Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark (FBL) is published by IMR Press from Volume 26 Issue 5 (2021). Previous articles were published by another publisher on a subscription basis, and they are hosted by IMR Press on imrpress.com as a courtesy and upon agreement with Frontiers in Bioscience.
1 Department of Physics, Institute of Chemical Technology, Mumbai 19, India
2 Department of Chemical Engineering, Institute of Chemical Technology, Mumbai 19, India
3 Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Northeastern University, 360 Huntington Ave, 8 Boston, MA 02115, USA
4 Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Technology, Institute of Chemical Technology, Mumbai 19, India
Abstract
Lack of suitable surface properties in biomaterials is an acute challenge for their utilization in nucleic acid delivery, since surface plays a vital role in cell adhesion/uptake and immunity. Low pressure cold plasma is a promising technology for functionalization and surface modification of materials, in an effective, environment friendly and economical way. In this investigation we have modified the surface of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with chitosan biopolymer, using plasma treatment, to extend their application scope in intracellular DNA delivery. The plasma functionalized; chitosan modified AgNPs (MetaloPolymeric Nanocarriers; MPNCs) possessed superior biocompatibility compared to unmodified AgNPs. Carboxylic groups were incorporated on the surface of nanosilver using 3600 rotating pulsed plasma reactor and acrylic acid vapors were used as precursor gas. Pulsed plasma polymerization process was optimized with respect to working pressure of the system, duty cycle for pulsing, time of treatment and flow rate. Biocompatibility of the plasma functionalized nanosilver was enhanced by coupling it with Chitosan Oligosaccharide (COS), using EDC (1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide) to form amide linkages. The resulting MPNCs showed high cell viability and bio-stability, which was attributed to plasma processing of nanosilver and its association with COS. In vitro cellular studies illustrated significant uptake of nanoplexes. The study suggested the potential of plasma functionalization for manipulating surfaces of metallic nanoparticles to enhance their application in intracellular gene delivery.
Keywords
- Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
- Low pressure cold plasma
- surface functionalization
- Chitosan Oligosaccharide
- COS
- non-viral gene delivery
Researchers working in gene delivery have been persistently working towards development of suitable biocompatible carrier/s to deliver nucleic acids, intracellularly using novel polymeric nanoparticles (1). Till the end of 2015, a total of 2210 clinical trials were approved for gene therapy related applications. Amongst these, 78.1% have reached either phase I or I/II clinical trials (2). The success of gene therapy lies in efficient transfection of nucleic acid into the targeted cells. However, this remains as a daunting challenge due to several obstacles, the major being lack of safe and efficient gene delivery vectors that can effectively cross extra- and intracellular barriers to reach cytoplasmic or nuclear region (especially, crossing the cell membrane by endocytosis, escape from nucleases and endosomes). Repulsion between like charges of cell membranes and negatively charged DNA molecules, adversely affects their cellular uptake (3). This necessitates a carrier with a net positive charge on its surface to facilitate entry of DNA/nucleic acids into the intracellular milieu.
Nanoparticles, have shown a great potential to be used as gene carriers due to their size, stimuli-responsive nature and precise control over surface modification.(4, 5) Amongst these, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in particular, have gained immense popularity in recent years owing to their unique optical and electronic properties (6, 7). Due to ease of synthesis, ability to control particle shape and size, and flexibility in surface modification, AgNPs have been increasingly used in diverse biomedical applications. Although numerous investigations suggested cytotoxicity of AgNPs (8), it is now apparent that this drawback is dependent on the concentration, size and surface modification of AgNPs (9). Chitosan Oligosaccharide (COS; 20 kDa) is a low molecular weight chitosan derivative that is biocompatible, biodegradable, and non-immunogenic. It is soluble at the physiological pH compared to its high molecular weight counterpart, which renders it more attractive for biomedical applications. Chitosan, when used as a biomaterial to coat metal nanoparticles, has shown significant reduction in their cytotoxicity (10, 11).
Surface property of nanomaterial plays a vital role during delivery of therapeutic moieties and hence in enhancing therapeutic activity of nanoparticulate delivery vehicles (12, 13). Plasma processing is one of the most favorable methods of achieving a reliable, flexible, reproducible, uniform, conformal, cost-effective and continuous method for tailoring surface properties of biomaterials (14-17). The reproducibility of plasma technology depends on accurate optimization of several parameters like applied power, working pressure of the system, geometry of plasma reactor, duty cycle for pulsing, time of treatment, flow rate, type of gases/monomers and substrate polymers used (18-20). The functionalization (limited to few tens of nanometers) does not change bulk characteristics of the material. The modified nanoparticles acquire unique surface chemistry and specificity upon incorporation of functional groups (21, 22) and has several applications (23, 24). To the best of our knowledge, there are no published reports on the use of pulsed plasma processing for gene delivery.
Herein, we report for first time the use of low-pressure cold plasma to modify surface of AgNPs to make them suitable for gene delivery. EDC-mediated chemistry was employed to covalently attach COS on the surface of AgNPs. The resulting MetaloPolymeric Nanocarriers (MPNCs) displayed an overall positive charge, exhibiting superior plasmid DNA (pDNA) binding abilities via electrostatic interactions. Also, the reversible nature of this interaction facilitated release of pDNA in the cell. The studies confirmed suitability of plasma-mediated modification to alter surface properties of metal nanoparticles to render them suitable for intracellular gene delivery.
AgNPs were synthesized using a previously established method, involving silver nitrate (AgNO3), sodium borohydride (NaBH4), n-Butanol and iso-octane. These chemicals were purchased from SD Fine-Chem. Ltd. (Mumbai, India). 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) was procured from Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. (Mumbai, India), chitosan oligosaccharide (COS; molecular weight/Mw of 20 kDa) was a kind gift by Amicogen (Jinju, South Korea). Carbon/ formavar coated copper grids (200 mesh) used for Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) were purchased from Electron Microscopy Sciences, PA, USA. Dharmacon pGIPZ plasmid DNA was obtained from GE Healthcare Life Sciences, India. HiPurATM Plasmid DNA Maxiprep Purification Kit, used for pDNA isolation, was procured from HiMedia Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. (Mumbai, India), DNaseI, CutSmart® digestion buffer and restriction enzymes, XbaI and XhoI were purchased from New England Biolabs (UK) Ltd. MTT (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide) and LIVE/DEAD® Viability/Cytotoxicity Kit was purchased from Molecular ProbesTM, Invitrogen (Mumbai, India). All chemicals were used without further purification. Deionized and double distilled water was used in all assays.
The AgNPs were synthesized using micellar nanoreactors as reported earlier (25, 26). Briefly, n-Butanol and Iso-octane were taken in v/v ratio of 3:7. To this, 2.5g of sucrose ester DKSS was added to this solvent system. 0.57g of sodium borohydride was added once sucrose ester completely dissolved to form a uniform solution. 2.55g of silver nitrate was added slowly and the reaction was allowed to proceed for 3 hrs. The reaction mixture was allowed to dry. Further, Ethanol wash was given to remove excess sodium borohydride and by-product sodium nitrate. After the wash, the nanoparticles were triturated to make a homogenous powder. The resulting silver nanoparticles were triturated to make a homogenous powder and henceforth referred to as AgNPs. In order to incorporate the carboxylic groups on surface of AgNPs, acrylic acid vapors were used as the precursor gas. Pulsed plasma polymerization was conducted using optimized parameters such as duty cycle, treatment time, working pressure, precursor gas flow rate and reactor rotation speed (27). Need of low pressure cold plasma for gene delivery lies in surface functionalization of metallic silver nano particles with acrylic functionalities for anchoring of chitosan oligosaccharide (COS) by covalent bonding. –CONH functionality is achieved through surface functionalization of silver nano particles and adding chitosan by using EDC wet chemistry. This approach makes low pressure cold plasma technology viable to make polymeric metallo-nano composite carrier for gene delivery.
There were two approaches to anchor chitosan with silver nano particles by functionalizing it via chemical or physical route. In our work we chose physical route by employing low pressure cold plasma technology, because of its advantages over conventional functionalizing methods. Low pressure cold plasma technology is efficient because of following reasons –
1. Free from use of wet chemicals hence reducing toxins and pollution,
2. Environment friendly,
3. Protection to thermo labile surfaces,
4. Modifies surface properties while bulk properties remain intact
5. Uniform, conformal and pinhole free coatings with excellent adhesion to the substrate.
6. Reliable, reproducible and relatively inexpensive technique.
The use of this plasma chamber ensured maximum efficiency of functionalization, uniformly throughout the surface of nanoparticles (28).
EDC was used as a coupling agent to form amide linkages between AgNPs/COOH and COS. Briefly, 0.1% w/v of cold plasma carboxylic acid functionalized AgNPs (AgNPs/COOH) were mixed with 0.1% w/v of EDC, to activate the carboxyl groups on AgNPs/COOH. The reaction mixture was stirred at 300 rpm for 30 min. Thereafter, 0.5% w/v COS was added to the reaction mixture, followed by incubation at room temperature (RT; 25°C and 60% RH) for 4 h. The MPNCs were freeze-dried (FreeZone Plus 6 Liter Cascade Console Freeze Dry Systems, Labconco Corporation, Kansas City, MO) and stored in a desiccator until further use.
AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH and MPNCs were analyzed using Varian Cary 50 Bio UV-Visible Spectrophotometer (Mumbai, India). Surface functionalization of AgNPs with carboxylic groups (AgNPs/COOH) and EDC-mediated amide linkages in MPNCs were confirmed using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (Bruker Tensor 27, Bruker Optics, Germany). AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH and MPNCs were dispersed in double distilled water, loaded on sodium chloride (NaCl) window and dried at RT for FTIR analysis.
