Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark (FBL) is published by IMR Press from Volume 26 Issue 5 (2021). Previous articles were published by another publisher on a subscription basis, and they are hosted by IMR Press on imrpress.com as a courtesy and upon agreement with Frontiers in Bioscience.
1 Department of Physiology, Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA
2 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA
Abstract
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are evolutionarily conserved molecules that detect exogenous and endogenous molecular patterns and trigger both the innate and adaptive immune systems to initiate a pathogen-specific immune response and eliminate the threat. However, sustained, or prolonged activation of the immune system disrupts immunological homeostasis and leads to chronic or acute inflammatory diseases. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) can intervene in the initiation and modulation of the complex immunoregulatory networks via regulating the expression of TLRs and multiple components of TLR-signaling pathways including signaling proteins, transcription factors, and cytokines. Moreover, the aberrant expression of TLRs can induce the expression of several miRNAs which in turn regulate the expression of TLR signaling components and TLR-induced cytokines. The present review aims to highlight the emerging roles of miRNA in the regulation of TLR signaling, the interaction between the miRNAs and TLRs, and their implication in inflammatory diseases.
Keywords
- miRNA
- TLR
- Immunity
- Cytokine
- SNAP
- Chemokine
- Review
The immune system is a complex network of immune organs, cells, and soluble factors (cytokines) that act locally or systemically through an immediate (innate) inflammatory response by cytokines and phagocytes, and a specific tailored immune response through adaptive immune cells, or a regulated immune-tolerant response. The differing, and sometimes opposing, roles of the immune system are mediated by a complex interplay of intracellular and extracellular signaling pathways. Cells of the immune system participate in the protection of the host from invading pathogens, foreign antigens, and incipient tumor cells, and in development, maintenance of homeostasis, tissue repair and regeneration processes for wound healing (1). The innate immune system depends on the pattern recognizing receptors (PRRs), includes components of the complement system and Toll-like receptors (TLRs) family. TLRs are membrane-associated innate-immune sensors that detect the external pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or the internal damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and execute subsequent immune cell response (2); (3); (4). TLRs, the most extensively studied PRRs, are type-I transmembrane glycoprotein receptors. TLRs consist of three structurally important domains namely an ectodomain consisting of hydrophobic leucine-rich repeat region (LRR) for ligand recognition/binding at N-terminus and formation of functional dimers to initiate the signaling cascade, a single transmembrane helix, and a conserved cytoplasmic Toll/Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor (TIR) domain at C-terminus required for the activation of downstream intracellular signal transduction pathways (5); (6). Interestingly, the extracellular ligand-binding domains of TLRs contain hydrophobic leucine-rich repeat motifs that form horseshoe-shaped solenoid structures and contain an extensive β-sheet on its concave surface, and numerous ligand-binding insertions (7). TLRs are distinguished based on their ligand specificity, signal transduction pathways, and subcellular localization (8). In mammals, ten human (TLR1-10), and 13 murine TLR protein subfamily (TLR1-9, TLR11-13) have been identified with a functional difference among humans and mice (9); (5), (10); (11). TLRs are functionally classified into two categories. The group I TLRs include TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, and TLR10, and are expressed on the cell membrane and recognize microbially derived lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and lipopeptide ligands (12). The group II TLRs include TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9, and are primarily expressed on vesicles and located intracellularly in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), endosomes, and lysosomes compartments and recognize microbial nucleic acids released from stressed or dying cells (13); (14); (15). Unlike the other TLRs, TLR3 is expressed both on the cell surface and in intracellular vesicles and recognize viral dsRNA (16). Thus, TLRs are expressed in all tissues including macrophages, NK cells, DCs, circulating monocytes and neutrophils of the innate immune system; the adaptive immune cells (T and B lymphocytes), as well as non-immune cells and organs, e.g. epithelial and endothelial cells, fibroblasts, brain, skeletal muscle, heart, lung, small intestine, liver, pancreas, colon, kidney, ovary, placenta, testis and prostate (17); (18).
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have received considerable attention due to their involvement in the post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms in almost all known cellular processes including development, differentiation, apoptosis, and the innate and adaptive immune responses to pathogen infections (19); (20); (21); (22); (23); (24); (25); (26). Besides, extracellular miRNAs secreted from the donor cells could be delivered into recipient cells via extracellular vesicles and exosomes to establish a cell-cell communication system during various physiological and pathological processes (27); (28); (29); (30); (31); (32). Selective miRNA studies in context to the regulation of TLRs suggest that miRNAs can modulate TLR signaling either through their involvement via transcriptional regulation or serving as physiological ligands of TLRs. Moreover, studies suggest that miRNA expression can be directly regulated by TLRs pathway (33). Interestingly, TLR activation modulates the expression of miRNAs that regulate TLR signaling either by the direct targeting of the molecules in the TLR pathway or indirectly through altering the activity of other cellular pathways that participate in crosstalk. The present review is highlighting the implication of TLRs in diseases and the emerging roles of microRNA (miRNA) in regulation of TLRs signaling.
