Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark (FBL) is published by IMR Press from Volume 26 Issue 5 (2021). Previous articles were published by another publisher on a subscription basis, and they are hosted by IMR Press on imrpress.com as a courtesy and upon agreement with Frontiers in Bioscience.
1 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Drug Screening, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, China
2 Laboratory Animal Center of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, China
3 Jiangsu Center for Pharmacodynamics Research and Evaluation, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, China
4 Key Laboratory of Drug Quality Control and Pharmacovigilance, China Pharmaceutical University, Ministry of Education, Nanjing 210009, China
5 Center for Drug Screening and Pharmacodynamics Evaluation, School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China
Abstract
The extract of the medicinal plant, Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. (TW), has been used in the treatment of diverse autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis. However, the high frequency of toxic side effects has limited its clinical use. In order to reduce toxicity without losing the therapeutic benefit, the pharmacological activity and toxicity of four compounds (T-96, triptolide, neotripterifordin, and tripterifordin) from TW were evaluated. The current study revealed that these compounds interfere with the IL-1β signaling pathway, which stimulates the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6) in primary rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts (RASFs). These compounds inhibit IL-6 production, and among these, T-96 was the most effective. Moreover, T-96 blocks activation of NF-kappa B and p38 and ameliorates the joint destruction and the clinical signs of the disease in adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. These data suggest that among the four compounds of the TW, T-96 possesses highest anti-rheumatoid arthritis activity though inhibiting IL-1-mediated inflammatory signaling pathways.
Keywords
- T-96
- NF-kappaB
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Fibroblast-like synoviocytes
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune joint disease that affects approximately 1% of the population (1). RA causes disability decreases the quality and expectancy of life, and also accelerates atherosclerosis (2). Since the pathophysiology/etiology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is unclear; however, many cell types, including T cells, B cells, and macrophages, play critical roles in RA pathogenesis, so a new, clinically efficacious RA treatment strategies is needed (3-5).
Complete freund's adjuvant (CFA), which emulsified with an antigen, is a widely used method to induce an autoimmune disease in animal models. The rat model of complete Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis has several characteristics with human RA including oxidative stress injury, inflammatory cells infiltrated in synovial membrane and joints swelling/destruction (6, 7).
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs), which represent a specialized cell type located inside joints in the synovial intimal lining, also play a crucial role by producing cytokines that induce inflammation and proteases that increase osteoclast activity (8, 9). FLSs are the main source of IL-1, IL-6, IL-11, IL-17, TNF-α, and RANKL under the pathological conditions of arthritic RA joints. These cytokines influence and tend the process of osteoclastogenesis in RA (9, 10). Thus, FLSs assume an important role in maintaining the internal joint homeostasis and the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Natural products have potential anti-inflammatory activity, as noted in previous studies (11, 12). Thunder duke vine/lei gong teng (Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. (TW)) is a medicinal plant and traditional herb that has been widely used for medicinal purposes in ancient Chinese long before recorded history, and it has been proven effective for anti-inflammatory and/or immunomodulatory activity (13). It appears to be efficacious in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and its extract effectively inhibits the production of cytokines and other mediators from mononuclear phagocytes by blocking the upregulation of a number of proinflammatory genes, including TNF-alpha, cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), interferon-gamma, IL-2, prostaglandin, and iNOS (13-15). However, its molecular pharmacological mechanisms remain largely undefined.
In the current study, we chose four types of the major constituents of TW (triptolide, T-96, neotripterifordin, and tripterifordin) and evaluated the effect of their cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory activity on FLS. We found that T-96 exhibits the most effective inhibition efficiency in the safe dosage. Then, we examined the phosphorylation of the key proteins in the IL-1β signaling pathway and the target protein expression of NF-κB (iNOS, COX2, MMP2) by Western blotting (16, 17). We subsequently used a model with adjuvant-induced arthritic rats to study the anti-inflammatory activity of T-96 in vivo. This research may explain the anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects of TW and could contribute to the immediate benefit noted in patients treated with these components.