The elemental surface chemical composition at every stage (from AgNPs to MPNCs) was determined by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) using Omicron ESCA+, (Omicron Nanotechnology, Oxford Instrument, Germany) equipped with monochromatic Aluminium Source (Al Kα radiation hν =1486.7 eV). The instrument was operated at 15 kV and 20 mA. The pass energy for short scan and survey spectral scan was 20 eV and 50 eV respectively. Samples were taken in pellet form and placed on Cu tape and degassed overnight in XPS Fast Entry Lock (FEL) chamber. This step minimized any possible air contamination at sample surface as well as the degassing process in main chamber. To overcome the charging problem, a charge neutralizer of 2 eV was applied and binding energy of C1s core (284.6 eV) was taken as reference. A next generation analyzer Argus (mean radius: 124 mm, Inner radius: 120.8 mm, Outer radius: 127.2 mm) was used for the analysis. Angle between analyzer and source was maintained at 90°. The resolutions were confirmed by considering FWMH at about 0.60 eV. The extracted data for peak fitting were analyzed using CASA XPS software.
X-Ray diffraction patterns in all types of nanoparticles were observed by coating several layers of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH and MPNCs on a glass slide. The samples were analyzed in transmission mode on a D8 Advanced Bruker Instrument with Cu Kα radiation using λ = 1.54 Å. The mean hydrodynamic diameter, polydispersity index (PDI) and zeta potential (ζ) of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH and MPNCs were studied using dynamic light scattering (Zetasizer Nano ZSP, Malvern, UK). All samples were prepared in deionized water and were analyzed in triplicates.
The morphology and distribution of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH and MPNCs was investigated using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). The nanoparticles (0.1% w/v) were loaded on carbon/ formavar coated copper grids (200 mesh size) and air-dried. Thereafter, the samples were examined on a Zeiss Libra 120 Transmission Electron Microscope (Carl Zeiss NTS, Oberkochen, Germany), operated with an acceleration voltage of 120 kV. The surface morphology of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH and MPNCs were visualized using a Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) (Philips XL-30 SEM, MA, USA). The nanoparticles were dried on a silicon wafer and analyzed with an accelerating voltage of 10kV. Samples for AFM were prepared on a glass coverslip, as a thin film, and recorded on JEOL JSPM-5200, Scanning Probe Microscope (JEOL Ltd., Japan).
The plasmid DNA (pGIPZ) was propagated by growing Escherichia coli BL21 strain on Luria Bertani (LB) broth at 37°C, overnight, under shaking conditions. The plasmid was extracted according to the manufacturer’s protocol. 1μg of pGIPZ was complexed with MPNCs at various w/w ratios of 1:1; 1:5, 1:10, 1:20 and 1:50, respectively. The mixtures were incubated at RT for 15 min to allow nanoplex formation via self-assembly. The particle size and zeta potential were evaluated by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) instrument. The stability of MPNCs was studied over a broad pH range (5.5, 6.5, 7.2, 8 and 9.2). Briefly, MPNCs were suspended in buffers of different pH, at a concentration of 0.1% w/v, and allowed to complex with the plasmid via self-assembly. MPNCs dispersed in deionized water were used as control. The retardation and stability of complexed plasmid was confirmed using 0.8% w/v agarose gel electrophoresis, in Tris-Acetate EDTA (TAE) buffer, at 80V and visualized using 0.2 μg/mL ethidium bromide.
The DNase I protection assay was performed to examine the capacity of MPNCs to protect pDNA from non-specific endonuclease degradation. The nanoplexes were incubated using DNase I (0.5U/μg pDNA) at 37°C, followed by heat denaturation of DNase I at 70°C for 10 min. Aliquots were taken every 5 min upto 20 min to monitor the extent of DNase I activity. Naked pDNA and nanoplexes without the enzyme were used as respective positive and negative controls (29). Restriction digestion assay was conducted to achieve sequence-specific digestion of pGIPZ. The digestion profile of nanoplex and naked pGIPZ were assessed with Xho1 and Xba1 enzymes (New England Biolabs Ltd, UK) (30). The reaction mixture was incubated with CutSmart® digestion buffer at 37°C for 3 h. The degree of protection against non-specific endonuclease (DNase I) and pGIPZ-specific digestion was confirmed using 0.8% w/v agarose gel electrophoresis, in Tris-Acetate EDTA (TAE) buffer, at 80V and visualized using ethidium bromide (0.2 μg/mL).
A549 and HeLa cell lines were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) without antibiotics, and incubated at 37°C with 5% CO2. The cell lines were maintained by medium replenishment and passaging at 70-80% confluence.
The biocompatibility of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH, EDC, COS 20 kDa and MPNCs was evaluated on A549 and HeLa cell lines using MTT assay. 3×104 cells/ well (A549) and 1.5×104 cells/ well (HeLa) were seeded in a 96-well plate (Eppendorf) and incubated overnight in 200 μL of DMEM, supplemented with 10% FBS, at 37°C and 5% CO2. The cells were incubated with 200 μL of DMEM containing 20 μL each of 0.14% w/v AgNPs, 0.14% w/v AgNPs/COOH, 0.14% w/v EDC, 0.71% w/v 20 kDa COS and MPNCs (0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1 % w/v). 20 μL of deionized water and 0.01% Triton X-100 were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. After 6 h of incubation, the cells were washed with Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), following which 200 μL of medium, containing 50 μL of MTT (0.5% w/v), was added. The medium was removed after 3 h and the formazan crystals were dissolved in 200 μl of DMSO. The intensity of formazan was assayed at 570 and 600 nm using a microplate reader (BioTek Synergy H1, Mumbai, India). The cell viability was calculated with respect to negative control (n=6).
Cell viability/ % = ((OD570sample - OD600sample) / OD570control - OD600control)) X 100
A549 and HeLa cells were seeded in a 24-well plate (Eppendorf Cell Culture Plate, India), each at a density of 1.5×104 cells/ well. The cells were incubated overnight in complete medium without antibiotics, at 37°C with 5% CO2. They were washed with PBS and finally replaced with medium containing 220 μL of DMEM and 30 μL of sample (0.5μg pGIPZ). X-tremeGENE™ HP DNA Transfection Reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) was used as positive control to understand the extent of pGIPZ expression. The positive control samples were prepared as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. PBS was used as negative control. The ratio of plasmid DNA: MPNCs was varied as 1:1, 1:2, 1:4, 1:6, 1:8, 1:10, 1:15 and 1:20 w/w. The ratio was optimized based on the cellular uptake of nanoplexes (MPNCs/pDNA). The medium was replenished after two days and cellular uptake was monitored by phase contrast microscopy every 24 h, upto 96 h.
Flow cytometry was performed to quantify the uptake of MPNCs in mammalian cell lines. A549 and HeLa cells were cultured as described in the earlier section. The media was replenished after two days and MPNC uptake was monitored using a flow cytometer (ImageStreamX® Mark II Imaging Flow Cytometer, Amnis®, EMD Millipore), every 24 h, up to 96 h. For flow cytometry experiments, the cells were incubated overnight in complete medium without antibiotics, at 37°C with 5% CO2, harvested and washed with PBS. Finally, the cells were resuspended in PBS before analysis and the data was analyzed using IDEAS® software (ImageStream Data Exploration and Analysis Software, EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA).
Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. A value of p < 0.05 was considered significant. All data are presented as mean ± S.D. with a probability set of *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001, using the GraphPad Prism (GraphPad software Inc., CA, USA).
After loading the AgNPs, vacuum was created in the reactor for 3-5 min using a rotary pump (Edwards Rotary pump, No. 8, UK) to eliminate gases adsorbed on the nanoparticles, if any. After the desired vacuum (0.05 mBar) was achieved, reactor was purged thrice with precursor acrylic acid vapors such that the atmospheric molecules were replaced by precursor moieties. The reactor rotation speed was set at 30 rpm, such that a free fall of nanoparticles was achieved. The flow-rate of acrylic acid vapors, working pressure, voltage, plasma processing time and pulse parameter were optimized at 200 cc/min, 0.15 mbar, Vmin = 120 V to Vmax = 800 V, 60 min and 5/20 ms (ON/OFF), respectively. The reactor exhibited plasma glow discharge for 5 ms and the precursor gas was subjected to molecular fragmentation during this period. Further, the plasma glow was stopped for 20 ms, thereby providing a relaxation time for the fragmented species to adhere onto the surface of nanoparticles. This allowed replenishment of unfragmented precursor molecules in the reactor, for being acted upon by the next pulse of 5 ms. These parameters ensured a favorable reactor environment for plasma treatment of AgNPs. Pulsed plasma polymerization technique was found to be useful to incorporate carboxylic groups on to the AgNPs surface as evident from FTIR and XPS studies discussed in the next section.
The cold plasma functionalized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs/COOH) were used further for synthesizing MPNCs. 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) has been reported in the literature as an effective cross-linking agent (31-33). Bax et al. have extensively studied the cytotoxicity of EDC for activating the carboxylic acid groups of collagen. The authors concluded that EDC was biocompatible and showed lower cellular toxicity. EDC, called as ‘zero-length’ cross-linker, forms a water-soluble, non-toxic urea derivative (32). In this study, the cross-linking reaction resulted in formation of amide bonds between carboxyl groups of AgNPs/COOH and amine groups of COS. The concentrations of EDC and COS were optimized to 1 mg/mL and 5 mg/mL respectively (Figure 1).