TLRs are the cell-surface initiators that trigger the inflammatory process. TLRs recognize conserved microbial-associated molecular patterns including LPS (TLR4), diacyl and triacyl lipopeptides, and zymosan (TLR2 associated with TLR1 or TLR6), peptidoglycan and lipoarabinomannan (TLR2), bacterial flagellin (TLR5), viral dsRNA (TLR3), viral or bacterial ssRNA (TLRs 7 and 8), HMGB1 (TLR2 and TLR4), and CpG-rich unmethylated DNA (TLR9) among others (34); (35); (36) (Figure 1). Several TLRs require to interact with their coreceptors to form homo- or heterodimers for ligand binding, such as TLR1 or TLR6 for TLR2, MD2 for TLR4, and CD14 for TLR2, TLR4, and TLR3 (37). Being a critical component of the inflammatory response system to pathogen invasion, TLR-signaling is regulated at multiple levels. These include binding of TLRs to ligands, cooperation with coreceptor molecules and dimerization, recruiting adaptor molecules upon ligand binding, leading to transcription factor activation and downstream signaling (38).
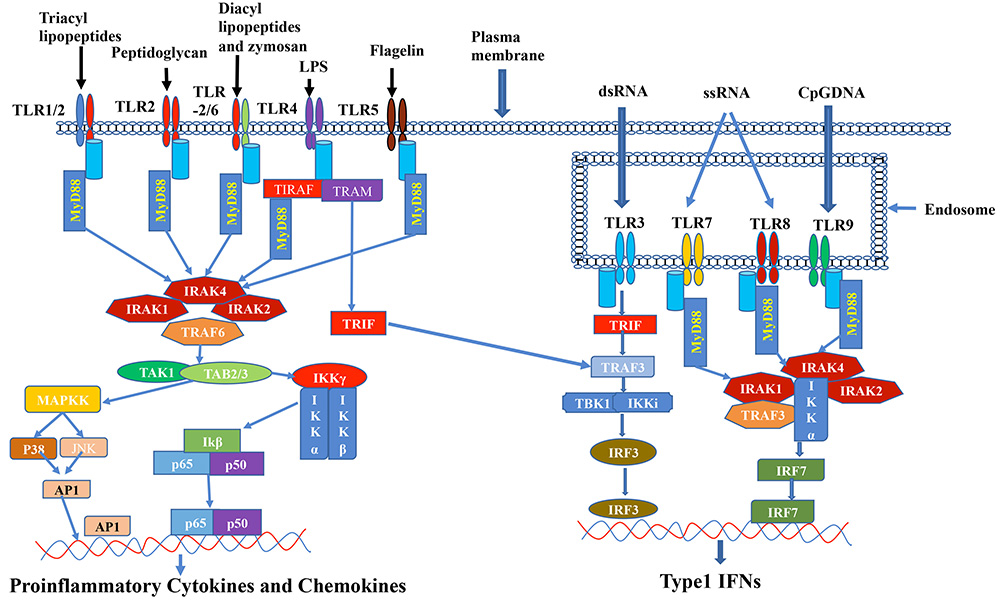 Figure 1
Figure 1A schematic diagram is showing the Toll-like receptors (TLR) signaling pathway and downstream effector molecules. Depicted are key TLR molecules, their signaling adaptors and downstream mediators that are essential for TLR signaling and function. TLRs 1, 2, 4, 5 and 6 are expressed on the cell surface, while TLRs 3, 7, 8 and 9 are expressed intracellularly on endosomal membranes. Activation of the TLRs leads to recruitment of the adaptor molecules MyD88, TIRAP, TRIF and TRAM. Downstream signals involve TAK1, MAPKs, TRAF3, TBK1 and IKKs, resulting in nuclear translocation of transcriptions factors (AP-1, NF-κB, IRF-3 or IRF-7) into the nucleus and transcription of inflammatory genes.
Upon binding to the ligand two extracellular domains form an “m”-shaped structure sandwiching the ligand molecule and bringing the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains close by to induce the downstream signals (39). After activation of TLR signaling pathways, the TIR domain recruits five different types of intracellular adaptor proteins including Myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88), Sterile α- and armadillo-motif-containing protein (SARM), TIR domain-containing adaptor protein (TIRAP or MAL), TIR domain-containing adaptor protein inducing IFN-β (TRIF) and TRIF-related adaptor molecule (TRAM) (2), (40); (41). Based on the recruited adaptor protein the TLR induced signaling cascade can be activated either by MyD88-dependent or by TRIF-dependent pathway (42); (43); (44); (45). Signaling through TLR1, TLR2, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 are activated via MyD88-dependent pathway that subsequently leads to the activation of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and mitogen-associated protein kinase (MAPK) and produces the pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (11). Activation through TIRAP is also linked via MyD88 and is associated with TLR2 and TLR4 (46); (47). TLR3-induced signaling is activated by the TRIF-dependent pathway and associated with the production of Interferon type-1 (6). Whereas TLR4 signaling is mediated by both MYD88-dependent as well as TRAM/TRIF dependent pathways (42); (6); (43), (48). In contrast, SARM negatively regulates TRIF thus controlling the TLR3 and TL4 signaling pathways (49); (50).
