1 Department of Restorative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Saint-Joseph University, 1107 2180 Beirut, Lebanon
2 Department of Cardiology, Institute CARDIOMET, University Hospital of Toulouse, 31059 Toulouse, France
3 Faculty of Medicine, Holy Spirit University of Kaslik, 42160 Jounieh, Lebanon
4 Dental Materials Laboratory, Academic Area of Dentistry, Autonomous University of Hidalgo State, 42160 San Agustín Tlaxiaca, Mexico
5 Independent Researcher, 16030 Sestri Levante, Italy
6 Private Practice, “NZOZ SPS Dentist'' Dental Clinic and Postgraduate Course Centre, 30-033 Cracow, Poland
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: The link between dental, infective and obstructive cardiovascular diseases is debatable. Aim: To systematically review the literature to assess the association between dental conditions and development of cardiovascular disease. Methods: The systematic review was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines using PubMed (Medline), Web of Science, Scopus, EMBASE and SciELO. Results: Out of 6680 records, 82 articles were eligible for inclusion after reviewing titles and abstracts. No association between dental disease and cardiovascular disease has been observed in 10 studies while a potential link has been suggested by the remaining trials. Tooth loss and periodontitis are the main evaluated oral conditions while coronary artery disease, stroke, atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction represent the major cardiovascular events. The interaction between these two clinical entities is based on direct mechanism mediated by systemic inflammatory response, leakage of cytokines and endothelial cells invasion by oral pathogens and indirect mechanism mediated by common risk factors or confounders. Conclusions: It seems that tooth loss, periodontitis and poor oral hygiene increase the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular events, and subsequently oral health care professionals could contribute to public health cardiovascular control efforts.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
- cardiovascular disease
- clinical trials
- dental
- infection
- tooth disease
Despite the recommendations on aggressive management of cardiovascular risk factors for primary and secondary prevention in parallel to the impressive progression of the available medical and interventional therapeutic strategies, cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are still the main cause of death in the developed and developing countries [1, 2]. CVD includes a broad spectrum of infective and obstructive diseases like endocarditis, myocarditis, pericarditis, acute coronary syndrome including myocardial infarction, chronic coronary artery disease (CAD), stroke and peripheral artery disease. In the acute setting of cardiovascular events or during the follow-up of patients suffering from chronic coronary syndrome, medical practitioners systematically screened for the classical risk factors like smoking, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, systemic hypertension, family history of CAD, and obesity [3]. However, searching for the potentially cardiogenic atypical factors and understanding how they could affect the cardiovascular system may minimize the burden of CVD on the economic and health systems respectively [4]. For decades, researchers have been concerned by the link between oral disease and heart disease. Data from literature are conflicting and heterogeneous. Up to date, it is unclear whether the linking between these two diseases is a direct connection based on pathophysiological mechanisms making periodontal disease as independent predictor of CVD or indirect connection since these two entities commonly share multiple risk factors like smoking and unhealthy diet [5, 6]. People with oral disease are at higher risk for stroke, heart attack, and serious cardiovascular events [7, 8, 9, 10]. Periodontal disease, vertical bone lesions, endodontic disease, dental caries, dental infection were considered as dental conditions with some risk of entrapping a relationship with CVD [11, 12, 13, 14, 15]. Study findings revealed a positive association between the reduction in teeth number, abdominal aortic calcification [16], ischemic events [9, 10] and cardiovascular mortality [7, 8]. In addition, lesion originating from endodontic disease is able to trigger a systemic illness [17, 18]. Simultaneously, patients with CVD significantly present a lower teeth number and poor oral hygiene [19].
Considering that oral health status could directly influence the incidence, pathophysiology, and course of CVD, it is important to summarize the literature to better describe this potential association and the mechanisms which can explain this link. Herein, this paper aimed to systematically review the association between dental conditions and development of CVD.
A systematic review of clinical trials that examine the association of dental disease and CVD disease was performed according to the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA statement) [20]. The registration protocol was carried out in Open Science Framework with the registration number 0000-0002-2759-8984. The following PICOS strategy was used: population, human; intervention, dental disease, control, patients without CVD; outcome: CVD; type of study, observational studies, clinical trials. The research question was: Does the presence of dental disease is associated with the development of CVD?
An unlimited literature search was performed by two independent reviewers (RB and CECS) until November 11th, 2021 using PubMed (MEDLINE), Web of Science, Scopus, EMBASE and SciELO. The MeSH search terms in the previously cited databases are summarized in Table 1. All research studies were imported into Rayyan QCRI platform.
| Search strategy | |
|---|---|
| # 1 | Caries OR Dental health OR Periodontal disease OR Periapical Disease OR Tooth Diseases OR Oral pathology OR dental infection OR oral infection OR Dental Pulp Disease OR Oral Health |
| # 2 | Heart Disease OR Vascular Disease OR Coronary Artery Disease OR Coronary heart disease OR Atherothrombotic cardiovascular disease |
| # 3 | Clinical trials OR Controlled Clinical Trial OR Retrospective Studies OR Randomized Controlled Trial OR Prospective clinical trial OR Retrospective Study OR Prospective Studies OR Prospective Study OR Clinical Trial OR Randomized clinical trial |
| # 4 | # 1 AND # 2 AND # 3 |
The title and abstract of each recognized manuscript were examined by two independent reviewers (RB and CECS) to determine if the article should be considered for full-text review according to the following eligibility criteria: (1) Case-control and cross-sectional studies, cohorts, and randomized clinical trials reporting the relationship of any cardiovascular condition with the presence of any oral disease; (2) studies where the presence of an oral disease was clinically diagnosed; (3) studies where CVD was clearly defined; and (4) peer-reviewed articles published in the English, Spanish or Portuguese languages.