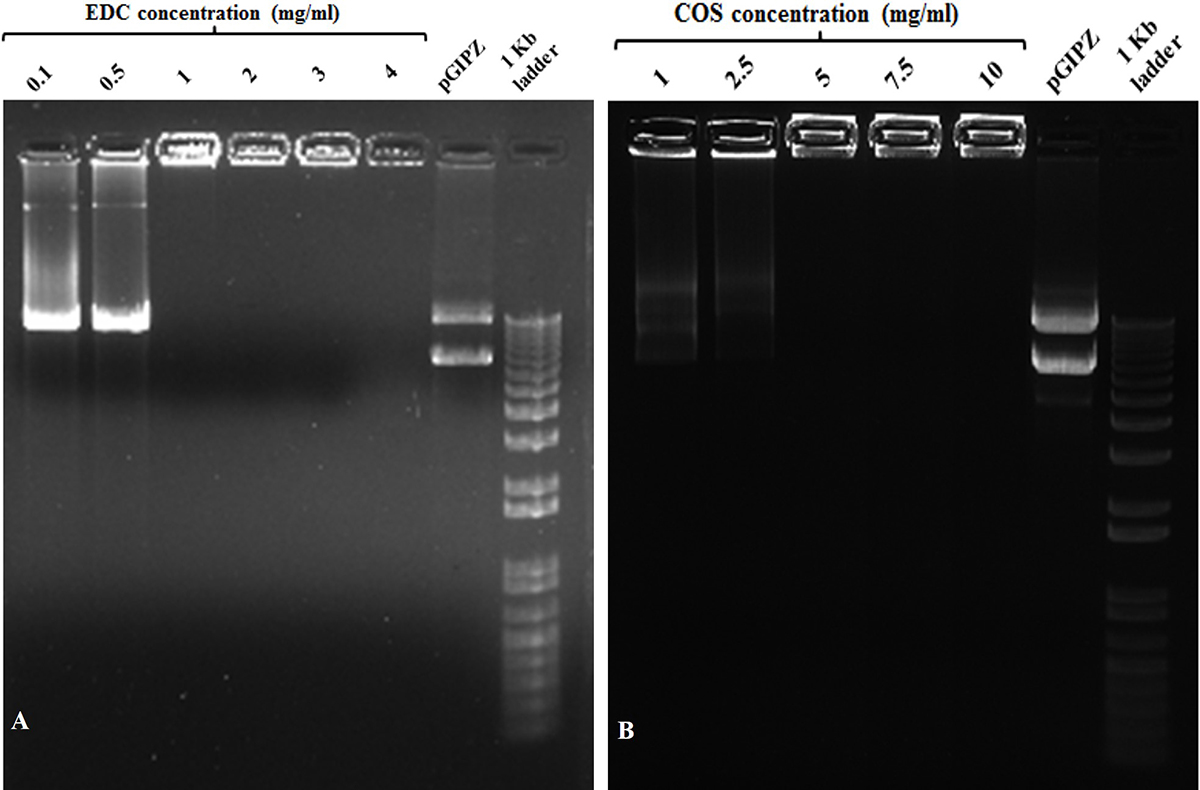 Figure 1
Figure 1Gel retardation assay with different w/v concentrations of (A) EDC and (B) COS used during coupling reaction at w/w ratio of MPNCs : pDNA :: 6 : 1. (A) Lanes (from left to right) 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, 3 and 4 (mg/mL) EDC, naked pGIPZ and1 kb plus DNA ladder. (B) Lanes (from left to right) 1, 2.5, 5, 7.5 and 10 (mg/mL) COS, naked pGIPZ and 1 kb plus DNA ladder.
Formation of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH and MPNCs was confirmed using UV-Visible Spectroscopy (Figure 2). The spectrum showed surface plasmon resonance typically at 424 nm for AgNPs, 422 nm for AgNPs/COOH and 397 nm for MPNCs (34, 35) Incorporation of functional groups was confirmed with FTIR spectroscopy (Figure 3). The peaks observed in case of AgNPs included a sharp peak at 1364 cm-1 indicating the N-O stretching of nitro group, at 1711 cm-1 suggesting C=O stretching of ester group, a broad peak around 3425 cm-1 due to O-H stretching of sugar ester and at 1086 cm-1 signifying the C-O stretching from alcohol. Two peaks between 2953 cm-1 to 2809 cm-1 corresponds to the alkyl group of sucrose ester (36). The FTIR spectrum of AgNPs/COOH showed broad peak corresponding to -OH stretching vibrations of carboxylic acid at 3466 cm-1 and characteristic peaks at 1246, 1370 and 1734 cm-1 suggesting C=O group stretching (37). In case of MPNCs, the peaks observed at 1637 cm-1 and 1521 cm-1 matched to the amide bands I and II, respectively (31). Conversely, an absence of C=O peak at 1734 cm-1 ensured reaction of plasma functionalized carboxyl groups on AgNPs with amine groups of COS. A peak shift was observed in one of the amide bands in MPNCs from 1544 cm-1 to 1521 cm-1, as compared to in COS, which was attributed to amide bonds between AgNPs/COOH and COS. This confirms coupling of COS to AgNPs/COOH through EDC reaction.
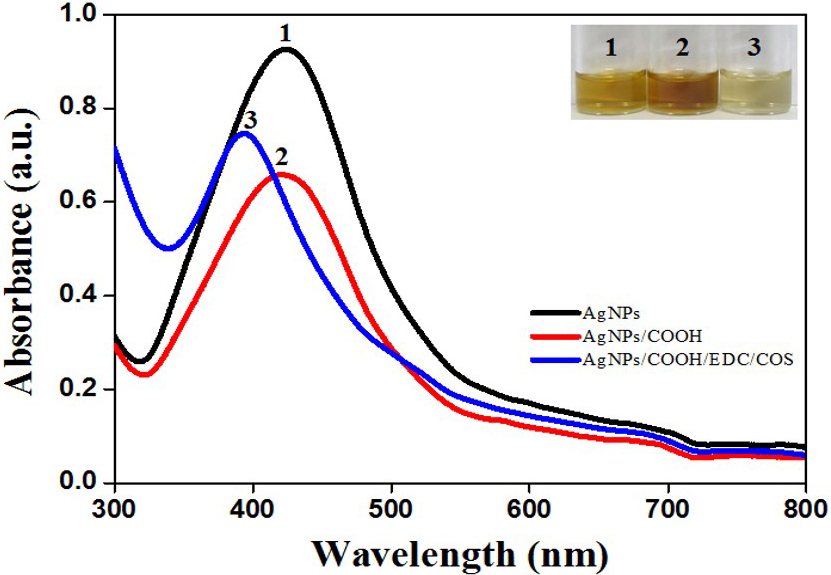 Figure 2
Figure 2UV-Visible spectrum of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH and MPNCs.
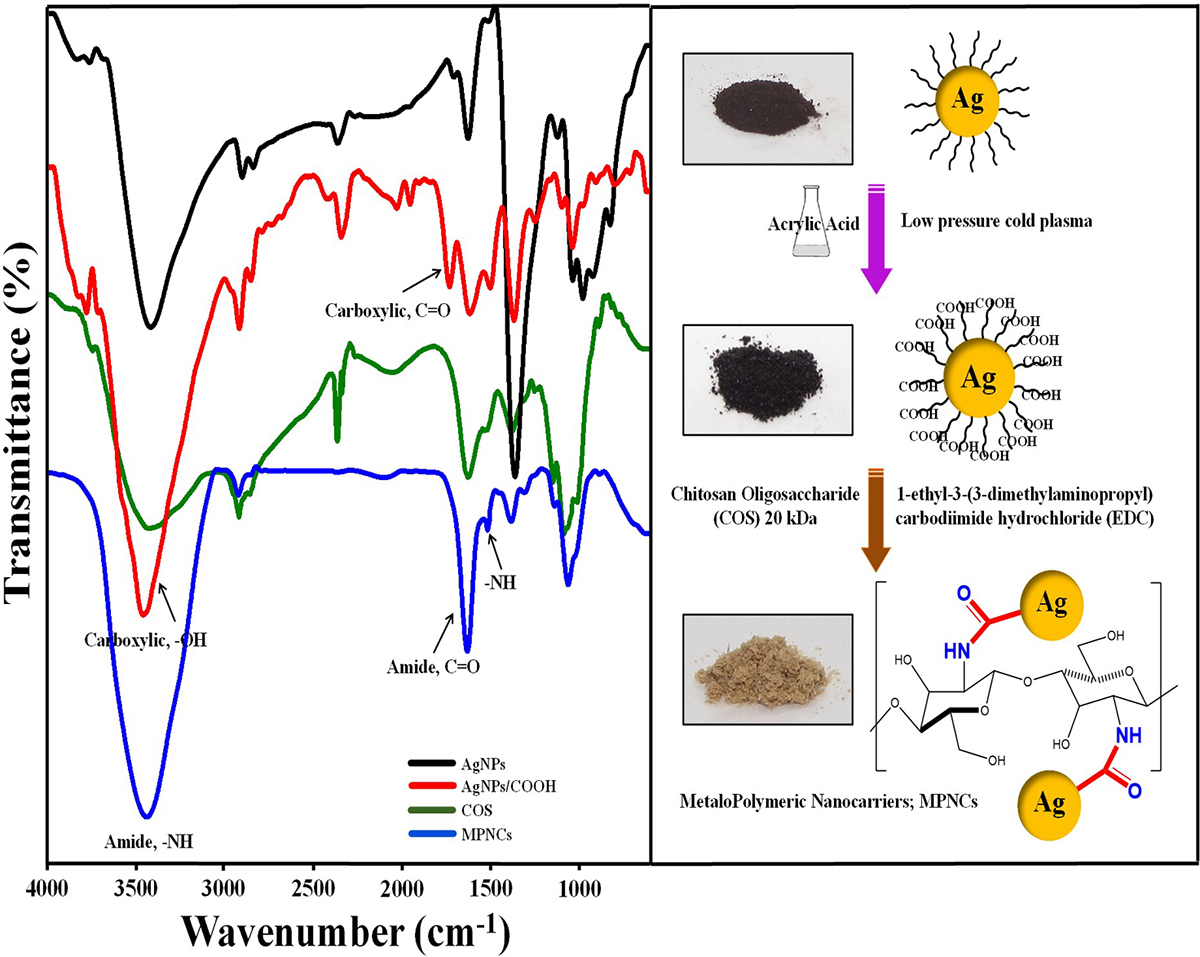 Figure 3
Figure 3Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) profile of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH, COS and MPNCs.
