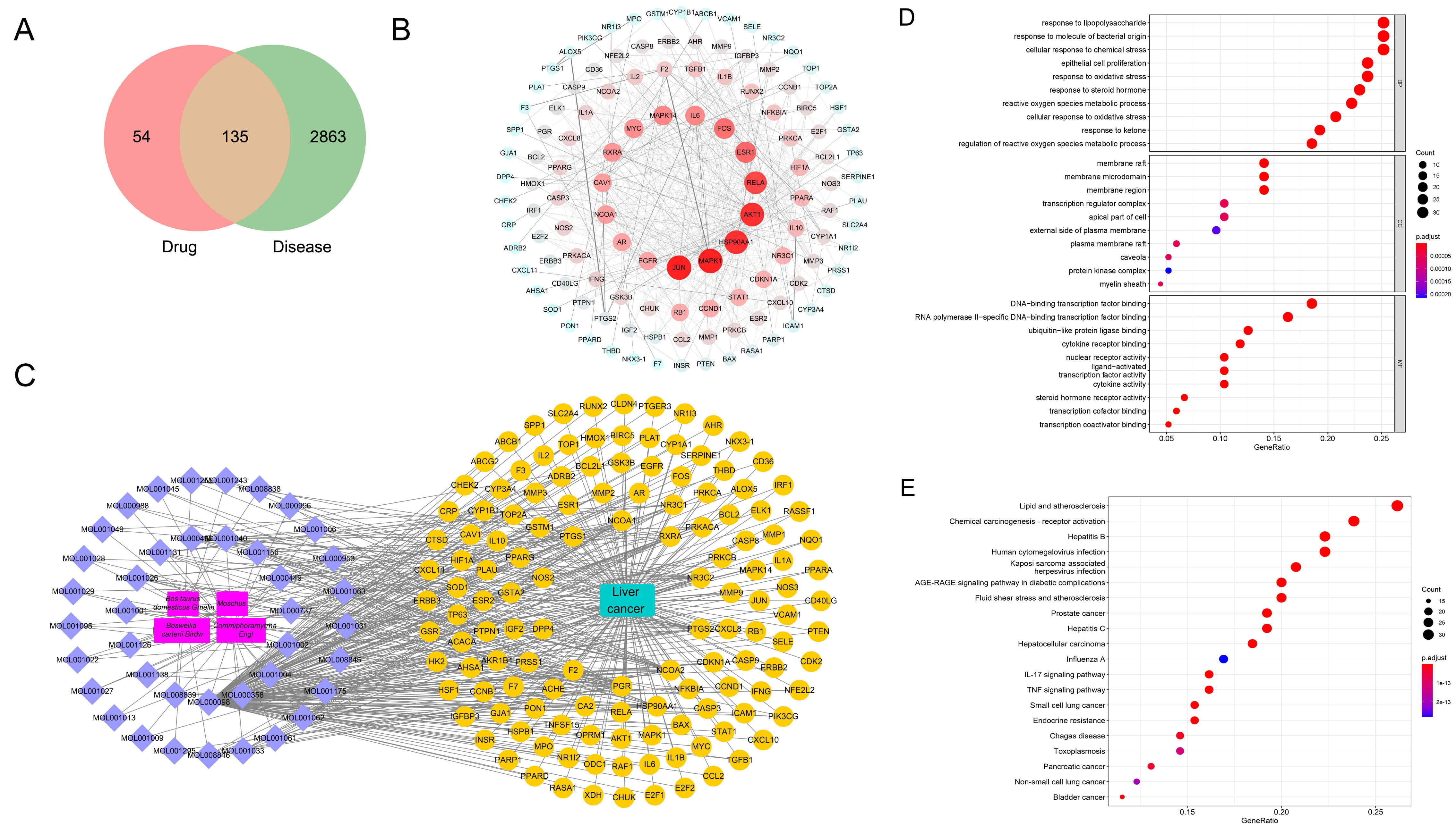 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Network pharmacological analysis of Xihuang Pills. (A) Venn diagram shows the targets of Xihuang Pills and liver cancer. (B) PPI network shows the interaction of common targets of drug diseases. (C) The component-disease-target network diagram in Xihuang Pills. The main components, the ID of active ingredients, liver cancer-related targets, related pathways and liver cancer are marked with red, purple, yellow and green, respectively. (D, E) Bubble chart of GO and KEGG analysis.
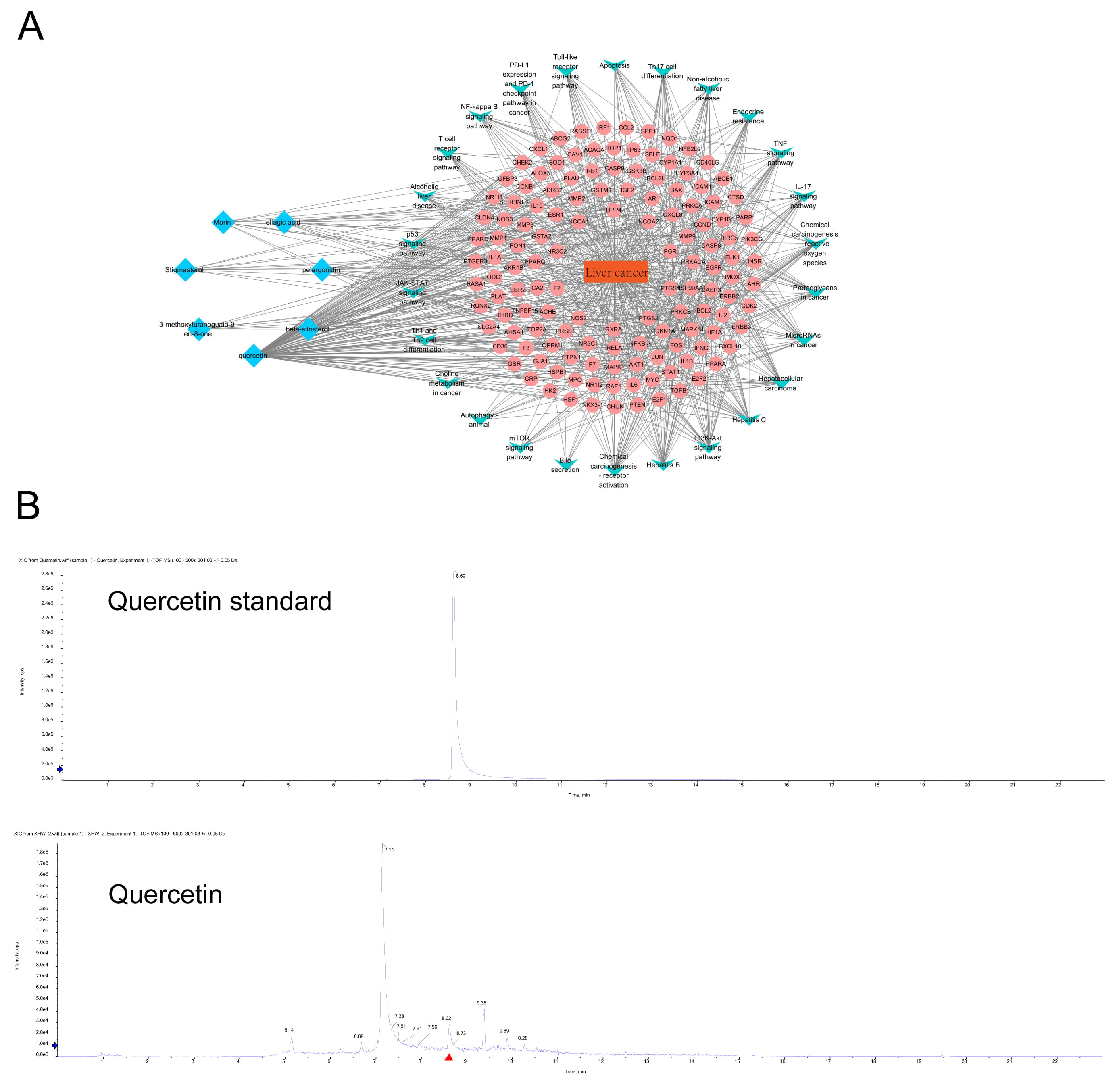
From the ingredients/diseases/pathways/targets network diagram of Xihuang Pills, we found that the principal active ingredients of Xihuang Pills were quercetin, beta-sitosterol, pelargonidin, ellagic acid, morin, stigmasterol, and 3-methoxyfuranoguaia-9-en-8-one. Among these, quercetin had the highest degree score (Fig. 2A and Table 1). The core components of Xihuang Pills were identified via UPLC-MS and it was confirmed that quercetin was one of the key components of the Xihuang Pills (Fig. 2B) and thus we focused our investigation on quercetin action in HCC.
