Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark (FBL) is published by IMR Press from Volume 26 Issue 5 (2021). Previous articles were published by another publisher on a subscription basis, and they are hosted by IMR Press on imrpress.com as a courtesy and upon agreement with Frontiers in Bioscience.
1 Molecular and Structural Biophysics Laboratory, Department of Biochemistry, North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong 793022, India
Abstract
The tropical liver fluke, Fasciola gigantica is a food-borne parasite responsible for the hepatobiliary disease fascioliasis. The recent completion of F. gigantica genome sequencing by our group has provided a platform for the systematic analysis of the parasite genome. Eukaryotic protein kinases (ePKs) are regulators of cellular phosphorylation. In the present study, we used various computational and bioinformatics tools to extensively analyse the ePKs in F. gigantica (FgePKs) genome. A total of 455 ePKs were identified that represent ~2% of the parasite genome. Out of these, 214 ePKs are typical kinases (Ser/Thr- and Tyr-specific ePKs), and 241 were other kinases. Several FgePKs were found to possess unusual domain architectures, which suggests the diverse nature of the proteins that can be exploited for designing novel inhibitors. 115 kinases showed <35% query coverage when compared to human ePKs highlighting significant divergences in their respective kinomes, further providing a platform for novel structure-based drug designing. This study provides a platform that may open new avenues into our understanding of helminth biochemistry and drug discovery.
Keywords
- Anthelmintic
- Flukes
- Protein Kinases
- Domain Organization
- Drug Targets
- Helminth
- Parasite
Fascioliasis is primarily an infection of the livestock caused by F. hepatica and F. gigantica. It is a severe food-borne neglected tropical disease (NTD) that causes massive health and economic loss in the developing countries of the tropics and subtropical areas (1-4). Fasciola spp. has a worldwide distribution and it infects livestock, such as cattle, sheep, and goats resulting in an estimated economic loss of more than 3 billion USD per annum worldwide (4-6). Humans become accidental hosts through consumption of watercress or other fresh aquatic vegetation or by drinking water contaminated with viable parasite metacercariae. Once the larvae are ingested, they develop into adult flukes inside the host and start feeding on the liver tissues. As a result, the liver becomes dysfunctional, and the pathology is characterized by severe damage to the liver tissues and bile ducts (7). According to the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates, at least 2.4 million people are infected worldwide, and 180 million are at risk of infections (8, 9). Fascioliasis is principally treated with a single WHO-approved drug triclabendazole (TCBZ), but recent studies report increasing cases of TCBZ-resistant flukes in Europe, Australia, and in more than 70 countries across the world (10-14). Therefore, the development of new therapeutics against these platyhelminthic parasites is one of the most important challenges for researchers.
Signal transduction through the integration of protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylation by specialized enzymes are essential to respond to certain extracellular signals that help maintain homeostasis as well as other complex cellular adaptation in parasites. Various protein functions, such as cell division, cellular metabolism, growth, differentiation, survival, and apoptosis are regulated through phosphorylation by protein kinases (PKs) that cause alterations in the protein structure by covalent modifications, and hence, facilitates the formation of hydrogen bonds among specific amino acid residues for mediating intracellular signals (15). Protein kinases catalyse the transfer of γ-phosphate from high energy molecules like ATP or GTP to its polypeptide substrates, thereby, modulating their structures and functions. The action of PKs is reversed by phosphatases that remove phosphoryl moieties from their substrates. Structurally, most PKs contain a catalytic domain responsible for binding and phosphorylating target proteins, and a regulatory domain for maintaining a catalytically inactive state to prevent constitutive substrate phosphorylation (16). Protein kinases are either auto phosphorylated or get phosphorylated by other PKs (17). The catalytic core of the PKs consists of a Gly-rich ATP/GTP binding domain in the N-terminus and a conserved Asp residue in the centre (18). Substrate recognition by PKs employs two types of interactions: (i) recognition of the consensus phosphorylation sequence by the active site residues and (ii) distal interactions between the PK and the substrate mediated by regions away from the phosphorylation site in the substrate and regions in PK located distally from its active site. Protein kinases are classified into two superfamilies: (i) the eukaryotic or conventional protein kinases (ePKs), and (ii) the atypical protein kinases (aPKs). The sequences of the aPKs are different than those of ePKs but show kinase activity (18). Based on the phosphate acceptor site in the substrate, ePKs are classified into Ser/Thr kinases (STKs) and Tyr kinases (TKs). Kinases that specifically phosphorylate both Ser/Thr and Tyr are also found (19). The ePKs are grouped according to their homologous catalytic domains, which generally consist of 250-300 amino acid residues (20, 21). According to KinBase (19), ePKs have been classified into eight groups: AGC (cAMP-dependent Protein Kinase or Protein Kinase A/Protein Kinase G/Protein Kinase C), CAMK (Calcium/Calmodulin regulated Kinases), CK1 (Cell Kinase I), CMGC (Cyclin-dependent Kinases and other close relatives), RGC (Receptor Guanylate Cyclases), STE (Sterile Ser/Thr Kinases), TK (Tyr Kinase), and TKL (Tyr Kinase-Like). In addition, a ninth group called ''Other kinases'' exists, consisting of several kinases that cannot be classified into any of the above families (22). Many PK inhibitors have been developed and approved for the treatment of different human diseases, including infections with parasitic helminth, like Schistosoma mansoni (the blood fluke) (23, 24).
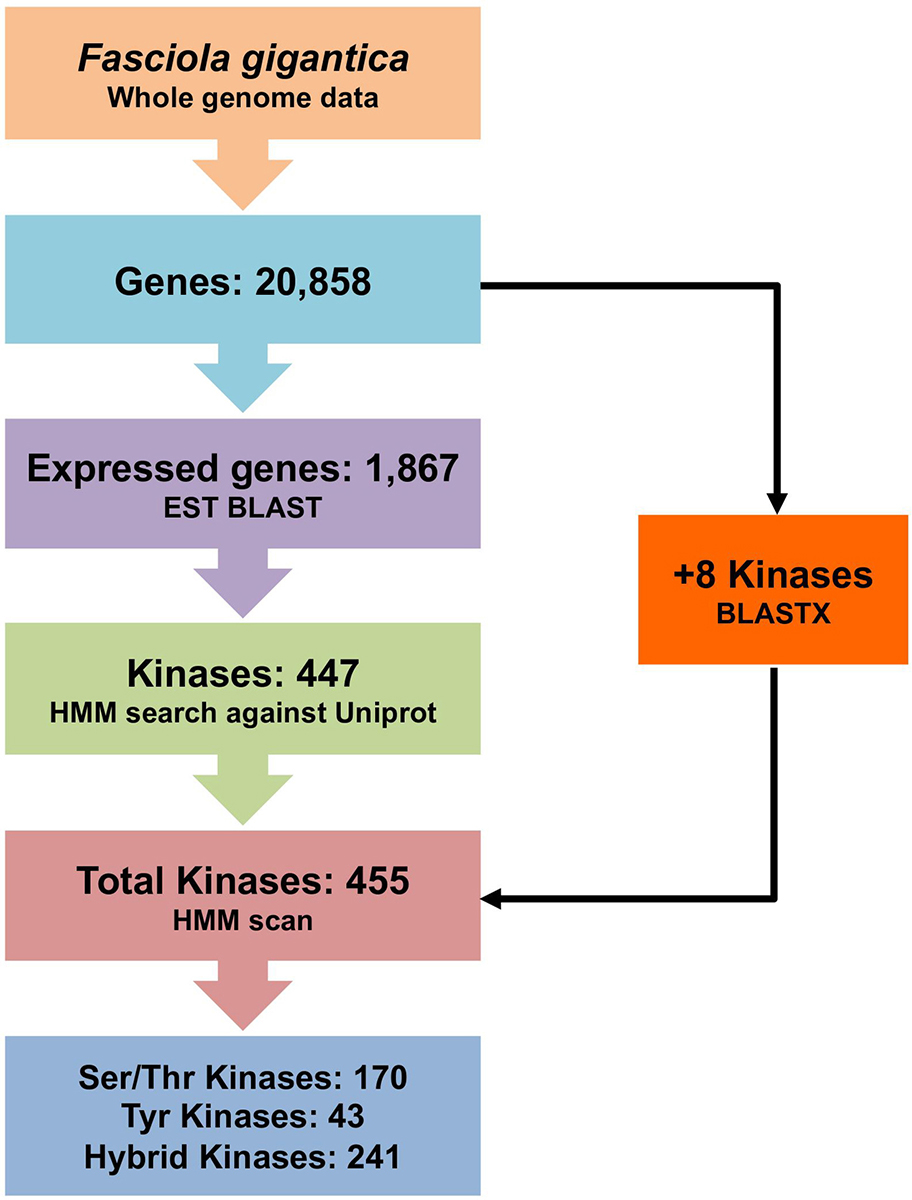
Recent sequencing of the F. gigantica genome (25) has provided a crucial platform for further exploration of the biochemistry of the parasite. Understanding the structure and function of proteins encoded by the genome of this platyhelminthic parasite will provide information for structure-based drug design and development. Therefore, the study of the ePKs of F. gigantica is a major step towards these goals. Alteration in the functionality of these enzymes may result in a cascade of pathological signs that might contribute to the mortality of the parasite. Thus, the present work aims at analysing the F. gigantica genome by combined computational approaches, including Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) and phylogenetic analyses to identify all the ePKs encoded in the genome; and to identify potential kinases having a special role in the signalling process of the parasite to utilize them as a novel drug target against F. gigantica. The schematic representation of the methodology is shown in Figure 1.
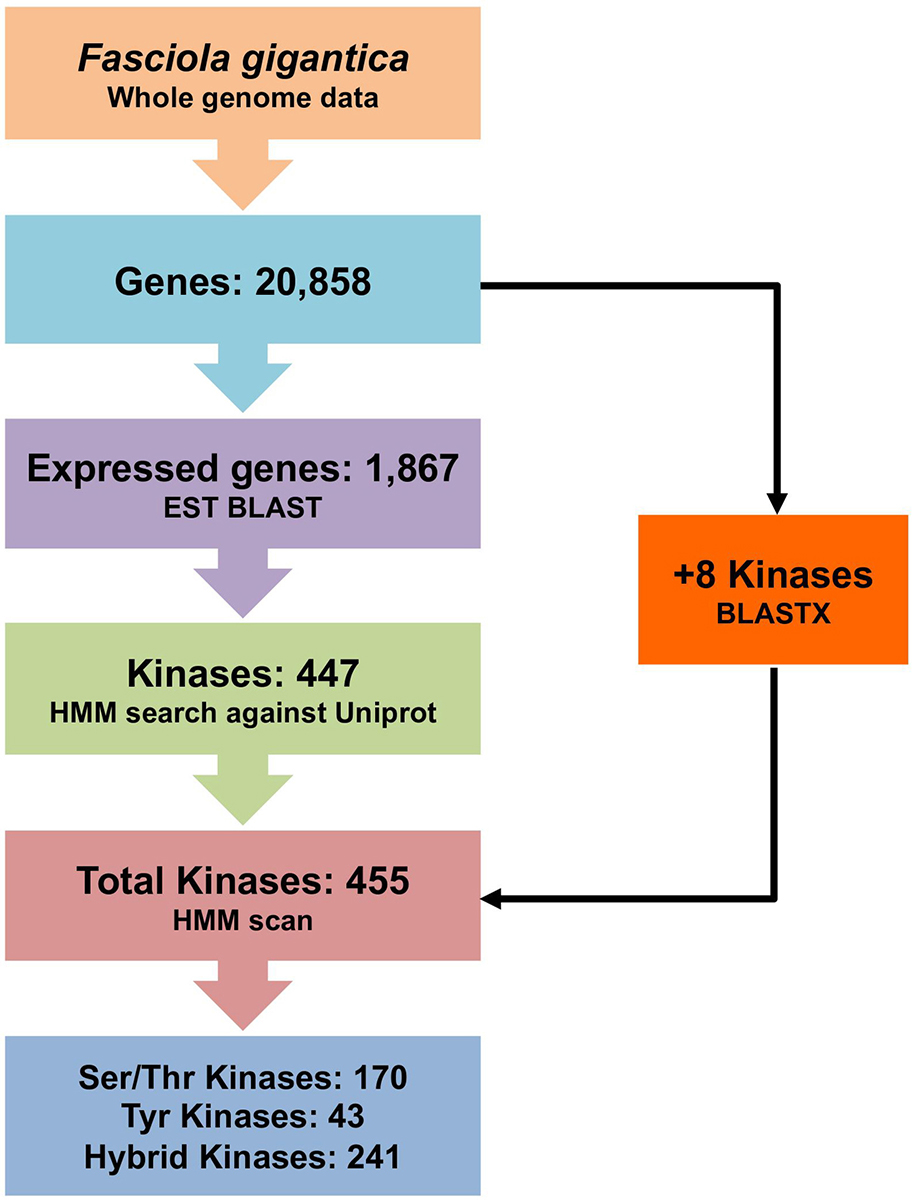 Figure 1
Figure 1Schematic representation of the methods used for prediction and classification of the F. gigantica ePKs.
The whole genome data of F. gigantica (accession number: MKHB00000000) showed a total of 20,858 genes (25). Gene sequences were then submitted to BLAST against expressed search tag (EST) to ascertain the expressed genes.
Potential ePKs of F. gigantica (FgePKs) were identified and characterized by combined approaches based on sequence similarity and phylogenetic relationships. The gene sequences were further translated to amino acid sequences using SMS server (http://www.bioinformatics.org/sms2/translate.html) to run HMMs. Alignments were generated in Mega v7 (www.megasoftware.net) using the clustalW algorithm with default parameters. The HMM search was performed against the Uniprot database for identifying ePK-like proteins of F. gigantica based on similarity. Also, the 20,858 F. gigantica genes were directly submitted to BLASTX that annotates the genes based on sequence similarity by converting the gene sequences into protein sequences. The potential FgePKs, obtained from both HMMsearch and BLASTX results, were compared and used for further analysis.
The obtained FgePKs were functionally classified into groups, families, and subfamilies and their conserved domains were identified. The classified ePKs were further evaluated in Kinbase. Domain analysis was performed by HMMscan for identifying the conserved catalytic domain of the FgePKs based on the data available at the Protein families database (Pfam) (26). Further phylogenetic analyses of the FgePKs groups were also performed. The sequences were first aligned and then used for the construction of phylogenetic tree using Mega7 server (www.megasoftware.net). Initially, 1000 random datasets (in replicates) were created for each alignment using Seqboot with default parameters. The multiple sequence alignment was used in the Mega7 server to construct the phylogenetic tree using the maximum likelihood method, based on the model of Tamura and Nei (27); all the parameters were kept default.