The survey scan in Figure 4A corresponds to the AgNPs stabilized with sucrose ester. The C1s, Ag3d and O1s peaks with their atomic concentration (%) were observed at 284.6 eV (71.53%), 368.6 eV (2.77%) and 532.6 eV (25.7%) respectively. The elemental and functional composition of AgNPs was determined by fitting high resolution spectra of C1s with four different functionalities (Figure 4D). The functionalities confirmed the presence of a stabilizing agent on the surface of AgNPs (38, 39). The survey scan in Figure 1B represents –COOH plasma functionalized AgNPs with their respective binding energies and atomic concentrations were observed as C1s peak at 284.6 eV (60.66%), Ag3d peak at 368.6 eV (6.24%), and O1s peak at 532.6 eV (33.1%). From survey scan it is clear that the relative concentration of oxygen increased after –COOH plasma functionalization on AgNPs (as evident from the O/C ratio in Figure 4B). The increase in relative concentration of AgNPs can be attributed to etching of stabilizing agent from the surface of AgNPs due to plasma treatment to create further reactive sites for –COOH functional moieties to adhere on AgNPs. Further, the C1s high resolution spectra and atomic concentrations of four different functionalities are illustrated in Figure 4E. Plasma functionalization of AgNPs showed marginal change in surface composition in terms of carboxylic and ester groups (40, 41). EDC-mediated coupling was confirmed by XPS analysis and the survey and C1s high resolution spectra are shown in Figure 4C and Figure 4F respectively. According to survey scan the binding energy and concentration of atomic species corresponding to MPNCs of C1s, N1s and O1s peak were recorded at 284.6 eV (73.26%), 400.50 eV (4.6%) and 532.6 eV (22.14%) respectively. The presence of C-N functionality confirmed the EDC coupling reaction (amide group formation) with respect to covalent interaction of amine group in COS. The presence of additional peak at 281.3 eV may be attributed to silicon contamination due to vacuum grease used in plasma reactor and/or XPS instrument.
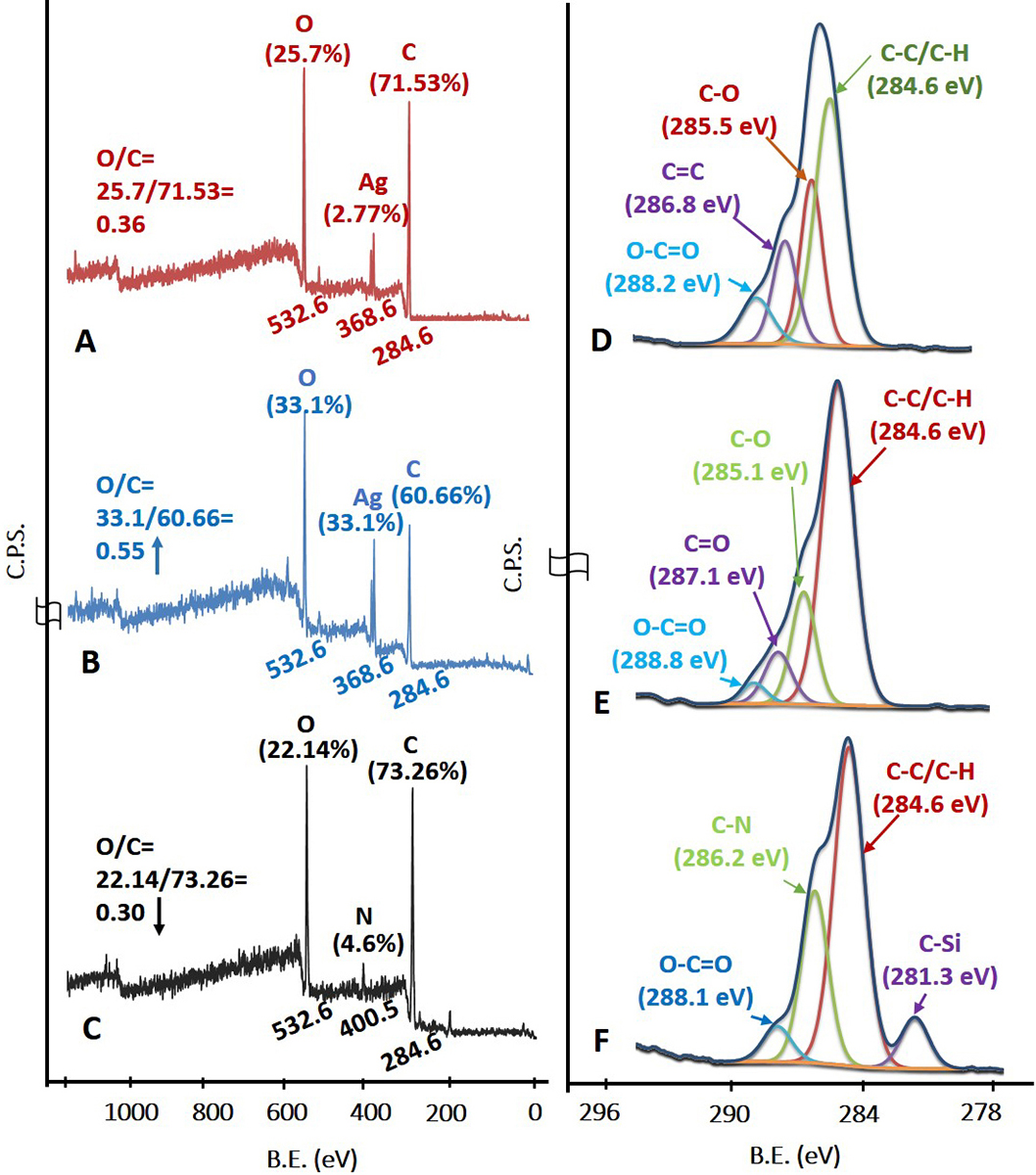 Figure 4
Figure 4X-Ray Photoelectron spectroscopy. (A), (B), (C) Survey scan and (D), (E), (F) C1s high resolution spectra of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH and MPNCs respectively
The XRD pattern of AgNPs and AgNPs/COOH showed four characteristic peaks at 2θ = 38.2°, 44.4°, 64.6° and 77.4° corresponding to (111), (200), (220) and (311) Miller indices (Figure 5). These 2θ values are in accordance with JCPDS database (JCPDS card no. 04-0783). It is interesting to note that there is an unassigned peak at 2θ = 29.3o in the XRD pattern, in addition to the typical peaks for AgNPs. This unassigned peak could be attributed to stabilizer sucrose ester, suggesting its possible crystallization on the surface of AgNPs. Similar results with additional (unassigned) peaks have been found in AgNPs synthesized using various processes (42, 43) In addition to these sharp XRD peaks, we also observed broad bump in the 2θ region from 14o to 22o, which can be attributed to amorphous regions of sucrose ester. The inter-planar spacing (d-value) was calculated as 0.2303 nm, corresponding to metallic silver nanoparticles, as reported in literature (44). In case of MPNCs, there were no peaks corresponding to AgNPs. However, broad peaks at 2θ = 19.18° and 27.83°, corresponds to the crystalline regions in chitosan and may be due to encapsulation of AgNPs by COS (45). The partial suppression of sucrose ester peak indicated functionalization of AgNPs by pulsed plasma polymerization.
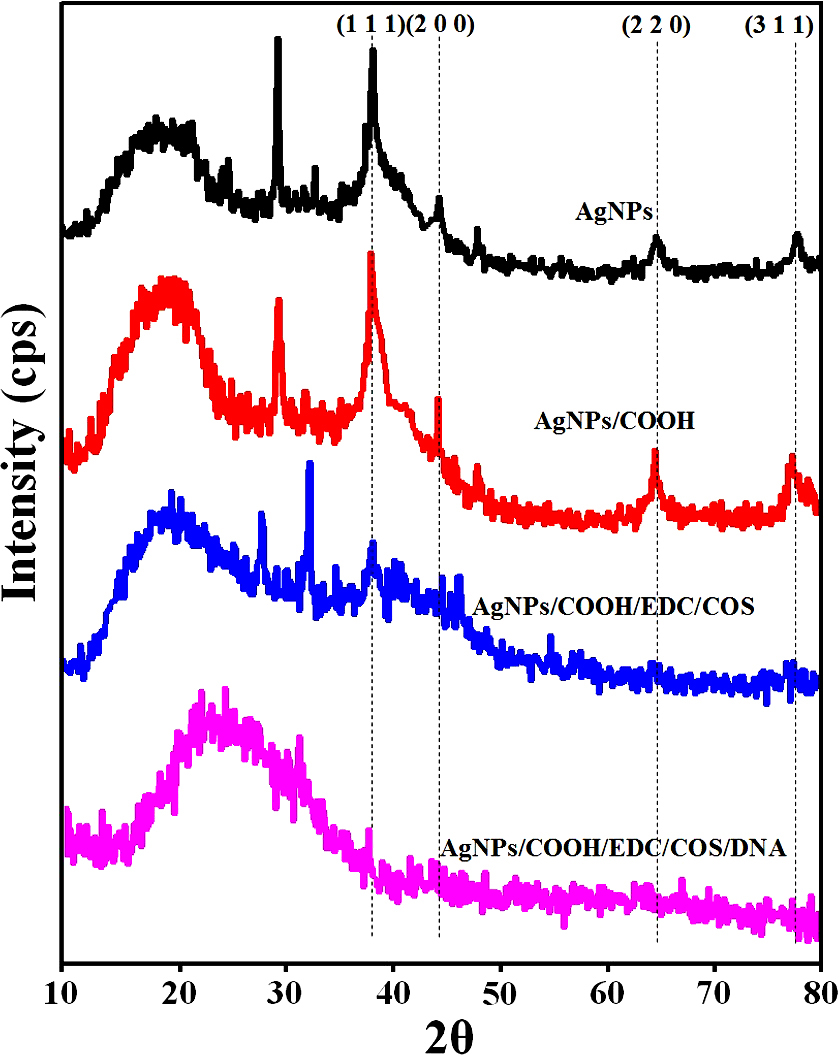 Figure 5
Figure 5X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) pattern of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH and MPNCs.
The Z-average for AgNPs and AgNPs/COOH was around 166.3±23.04 nm and 209.0±52.23 nm, respectively. Further, the size of MPNCs increased (46) to 249.6±12.04 nm after covalent attachment of COS to AgNPs/COOH (Figure 6A). Electrostatic bonding with pDNA resulted in gradual increment of nanoparticle size to 276.0±17.75 nm. This particle size was different from electron microscopy (TEM and SEM in Figure 7) due to the difference in sample preparation method and principle of measurement (47). The polydispersity index (PDI) of nanoparticles was found to decrease from 0.529 (AgNPs) to 0.436 (AgNPs/COOH) and further to 0.301 (MPNCs) (Figure 6A). There was no significant difference observed in the PDI of MPNCs/pDNA (0.302). There are several studies reported in the literature regarding the use of chitosan as a stabilizer (42-45). Thus, the decreased PDI for MPNCs and MPNCs-/pDNA was attributed to the increased stabilization of nanoparticles by COS.