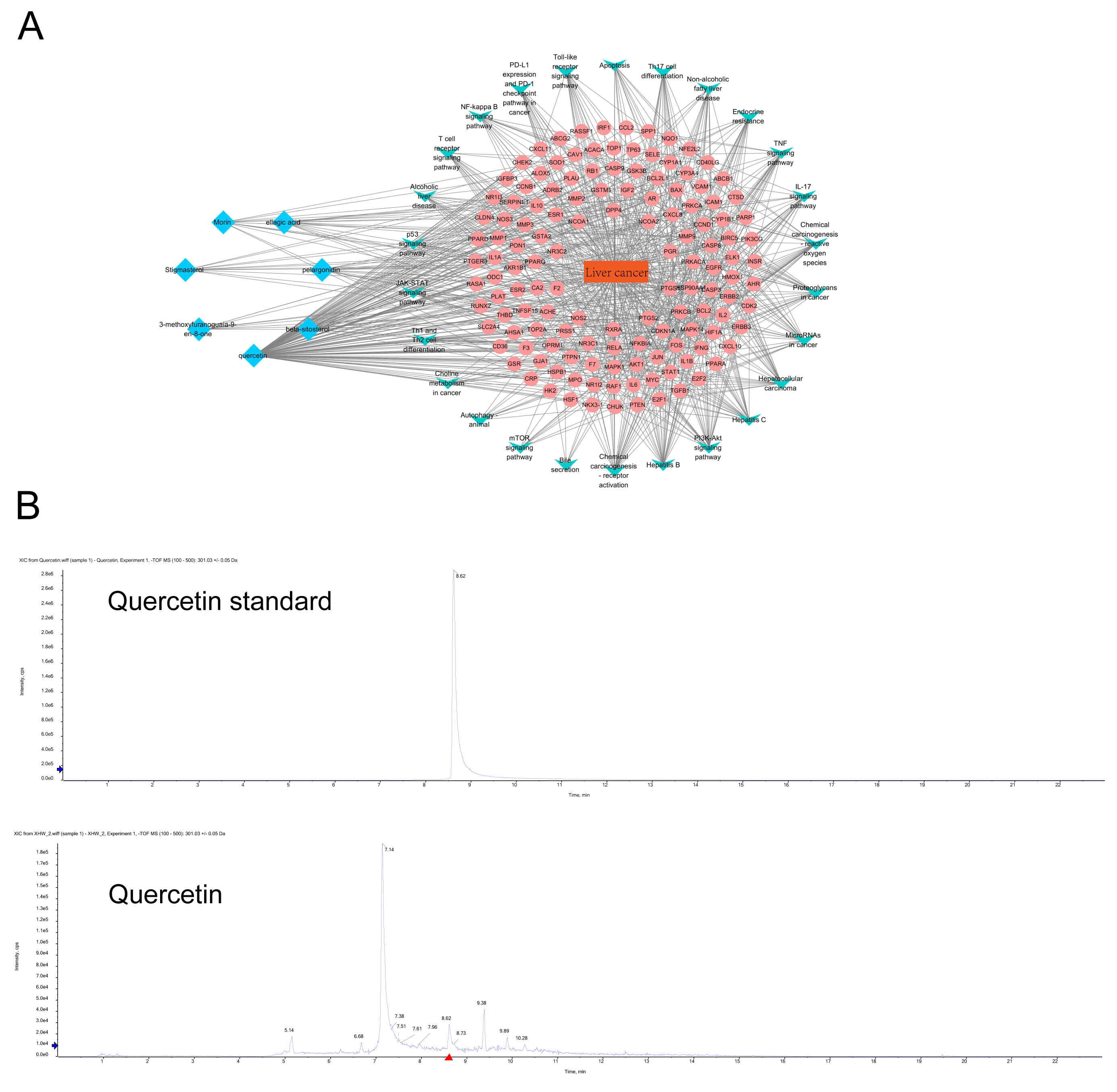 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.The identification of drug components in Xihuang Pills and the network analysis of liver cancer targets and pathways. (A) The network diagram of ingredients-diseases-pathways-targets in Xihuang Pills. The key active ingredients, liver cancer-related targets, related pathways and liver cancer are marked with blue, pink, green and orange, respectively. (B) HPLC was used to identify the core active ingredients of Xihuang Pills (quercetin).