A total of 20,858 genes are annotated in the F. gigantica genome data (25). A total of 1,867 expressed gene sequences were found when the above gene sequences were submitted to BLAST against EST. The FgePK proteome (F. gigantica ePKinome) was predicted using HMMs. This analysis revealed a total of 455 ePKs in the F. gigantica proteome, of which 447 were identified in the HMMsearch, while BLASTX revealed the other 8 kinases representing ~2% of the total proteins encoded in the parasite genome (Table 1).
| Scaffold ID | Kinase Types | Protein Accession ID |
|---|---|---|
| scaffold81990.g8225.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase dclk3 | GAA49714 |
| scaffold82009.g8227.t1 | protein phosphatase 1 inhibitor potentiated by protein kinase c | XP_009162854 |
| scaffold82644.g8269.t1 | thymidine kinase | CCD80663 |
| scaffold82730.g8278.t1 | casein kinase i isoform alpha | XP_012792480 |
| scaffold83122.g8300.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase beta-2 | GAA36606 |
| scaffold83122.g8301.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase beta-2 | CCD77010 |
| scaffold84224.g8419.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase beta-1 | XP_009176756 |
| scaffold85190.g8506.t1 | neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5 | CAX75067 |
| scaffold85190.g8508.t1 | neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5 | GAA34774 |
| scaffold85530.g8549.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase partial | XP_009171539 |
| scaffold86191.g8598.t1 | ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase 1 | XP_012801401 |
| scaffold87509.g8711.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase partial | CCD78166 |
| scaffold87509.g8712.t1 | serine threonine kinase | CCD78166 |
| scaffold86513.g8721.t1 | microtubule-associated serine threonine-protein kinase 4 | XP_009162171 |
| scaffold90366.g8973.t1 | n-terminal kinase-like protein | GAA49046 |
| scaffold91353.g9056.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase partial | XP_012797255 |
| scaffold92882.g9180.t1 | dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 | XP_013914280 |
| scaffold93666.g9228.t1 | snf1a amp-activated protein kinase | AAX26331 |
| scaffold93812.g9246.t1 | serine threonine kinase | CCD76345 |
| scaffold98637.g9653.t1 | beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | XP_012795536 |
| scaffold99327.g9715.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 15 | XP_012798488 |
| scaffold99613.g9745.t1 | tau-tubulin kinase 1 | XP_009174870 |
| scaffold99759.g9753.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase partial | GAA55797 |
| scaffold99996.g9790.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase partial | XP_012795852 |
| scaffold98852.g9822.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase mitochondrial | XP_009165539 |
| scaffold101667.g9953.t1 | protein serine threonine kinase | XP_009173763 |
| scaffold103114.g10101.t1 | adenylate kinase 7 | XP_009168794 |
| scaffold103547.g10134.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase atr | AAX30846 |
| scaffold103547.g10135.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase atr | XP_009164520 |
| scaffold104001.g10181.t1 | adenylate kinase 9 | GAA56322 |
| scaffold104648.g10249.t1 | serine threonine protein kinase | XP_009164480 |
| scaffold105136.g10285.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase | XP_012796691 |
| scaffold106049.g10389.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase hck | GAA51878 |
| scaffold106986.g10499.t1 | casein kinase i isoform alpha | CAX69538 |
| scaffold108222.g10612.t1 | camp-dependent protein kinase type ii regulatory subunit | AAW24538 |
| scaffold108312.g10628.t1 | type ii pantothenate kinase | GAA47929 |
| scaffold108332.g10629.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase partial | GAA55039 |
| scaffold109147.g10697.t1 | phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type-1 partial | GAA56497 |
| scaffold109778.g10755.t1 | rho-associated protein kinase 2 | XP_009174321 |
| scaffold110240.g10782.t1 | protein kinase c zeta type | XP_009166221 |
| scaffold111099.g10853.t1 | putative gluconokinase | CCD78153 |
| scaffold111430.g10882.t1 | glycerate kinase | XP_009171759 |
| scaffold112912.g11016.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 10 | GAA56055 |
| scaffold113735.g11112.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 10 | CCD80387 |
| scaffold114344.g11150.t1 | myosin light chain smooth muscle | XP_012794520 |
| scaffold115493.g11250.t1 | abl kinase 2 | CBH50762 |
| scaffold115827.g11286.t1 | thymidylate kinase 251l | XP_009171769 |
| scaffold116064.g11303.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase htk16 | GAA55551 |
| scaffold116204.g11318.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase ulk4 | GAA30022 |
| scaffold116667.g11363.t1 | polynucleotide 5 -hydroxyl-kinase grc3 | XP_009167129 |
| scaffold117817.g11463.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | GAA48921 |
| scaffold119252.g11592.t1 | dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 | XP_009165442 |
| scaffold120222.g11666.t1 | adenylate kinase isoenzyme 5 | XP_009174960 |
| scaffold121069.g11738.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase nek1 | GAA54400 |
| scaffold121930.g11813.t1 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 4 | XP_012798021 |
| scaffold122760.g11885.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase prp4-like partial | GAA39797 |
| scaffold123427.g11953.t1 | protein kinase partial | XP_009169988 |
| scaffold123580.g11971.t1 | adenylate kinase 9 | GAA56322 |
| scaffold123580.g11972.t1 | adenylate kinase 9 | XP_009166046 |
| scaffold124614.g12058.t1 | diacylglycerol kinase theta | GAA50183 |
| scaffold124788.g12071.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | XP_012799908 |
| scaffold125857.g12179.t1 | inositol hexakisphosphate diphosphoinositol-pentakisphosphate kinase | GAA50830 |
| scaffold127146.g12322.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase | GAA53851 |
| scaffold128529.g12436.t1 | mevalonate kinase | GAA48262 |
| scaffold129431.g12518.t1 | tousled-like kinase | GAA32772 |
| scaffold129895.g12556.t1 | membrane-associated guanylate ww and pdz domain-containing protein partial | GAA30280 |
| scaffold130209.g12587.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase beta-1 | GAA31256 |
| scaffold131200.g12686.t1 | p90 ribosomal s6 kinase | GAA30943 |
| scaffold131957.g12737.t1 | beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | GAA51725 |
| scaffold132212.g12753.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase plk3 | GAA48207 |
| scaffold132848.g12815.t1 | rna-binding motif single-stranded-interacting protein 3 | CCD79055 |
| scaffold132968.g12880.t1 | inositol hexakisphosphate diphosphoinositol-pentakisphosphate kinase | GAA50830 |
| scaffold133786.g12904.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase tao1 | XP_012795539 |
| scaffold133786.g12905.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase tao1 | CCD75805 |
| scaffold134286.g12969.t1 | tau-tubulin kinase 1 | XP_009174870 |
| scaffold134663.g13011.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase 2 alpha | GAA36861 |
| scaffold135635.g13086.t1 | 5 -amp-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha- partial | XP_012801127 |
| scaffold116667.g11363.t1 | polynucleotide 5 -hydroxyl-kinase grc3 | XP_009167129 |
| scaffold124614.g12059.t1 | diacylglycerol partial | GAA50183 |
| scaffold128529.g12436.t1 | mevalonate kinase | GAA48262 |
| scaffold129895.g12556.t1 | membrane-associated guanylate ww and pdz domain-containing protein partial | GAA30280 |
| scaffold131957.g12737.t1 | beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | GAA51725 |
| scaffold132968.g12880.t1 | inositol hexakisphosphate diphosphoinositol-pentakisphosphate kinase | GAA50830 |
| scaffold135635.g13086.t1 | 5 -amp-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha- partial | XP_012801127 |
| scaffold136908.g13236.t1 | protein kinase 3 | GAA55512 |
| scaffold136908.g13237.t1 | protein kinase 3 | XP_009162037 |
| scaffold137283.g13253.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase stk | XP_012796782 |
| scaffold139374.g13438.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase mrck beta | GAA54209 |
| scaffold138090.g13441.t1 | homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 1 | GAA49629 |
| scaffold139598.g13455.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase partial | GAA55594 |
| scaffold140012.g13495.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase abl | XP_009168897 |
| scaffold141241.g13605.t1 | elongation factor 2 kinase | XP_009168017 |
| scaffold144490.g13922.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase chk1 | GAA28009 |
| scaffold144490.g13923.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase chk1 | GAA28009 |
| scaffold145028.g13979.t1 | serine threonine kinase | CCD82120 |
| scaffold145802.g14048.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase-like 2 isoform x4 | XP_009171363 |
| scaffold146118.g14081.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 6 | GAA51789 |
| scaffold146118.g14082.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 6 | GAA51789 |
| scaffold146827.g14142.t1 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase | XP_012797490 |
| scaffold147047.g14162.t1 | camp-dependent protein kinase type ii regulatory partial | XP_012798738 |
| scaffold147100.g14166.t1 | dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase partial | XP_012797184 |
| scaffold147477.g14205.t1 | phosphorylase b kinase regulatory subunit beta | XP_009164328 |
| scaffold147670.g14213.t1 | calcium-dependent protein kinase c | XP_009171744 |
| scaffold148103.g14256.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase lats1 | CCD81677 |
| scaffold148466.g14303.t1 | mob kinase activator-like partial | AAW24793 |
| scaffold148926.g14343.t1 | 5 -amp-activated protein kinase subunit beta-2 | XP_009174022 |
| scaffold149215.g14363.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 5 | GAA56189 |
| scaffold150374.g14477.t1 | ca2+ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase | GAA29102 |
| scaffold150959.g14519.t1 | map microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 | XP_009176240 |
| scaffold150970.g14520.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase wnk1 | GAA48562 |
| scaffold151376.g14549.t1 | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase | GAA38235 |
| scaffold152150.g14627.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase partial | GAA54879 |
| scaffold153329.g14745.t1 | phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulatory subunit 4 | GAA49419 |
| scaffold153478.g14761.t1 | taurocyamine kinase | AHH34783 |
| scaffold153833.g14788.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 13 | XP_009174195 |
| scaffold153909.g14795.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase haspin | XP_009164915 |
| scaffold153916.g14798.t1 | activated cdc42 kinase partial | GAA57037 |
| scaffold153437.g14804.t1 | casein kinase 1 partial | GAA55251 |
| scaffold155859.g14974.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 | XP_009171222 |
| scaffold156670.g15039.t1 | calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type ii subunit alpha | CDQ66143 |
| scaffold156781.g15048.t1 | g protein-coupled receptor kinase partial | XP_009162757 |
| scaffold157083.g15083.t1 | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase | GAA49544 |
| scaffold157342.g15097.t1 | snf-related serine threonine-protein kinase | XP_012798543 |
| scaffold157492.g15105.t1 | adenosine partial | GAA53109 |
| scaffold158476.g15192.t1 | serine threonine kinase | CCD58816 |
| scaffold160028.g15313.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase tousled-like 2 | XP_009166033 |
| scaffold160086.g15315.t1 | phosphorylase b kinase gamma catalytic chain skeletal muscle isoform | GAA31007 |
| scaffold160456.g15347.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase subunit 30a | XP_009168739 |
| scaffold160503.g15351.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 8 | XP_012800009 |
| scaffold160503.g15352.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase | AAX26212 |
| scaffold160522.g15354.t1 | glycerol kinase 5 | XP_009174737 |
| scaffold160883.g15375.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 4 | XP_009164898 |
| scaffold161242.g15416.t1 | carbohydrate kinase domain-containing protein | XP_009163381 |
| scaffold162051.g15481.t1 | death-associated protein kinase partial | CCD78383 |
| scaffold163718.g15627.t1 | adenylate kinase 7 | XP_01279558 |
| scaffold164010.g15647.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase par-1 | GAA29957 |
| scaffold164104.g15655.t1 | dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 | GAA55476 |
| scaffold164342.g15673.t1 | adenylate kinase domain-containing protein 1 | GAA56322 |
| scaffold164397.g15678.t1 | beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | GAA51725 |
| scaffold165830.g15806.t1 | polo-like kinase 4 | GAA29214 |
| scaffold165944.g15821.t1 | adenylate kinase 7 | XP_012792064 |
| scaffold166078.g15837.t1 | ceramide kinase | CDS41064 |
| scaffold166249.g15858.t1 | serine threonine kinase | GAA48273 |
| scaffold167835.g16006.t1 | diacylglycerol kinase | XP_009171139 |
| scaffold168609.g16075.t1 | 5 -amp-activated protein kinase subunit partial | XP_009168445 |
| scaffold168898.g16108.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase alpha | XP_012791939 |
| scaffold168988.g16116.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase fps85d | CCD60647 |
| scaffold169120.g16126.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase-like | XP_009171362 |
| scaffold170161.g16225.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase baz1b | XP_009171539 |
| scaffold171076.g16317.t1 | tyrosine kinase | CCD78239 |