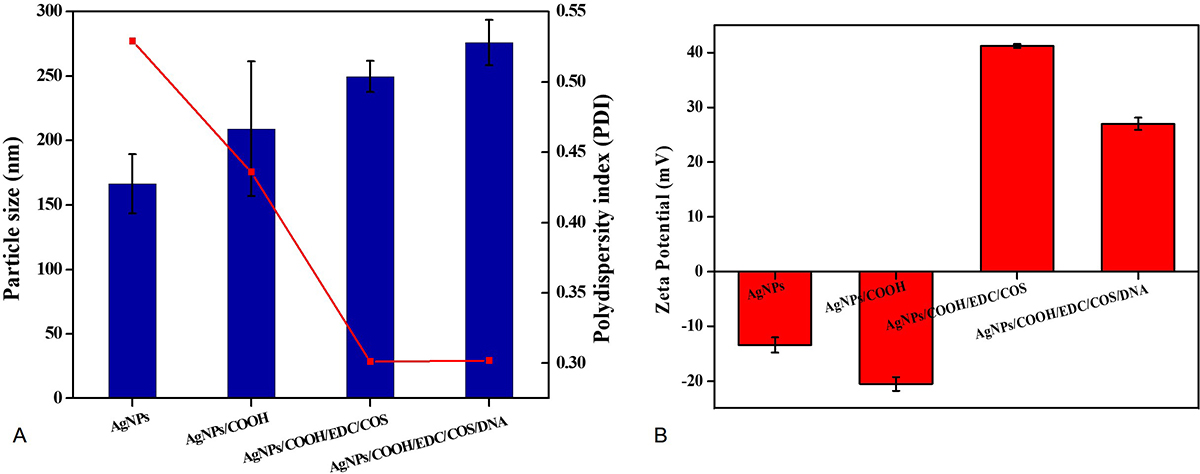 Figure 6
Figure 6Dynamic Light Scattering (A) Mean hydrodynamic diameter and poly-dispersity index (PDI) and (B) Zeta potential analysis of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH, MPNCs and MPNCs/pDNA. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3)
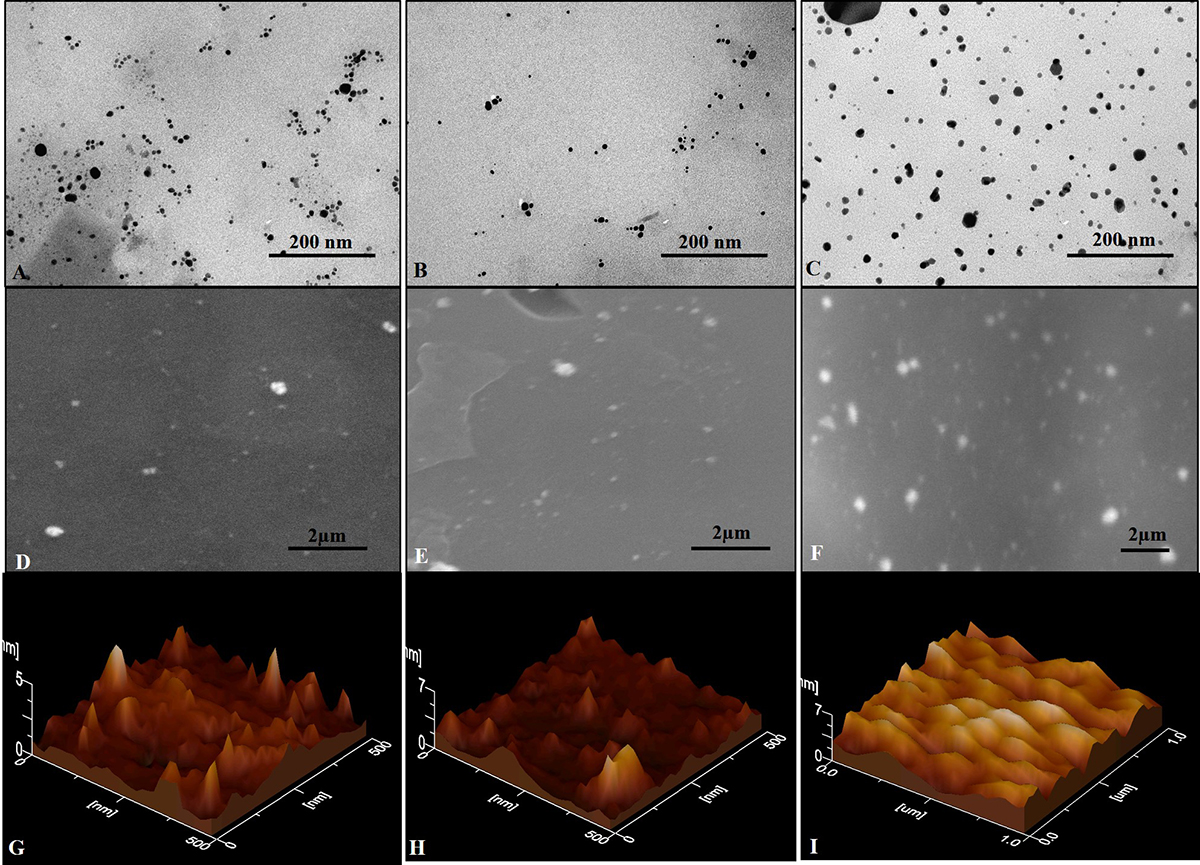 Figure 7
Figure 7Representative Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) of (A) AgNPs, (B) AgNPs/COOH and (C) MPNCs (scale bar is 200nm), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images of (D) AgNPs, (E) AgNPs/COOH and (F) MPNCs (scale bar is 1μm), Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) images of (G) AgNPs, (H) AgNPs/COOH and (I) MPNCs.
Measurement of zeta potential is crucial for fine-tuning the interactions between delivery vehicle and cell membrane.(48, 49). The zeta potential of AgNPs was recorded as -13.4±1.39 mV. Upon functionalization with carboxyl groups on the surface of AgNPs, the zeta potential shifted to -20.5±0.15 mV (Figure 6B). This shift could be attributed to the deposition of electronegative carboxyl groups by virtue of cold plasma. Further, the covalently bound COS was responsible for conferring a net positive charge (41.2±0.35 mV) on MPNCs. The MPNCs interacted electrostatically with negatively charged pDNA thereby reducing the zeta potential of MPNCs/pDNA to 27.0±1.1 mV (Figure 6B). Thus, the pDNA bound particles were sufficiently cationic to interact with the negatively charged cell membranes of mammalian cells.
TEM images showed that AgNPs (Figure 7A), AgNPs/COOH (Figure 7B) and MPNCs (Figure 7C) were spherical in shape, with size ranging from 15-25 nm, confirming the stability of nanostructures after plasma functionalization. The particle size of AgNPs (Figure 7D) and AgNPs/COOH (Figure 7E), obtained using SEM (15-45 nm) was in agreement with the size obtained through TEM analysis (Figure 7A and Figure 7B respectively). The particle size of MPNCs was found to be around ~100 nm (Figure 7F) (30). However few aggregates were also observed.
During AFM analysis, the particle size for AgNPs (Figure 7G) and AgNPs/COOH (Figure 7H) was found to be between 15-20 nm, which was in accordance with the size obtained by TEM, SEM and XRD analysis, respectively (50). Further, in case of MPNCs, the particle size was found to be ~100 nm (Figure 7I) as evident from SEM images.
The ability of MPNCs to form a stable complex with pDNA is crucial step as the nanoplex traverses the cell membrane into the cytoplasm or nucleus to deliver the nucleic acid payload. Gel retardation assay was carried out to analyse the degree of complexation between pDNA and MPNCs (Figure 8A). The w/w ratio of pDNA to MPNCs was varied to optimize a suitable ratio such that the plasmid remains unseparated from MPNCs. As evident from Figure 8A, the pDNA did not detach from MPNCs at ratio of 1:6 w/w or higher. This inhibition of pDNA on the agarose gel confirmed electrostatic interaction and nanoplex formation between pDNA and MPNCs. As no DNA separated during electrophoresis beyond 1:6 w/w ratio, the number of free amino groups on COS were sufficient to bind to the phosphate groups of pDNA. Hence, nanoplex formulated at this weight ratio was used for further experiments.