Case reports, case series, pilot studies, expert opinions, conference abstracts and reviews were excluded. In case of disagreements at the time of the collection of the papers for the full-text review, they were resolved by discussion and agreement by a third reviewer (LH).
Data of interest were extracted from the enrolled manuscripts via the Microsoft Office Excel 2019 program (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) and subsequently placed on a standardized form. Two reviewers (RB and LH), who received training in this software, performed data analysis. The extracted data from each manuscript include author names, year of publication, study type, number of participants, oral health condition, CVD, biomarkers, and principal outcomes.
The search resulted in the retrieval of 6680 records. After removal of duplicates, 6384 articles were screened, and 6294 were excluded based on the title or abstract. A total of 90 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility [20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110]. Of these, eight were not considered for the qualitative analysis: two were reviews [24, 54], two did not evaluated any CVD [51, 63], one was a pilot intervention study [32], one was an editorial letter [37], one was a clinical protocol [56] and one was a congress abstract [67]. Finally, 82 manuscripts were considered for the qualitative analysis (Fig. 1). Characteristics of the included studies in this systematic review are summarized in Table 2 (Ref. [21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 33, 34, 35, 36, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 52, 53, 55, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 64, 65, 66, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110]).
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Search flowchart according to the PRISMA Statement.
| Study (year) | Type of study | Number of participants | Oral health condition | Cardiovascular disease | Biomarkers measured | Principal outcomes |
| Abnet 2005 [21] | Cohort | 29,584 | Tooth loss | Heart disease | Not measured | Individuals with greater median number of teeth lost had statistically significant increased risk of death from heart disease and stroke of 28% and 12%, respectively. |
| Stroke | ||||||
| Aoyama 2018 [22] | Clinical trial | 897 | Periodontal conditions | Coronary heart disease | Not measured | The coronary artery disease patients generally had worse oral condition than the non-coronary artery disease patients. |
| Batty 2018 [23] | Cohort | 975,685 | Tooth loss | Coronary heart disease | Not measured | There was a moderate, positive association between tooth loss and coronary artery disease. |
| Berent 2011 [25] | Cross-sectional study | 466 | Periodontal conditions | Coronary heart disease | Not measured | Periodontal disease is a potentially risk factor for developing coronary artery disease. |
| Boillot 2015 [26] | Prospective cohort | 841 | Periodontal infections | Cardiovascular disease | Quantitative assessment of 11 bacterial species. Secretory phospholipase A2 (s-PLA2) and Lipoprotein-associated PLA2 | The relationship between periodontal microbiota and vascular diseases maybe linked to Greater s-PLA2 activity at higher tertiles. |
| Boillot 2016 [27] | Prospective multicentre observational study | 975 | Periodontal conditions | Acute myocardial infarction | Levels of IgG and IgA against Porphyromonas gingivalis, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Prevotella intermedia and Tannerella forsythia | In the setting of prior myocardial infarction, the risk of major cardiovascular events was not increased in association with the levels of circulating periodontopathogens antibodies. |
| Bokhari 2014 [28] | Cross-sectional study | 317 | Periodontitis | Coronary heart disease | Bleeding on probing, probing depth, clinical attachment level, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, fibrinogen and white blood cells | Bleeding on probing is strongly associated with systemic high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. |
| Caplan 2009 [29] | Cohort | 6651 | Endodontic therapy | Coronary heart disease | Not measured | Greater self-reported history of endodontic therapy was more likely to have coronary artery disease than those reporting no history of endodontic therapy. |
| Cho 2020 [30] | Cohort | 514,832 | Periodontal disease | Peripheral arterial disease | Not measured | The hazard ratio of peripheral arterial disease in the periodontitis group compared with that in the control group was 1.15. |
| Cho 2021 [31] | Retrospective cohort study | 298,128 | Periodontal Disease | Acute Myocardial Infarction and Stroke | Not measured | Severe periodontal disease increased total acute myocardial infarction events by 4.3%, total stroke events by 1.4%, and the total nonfatal major adverse cardiovascular events by 1.6%. |
| D’Aiuto 2006 [33] | Parallel-arm randomized clinical trial | 40 | Periodontal infections | Cardiovascular disease | C-reactive protein | Periodontal treatment reduces systemic inflammatory markers and improves lipid profiles. |
| Interleukin-6 | ||||||
| Leukocyte counts | ||||||
| High-density | ||||||
| lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| Desvarieux 2003 [34] | Prospective population-based cohort | 711 | Periodontal Disease and Tooth Loss | Carotid Artery Plaque | Serum total cholesterol | Tooth loss is related to subclinical atherosclerosis. |
| High-density | ||||||
| lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| Low-density | ||||||
| lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| Glodny 2013 [35] | Cross-sectional | 292 | Dental caries and chronic apical periodontitis | Atherosclerosis | Not measured | Dental caries, pulpal caries, and chronic apical periodontitis are associated positively with aortic atherosclerotic burden. |
| Gurkan 2014 [36] | Case Control | 32 | Periodontitis | Coronary Artery Ectasia | Not measured | There is an association between periodontitis and coronary artery ectasia. |
| Howell 2001 [38] | Double-blind placebo-controlled trial | 22,037 | Periodontal Disease | Nonfatal myocardial infarction | Not measured | Periodontal disease is not an independent predictor of subsequent cardiovascular disease. |
| Nonfatal stroke | ||||||
| Cardiovascular death | ||||||
| Hujoel 2000 [39] | Prospective cohort | 8032 | Periodontal disease | Coronary heart disease | Total serum cholesterol level | There is no evidence of a causal association between periodontal disease and coronary artery disease. |
| Hung 2003 [40] | Prospective cohort | 45,136 | Tooth loss | Peripheral arterial disease | High-density | Tooth loss is associated with peripheral arterial disease, especially among men with periodontal diseases. |
| lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| Janket 2013 [41] | Case Control | 256 | Tooth loss | Coronary artery disease | Low-density | The number and quality of remaining teeth impact on cardiovascular survival. |
| lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| C-Reactive Protein | ||||||
| Johansson 2014 [42] | Case Control | 161 | Periodontal disease | Coronary artery disease | Non measured | There is not a significant association coronary artery disease and periodontal status. |
| Joshipura 1996 [43] | Prospective cohort | 44,119 | Tooth loss and periodontal disease | Coronary heart disease | Non measured | Periodontal disease was not associated with coronary heart disease. Tooth loss may increase the risk of the later one. |
| Khouja 2019 [44] | Prospective cohort | 320 | Periodontal disease | Coronary artery disease | Non measured | Periodontal disease was a significant predictor of coronary heart disease among current smokers with diabetes. |
| Kotronia 2020 [45] | Cross-sectional | 5222 | Periodontal disease | Cardiovascular disease | C-reactive | Tooth loss was associated with some inflammatory, haemostatic and cardiac biomarkers. |
| Tooth loss | protein | |||||
| Dry mouth | interleukin-6 | |||||
| tissue plasminogen activator von Willebrand Factor | ||||||
| fibrin D-dimer | ||||||
| high sensitivity Troponin T | ||||||
| N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide | ||||||
| Li 2010 [46] | Prospective cohort study | 10,958 | Periodontal disease | Cardiovascular disease | Total cholesterol | Tooth loss was related to an increased risk of death due to cardiovascular disease. |
| Tooth loss | High-density | |||||
| lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| Lockhart 2009 [47] | Double-blind randomized placebo controlled study | 194 | Periodontal disease | Infective endocarditis–related bacteremia | Non measured | Bacteremia is associated with poor oral hygiene and gingival bleeding after toothbrushing. |
| Montenegro 2019 [48] | Single-blind parallel-design randomized controlled trial | 82 | Severe chronic periodontitis | Coronary artery disease | C-reactive | Periodontal therapy lower levels of systemic inflammation. |
| Glucose | ||||||
| Glycated hemoglobin | ||||||
| Triglycerides | ||||||
| Total cholesterol | ||||||
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| low-density lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| IL-1 | ||||||
| IL-6 | ||||||
| IL-8 | ||||||
| IL-10 | ||||||
| IFN- | ||||||
| TNF- | ||||||
| Morrison 1999 [49] | Retrospective cohort study | 12,795 | Periodontal disease | Coronary heart | Non measured | Poor dental health is associated with an increased risk of fatal coronary heart disease. |
| Cerebrovascular diseases | ||||||
| Nakib 2004 [50] | Cohort | 6931 | Periodontitis | Coronary artery calcification | Total cholesterol | Periodontitis is not associated with coronary artery calcification. |
| Triglycerides | ||||||
| High-density | ||||||
| lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| Napora 2016 [52] | Cross-sectional study | 119 | Periodontal disease | Risk cardiovascular parameters | Non measured | The most significant periodontal parameter in relation to the progression of atherosclerosis and left ventricle hypertrophy was shown to be clinical attachment loss. |
| Offenbacher 2009 [53] | Multicentered Randomized Controlled Trial | 303 | Periodontal status | Systemic levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein | High-sensitivity C-reactive protein | Periodontal therapy may lower hs-CRP levels among non-obese cardiovascular patients. |
| Peng 2017 [55] | Retrospective Cohort Study | 15,195 | Periodontal disease | Myocardial infarction | Non measured | Periodontal therapy lowers the rate of myocardial infarction and heart failure. |
| Heart failure Stroke | ||||||
| Saffi 2018 [57] | Randomized parallel-design examiner-blinded controlled trial | 69 | Periodontal disease | Endothelial function in coronary artery disease | C-reactive protein | Periodontal treatment maintained blood concentrations of markers of vascular inflammation. |
| Glucose | ||||||
| Glycated hemoglobin | ||||||
| Triglycerides | ||||||