| scaffold172018.g16393.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase mtor | CAX72673 |
| scaffold172138.g16399.t1 | death-associated protein kinase 1 | GAA55809 |
| scaffold172297.g16424.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase doa | GAA51059 |
| scaffold172730.g16462.t1 | beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | GAA51725 |
| scaffold172754.g16467.t1 | serine threonine protein kinase | XP_009164480 |
| scaffold172918.g16477.t1 | calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase i | XP_009163606 |
| scaffold172996.g16483.t1 | adenylate kinase 7 | XP_009169040 |
| scaffold172885.g16486.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase fps85d | GAA57407 |
| scaffold173065.g16489.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 1 | AAW26946 |
| scaffold173506.g16519.t1 | pi-3-kinase-related kinase smg-1 | GAA36649 |
| scaffold173663.g16531.t1 | diacylglycerol kinase theta | XP_012796233 |
| scaffold39358.g4339.t1 | protein kinase | XP_009164838 |
| scaffold39378.g4343.t1 | dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase partial | GAA39252 |
| scaffold39474.g4356.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | GAA48921 |
| scaffold40181.g4436.t1 | serine-protein kinase atm | GAA48414 |
| scaffold40495.g4467.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase syk | AIK22521 |
| scaffold40541.g4471.t1 | non metastatic cells 7 protein expressed | CCD82223 |
| scaffold45820.g4968.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase beta-1 | AAX26344 |
| scaffold45993.g4997.t1 | rho-associated protein kinase let-502 | XP_009163529 |
| scaffold46381.g5020.t1 | protein kinase | XP_012794989 |
| scaffold46405.g5023.t1 | pyruvate kinase | GAA54498 |
| scaffold46405.g5024.t1 | pyruvate kinase | GAA54498 |
| scaffold48379.g5192.t1 | histidine kinase | GAA48109 |
| scaffold48455.g5203.t1 | pi-3-kinase-related kinase smg- partial | XP_009169681 |
| scaffold50139.g5360.t1 | calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase | CCD77707 |
| scaffold51392.g5462.t1 | 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate 5-kinase | GAA53571 |
| scaffold51517.g5476.t1 | traf2 and nck-interacting protein kinase | XP_009165965 |
| scaffold51608.g5486.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase mtor | XP_009174377 |
| scaffold51916.g5509.t1 | srsf protein kinase partial | GAA55409 |
| scaffold54190.g5722.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase partial | CCD60993 |
| scaffold53025.g5731.t1 | chaperone activity of bc1 complex- mitochondrial | GAA28956 |
| scaffold54967.g5799.t1 | taurocyamine kinase | AHH34783 |
| scaffold55534.g5863.t1 | cyclin-g-associated kinase | GAA31493 |
| scaffold55721.g5880.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase-like 1 | XP_009168678 |
| scaffold56825.g5985.t1 | rho-associated protein kinase partial | XP_009174321 |
| scaffold57112.g6016.t1 | phosphoglycerate kinase | AAZ17561 |
| scaffold58078.g6097.t1 | glycogen synthase kinase-3 partial | GAA34354 |
| scaffold59233.g6207.t1 | arginine kinase | XP_009168180 |
| scaffold59371.g6220.t1 | protein kinase | CCD76945 |
| scaffold59371.g6222.t1 | protein kinase | CCD76945 |
| scaffold59967.g6277.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | XP_013384334 |
| scaffold60394.g6321.t1 | receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbb-4 | XP_009164236 |
| scaffold61362.g6408.t1 | protein sevenless | CCD81921 |
| scaffold61420.g6417.t1 | homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3 | GAA49629 |
| scaffold62078.g6467.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase 6-a | GAA54088 |
| scaffold63091.g6564.t1 | tyrosine kinase partial | AIK22521 |
| scaffold63540.g6586.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase osr1 | GAA55576 |
| scaffold63811.g6631.t1 | serine threonine kinase | XP_009172103 |
| scaffold64120.g6661.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase tao1 | XP_009174151 |
| scaffold64348.g6686.t1 | 5 -amp-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | GAA51741 |
| scaffold64716.g6709.t1 | nucleoside diphosphate kinase | XP_009174910 |
| scaffold65182.g6731.t1 | phosphorylase b kinase | XP_009161949 |
| scaffold65210.g6738.t1 | diacylglycerol kinase | XP_009171139 |
| scaffold66004.g6810.t1 | rac serine threonine-protein kinase | GAA49945 |
| scaffold66109.g6826.t1 | lim domain kinase 1 | GAA57757 |
| scaffold68941.g7106.t1 | tyrosine kinase | CCD80719 |
| scaffold69756.g7131.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase btk | XP_012800589 |
| scaffold70197.g7157.t1 | pantothenate kinase 4 | XP_009165901 |
| scaffold70588.g7206.t1 | xylulose kinase-like | XP_013080007 |
| scaffold71004.g7251.t1 | nucleoside diphosphate kinase | XP_009174910 |
| scaffold71056.g7253.t1 | g protein-coupled receptor kinase | GAA48257 |
| scaffold71376.g7285.t1 | mps one binder kinase activator-like 2 | XP_009176739 |
| scaffold74251.g7535.t1 | insulin receptor-related protein | AAL67949 |
| scaffold74856.g7593.t1 | elongation factor 2 kinase | GAA53143 |
| scaffold76198.g7715.t1 | pas domain-containing serine threonine-protein kinase | XP_001622648 |
| scaffold76429.g7737.t1 | selenide water dikinase | GAA37296 |
| scaffold76816.g7771.t1 | polyribonucleotide 5 -hydroxyl-kinase clp1 | XP_009176868 |
| scaffold77098.g7809.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase tao1 | XP_009174151 |
| scaffold77496.g7846.t1 | inositol hexakisphosphate and diphosphoinositol-pentakisphosphate kinase 2 | GAA42009 |
| scaffold77698.g7871.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase partial | GAA47566 |
| scaffold78519.g7937.t1 | casein kinase i isoform alpha | XP_012800330 |
| scaffold79782.g8054.t1 | 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase fructose- -bisphosphatase 1 | GAA56065 |
| scaffold80904.g8159.t1 | tau-tubulin kinase 1 | XP_009168311 |
| scaffold80904.g8160.t1 | tau-tubulin kinase 1 | GAA33234 |
| scaffold81576.g8197.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | GAA48921 |
| scaffold81874.g8213.t1 | casein kinase ii subunit beta | XP_012799477 |
| scaffold208988.g20715.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase rio1 | GAA42679 |
| scaffold209153.g20744.t1 | camp-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit gamma isoform x3 | XP_010361270 |
| scaffold209819.g20917.t1 | 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate 5-kinase | XP_009172830 |
| scaffold210356.g21066.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase nim1 | GAA27349 |
| scaffold210361.g21070.t1 | camp-dependent protein kinase type ii regulatory partial | AAW27091 |
| scaffold210374.g21073.t1 | inactive tyrosine-protein kinase 7 | XP_009170369 |
| scaffold210465.g21102.t1 | dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 | GAA51135 |
| scaffold210465.g21103.t1 | dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 2 | XP_009176533 |
| scaffold210673.g21172.t1 | phosphomevalonate kinase | XP_009176660 |
| scaffold210664.g21177.t1 | pyridoxal kinase | XP_009169816 |
| scaffold210838.g21234.t1 | protein kinase a | GAA31871 |
| C20393866.g21302.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase-like | GAA51647 |
| C20396832.g21322.t1 | camp-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit | XP_012798212 |
| C20501678.g21723.t1 | guanylate partial | CAX69740 |
| C20512058.g21774.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase smg1 | CCD82625 |
| C20526748.g21847.t1 | adenylate kinase 9 | GAA50613 |
| C20527094.g21849.t1 | protein kinase | CCD82438 |
| C20539732.g21908.t1 | camp-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit | XP_009167378 |
| C20559732.g22014.t1 | map microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 2 k08798 map microtubule affinity-regulating kinase | GAA54404 |
| C20565992.g22051.t1 | beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | GAA51725 |
| C20567188.g22055.t1 | mitochondrial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 2 | ACI45965 |
| C20575826.g22096.t1 | n-terminal kinase-like protein | GAA49046 |
| C20577228.g22102.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase pak 3 | XP_012794399 |
| C20581104.g22121.t1 | protein kinase c epsilon type | XP_012802529 |
| C20586014.g22144.t1 | map microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 | GAA57025 |
| C20599222.g22234.t1 | membrane-associated guanylate kinase ww and pdz domain-containing protein partial | GAA39731 |
| C20623860.g22387.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha | CCD82689 |
| C20626348.g22406.t1 | calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase i | GAA40887 |
| C20630912.g22430.t1 | pctaire protein kinase | XP_009164575 |
| C20639892.g22470.t1 | traf2 and nck-interacting protein kinase | GAA51906 |
| C20646538.g22512.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase beta-2 | AAX25829 |
| C20654430.g22556.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase htk16 | GAA55551 |
| C20673958.g22681.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha | GAA53277 |
| C20677314.g22699.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase beta-2 | GAA36606 |
| C20695906.g22830.t1 | casein kinase i isoform alpha | XP_009173421 |
| C20700092.g22852.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase mtor | XP_012798184 |
| C20708402.g22904.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase organizer 1 | GAA30213 |
| C20721854.g22987.t1 | chaperone activity of bc1 complex- mitochondrial | GAA28956 |
| C20721994.g22990.t1 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 4 | CCD74887 |
| C20728984.g23037.t1 | phosphorylase kinase alpha beta subunit | XP_009161949 |
| C20730640.g23047.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase pak 6-like isoform x1 | XP_007238430 |
| C20735692.g23093.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase partial | XP_012802127 |
| C20743024.g23134.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase par-1 | AAP06096 |
| C20758688.g23249.t1 | proto-oncogene serine threonine-protein kinase pim-1 | XP_009165098 |
| C20770334.g23326.t1 | protein kinase 3 | XP_009162037 |
| C20784968.g23422.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase htk16 | XP_009164161 |
| C20797450.g23513.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7-like | GAA49925 |
| C20797626.g23521.t1 | serine threonine kinase | CCD78918 |
| C20799826.g23548.t1 | protein kinase | XP_005853141 |
| C20801766.g23561.t1 | nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase 6 | XP_009173762 |
| C20803968.g23575.t1 | calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase i | XP_009163606 |
| C20810620.g23624.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | GAA48921 |
| C20811108.g23630.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase atr | GAA47692 |
| C20811236.g23635.t1 | protein-serine threonine partial | GAA49927 |
| C20812888.g23646.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase haspin | XP_009164915 |
| C20817450.g23678.t1 | inactive tyrosine-protein kinase 7 | CCD75549 |
| C20818984.g23693.t1 | citron rho-interacting kinase | GAA53903 |
| C20824192.g23718.t1 | adenylate kinase | XP_012800559 |
| C20832302.g23781.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | GAA48921 |
| C20833320.g23794.t1 | serine threonine kinase | XP_009163024 |
| C20841020.g23856.t1 | phosphoglycerate partial | ACN50260 |
| C20841582.g23859.t1 | integrin-linked protein kinase | XP_009162756 |
| C20834598.g23891.t1 | adenylate kinase | GAA29349 |
| C20848972.g23928.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase wnk1 | GAA48562 |
| C20862412.g24063.t1 | map microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 2 k08798 map microtubule affinity-regulating kinase | GAA54404 |
| C20863690.g24087.t1 | citron rho-interacting kinase | XP_009165112 |
| C20865820.g24099.t1 | dual specificity protein kinase clk2 | XP_009171633 |
| C20871600.g24158.t1 | 6-phosphofructokinase | GAA28132 |
| C20882046.g24252.t1 | 5 -amp-activated protein kinase subunit gamma-1 | XP_009166275 |
| C20883854.g24271.t1 | casein kinase i isoform alpha | XP_012792480 |
| C20896960.g24396.t1 | phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase dephospho- kinase | GAA31214 |
| C20897148.g24403.t1 | pi-3-kinase-related kinase smg- partial | GAA38308 |
| C20899350.g24433.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase pmk-1 | XP_012799766 |
| C20903520.g24491.t1 | cdk-activating kinase assembly factor mat1 | GAA31314 |
| C20904610.g24507.t1 | calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type 1g | GAA48272 |
| C20908904.g24564.t1 | rho-associated protein kinase 1 | AAP06025 |
| C20909552.g24578.t1 | dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 3 | XP_009165832 |
| C20909730.g24581.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 1 | AAW26946 |
| C20909724.g24587.t1 | serum glucocorticoid regulated kinase partial | AEK51852 |
| C20911876.g24608.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase partial | XP_012797256 |
| C20913048.g24631.t1 | receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbb-4 | XP_009164236 |
| C20913970.g24641.t1 | protein kinase cgmp-dependent | XP_009172880 |
| C20914130.g24644.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase nek1 | XP_012793943 |
| C20917982.g24716.t1 | receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbb-4 | CCD82053 |
| C20921542.g24797.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase abl1 | GAA50613 |
| C20924036.g24851.t1 | hxk_schma ame: full=hexokinase | GAA52956 |
| C20924852.g24887.t1 | glycerol kinase | GAA30665 |
| C20925382.g24898.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase nek1 | GAA54400 |
| C20926756.g24939.t1 | serine threonine kinase | XP_009169364 |
| C20926816.g24946.t1 | diacylglycerol kinase partial | GAA50183 |
| C20927120.g24969.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 14 | GAA49696 |
