1 Institute of Geriatrics (Shanghai University), Affiliated Nantong Hospital of Shanghai University (The Sixth People's Hospital of Nantong), School of Medicine, Shanghai University, 226011 Nantong, Jiangsu, China
2 Cardiac Regeneration and Ageing Lab, Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Organ Repair, School of Life Science, Shanghai University, 200444 Shanghai, China
3 Cardiovascular Division of the Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114, USA
4 Biologics Development, Sanofi, Framingham, MA 01701, USA
5 Department of Nursing, Union Hospital, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, 350001 Fuzhou, Fujian, China
6 Fujian Provincial Special Reserve Talents Laboratory, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, 350001 Fuzhou, Fujian, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Exercise training (ET) is an important non-drug adjuvant therapy against many human diseases, including cardiovascular diseases. The appropriate ET intensity induces beneficial adaptions and improves physiological function and cardiopulmonary fitness. The mechanisms of exercise-induced cardioprotective effects are still not fully understood. However, mounting evidence suggest that microRNAs (miRNAs) play crucial role in this process and are essential in responding to exercise-stress and mediating exercise-protective effects. Thus, this review summarizes the biogenesis of miRNAs, the mechanism of miRNA action, and specifically the miRNAs involved in exercise-induced cardio-protection used as therapeutic targets for treating cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords
- exercise training
- beneficial adaption
- cardiovascular diseases
- microRNA
- therapeutic targets
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, single-stranded, evolutionally conserved, non-coding RNAs composed of 19 to 24 nucleotides (nt). The first miRNA, lin-4, was discovered in 1993 in Caenorhabditis elegans and is essential in regulating postembryonic developmental processes [1]. Since then, numerous miRNAs have been identified in different types of organisms with diverse functions substantially elucidated [2, 3, 4]. Currently, more than 2000 miRNAs have been discovered in humans, which regulate about one-third of the protein-coding genes. miRNAs are closely associated with many diseases and are being explored as novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies [5].
miRNAs recognize and bind to their target mRNAs via base-paring and exert their activity either by inhibiting mRNA translation or by promoting messenger RNA (mRNA) decay at the post-transcriptional level. miRNAs are involved in many fundamental biological processes based on cell-signaling, such as cell proliferation, cell growth, cell metabolism, cell morphogenesis, and apoptosis. The function of an individual miRNA has been understood by miRNA silencing or overexpression in vitro or in vivo [6]. Dysregulation of miRNAs leads to development of various diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, nervous system diseases, cancer, and infectious diseases [7, 8].