The interaction between a TLR and a microbial component triggers the initiation and the activation of the innate immune system, which not only initiates immediate host defensive responses such as inflammation but also prime and orchestrate antigen-specific adaptive immune responses (51). Upon engagement with PAMPs or DAMPs, TLRs recruit the adaptor proteins that lead to the activation of different transcription factors like NF-휅B, interferon regulatory factor IRF3, IRF7, activator protein-1 (AP1), and releasing the pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 and type 1 interferon (IFN-α, β), chemokines (CXCL8 and CXCL10), and antimicrobial peptides (52); (53); (54). Ultimately, all together they activate the adaptive immune system. Although the TLR-induced inflammatory cytokines are required as a part of the defense system to clear pathogens, however, the overproduction of many of these cytokines and chemokines are toxic and can cause pathological inflammation in the host. Overactivation of the TLR pathway disrupts the immune homeostasis through sustain pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines production and consequently contributes to the development of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Behcet's disease, chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV), sepsis, Alzheimer's disease, and even cancer (55); (56); (57); (58). Thus, fine-tuning of the TLR-signaling pathways is required to prevent excessive inflammation and maintain the homeostasis (53); (59); (60), even though the transcription factors and message translation can be regulated by post-transcriptional modification of the key proteins involved in the signaling cascade.
miRNAs are small non-coding single-stranded RNA molecules with 18-24 nucleotides in length. miRNAs bind to the 3’ untranslated region (UTR) of the target mRNA leading to mRNA degradation, thus repressing translation of the respective targets (24). However, miRNAs are also known to interact with other regions, including the 5′ UTR and coding sequence and have silencing effects on gene expression (61); (62). Since a very short complementary sequence (6-8 nucleotide) is needed to bind to the target mRNA, a single miRNA can target hundreds or thousands of different mRNAs and thus being capable of controlling 30% of the human protein-encoding genes (63); (64). Ultimately, miRNAs in conjunction with other miRNAs and transcription factors post-transcriptionally regulate pathways and networks related to a variety of biological processes. Moreover, the interaction of miRNA with the promoter region has been also reported to modulate the gene expression (65).
The biogenesis of miRNAs is a complex process and is under tight temporal and spatial control. The dysregulation of miRNAs is found to be associated with the progression of multiple human diseases (27).; (66); (67); (68); (69); (70). miRNAs are transcribed from genomic DNA by RNA polymerases II and III, generating precursors primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) that undergo a series of cleavage events to form mature microRNA (71). The biogenesis starts with the processing of pri-miRNAs and follows either the canonical or non-canonical pathway. In the canonical pathway pri-miRNAs that are more than 200 nucleotides in length undergo a nuclear cleavage by an endonuclease complex consisting of RNase II enzyme Drosha and the DiGeorge critical region 8 protein (DGCR8) into a 60-70 nucleotide-long precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) (72); (73); (74); (75). The pre-miRNA is exported to the cytoplasm in an Exportin5/RanGTP-dependent manner and undergo cleavage by the RNase III family enzyme Dicer into ~22 nucleotide-long mature microRNA duplex (76); (77); (78); (79). Finally, either of the 5p or 3p strands of the mature miRNA duplex known as guide strand is loaded into the Argonaute (AGO) family of proteins to form a miRNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC) (80). Whereas the non-canonical pathway can be grouped into Drosha/DGCR8-independent and Dicer-independent pathways (81). Mirtrons have a pre-miRNA that is defined by the entire length of the intron in which they are located and are produced during splicing as the first step in their biogenesis (82); (83). The pre-miRNA excised by splicing which is subsequently linearized by the debranching enzyme, Ldbr (DBR1 in humans), allowing the intron to form a structure that is exported to the cytoplasm by XPO5/RanGTP, recognized and cleaved by the Dicer complex to form a mature miRNA (84); (82); (85). Albeit, 7-methylguanosine (m7G)-capped pre-miRNA is processed by a Drosha-independent pathway. Initially, the pre-miRNAs are directly exported to the cytoplasm through PHAX/exportin-1 and finally cleaved by Dicer to a mature miRNA. After Dicer cleavage, only the 3p-miRNA is efficiently loaded onto Argonaute to form a functional microRNP (86). Dicer-independent miRNAs are processed by Drosha from endogenous short hairpin RNA (shRNA) transcripts to generate pre-miRNAs hairpin that is directly cleaved by Ago2 and followed by resection of its 3′ terminus (87). All pathways ultimately lead to a functional miRISC complex as a biologically active miRNA that binds 3’-UTR of the target mRNA which leads to mRNA degradation or repression of protein translation. In most cases, miRISC binds to target mRNAs leading to mRNA degradation or repression of protein translation (88); (89).