| C20928138.g25052.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase d1 | CCD82849 |
| C20928322.g25074.t1 | map microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 | GAA51746 |
| scaffold1367.g133.t1 | protein kinase | GAA52406 |
| scaffold1373.g141.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 1 | GAA57007 |
| scaffold3591.g353.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | GAA48921 |
| scaffold3592.g354.t1 | death-associated protein kinase | GAA55809 |
| scaffold3891.g399.t1 | rac serine threonine-protein kinase | GAA49945 |
| scaffold6844.g777.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase nek4 | CCD78918 |
| scaffold6906.g788.t1 | inositol polyphosphate multikinase | XP_012795701 |
| scaffold7497.g863.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase 2 beta-like isoform x1 | XP_014771715 |
| scaffold8389.g983.t1 | wee1-like protein kinase | XP_012801093 |
| scaffold8695.g1039.t1 | choline ethanolamine kinase | GAA56022 |
| scaffold9505.g1137.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3 | XP_009166012 |
| scaffold8572.g1195.t1 | leucine-rich repeat serine threonine-protein kinase 1 | GAA54147 |
| scaffold10047.g1200.t1 | protein partial | GAA51975 |
| scaffold10992.g1394.t1 | 3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase-1 | XP_009170318 |
| scaffold12227.g1468.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | GAA48921 |
| scaffold12537.g1492.t1 | n-acetyl-d-glucosamine kinase | GAA38326 |
| scaffold12470.g1546.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase htk16 | GAA55551 |
| scaffold13490.g1630.t1 | wee1-like protein kinase | XP_009169623 |
| scaffold13569.g1633.t1 | p21-activated protein kinase-interacting protein 1-like | XP_009174334 |
| scaffold13936.g1677.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase par-1 | XP_009176067 |
| scaffold13936.g1678.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase par-1 | GAA29957 |
| scaffold14268.g1738.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type 2-beta | XP_009164426 |
| scaffold16202.g1910.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | XP_009171389 |
| scaffold16705.g1971.t1 | elongation factor 2 kinase | XP_009164726 |
| scaffold18667.g2229.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | XP_009171389 |
| scaffold18762.g2243.t1 | glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha | XP_009176335 |
| scaffold20057.g2386.t1 | 5 -amp-activated protein kinase subunit beta-1 | GAA50585 |
| scaffold20656.g2462.t1 | serine-protein kinase atm | GAA48414 |
| scaffold21586.g2577.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase partial | XP_012797255 |
| scaffold22685.g2674.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase tao1 | XP_012795539 |
| scaffold23238.g2741.t1 | calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase i | GAA40887 |
| scaffold23493.g2770.t1 | rho-associated protein kinase 2 | GAA38101 |
| scaffold23761.g2786.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type 2-beta | XP_009164426 |
| scaffold24235.g2848.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase ulk4 | XP_009164100 |
| scaffold24235.g2849.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase ulk4 | GAA30022 |
| scaffold24409.g2868.t1 | dual serine threonine and tyrosine protein kinase-like isoform x1 | XP_015171402 |
| scaffold24658.g2892.t1 | inactive tyrosine-protein kinase 7 | XP_012795581 |
| scaffold24662.g2896.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase unc- partial | XP_012792922 |
| scaffold25482.g2985.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase pak 1 | XP_009162522 |
| scaffold25578.g2996.t1 | protein kinase a | GAA31871 |
| scaffold28791.g3349.t1 | serine threonine kinase | CCD78043 |
| scaffold30603.g3531.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | XP_009172448 |
| scaffold30770.g3545.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase | GAA53851 |
| scaffold32727.g3733.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase mtor | XP_012798184 |
| scaffold32762.g3748.t1 | polo-like kinase partial | GAA32461 |
| scaffold33109.g3761.t1 | serine threonine kinase 33 | GAA37039 |
| scaffold33659.g3813.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 15 | KOF91810 |
| scaffold34431.g3878.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase htk16 | GAA55551 |
| scaffold36068.g4022.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase mtor | GAA51003 |
| scaffold175597.g16708.t1 | phosphatidylinositol-4 5-bisphosphate 3-kinase | GAA28095 |
| scaffold175597.g16709.t1 | phosphatidylinositol- -bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha pi3k | CCD74891 |
| scaffold176388.g16719.t1 | serine threonine protein kinase | GAA50474 |
| scaffold176825.g16756.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase tousled-like 2 | GAA32772 |
| scaffold177382.g16795.t1 | thiamin pyrophosphokinase 1 | CDS29031 |
| scaffold178214.g16848.t1 | protein kinase | XP_012794989 |
| scaffold180218.g16988.t1 | dolichol kinase | GAA48993 |
| scaffold180569.g17019.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase alpha | XP_009162460 |
| scaffold181707.g17100.t1 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase partial | XP_009168205 |
| scaffold182419.g17151.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase tao1 | GAA40895 |
| scaffold183458.g17223.t1 | g protein-coupled receptor kinase | GAA48257 |
| scaffold183347.g17226.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase-binding protein 1 | XP_009173588 |
| scaffold184978.g17316.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase | GAA28363 |
| scaffold186541.g17445.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase partial | GAA50738 |
| scaffold186815.g17475.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase partial | GAA36654 |
| scaffold187349.g17519.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 8 | XP_009166059 |
| scaffold188410.g17608.t1 | protein kinase | CCD76945 |
| scaffold188410.g17609.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 5 | XP_009176379 |
| scaffold189129.g17674.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase-like | GAA51647 |
| scaffold189277.g17685.t1 | n-acetylglucosamine kinase | GAA38326 |
| scaffold189626.g17723.t1 | camp dependent protein kinase regulatory | GAA30981 |
| scaffold189778.g17735.t1 | casein kinase i isoform delta | GAA29696 |
| scaffold189816.g17740.t1 | bifunctional 3 -phosphoadenosine 5 -phosphosulfate synthase | CCD80639 |
| scaffold190674.g17807.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase vrk1 | GAA51907 |
| scaffold190699.g17809.t1 | pi-3-kinase-related kinase smg- partial | GAA38308 |
| scaffold190720.g17811.t1 | nek6 si:ch211- nima (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase partial | GAA48921 |
| scaffold191153.g17861.t1 | glycogen synthase kinase 3-related | XP_009172337 |
| scaffold191247.g17880.t1 | acylglycerol kinase mitochondrial | XP_009175271 |
| scaffold191378.g17895.t1 | diacylglycerol kinase theta | XP_012799868 |
| scaffold191390.g17896.t1 | microtubule-associated serine threonine-protein kinase 4 | XP_012795504 |
| scaffold191677.g17918.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase-like | XP_009171362 |
| scaffold191790.g17927.t1 | phosphorylase b kinase gamma catalytic chain skeletal muscle isoform | GAA57498 |
| scaffold192330.g17978.t1 | protein-serine threonine partial | GAA49927 |
| scaffold192611.g18001.t1 | tbc domain-containing protein kinase-like protein | GAA56933 |
| scaffold192645.g18009.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 7 | CCD79071 |
| scaffold193004.g18057.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase hck | GAA51878 |
| scaffold193592.g18121.t1 | phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase | XP_009162460 |
| scaffold193690.g18132.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase partial | GAA37326 |
| scaffold193754.g18135.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase beta-1 | XP_012800703 |
| scaffold193782.g18137.t1 | gamma-tubulin complex component 5 | GAA53903 |
| scaffold193784.g18140.t1 | adenylate kinase 7 | XP_009169040 |
| scaffold195468.g18291.t1 | tyrosine kinase, putative | XP_002410064 |
| scaffold195886.g18324.t1 | calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type ii subunit delta | AAX26206 |
| scaffold196099.g18353.t1 | protein kinase | XP_012794989 |
| scaffold196799.g18440.t1 | tau-tubulin kinase 1 | GAA27984 |
| scaffold197681.g18547.t1 | alpha subunit of casein kinase ii | XP_009170248 |
| scaffold197729.g18559.t1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase partial | XP_009174627 |
| scaffold197789.g18575.t1 | cgmp-dependent protein kinase 1-like | XP_014786419 |
| scaffold198520.g18670.t1 | probable inactive serine threonine-protein kinase partial | CCD75132 |
| scaffold199564.g18799.t1 | ste20-like serine threonine-protein kinase | GAA30009 |
| scaffold200263.g18924.t1 | calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase i | XP_009163606 |
| scaffold200316.g18936.t1 | rho-associated protein kinase 2 | XP_009174321 |
| scaffold200365.g18945.t1 | adenylate kinase 9 | XP_009166046 |
| scaffold201128.g19061.t1 | 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate 5-kinase | GAA53571 |
| scaffold201420.g19105.t1 | casein kinase ii subunit alpha | GAA27226 |
| scaffold202171.g19233.t1 | serine threonine kinase | XP_009163529 |
| scaffold202411.g19283.t1 | pyruvate kinase | XP_009174349 |
| scaffold202847.g19382.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase partial | GAA36654 |
| scaffold203109.g19407.t1 | dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1a-like | XP_014775920 |
| scaffold203314.g19441.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase pak 3 | CCD60856 |
| scaffold203211.g19446.t1 | protein kinase | CCD77323 |
| scaffold203926.g19579.t1 | p21-activated kinase 1 | GAA53709 |
| scaffold205155.g19800.t1 | tyrosine-protein kinase csk | GAA57437 |
| scaffold205213.g19811.t1 | serine threonine kinase | CCD75803 |
| scaffold205261.g19824.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase dclk3 | XP_012796123 |
| scaffold205354.g19843.t1 | polo-like kinase 4 | XP_009171351 |
| scaffold205426.g19857.t1 | dtmp kinase | GAA40579 |
| scaffold205807.g19939.t1 | ribosomal protein s6 kinase alpha- partial | KHN83816 |
| scaffold206173.g20012.t1 | cell division protein kinase 10 (serine threonine-protein kinase pisslre) | CCD76518 |
| scaffold206659.g20117.t1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 11b | GAA27650 |
| scaffold207144.g20227.t1 | unc51-like kinase | GAA30160 |
| scaffold207155.g20229.t1 | 6-phosphofructokinase | GAA28132 |
| scaffold207268.g20254.t1 | novel protein kinase c | XP_009174694 |
| scaffold207326.g20278.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase partial | XP_009175358 |
| scaffold207404.g20284.t1 | citron rho-interacting kinase | XP_009165112 |
| scaffold207404.g20285.t1 | citron rho-interacting kinase | XP_012801058 |
| scaffold207588.g20320.t1 | rho-associated protein kinase 2 | GAA38101 |
| scaffold207591.g20321.t1 | Phosphofructokinase | CAX73065 |
| scaffold207685.g20343.t1 | map microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4 | XP_009176240 |
| scaffold207801.g20361.t1 | serine threonine kinase | XP_009176467 |
| scaffold207958.g20411.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase pak 1 | XP_009162522 |
| scaffold207738.g20426.t1 | rio kinase 2 | XP_009169852 |
| scaffold208600.g20577.t1 | phosphatidylinositol-4 5-bisphosphate 3-kinase | GAA28095 |
| scaffold208687.g20600.t1 | tau-tubulin kinase 1 | GAA27984 |
| scaffold208848.g20655.t1 | probable adp-dependent glucokinase | XP_009171303 |
| scaffold208863.g20668.t1 | serine threonine-protein kinase lats1 | XP_012797980 |
| scaffold208961.g20690.t1 | serine threonine kinase | GAA48273 |
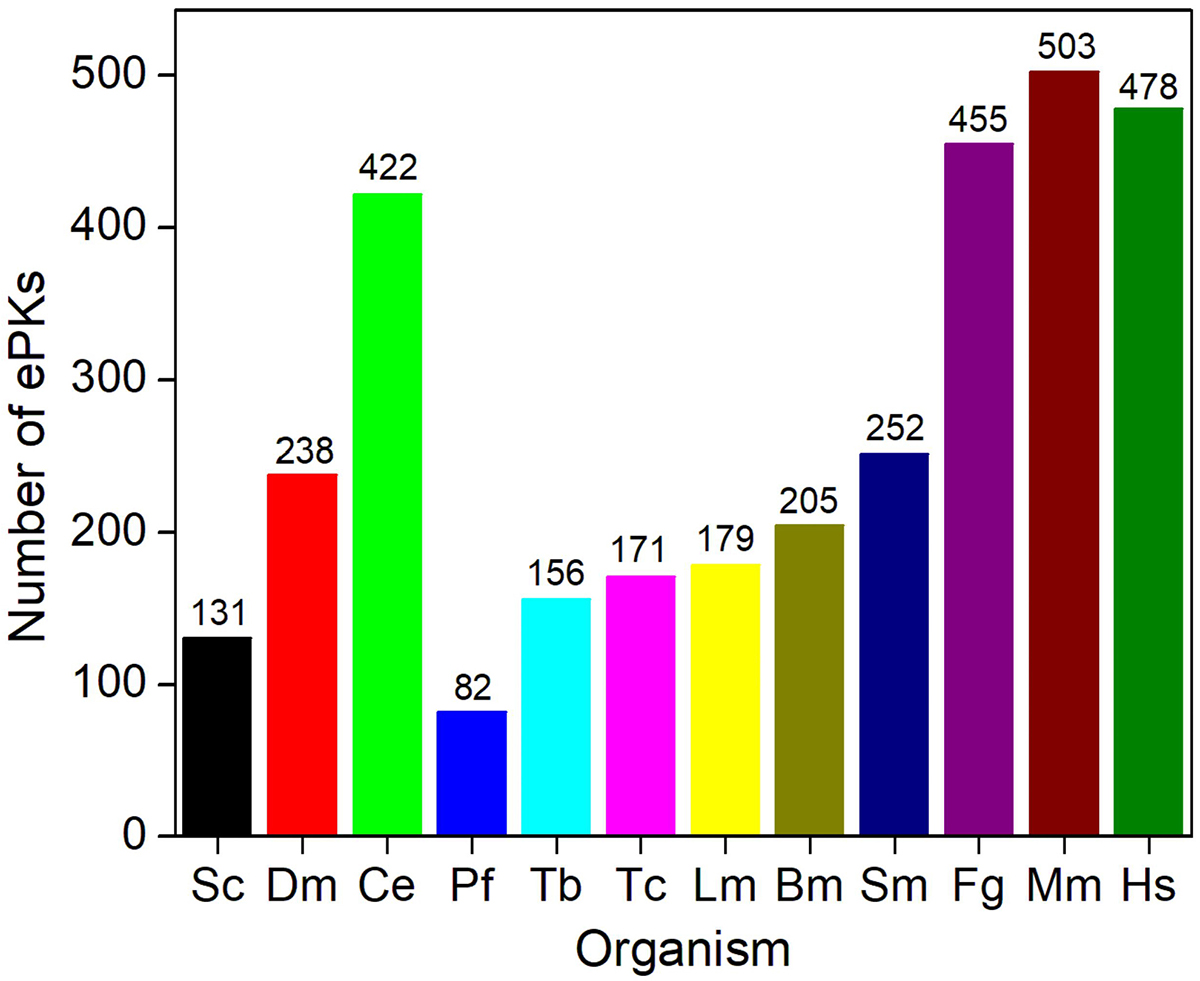
The FgePKs were identified by analyzing the parasite genome. The total number of ePKs varied in different organisms (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Drosophila melanogaster, Caernorhabditis elegens, Plasmodium falciparum, Trypanosoma brucei, Trypanosoma cruzi, Leishmania major, Brugia malayi, Schistosoma mansoni, Mus musculus, and Homo sapiens) and ranged from 82 to 503 (Figure 2). We observed that F. gigantica contains almost twice the number of ePKs compared to the related parasites.
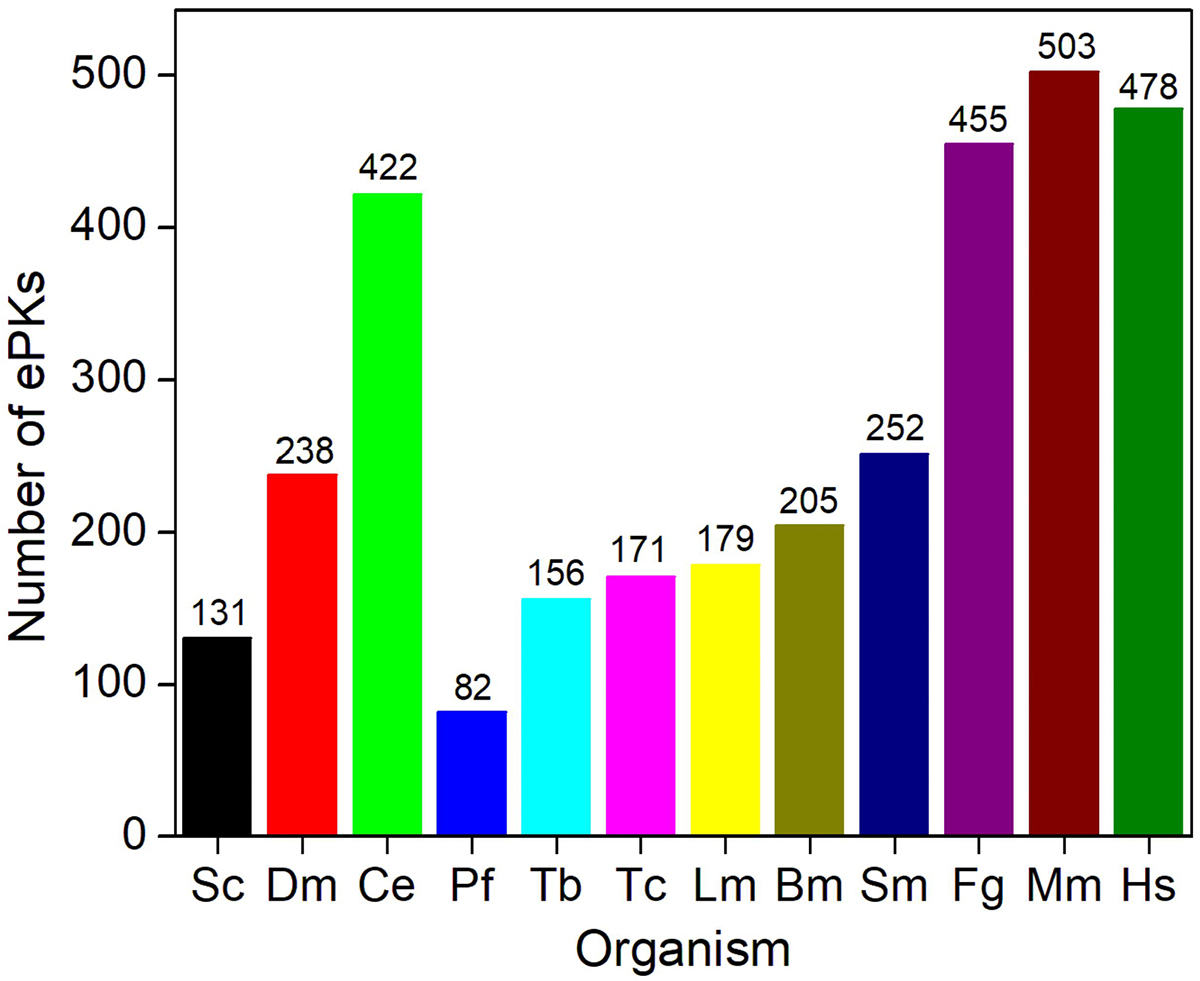 Figure 2
Figure 2ePKs in the predicted proteomes of diverse taxa. A total of 252 PKs were identified in the predicted proteome of F. gigantica. For comparison, the number of the total predicted proteome that codes for ePKs is shown for Sc – S. cerevisiae, Dm – D. melanogaster, Ce – C. elegans, Pf – P. falciparum, Tb – T. brucei, Tc – T. cruzi, Lm – L. major, Bm – B. malayi, S. mansoni, Mm – M. musculus, and Hm – H. sapiens.
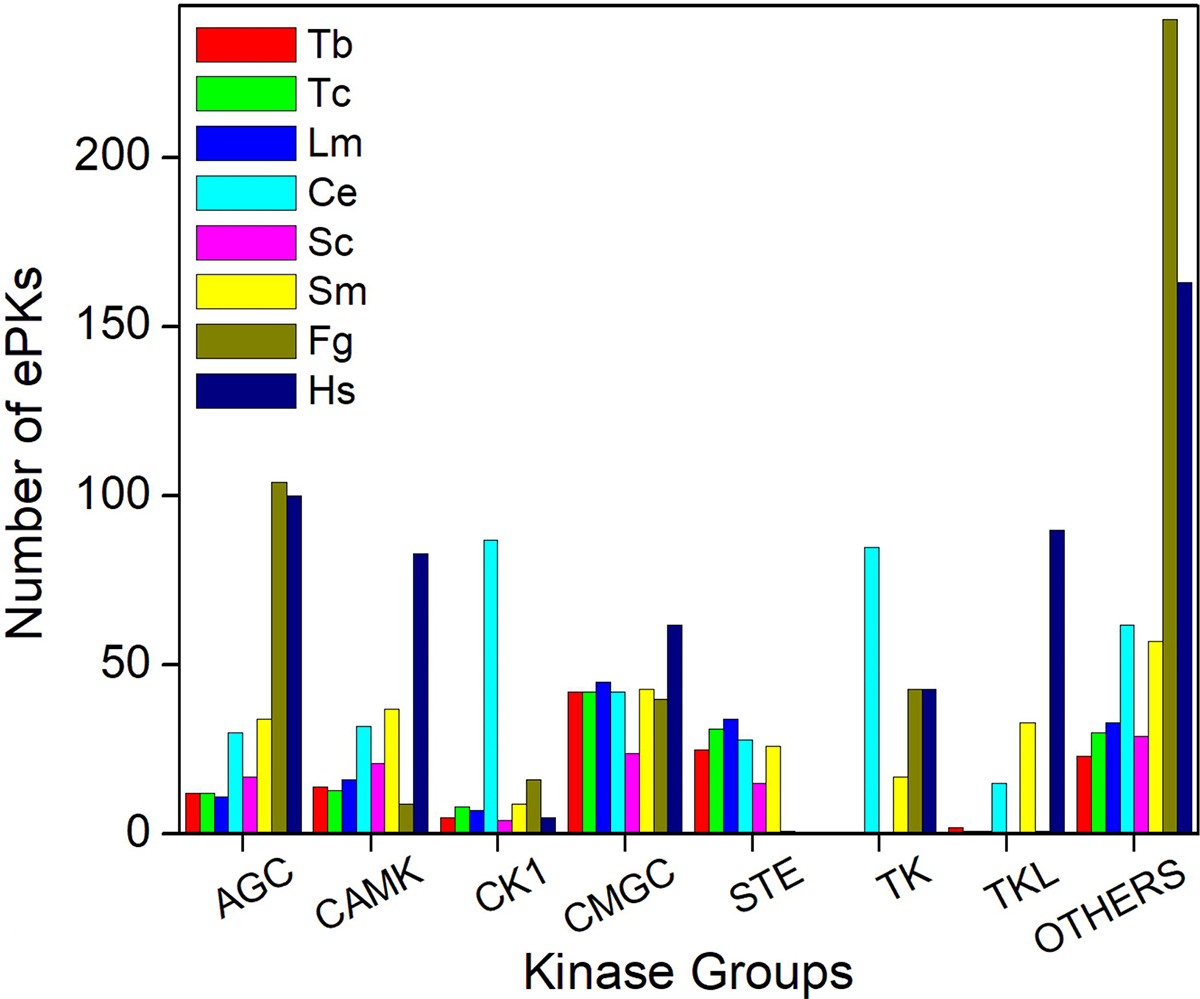
Our data show that F. gigantica has representatives in all ePKs groups. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that most of them are distinctly clustered with known ePKs in other eukaryotes. Those ePKs that do not fall into these groups were categorized as “Other”. In F. gigantica the largest ePKs group was Ser/Thr kinase (170 members), a common feature shared with many organisms, and the smallest group was TKL (only 1 member). The largest and the smallest ePKs group within the Ser/Thr group of FgePKs was AGC (104 members), and STE (only 1 member), respectively. Similarly, in the Tyr kinase group, we found 43 sequences. A total of 241 sequences were designated as other kinases (Figure 3).
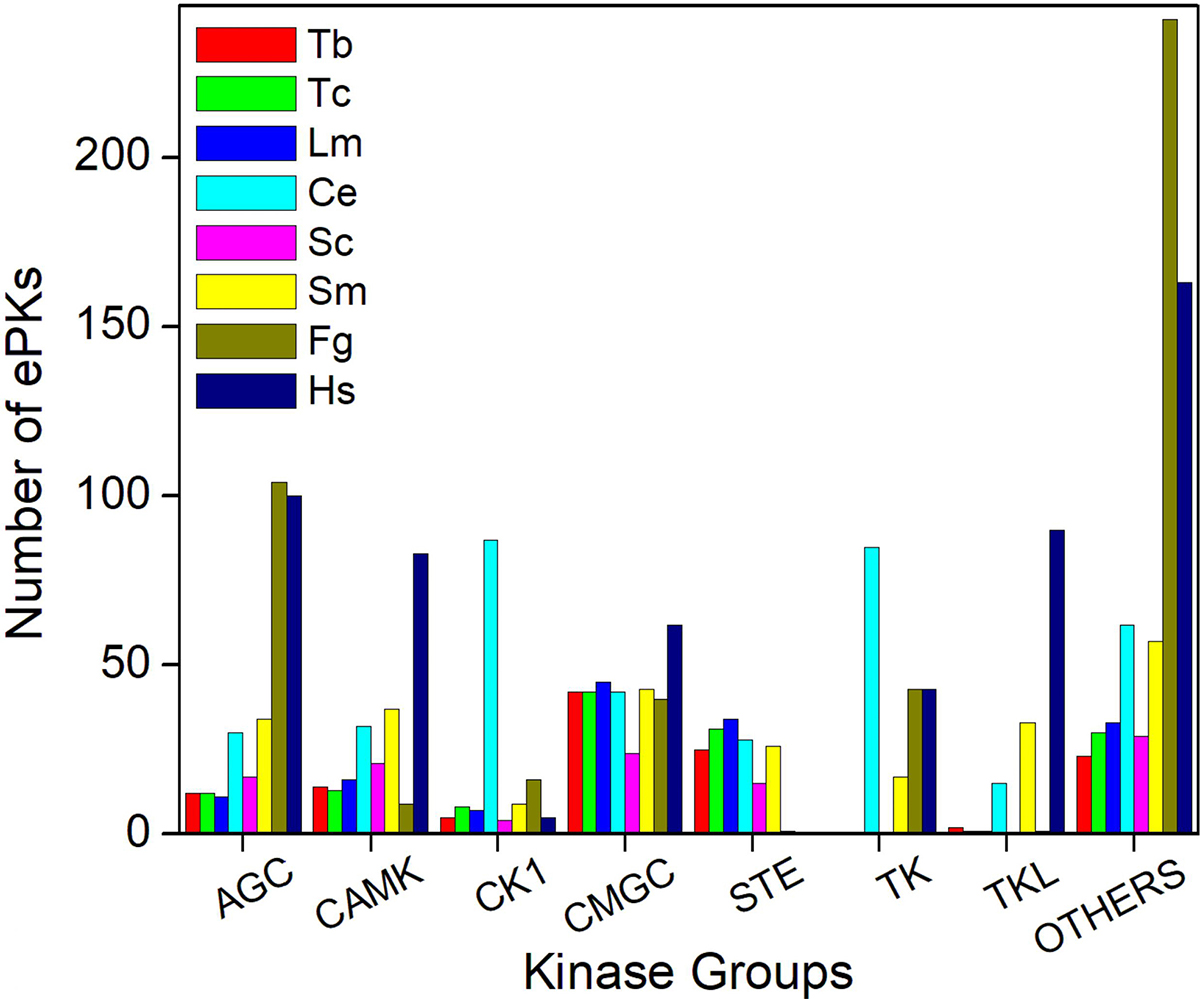 Figure 3
Figure 3Distribution of ePKs groups in F. gigantica and other organisms. For comparison, occurrence of the different ePKs groups in Tb – T. brucei, Tc – T. cruzi, Lm – L. major, Ce - C. elegans, Sc- S. cerevisiae, Sm - S. mansoni, and Hs - H. sapiens are shown.