Exercise-training (ET) causes physical stress and affects the body in different ways. Muscle tissues, cardiopulmonary systems, and multiple organs respond to the exercise stimulus. Appropriate exercise stress induces beneficial changes in the whole body, improves tissue metabolism, and increases oxidative capacity as well as cardiopulmonary fitness [9, 10]. Various response factors mediate the adaptive changes induced by exercise, and miRNAs are one of the crucial executors [11, 12].
Here, we elucidate the biogenesis of miRNAs along with their mechanism of action, emphasizing on miRNAs involved in exercise-induced cardio-protection, especially because they could be used as therapeutic targets for cardiovascular diseases.
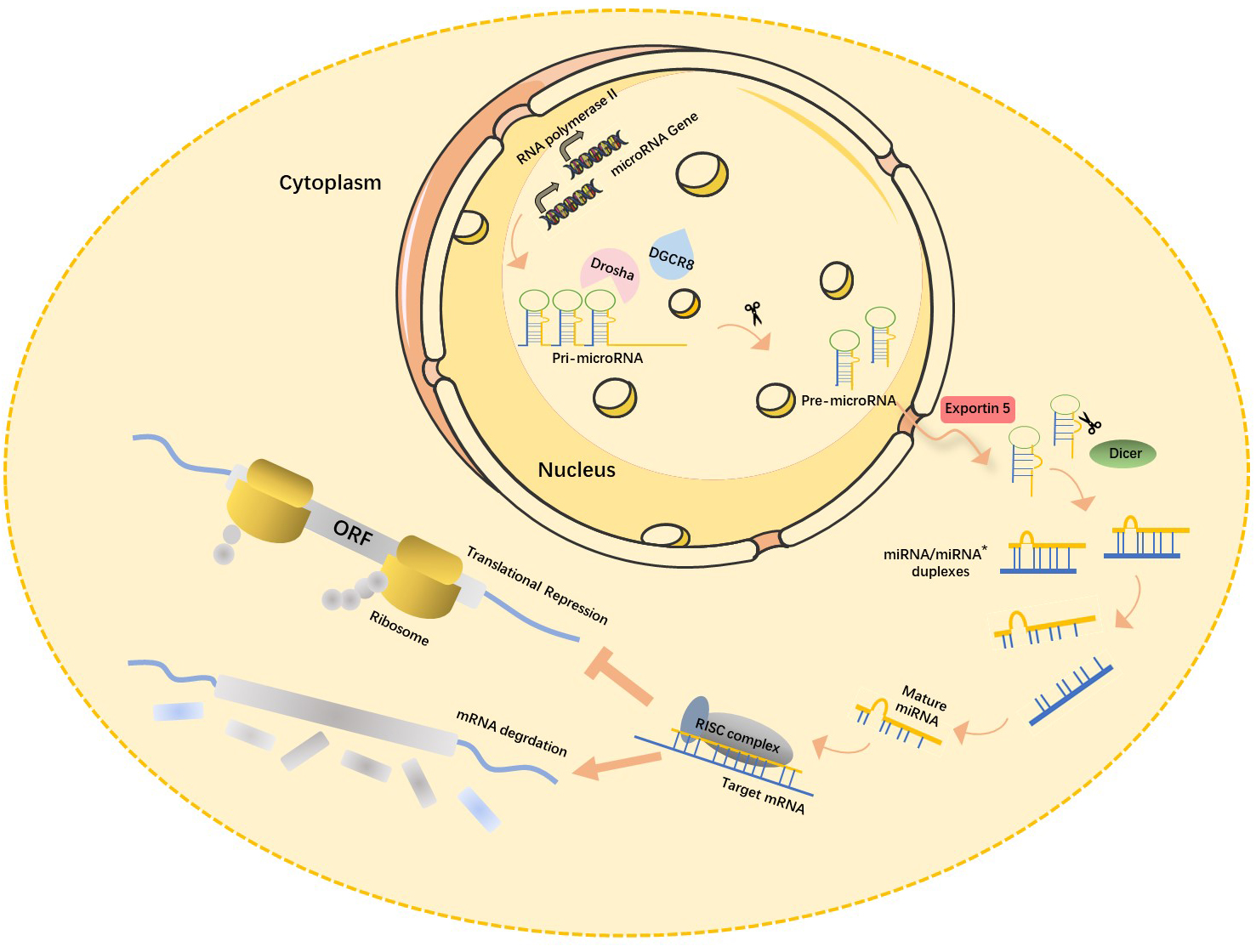
Recent studies have shown that about 70% of mammalian miRNA genes are located in the transcription units (TUs) regions, mostly in their intronic region. miRNA-encoding genes located in the intron region are usually highly conserved among different species both in their genome locus and sequence homology of mature miRNA [13], which in turn is closely associated with their functional importance. Most miRNA-encoding genes exist either as a single copy, multiple copies, or clusters in the genome [14]. The biogenesis of miRNAs is under strict temporal and spatial transcriptional control, resulting in a high diversity of their expression profile. miRNA encoding genes are generally transcribed by RNA polymerase II in the nucleus, and the length of the primary miRNA transcripts (pri-miRNA) can be more than 1000 nucleotides. Canonical miRNAs are processed in multiple steps (Fig. 1) [15]. First, double-stranded RNA-specific endoribonuclease (DROSHA) forms a microprocessor complex with DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 (DGCR8). It then recognizes the specific hairpin structure and the length of pri-miRNA and cleaves it into miRNA precursors (pre-miRNA, normally 60–70 nt) using its ribonuclease enzyme activity. Next, the Exportin5 (Exp5)/RanGTP mediates the nuclear export of pre-miRNA by forming a pre-miRNA/Exp5/RanGTP complex. Then, Dicer, a Ribonuclease III (RNase III) endonuclease, cleaves the hairpin miRNA precursors into mature miRNA duplex (miRNA:miRNA*), a form of short double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) [16].
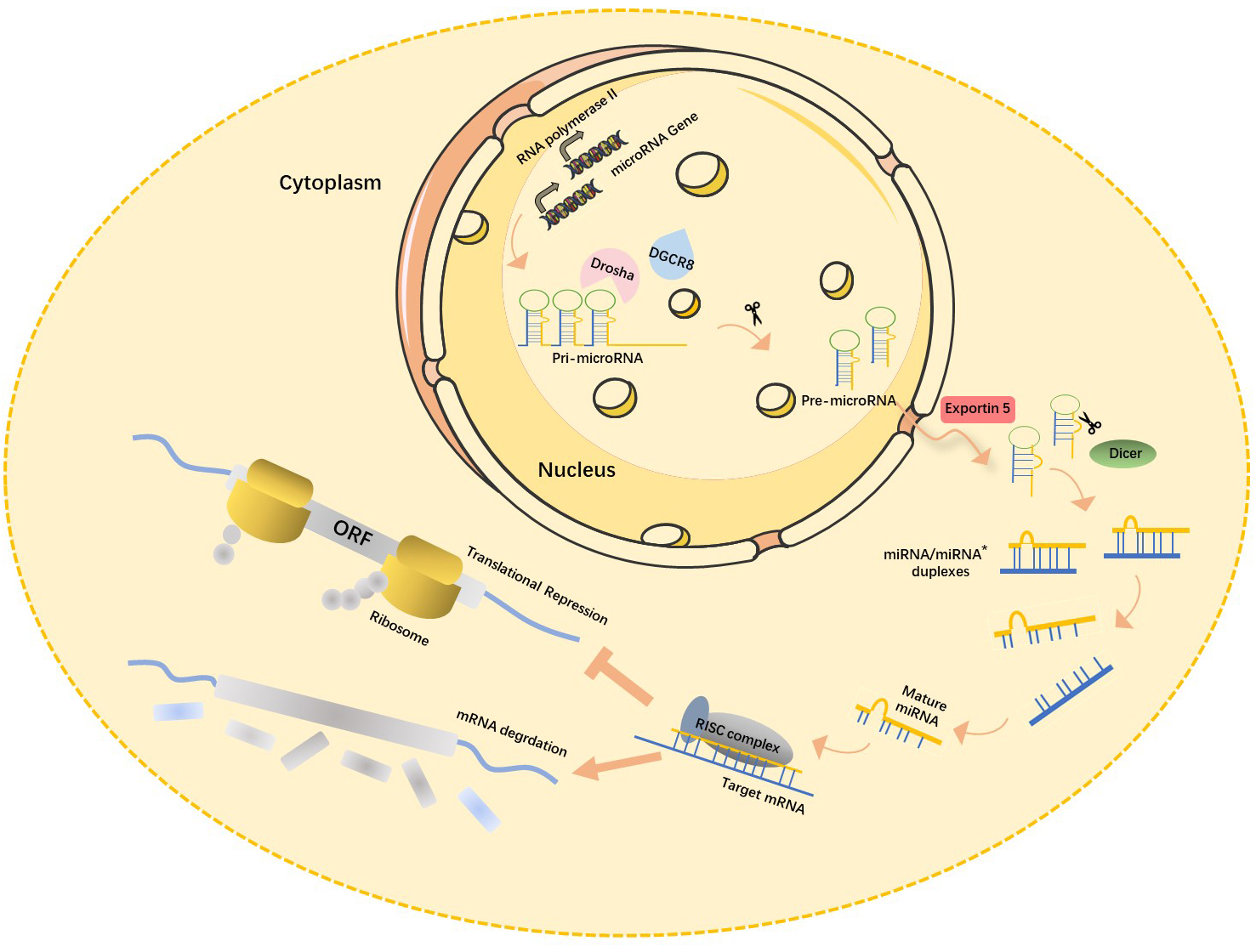 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Canonical miRNAs biogenesis pathway. In the nucleus, pri-miRNA, the primary transcription product of the miRNA gene, is cleaved by RNase III-Drosha enzyme to become hairpin precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA). After preliminary shearing, the pre-miRNA is transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm under the action of the transporter Esportin-5, and then further cleaved by another RNase III Dicer enzyme to produce mature miRNA. The mature miRNAs then bind with other proteins to form RISC (RNA-induced silencing complex), which leads to target mRNA degradation or translation inhibition. miRNA, microRNAs; pri-miRNA, primary miRNA transcripts; DGCR8, DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8; ORF, open reading frame; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid; miRNA*, star strand of microRNA.