Emerging pieces of evidence implicated the regulatory role of miRNA in biological and pathological processes including innate and adaptive immune responses (90). Although aberrant alterations in miRNA function are associated with the pathogenesis and progression of multiple human diseases (91); (92); (93); (94). Several studies indicated that miRNAs act as a key component of the complex immunoregulatory networks via modulating the expression of TLRs and multiple components of TLR-signaling pathways including signaling proteins, regulatory molecules, transcription factors, and cytokines (95); (96). Here we selectively highlighted a few miRNAs in context to their regulatory functions on TLR-signaling (Tables 1-2, Figure 1).
| mRNA | Seed sequence | Chromosome location | Target | Targets /Signaling molecules/pathway | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-19a | aguuuugcauaguugcacuaca | chr13: 91350891-91350972 [+] | TLR2 ↓ | IL6 & MMP3 | 97 |
| hsa-miR--19b | ugugcaaauccaugcaaaacuga | chrX: 134169671-134169766 [-] | TLR2↓ | IL6 & MMP3 | 97 |
| hsa-miR-105 | ucaaaugcucagacuccuguggu | chrX: 152392219-152392299 [-] | TLR2 & TLR4 ↓ | IL6 & TNFα | 98 |
| hsa-miR-146a | ugagaacugaauuccauggguu | chr5: 160485352-160485450 [+] | TLR2, TLR4 ↓ | IL1, IRAK1, TNFα/NFkB | 99, 117, 116, 118 |
| hsa-miR-143 | ggugcagugcugcaucucuggu | chr5: 149428918-149429023 [+] | TLR2 ↓ | CD44, KLF5, & BRAF | 100 |
| hsa-miR-195 | uagcagcacagaaauauuggc | chr17: 7017615-7017701 [-] | TLR2 ↓ | IL-1β, IL-6 & TNFα | 104 |
| rno-miR-26a | uucaaguaauccaggauaggcu | chr8: 127714441-127714530 [+] | TLR3 ↓ | IFNβ & TNFα | 107 |
| mmu-miR-223 | cguguauuugacaagcugaguug | chrX: 96242817-96242926 [+] | TLR3 ↓ | IL-1β, MCP-1, IL-8 & IL-18 | 109 |
| gga-miR-155 |
uuaaugcuaaucgugauagggg | chr1: 102485099-102485161 [+] | TLR3 ↓ | IFN-β | 108 |
| hsa-miR-let7i | ugagguaguaguuugugcuguu | chr12: 62603686-62603769 [+] | TLR4 ↓ | MyD88/NF-kappaB, Ikk2 | 110, 111 |
| hsa-miR-let7d | agagguaguagguugcauaguu | chr9: 94178834-94178920 [+] | TLR4 ↓ | SNAP23 | 111 |
| hsa-miR-let-7f | ugagguaguagauuguauaguu | chrX: 53557192-53557274 [-] | TLR4 ↓ | SNAP23 | 111 |
| hsa-miR-Let7e | ugagguaggagguuguauaguu | chr19: 51692786-51692864 [+] | TLR4 ↓ | SNAP23 | 111, 112 |
| hsa-miR-98 | ugagguaguaaguuguauuguu | chrX: 53556223-53556341 [-] | TLR4 ↓ | SNAP23 | 111, 112 |
| hsa-miR-223-3P | cguguauuugacaagcugaguu | chrX: 66018870-66018979 [+] | TLR4 ↓ | IL-6, IL-β, TNFα/NFkB/STAT3 | 114, 115 |
| hsa-miR-2909 | guuagggccaacaucucuugg | chr17: 37033745-37033813 [+] | TLR2/TLR4 ↓ | IL-6, IL-β, TNFα/NFkB/STAT3 | 114 |
| hsa-miR-511 | gugucuuuugcucugcaguca | chr10: 17845107-17845193 [+] | TLR4 ↓ | 119 | |
| mmu-miR-21a | uagcuuaucagacugauguuga | chr11: 86584067-86584158 [-] | TLR4 ↓ | IL-6, NF-kB/MY-88/PDCD4 | 120 |
| hsa-miR-21 | uagcuuaucagacugauguuga | chr17: 59841266-59841337 [+] | TLR4 ↓ | IRAK3 & CXCL10 | 122, 121 |
| mmu-miR-100-5p | aacccguagauccgaacuugug | chr9: 41531425-41531504 [+] | TLR4 ↓ | Il6, Ptgs1/2 | 123 |
| hsa-miR-150-5p | ucucccaacccuuguaccagug | chr19: 49500785-49500868 [-] | TLR7 ↓ | IFN-β & IFN-α | 126 |
| hsa-miR-152-5p | agguucugugauacacuccgacu | chr17: 48037161-48037247 [-] | TLR7 ↓ | IFN-β & IFN-α | 126 |
| hsa-miR-375-5p | gcgacgagccccucgcacaaacc | chr2: 219001645-219001708 [-] | TLR7 ↓ | IFN-β & IFN-α | 126 |
| let-7b | ugagguaguagguugugugguu | chr22: 46113686-46113768 [+] | TLR-7 ↓ | TNF-α / My88/TRPA1 | 30, 131 |
| hsa-miR-21 | uagcuuaucagacugauguuga | chr17: 59841266-59841337 [+] | TLR7/TLR8 ↓ | IL-6, TNF-α | 28 |