Triptolide was purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). T-96 was got from Selleck Chemicals Company. Neotripterifordin and tripterifordin were kindly provided by BioBioPha Pharmaceutical Co. (Yun Nan, China). Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) and OPTI-MEM medium, solution of 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 mg/ml streptomycin, and fetal calf serum were purchased from Life Technologies Inc. (Gaithersburg, MD, USA). Recombinant rat IL-1β was purchased from Peprotech Inc. (MA, USA). The antibodies were obtained from Abcam (Cambridge, UK). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits for prostaglandin IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, and TNF-α were purchased from Millipore Co. (MI, USA).
According to a previously described procedure, the normal and arthritic rats were killed, and the synovial tissue was minced and digested with collagenase and trypsin to obtain the FLSs (18). FLSs were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin at 37°C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. When a homogeneous population of cells was obtained, passages 3 to 7 of the FLSs were used for experiments. The cells were plated in 6-well plates at a density of 4 × 104 cells/well and used for the following experiments.
The effect of T-96, triptolide, neotripterifordin, and tripterifordin on the viability of normal cells was determined using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay as previously described (19, 20). Briefly, normal FLSs were plated at a density of 5 × 103 cells/well in 96-well tissue culture plates and treated with various concentrations of triptolide, T-96, neotripterifordin, and tripterifordin for 24 h. MTT solution was added to each well, and then the plates were incubated for an additional 4 h. The supernatant was removed, and the formazan crystals were dissolved in 150 μl of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The absorbance was recorded at 570 nm by a BioTek microplate reader (Winooski, VT, USA).
The cytokine levels in the culture supernatant of FLSs and serum of arthritic rats were determined by ELISA kits for IL-1b, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, and TNF-α according to the manufacturer's instructions. The optical density (OD) of the samples was read using a BioTek microplate reader (Winooski, VT, USA) at a wavelength of 405 nm.
FLSs were stimulated with 10ng/ml of IL-1β for 24h. Culture supernatants were collected and NO production was monitored by the Griess reaction as previously described (21).
FLSs were lysed in RAPI buffer (Beyotime Co., China). Whole lysates were separated on 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) polyacrylamide gels and electroblotted onto 0.22-μm polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes. The membranes were blocked for 2 h in 5% (w/v) nonfat milk in Tris-buffered saline (TBS) containing 0.1% Tween-20 (TBS-T) buffer. The membrane was incubated with primary antibody (P65, p-P65, p38, p-P38, IκBα, p-IκBα, COX-2, iNOS, MMP2, and GAPDH) in a cold room (4°C) for 12 h. GAPDH acted as the loading control. Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit was used as the secondary antibody. Signals were detected using enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) Western blotting detection reagents (Thermo Co.) and the Alpha View Software system were used to quantify the expression of specific proteins.
SD rats, which were housed under controlled environmental conditions with free access to standard laboratory diet and water, were chosen for the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model establishment. First, Freund’s adjuvant incomplete was mixed with bovine collagen type 2 glacial acetic acid. Second, a 0.2-ml dose of this mixture was subcutaneously injected into one rat in the back and tail root. Third, rats were injected with the same concentration of this mixture once again on the 7th day (22). The control group was injected with the same amount of 0.9% saline. All of the animal experiments were approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine.
The rats were randomly divided into four groups: Normal group, Model group, T-96-Low-dose treatment group, and T-96-High-dose treatment group. Drugs T-96-Low-dose and T-96-High-dose were each intraperitoneally injected at concentrations of 1 mg/kg/d, 2 mg/kg/d. The weight, arthritis score, and foot swelling were measured once weekly during the dosing period. On the 35th day, the animals were killed, and blood was collected for serum separation. The hind limbs were dissected for histopathological and immunohistochemical assessment.
The synovial tissues were preserved in 10% formalin for 24 h, dehydrated with a sequence of ethanol solutions, and were processed for embedding in paraffin. Sections of 5–6 μm in thickness were cut, de-paraffinized, rehydrated, and then stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for the estimation of histopathology.