| Total cholesterol | ||||||
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol | ||||||
| Seinost 2020 [58] | three-armed observer-blinded randomized controlled trial | 90 | Severe periodontitis | Peripheral arterial disease | C-reactive protein | Periodontal treatment did not reduce vascular inflammation in patients with peripheral arterial disease. |
| IL-6 | ||||||
| Leukocyte | ||||||
| HbA1c | ||||||
| Total cholesterol | ||||||
| HDL cholesterol | ||||||
| LDL cholesterol | ||||||
| Triglycerides | ||||||
| Shearer 2018 [59] | Cohort | 1139 | Periodontitis | Markers of cardiometabolic risk | glycated haemoglobin | Periodontitis was not associated with markers of cardiometabolic risk. |
| triglycerides | ||||||
| HDL cholesterol | ||||||
| Sia 2021 [60] | Cohort | 13,402 | Periodontitis | Incidental valvular heart disease | Non measured | Periodontitis was associated with a significant risk for valvular heart disease. Treatment of periodontal disease reduced the risk. |
| Spahr 2006 [61] | Case control study | 1315 | Periodontal infection | Coronary heart disease | Non measured | An association between periodontitis and presence of coronary heart disease was found. |
| Subha 2017 [62] | Double blinded randomized clinical trial | 45 | Generalized severe periodontitis | Serum markers of cardiovascular diseases | C-Reactive Protein | Periodontal treatment reduced the level of serum markers of cardiovascular diseases. |
| Total Cholesterol | ||||||
| High Density Lipid | ||||||
| Low Density Lipid | ||||||
| Triglycerides | ||||||
| Tiensripojamarn 2021 [64] | Cohort | 1850 | Periodontitis | Coronary heart disease | Non measured | Severe periodontitis is associated with an increased incidence of coronary heart disease. |
| Stroke | ||||||
| Tonetti 2009 [65] | Exclude. Review article. | |||||
| Ueno 2012 [66] | Case-control | 573 | Periodontitis | Coronary heart disease | Antibody levels of periodontopathic bacteria | Elevated antibody levels to periodontopathic bacteria is associated with an increased risk of coronary artery disease. |
| Vedin 2014 [68] | Cohort | 15,828 | Periodontitis | Coronary heart disease | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol | indicators of periodontal disease were common in the population with coronary heart disease. |
| Fasting p-glucose | ||||||
| High sensitivity C-reactive protein | ||||||
| Vedin 2015 [69] | Cohort | 15,456 | Tooth loss | Coronary heart disease | Non measured | Tooth loss predicted adverse cardiovascular outcomes. |
| Vernon 2011 [70] | Prospective longitudinal study | 43 | Periodontal disease | Cardiovascular disease | Carotid artery intima media thickness | Periodontal disease may contribute to cardiovascular risk. |
| Brachial artery flow-mediated dilation | ||||||
| Wilson 2018 [71] | Prospective cohort | 20,133 | Number of teeth, severity of dental plaque and the presence of oral lesions. | Incident myocardial infarction | Non measured | Poor oral health is associated with a slightly increased risk of myocardial infarction. |
| Xu 2011 [72] | Cohort | 10,849 | Periodontal disease | Heart disease | High sensitivity C-reactive protein | An association between periodontal disease and cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality was found. |
| Cerebrovascular diseases | White cell count | |||||
| Fibrinogen | ||||||
| Gomes 2015 [73] | Longitudinal Study | 278 dentate participants | Apical periodontitis (AP) | Cardiovascular events (CVE) including angina, myocardial infarction, and cardiovascular-related death | The total number of AP and RCT sites was determined from panoramic radiographs. EB was calculated as the sum of AP and RCT sites. Oral inflammatory burden (OIB) was calculated combining periodontal disease and EB | EB in midlife was an autonomous predictor of CVE. |
| Root canal treatment (RCT) | ||||||
| Endodontic burden (EB) | ||||||
| Isola 2019 [74] | Clinical trials | 143 patients | Periodontitis | Ischemic heart disease | Levels of vitamin C, antioxidants, and C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) were assessed with a commercially available kit | Patients with ischemic heart disease and periodontitis plus ischemic heart disease presented lower levels of salivary and serum vitamin C compared to healthy subjects and periodontitis patients. hs-CRP was a significant predictor of decreased salivary and serum vitamin C levels. |
| Gingival health | ||||||
| Pasqualini 2012 [75] | A case-controlled clinical trial | 100 participants | Oral infections | Acute myocardial infarction or unstable angina | Non-measured | Chronic oral diseases might increase the risk of coronary artery disease (CHD) and could be a risk factor for CHD. |
| Lee 2019 [76] | Observational study | Eighty-eight patients | Periodontal disease | Coronary artery disease | White blood cell count. | Tooth loss was linked with the presence of obstructive CAD in patients experiencing coronary assessment. |
| Haemoglobin | ||||||
| Total cholesterol | ||||||
| LDL cholesterol | ||||||
| HDL cholesterol | ||||||
| Triglyceride | ||||||
| Fasting glucose | ||||||
| Glycated haemoglobin | ||||||
| Emingil 2000 [77] | Clinical study | 120 patients | Periodontal disease | Acute myocardial infarction and chronic coronary heart disease | Missing teeth, restorations, probing depth (PD) and bleeding on probing (BOP) were recorded. Blood samples were taken on admission for measurements of serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-cholesterol), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-cholesterol), and fasting blood glucose level | Periodontal disease might be linked with acute myocardial infarction. |