| mmu-miR-21a | uagcuuaucagacugauguuga | chr11: 86584067-86584158 [-] | TLR7 ↓ | c-jun_N-terminal kinase | 128 |
| hsa-miR-29a | acugauuucuuuugguguucag | chr7: 130876747-130876810 [-] | TLR7/TLR8 ↓ | IL-6, TNF-α | 28 |
| mmu-miR-29a | acugauuucuuuugguguucag | chr6: 31062660-31062747 [-] | TLR7/TLR8 ↓ | IL-6, TNF-α/NF-kB | 129 |
| kshv-miR-K12-12 | aaccaggccaccauuccucuccg | KSU75698: 117674-117771 [-] | TLR8 ↓ | IL-6 & IL-10 | 140 |
| kshv-miR-K12-10b | ugguguuguccccccgaguggc | TLR-8 ↓ | IL-6 & IL-10 | 140 |
| Inducer | TLRs | miRNA | Signaling Molecule | Signaling pathway | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR2 | miR-155↑ | SHIP1 ↓ | TLR2/MY88/PI3K & MAPKs/NF-kB | 145 | |
| TLR3 | miR- 155 ↑ | IFN-β ↑ | TLR3/TRIF/AKT | 146 | |
| IL-10 | TLR4 | miR- 155↓ | SHIP ↑ | STAT3 | 147 |
| TLR7 | miR-155 ↑ |
TAB2↓ |
c-jun N-terminal kinase | 148 | |
| IL-10/TGFβ | TLR3 | 155↓ | IRF-3/NF-kB | 149 | |
| IL-10 | miR-155↓ | ETS2↓ | 150 | ||
| IFN-β | miR-155↑ | MY88/TRIF/JNK pathway | 151 | ||
| TNF-α | miR-155↑ | IL6-JAK2_STAT3↓ | 152 | ||
| IFN-γ & TNF-α | miR-155↑ | PD-L1↓ | 153 | ||
| TNF-α | miR-155↑ | SOCS1↓ | SAPK/JNK | 80 | |
| Pregesterone | TLR4 | miR-155↓ | SOCS↑ | 156 | |
| SEB | miR-155↑ | SOCS1↓ | 157 | ||
| Ikk16 | 155↓ | IL-6, TNF-α↓ | 158 | ||
| hypothermia | miR-155↑ | IL-10, SHIP1, SOCS1↓ | 159 | ||
| Angp1 | miR-146b-5p ↑ | IRAK1& TRAF6↓ | 166 | ||
| HMGB1 | TLR2 | miR-155 | Ets1↓ | TLR2-My88 | 162 |
| LPS | TLR4 | let7e↑ miR181c↑ |
SOCS1↓ | 113 | |
| Foxo3a | miR-21 ↓ | 163 | |||
| Foxo3a & Foxo1 | miR-145 ↑ | 164 | |||
| LPS | TLR3 |
miR-155 ↑ | ADAM10, TNPO3, Nup153, LEDGF/p75 ↓ | 161 |
Studies revealed that TLR2 is highly expressed by lymphocytes and plasma cells and the expression is differentially regulated by different miRNAs. Also, TLR2 along with TLR4 is highly expressed in rheumatoid arthritis patients (55). In rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes, the expression of miR-19a/b is down-regulated with the upregulation of TLR2 and inflammatory cytokines associated with TLR2 signaling including IL-6 and matrix metalloproteinase 3 (MMP3) (97). In silico analysis data predicted that miR-105 has complementarity for TLR2 mRNA, and increased expression of miR-105 downregulates the production of inflammatory cytokines in human gingival keratinocytes (98). Also, miRNA-146a (miR-146a) plays an important role in endotoxin tolerance by downregulation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK-1). miR-146a has shown to be upregulated in response to bacterial lipoprotein (BLP) and bacterial stimulation in both naive and BLP-tolerised human THP-1 promonocytic cells which is associated with downregulation of TLR2, TNFα and IRAK-1(99). Similarly, miR-143 blocks the TLR2 signaling pathways in human colorectal carcinoma cells and suppresses the invasion and migration of a subset of human CRC (100). Whereas, the treatment with LPS, synthetic lipid A, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-15, IFN-γ, and TNFα induced TLR2 gene expression in murine macrophages and promoted the inflammation and atherosclerosis (101) (102); (103). A recent study demonstrated that over-expression of miR-195 is involved in THP1 macrophage polarization, which reduces the levels of TLR2 along with pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα), and reduces phosphorylated forms of p54 JNK, p46 JNK and p38 MAPK (104). These studies suggest that miRNA-19a/b, miRNA-105, miRNA-143, miRNA-146a, and miR-195 act as a negative regulator of TLR2 expression and inflammation.
