1 National Institute of Food Science and Technology, University of Agriculture, 38000 Faisalabad, Pakistan
2 School of Pharmaceutical Science, Health Science Center, Shenzhen University, 518060 Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
3 Food and Feed Immunology Group, Laboratory of Animal Food Function, Graduate School of Agricultural Science, Tohoku University, 980-8572 Sendai, Japan
4 Centro Tecnológico de la Carne de Galicia, Avda. Galicia Nº 4, Parque Tecnológico de Galicia, San Cibrao das Viñas, 32900 Ourense, Spain
5 Área de Tecnología de los Alimentos, Facultad de Ciencias de Ourense, Universidad de Vigo, 32004 Ourense, Spain
6 Department of Food Biotechnology and Microbiology, Institute of Food Sciences, Warsaw University of Life Sciences—SGGW, Nowoursynowska 159 C, 02-776 Warsaw, Poland
7 Department of Livestock and Poultry Production, Faculty of Veterinary Sciences, Bahauddin Zakariya University, 60800 Multan, Pakistan
Abstract
Chia (S. hispanica L.) is an annual herbaceous plant that has gained
popularity for its seeds of high-quality vegetative proteins, richest contents of
omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (
Keywords
- Chia hydrolysates
- Antioxidative
- Antiinflammatory
- Antihypertensive
- Chia bioactive peptides
The hunt for natural protein sources with bioactive ingredients for the creation of functional foods with a high nutritional impact and concurrent health benefits is rising [1]. But there is still a gap among experiments done in laboratories and the innovations at industrial levels, which needs to be filled [2]. Such utilization of bioactive constituents into the routine diet for therapeutic purposes is known as alternative medicine [3], which has been proven effective for preventing, slowing the progression, and overall complete regression of many diseases. This surge in demand for functional foods has directed human efforts toward the fortification of their bioactive constituent to deliver potential health benefits and disease prevention [3, 4, 5].