| Stenman 2009 [78] | A cross-sectional study | n = 1056 | Chronic periodontitis (CP) | Ischemic heart disease (IHD) | Number of missing teeth, age, body mass index, waist/hip ratio, life satisfaction, hypertension, and levels of cholesterol and triglycerides | Periodontitis did not seem to have a statistically significant relationship with IHD. The number of missing teeth showed a strong association with IHD. |
| Eno Belinga 2018 [79] | A prospective observational study | 558 patients | Periodontal disease | Cardiovascular diseases | Non measured | A link between periodontal diseases and cardiovascular diseases were highlighted in this study. |
| Petersen 2013 [80] | Retroscpective | 531 patients | Chronic apical periodontitis (CAP) | Atherosclerosis | The volume of the aortic atherosclerotic burden | A correlation between CAP without endodontic treatment and aortic atherosclerotic burden was found. |
| Endodontic therapy | ||||||
| Cotti 2011 [81] | Prospective | 40 mens | AP | Atherosclerosis | All subjects underwent dental examination and complete cardiac assessment: physical examination, electrocardiogram, conventional and tissue Doppler echocardiography, and measurement of endothelial flow reserve (EFR). The following laboratory parameters were tested: interleukins -1, -2, and -6 (IL-1, IL-2, IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha, and asymmetrical dimethylarginine (ADMA) | Increased ADMA levels and their relationship with poor EFR and increased IL-2 might suggest the existence of an early endothelial dysfunction in young adults with AP. |
| Byon 2020 [82] | Retrospective Matched | 52,425 participants | Periodontitis | Atherosclerotic | Propensity score matching | The presence of periodontitis increased the risk of atherosclerosis. |
| Cohort Study | ||||||
| Çalapkorur 2016 [83] | Cross-sectional study | 60 patients | Periodontal disease | Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) | Ankle–brachial index values | Periodontitis did increase the odds ratio for having PAD. |
| Chen 2012 [84] | Prospective cohort design | 1 million persons | Tooth scaling | Cardiovascular events | Propensity score matching | Tooth scaling was associated with a reduced risk for upcoming cardiovascular events. |
| Vedin 2017 [85] | Clinical trial | 15,828 participants | Tooth loss | Coronary heart disease | Tooth loss levels | An association between tooth loss and coronary heart disease was found. |
| Linear and Cox regression models | ||||||
| Gugnani 2021 [86] | Parallel-group, unicentric, randomized, assessor- blinded, superiority trial | 48 patients | Severe periodontitis | Endothelial function | Cytokine levels | Treatment of severe periodontitis improved the endothelial function. |
| Santos‐Paul 2019 [87] | Single‐center, observational study | 409 patients | Periodontitis | Cardiovascular mortality | Demographic, clinical, and laboratory characteristics | Treatment of periodontitis reduced the incidence of cardiovascular events. |
| Oliver 2018 [88] | Retrospective | 428 children | Poor oral health | Infective endocarditis | Medical and dental records | Age, socio-economic status, and enamel defects were associated with caries experience, not severity of cardiac diagnoses. |
| Mariott 2013 [89] | Controlled clinical trial | 64 patients | CP | Heart disease | C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels | Treatment of periodontal disease reduced the risk of heart disease. |
| Persson 2003 [90] | Clinical research | 80 subjects | CP | Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) | Non-measured | Patients who at routine dental visits establish sign of bone loss nearby numerous teeth can probably be recognized as being at risk for future AMI. |
| Byun 2020 [91] | Cross-Sectional Analysis | 173,209 participants | Periodontitis | Cerebral stroke/ischemic heart disease | History of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia cerebral stroke (hemorrhagic or ischemic), ischemic heart disease (angina or myocardial infarction), and periodontitis. Their body mass index, smoking habit, alcohol intake nutritional intake, and income were recorded | An association between periodontitis and cardiovascular disease existed. |
| DeStefano 1993 [92] | Prospective cohort study | 9760 subjects | Dental disease | Coronary heart disease | Incidence of mortality or admission to hospital because of coronary heart disease; total mortality | Dental disease was associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease. |
| Naudi 2006 [93] | Retrospective study | 195 subjects | Dental health and preventive practices of child patients | Congenital heart disease | Oral examination | Children with cardiac problems should be identified in early infancy through liaison with medical colleagues and the family offered all the preventive advice and regular dental care necessary to prevent dental disease. |
| Findler 2013 [94] | A retrospective observational comparison study | 54 patients | Dental disease | Refractory heart failure | Non measured | This study provided essential dental treatment for severe heart failure patients with special attention to their medical problems and the use of medications and supporting means to prevent health-compromising situations is recommended. |