| MOL ID | Name | Average shortest path length | Betweenness centrality | Closeness centrality | Degree |
| MOL000098 | quercetin | 1.469274 | 0.324187 | 0.680608 | 118 |
| MOL000358 | beta-sitosterol | 2.564246 | 0.014017 | 0.389978 | 19 |
| MOL001004 | pelargonidin | 2.597765 | 0.009671 | 0.384946 | 16 |
| MOL001002 | ellagic acid | 2.642458 | 0.008912 | 0.378436 | 15 |
| MOL000737 | Morin | 2.877095 | 0.011215 | 0.347573 | 13 |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | 2.642458 | 0.005531 | 0.378436 | 12 |
| MOL001156 | 3-methoxyfuranoguaia-9- en-8-one | 2.675978 | 0.003721 | 0.373695 | 10 |
| The main active ingredient information of Xihuang Pills was analyzed by network pharmacology. | |||||
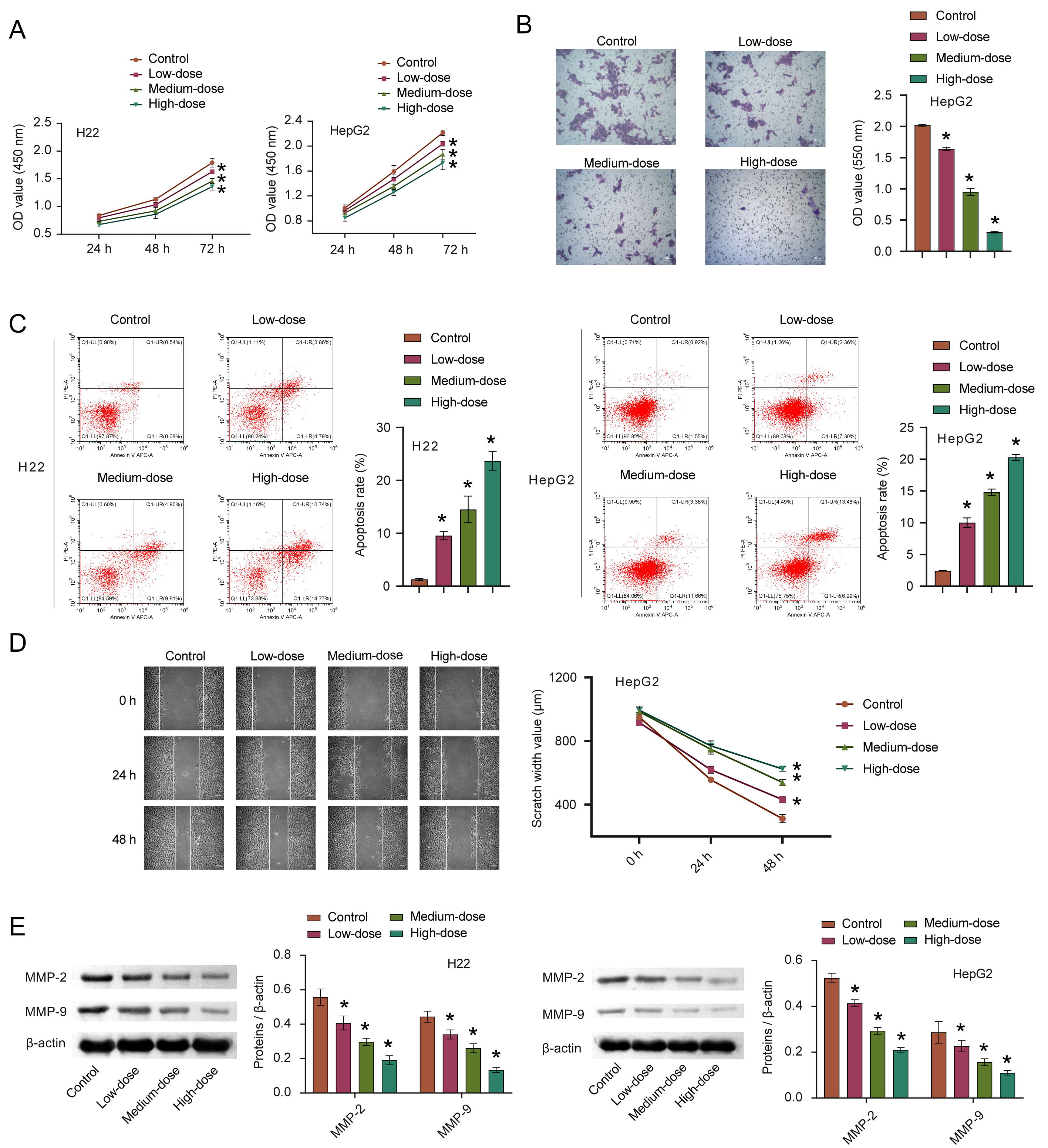
To verify whether quercetin has an anti-cancer effect, we first explored the effect of quercetin on HCC in vitro. CCK8 was used to detect cell proliferation and we observed that the proliferation ability of cells treated with quercetin decreased compared to the control group, and that this was proportional to the quercetin concentration (Fig. 3A). After 72 h of quercetin treatment, the average inhibition rate was the highest, thus this time point was adopted for all subsequent cell experiments. Invasion characteristics of HepG2 were detected by transwell migration assays. Data gathered (Fig. 3B) indicates that with increasing quercetin concentrations, reduced cell migration was observed, suggesting that quercetin inhibits the cell invasion ability. We found that quercetin could promote the apoptosis of HCC cells while inhibiting the migration in a concentration-dependent manner, as shown in Fig. 3C,D. The expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in HCC cells gradually decreased with increased quercetin concentration (Fig. 3E). These results suggest that quercetin could significantly inhibit HCC invasiveness.