Dietary protein serves as a source of exogenous peptides that can perform comparable regulatory activities as endogenous peptides (hormones) do in our body to control our endocrine and neurological systems. These exogenous peptides are referred to as “bioactive peptides” because of their physiological relevance and nutritional significance. These peptides typically range in length from 2 to 20 amino acids (AA) and can be found in any encrypted section of a protein sequence [4, 6]. Numerous epidemiological and clinical research back up the idea that higher consumption of functional foods from plant origin can help to reduce the risk of many chronic ailments [5, 7]. Moreover, these vegetative food sources continue to be an essential primary source of protein in developing countries, therefore increasing the agricultural output of such beneficial crops to provide balanced and appropriate nutritional intake for the population is critical [1].
Among those functional foods, chia (Salvia hispanica L.), a herbaceous
annual plant that belongs to the Lamiales order, Lamiaceae
family, Nepetoideae subfamily, and Salvia genus [8], has attracted worldwide
interest owing to its nutraceutical advantages. Several studies have shown that
the chia seed might be a useful tool in the fight against many diseases [9, 10].
The word “chia” has been adapted from the Spanish word “Chien” or “Chian”
meaning “oily” [11]. While all of its leaves, flowers, and seeds can be used
and its beautifully marbled grey to dark brown seeds has been reported for their
proven health protection against multiple metabolic disorders. With the
progression of research, chia seeds have emerged as plant-based nutraceuticals
and have gained the attention of nutritionists due to their balanced nutritional
composition of proteins, fibre, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (
All in all, chia seed has now been recognized by dietitians as a product with a
long list of possible health advantages about various ailments. Multiple recent
studies have shifted their focus from its rich
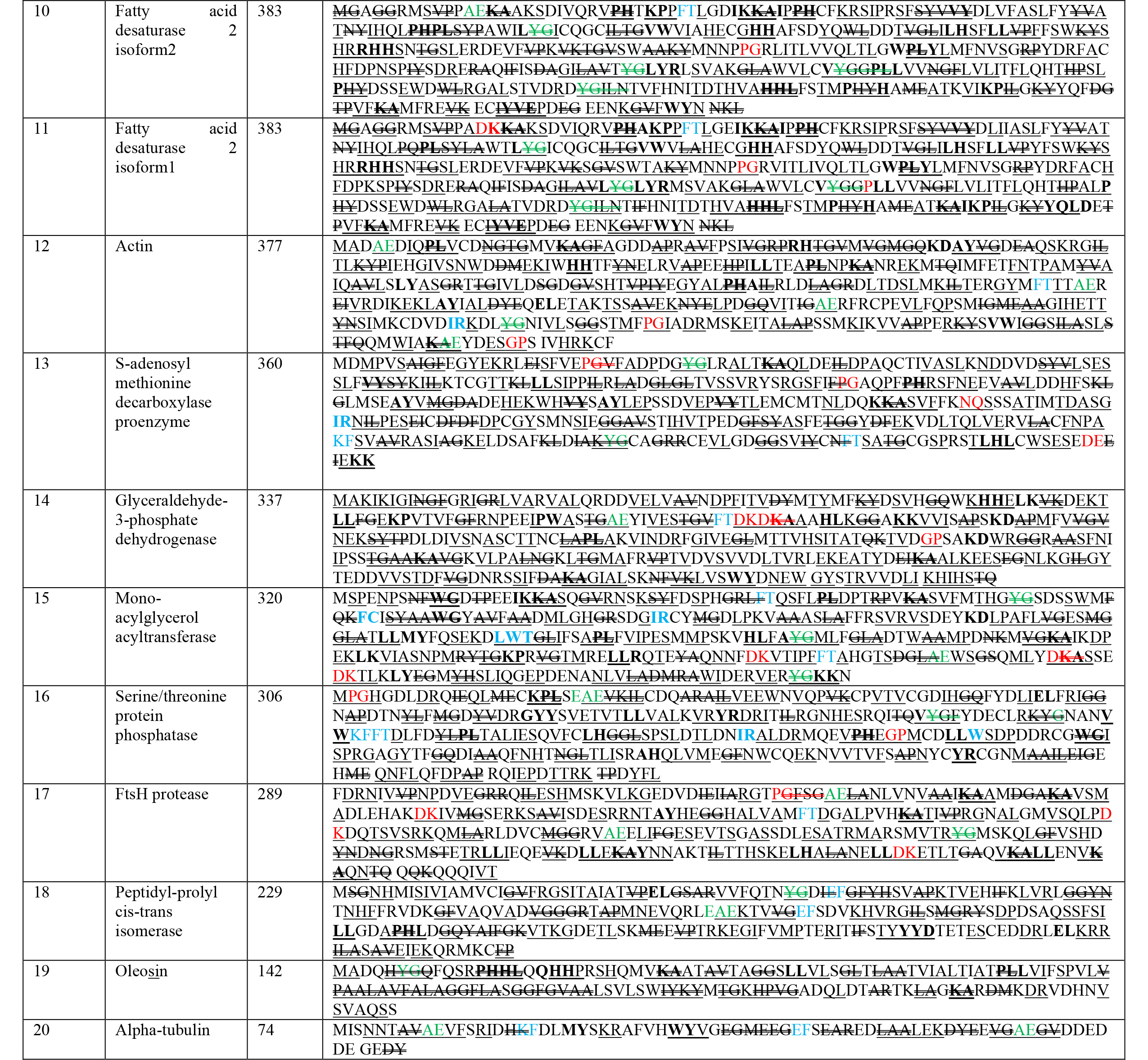
The nutritional composition of chia seeds is elaborated in Fig. 1. Previous
literature revealed healthy fat contents ranging from 31 to 35% [14, 15, 16, 17, 18], with
distinctive ALA, that is vegetative
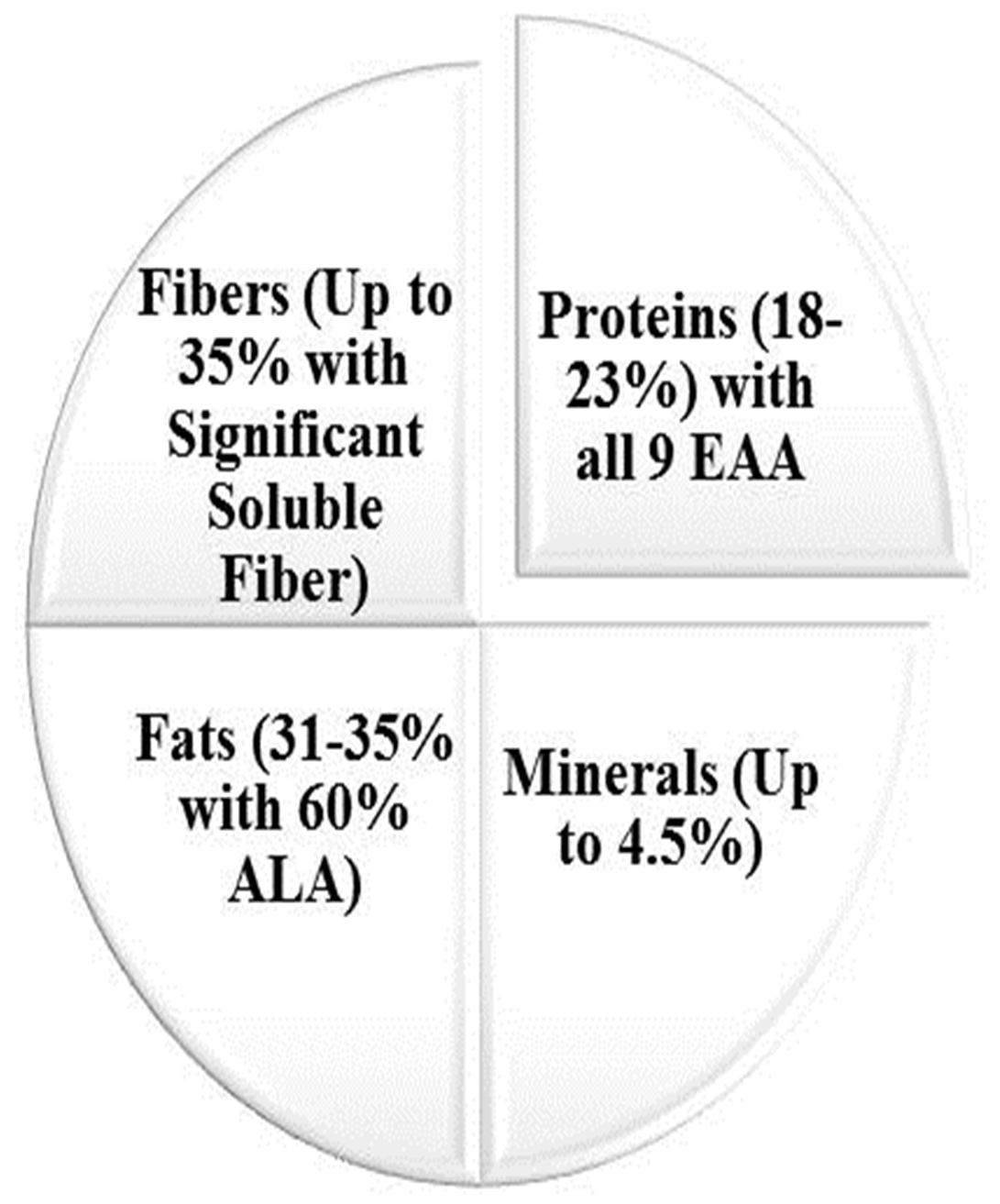 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Nutritional composition of chia seed.