| Skilton 2011 [95] | A randomized, controlled trial study | 450 adults | Periodontal disease | Vascular health and inflammation | Inflammatory mediators (IL-1, IL-6, TNF) | Periodontal disease was related to CVD. |
| Saffi 2013 [96] | A randomized, parallel design, examiner blinded, controlled clinical trial | 100 participants | Periodontal therapy | Coronary artery disease | C-reactive protein, endothelial function, lipids and proinflammatory biomarkers | A relation between periodontal treatment and coronary artery disease existed. |
| Caúla 2014 [97] | Randomized clinical trial | 64 patients | Severe chronic periodontitis | Cardiovascular risk markers | Inflammatory markers | A reduction in the level of inflammatory biomarkers and improvement in lipid profiles were observed after medical treatment in patients with chronic periodontitis. |
| Gunupati, 2011 [98] | Cross-sectional randomized clinical study | 72 patients | CP | Acute myocardial infarction | Serum IgG and IgM aCL antibodies | The phase I periodontal therapy altered levels of serum IgG and IgM aCL antibodies in patients with AMI associated with chronic periodontitis. |
| Ide 2013 [99] | Randomized clinical study | 39 patients | CP | Acute-phase inflammatory and vascular responses | Circulating levels of cardiovascular and systemic inflammatory markers | Improvement in periodontal health did not influence the levels of vascular markers. |
| Tüter 2007 [100] | Clinical trial study | 36 patients | CP | Coronary artery disease | Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) levels of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) -1, -8, -13 and on serum levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hscrp) and lipid fractions | A combination produced statistically significant benefits in both local periodontal disease (GI and PD) and systemic biomarkers. |
| Cowan 2020 [101] | Multicenter population-based prospec- tive cohort study | 6638 participants | Endodontic infection (EI) | Risk of coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic stroke (IS), heart failure (HF), or venous thromboembolism (VTE) | Cox- proportional hazards regression models were used to estimate hazard ratios | Our results do not support an independent association between ET and development of CHD, IS, HF, or VTE. |
| Koppolu 2013 [102] | Clinical study | 40 subjects | Periodontitis | CVD | CRP & TNF- | Periodontal disease treatment significantly reduced the level of inflammatory biomarkers reflecting a possible relationship periodontitis and the pathogenesis of CVD. |
| Toregeani 2015 [103] | Clinical research | 98 patients | Periodontal disease | Atherosclerosis | Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and expression of laboratory markers | Preventing periodontal disease helped in preventing atherosclerosis. |
| Hoke 2011 [104] | Prospective | 411 patients | Dental disease | Atherosclerosis | Hyperlipidaemia | Dental status and oral hygiene were associated with mortality in patients with carotid atherosclerosis regardless of conventional cardiovascular risk factors. |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | ||||||
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol High-density lipoprotein cholesterol Glycated haemoglobin | ||||||
| Huang 2018 [105] | Cohort | 3613 patients | Periodontal disease | Atherosclerotic vascular disease | Cox proportional hazard model | A reduction in cardiovascular risk was observed after an intensive treatment of periodontal disease. |
| Bresolin 2013 [106] | Prospective clinical study | 33 children | Periodontal treatment | Atherosclerosis | Lipid profiles and inflammatory markers | Periodontal treatments were effective in children with congenital heart disease. |
| Chou 2015 [107] | A population-based follow-Up Study | 32,504 adult patients | Treated Periodontitis | Cardiovascular Events | Gender, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus | Periodontitis was linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular events. |
| Bokhari 2012 [108] | Randomized controlled trial | 317 patients | Non-surgical periodontal therapy | Coronary heart disease | Serum CRP levels | In the context of coexisting periodontitis and coronary artery disease, non-surgical mechanical periodontal approach decreased the levels of hs C-reactive protein, fibrinogen and white blood cells. |
| Fibrinogen and white blood cells | ||||||
| Holmlund 2010 [109] | Cohort | 7674 Subjects | Oral health | Cardiovascular mortality | Evaluation of the relation between remaining teeth, grading of periodontal disease, deep of periodontal pockets, bleeding on probe and cause of mortality | CVD is linked to oral health status. |
| Janket 2014 [110] | Cohort | 256 consecutive coronary artery disease patients | Oral infection | Cardiovascular mortality | C-reactive protein, fibrinogen | An improvement of 27% in CVD survival has been observed after incrementation of 10 teeth. |
Regarding oral health conditions, most of the studies evaluated the tooth loss and periodontal disease while the assessed cardiovascular events were stroke, CAD, acute myocardial infarction, peripheral artery disease, and atherosclerotic disease. Findings from the included studies in this systematic review were in favor of an association between the poor oral conditions (especially for the reduction in tooth number and periodontal disease) and the incidence of cardiovascular events (particularly for stroke and CAD). Also, the presence of periodontal disease was associated with higher level of inflammatory biomarkers.