While mature miRNA, also called the guide or leading strand, was considered the
biologically active miRNA, the miRNA star (miRNA*)/passenger strand/carrier
strand, was formerly thought to be inactive. Currently, the miRNA duplex is named
according to its position in the pre-miRNA hairpin structure. While the miRNA-5p
strand is located in the forward (5
One strand of miRNA (either -5p or -3p) is incorporated into an RNA-induced
silencing complex (RISC), a multi-protein large molecular weight complex. It is
used as a template to recognize and bind to its target mRNA by
base-paring, leading to mRNA degradation or translation inhibition through
different mechanisms [23]. In plants, most miRNAs bind to their target mRNAs by
exact or nearly exact complementary base-pairing. However, most miRNAs and their
mRNA targets in animals have imperfect complements and fewer sequence homologies.
The miRNA binding sites are located in all the regions of mRNAs, including coding
sequence, 5
The function of the RISC complex is mainly mediated by the argonaute (AGO) protein together with multiple associated proteins, and the miRNA function is primarily due to its incorporation into the RISC complex. Four AGO proteins (AGO1–4) were encoded in the mammalian genome, and AGO2 is the most highly expressed and the only AGO protein that retains the nuclease activity to cleave miRNA targets in humans [26]. AGO proteins can determine the mechanism by which RISC plays a role in gene regulation. In the cytoplasm, miRNAs can recognize and bind to their mRNA targets. Further, they can also be released from their former mRNA targets and rebind to different mRNA targets, thereby continuously modulating many target molecules. Emerging evidence shows that miRNAs not only regulate genes at the post-transcriptional level resulting in transcriptional gene silencing (TGS), but also mediate transcriptional gene activation (TGA) in the nucleus, acting at a transcriptional level [27]. In addition to regulating the mRNA decay or mRNA translation in the cytoplasm, miRNAs could affect gene transcription and expression in the nucleus by altering the epigenetic status of gene promoters and enhancers, and by regulating gene-derived transcripts in the mitochondrion [28]. miRNAs hybridize with double-stranded DNA and bind specifically to the promoter region of a gene, therefore regulating gene transcription. miRNAs can inhibit the maturation of noncoding RNA by interacting with them through complementary sequences. miRNAs affect alternative splicing through mediators such as AGO proteins. In the nucleolus, miRNAs also regulate the stability of mRNA and ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) [29]. In addition, miRNAs can interact directly with proteins and affect their functions, thus exerting crucial impact on cardiovascular biology. Endothelial miR-126-5p was found to bind to caspase-3 (CASP3), to suppress caspase dimerization and inhibit its activity thus reducing cell apoptosis [21]. miR-1-3p could bind to cardiac membrane protein, such as inward-rectifier potassium channel KIR2.1, playing a critical role in the regulation of cardiac electrophysiology and arrhythmia [30].