The Ser/Thr kinases are generally classified into 5 groups: AGC, CaMK, CMGC, STE, and CK1. In FgePKs, we found proteins belonging to all these groups (Table 2). The AGC group is comprised of protein kinase A (PKA), protein kinase G (PKG), and protein kinase C (PKC). The CaMK represents Calcium and Calmodulin regulated kinases, whereas the CMGC group is comprised of CDK (Cyclin Dependent Kinase), MAPK (Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase), GSK (Glycogen Synthase 3 Kinase), CLK (CDC-Like Kinase), SRPK (SR-rich Protein Kinase), CK2 (Cell/Casein Kinase 2), DYRK (Dual-specificity Tyr Regulated Kinase), and RCK (named after resistance to complement killing, rck gene of mouse). The STE and CK1 represent sterile kinase and Casein Kinase 1, respectively.
| AGC Kinases | CK1 Kinases | CaMK Kinases | CMGC Kinases | STE Kinases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| scaffold81990.g8225.t1 | scaffold106986.g10499.t1 | scaffold156670.g15039scaffold172918.g16477.t1 | scaffold85190.g8508.t1 | scaffold199564.g18799.t1 |
| scaffold87509.g8711.t1 | scaffold153437.g14804.t1 | scaffold50139.g5360.t1 | scaffold99759.g9753.t1 | |
| scaffold87509.g8712.t1 | scaffold78519.g7937.t1 | C20626348.g22406.t1 | scaffold145802.g14048.t1 | |
| scaffold86513.g8721.t1 | scaffold81874.g8213.t1 | C20803968.g23575.t1 | scaffold146118.g14081.t1 | |
| scaffold93812.g9246.t1 | C20695906.g22830.t1 | scaffold23238.g2741.t1 | scaffold146118.g14082.t1 | |
| scaffold98852.g9822.t1 | C20883854.g24271.t1 | scaffold195886.g18324.t1 | scaffold153833.g14788.t1 | |
| scaffold101667.g9953.t1 | scaffold189778.g17735.t1 | scaffold200263.g18924.t1 | scaffold160456.g15347.t1 | |
| scaffold103547.g10134.t1 | scaffold197681.g18547.t1 | C20904610.g24507.t1.g17807.t1 | scaffold160503.g15351.t1 | |
| scaffold103547.g10135.t1 | scaffold201420.g19105.t1 | scaffold160503.g15352.t1 | ||
| scaffold104648.g10249.t1 | scaffold99613.g9745.t1 | scaffold169120.g16126.t1 | ||
| scaffold105136.g10285.t1 | scaffold134286.g12969.t1 | scaffold173065.g16489.t1 | ||
| scaffold116204.g11318.t1 | scaffold80904.g8159.t1 | scaffold55721.g5880.t1 | ||
| scaffold121069.g11738.t1 | scaffold80904.g8160.t1 | C20393866.g21302.t1 | ||
| scaffold122760.g11885.t1 | scaffold196799.g18440.t1 | C20909730.g24581.t1 | ||
| scaffold132212.g12753.t1 | scaffold208687.g20600.t1 | C20927120.g24969.t1 | ||
| scaffold133786.g12904.t1 | scaffold190674.g17807.t1 | scaffold1373.g141.t1 | ||
| scaffold133786.g12905.t1 | scaffold186541.g17445.t1 | |||
| scaffold139374.g13438.t1 | scaffold187349.g17519.t1 | |||
| scaffold144490.g13922.t1 | scaffold189129.g17674.t1 | |||
| scaffold144490.g13923.t1 | scaffold191677.g17918.t1 | |||
| scaffold145028.g13979.t1 | scaffold192645.g18009.t1 | |||
| scaffold148103.g14256.t1 | scaffold206659.g20117.t1 | |||
| scaffold150970.g14520.t1 | scaffold92882.g9180.t1 | |||
| scaffold153909.g14795.t1 | scaffold99327.g9715.t1 | |||
| scaffold157342.g15097.t1 | scaffold108332.g10629.t1 | |||
| scaffold158476.g15192.t1 | scaffold112912.g11016.t1 | |||
| scaffold160028.g15313.t1 | scaffold113735.g11112.t1 | |||
| scaffold164010.g15647.t1 | scaffold124788.g12071.t1 | |||
| scaffold166249.g15858.t1 | scaffold149215.g14363.t1 | |||
| scaffold172018.g16393.t1 | scaffold155859.g14974.t1 | |||
| scaffold172297.g16424.t1 | scaffold160883.g15375.t1 | |||
| scaffold172754.g16467.t1 | scaffold39378.g4343.t1 | |||
| scaffold51608.g5486.t1 | C20708402.g22904.t1 | |||
| scaffold54190.g5722.t1 | C20797450.g23513.t1 | |||
| scaffold58789.g6160.t1 | C20899350.g24433.t1 | |||
| scaffold62078.g6467.t1 | scaffold33659.g3813.t1 | |||
| scaffold63540.g6586.t1 | scaffold183347.g17226.t1 | |||
| scaffold63811.g6631.t1 | scaffold188410.g17609.t1 | |||
| scaffold64120.g6661.t1 | scaffold197729.g18559.t1 | |||
| scaffold66004.g6810.t1 | scaffold203109.g19407.t1 | |||
| scaffold70353.g7173.t1 | scaffold191153.g17861.t1 | |||
| scaffold76198.g7715.t1 | ||||
| scaffold77098.g7809.t1 | ||||
| scaffold77698.g7871.t1 | ||||
| scaffold208988.g20715.t1 | ||||
| scaffold210356.g21066.t1 | ||||
| C20512058.g21774.t1 | ||||
| C20577228.g22102.t1 | ||||
| C20700092.g22852.t1 | ||||
| C20730640.g23047.t1 | ||||
| C20735692.g23093.t1 | ||||
| C20743024.g23134.t1 | ||||
| C20758688.g23249.t1 | ||||
| C20797626.g23521.t1 | ||||
| C20811108.g23630.t1 | ||||
| C20811236.g23635.t1 | ||||
| C20812888.g23646.t1 | ||||
| C20833320.g23794.t1 | ||||
| C20848972.g23928.t1 | ||||
| C20914130.g24644.t1 | ||||
| C20925382.g24898.t1 | ||||
| C20926756.g24939.t1 | ||||
| C20928138.g25052.t1 | ||||
| scaffold3891.g399.t1 | ||||
| scaffold6844.g777.t1 | ||||
| scaffold8572.g1195.t1 | ||||
| scaffold13936.g1677.t1 | ||||
| scaffold13936.g1678.t1 | ||||
| scaffold22685.g2674.t1 | ||||
| scaffold24235.g2848.t1 | ||||
| scaffold24235.g2849.t1 | ||||
| scaffold24409.g2868.t1 | ||||
| scaffold24662.g2896.t1 | ||||
| scaffold25482.g2985.t1 | ||||
| scaffold28791.g3349.t1 | ||||
| scaffold32727.g3733.t1 | ||||
| scaffold33109.g3761.t1 | ||||
| scaffold36068.g4022.t1 | ||||
| scaffold176388.g16719.t1 | ||||
| scaffold176825.g16756.t1 | ||||
| scaffold182419.g17151.t1 | ||||
| scaffold186815.g17475.t1 | ||||
| scaffold190674.g17807.t1 | ||||
| scaffold191390.g17896.t1 | ||||
| scaffold192330.g17978.t1 | ||||
| scaffold193690.g18132.t1 | ||||
| scaffold198520.g18670.t1 | ||||
| scaffold202171.g19233.t1 | ||||
| scaffold202847.g19382.t1 | ||||
| scaffold203314.g19441.t1 | ||||
| scaffold205213.g19811.t1 | ||||
| scaffold205261.g19824.t1 | ||||
| scaffold206173.g20012.t1 | ||||
| scaffold207326.g20278.t1 | ||||
| scaffold207801.g20361.t1 | ||||
| scaffold207958.g20411.t1 | ||||
| scaffold208863.g20668.t1 | ||||
| scaffold208961.g20690.t1 | ||||
| scaffold210838.g21234.t1 | ||||
| scaffold25578.g2996.t1 | ||||
| scaffold156781.g15048.t1 | ||||
| scaffold71056.g7253.t1 | ||||
| scaffold183458.g17223.t1 |
The AGC kinases are known to phosphorylate the substrates at Ser/Thr residues present near the basic amino acid residues (Arg and Lys). In eukaryotic organisms, AGC group is comprised of three types of cytoplasmic Ser/Thr kinases PKA, PKG, and PKC, which are further divided into 16 families, specifically distributed into different forms of life. In the F. gigantica ePKs, we found 101 AGC kinases, of which 99 belonged to PKC, and 2 belonged to PKA; 3 members were G-protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRK), a member of PKC.
Protein kinase C is regarded as a fundamental regulator of the developmental processes in vertebrates for its pivotal role in cell growth and differentiation (15, 28). Role of PKC is also implicated in lipid signalling. The greater number of PKCs in the FgePKs suggests that this family is crucial for F. gigantica, and may be suitable targets for drug development. The PKC belongs to a large protein family that is classified into four subfamilies: PKC alpha (α), eta (η), iota (ι), and delta (δ). In the F. gigantica ePKs, we found 6 alpha, 46 eta, 23 iota, and 24 delta PKCs. The PKC alpha family consists of gamma (γ), beta I (βI), beta II (βII), and alpha subfamilies and are regulated by Ca2+ and diacylglycerol (DAG). Further, the PKC eta and delta subfamilies encompass the novel PKCs {epsilon (ε), delta, eta, and theta (θ)}, which are sensitive to DAG; and PKC iota subfamily contain the atypical PKCs (ζ (zeta) and ι)), which are insensitive to both Ca2+ and DAG (15, 29).
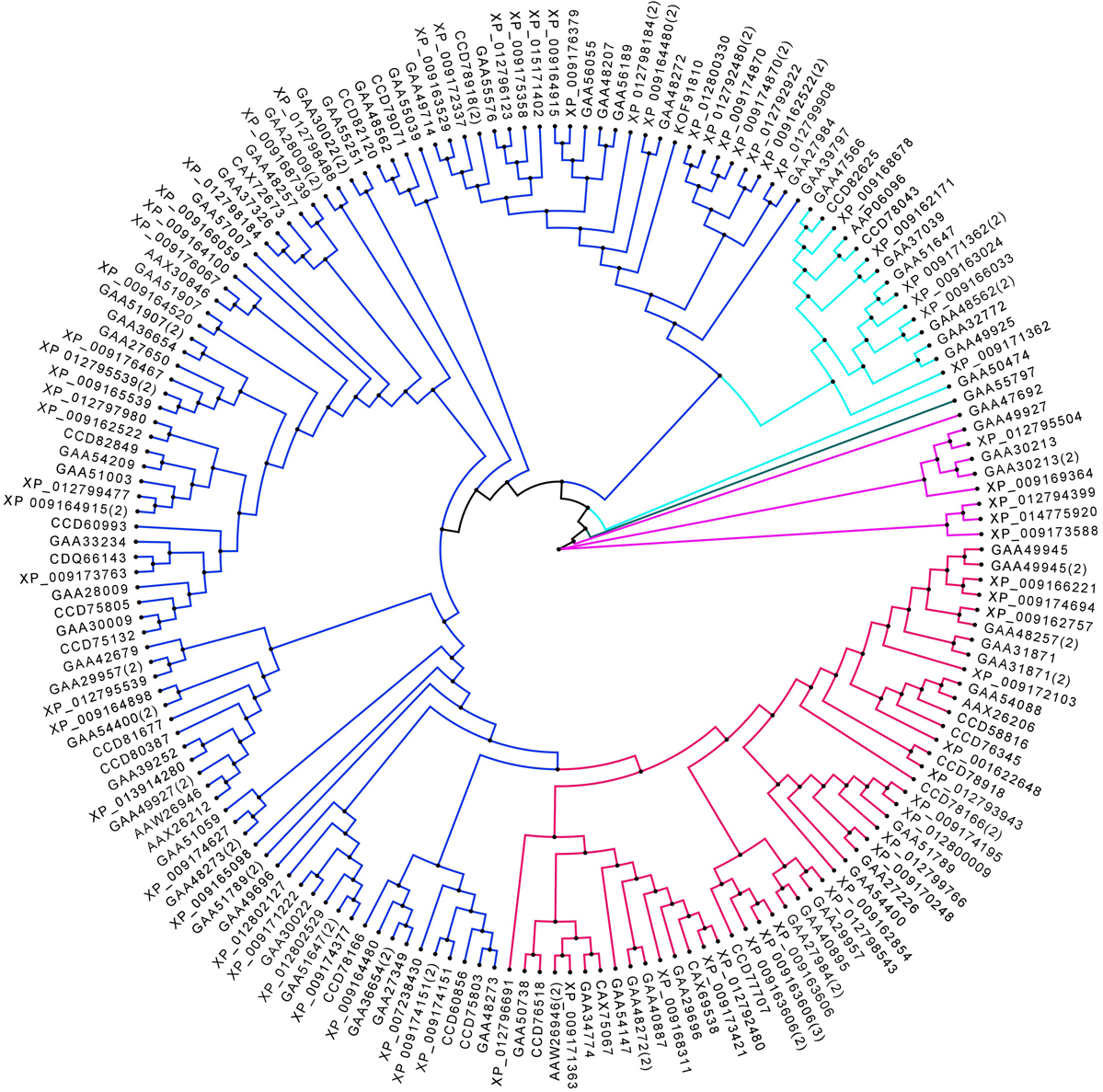
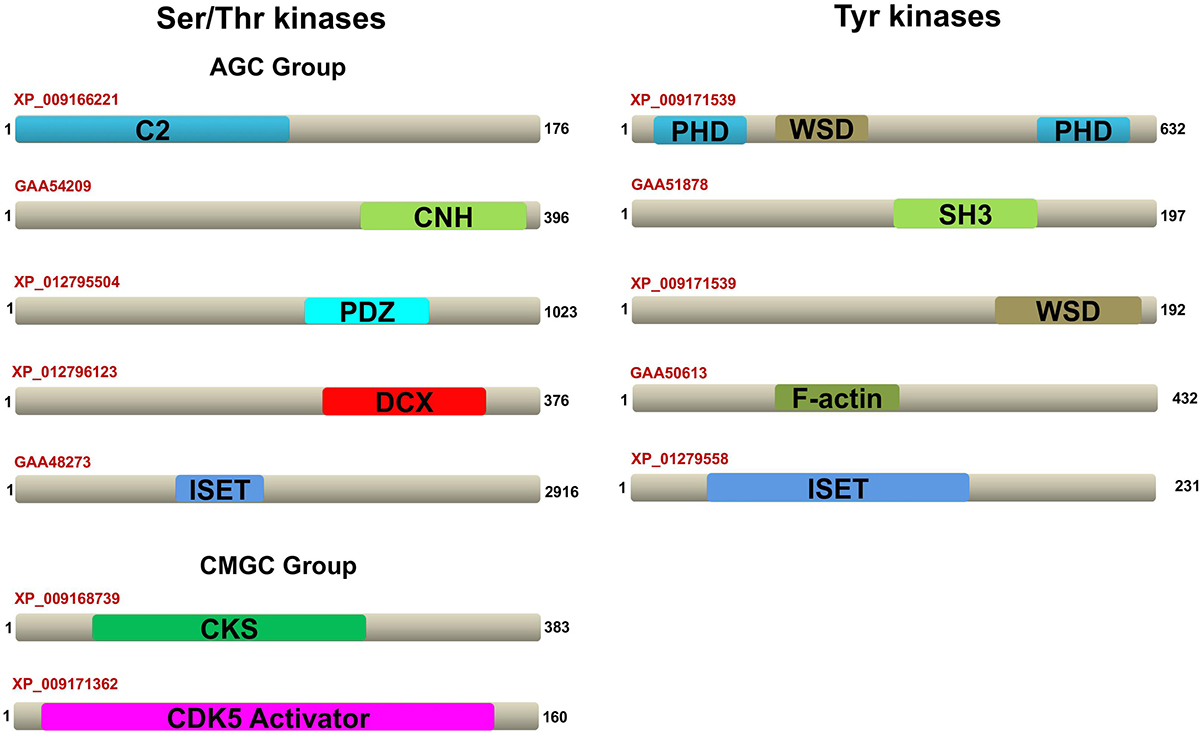
F. gigantica contains representatives from three out of four PKC alpha subfamilies mentioned above. The six PKC alpha proteins found in F. gigantica were γ: XP_009162854, XP_009166221, XP_012802529, βI: XP_009164837, XP_9164836, XP_009174694, and βII: XP_009166221. XP_009166221 contains a unique domain C2 (Ca domain; 6-116 residues), which is involved in targeting proteins to cell membranes (Figure 4). A typical PKC-C2 domain has a β-sandwich composed of 8 β-strands that co-ordinate the Ca2+ ions that bind in a cavity shaped by two loops of the domain (29).