TLR3 is known to be conserved across the taxonomic kingdom and constitutively expressed by endosomes of myeloid and monocyte-derived dendritic cells (105). Studies have shown that the upregulation of TLR3 in macrophages induces the expression of IFN-β and TNFα, and promotes pristane-induced arthritis in rats, while inhibition of TLR3 reduces the severity of the disease (106). Further studies demonstrated that miR-26a-5p downregulates the expression of TLR3 in rat macrophages, whereas administration of miR-26a- mimic leads to the suppression of TLR3 protein expression and ameliorate arthritis in PIA rats (107). miR-155 has been known to be an important regulator of TLR3 signaling. Both endogenous miR-155 and virus-encoded miR-155 ortholog can inhibit IFN-β production by targeting the t-coding sequence of TLR3 in macrophages (108). Similarly, miR-223 regulates TLR3 expression in granulocyte and regulates the inflammatory response in mice (109)
TLR4 recognizes intrinsic mediators including heat-shock proteins and high-mobility group box-1 as well as LPS of gram-negative bacteria. Initial studies involving the role of miRNAs in immune response prevailed that let7i, a member of the let7 family regulate the expression of TLR4 in human biliary epithelial cells (cholangiocytes) through post-transcriptional suppression (110). The expression of let7i is decreased via a MyD88/NF-κB dependent mechanism with increased expression of TLR4 and TLR4-IKK2-signaling promotes the SNAP23-associated vesicular exocytotic process (111). Cryptosporidium parvum infection in non-malignant human cholangiocytes induces the luminal release of exosomes from the biliary and intestinal epithelium as a part of the microbial defense with reduced expression of miRNAs including let-7i, let-7d, let-7f, let-7e, and miR-98, and an increase in phosphorylation of SNAP23. Later studies have demonstrated that the parasitic protozoan C. parvum infection or LPS stimulation reduces the expression of let7 and miR-98, and also stimulates the expression of the Src homology 2-containing protein (CIS), an important negative regulator for inflammatory cytokine signaling in cholangiocytes ((112). In mouse macrophages, overexpression of let7e reduces the expression of TLR4 whereas inhibition of let7e induces the expression of TLR4 (113).
LPS treatment reduces the expression of miR-223-3P and miR-2909 in human adipose stem cells, while promotes the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNFα) through TLR4/TLR2/NF-κB-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)-3 signaling pathways. Also, miR-2909 regulates the expression of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNFα. STAT3 directly targets TLR4 and TLR2, and promote the production of IL-6. Similarly, TNFα promotes the expression of miR-223-3p which inhibits Stat3 and led to a negative feedback loop regulation of TNF-α secretion via the LPS/TLR2/TLR4/STAT3 signaling pathway (114). Also, miRNA-223 attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in an acute lung injury model by suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway (115).
miR-146a inhibits both LDL accumulation and inflammatory response by negatively regulating TLR4 and thereby inhibiting the activation of TLR4-dependent signaling pathways in macrophages (116). Moreover, miR-146a inhibits the proliferation and inflammatory response of rheumatoid arthritis or fibroblast-like synoviocytes by down-regulating the TLR4/NF-κB pathway (117). Furthermore, miR-146 directly targets IRAK1 and TRAF6, which are key adapter molecules in the TLR4/NF-κB pathway (118). Similarly, miR-511 is highly expressed in differentiating dendritic cells and macrophages and acts as a negative regulator of TLR4 (119).
miR-21 is a multifunctional RNA and overexpressed under inflammatory conditions. Studies showed that miR-21 targets pro-inflammatory protein PDCD4 and acts as a negative regulator of TLR4 in LPS-treated mouse murine macrophage ((120). In primary human lung cancer cells, LPS treatment increases the expression of miR-21 which promotes TLR4 and reactive oxygen species expression (121). In human lung transplants, miR-21 causes severe pathogenesis of primary graft dysfunction through the TLR4-signaling pathway (122). miR-100-5p was found to be expressed in follicular dendritic cells. Inhibition of miR-100-5p significantly enhanced expression of IL6, Ptgs1/2, and TLR4 mRNA in dendritic cells suggesting an indirect role of miR-100-5p in TLR4 signaling (123).
Besides the role of cellular miRNAs in TLR signaling, recent reports established an intriguing role of extracellular miRNAs in the binding and activation of intracellular TLRs (124). TLR7 recognizes viral RNA following endocytosis, an immune response, that is characterized by Type I IFN and pro-inflammatory cytokine production, whereas reduced expression of TLR7 is associated with a poor response to IFNs (125). In severe asthma, TLR7 deficiency is associated with elevated expression of miR-150-5p, mir-152-5p, and miR-375-5p in alveolar macrophages. Ex vivo knockdown of these microRNAs restored TLR7 expression with an increased IFN response to the virus (126). An elevated level of let-7b from the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from individuals with Alzheimer's disease activates the TLR7 and induces neurodegeneration in mice model (30). In a breast cancer mouse model, the specific delivery of let-7b efficiently reprogrammed the functions of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells (TIDCs), reversed the suppressive tumor microenvironment, and inhibited tumor growth by acting as a TLR-7 agonist and suppressing IL-10 production (127).
Other studies showed that tumor-secreted miR-21 and miR-29a bind as ligands to murine TLR7 and human TLR8, in immune cells, triggering a TLR-mediated pro-metastatic inflammatory response that leads to tumor growth and metastasis (28). miR-21 was also demonstrated to induce myoblast apoptosis in cancer cachexia via a TLR7-c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent pathway (128). In a mouse model of Acute graft-versus-host disease showed that the circulating extracellular miR-29a activates dendritic cells via TLR7 and TLR8, resulting in the activation of the NF-κB pathway and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines TNFα and IL-6 (129). Moreover, miR-21 released from the synovial tissue mediates knee OA pain through TLR7 activation in the surgical OA rat model (130).