Interestingly, miRNAs not only regulate the host cells from which they are generated. Mature miRNA duplexes could also be directly transferred to neighboring cells through gap junctions. Further, miRNAs can be secreted and transferred via exosomes or different types of small extracellular vesicles regulating corresponding mRNA targets in distal cells. In addition, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) has been shown to transport miRNAs into cells [7]. miRNAs also exist in serum and other body fluids termed circulating miRNAs, which can be used as risk factors or biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of certain diseases [31]. Robust evidence has shown the predictive value of circulating miR-30d as a functionally validated RNA biomarker in acute heart failure (AHF) patients [19, 32, 33]. The sensitivity and specificity of miR-30d as a novel biomarker imply its promising role in a clinical setting. There is evidence of a prognostic role for miR-125b-5p in patients with cardiovascular disease. Stroke is currently the second most common cause of death worldwide and a leading cause of long-term disability. Computed tomography (CT) is normally used to diagnose hemorrhagic stroke in clinical settings. However, 40–50% of acute ischemic stroke (IS) cases showed no abnormality in admission CT scan. It was found that the expression levels of miR-125a-5p, miR-125b-5p and miR-143-3p were correlated with infarct size and stroke etiology. Area under the curve (AUC) of three miRNAs was 0.90 (sensitivity: 85.6%; specificity: 76.3%). This was far better than multiple previously reported biomarkers of acute IS, suggesting their potential use as widely useful diagnostic markers. Specifically, elevated levels of these three miRNAs indicate the early stages after stroke, and their peak expression could more accurately determine symptom onset [34]. In a screening for circulating miRNA with prognostic value for heart failure (HF) drug-refractory patients undergoing cardiac resynchronization therapy revealed that lower expression of miR-499a-5p and miR-125b-5p is closely associated with the improved left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF). This provides evidence for their predictive potency [35]. Further studies on patients with both acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and multivessel disease (MVD) confirmed that those patients with plasma miR-125b-5p expression levels below 4.6 had better long-term all-cause survival [36]. Therefore, miRNAs can be secreted from donor cells and transferred to adjacent or remote recipient cells by different carriers, such as exosomes, microvesicles, and HDL, playing essential roles in intercellular communication [7].
The role of miRNAs in cardiovascular physiology and pathology has been comprehensively studied [37]. The expression of a set of cardiac miRNAs in response to exercise with cardio-protective roles to regulate cell proliferation, metabolism, and apoptosis has been reported [38, 39, 40] (Table 1, Ref. [41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62]). In response to physical exercise, these exercise-driven miRNAs have important roles in regulating exercise adaptation and could be used as promising therapeutic intervention. Moreover, exercise-regulated miRNAs can also be used as novel prognostic tools in many subareas of cardiology, such as HF [39, 40].
| miRNA | Changes of miRNA after exercise | Targets | Functional effects | References |
| miR-126-3p | up | SPRED1, PIK3R2 | Increased angiogenesis | [41, 42] |
| miR-21a-5p | up | FABP7, HMGCR, ACAT1, OLR1 | Regulated lipid metabolism and improved hyperlipidemia | [43] |
| miR-214-3p | down | SERCA2A | Improved cardiac contractility and LV compliance | [44] |
| miRNA-1-5p | up | NCX1 | Improved cardiac contractility and LV compliance | [44] |
| miR-133a-5p | up | CASP3, CASP8, CASP9 | Reduced cardiac fibrosis and apoptosis | [45] |
| miR-1192 | up | CASP3 | Reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis | [46] |
| miRNA-497-5p | down | CLCN3, BCL-2 | Reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammation | [47] |
| miR-29a-3p | up | TGF- |
Reduced cardiac fibrosis | [48] |
| miR-101a-3p | up | FOS, TGF- |
Reduced cardiac fibrosis | [48] |
| miR-29c-3p | up | COL1A1, COL3A1 | Reduced cardiac fibrosis, improved LV compliance | [49] |
| miR-20a-5p | up | PTEN | Promoted the survival and proliferation of endothelial cells | [50] |
| miR-146a-5p | up | TRAF6 | Reduced vascular inflammation injury | [51] |
| miR-125b-5p | up | MAP3K5, MAP2K7, MAP2K4 | Reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis | [52] |
| miR-128-3p | up | MAP3K5, MAP2K7, MAP2K4 | Reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis | [52] |
| miR-30d-5p | up | MAP3K5, MAP2K7, MAP2K4 | Reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis | [52] |
| miR-342-5p | up | CASP9, JNK2, PPM1F | Reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis | [53] |
| miR-17-3p | up | TIMP-3 | Promoted cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, proliferation, and survival | [54] |
| miR-222-3p | up | HIPK1, HMBOX1, P27 | Promoted cardiomyocyte growth, proliferation, and survival | [55] |
| miR-486-5p | up | PTEN, FOXO1, MST1 (STK4) | Reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis | [55] |
| miR-16-5p | down | VEGF, BCL-2 | Increased angiogenesis | [56] |
| miR-344g-5p | up | HMGCS2 | Reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis | [57] |
| miR-455-5p | up | MMP9 | Reduced cardiac fibrosis and myocyte uncoupling | [58] |
| miR-181b-5p | up | PTEN, KPNA4 | Alleviated endothelial dysfunction and vascular inflammation | [59] |
| miRNA-208a-3p | down | MED13, SOX6, SP3, PUR |
Induced physiological hypertrophy | [60] |
| miR-210-3p | down | EFNA3 | Increased angiogenesis | [61] |
| miR-34a-5p | down | SIRT1, CYCLIN D1, BCL-2 | Promoted cardiomyocyte proliferation and survival | [62] |
Table notes: miRNA, microRNA; SPRED1, sprouty related EVH1 domain containing 1;
PIK3R2, phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 2; FABP7, fatty acid binding
protein 7; HMGCR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; ACAT1, acetyl-CoA
acetyltransferase 1; OLR1, oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor 1; SERCA2A,
Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase; NCX1, Sodium/Calcium exchanger
protein; CASP3, cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 3; CASP8, cysteinyl
aspartate specific proteinase 8; CASP9, cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase
9; CLCN3, chloride voltage-gated channel 3; BCL-2, B-cell lymphoma-2;
TGF-
Several risk factors, including abdominal obesity, high blood pressure,
dyslipidemia, elevated triglycerides (TG), low HDL cholesterol and elevated
fasting blood sugar, lead to oxidative stress, systemic inflammation, myocardial
lipotoxicity, disturbed energy homeostasis, coronary endothelial dysfunction, as
well as left ventricular remodeling and dysfunction. These, in turn, result in a
spectrum of cardiometabolic diseases, such as hypertension, insulin resistance,
diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, representing some of the most
serious health challenges of the 21st century [63, 64]. Although medications for
the treatment of cardiometabolic diseases have made significant advances, the
risk of HF in patients with cardiometabolic diseases does not decline.