An examination of the AA makeup in chia seed revealed a total of 10 AA, including all nine essential AA (leucine, isoleucine, lysine, phenylalanine, methionine, tryptophan, threonine, histidine, and valine), and this quality makes it a complete protein source for human nutrition [24], where arginine, phenylalanine, leucine, valine, and lysine are exogeneous, while glutamic, alanine, aspartic acids, serine, and glycine are endogenous AA [11]. As a result, these seeds have been hailed as the super new golden seed, and also known as the seed for the twenty-first century, and have been chosen for present use [25].
Chia seed has been remained a seed of hidden potential for strength and energy
in history and was consumed by Aztec soldiers and pre-Columbian populations in
the 16th century during their battles and expeditions [8]. Highly nutritious
gluten free bread was prepared by incorporating 5%–14% whole chia flour in the
recipe [26]. Chia seed mucilage spreads by breaking the primary layer of cells
and swells, resulting in the appearance of gel that has been widely used in
drinks, salads, and ice creams. It can be consumed as whole seed topped on
desserts, socked to make gel in beverages, in its flour form alone, or by its
supplementation in other foods like yogurts, fruits, salads, and bakery, etc.
[8]. It is available not just as seeds, but
also as oil, which also has health-protective and anti-inflammatory properties
due to rich
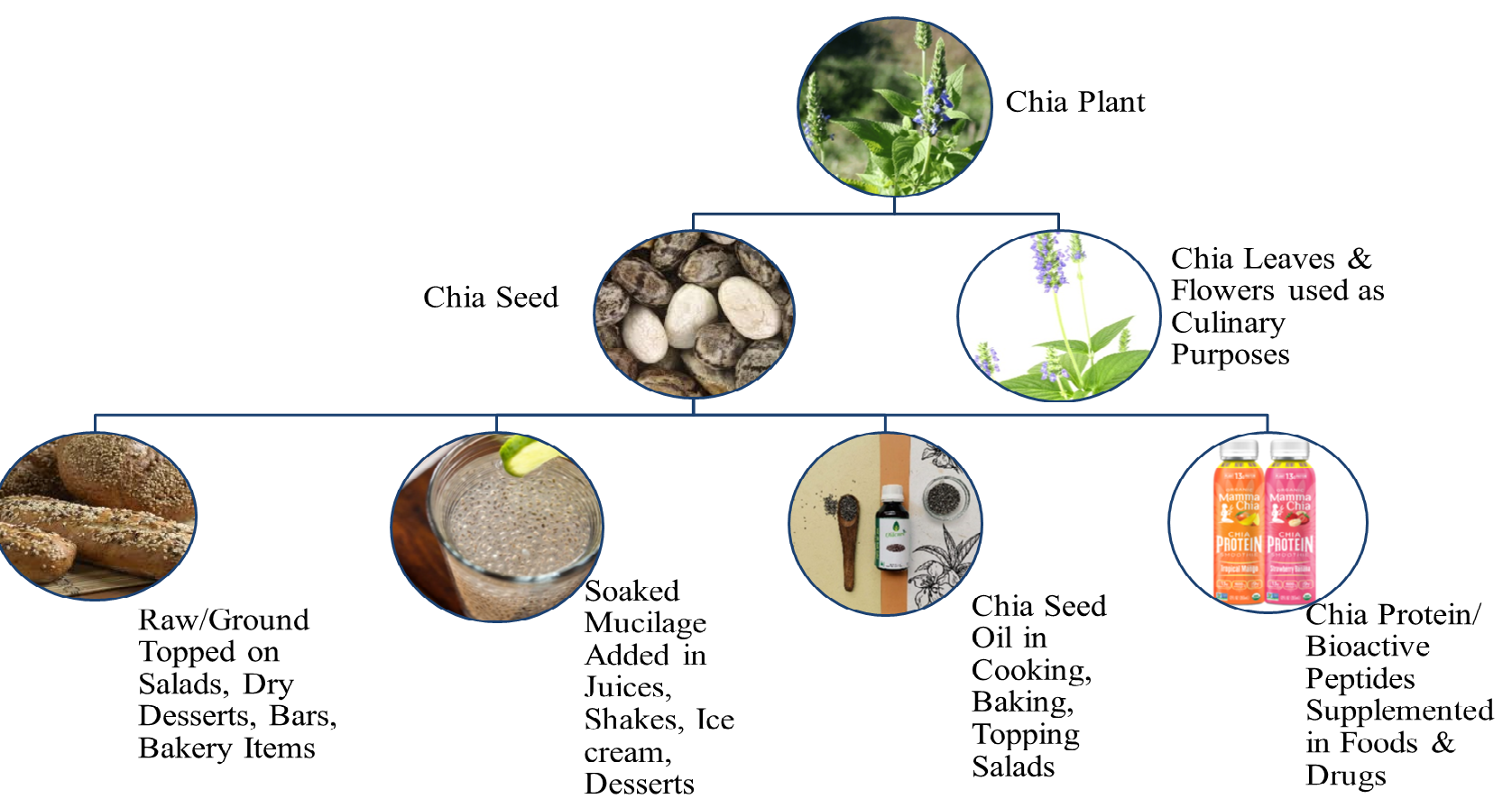 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) utilization in various dietary forms.