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded joint tissues were cut into consecutive 5-μm-thick sections. After the sections were dewaxed, antigen retrieval was performed by heating the sections for 30 min at 100°C in citrate solution. Then, the sections were cooled in PBS for 5 min, and blocked using 3% bovine serum albumin. At 4°C overnight, the sections were then incubated with primary antibody IL-10 and IL-17. After rinsing three times in PBS, the sections were incubated with secondary antibody. Then the sections were washed in PBS for 5 min and incubated in a solution of 3,3’-diaminobenzidine (DAB) for reaction. The DAB reaction was monitored with a microscope (2–10 min). Finally, the sections were examined with a light (Nikon) microscope. Scores were evaluated semi-quantitatively, using a four-point scale (0 scale means no staining, 1 scale means low amounts of staining, 2 scale means moderate amounts of staining, 3 scale means high amounts of staining) as previously described (23, 24).
The results were statistically analyzed by ANOVA, followed by Dunn’s post Test. The data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.). P < 0.05 was considered significant.
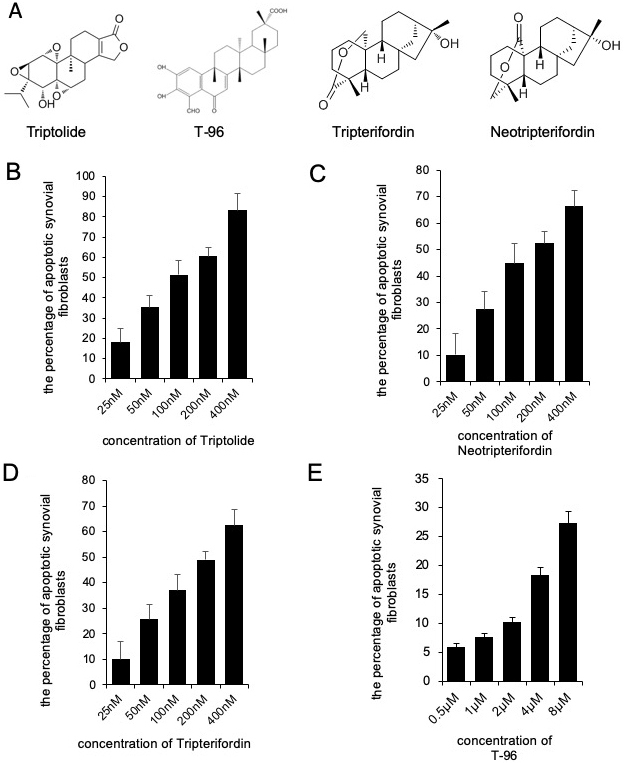
We determined the effects of triptolide, T-96, neotripterifordin, and tripterifordin on cytotoxicity. FLSs were treated with different concentrations of each compound for 24 h. The concentration of the MTT assay for the different treatment groups that showed no significant effect on the viability of FLSs were used for future experiments. (fig 1). T-96 is safer than triptolide, neotripterifordin, and tripterifordin in FLSs.
We assessed the efficacy of the selected triptolide, T-96, neotripterifordin, and tripterifordin in inhibiting IL-1β pro-inflammatory cytokine production. FLSs were pre-treated with triptolide, T-96, neotripterifordin, or tripterifordin overnight, followed by stimulation with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. The supernatant was removed and analyzed by ELISA for the production of IL-6 (Figure 2). Our results showed that T-96 was the most effective compound for inhibition of the production of IL-6 by 59%. Surprisingly, T-96 displayed an inhibitory effect on IL-1β-induced IL-6 production, suggesting that it plays one of the key roles in the anti-inflammatory effects of the constituents present of TW.