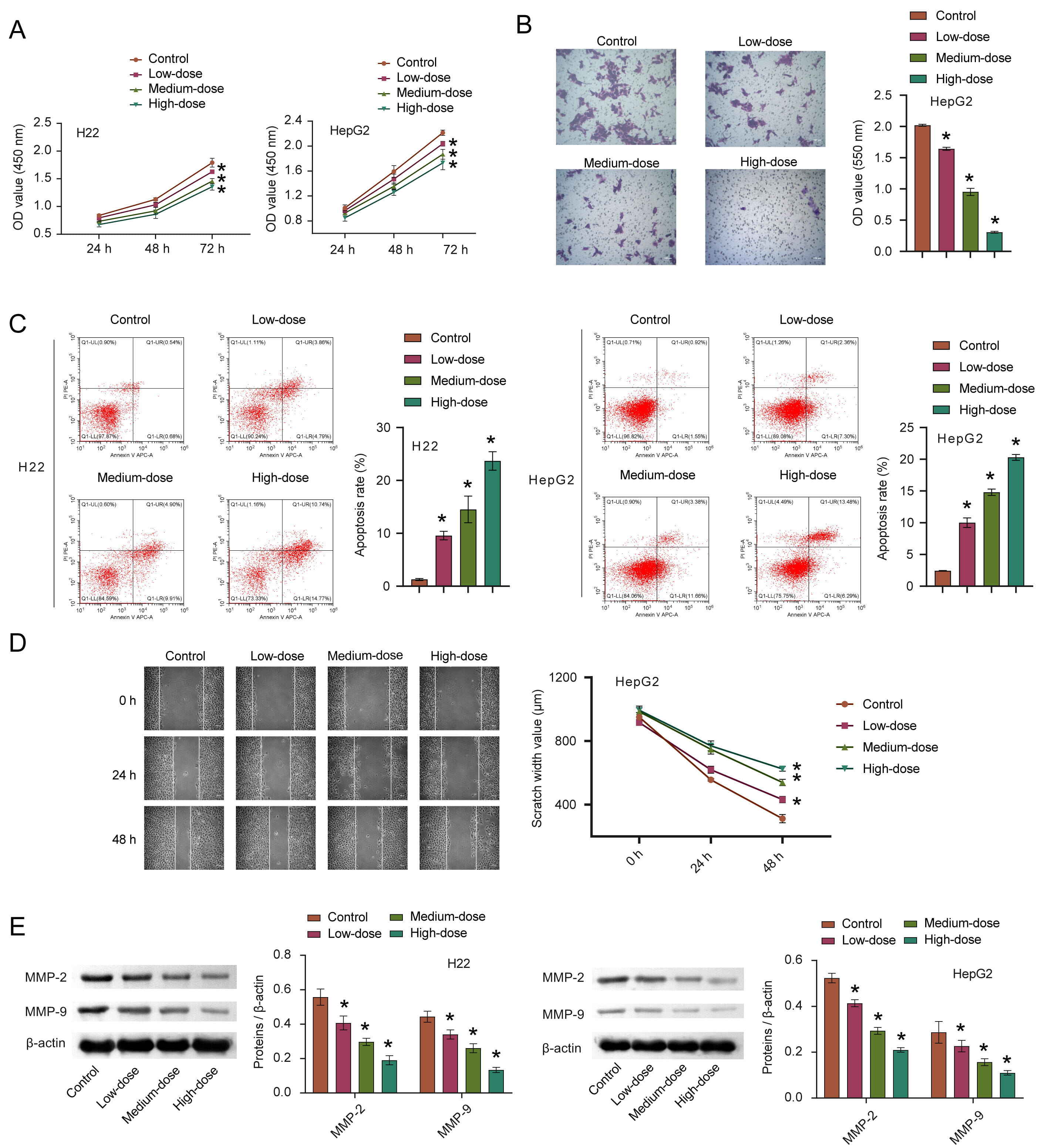 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.The effects of quercetin on the proliferation,
apoptosis, invasion and migration of HCC. (A–D) The proliferation, invasion,
apoptosis, and migration of HCC cells after quercetin treatment were measured by
CCK8, transwell, FCM, and scratch test, respectively. (E) The MMP-2 and MMP-9
expression were detected via WB. *p
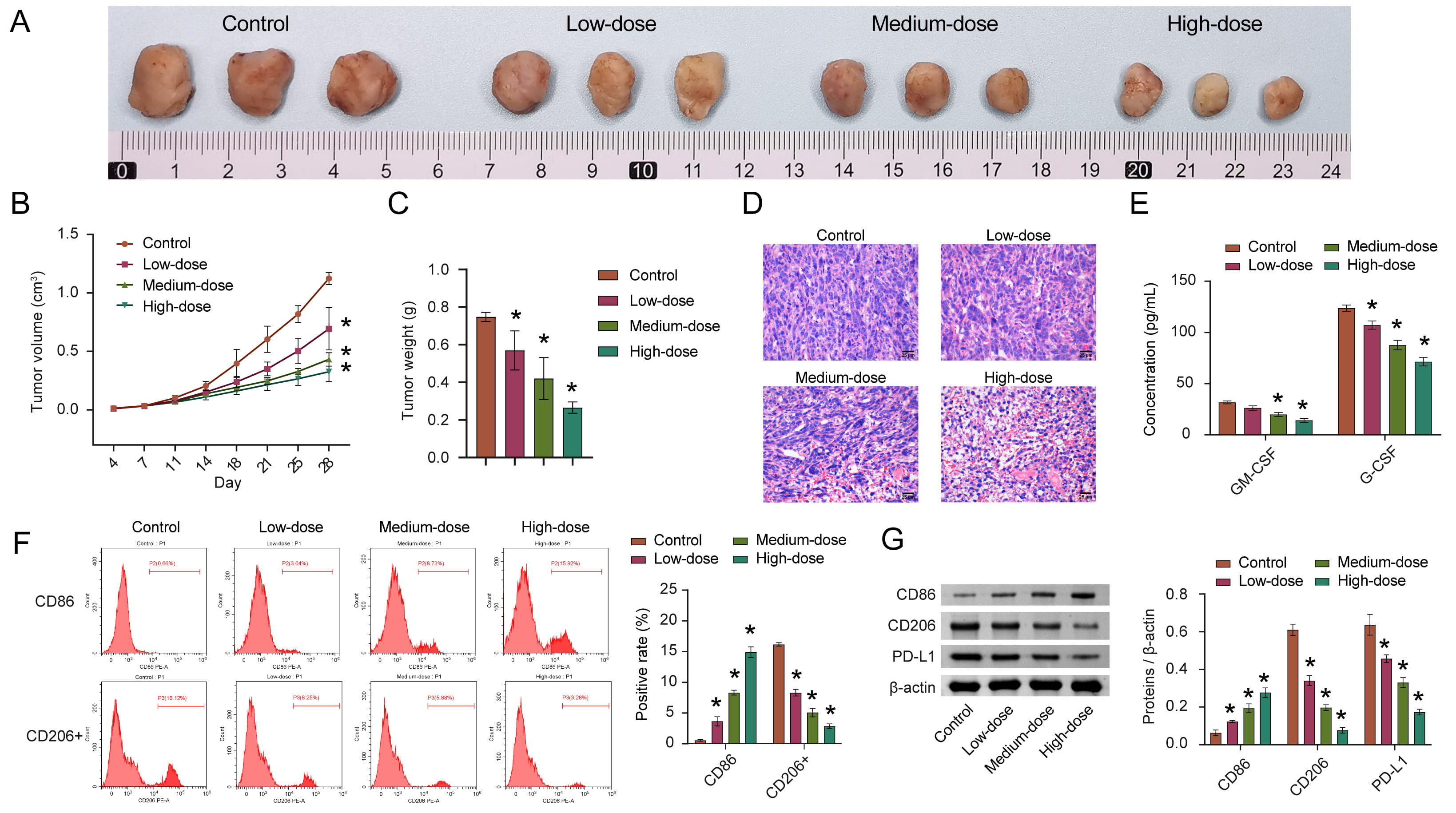
In order to evaluate whether quercetin also plays a role in inhibiting HCC in vivo, we employed animal modeling. The experimental results obtained were consistent with the results obtained from cultured cells. The tumor volume and weight in the quercetin treatment group were significantly reduced (Fig. 4A–C). With increased quercetin concentration, its inhibitory effects on tumor development were measurably stronger. Similarly, after quercetin treatment, the density of cells decreased, and the nuclei appeared pyknotic and fission. The highest quercetin concentration group displayed the most significant results on tumor development (Fig. 4D).