The addition of chia in bakery products not only provides nutraceutical and nutritional benefits but also increases its textural properties of holding water contents and increasing sensorial appraisal due to its gelling ability and rich protein and fiber contents as compared to ordinary wheat flour [26, 28].
All naturally existing proteins can be processed to yield peptides, but it is better to use the leftover policy at the industrial level because 10–50% of protein content is wasted in leftover by-products of agro-industry that can serve as bioactive peptides. We can utilize the solid residual by-products of the chia seed oil extrusion process that is known as chia expeller to produce value-added products in the food and medicinal industry. Therefore, utilization of this chia expeller has been gaining popularity to produce maximum bioactive peptides by using different techniques, as highlighted below. These peptides can serve many functional benefits in the food industry due to their antioxidative and nutraceutical potentials [1, 22, 29]. Therefore, bioactive peptides and their nutraceutical benefits have driven human interest towards the plant food proteins and their utilization as predictive medicine, hence modulating current food trends towards fortification of functional bioactive peptides [4, 6].
Bioactive peptides remain inactive when bound inside the parent protein sequence of plants, animals, or marine foods. They need to be activated by hydrolysis/digestion using enzymes, fermentation, chemical or gastrointestinal digestion The resultant peptides formed can act as regulatory factors of hormone-like activity as hypotensive, anti-cancer, hypocholesterolemic, and immunomodulatory agents that represent the potential nutraceutical properties of health-enhancing for food and drug [8]. Besides, the human body can produce these bioactive peptides from dietary proteins during enzymatic hydrolysis in the gastrointestinal tract, but in laboratory proteolysis, specific proteases are used to obtain bioactive peptides of a specific activity. These industrial food-grade proteinases can be derived either from microorganisms (proteinase K, collagenase, pronase, subtilisin A, Flavourzyme® and Alcalase®) or plant (Papain, ficin, bromelain) or animal sources (trypsin or pepsin, chymotrypsin) [6]. The most adapted methods used for protein digestion to yield peptides of interest are microbial fermentation and enzymatic hydrolysis that could be microwave or ultrasound-assisted followed by any suitable separation technique, i.e., ion exchange chromatography (IEC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry (MS), size exclusion chromatography (SEC), affinity chromatography (AC) and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) as explained in Fig. 3.
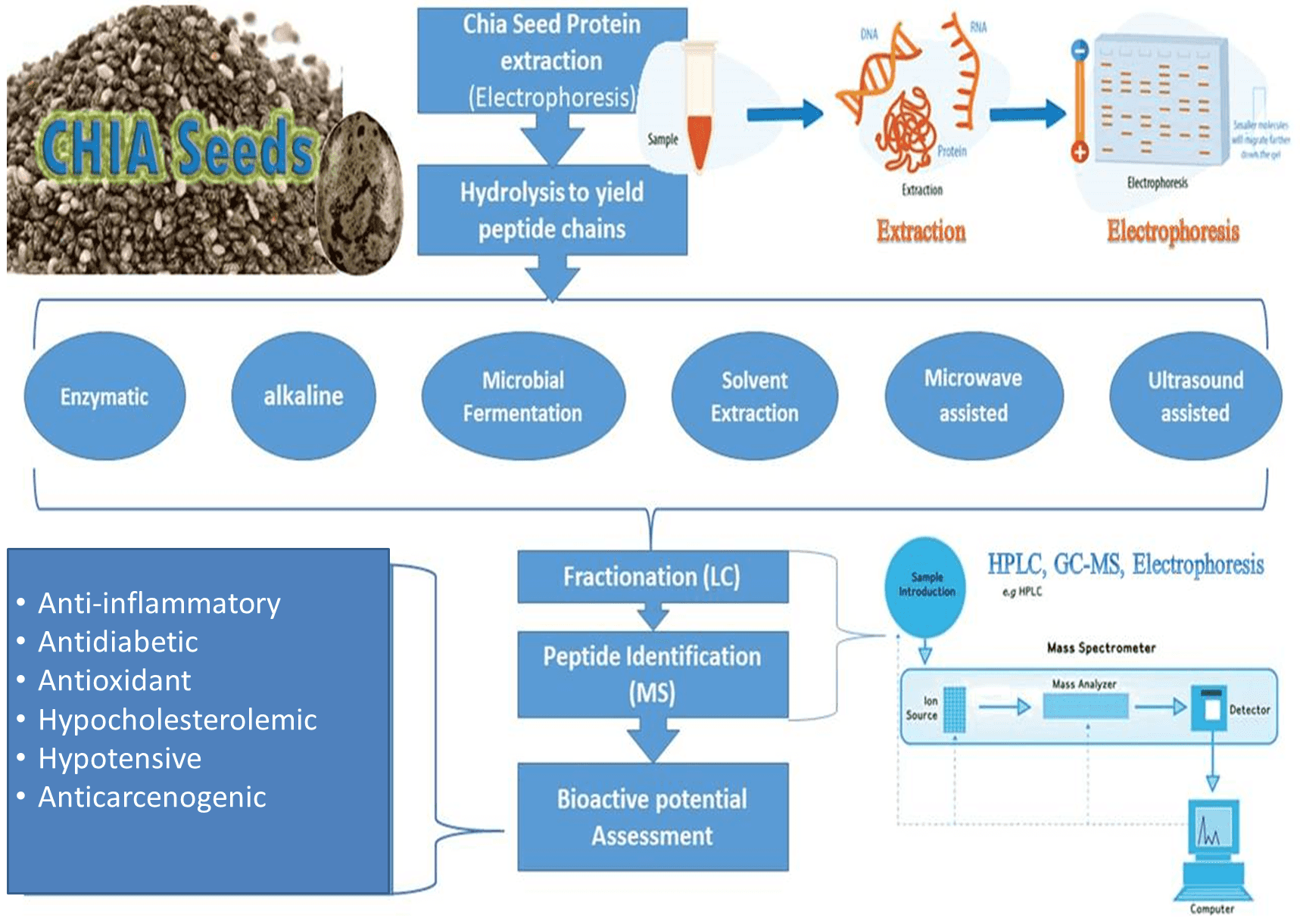 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Schematic diagram for chia seed bioactive peptides derivation.