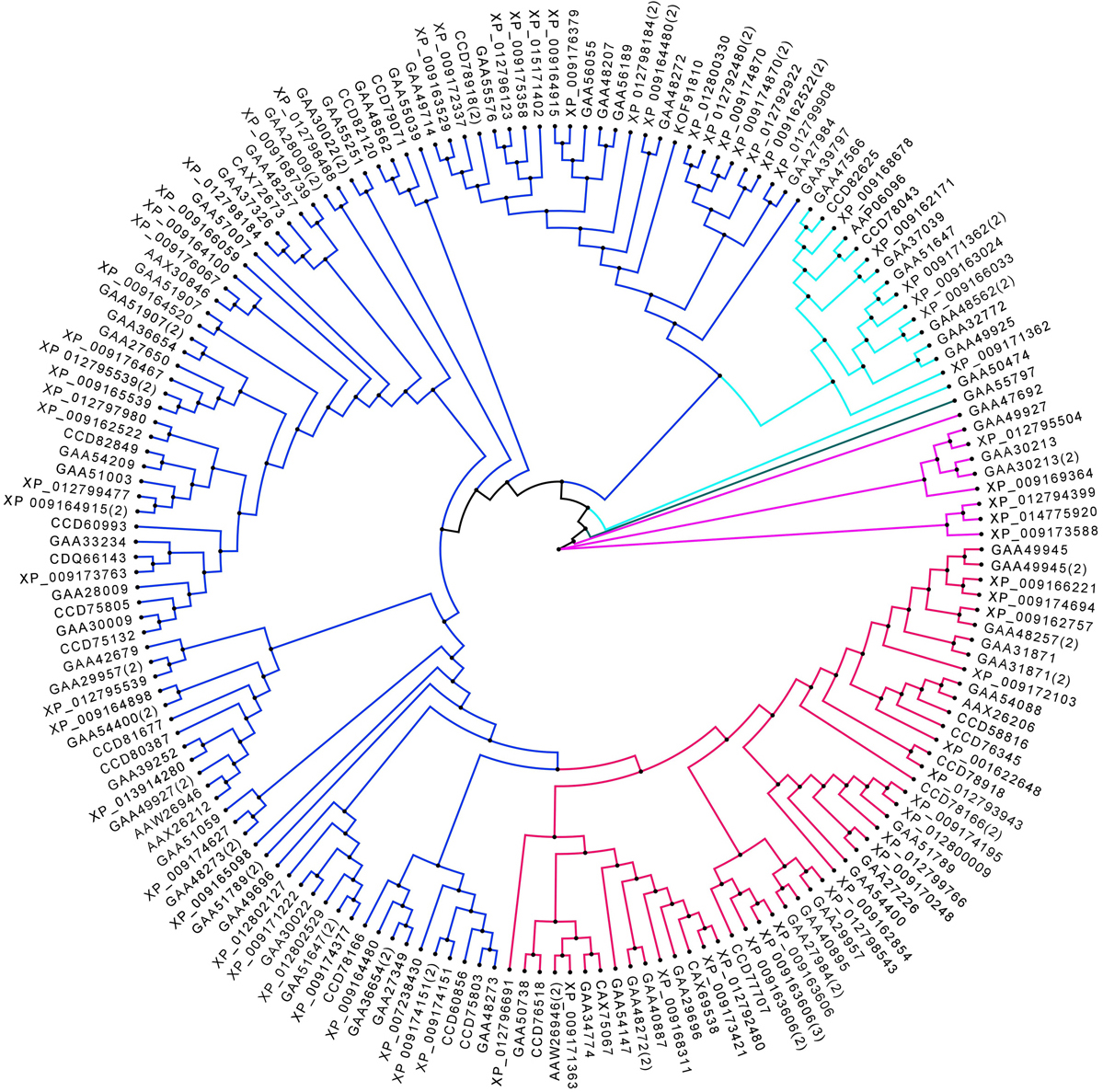 Figure 4
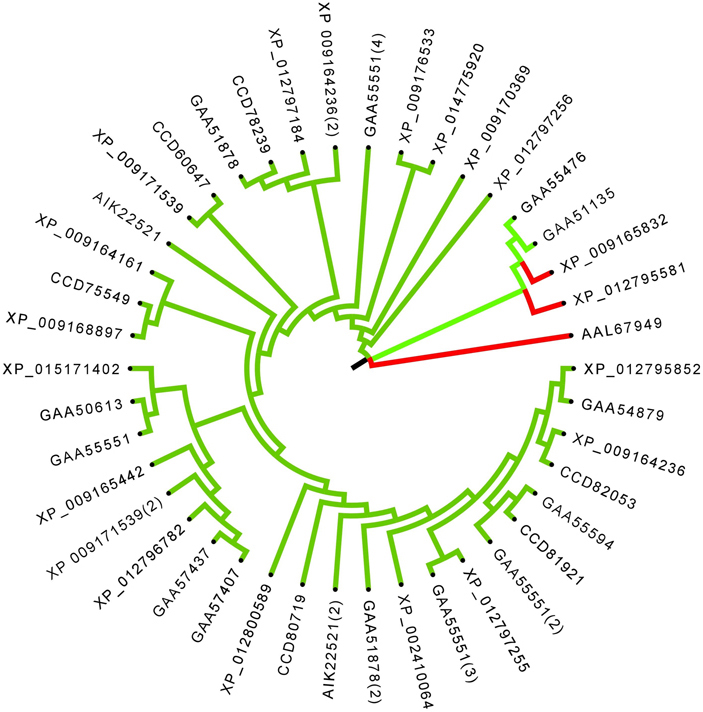
Figure 4Phylogenetic analysis of the F. gigantica Ser/Thr kinases. The F. gigantica AGC group is shown in blue, the CK1 group is shown in light blue clade and the single STE group member found is shown in green clade, the CaMK group is shown in pink clade and the CMGC group is shown in red clade. Color code: AGC (Blue), CK1 (Cyan), GSK3 (Green), CaMK (pink), and CMGC (Red).
In PKC eta group, protein GAA54209 contains a CNH domain (30), which is found in NIK1-Like kinase, mouse citron, and yeast ROM1, ROM2. In PKC iota group, protein XP_012796123 had a unique domain called doublecortin (31), which is a microtubule-associated protein expressed by neuronal precursor cells and immature neurons in the embryonic and adult brain cortex. Also, XP_012795504 showed a unique domain PDZ, which is found in several signalling proteins in all domains of life ranging from bacteria to animals (32). It plays a key role in anchoring membrane receptor proteins to cytoskeletal components and helps the formation of signal transduction complexes. In PKC delta group, the protein GAA48273 had a unique domain called I-set domain. This domain is present in several cell adhesion molecules and in Tyr protein kinase receptors (33, 34).
The GRKs modulates G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), including the rhodopsin light-sensitive GPCR, and a variety of neurotransmitter receptors. We found 3 GRK proteins in FgePKs: XP_009162757, GAA48257, and GAA48257.
The PKA activity is dependent on the cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP), hence also known as the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. cAMP binds to the regulatory subunit of PKA, and then, activate the catalytic subunit. They have several functions, including regulation of glycogen, sugar, and lipid metabolism. The regulatory and catalytic activities are performed by separate gene products known as PKA-R and PKA-C. PKA exists as an inactive heterotetramer with two PKA-R and PKA-C subunits (35). In the FgePKs, two PKA proteins (GAA31871, GAA31871) were found.
Like AGC kinases, the members of CaM kinase also phosphorylate near basic amino acid residues at specific positions in their substrates. Ca2+ acts as a second messenger in many cellular signaling processes, which in turn, is controlled by CaM-binding kinases. Some members of the CaMK group, such as CaMK1, CaMK2, CaMK4, and MLCK are activated by binding of Ca2+/CaM at a domain located in the C-terminus of their catalytic domains (36). In the FgePKs, 9 proteins were classified as CaMK (CDQ66143, XP_009163606, CCD77707, GAA40887, XP_009163606, GAA48272, GAA40887, AAX26206, and XP_009163606).
As in S. mansoni, the CMGC kinases are relatively abundant in F. gigantica, signifying its requirement in the regulation of cell proliferation, replication, and segregation of organelles, which are indispensable metabolic processes for parasites with a complex life cycle. In the FgePKs, members belonging to the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK), such as mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), glycogen synthetase kinase 3 (GSK3), and dual-specificity Tyr regulated kinase (DYRK) were found.
In eukaryotes, CDKs interact with cyclin to regulate cell cycle progression (37-39). Twenty-three CDKs were present in FgePKs. The protein XP_009168739 contains a unique cyclin-dependent kinase regulatory subunit (CKS; 127-182 residues) domain (40). The CKS is a small hexameric protein (79-150 residues) that can bind six CDKs and is essential for the functioning of CDKs. In yeast (gene cks1) and in fission yeast (gene suc1), a single isoform is known, while mammals have two highly related isoforms (39).
The protein XP_009171362 contains a unique domain of cdk5 (cell division protein kinase 5) activator (23-155 residues) (41). It is involved in the phosphorylation of the neurofilament proteins, and the Alzheimer's tau protein, and thought to be catalyzed by a protein kinase with Cdc2-Like substrate specificity.
The MAPK are the closest relatives of CDKs and are involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, gene expression, differentiation, motility, stress response, mitosis, cell survival, and apoptosis (42). They are activated in response to the extracellular stimuli, including mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock, and pro-inflammatory cytokines. In F. gigantica, a total of 15 sequences were found that coded for PKs belonging to MAPK.
The GSK3 is a member of Ser/Thr kinase that mediates the addition of phosphate group to over 40 different proteins involved in a variety of different cellular pathways, including cellular proliferation, migration, glucose regulation, and apoptosis (43). In mammals, GSK3 is encoded by the genes GSK3 alpha (GSK3A) and GSK-3 beta (GSK3B). The role of GSK3 has recently been implicated in a number of diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, type II diabetes, inflammation, cancer, and bipolar disorder. One GSK3 kinase XP_009172337 was present in the FgePKs.
The DYRKs belong to Ser/Thr kinase groups and also phosphorylate the Tyr residues in the substrates. One DYRK kinase XP_014775920 was present in the FgePKs.
The STE group consists of homologs of three yeast sterile kinases: STE11, STE7, and STE20. They sequentially activate each other, and then, activate the MAPK family (44). The members of STE11 (MAP3K) phosphorylate STE7 kinases, STE20 members (MAP4K) act on STE11 kinases, and STE7 (MAP2K) members directly phosphorylate MAPKs. The STE20 is the largest of these three and is classified into p21-activated kinase (PAK) and germinal center kinase (GCK) families. One STE20 kinase, GAA30009 was present in the FgePKs.
The members of this group prefer Ser/Thr residues present in the C-terminus of a phosphoserine/phospho threonine, although it may often be substituted by a stretch of acidic residues (45). They are involved in Wnt signaling, circadian rhythms, nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of transcription factors, DNA repair, and DNA transcription. The CK1 group consists of three main ePK families: CK1, vaccinia related kinase VRK (VRK), and tau tubulin kinase TTBK (TTBK). The FgePKs contained 9 CK1, one VRK kinase, and 6 TTBK kinases.
The protein Tyr kinase group has catalytic domains that specifically phosphorylate the Tyr residues in their substrates (46). The TKs can be classified, based on the presence or absence of transmembrane domains, into receptor Tyr kinase and non-receptor Tyr kinase (47). The RTKs have a ligand-binding extracellular domain and an intracellular catalytic domain. The non-RTKs are mainly found in the cytosol, nucleus and in the inner side of the plasma membrane; they are devoid of the transmembrane domain. The FgePKs contained 43 sequences that had Tyr kinase domain (Table 3), of which, 4 were receptor Tyr kinases and 39 were non-receptor Tyr kinases (Figure 5).
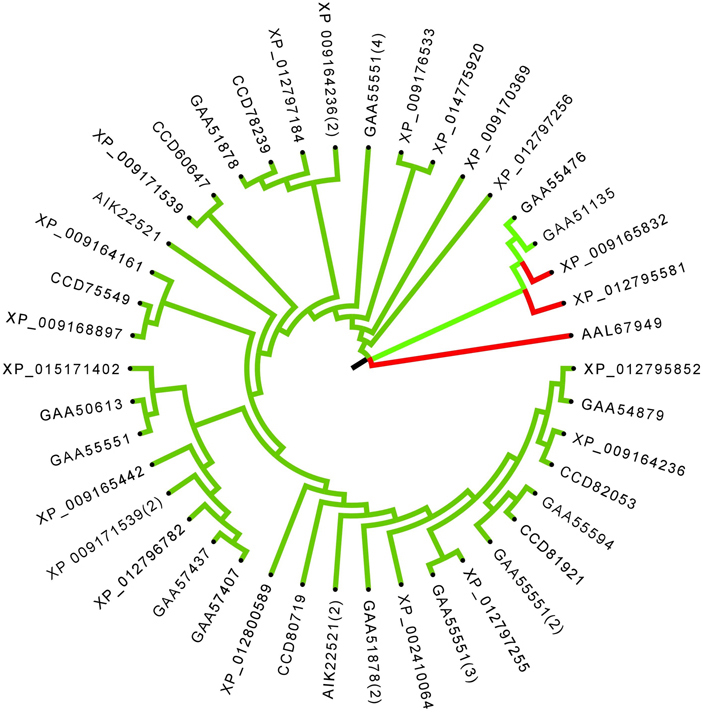 Figure 5
Figure 5Phylogenetic analysis of the F. gigantica Tyr kinases. Color code: RTK (Green), Non-RTK (Pink).
| Receptor Tyr Kinases | Non-Receptor Tyr Kinases |
|---|---|
| scaffold85530.g8549.t1 | scaffold60394.g6321.t1 |
| scaffold91353.g9056.t1 | scaffold74251.g7535.t1 |
| scaffold99996.g9790.t1 | C20913048.g24631.t1 |
| scaffold106049.g10389.t1 | C20917982.g24716.t1 |
| scaffold116064.g11303.t1 | |
| scaffold119252.g11592.t1 | |
| scaffold137283.g13253.t1 | |
| scaffold139598.g13455.t1 | |
| scaffold140012.g13495.t1 | |
| scaffold147100.g14166.t1 | |
| scaffold152150.g14627.t1 | |
| scaffold164104.g15655.t1 | |
| scaffold168988.g16116.t1 | |
| scaffold170161.g16225.t1 | |
| scaffold171076.g16317.t1 | |
| scaffold172885.g16486.t1 | |
| scaffold40495.g4467.t1 | |
| scaffold61362.g6408.t1 | |
| scaffold63091.g6564.t1 | |
| scaffold68941.g7106.t1 | |
| scaffold69756.g7131.t1 | |
| scaffold210374.g21073.t1 | |
| scaffold210465.g21102.t1 | |
| scaffold210465.g21103.t1 | |
| C20654430.g22556.t1 | |
| C20784968.g23422.t1 | |
| C20817450.g23678.t1 | |
| C20909552.g24578.t1 | |
| C20911876.g24608.t1 | |
| C20921542.g24797.t1 | |
| scaffold12470.g1546.t1 | |
| scaffold21586.g2577.t1 | |
| scaffold24409.g2868.t1 | |
| scaffold24658.g2892.t1 | |
| scaffold34431.g3878.t1 | |
| scaffold193004.g18057.t1 | |
| scaffold195468.g18291.t1 | |
| scaffold203109.g19407.t1 | |
| scaffold205155.g19800.t1 |
The protein XP_009171539 (scaffold85530.g8549.t1 showed three unique domains: 2 PHD (plant homeodomain) (48, 49) and 1 Williams-Beuren syndrome DDT (WSD), D-TOX E motif) domain (49, 50). The PHD finger was discovered in 1993 as a Cys4-His-Cys3 motif in the plant homeodomain (hence, PHD) protein HAT3.1 in A. thaliana and maize ZmHox1a. The WSD domain family represents the combined α-helical module found in diverse eukaryotic chromatin proteins. The protein XP_009171539 (scaffold170161.g16225.t1) also showed the presence of the WSD domain. GAA51878 showed three unique domains called SRC Homology Domain (SH3) (51). The SH3 is a small domain consisting of about 60 amino acid residues. This domain is present in phospholipase and several cytoplasmic Tyr kinases, such as Abl and Src (51, 52). It is also present in many other protein families, such as PI3 kinase, Ras GTPase-activating protein, CDC24 and CDC25 (52-54).