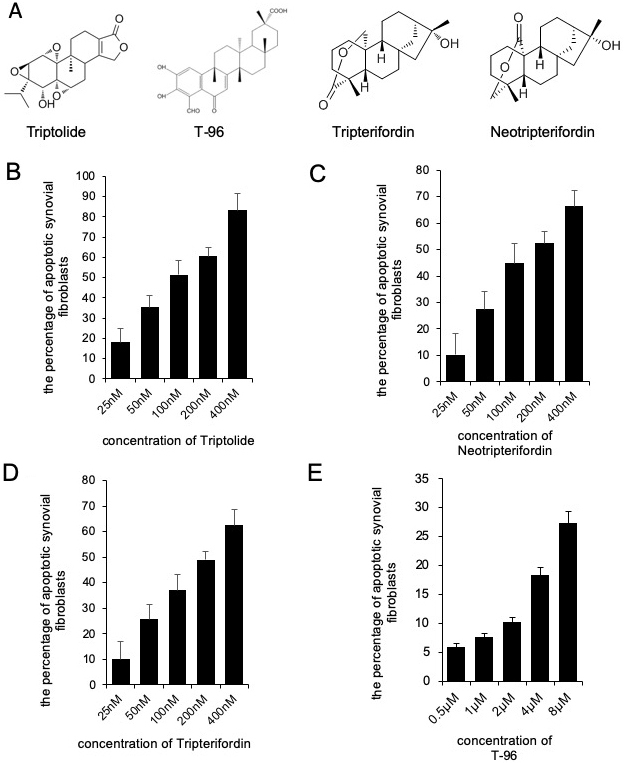 Figure 1
Figure 1Cytotoxicity of Triptolide, T-96, Neotripterifordin and Tripterifordin affect FLSs viability by MTT assay. A, structure of Triptolide, T-96, Neotripterifordin and Tripterifordin; B, cytotoxicity of Triptolide on growth inhibition at 24 hours in FLSs; C, cytotoxicity of T-96 on growth inhibition at 24 hours in FLSs; D, cytotoxicity of Neotripterifordin on growth inhibition at 24 hours in FLSs; E, cytotoxicity of Tripterifordin on growth inhibition at 24 hours in FLSs. Data is representative of three independent experiments.
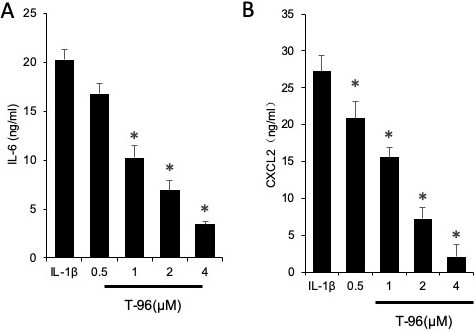 Figure 2
Figure 2The efficacy of T-96 in inhibiting IL-1β pro-inflammatory cytokine production in FLSs. FLSs were pre-treated T-96 overnight, followed to stimulate with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. IL-6 production was quantitated with ELISA assay. Data is representative of three independent experiments. Treatment groups are compared with IL-1β group. Values are statistically significant at * P < 0.05.
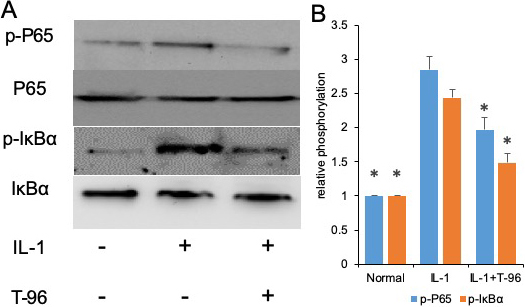
The activation of the NF-κB and P38 signaling pathways induced by IL-1β is of great importance to the regulation of cytokine expression (25, 26). We investigated the effects of IL-1β on the phosphorylation of IκBα and NF-κB p65. In the control group, a low level of basal phospho-IκBα and NF-κB p65 was detected in FLSs cells, and stimulation with IL-1β enhanced IκBα and NF-κB p65 phosphorylation. Compared with the IL-1β group, the phosphorylation of NF-κB p65, and IκBα in the FLSs were decreased by treating with T-96, but not significantly (Figure 3A, B). Additionally, the ratio of cytoplasmic to nuclear p65 localization was determined by cell immunofluorescence.