The methodology followed to derive bioactive peptide should be chosen very carefully as, the final molecular weights are highly affected by the method adopted i.e., enzymatic, alkaline, microwave-assisted, ultrasound-assisted, nature of extraction solvent, purification protocol, and drying techniques, etc. Moreover, the consequent molecular weights, amino acid sequences (AAS), their interrelationship, and their hydrophobic or hydrophilic nature of derived peptides are responsible for their functional potential and nutraceutical advantages [22]. Table 1 summerizes the latest techniques adapted for peptide derivation from chia protein.
| Year | Method | Derivation | Separation | Results & Bioactivity | Reference |
| 2020, 2013 | Enzymatic hydrolysis + Enzymatic (Microbial Fermentaion) | Two different proteases (Papain and Alcalase®), extraction pH10-12; precipitation pH | - | Alcalase® and papain both increased the degree of hydrolysis, peptides content, protein solubility, antioxidant capability. | [30, 31] |
| 3.5–4.0. Diethyl ethoxymethylenemalonate | But antioxidant activity was highest by Alcalase® at 60 mins of hydrolysis | ||||
| 2020 | Microwave assisted, Enzymatic (Microbial Fermentaion) | Sequential enzymatic (alcalase followed by flavourzyme) | size exclusion chromatography (SEC) | The |
[21] |
| 2019 | Microwave assisted, Enzymatic (Microbial Fermentaion) | Ultrasonication to remove mucilage, alcalase + flavourzyme | SDS- PAGE | Peptides of molecular weight 25 kDa; highest antioxidant and ACE inhibition activity observed | [32] |
| 2019 | Enzymatic hydrolysis | Papain | SDS-PAGE and MALDI-TOF/MS | Peptides of low molecular weight |
[1] |
| 2019 | Enzymatic hydrolysis | Pepsin and Pancreatin | ultrafiltration membranes with molecular weight cut-off | Peptide fractions ( |
[33] |
| 2019 | Enzymatic hydrolysis | Sequential enzyme digestion with pepsin + pancreatin | SDS-PAGE | Digested albumin, globulin, and glutelin showed increased antioxidant potentials | [34] |
| 2019 | Enzymatic (Microbial Fermentaion) | Alcalase + flavourzyme | UHP 76 (Advantec MFS) ultrafiltration unit | Peptide fractions ( |
[29] |
| 2018 | Enzymatic (Microbial Fermentaion) | Alcalase + flavourzyme | ultrafiltration through a membrane with 3 kDa nominal molecular weight | Peptides with lower molecular weight than 3 kDa reduced 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA reductase) | [35] |
| 2018 | Isoelectric pH gradient | Isoelectric precipitation method at different pHs (pH 2.0–6.0) | SDS-PAGE | Protein isolates ate pH 3.0 showed highest anti-inflammatory activity, while at pH 6.0 showed antioxidative | [36] |
When protein is hydrolyzed enzymatically at a specific pH and temperature, it is
known as enzymatic hydrolysis. Any crude or purified proteolytic enzyme can be
used to hydrolyze proteins into hydrolysates holding short peptide sequences. The
simultaneous or sequential addition of enzymes depends upon the temperature and
optimal pH of the enzymes. After enzymatic hydrolysis, the supernatant can be
separated from the mixture by centrifugation, cross-flow membrane filtration,
freeze-drying, desalting, and column chromatography like gel filtration, which
quickly desalt the peptides of low molecular weight [4]. During the enzymatic
hydrolysis of bioactive peptides, many factors like enzyme specificity, enzyme to
substrate ratio, hydrolysis time, and protein pretreatment before hydrolysis can
affect the resulting peptide structural physicochemical properties. Enzymatic
hydrolysis may be performed using specific or non-specific single or multiple
proteases for the production of angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
and antioxidant peptides [37, 38, 39]. Papain-based hydrolysis was used to yield
peptides of low molecular weight of