Out of the 84 studies, ten studies failed to reveal a link between gum disease and CVD [5, 27, 38, 39, 42, 50, 58, 59, 99, 101]. Two studies declined the connection between periodontitis and ischemic heart disease while it showed an association between tooth loss and ischemic heart disease [43, 78]. Otherwise, tooth loss was associated with increased in cardiac mortality [21, 46], death from stroke [21], CAD [23, 85, 76], adverse cardiovascular outcomes [69], atherosclerosis [34], peripheral artery disease [40], inflammatory, hemostatic, and cardiac biomarkers [45] and impaired cardiovascular survival [41]. Periodontal disease was associated with CAD [25, 44, 64, 96], peripheral artery disease [30, 83], acute myocardial infarction [31, 77], stroke [31], adverse cardiovascular events [31, 70, 72, 107], coronary artery ectasia [36], valvular heart disease [60], cardiovascular disease [79, 91, 95, 102] and atherosclerosis [82]. In parallel, patients with CAD express higher level of periodontal disease indicators and have poor oral conditions [22, 68]. A reduction in systemic inflammatory and cardiac biomarkers [33, 48, 57, 62], improvement in lipid profile [33], decreasing in prevalence of acute myocardial infarction [55], heart failure [55], cardiovascular events [87], heart disease [89] and improvement in endothelial function [86] have been observed after periodontitis treatment and good oral health care. Lastly, increment of 10 teeth from the edentulous state resulted in 27% improvement in CVD survival [110].
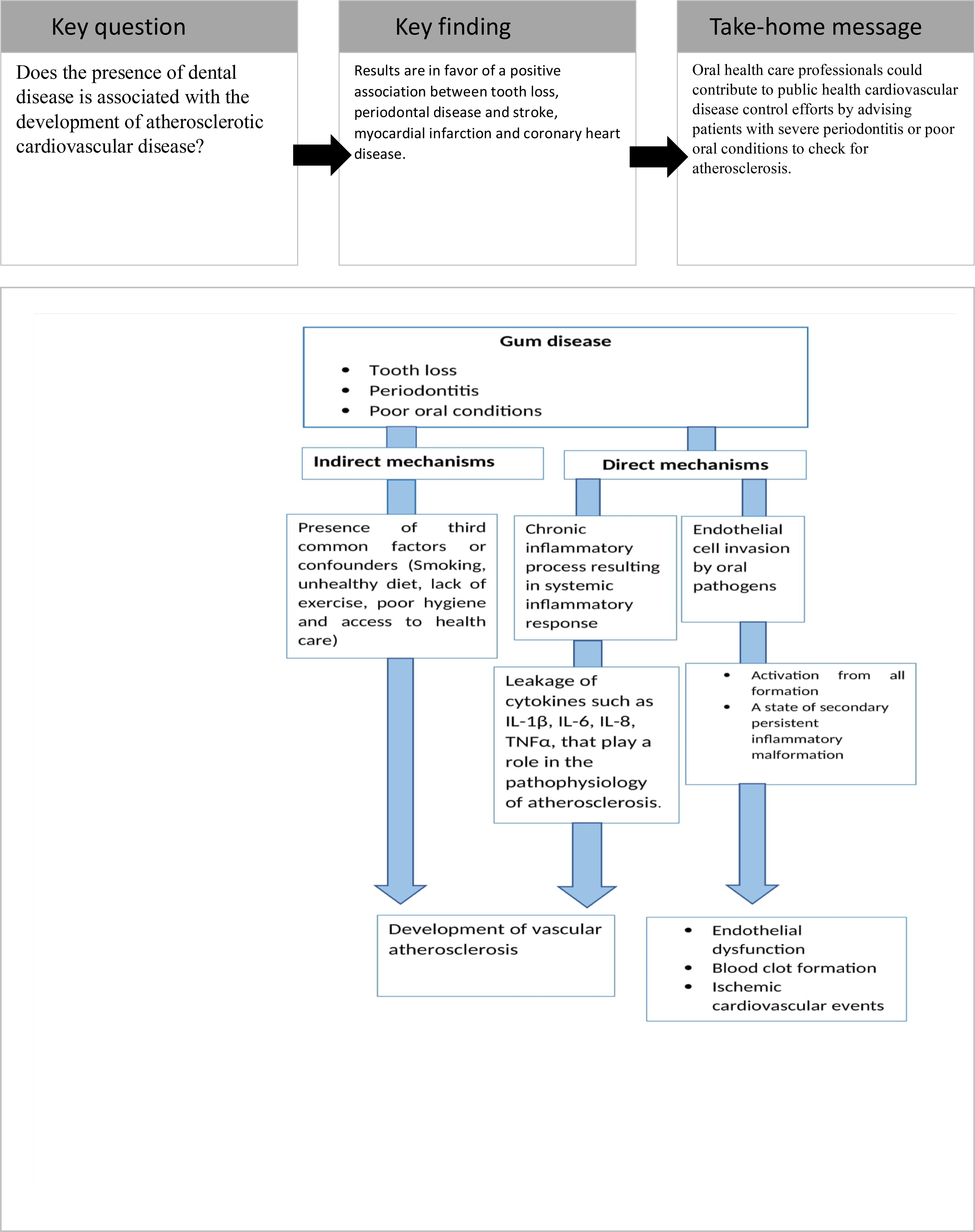
In this review, the association between dental conditions and development of CVD was studied and results were in favor for a positive association between tooth loss, periodontal disease, and CVD (Fig. 2). Conventional risk factors for atherosclerosis and CAD such as smoking, diabetes, hypertension, high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) serum level, obesity, male gender, and genetic predisposition have been evidently recognized and systematically searched after cardiovascular event [111]. Smoking and familial history play the pivotal role in the development of CVD in young patients [112]. Unconventional risk factors like chronic inflammatory reactions have also been identified as predictors of CVD. When the inflammation occurs, circulating markers and hemostatic factors were diligently linked with the development of myocardial infarction [113]. Particularly, chronic oral infection was associated with chronic heart diseases [114, 115]. Dental infections were associated with an increased prevalence of heart disease [75, 116], as the oral cavity was the main site of inflammation and chronic infection, especially in cases of tooth loss and chronic periodontal diseases [75, 117]. Many studies have discovered that the long-standing inflammatory stimuli of dental infection was implicated in the pathogenesis of CVD [117, 118], though further analyses have failed to notice a strong relationship between CVD and dental infection [39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114]. Oikarinen et al. [119] have documented a higher rate of periodontal infection among patients with CAD and Söder B et al. [118] have revealed that a high dental calculus score was correlated with increased incidence of angina pectoris. With regards to tooth loss and CAD and stroke risk, there are several unsolved issues [120]. The results obtained from this review suggest that there is a relationship between the number of teeth loss and the presence of cardiovascular events, like CAD, peripheral arterial disease, and increased risk of stroke death. This could be explained by the fact that first the number of tooth loss might be linked to some inflammatory, hemostatic, and cardiac biomarkers [45]. Second, one should consider that the main cause of tooth loss is dental caries, and carbohydrate intake is the chief dental caries cause. If specialist consider that carbohydrate intake is associated with increased risk of CVD and stroke, then the number of tooth loss could have indirect impact on these two last mentioned diseases [121]. Third, as the progress of tooth damage destroys periodontal tissues, thus oral microbial will accumulate into oral tissue, therefore promoting its growth and resulting in an increased risk of CVD and stroke [122]. All these factors were trustworthy for elucidating the relation between the CVD and tooth loss. Also, the release and persistence of early inflammatory biomarkers of periodontitis like TGF-