Interestingly, a sustainable intensity of exercise has emerged as an effective
synergistic therapy to mitigate and combat adverse alterations that impair
cardiovascular function. Further, this can regulate miRNA levels, which have
emerged as key molecular modulators of beneficial adaption and pathophysiological
stresses [65]. Dysregulation of miRNAs occurs in multiple pathologic processes
that regulate cell apoptosis and other cellular functions leading to
cardiometabolic diseases, including diabetic cardiomyopathy [45]. The protective
effects of exercise on the coronary arteries and heart during the onset and
progression of diabetic heart disease (DHD) are found to be mediated by the
normalization of cardiovascular-enriched miRNAs [66, 67]. Several studies have
shown that exercise training (ET) could upregulate miRNA-126-3p levels and is
cardio-protective [61, 68, 69, 70, 71]. A significant reduction of miR-126-3p expression
was associated with the downregulation of RAF1 (raf-1 proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), high blood
glucose level, insulin resistance, and angiogenesis impairment in diabetes, all
of which could be reversed by exercise. This suggests that miRNA-126-3p could be
a valuable therapeutic strategy against diabetes [70]. Another study found that
in Wistar rats with diabetes, miR-126-3p and angiogenesis were reduced, while
miR-210-3p was increased. These adverse events could be reversed by garlic
treatment or long-term voluntary exercise. miR-126-3p and miR-210-3p correction
mediated by exercise could be important for improving these functions [61].
Consistently, miR-126-3p was found to be downregulated in castrated
streptozotocin-induced type I diabetes rats. Testosterone and ET could both
enhance miR-126-3p expression and positively improve diabetic cardiomyopathy
[71]. Many pathological changes were found in the cardiac tissue of diabetic
ovariectomized rats, including increased cholesterol, triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein (LDL),
decreased HDL, upregulated cell-apoptosis related proteins such as B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2)-associated X protein (BAX), CASP3,
CASP8, and decreased miR-133a-5p. Exercise could promote miR-133a-5p expression,
reverse nearly all the above deleterious alterations and improve the adverse
effects of estrogen deficiency and diabetes. Moreover, overexpression of
miR-133a-5p could reduce the extracellular matrix protein, significantly reducing
cardiac fibrosis and the heart injury caused by diabetes [45, 72]. Obesity occurs
owing to excessive fat accumulation in the body, which is now a global epidemic,
and the incidence rate is still rising yearly. Obesity is closely associated with
multiple cardiovascular and skeletal muscle diseases and could be used as an
important risk marker. Considerable efforts have been made to elucidate
obesity-related molecular pathways. Among them, miRNAs and their target genes are
identified to play critical roles in regulating the obese phenotype and its
associated comorbidities [73]. ET has been widely used for treating obesity and
could combat aberrant metabolism and counteract weight gain. miR-208a-3p, a
cardiac-specific miRNA, could regulate
Myocardial infarction (MI) is the most common medical emergency among
cardiovascular diseases, with high morbidity and mortality. With the shift in
diet structure and increase in aging population, the prevalence of MI is
consistently rising, with an increasingly younger population suffering from MI.
Numerous studies have suggested that exercise provides direct endogenous benefits
against MI and could be used as a necessary adjuvant therapy against cardiac
dysfunction post-MI. Using left anterior descending (LAD) ligation-induced MI
combined with ET rat models, miRNA-497-5p expression was found to be enhanced by
MI. ET could reduce miRNA-497-5p expression under physiological and under MI
pathological conditions. A miRNA-497-5p antagomir (inhibitor) could mimic the
benefits of exercise on MI, including reduced infarct size and improved cardiac
function, whereas miRNA-497-5p agomir aggravated the infarct size post-MI and
abrogated the positive effects of ET maybe through its target chloride
voltage-gated channel 3 (CLCN3) [47]. Through a plasma miRNA profiling
assay, miR-1192 was found to be increased by a four-week swim training. miR-1192
overexpression provided significant beneficial effects against hypoxia in
cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCMs) by targeting CASP3.