Interestingly, in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, the extracellular let-7b couples with TRPA1 ion channel and support rapid excitation of nociceptor neurons via TLR7 and induces rapid inward currents and action potentials (131). The let-7b coupling with TRPA1 requires a core GU-rich motif (GUUGUGU motif), similar to HIV ssRNA40 (132). The GU-rich motif is required to bind to both TLR7 and TLR8 (133); (134); (135); (136). Moreover, the GU-rich motifs also contribute to the immune stimulation, and modification of this motif is an effective mechanism in preventing immune stimulation of endogenous miR-122 (137); (138).
During viral infection, viral miRNAs can also activate pro-inflammatory cytokines through TLR pathways. Studies showed that TLR8 signaling stimulates monocytes to express type I interferon and cytokines and promotes CD4+ T helper 1 (TH1) cell differentiation, whereas TLR7 signaling promotes the production of cytokines and induces TH17 cell differentiation (139). DNA virus-encoded miRNAs (e.g., KSHV-miR-K-10b, KSHV-miR-K12-12) are involved in sepsis by interacting with TLR8 as agonists and promote the secretion of IL-6 and IL10 that leads to increased inflammation and subsequent immunosuppression (140); (141). Epstein-Barr virus infection has been associated with the development of a variety of human malignancies, including several types of lymphoma, lymphoproliferative disorder, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (142). Viral miRNA BHRF1-1 is expressed significantly higher in plasma of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and BHRF1-1 expression in B cells of patients with CLL causes a shorter overall survival rate (143); (144).
Various studies have demonstrated that both TLRs and miRNA are differentially express and interdependent in the regulation of pathogenic infection, endotoxin sensitivity, and tolerance in the innate immune system. The pathogenic gram-negative bacteria, Francisella, is recognized on the host cell surface by TLR2, recruiting the adaptor protein MyD88, and activating MAPKs, PI3K, and Akt pathways, which leads to enhanced NF-κB activity, inflammatory cytokine production, as a part of an effective host response. Src homology 2 domain-containing inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase 1 (SHIP1) acts as a critical modulator and negatively regulates the activation of Akt to prevent effective host response. During Francisella infection, miR-155 is induced through the TLR signaling pathway, in turn, down-regulates SHIP1 to promote the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and inflammatory cytokine production in human monocytes (145). Also in macrophages infected with Leishmania RNA virus 1 (LRV1), miR-155 expression is dependent on TLR-3/TRIF signaling which enhances macrophage survival through Akt activation (146). In immortalized bone marrow-derived macrophages, IL-10 inhibits TLR-induced expression of miR-155 from the BIC gene in a STAT3-dependent manner leading to the elevated expression of SHIP1 (147). Similarly, in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells, TLR7 induces the expression of miR-155 through the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. miR-155 augmented interferon-α/β expression by suppressing IRAKM, whereas miR-155 inhibited their expression by targeting TAB2. Both were inversely regulated by autocrine/paracrine type I interferon and TLR7-activated KHSRP at the posttranscriptional level (148).
In non-parenchymal liver cells (NPCs), IL-10 or TGF-β potently reduces the expression of TLR3 and TLR3 dependent miR-155 expressions and suppression of the transcription factors IRF-3 and NF-κB which regulate antiviral and inflammatory activity (149). IL-10 also suppresses Ets2 expression which is a TLR regulated gene and thereby inhibits the induction of miR-155 by LPS (150). In primary murine macrophages, treatment with polyriboinosinic:cpolyribocytidylic (16) acid or the cytokine IFN-β, miR-155 is substantially up-regulated through several TLR ligands including myeloid differentiation factor 88- or TRIF-dependent pathways. miR-155-induce signals through the JNK pathway (151). Studies have shown that in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts, TNF-α stimulation induces the expression of miR-155 and inhibits IL-6-mediated JAK2/STAT3 activation (152). Similarly, treatment of human dermal lymphatic endothelial cells (HDLECs) and dermal fibroblast with the pro-inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ and TNFα synergistically up-regulated miR-155 expressions which suppresses the programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression (153). The serum TNFα and miR-155-5p are upregulated in patients with subacute thyroiditis. TNFα inhibits proliferation and induce apoptosis of rat thyroid follicle FRTL-5 cells through modulating the IL-6-JAK2/STAT3 pathway and miR-155-5p signaling (154). TNFα negatively regulates ectopic bone formation by regulating BMP signaling. Study in MC3T3-E1 cells showed that TNFα is up-regulated miR-155 expression, whereas knockdown of miR-155 partially mitigated the inhibition of TNFα on BMP-2-induced osteogenic differentiation (155). TNFα dependent osteogenic differentiation is through SOCS1 and the SAPK/JNK pathway. Similarly, progesterone can inhibit TLR4 dependent immune response and down-regulates LPS- and poly(I:C)-induced miR-155 expression in macrophages which inhibits TLR-induced IL-6 and IFN-β via increased SOCS1 expression (156).