Microbial fermentation is done by involving culture media of bacteria or yeast on protein substrates for protein hydrolysis. Microbial fermentation is preferred over enzymatic hydrolysis when the lowered cost of the protocol is concerned as microorganisms are a cheap supply for producing proteases [42]. The growing microorganism secretes its proteolytic enzymes, which act on protein to release peptides. Most often, the preferred bacterium is cultivated in a broth at a suitable temperature. Then suspension of microbial cells in sterile water is done that can be used as a starter for inoculation into sterilized protein substrate. The extent of analysis depends on the used strain, protein type, and fermentation time. The utilization of lactic acid bacteria such as lactobacilli is a successful technique for the development and commercialization of novel bioactive peptides. Proteolytic activity of lactobacilli varies according to strain and species, i.e., each species has a varied proteinase composition, resulting in a wide range of proteolytic activities [43]. This demonstrates Lactobacillus strains’ strong potential for producing new hydrolysates and bioactive peptides of great interest. For example, utilization of Lactobacillusbrevis for stronger ACE inhibition ability has been reported when compared with other species of Lactobacillus origin. Hence protein hydrolysates functionality may differ between cultures due to different proteolytic systems [4]. Similarly, microbial enzyme Alcalase® was used to enzymatically hydrolyze the chia protein-rich fractions for 60 min, followed by Flavourzyme® for up to 150 min. Hydrolysates generated were tested for ACE-inhibitory, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties. The hydrolysate generated at 150 and 90 min had the strongest ACE-inhibitory and antioxidant activities respectively. Antioxidative and antihypertensive peptides are better liberated using fermentation [41, 44]. Mucilage on chia seed hinders proper hydrolysis of chia seed proteins, therefore ultrasonic treatment was employed for its separation. Following that, defatted chia seed meal was microwave-assisted hydrolyzed utilizing sequential enzymatic (Alcalase® followed by Flavourzyme®) hydrolysis. The hydrolysate was then separated using ultrafiltration with a 3 kDa cutoff membrane. Chia seed hydrolysates exhibited superior antioxidative activity in vitro. DPP-IV inhibition was also greater [21, 32]. Microwave-assisted hydrolysis was used to yield chia seed-derived bioactive peptides after removal of chia seed mucilage using a combination of ultrasonic treatment and vacuum-assisted filtration. Hence, bioactive peptides derived by microwave and enzymatic hydrolysis from chia seed can be employed in therapeutic foods as antimicrobial agents [21].
Following the synthesis of the peptide, they are allowed to undergo a separation
technique that includes centrifugation and washing to remove reagent residues as
well as side reaction products. Following that, the peptides are cleaved and
filtered. The most often used procedures for peptide purification include HPLC,
IEC, SEC, AC, and capillary electrophoresis [42]. Peptides when separated by
denaturing sodium dodecyl sulfate SDS-PAGE after being released enzymatically,
revealed globulin as the most abundant protein profile, followed by albumin [45].
Similarly, upon fractionation chia protein revealed globulins as a major fraction
(52%), where globulin fraction comprises predominantly 11S and 7S proteins,
according to sedimentation coefficient studies. All of the reduced fractions had
molecular weights of 15–50 kDa [41]. In another previous study, electrophoresis
revealed four bands (104–628 kDa) of proteins including albumins, globulins,
prolamins, and glutelins with denaturation temperatures of 103, 105, 85.6, and 91
Twelve proteins are found responsible for the metabolic functions like metabolism and cell division of seed, whereas the remaining eight are related to lipid production and storage [8]. The ability of 3 kDa chia seed peptides to suppress aging-related enzymes such as collagenase, hyaluronidase, tyrosinase, and elastase was tested. SEC was used to extract additional fractions, which were then evaluated for enzyme inhibitory activity. The 3 kDa peptides inhibited the enzymes elastase, tyrosinase, hyaluronidase, and collagenase. The second SEC fraction showed stronger enzyme inhibitory activity and included these 7 peptides (APHWYTN, DQNPRSF, GDAHWAY, GDAHWTY, GDAHWVY, GFEWITF, & KKLKRVYV) having 19–29 enzyme–peptide pair interactions towards these enzymes. These findings suggest that chia seed peptides may help to promote skin health by providing protection against aging-related enzymes and reducing the breakdown of the protein matrix on the skin [21].