 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Review’s rational and findings with the potential mechanisms linking gum disease and development of cardiovascular disease.
In this context studying the link between oral and cardiovascular diseases, there is another topic of great importance that is worth mentioning. It is the concern of patients taking anticoagulant for cardiovascular disease and who undergo dental procedures. The management of such as patients seems much more complicated by dentists especially in the absence of a clear implemented protocol [126].
Several hypotheses have been raised to explain the association between dental and CVD. For example, pathogens causing gingivitis and periodontitis can travel into blood vessels elsewhere in the organism resulting in inflammation of the vascular wall, parietal damage and blood clots formation [122]. This rational was supported by polymerase chain reaction detection of oral bacterial remnants like streptococcus mutans, porphyromonas gingivalis, prevotella intermedia and tannerella forsythia in the fatty deposits within the atherosclerotic vessels [127, 128, 129]. It remains unclear by which mechanism periodontal pathogens could influence atherosclerosis after direct endothelial cells invasion. Triggering foam cell formation or provoking a state of secondary inflammation through their intracellular persistence leading to endothelial dysfunction have been suggested [130]. Another theory depends on the body’s immune response to chronic inflammatory process that sets off a cascade of vascular damage throughout the body including heart and brain. Periodontitis activates a systematic inflammatory response that produces high levels of different cytokines like Il-1
Overall, gum disease and CVD are multifactorial disorders requiring interaction between several factors and any potential contribution of one disease to the pathology of other should be carefully interpreted as many confounding variables affect both conditions. Health care professionals have to be aware of this association. Thus, dental practitioners should advise patients with severe periodontitis to check with physicians for atherosclerosis and cardiologists should insist on the importance of good oral hygiene.
In conclusion, the results obtained from this systematic review suggests that oral condition, especially the number of remaining teeth and the presence of periodontal disease increase the risk of cardiovascular events. It is likelihood that the association is mainly related to a chronic persistent systemic inflammatory reaction. Future research must be directed, especially randomized controlled clinical trials, with the purpose of gaining a better understanding of the link between oral and cardiac diseases.
AM, LH and JR designed the research study. RB, CECS and LH performed the research. All authors analyzed the data. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
Toulouse University Hospital provides article processing charge.
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Anthony Matta and Jerome Roncalli are serving as Guest Editors of this journal. We declare that Anthony Matta and Jerome Roncalli had no involvement in the peer review of this article and has no access to information regarding its peer review. Full responsibility for the editorial process for this article was delegated to Gary Tse, Sharen Lee and Tong Liu.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.