GAA50613 and XP_01279558 showed the presence of unique domains. GAA50613 contains the F-actin binding domain that forms a compact bundle of four antiparallel α-helices, which are arranged in a left-handed topology. Binding of F-actin to the F-actin binding domain may result in cytoplasmic retention and subcellular distribution of the protein, as well as possible inhibition of protein function (55). XP_01279558 contains one I-set domain, which is described above in section 4.2.1.1.1 (34).
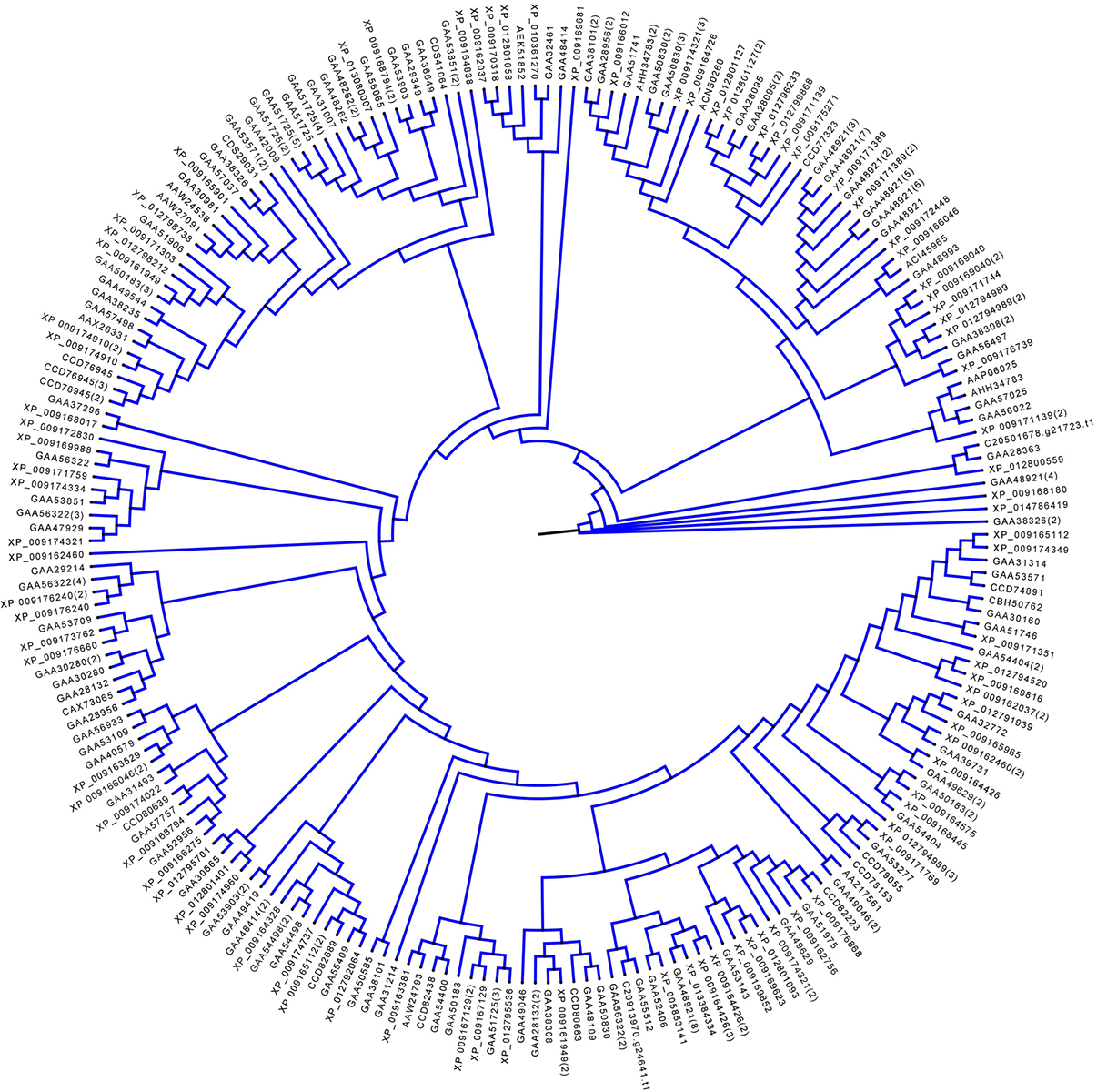
Hybrid group is divided into two types: TKL (Tyr Kinase-Like) and ‘others’. We found total 241 members in this group (Figure 6) (Table 4). The hybrid kinases containing various unique domains are discussed below.
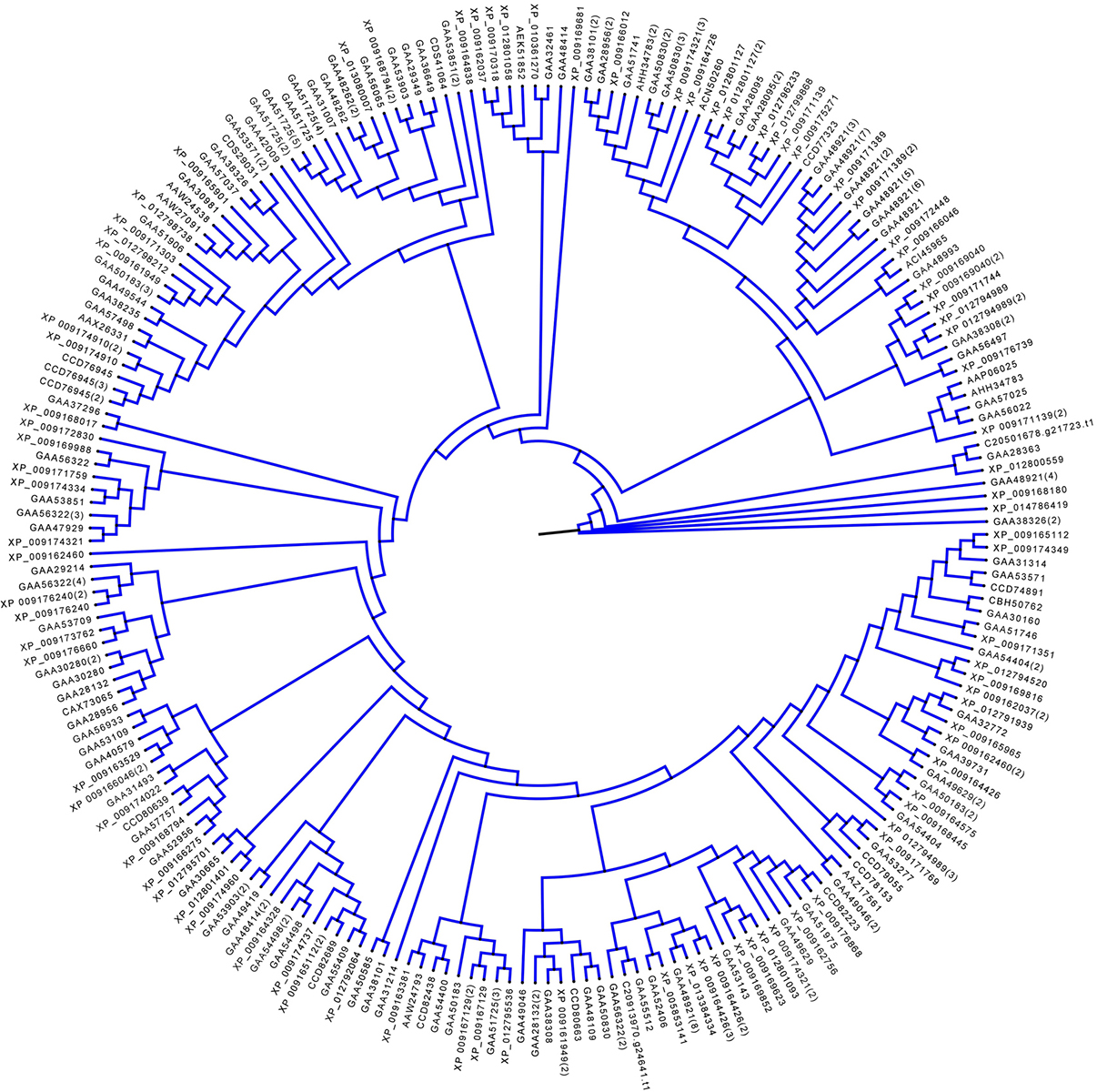 Figure 6
Figure 6Phylogenetic analysis of the F. gigantica hybrid kinases. The F. gigantica ePKs that were classified into ‘others’ group are shown here in blue clade.
| OTHERS | TKL |
|---|---|
| scaffold82644.g8269.t1 | scaffold66109.g6826.t1 |
| scaffold86191.g8598.t1 | |
| scaffold90366.g8973.t1 | |
| scaffold93666.g9228.t1 | |
| scaffold98637.g9653.t1 | |
| scaffold108222.g10612.t1 | |
| scaffold108312.g10628.t1 | |
| scaffold109147.g10697.t1 | |
| scaffold111099.g10853.t1 | |
| scaffold111430.g10882.t1 | |
| scaffold114344.g11150.t1 | |
| scaffold115493.g11250.t1 | |
| scaffold115827.g11286.t1 | |
| scaffold116040.g11301.t1 | |
| scaffold116667.g11363.t1 | |
| scaffold123427.g11953.t1 | |
| scaffold125857.g12179.t1 | |
| scaffold128529.g12436.t1 | |
| scaffold129431.g12518.t1 | |
| scaffold129895.g12556.t1 | |
| scaffold131957.g12737.t1 | |
| scaffold132848.g12815.t1 | |
| scaffold132968.g12880.t1 | |
| scaffold135635.g13086.t1 | |
| scaffold116667.g11363.t1 | |
| scaffold121069.g11738.t1 | |
| scaffold123427.g11953.t1 | |
| scaffold125857.g12179.t1 | |
| scaffold127241.g12337.t1 | |
| scaffold128529.g12436.t1 | |
| scaffold129431.g12518.t1 | |
| scaffold129895.g12556.t1 | |
| scaffold131957.g12737.t1 | |
| scaffold1367.g133.t1 | |
| scaffold6906.g788.t1 | |
| scaffold8389.g983.t1 | |
| scaffold188410.g17608.t1 | |
| scaffold189277.g17685.t1 | |
| scaffold189626.g17723.t1 | |
| scaffold189816.g17740.t1 | |
| scaffold190699.g17809.t1 | |
| scaffold191247.g17880.t1 | |
| scaffold191790.g17927.t1 | |
| scaffold207591.g20321.t1 | |
| scaffold207685.g20343.t1 | |
| scaffold207738.g20426.t1 | |
| scaffold132848.g12815.t1 | |
| scaffold132968.g12880.t1 | |
| scaffold135635.g13086.t1 | |
| scaffold136908.g13236.t1 | |
| scaffold136908.g13237.t1 | |
| scaffold138090.g13441.t1 | |
| scaffold141241.g13605.t1 | |
| scaffold147047.g14162.t1 | |
| scaffold147477.g14205.t1 | |
| scaffold147670.g14213.t1 | |
| scaffold148466.g14303.t1 | |
| scaffold148926.g14343.t1 | |
| scaffold150374.g14477.t1 | |
| scaffold150959.g14519.t1 | |
| scaffold151376.g14549.t1 | |
| scaffold153329.g14745.t1 | |
| scaffold153478.g14761.t1 | |
| scaffold153916.g14798.t1 | |
| scaffold157083.g15083.t1 | |
| scaffold157492.g15105.t1 | |
| scaffold160086.g15315.t1 | |
| scaffold160522.g15354.t1 | |
| scaffold161242.g15416.t1 | |
| scaffold164397.g15678.t1 | |
| scaffold165830.g15806.t1 | |
| scaffold166078.g15837.t1 | |
| scaffold168609.g16075.t1 | |
| scaffold172730.g16462.t1 | |
| scaffold173506.g16519.t1 | |
| scaffold8695.g1039.t1 | |
| scaffold9505.g1137.t1 | |
| scaffold10047.g1200.t1 | |
| scaffold10992.g1394.t1 | |
| scaffold12537.g1492.t1 | |
| scaffold13490.g1630.t1 | |
| scaffold13569.g1633.t1 | |
| scaffold192611.g18001.t1 | |
| scaffold193782.g18137.t1 | |
| scaffold196099.g18353.t1 | |
| scaffold197789.g18575.t1 | |
| scaffold201128.g19061.t1 | |
| scaffold202411.g19283.t1 | |
| scaffold203211.g19446.t1 | |
| scaffold203926.g19579.t1 | |
| scaffold205354.g19843.t1 | |
| scaffold208600.g20577.t1 | |
| scaffold39358.g4339.t1 | |
| scaffold40181.g4436.t1 | |
| scaffold40541.g4471.t1 | |
| scaffold46381.g5020.t1 | |
| scaffold46405.g5023.t1 | |
| scaffold46405.g5024.t1 | |
| scaffold48379.g5192.t1 | |
| scaffold48455.g5203.t1 | |
| scaffold51392.g5462.t1 | |
| scaffold51517.g5476.t1 | |
| scaffold51916.g5509.t1 | |
| scaffold53025.g5731.t1 | |
| scaffold54967.g5799.t1 | |
| scaffold55534.g5863.t1 | |
| scaffold57112.g6016.t1 | |
| scaffold58078.g6097.t1 | |
| scaffold59233.g6207.t1 | |
| scaffold59371.g6220.t1 | |
| scaffold59371.g6222.t1 | |
| scaffold61420.g6417.t1 | |
| scaffold64348.g6686.t1 | |
| scaffold64716.g6709.t1 | |
| scaffold65182.g6731.t1 | |
| scaffold66109.g6826.t1 | |
| scaffold70197.g7157.t1 | |
| scaffold70588.g7206.t1 | |
| scaffold71004.g7251.t1 | |
| scaffold16705.g1971.t1 | |
| scaffold18762.g2243.t1 | |
| scaffold20057.g2386.t1 | |
| scaffold20656.g2462.t1 | |
| scaffold23761.g2786.t1 | |
| scaffold25578.g2996.t1 | |
| scaffold32762.g3748.t1 | |
| scaffold175597.g16708.t1 | |
| scaffold175597.g16709.t1 | |
| scaffold177382.g16795.t1 | |
| scaffold178214.g16848.t1 | |
| scaffold180218.g16988.t1 | |
| scaffold184978.g17316.t1 | |
| scaffold205426.g19857.t1 | |
| scaffold207144.g20227.t1 | |
| scaffold207155.g20229.t1 | |
| scaffold207404.g20284.t1 | |
| scaffold207404.g20285.t1 | |
| scaffold208848.g20655.t1 | |
| scaffold71376.g7285.t1 | |
| scaffold74856.g7593.t1 | |
| scaffold76429.g7737.t1 | |
| scaffold76816.g7771.t1 | |
| scaffold77496.g7846.t1 | |
| scaffold79782.g8054.t1 | |
| scaffold209153.g20744.t1 | |
| scaffold209819.g20917.t1 | |
| scaffold210361.g21070.t1 | |
| scaffold210673.g21172.t1 | |
| scaffold210664.g21177.t1 | |
| C20721854.g22987.t1 | |
| C20396832.g21322.t1 | |
| C20501678.g21723.t1 | |
| C20527094.g21849.t1 | |
| C20539732.g21908.t1 | |
| C20559732.g22014.t1 | |
| C20565992.g22051.t1 | |
| C20567188.g22055.t1 | |
| C20575826.g22096.t1 | |
| C20586014.g22144.t1 | |
| C20599222.g22234.t1 | |
| C20623860.g22387.t1 | |
| C20630912.g22430.t1 | |
| C20639892.g22470.t1 | |
| C20673958.g22681.t1 | |
| C20728984.g23037.t1 | |
| C20770334.g23326.t1 | |
| C20799826.g23548.t1 | |
| C20801766.g23561.t1 | |
| C20818984.g23693.t1 | |
| C20841020.g23856.t1 | |
| C20841582.g23859.t1 | |
| C20862412.g24063.t1 | |
| C20863690.g24087.t1 | |
| C20871600.g24158.t1 | |
| C20882046.g24252.t1 | |
| C20896960.g24396.t1 | |
| C20897148.g24403.t1 | |
| C20903520.g24491.t1 | |
| C20909724.g24587.t1 | |
| C20913970.g24641.t1 | |
| C20924036.g24851.t1 | |
| C20924852.g24887.t1 | |
| C20928322.g25074.t1 |
The TKL group is composed of 8 families, including the LISK family that consists of two main subfamilies: LIMK (LIM domain kinases), and TESK (Testis Expressed Serine Kinases) (56). Both TESK and LIMK subfamilies phosphorylate cofilin and inhibit its actin-capping function. In the FgePKs, we found one member from the LIMK (GAA57757) subfamily.
The kinases that were not classified in the previous groups are discussed here. A total of 240 FgePKs were found that belongs to this group (Figure 6).
The function of adenylate kinase has been ascribed to de novo adenine nucleotide synthesis and cell energy economy through the regulation of nucleotide ratios in different intracellular compartments and AMP-sensitive metabolic enzymes (57). Fourteen adenylate kinases were found in the FgePKs.