Chia seed consumption has been gained due to its nutritional composition being
rich in
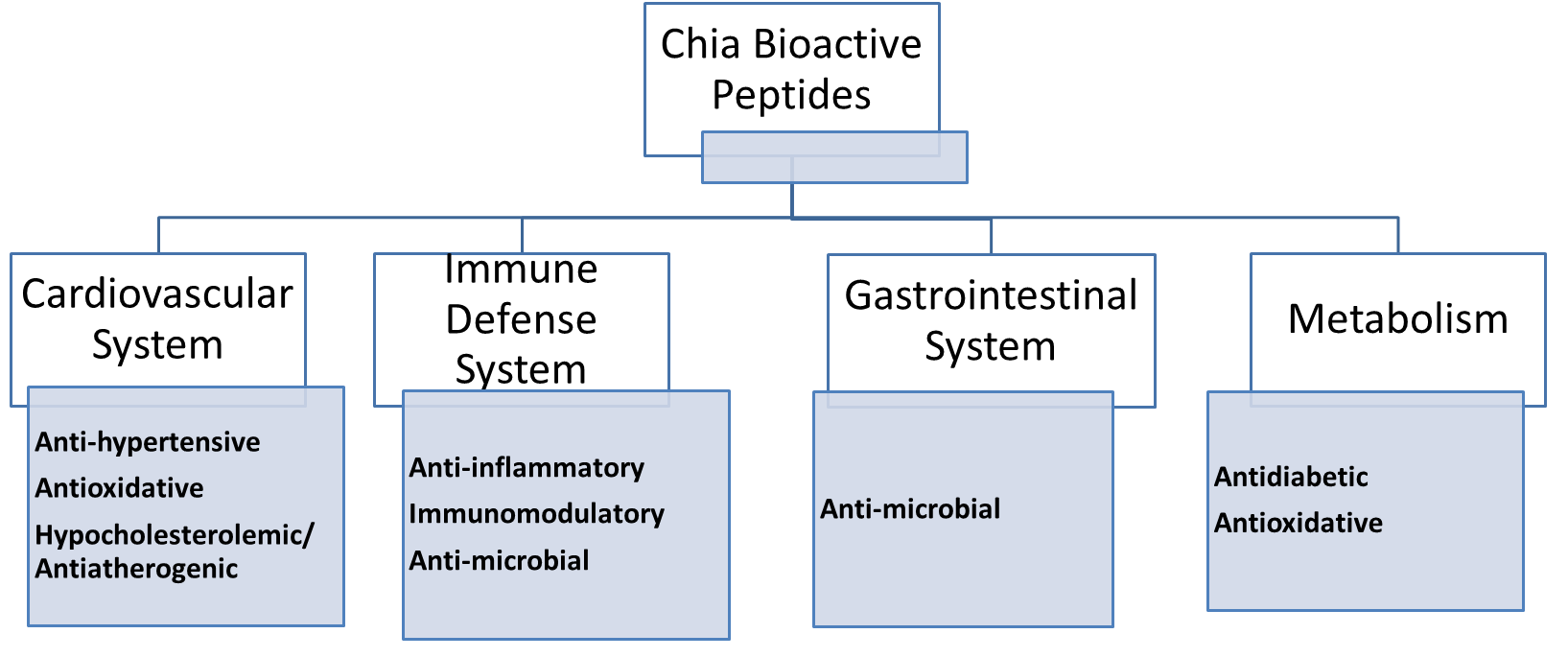 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Nutraceutical potentials of chia seed bioactive peptides.
The bioactive potential of chia-derived peptides was reported active for ACE
inhibitors, DPP-IV inhibitors, and antioxidant capacity. Hence reinforcing the
health benefits of chia for its hypotensive, hypocholesterolemic, hypoglycemic
and antioxidant potential [8]. Chia seed is a rich source of antioxidants like
chlorogenic acid, myricetin, caffeic acid, quercetin, and kaempferol, which is
believed to possess protective effects on cardiac, hepatic, aging, and
carcinogenic characteristics. Its rich contents of dietary fibre are beneficial
for controlling diabetes and assisting the digestive system, whereas its healthy
Chia seed peptides were found highly antioxidant using sequential and
traditional hydrolysis with microwave treatment [32]. Chia seed consumption in
either way has also been reported active for its radical scavenging property and
deactivating 2,2
CPH produced in either way was found active for ACE inhibition activity [32]. Albumin and globulin from chia seed protein were reported with higher ACE activity [45]. Chia seed bioactive peptides consumption showed inhibition activity of ACE directly proportional to the duration of peptides hydrolysis process [44]. The inhibitory effect of ACE by chia seed protein fractions was reported to be strongest for albumin and globulin [25].
Several chia protein peptides interacted with inflammation and atherosclerosis
indicators. For several peptides, this interaction proved more effective than the
pharmacological controls [34]. Digested total proteins and isolated protein
fractions from chia yielded albumin, globulin, prolamin, and glutelin peptides
interacted with COX-2, p65- nuclear factor kappa B, LOX-1, and toll-like receptor
4. Anti-inflammatory potential was marked positive for H
Peptides from chia protein with molecular mass less than 3 kDa inhibited the velocity of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA reductase) by up to 80.7 percent. It was suppressed by pravastatin by 81.5%. The bioactive peptides discovered in this study are structurally different from known statins, they constitute a unique class of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors that can directly interact with this enzyme to block the mevalonate pathway and prevent hypercholesterolemia [35].
Chia seed bioactive peptides were derived with microwave-assisted hydrolysis
using sequential enzymes and fractionated into
This review reveals that most of the peptides identified from chia seeds up till now have been proved to exert their active potential against various disease markers like antioxidative, hypoglycemic, immune-modulatory, anti-inflammatory, hypocholesterolemic, and antihypertensive potential. When these bioactive peptides are consumed daily either by direct consumption or indirect in the form of supplemented products, nutraceutical benefits can be attained for various disease biomarkers as highlighted above. Although there is considerable work done on the production, processing, and utilization of bioactive peptides from various proteins there is still a need to go for comprehensive nutraceutical studies on selected proteins and their peptides to identify their bioactivity for various individual disease biomarkers. In the case of chia proteins and their bioactive peptides, there is a wide gap to be filled in research and literature to draw the attention of nutrition professionals to discover the mechanisms behind their role and their modes of implementation in daily life.
This paper summarizes the nutraceutical benefits of chia seed derived peptides, their bioactivity potentials along with the most adapted techniques used for their derivation. Still, there is a lot more gap to be filled by clinical investigations and critical evaluation of the chia seed derived peptides.