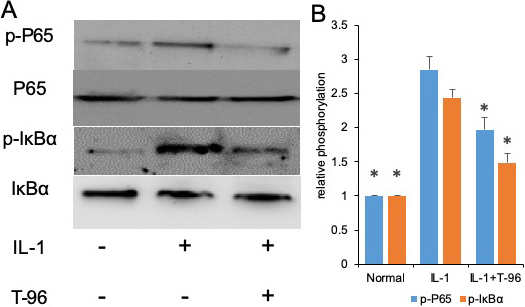 Figure 3
Figure 3T-96 (1μM) reversed IL-1-induced the phosphorylation of P65, IκBα and P38 in FLSs. FLSs were pre-treated T-96 overnight, followed to stimulate with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. A, T-96 inhibit phosphorylation of P65, p-IκBα and P38. IL-1β is compared with normal control and T-96 by western bolting. B, quantitative western bloting analysis of phosphorylation of P65, p-IκBα and P38 in FLSs. Control group and T-96 group are compared with IL-1β group. Values are statistically significant at * P < 0.05.
We have shown that T-96 is a potent inhibitor of the IL-1β-induced NF-κB and P38 signaling pathways in FLSs. Inflammation is directly driven by IL-1β, which results in the upregulation of the protein expression of iNOS, COX-2, and MMP-3 (27). Therefore, we extended our studies to evaluate the differences in the concentration of T-96 inhibiting IL-1β-induced protein expression of iNOS, COX-2, and MMP-3 (Figure 4). Our results showed that IL-1β significantly induced the protein expression of iNOS, COX-2, and MMP-3 in FLSs. Pretreatment with T-96 showed a significant reduction in the protein expression of iNOS, COX-2, and MMP-3. Additionally, the data showed that T-96 pretreatment significantly reduced the production of NO (Figure 5).
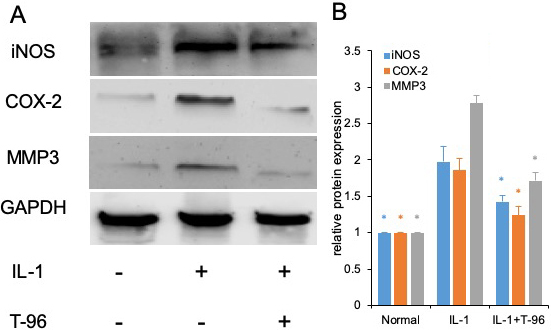 Figure 4
Figure 4T-96 (1μM) inhibit target protein expression of P65 and P38 in FLSs. FLSs were pre-treated T-96 overnight, followed to stimulate with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. A, T-96 inhibit the protein expression of iNOS, COX-2 and MMP3. IL-1β is compared with normal control and T-96; B, quantitative western blotting analysis of protein expression of iNOS, COX-2 and MMP3 in FLSs. Data is representative of three independent experiments. Control group and T-96 group are compared with IL-1β group. Values are statistically significant at * P < 0.05.
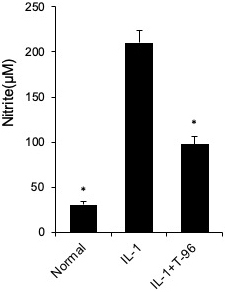 Figure 5
Figure 5T-96 (1μM) inhibit NO production in FLSs. FLSs were pre-treated T-96 overnight, followed to stimulate with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. NO generation was measured using the Griess reaction. Data is representative of three independent experiments. Control group and T-96 group are compared with IL-1β group. Values are statistically significant at * P < 0.05.
The arthritis rat model was prepared to evaluate the pharmacological activity of T-96. As shown in Figure 6A, B, C, compared with the normal rats, significant RA symptoms were observed when the rats were immunized with Freund's complete adjuvant, including paw swelling (p < 0.05), higher arthritis indices (p < 0.05), and weight loss (p < 0.05). These symptoms significantly improved after treatment with T-96 and methotrexate (Met, as positive compound). Compared with the model group, administration of T-96-H significantly reduced paw swelling and the arthritis score.