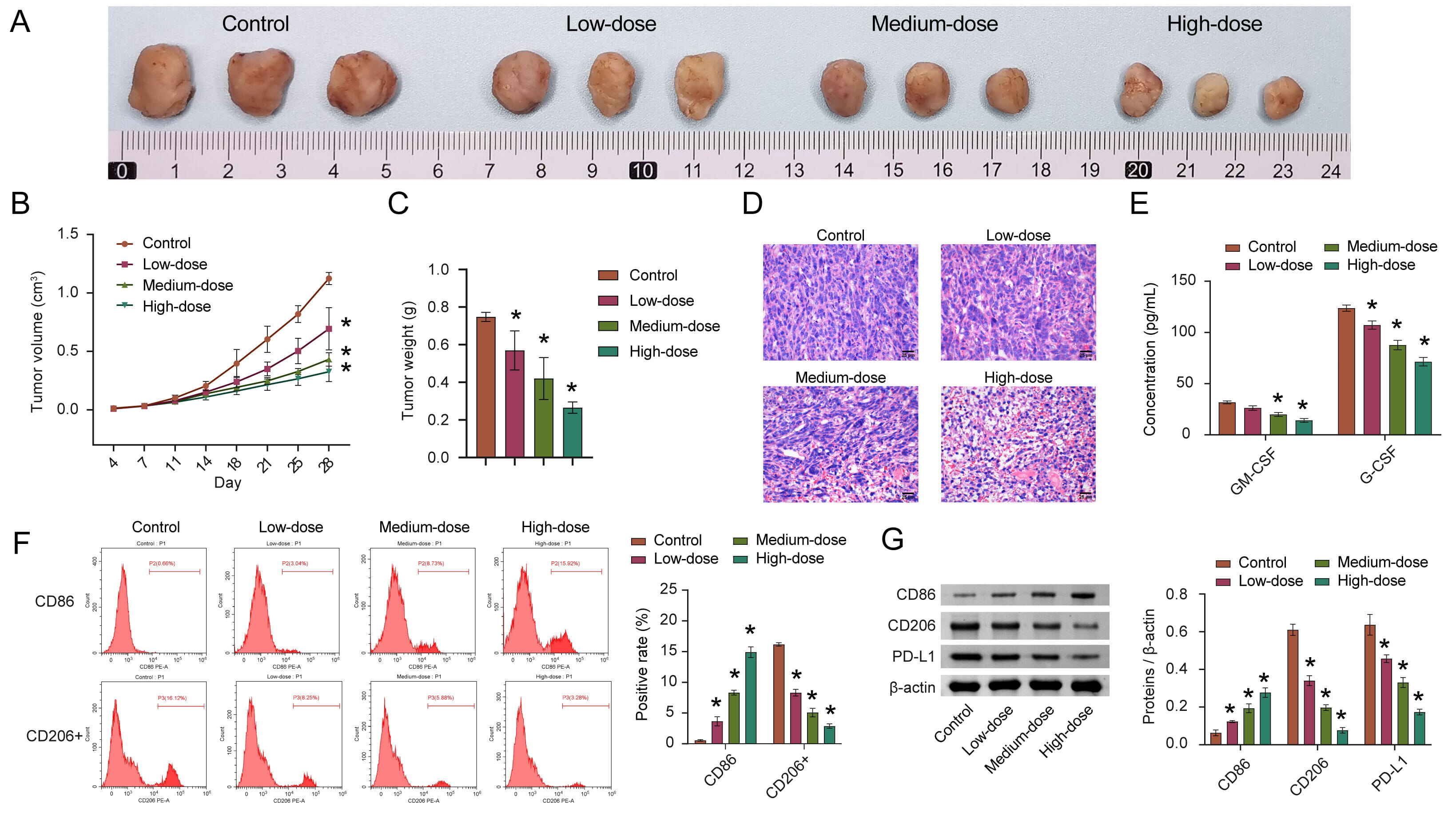 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Quercetin inhibits the development of HCC by inducing M1
polarization of macrophages. (A) Representative pictures of tumor morphology.
(B,C) Quantitative statistics of changes in tumor volume and weight. (D)
Representative images in the pathological changes. (E) The concentration of
GM-CSF and G-CSF in cancer tissue homogenate was detected via ELISA. (F) The
percentage of CD86 and CD206+ macrophages in tumor tissue were analyzed by FCM.
(G) The CD86, CD206, and PD-L1 levels were measured by WB. n = 8 mice/group.
*p
GM-CSF and G-CSF are important factors regulating the immune microenvironment [32, 33]. Therefore, the GM-CSF and G-CSF were measured by ELISA in HCC tissue homogenates. The concentrations of GM-CSF and G-CSF after quercetin treatment were lower than those in the control group (Fig. 4E). In addition, flow cytometry was used to analyze the percentages of M1 macrophages (CD86+) and M2 macrophages (CD206+). After quercetin treatment, the abundance of M1 macrophages increased, while the abundance of M2 macrophages decreased (Fig. 4F). At the protein level, CD86 and CD206 levels were consistent with flow cytometry results (Fig. 4G), suggesting that macrophages in the HCC tissue were induced to polarize towards the M1 phenotype after quercetin treatment. PD-L1 is significantly locally upregulated in the tumor microenvironment of HCC [34] and it was observed that PD-L1 was obviously down-regulated in the low, medium, and high-quercetin groups (Fig. 4G). We speculate that these results indicate that quercetin may inhibit tumor growth by regulating macrophage polarization.