Studies have demonstrated that Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) inhalation results in acute inflammatory lung injury with overexpression of miR-155 and IFNγ, whereas suppression of SOCS1 (157). Similarly, IκK-16 treatment of primary human monocytes decreases miR-155 expression and decreases the secretion of TNFα and IL-10, ultimately attenuates the monocyte inflammatory response (158). Moreover, hypothermia induces an increase in miR-155 expression and reduced production of IL-10, Ship1, and SOCS1 while the expression of proinflammatory cytokines is increased in monocytes and macrophages (159). In ischemia-induced cerebral inflammation, miR-155 promotes TNFα and IL-1β expression through TLR4 expression and inhibition of MyD88 and SOCS1 expression (160). Another study revealed that stimulation of monocyte-derived macrophages reduces their susceptibility to HIV-1 infection through TLR3 or TLR4 by inducing the expression of miR-155 (161). The nuclear protein HMGB1 induces the TLR2 mediated and MyD88-dependent upregulation of miR-155 with a decreased expression of Ets-1 during double-stranded antibody induction involved in the pathogenesis of SLE (162).
Studies are further demonstrated that LPS dependent activation of protein kinase Akt1 promotes miRNAs let-7e and miR-181c expressions, whereas downregulate miR-155 and miR-125b. Both miRNA and TLRs are differentially regulated with interdependent manner such as Let-7e repress TLR4, whereas miR-155 repress SOCS1 (113). Several other transcription factors such as Foxo3a regulates apoptosis by negatively targeting miR-21, whereas Foxo1 and Foxo3a positively regulate miR-145 in renal tumor development (163); (164). miR-145 serves as a key component of the Foxo-Mxi1-SRα/miR-145 axis as a major inhibitor of renal tumor development. Similarly, miRNA-27b-3p and miRNA-455-3p promote cancer cell quiescence by facilitating the stabilization of p27 (165). Another study showed that angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) disrupts TLR4 signaling with inhibition of LPS-induced inflammatory responses in endothelial cells through selective targeting of IRAK1 and TRAF6 proteins by miR-146b-5p (166).
Studies also implicated that TLR4 is up-regulated in LPS-treated human polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) and monocytes and induces the transcription of miR-9 in a MyD88- and NF-kB-dependent manner. miR-9 is also induced by TLR2 and TLR7/8 agonists and by the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β, but not by IFN-γ (Bazzoni et al, 2009). Also, miR-147 was induced upon stimulation of multiple TLRs (TLR2/3 and 4) in LPS-treated murine macrophages while stimulation of TLR4 was more effective in inducing miR-147 expression. TLR4-induced miR-147 expression needs activation of both NF-κB and IRF3 to prevent excessive inflammatory responses (Liu et al, 2009; 19721002).
TLRs are the key innate immune PRRs and are tightly regulated system to ensure a host immune response to foreign invaders. At present, our understanding of the complex biology of the miRNAs in innate immunity is limited and functional studies remain a work in progress. We have provided some of the experimental shreds of evidence supporting a conserved role for the miRNAs in TLR-signaling or vise-versa. However, the individual miRNAs are likely to have functionally different effects compared to the TLRs, since a single miRNA may have overlapping functions in modulating gene expression. Moreover, miRNAs regulate TLR signaling at different levels by targeting multiple molecules involved in the TLR pathway, such as the expression of TLRs themselves, TLR recruited adaptor molecules, TLR-induced signaling cascade proteins, transcription factors, and even the pro-inflammatory cytokines of TLR signaling. Both intracellular and extracellular miRNAs can modulate TLR signaling pathways mainly either through their involvement via transcriptional regulation or serving as physiological ligands of TLRs. Given that crosstalk between the miRNAs and TLR signaling pathways suggesting further studies are needed for designing new therapies that target specific signaling pathways which could restore the adequate immune response necessary to address an invading pathogen.
This study was supported in part by National Institutes of Health Grants 1SC3 GM113751, U54 MD007602 and G12-MD007602. This investigation was conducted in a facility constructed with support from Research Facilities Improvement Grant #C06 RR018386 from NIH/NCRR.
AP1
activator protein-1
argonaute
bacterial lipoprotein
cerebrospinal fluid
damage-associated molecular patterns
Drosha and the DiGeorge critical region 8 protein
hepatitis B virus
interleukin
interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1
leucine-rich repeat region
lipopolysaccharide
matrix metalloproteinase 3
MicroRNAs
miRNA-induced silencing complex
mitogen-associated protein kinase
Myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88
nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
pathogen-associated molecular patterns
primary miRNAs
rheumatoid arthritis
Src homology 2 domain-containing inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase 1
Sterile α- and armadillo-motif-containing protein
systemic lupus erythematosus
T helper 1
TIR domain-containing adaptor protein
TIR domain-containing adaptor protein inducing IFN-β
Toll/Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor
Toll-like receptors
TRIF-related adaptor molecule
tumor necrosis factor-alpha
tumor-associated macrophages
tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells
untranslated region.