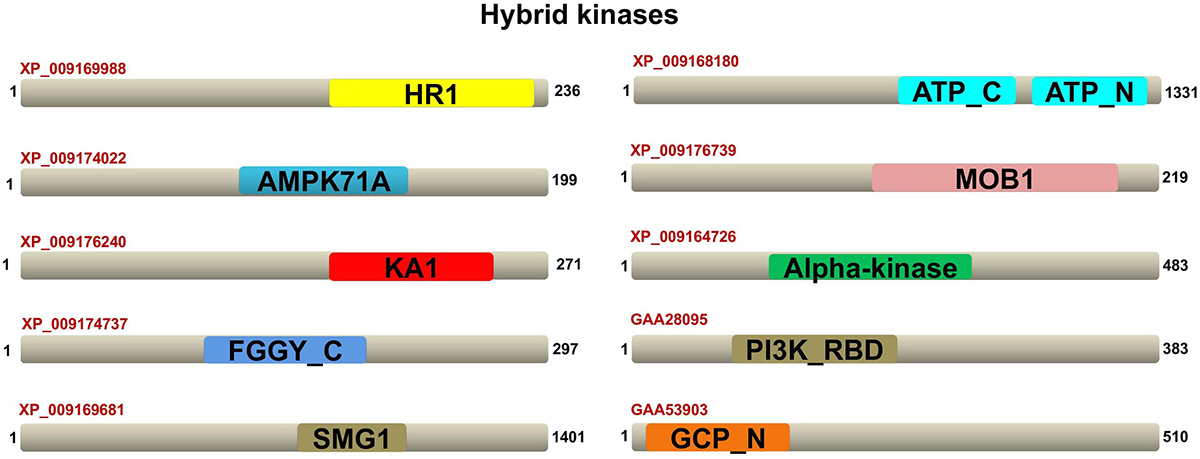
In addition to the two adenylate kinases, few more proteins from the ‘others’ kinase group possessed unique domains. XP_009169988 contains the HR1 domain. The HR1 repeat was first defined in the N-terminal non-catalytic part of protein kinase PRK1 (PKN) (58, 59). The sequences represented by XP_009176240 (scaffold207685.g20343.t1) show the presence of the unique KA1 domain whose function is not yet determined. XP_009174022 contains the glycogen recognition site of AMP-activated protein kinase. The AMPK1_CBM is a closely related protein family associated with AMPKBI PF04739. The surface of AMPK1_CBM carries a carbohydrate-binding pocket (60). XP_009174737 contains FGGY domain that adopts a ribonuclease H-like fold and is structurally related to the C-terminal domains of carbohydrate kinase enzymes (61). XP_009169681 contains the unique domain SMG1, which is a family of eukaryotic proteins that acts as an mRNA-surveillance protein in humans (62). In C. elegans, -SMG1 is a phosphatidylinositol kinase-related PK, known as a key regulator of growth. XP_009168180 contains a unique domain called ATP-Gua Trans C and N terminal. The ATP:guanido phosphotransferase family consists of structurally and functionally related enzymes (63, 64) that reversibly catalyse the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphogens. Protein XP_009176739 contains a unique domain Mob1/phocein family. Mob1 is an essential S. cerevisiae protein that binds Mps1p, a protein kinase required for spindle pole body duplication and mitotic checkpoint regulation (65). Protein XP_009164726 (scaffold16705.g1971.t1) contains the alpha kinase domain of ePKs catalytic domain. Protein XP_009164726 (scaffold16705.g1971.t1) contains the alpha kinase family domain that are different from conventional kinases but shows an unexpected similarity with ePKs in the catalytic core (66, 67).
GAA28095 contains a novel domain PI3 kinase family. Certain members of the PI3K family possess Ras-binding domains in their N-terminal. These regions show some similarity to Ras-binding PF00788 domains (68). GAA53903 contains the γ-tubulin complex component, an N-terminal domain found in the components of the γ-tubulin complex proteins. The family members include spindle pole body components, such as Spc97 and Spc98, which function as the microtubule-organizing centre in yeast (69).
The kinases from Ser/Thr and Tyr kinase group with unique domains are shown in Figure 7, while the kinases from other group with their unique domains are shown in Figure 8.
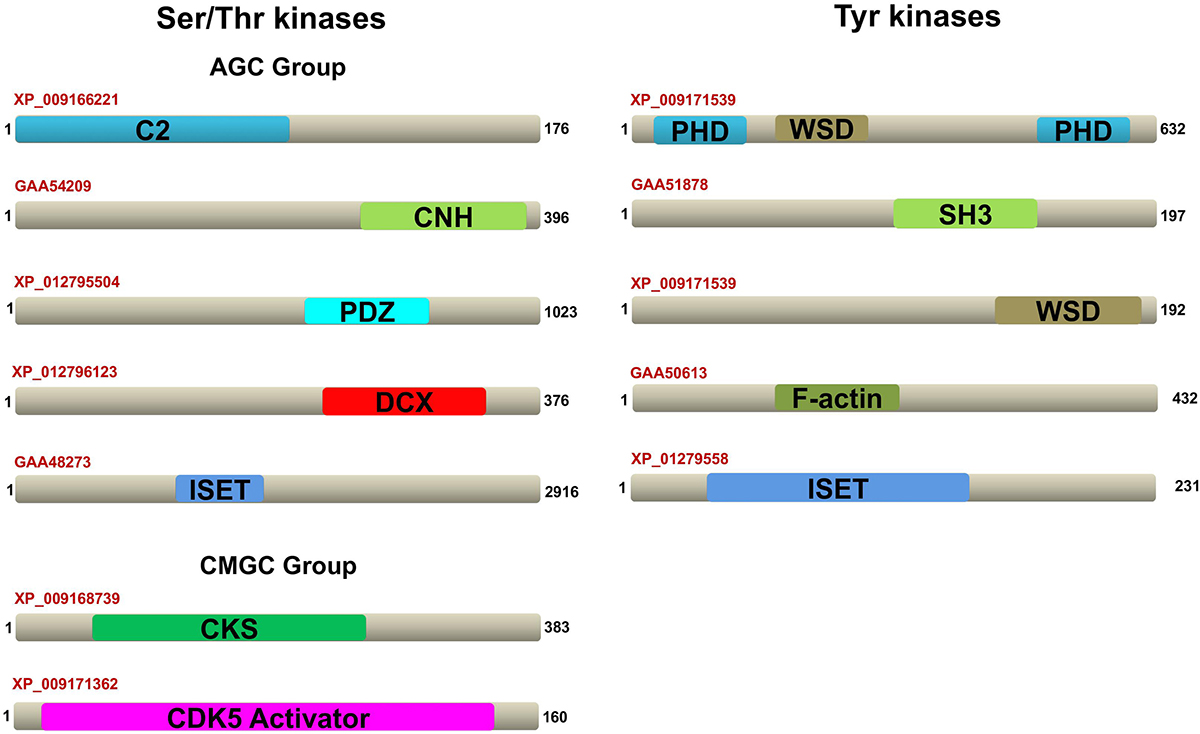 Figure 7
Figure 7F. gigantica Ser/Thr and Tyr ePKs domain architectures. Representative domain organizations of some F. gigantica ePKs possessing unique domains are shown. The accession ID of the proteins are shown and their unique domains are highlighted in different colours.
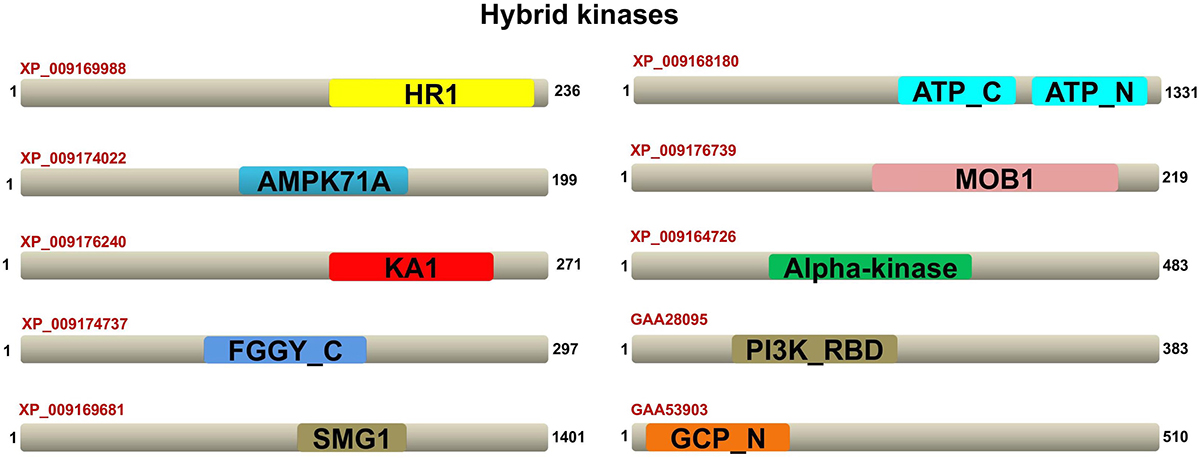 Figure 8
Figure 8.F. gigantica ‘others’ ePKs domain architectures. Representative domain organizations of some F. gigantica ePKs possessing unique domains are shown. The accession ID of the proteins are shown and their unique domains are highlighted in different colours.
More than 90% of all the cellular proteins undergo phosphorylation at some point or other, which is primarily dependent on the balance between protein kinases and phosphatases. Any perturbation in this equilibrium may result in important cellular processes in an organism. In the present study we identified and classified 455 ePKs encoded in F. gigantica genome, which represents ~2% of the genes encoded in its genome, indicating the importance of protein phosphorylation for regulating the signal transduction processes of the parasite. F. gigantica represented kinases from each major ePKs group. Certain FgePKs have unique domains, which suggests the diverse nature of the proteins that can be exploited for designing novel inhibitors. For this, the FgePKs anticipated to have essential function in parasite survival can be selected followed by heterologous recombinant expression, purification and characterization of the ePKs. Nowadays, libraries based on the inhibitory scaffold structure of PKs are also available. Inhibitor library screening will allow identification and optimization of the predicted hits. Co-crystallization of the hits with the target ePKs can provide detailed view of the several interactions between the hit and the target ePKs (70). Reverse genetics approach has been utilised to characterise various parasitic kinomes (70, 71). Moreover, from this analysis of the F. gigantica genome, 115 kinases were derived that showed <35% query coverage when compared to human ePKs (Table 5). This phylogenetic distance between ePKs of F. gigantica parasite and their human host highlights significant divergences in their respective kinomes, further providing a platform for novel structure-based drug designing. Also, this information can be used to identify many of the associated proteins that regulate ePKs activity. ePKs has been validated as potential targets for drug design and development as they play an essential role in several parasites. Furthermore, latest successful drugs bind ePKs near to the ATP binding site and block ATP access to the kinase to compromise enzyme activity (24). Thus, ePKs of F. gigantica with high sequence similarity to host proteins can also be used as targets since the inhibitor binds in non-conserved residues outside the ATP binding site. Also, the unusual domains found in FgePKs can be used for designing more specific F. gigantica inhibitors. Since ePKs currently represents one of the most attractive drug targets, we are performing studies on the biochemical and structural analysis of FgePKs that we will address in further studies.
| scaffold82009.g8227.t1 |
| scaffold156670.g15039.t1 |
| C20904610.g24507.t1 |
| scaffold153437.g14804.t1 |
| scaffold190674.g17807.t1 |
| scaffold99613.g9745.t1 |
| scaffold134286.g12969.t1 |
| scaffold80904.g8160.t1 |
| scaffold196799.g18440.t1 |
| scaffold85190.g8506.t1 |
| scaffold99759.g9753.t1 |
| scaffold146118.g14082.t1 |
| scaffold160456.g15347.t1 |
| scaffold55721.g5880.t1 |
| scaffold169120.g16126.t1 |
| C20393866.g21302.t1 |
| C20927120.g24969.t1 |
| C20927120.g24969.t1 |
| scaffold189129.g17674.t1 |
| scaffold191677.g17918.t1 |
| scaffold206659.g20117.t1 |
| scaffold92882.g9180.t1 |
| scaffold112912.g11016.t1 |
| scaffold113735.g11112.t1 |
| scaffold149215.g14363.t1 |
| scaffold155859.g14974.t1 |
| scaffold183347.g17226.t1 |
| scaffold188410.g17609.t1 |
| scaffold59967.g6277.t1 |
| C20832302.g23781.t1 |
| scaffold12227.g1468.t1 |
| scaffold3591.g353.t1 |
| scaffold81576.g8197.t1 |
| C20810620.g23624.t1 |
| scaffold197729.g18559.t1 |
| scaffold117817.g11463.t1 |
| scaffold39474.g4356.t1 |
| scaffold207801.g20361.t1 |
| scaffold208961.g20690.t1 |
| scaffold116064.g11303.t1 |
| scaffold123427.g11953.t1 |
| scaffold140012.g13495.t1 |
| scaffold147100.g14166.t1 |
| scaffold152150.g14627.t1 |
| scaffold163718.g15627.t1 |
| scaffold168988.g16116.t1 |
| scaffold172885.g16486.t1 |
| scaffold40495.g4467.t1 |
| scaffold70588.g7206.t1 |
| scaffold69756.g7131.t1 |
| scaffold74251.g7535.t1 |
| scaffold210374.g21073.t1 |
| C20817450.g23678.t1 |
| C20911876.g24608.t1 |
| C20913048.g24631.t1 |
| C20921542.g24797.t1 |
| scaffold3591.g353.t1 |
| scaffold104001.g10181.t1 |
| scaffold172996.g16483.t1 |
| C20834598.g23891.t1 |
| scaffold193784.g18140.t1 |
| scaffold16202.g1910.t1 |
| scaffold18667.g2229.t1 |
| scaffold30603.g3531.t1 |
| scaffold190720.g17811.t1 |
| scaffold86191.g8598.t1 |
| scaffold123427.g11953.t1 |
| scaffold148926.g14343.t1 |
| scaffold150959.g14519.t1 |
| scaffold48455.g5203.t1 |
| scaffold59233.g6207.t1 |
| scaffold71376.g7285.t1 |
| scaffold175597.g16709.t1 |
| scaffold16705.g1971.t1 |
| scaffold193782.g18137.t1 |
| scaffold207685.g20343.t1 |
| scaffold83122.g8300.t1 |
| scaffold87509.g8711.t1 |
| scaffold98852.g9822.t1 |
| scaffold101667.g9953.t1 |
| scaffold103547.g10134.t1 |
| scaffold104648.g10249.t1 |
| scaffold116204.g11318.t1 |
| scaffold133786.g12904.t1 |
| scaffold133786.g12905.t1 |
| scaffold121069.g11738.t1 |
| scaffold150970.g14520.t1 |
| scaffold166249.g15858.t1 |
| scaffold172018.g16393.t1 |
| scaffold172297.g16424.t1 |
| scaffold172754.g16467.t1 |
| scaffold51608.g5486.t1 |
| scaffold54190.g5722.t1 |
| C20577228.g22102.t1 |
| C20812888.g23646.t1 |
| C20833320.g23794.t1 |
| C20848972.g23928.t1 |
| C20925382.g24898.t1 |
| C20926756.g24939.t1 |
| C20928138.g25052.t1 |
| scaffold6844.g777.t1 |
| scaffold13936.g1677.t1 |
| scaffold24235.g2848.t1 |
| scaffold24235.g2849.t1 |
| scaffold24409.g2868.t1 |
| scaffold24662.g2896.t1 |
| scaffold176388.g16719.t1 |
| scaffold176825.g16756.t1 |
| scaffold182419.g17151.t1 |
| scaffold190674.g17807.t1 |
| scaffold191390.g17896.t1 |
| scaffold198520.g18670.t1 |
| scaffold203314.g19441.t1 |
| scaffold205261.g19824.t1 |
| scaffold207326.g20278.t1 |
The present study provides a useful resource for the selection of high-priority candidates for functional genomic and biological studies in F. gigantica. Methods, such as RNA interference, can now be used for the functional validation of ePKs-encoding genes in F. gigantica. In addition, immunological methods can be used for the identification of ePKs ligands and their localization in flukes. Using these tools, future insights into the roles of ePKs in these parasites could provide a path to understanding the molecular biology, biochemistry and parasite-host interactions of these flukes, and might help in the design of novel interventions. Evidently, this study provides information on ePKs for F. gigantica that will assist future investigations on both fundamental and applied levels. Improved annotation of ePKs from other flukes might also trigger broader comparative investigations.
Mr. Kanhu Charan Das and Dr. Parismita Kalita contributed equally to this paper. The authors declare that there are no competing interests. KCD and PK carried out the experiments. KCD, PK and TT analysed the data, conceived the study, participated in its design and drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
ePKs
eukaryotic protein kinases
protein kinases
atypical protein kinases
Ser/Thr kinases
Tyr kinases
cAMP-dependent protein kinase or protein kinase A/protein kinase G/protein kinase C
calcium/calmodulin regulated kinases
cell kinase I
cyclin-dependent kinases and other close relatives
receptor guanylate cyclases
sterile Ser/Thr kinases
Tyr kinase-like
expressed search tag
Hidden Markov Models
cyclin dependent kinase
mitogen activated protein kinase
dual-specificity Tyr regulated kinase