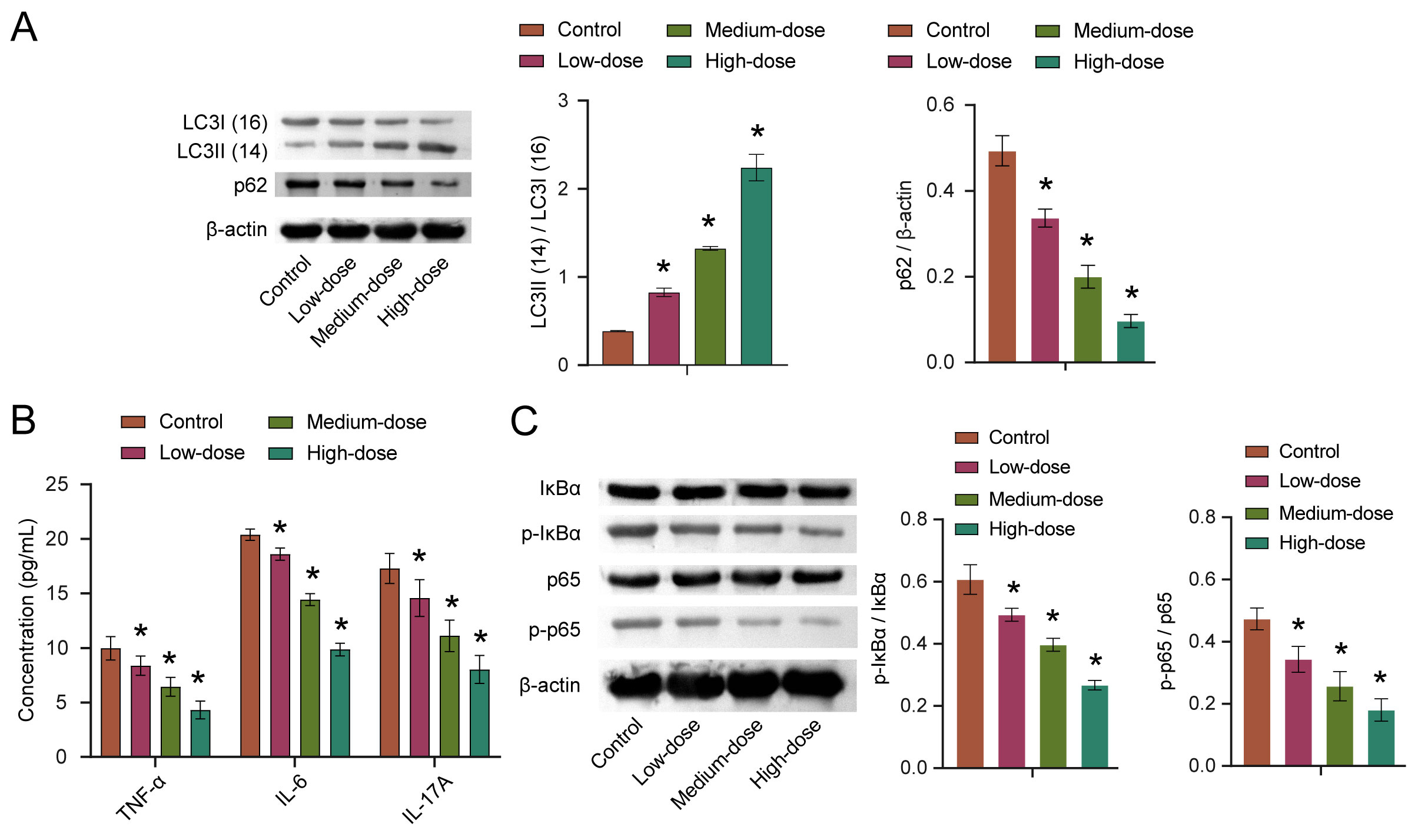
Autophagy is critical for antigen presentation and homeostasis in immune cells
and the tumor microenvironment [17]. To explore the effects of quercetin on
autophagy, we detected the expression of autophagy-related proteins LC3 and p62.
The results showed that the LC3II/LC3I ratio was increased with the increase of
quercetin concentration, while the p62 expression was decreased with the increase
of quercetin concentration. Moreover, both findings were statistically
significant (Fig. 5A). The levels of TNF-
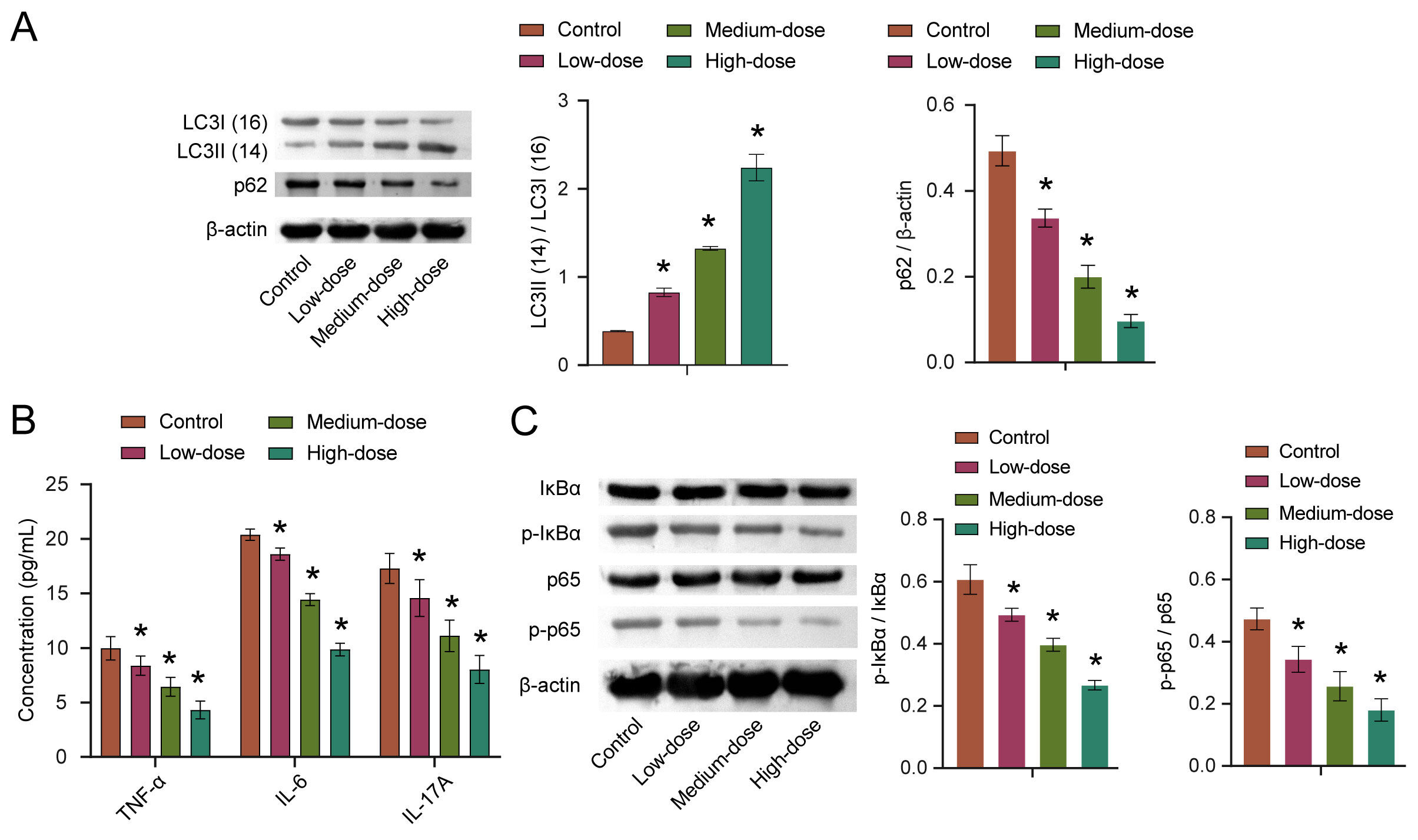 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Quercetin affects autophagy through the NF-
NF-
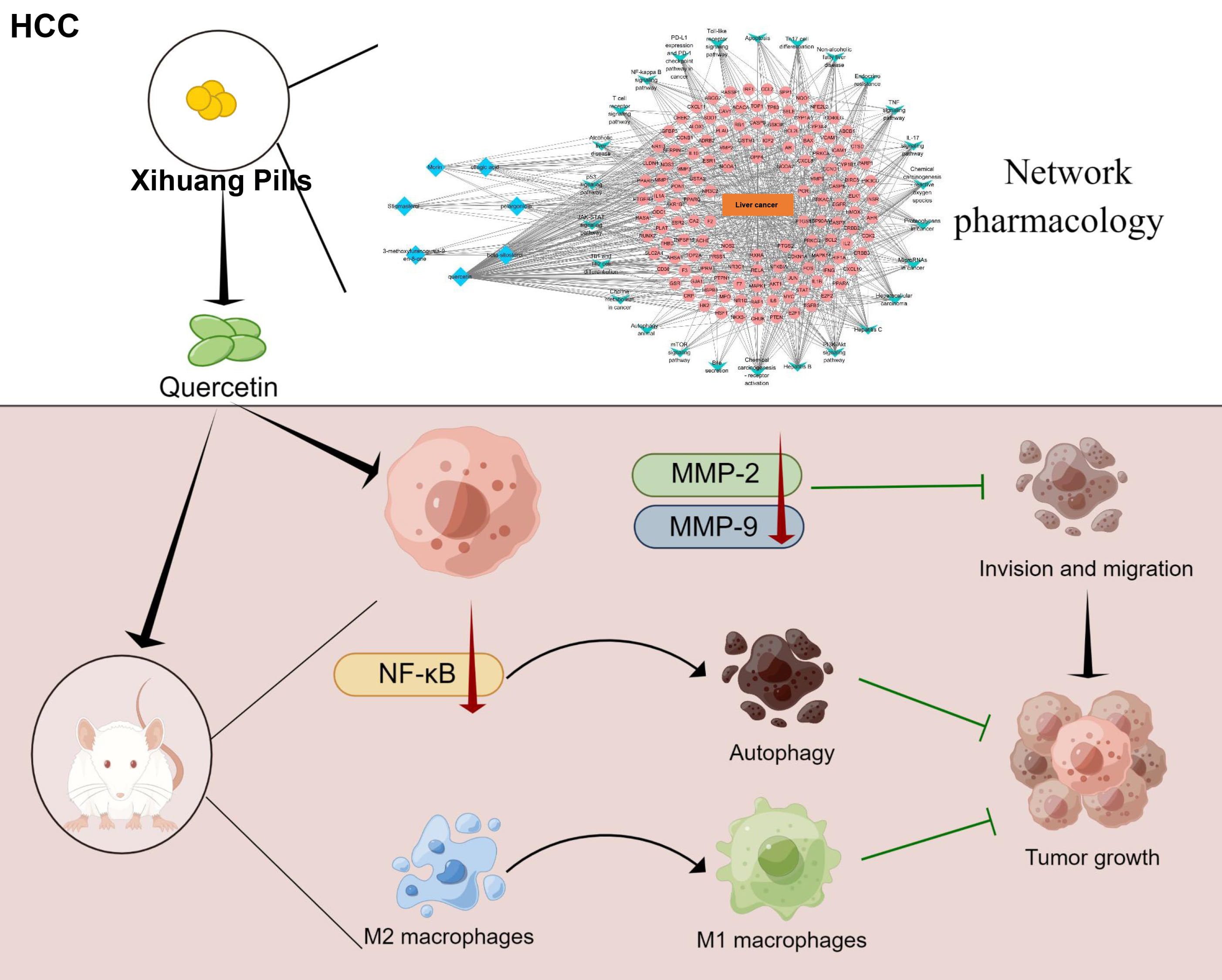
In sum, our findings indicate that quercetin inhibited HCC progression by inhibiting migration and invasion, promoting apoptosis and M1-type polarization (Fig. 6).
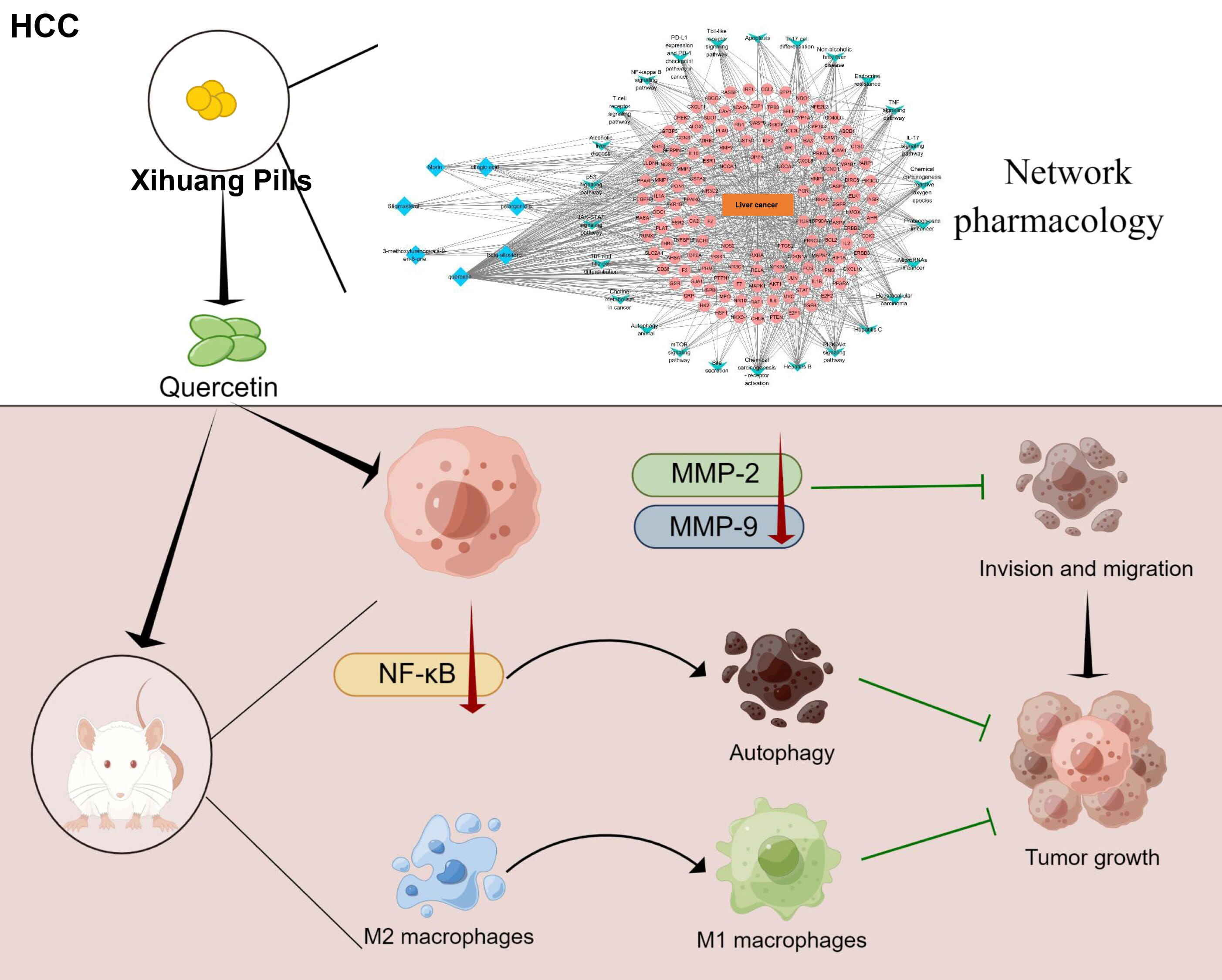 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.Schematic diagram of this study. Quercetin, the key active
ingredient of Xihuang Pills, was screened out by network pharmacology. Next,
quercetin was used to treat mice and cells in vivo and in
vitro. In vitro experiments showed that quercetin might inhibit cell
invasion and migration via the MMP-2/MMP-9 pathway. In vivo experiments
clarified that quercetin might blunt HCC development by inhibiting the
NF-
A previous study revealed that Xihuang Pills inhibited tumor growth in a Lewis lung cancer (LLC) mouse model by combining network pharmacology with metabolomics [37]. Another study, also using network pharmacology analysis, found that VEGFA and EGFR may be potential therapeutic targets of Xihuang Pill in the treatment of liver cancer [11]. While different from the above studies, we specifically analyzed the key components of Xihuang Pills for HCC treatment. Our study found that quercetin might be a key anti-HCC component in this TCM, based on network pharmacology and UPLC-MS. Following-up on these findings, the effects of quercetin on HCC and the potential mechanisms for these effects were analyzed through cultured cell and animal experiments. Quercetin inhibits the growth factor-induced migration of HCC cells by inhibiting AKT signaling [38]. Quercetin may also restrain the progress of HCC by inhibiting human glutamate dehydrogenase 1 to regulate mitochondrial function and metabolism [39]. Quercetin inhibits HCC cell migration and invasion, and promotes HCC apoptosis and autophagy by regulating JAK2 and STAT3 pathways [40]. Similarly, our study revealed that quercetin could inhibit the invasion and migration of H22 and HepG2 cells, thereby potentially inhibiting the progression of HCC.