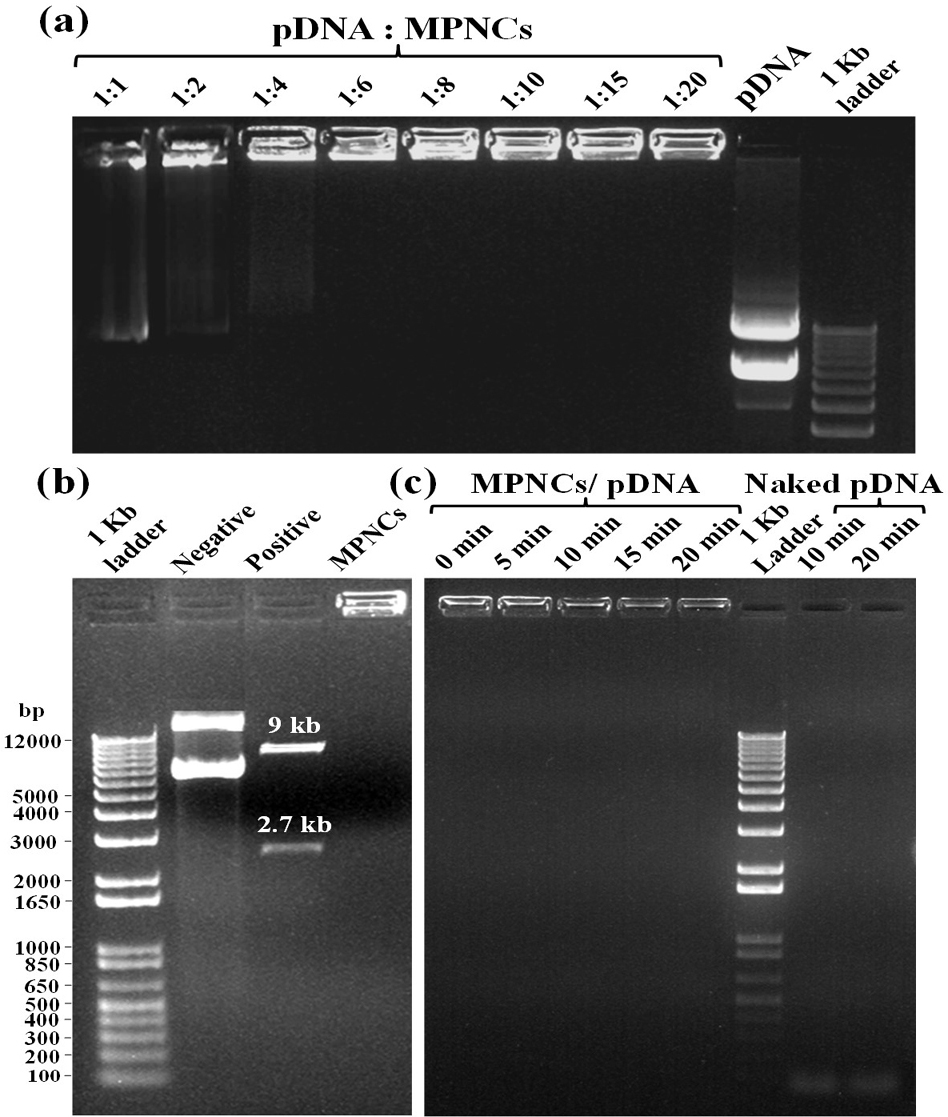 Figure 8
Figure 8(A) Gel Retardation assay with different w/w ratios of pDNA : MPNCs. Lanes (from left to right) 1:1, 1:2, 1:4, 1:6, 1:8, 1:10, 1:15, 1:20, naked pGIPZ and 1 kb plus DNA ladder. (B) Restriction digestion assay with XbaI and XhoI (pGIPZ specific) restriction enzymes. Lanes (from left to right) 1 kb plus DNA ladder, negative control (only pGIPZ), positive control (naked pGIPZ with restriction enzymes) and MPNCs/pDNA with restriction enzymes. (C) DNase I protection assay to check the shielding capacity of MPNCs against non-specific nuclease. Lanes (from left to right) (Time of incubation with DNase I) 0min, 5min, 10min, 15min and 20min, 1 kb plus DNA ladder, negative control (only pGIPZ with DNase I) 10min and 20min. The w/w ratio of pDNA : MPNCs was maintained at 1:6 in (B) and (C).
The cross-linker (EDC) played a dual role in nanoplex formation. In addition to cross-linking reaction between AgNPs/COOH and free amino groups of COS, it helped in activating the phosphate groups in pDNA, thereby assisting them to attach on the surface of MPNCs (51). The ability of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH, COS and MPNCs (w/ and w/o EDC) to complex with pDNA was ascertained using gel retardation assay. As it can be seen from the (Figure 9), the pDNA separated from AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH, COS only and MPNCs formulated without EDC, with an exception of MPNCs with EDC. The stability of MPNCs is crucial while delivering the gene of interest into cell. It is essential that the complexed pDNA is stable on nanocarrier surface, till the time they enter the cells and deliver their cargo. The stability of MPNCs/pDNA was evaluated in buffers of different pH (Figure 10). The nanoplex showed excellent stability over the pH range (5.5-9.2). This may be due to electrostatic interactions between free amino groups of COS and phosphate groups on pDNA (52).
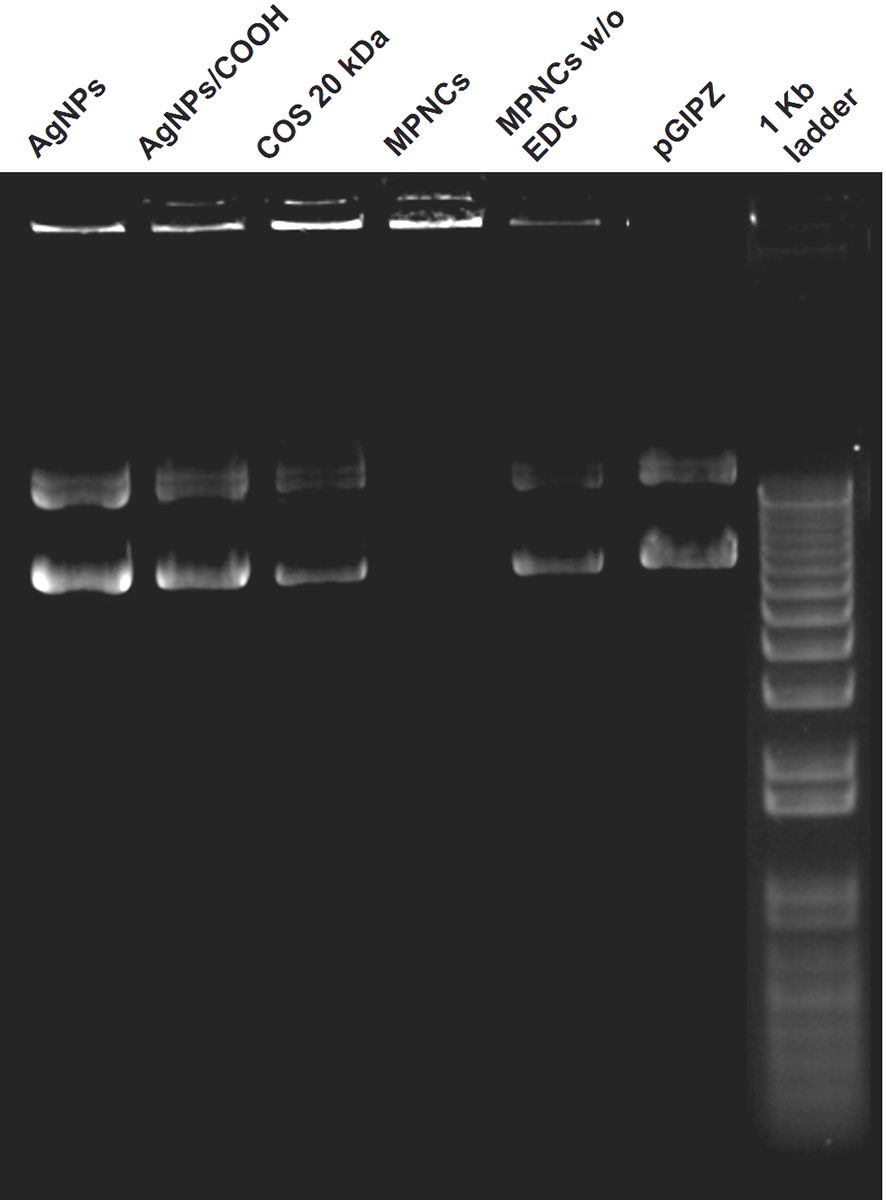 Figure 9
Figure 9Ability of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH, COS and MPNCs (w/ and w/o EDC) to complex with pDNA.
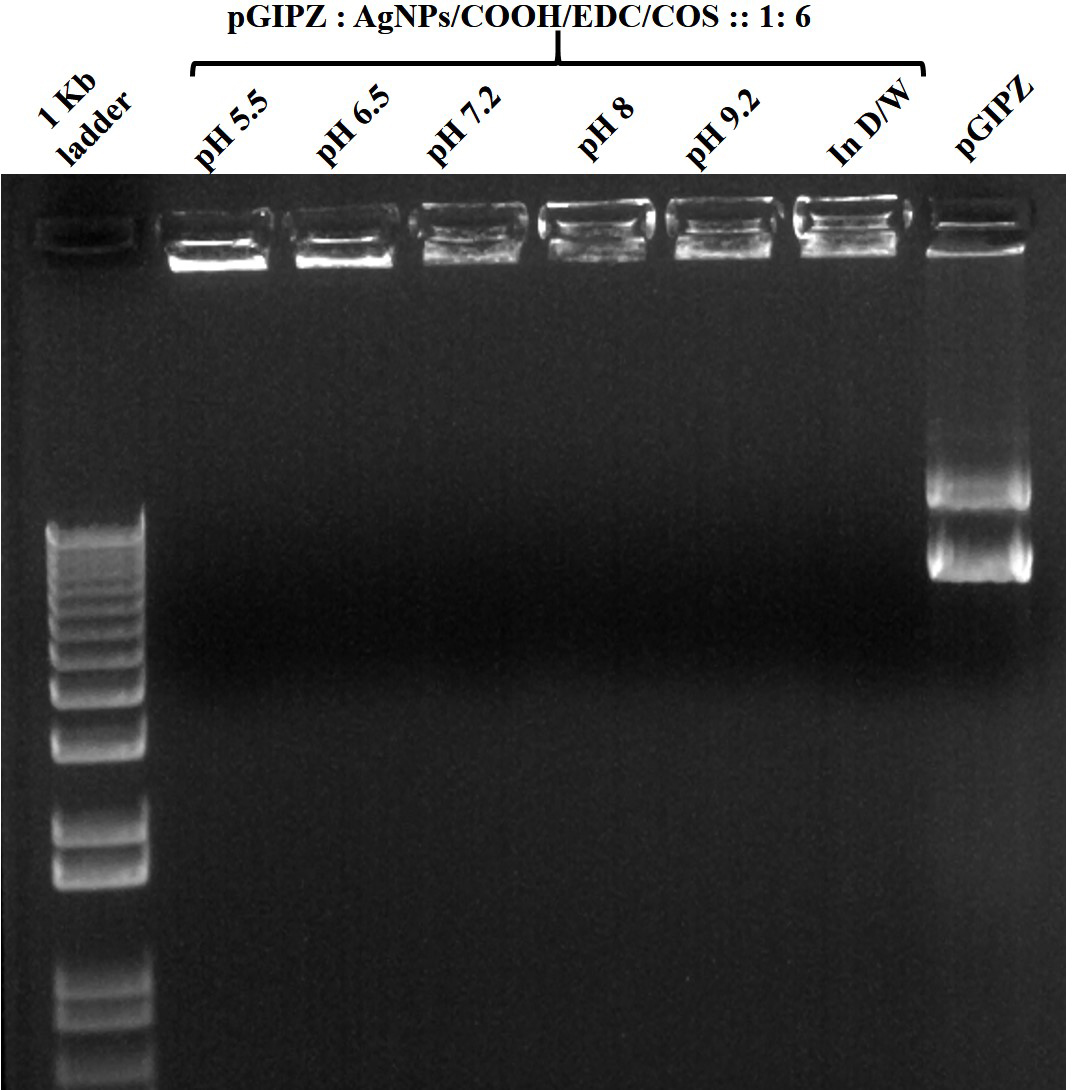 Figure 10
Figure 10Stability of MPNCs/pDNA in different pH buffers. The w/w ratio of pDNA : MPNCs was maintained at 1:6. Lanes (from left to right) 1 kb plus DNA ladder, pH 5.5, pH 6.5, pH 7.2, pH 8, pH 9.2, positive control (in deionized water) and naked pGIPZ.