RR, MRK, HMM, MSRR, JML, MK, ARK, MAS, RMA—manuscript preparation, MK, JML, RMA—Supervision.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
The authors are thankful to the University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan for their support. Thanks to GAIN (Axencia Galega de Innovación) for supporting this study (grant number IN607A2019/01).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
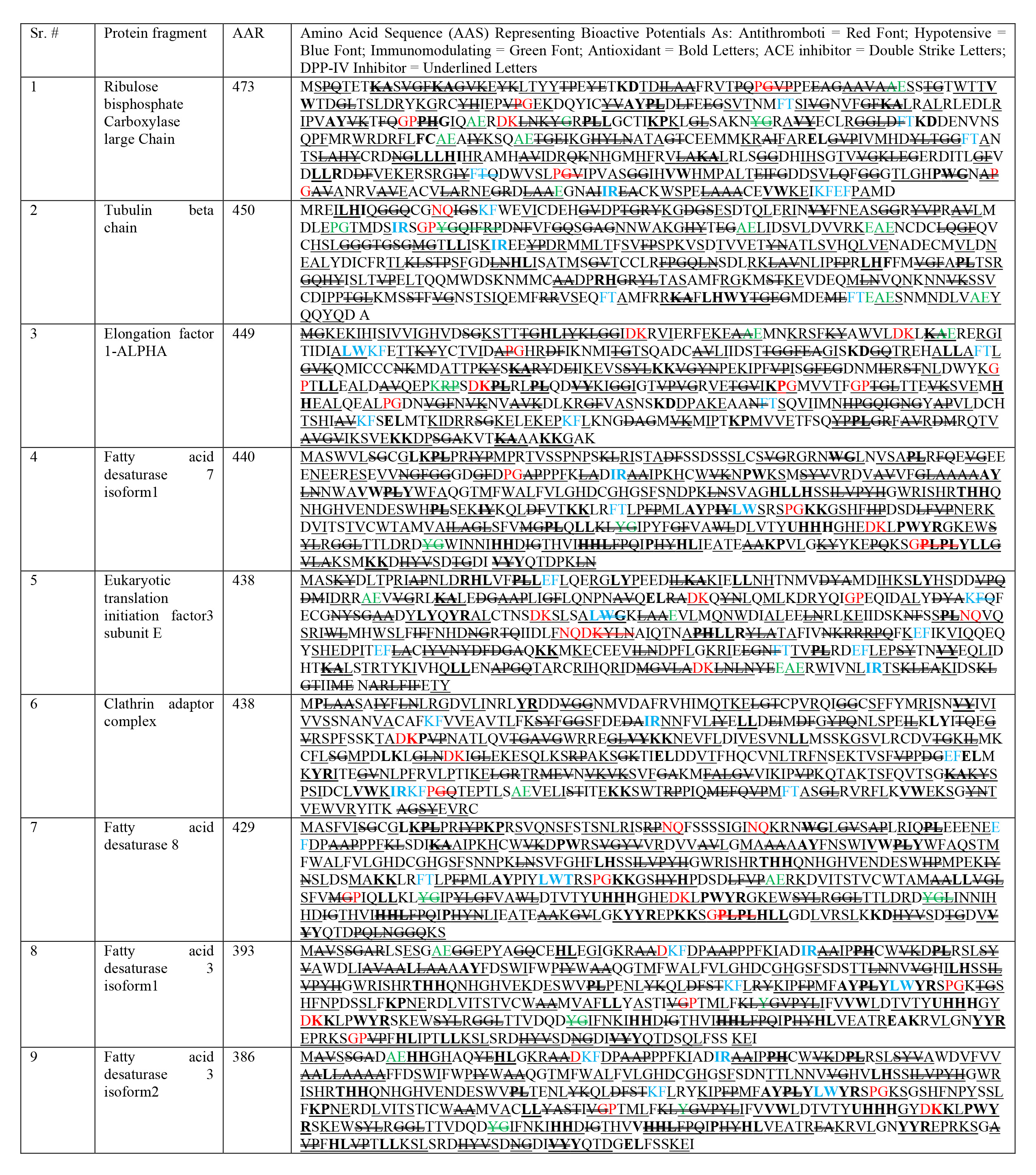
See Table 2.
|
|
| AAN, Amino acid nomenclature; H, his; histidine; C, cys; cysteine; I, ile; isoleucine; S, ser; serine; M, met; methionine; V, val; valine; G, gly; glycine; A, ala; alanine; L, leu; leucine; T, thr; threonine; P, pro; proline; F, phe; phenylalanine; Y, tyr; tyrosine; R, arg; arginine; W, trp; tryptophan; N, asn; asparagine; D, asp; aspartic acid; B, asx; either of D or N; Q, gin; glutamine; E, glu; glutamic acid; Z, glx; either of E or Q; K, lys; lysine; X, undetermined amino acid. AAN & AAS adapted and reproduced from Grancieri et al., (2019) [8]. Table reveals similar bioactivity mapping from AAS similarity, after tabulating previously derived chia peptides, and identifying their bioactive potential for multiple disease biomarkers in following way (Antithrombotic potential indicated as Red Font; Hypotensive potential indicated as Blue Font; Immunomodulating potential indicated as Green Font; Antioxidant potential indicated as Bold Letters; ACE inhibitor potential indicated as Double Striked Letters; DPP-IV Inhibitor potential indicated as Underlined Letters). |