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) play an important role within the
inflammatory microenvironment and promote the progression of HCC by promoting M1
and M2 polarization. TAM with M2 polarization induce cell proliferation,
angiogenesis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HCC [41]. Although it has
been reported that M1-polarized TAM may enhance
the viability of HCC through the NF-
Autophagy is a catabolic pathway that regulates hepatocyte function and affects
non-parenchymal cells such as endothelial cells, macrophages, and hepatic
stellate cells [46]. Emerging evidence suggests that autophagy can induce type II
programmed cell death in cancer cells and acts as a potential tumor-suppressive
mechanism [47]. P62, an important autophagic receptor, is also known as
Sequestosome 1 protein and is involved in a variety of cell signal transduction,
oxidative stress response, and autophagic processes [48]. During the process of
autophagy, the LC3II/I ratio can estimate the level of autophagy, while the level
of p62 protein is inversely proportional to the level of autophagy. Using western
blotting, LC3II/I was found to increase with the concentration of quercetin, and
p62 was coordinately down-regulated in this study. Data gathered indicated that
quercetin could improve the autophagic response in HCC. NF-
TCM have multi-component and multi-target pharmacological characteristics [50].
Our study found that the anti-tumor effects of quercetin might be related to the
promotion of autophagy and M1-type polarization of macrophages through the
NF-
Teng et al. [5] used ultra performance liquid chromatography with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) analysis to identify 12 other compounds excluding quercetin. Unlike the study by Teng et al. [5], our study used UPLC-MS to analyze the presence of quercetin in Xihuang Pills. Therefore, we speculate that the difference in experimental results may likely be due to the difference in analytical methods employed in these two studies. In the current study, network pharmacological analysis suggested that quercetin might be the key active ingredient in Xihuang Pills that targets HCC. UPLC-MS of Xihuang Pills, an anti-cancer TCM made of Commiphora myrrha Engl, Moschus, Boswellia carteri Birdwood and Bos taurus domesticus Gmelin [5], was conducted. The extract of Saudi Commiphora opobalsamum L has been shown to contain quercetin by MS and NMR spectra analysis [53]. The presence of polyphenols with possible anticancer effects in Commiphora leptophloeos extracts, such as rutin, vitexin, and quercetin diglycosides, was demonstrated by thin layer chromatography (TLC) and other analyses [54]. Similar to the above study, our results indicated the presence of quercetin in Xihuang Pills.