The restriction digestion assay was performed to check the shielding capacity of MPNCs towards the pGIPZ sequence specific restriction enzymes Xho1 and Xba1 (Figure 8B) (30). The calculated size of restricted fragments from the vector map was 2.6 and 9 kb. The results obtained were in agreement with the theoretical size of fragments. Two bands were seen in positive control lane, corresponding to the respective size of fragments. The bands in negative control reflect different conformations of pDNA. The MPNCs effectively protected the pGIPZ plasmid from degradation by restriction enzymes at respective sites. However, it is possible for the digested fragments to remain adhered electrostatically on the surface of MPNCs. This would be a false positive result as intact pDNA needs to be delivered into the cell for desired expression of a gene. To test this, DNase I protection assay was carried out to reaffirm the non-specific shielding capability of MPNCs against nucleases abundant in physiological fluids (Figure 8C) (31). In case of naked pDNA, degraded DNA oligonucleotides were observed at the bottom of gel (almost near dye front) due to complete degradation of pDNA by the nucleases. In case of MPNCs/pDNA (6:1 w/w ratio), the nanocarrier was successfully able to protect the plasmid from nuclease activity of DNase I. However, it has to be noted that the intensity of pDNA bound to MPNCs altered as the reaction continued upto 20 min. The plasmid may have been released without degradation as degraded DNA were not observed in case of MPNCs/pDNA (53).
Cell-viability assay was performed to assess the toxicity of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH, COS, EDC and MPNCs on A549 and HeLa cell-lines (n=6). The % cell viability was normalized to the untreated control cells. The results of the experiment are illustrated in Figure 11. The MPNCs at a concentration of 0.01, 0.05 and 0.1% w/w were non-toxic to A549 and HeLa cells as their viability was comparable to the negative control (p<0.05). However, A549 and HeLa cells treated with concentrations of 0.5 and 1% w/w of MPNCs showed reduced viability (12.94±3.98% and 6.47±1.65%) and (47.72±3.56% and 24.37±2.78%) respectively. There are several reports available in literature on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles (50-53). In this study, the toxicity of AgNPs and AgNPs/COOH was comparable to the Triton X-100 group. Moreover, the viability of cells incubated with EDC was 62.84±8.6% (A549) and 75.53±6.51% (HeLa). The biocompatible nature of COS significantly improved the cellular safety of MPNCs (92.05±9.46% and 102.79±2.85%) in A549 and HeLa cells respectively, after 6 hrs. of incubation in serum-free medium. Lack of cytotoxicity of MPNCs may be attributed to the biocompatibility and biodegradable character of COS. The results indicated that MPNCs had no obvious cytotoxicity in A549 and HeLa cell-lines due to the biocompatible COS coating as compared to the uncoated nanoparticles (54, 55).
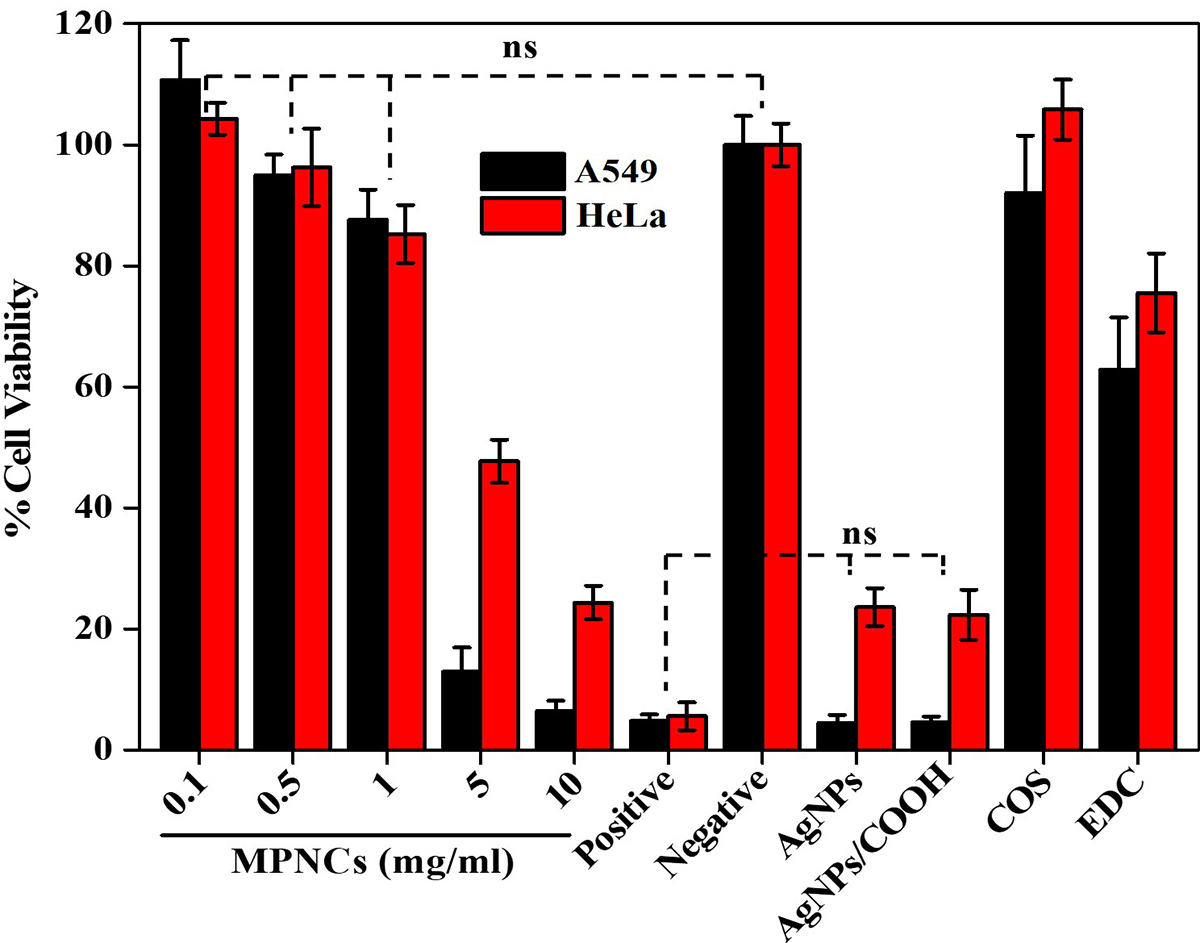 Figure 11
Figure 11An in vitro cell viability assay of AgNPs, AgNPs/COOH, COS, EDC and varying concentrations of MPNCs (0.1 to 10 mg/mL). 0.01% Triton X-100 and deionized water was used as positive and negative control respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 6) (ns: not significant; p>0.05).
Cellular uptake was investigated in A549 and HeLa cells. Serum-free medium was used in order to avoid interference of serum proteins with positively charged MPNCs/pDNA nanoplexes (56). Since pGIPZ carries a full-length sequence for Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP), GFP positive A549 cells were visualized under a fluorescence microscope (qualitative, real time analysis) as readout for uptake of pDNA in the cell (Figure 12). As evident from the figure, the cells internalized MPNCs/pDNA nanoplexes and not naked pDNA. GFP expression was observed after 24 h and continued upto 96 h only in case of pDNA delivered via MPNCs. No uptake was observed in case of naked pDNA while X-tremeGENE™ demonstrated substantial uptake of pDNA. There was no significant cellular uptake of MPNCs seen in case of HeLa cells.