Moreover, intramyocardially injection of miR-1192 agomir could mimic the positive
effects, while using its antagomir blocked the beneficial effects of exercise
against MI [46]. Studies showed that exercise stress induced by a 4-week ET MI
rat model could trigger hypoxia-inducible factor-1
Reperfusion therapy, including thrombolytic and fibrinolytic drugs, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), and coronary artery bypass grafting surgery, are the most common treatments for MI in clinical practice that greatly reduce acute death. However, restoring blood flow to ischemic cardiac tissue will inevitably lead to myocardial injury, pathological ventricular remodeling, and even cause chronic heart failure (CHF) and death. Effective ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) treatment is still an urgent requirement in current clinical practice. Accumulating evidence has shown that exercise-induced cardiac adaption can resist cardiac dysfunction caused by IRI, and miRNAs are essential during this process.
To identify miRNAs that mediate exercise-induced physiological cardiac growth, two ET models, a voluntary wheel running and a ramp swimming or sedentary control, were applied to mice for three weeks. miR-222-3p was found to be upregulated in both ET models. Overexpression of miR-222-3p could enhance cardiomyocyte growth and proliferation by targeting KIP1 (P27), homeodomain interacting protein kinase 1 (HIPK1), HIPK2, and homeobox-containing 1 (HMBOX1). miR-222-3p inhibition could enhance serum deprivation and doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis, while the converse was observed upon miR-222-3p overexpression. Functional rescue experiment by miR-222-3p inhibition showed that it was necessary for exercise-induced cardiac growth. Moreover, miR-222-3p overexpression significantly attenuated pathological cardiac remodeling and cardiac dysfunction after IRI [55]. Using the three-week swimming or voluntary wheel exercise model, miR-17-3p was also identified to be significantly upregulated by ET, specifically in heart tissue. miR-17-3p overexpression could promote cardiomyocyte growth and proliferation, and protect against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGDR)-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by directly targeting TIMP-3 and indirectly inhibiting PTEN. Inhibition of miR-17-3p can attenuate exercise-induced cardiac growth in vivo. In addition, mice administrated with miR-17-3p agomir (mimic) could be protected from adverse cardiac remodeling after myocardial IRI [54]. miR-486-5p was previously found to be upregulated in skeletal muscle and heart in ET [55, 74, 76]. Most recently, miR-486 was found to be significantly downregulated in the myocardial tissue post-IRI. In addition, miR-486-5p overexpression reduced OGDR-driven cardiomyocyte apoptosis. It protects mice against cardiac dysfunction and myocardial apoptosis post-IRI by targeting PTEN and FOXO1 and activating AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling. Depletion of miR-486 abrogated the ET’s protective effects, suggesting it is necessary for cardio-protection [77]. Collectively, these results showed that miR-222-3p, miR-17-3p and miR-486-5p are key participants in exercise-induced physiological cardiac adaption, and play critical roles in protecting against adverse cardiac stress and dysfunction.
It is not only the exercise-induced miRNAs from heart tissues that mediate protective effects for cardiac injury. Circulating exosome-delivering miRNAs in serum have also been found to be essential for exercise-induced cardioprotection [78, 79]. Circulating exosomes isolated from the plasma of 4-week swimming exercise-trained rats provided remarkable beneficial effects, especially against IRI. miRNA sequencing combined with quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) verification identified 12 differentially expressed exosome-derived miRNAs in exercise-induced rats. Functional analysis showed that miR-342-5p is necessary for reducing hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocytes apoptosis, attenuating cardiac dysfunction and myocardial injury by targeting Caspase 9 (CASP9) and JNK2. This enhances the survival signaling through the phosphorylation of Akt (p-Akt) by targeting phosphatase gene, PPM1F, in cardiac tissue after IRI [53]. Exercise could induce the expansion of brown adipose tissue (BAT), the thermogenic tissue in mice, and surgical BAT ablation could reduce the protective effects of exercise against IRI. The small extracellular vesicles (sEV) derived from BAT have been shown to communicate with the heart, regulate cardiomyocyte survival and mediate exercise-induced cardioprotection against myocardial IRI. BAT miRNAs, including miR-125b-5p, miR-128-3p, and miR-30d-5p, are involved in this process by targeting a series of molecules, such as MAP3K5, MAP2K7, and MAP2K4 to suppress the proapoptotic MAPK pathway [52]. Inhibition of the miRNAs in BAT specifically abrogated their increase in plasma sEVs and hearts of exercise-trained mice and consequently reduced the beneficial effects of ET.
Exosome-miRNAs are also found to regulate interorgan crosstalk. Cardiac dysfunction induced by particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) was found to be associated with miR-421-3p in sEV released from the injured lung. This was transferred to cardiac tissue and exerted its function by regulating its target gene, ACE2, causing myocardial cell apoptosis and myocardial injury. Cardiac injury caused by PM2.5 resulted from crosstalk between the lungs and heart and was secondary to lung injury. Inhibition of miR-421-3p could significantly attenuate cardiac dysfunction induced by PM2.5 in mice [80]. Cardiac homing peptide (CHP)-linked plasma circulating extracellular vesicles (EVs) delivered either by percutaneous intracoronary delivery (in a canine model) and myocardial injection just before reperfusion (in murine model), possibly mediated by miR-486-5p, could protect the heart against IRI. Moreover, the depletion of miR-486-5p in EVs abrogated the protective roles of circulating EVs on IRI, suggesting that EV-miR-486 is crucial for the cardioprotective effect [81]. Taken together, these suggest that miRNAs originating from heart tissue or those delivered by EVs derived from remote organs are essential for mediating cardioprotection.