H22 are suspension cells, and HepG2 are adherent cells. Compared with HepG2 cells, H22 cells can rapidly increase the number of cells required for tumorigenesis in a short time without digestion and passage. In view of the time and funding constraints, we chose to use H22 cells for our tumorigenesis studies. Our study confirmed the effect of drugs on H22 and HepG2 cells in vitro, providing a theoretical basis for the application of drugs. However, we did not explore the effects of quercetin on HepG2 cells tumorigenesis in vivo, which is a study limitation.
In sum, this study uncovered a key active ingredient in Xihuang Pills is
quercetin by using network pharmacology. Cell and animal experiments have proved
that quercetin could inhibit the development of HCC. At the same time, it was
found that the anti-tumor function of quercetin might be through the regulation
of macrophage polarization in coordination with the NF-
HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; ELISA, Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay; FCM, Flow cytometry; GM-CSF, Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; TCM, Traditional Chinese medicine; TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; OB, Oral bioavailability; DL, drug-likeness; PPI, Protein-Protein Interaction; GO, Gene Ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; UPLC-MS, Ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometer; DMEM, Dulbecco’s minimum essential medium; FBS, fetal bovine serum; CCK8, Cell Counting Kit-8; FCM, Flow Cytometry; WB, Western blot; PVDF, polyvinylidene fluoride; ECL, Enhanced Chemiluminescence; H&E, Hematoxylin-eosin; SD, standard deviation; LLC, Lewis lung cancer; TAM, Tumor-associated macrophages.
Data sharing is not applicable to this article, as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
RW and XT designed the research study. RW, TZ, JX, ZZ, ST, and XT performed the research. YW and JC analyzed the data. RW wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
According to the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, animal experiments were conducted and approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (No. ZYFY20210320).
Not applicable.
This work was supported by the Youth program of Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2021JJ40407); the Youth project of Hunan Administration of traditional Chinese Medicine (202101); the Outstanding youth project of Hunan Education Department (20B451); and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U20A20408 and 82074450).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.