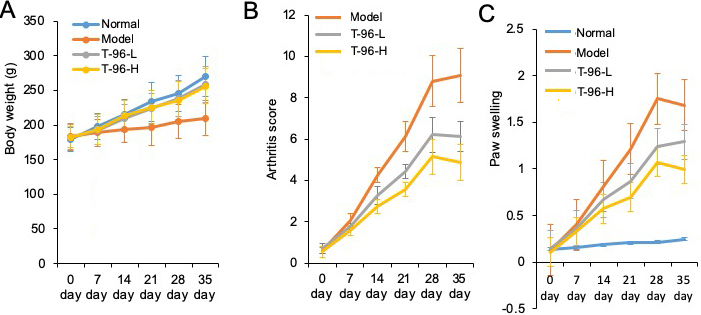 Figure 6
Figure 6Therapeutic effects of T-96 ameliorates RA in the collagen-induced arthritis rat model. Rats with clinical signs were randomized and orally administered vehicle, T-96 (1 or 2 mg/kg) once daily. A, T-96 influence the weight of arthritic rats; B, T-96 influence arthritis score of arthritic rats; C, T-96 influence Paw swelling of arthritic rats. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM (n=4/group).
Hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) staining was subsequently used to assess bone lesions in arthritic rats. As the results show in Figure 7A, no pathological changes of arthritis were observed in normal joints. On the contrary, the model group exhibited severe synovial hyperplasia in the joint tissues. By treating with T-96, synovial hyperplasia was noticeably decreased.
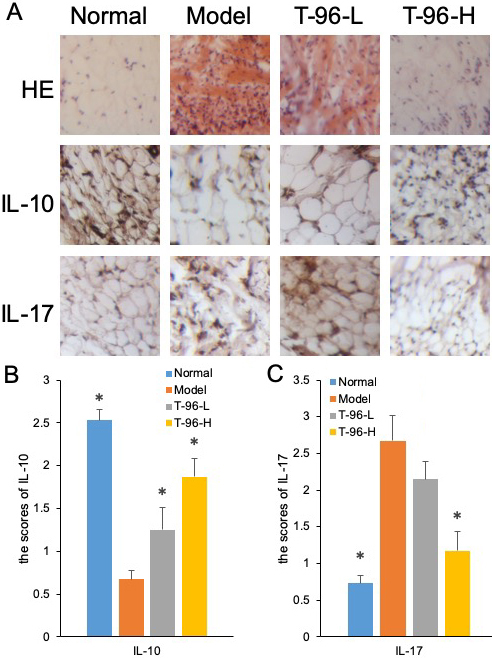 Figure 7
Figure 7T-96 ameliorates cytokines expression in the collagen-induced arthritis rat model by immunohistochemistry in the collagen-induced arthritis rat model. Rats with clinical signs were randomized and orally administered vehicle, T-96 (1 or 2 mg/kg) once daily. A, HE stain of synovial cavity; B, T-96 influence IL-10 expression by immunohistochemistry; C, T-96 influence IL-17 expression by immunohistochemistry. Control group and T-96 group are compared with Model group (n=4/group). Values are statistically significant at * P < 0.05.
We further examined IL-10 and IL-17 protein expression by immunohistochemical staining in the synovial tissues of control and experimental rats. The unregulated protein expression of IL-10 in the T-96-treated group of arthritic rats was further confirmed by immunohistochemistry, as shown in Figure 7B. Compared with the control group, the joint sections from the model group showed positive staining for IL-17, indicating higher expression of IL-17. In contrast, T-96 treatment suppressed the protein expression of IL-17 in the synovial tissue of arthritic rats in Figure 7C.
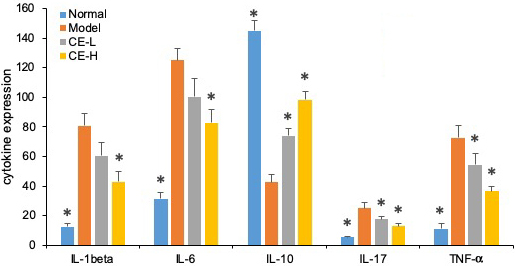
As summarized in Figure 8, the serum concentrations of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, and TNF-α from arthritic rats were significantly higher than normal ones (p<0.05). Both T-96 treatments significantly downregulated levels of these inflammatory cytokines in serum (p < 0.05). However, the serum concentrations of IL-10 were lower than normal (p <0.05). Both T-96 doses significantly reverse this, as shown in Figure 8.