Cardiac remodeling is well recognized as the primary pathological basis of multiple cardiovascular diseases. Pathological cardiac remodeling occurs in response to numerous stresses wherein the initial aim is to maintain cardiac function despite various stress conditions. Sustainable stress conditions would induce cardiac remodeling transition from the adaptive stage to maladaptive alterations, leading to cardiac dysfunction and HF. Mounting studies have shown that miRNAs are essential in regulating cardiac remodeling by controlling the target gene expression. Obesity is considered a low-level systemic inflammation state that contributes to the development of atherosclerosis, insulin resistance, hypertension, endothelial dysfunction, and cardiometabolic diseases, all of which are associated with pathological cardiac remodeling. miR-1-5p and miR-29c-3p were observed to regulate obesity-related cardiac remodeling by targeting the sodium/calcium exchanger NCX1 and collagen expression, respectively. While miRNA-29c-3p was decreased, collagen expression was increased, whereas when miR-1-5p was upregulated, the expression of its target gene, calcium signaling protein NCX1, was decreased in OZR. Aerobic ET could restore all these parameters, consequently attenuating cardiac dysfunction and protecting the heart from an abnormal increase in extracellular matrix components and pathological cardiac hypertrophy by regulating miRNAs [82].
Exercise could promote the dedifferentiation and proliferation of original cardiomyocytes and produce new cardiomyocytes by regulating various cytokines, transcription factors, and miRNAs. Some miRNAs involved in cardiomyocyte regeneration or proliferation have been found to promote heart repair after myocardial injury [83, 84, 85]. Beneficial cardiac remodeling against deleterious stressors also occurred in response to exercise-induced adaptions that cause significant changes in myocardial structure and function [83, 86]. Robust evidence has shown that exercise could upregulate cardiac miR-222-3p and miR17-3p, which in turn could induce significant cardiac hypertrophy [54, 55].
Several circulating miRNAs in serum are found to be altered by exercise, exhibiting numerous cardiac biological, and physiological effects mediating structural and functional adaptions. A total of thirty-six circulating cardiac-related miRNAs were investigated in a study. Most miRNAs upregulated by acute exercise and returned to normal for extended periods. Five of them (miR-1-5p, miR-133a-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-206-3p, and miR-221-3p) were found to be directly related to cardiac adaptation parameters. In contrast, two of them (miR-1-5p and miR-133a-5p) were associated with cardiac hypertrophy, suggesting that circulating microRNAs could act as promising biomarkers for evaluating the effects of exercise on cardiac hypertrophy and exercise-induced cardiac adaptation [87]. Bioinformatics databases, including MirPath v.3, TargetScan, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), and Gene Ontology (GO) analyses, were applied to analyze twenty-three exercise-regulated microRNAs from eight published studies to identify functional annotations and potential pathways associated with physiological cardiac hypertrophy induced by exercise. Various miRNA targets and biological pathways most likely associated with exercise-induced physiologic cardiac hypertrophy were identified, such as arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), fatty acid elongation, and extracellular matrix (ECM)-receptor interaction [88].
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of death in developed and
developing countries accounting for more than one-third of deaths globally. HF is
a common end phase in many CVDs and is one of the fastest-growing global health
problems [89]. There is still a lack of effective treatment that could reverse HF
in clinical setting. Studies on HF patients and HF animal models showed that ET
has cardio-protective effects, suggesting that ET could be used to excavate
targets for developing novel therapeutic strategies. miRNA expression patterns
are substantially altered following exercise stress due to changes in
transcription, post-transcriptional regulation, and miRNA biogenesis control, and
could reveal the cardio-protective mechanisms of ET [90]. The cause-effect
relationship between miRNA regulation and HF and the potency of ET in reversing
miRNAs toward baseline levels were investigated in a study using an
exercise-trained HF model in rats. HF caused the dysregulation of 55 miRNAs; 18
were restored to normal levels by high-intensity endurance training, thus,
contributing to the benefits of ET in improving cardiac function by bettering
Ca
miRNAs could act as novel therapeutic targets in treating human diseases,
particularly cardiovascular diseases. Based on preclinical studies, various
strategies are being developed to modulate miRNA activity to treat heart diseases
[95]. miR-210-3p has been reported to regulate angiogenesis after renal IRI by
targeting the VEGF signaling pathway. Huoxue-Anxin Recpe (HAR), a novel Chinese
Traditional Herb Medicine formulation, could upregulate the expression of
miR-210-3p and VEGF, thereby reducing the infarct size, alleviating interstitial
fibrosis and improving cardiac function in rats with acute MI [96]. Studies have
shown that miR-132-3p can be used as a therapeutic target for HF, and a
preclinical trial demonstrated the therapeutic efficacy of anti-miR-132-3p in
various models [97]. Inhibition of miR-92a-3p has been shown to exhibit several
beneficial effects towards cardiovascular diseases. Inhibiting miR-92a-3p with
antisense molecule can improve vascularization after myocardial infarction and
blood circulation after posterior limb ischemia. In addition, inhibition of
miR-92a-3p could accelerate wound healing in animal models with and without
metabolic syndrome. MRG-110 is a locked nucleic acid-based antisense
oligonucleotide targeting miR-92a-3p and has been shown to have therapeutic
effects on cardiovascular disease as well as wound healing in a human study [98].