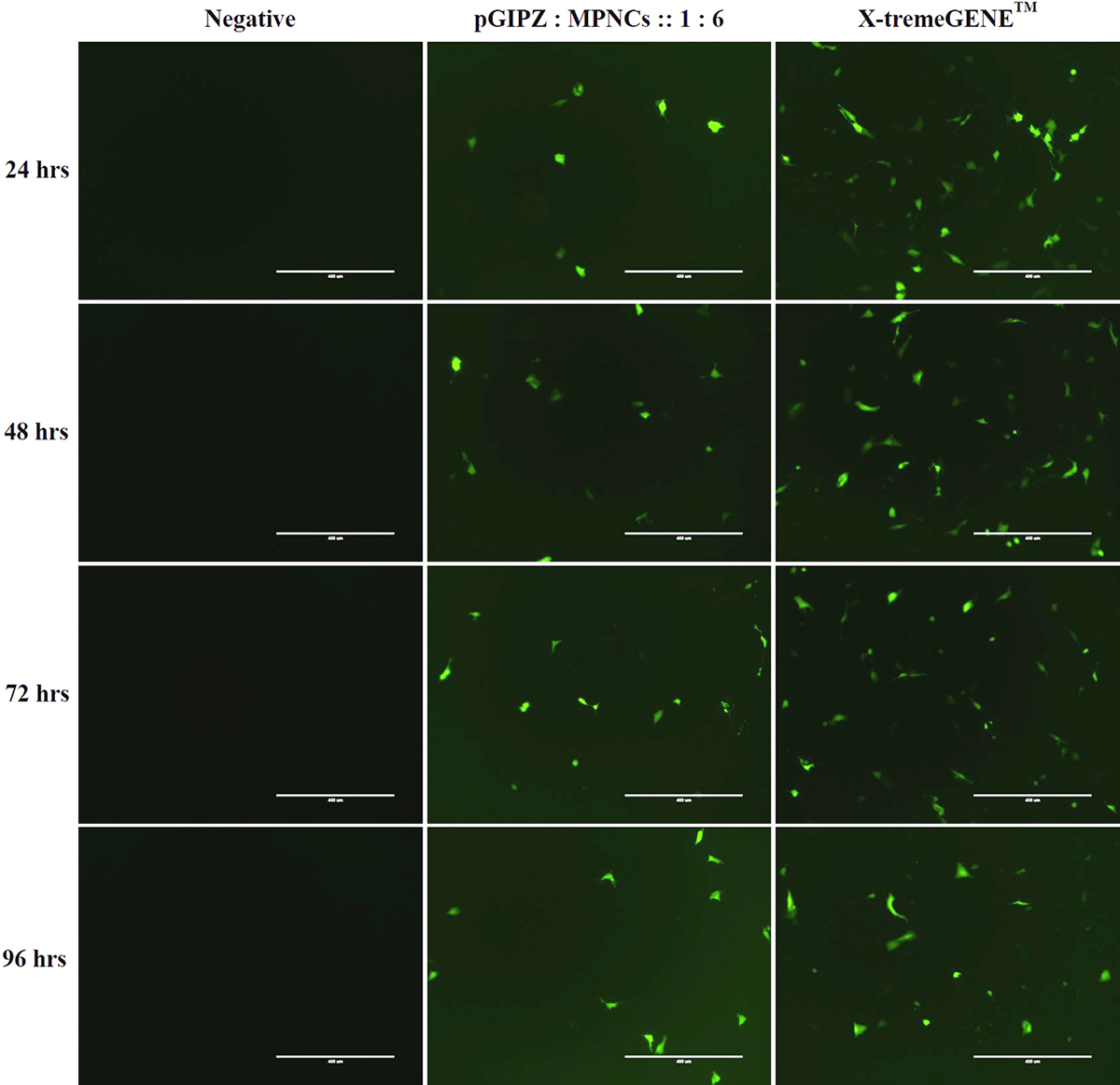 Figure 12
Figure 12In vitro cellular uptake of MPNCs in A549 cell-line. Representative fluorescence microscopy images of negative control, naked pDNA, pDNA : MPNCs at 1:6 and positive control (X-tremeGENE) every 24 hrs. upto 96 hrs.
Quantitative analysis of the GFP positive cells was performed using flow cytometry (Figure 13). GFP expression above Mean Fluorescence Intensity was considered as an indication of cellular uptake and delivery of pGIPZ in the cytoplasm. Data used for calculating the uptake of nanoplex was statistically significant (p < 0.05) as compared to negative control. The relative transfection efficiency was about 10% 24 h after transfection. Overall cellular uptake reduced over a period of 96 h in case of MPNC and X-tremeGENE™ mediated pDNA delivery due to superseding of GFP negative cells. The biocompatibility of MPNCs was confirmed since the cells appeared healthy in phase contrast microscopy (data not shown) and flow cytometry.
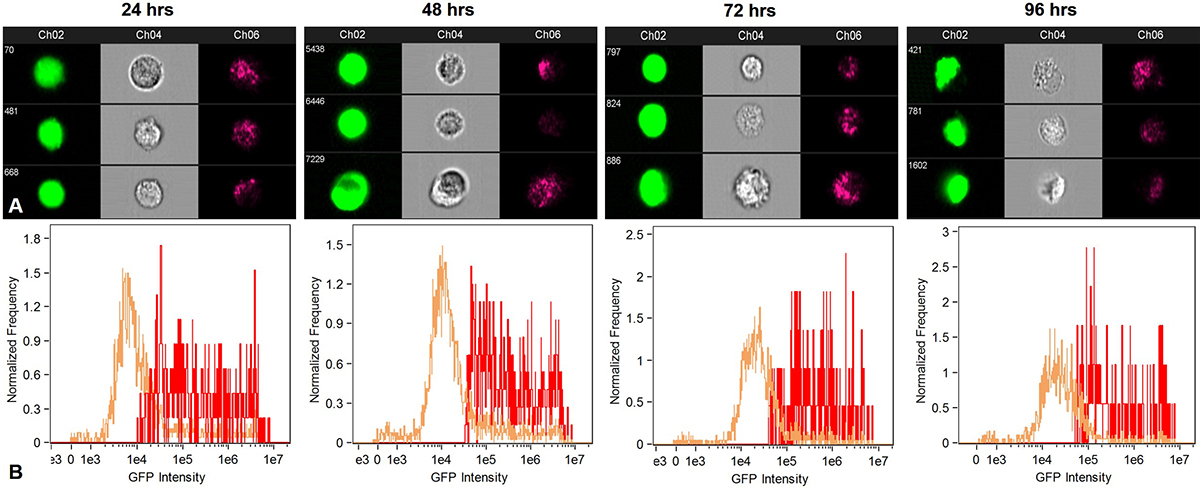 Figure 13
Figure 13Flow cytometry analysis to quantify uptake of MPNCs every 24 hrs. upto 96 hrs. (A) GFP positive cells, forward scatter and side scatter patterns in A549 and (B) Fluorescence intensity of GFP transformants (n=10,000 events). The w/w ratio of pDNA : MPNCs was maintained at 1:6.
Distribution of functional groups, particle size and shape, structural characteristics are some of the key attributes that underline effective application of non-viral vectors for gene delivery. In the present study, we have developed and characterized a biocompatible MetaloPolymeric Nanocarrier (MPNC) using low pressure pulsed plasma processing as a potential non-viral vector. The carboxyl group functionalization of AgNPs, and EDC-mediated amidation reaction between AgNPs/COOH and COS was confirmed by FTIR and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Figure 14). Further, the UV-Vis spectroscopy, FTIR and XRD patterns confirmed the physicochemical properties of the nanomaterial. The nanoparticles appeared spherical and the PDI decreased significantly from native AgNPs to MPNCs, due to stabilizing effect of COS. Additionally, the MPNCs exhibited a positive zeta potential, which is suitable to interact with negatively charged plasma membrane. The MPNCs formed stable complexes with pDNA and demonstrated very good colloidal stability over a wide =pH range. The MPNCs effectively shielded the pGIPZ plasmid against specific restriction enzymes and non-specific DNase I, making them a promising gene delivery vehicle. In general, a high cell viability of A549 and HeLa ensured that the nanoplexes were safe and biocompatible. The in vitro GFP expression reflected the cellular uptake of nanoplexes. Overall, the MPNCs showcased important features for gene delivery applications, including biocompatibility, stability, positive zeta potential, efficient shielding capacity and safety. The in vivo analysis would be the next step to get a better handle on the transfection efficiency in a relevant animal model. The surface of MPNCs could be modified with cell-specific targeted moieties to increase the cell interaction and uptake. MPNCs are nanobiomaterial which exhibits the properties of metal nanoparticles as well as polymeric component. The various applications include; Surface functionalized nanobiomaterial-based scaffolds could be used to regulate or control the cellular functions to culture stem cells and regenerate damaged tissues or organs. Additionally MPNCs provides platform for various surface modification techniques such as absorption, covalent modification, and surface patterning. Plasma technology can thus be explored as a novel platform for modifying the surface of nanomaterials to render them as an effective gene delivery vehicle.
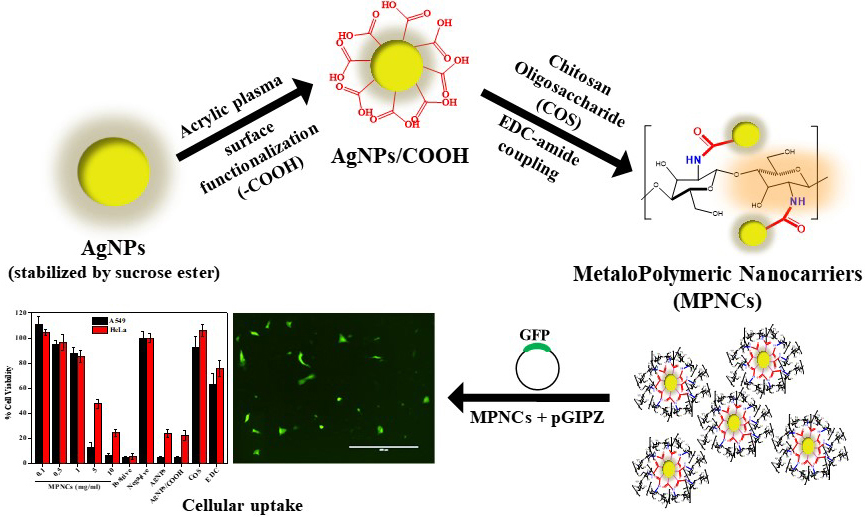 Figure 14
Figure 14Pulsed plasma surface functionalized nanosilver for gene delivery.
Drs Ajinkya M. Trimukhe, Prasad A. Pofali, contributed equally to this paper. R. J. and R. R. D. conceived and supervised the project. P. P., A. T. and A. V. designed and carried out experiments in detail, contributed in result analysis and wrote the manuscript. U. K. assisted in planning and performing flow cytometry and in vitro cellular uptake studies. P. D. contributed to writing the article. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript. The authors declare no competing source of financial interest. Ajinkya M. Trimukhe and Prasad A. Pofali contributed equally to this article. The authors would like to acknoweledge University Grants Commission (UGC) and Technical Education and Quality Improvement Program (TEQIP) for providing fellowship.
AgNPs
Silver Nanoparticles
MetaloPolymeric Nanocarriers
plasmid deoxyribose nucleic acid
1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Phosphate Buffered Saline
Room Temperature
Relative humidity
Carbon first shell