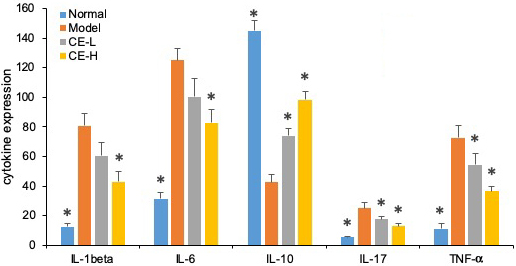 Figure 8
Figure 8T-96 ameliorates cytokines expression in the collagen-induced arthritis rat model ELISA. Rats with clinical signs were randomized and orally administered vehicle, T-96 (1 or 2 mg/kg) once daily. A, T-96 ameliorates IL-1β expression; B, T-96 ameliorates IL-6 expression; C, T-96 increase IL-10 expression; D, T-96 ameliorates IL-17 expression; E, T-96 ameliorates TNF-α expression. Control group and T-96 group are compared with Model group (n=4). Control group and T-96 group are compared with model group (n=4/group). Values are statistically significant at * P < 0.05.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common types of autoimmune diseases that cause chronic inflammation of the joints (28). Autoimmune diseases are illnesses characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking the body's tissues, and they can be accompanied by inflammation. The pathological characteristics of RA are inflammation, where the tissue swells around the joints and arthritis results, which can cause injury to multiple joints, leading to chronic pain, joint deformity, and functional disability (29).
TW has been widely used in clinical practice in China to treat RA (30-32). Pharmacological activity experiments have demonstrated that TW inhibits various experimental animal models of arthritis (33, 34). However, the molecular pharmacological mechanisms of TW remain largely unclear. Therefore, in this study, we chose four types of the major constituents of TW (triptolide, T-96, neotripterifordin, and tripterifordin) to detect the molecular pharmacological mechanisms of TW. The MTT assay was used for evaluating the cytotoxic effect of these compounds on normal FLSs. We found that T-96 had the lowest cytotoxicity.
IL-1β, one type of proinflammatory cytokine, mediates joint destruction and stimulates IL-6 secretion in synoviocytes, which are characteristics of RA (35, 36). Therefore, IL-1 is an excellent therapeutic target for the treatment of RA, and developing the antagonists of IL-1 is an excellent therapeutic strategy (37). IL-1β was used to stimulate the FLSs, which were then treated with these four compounds, and the concentration of IL-6 in the supernatant of FLSs were subsequently detected by ELISA. We found that T-96 exhibited the most effective inhibition efficiency at a safe dose. In FLSs, the NF-κB and p38 cell signaling pathway can be activated by IL-1β stimulation, which then increases the cytokine production of IL-6 (38-40). T-96 was used to intervene in IL-1β-mediated NF-κB and p38 activation in FLSs. T-96 significantly reduced the phosphorylation of p65, IκBα, and p38.
Next, we also found that T-96 attenuated the protein expression of iNOS, COX2, and MMP2, which could then be induced by IL-1β to decrease NO production. In order to verify the pharmacological activity of T-96 against rheumatoid arthritis, we used the adjuvant induced arthritis (AIA) animal model to evaluate the therapeutic effects of T-96 in vivo. Our results demonstrate that T-96 relieved RA symptoms and inhibited the inflammatory cytokine secretion that was induced by adjuvant in arthritic rats.
In summary, we found that the toxicity of triptolide, neotripterifordin, and tripterifordin was significantly higher than that of T-96. These compounds are diterpenoid epoxides, which indicates that diterpenoid epoxides are the main toxic ingredient in TW, and T-96 may be one of the major active components of TW that can be used for treating RA. Also, we found that T-96 inhibits the activity of NF-κB and p38 through decreasing the phosphorylation of p65, IκBα, and p38 in normal FLSs. T-96 decreases the protein expression of iNOS, COX2, and MMP2, which are downstream target genes of NF-κB and p38. Our experiments demonstrated that T-96 ameliorates the clinical signs and joint destruction in arthritic rats. T-96 may be one of the most important constituents of TW that can be utilized for its pharmacological activity against rheumatoid arthritis.
We would like to thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for providing linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript. And this research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.