The expression level of miR-1-5p was significantly upregulated in
H
Currently, many drug discovery programs focus on the development of miRNA-based therapies. In one such program, antisense oligonucleotide miravirsen, the first miRNA-targeting drug, modified by locked nucleic acid (LNA) antisense oligonucleotides, has been used to target miRNA-122 for the treatment of hepatitis C in the liver [105].
Many miRNA-targeting drugs are being investigated in clinical trials. Cardiac
microRNA-132-3p (miR-132) levels are elevated in patients with HF, and CDR132L, a
specific antisense oligonucleotide that inhibits miR-132-3p, is being used to
treat patients with HF. CDR132L improved cardiac function compared to the placebo
as well as being safe and well tolerated without significant dose-limiting
toxicity [106]. Rosuvastatin treatment significantly reduced the incidence of
cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing PCI,
compared with placebo, possibly by inhibiting miR-155-5p/Src homology
2-containing inositol phosphatase-1 (SHIP-1) signaling [107].
In addition, another study found that higher miR-33b-5p was associated with lower
ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABCA)1 mRNA in hypercholesterolemic patients, and rosuvastatin administration may
revert this condition. Mechanistically, Rosuvastatin could down-regulate the
miR-33b-5p and reverse the lower expression of ABCA1, playing a role in the
treatment of atherosclerosis [108]. In patients undergoing
noncoronary artery cardiac surgery, a randomized controlled trial showed that
simvastatin treatment significantly reduced miR-15a-5p levels, resulting in
increased expression of its target gene BCL-2 in cardiomyocytes. This
inhibited myocardial apoptosis and protected the myocardium, as demonstrated in
study [109]. Visceral obesity can cause various cardiovascular diseases.
Evidenced from the Cardiovascular Effects of Chronic Sildenafil in Men with Type 2 Diabetes (CECSID) trial demonstrated that sildenafil, a phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor,
decreased the expression of miR-22-3p compared to the placebo, and sirtuin1
(SIRT1), a target of miR-22-3p, was upregulated, leading to a shift in adipose
tissue cell composition towards a less inflammatory status [110]. Robust evidence
has elucidated that Propofol can ameliorate IRI in patients by increasing the
expression of miR-30b-5p and targeting Beclin-1, thereby inhibiting excessive
autophagy and apoptosis [111]. Several studies showed thatmiR-126-3p is important for maintaining vascular integrity [21, 112, 113, 114].
miR-126 deficiency was found to impair the differentiation and diversification of
embryonic ECs, suggesting its essential role in maintaining EC heterogeneity
[112]. miR-126-5p could maintain the integrity of endothelial cells under high
shear stress and autophagy by exerting non-canonical posttranslational functions.
The binding of miR-126-5p to argonaute-2 (AGO2) results in the formation of a
complex with MEX3A, which takes place on the surface of autophagic vesicles. This
complex subsequently enters the nucleus. Once inside, miR-126-5p dissociates from
AGO2 and interacts with CASP3 to suppress caspase dimerization and inhibit its
activity, thereby limiting cell apoptosis [21]. The potential roles of miR-126-3p
in resisting atherosclerosis were verified in human umbilical vein endothelial
cells (HUVECs). miR-126-3p was significantly reduced in the HUVECs treated with
ox-LDL. Whereas miR-126-3p mimics could restore the autophagic flux by inhibiting
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and reducing the ECs injury induced by ox-LDL
[113]. Another study found that miR-126-5p is expressed in endothelial cells and
retinal ganglion cells (RGC) of the postnatal retina and is involved in
protecting endothelial cells from apoptosis by regulating SET domain containing 5 (SETD5) during the
establishment of retinal vascular system [114]. miR-27a-3p can increase the
expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which leads to cardiovascular
inflammation and remodeling by the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-
It has been nearly 30 years since the discovery of these small non-coding single-stranded nucleic acids called miRNAs. These act as post-transcriptional gene regulators with a critical role in nearly all biological processes, including exercise-induced cardio-protection. Exercise-miRNAs are essential components for regulating the positive effects against pathological alterations. Furthermore, miRNA-drug therapies could mimic the beneficial effects of exercise and have a promising role in patients where exercise therapy is not an option. Using miRNAs as drug targets may aid in treating diseases with no viable therapeutic options, such as undruggable proteins. These can now be targeted and corrected through their upstream miRNA gene regulators. However, one of the main limitations is the chemical structure of miRNAs. Therefore, generating potential drug molecules with the necessary pharmacokinetic properties is still challenging and require careful optimization in the drug discovery process.
JJX and YJL had the idea for the paper, reviewed and edited it critically for important intellectual content. JG, JXS and YWY performed the literature search and analysis. JG, JXS, YWY, PG, GV, GPL, QYZ and FJ substantially contributed to the conception of the paper, drafted and critically revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This work was supported by the grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (82020108002 and 82225005 to JJ Xiao, 82170390 to J GAO), the grant from Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (21XD1421300 and 20DZ2255400 to JJ Xiao, 21ZR1422700 to J Gao), and the “Dawn” Program of Shanghai Education Commission (19SG34 to JJ Xiao).
The authors declare no conflict of interest. There is no financial, non-financial or intellectual involvement of the for-profit organization of Gururaja Vulugundam in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. Gururaja Vulugundam does not hold shares and/or stock options in the company Sanofi.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.