1 College of Rehabilitation Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 350122 Fuzhou, Fujian, China
2 National-Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Rehabilitation Medicine Technology, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 350122 Fuzhou, Fujian, China
3 Rehabilitation Industry Institute, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 350122 Fuzhou, Fujian, China
4 Traditional Chinese Medicine Rehabilitation Research Center of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 350122 Fuzhou, Fujian, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
This study aimed to explore attention alteration in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients and their association with abnormalities of autonomic brain activity within the attention network to reveal the neuroimaging basis behind these changes.
A total of 25 MCI patients and 31 normal controls (NCs) were recruited for the study. The Test of Attention Performance (TAP) version 2.3 was used to evaluate alertness, selective attention, and divided attention in MCI patients and NCs. Subsequently, participants underwent resting-state magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to compare whole-brain autonomic activity characteristics between groups using the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF). Data preprocessing and analysis were conducted using Data Processing & Analysis of Brain Imaging in MATLAB R2018b.
There were significant differences in omissions of intrinsic alertness, total omissions of divided attention, omissions and correct of visual divided attention between the two groups. Meanwhile, independent sample t-tests indicated that the MCI group exhibited higher z-scored ALFF (zALFF) in the left middle occipital gyrus, left superior frontal gyrus (orbital part), and right inferior frontal gyrus (orbital part) when compared with the NC group. The MCI group exhibited reduced zALFF in the left median cingulate and paracingulate gyrus, left precuneus, and right rolandic operculum. Notably, the decreased zALFF in the left precuneus showed a significant negative correlation with divided attention.
Our findings suggest that patients with MCI exhibit relatively normal performance in selective attention and phase alertness tasks, while they demonstrate a decline in capacity for divided attention and intrinsic alertness tasks. Divided attention in MCI patients may be associated with abnormalities in spontaneous neural activity in the left precuneus. This study provides new and complementary insights into the neural basis of divided attention in patients with MCI.
Keywords
- cognitive dysfunction
- attention
- brain
- magnetic resonance imaging
- precuneus
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a syndrome considered as a prodromal stage of dementia characterized by a decline in cognitive cognition in one or more domains, although daily functioning may remain unaffected [1]. It is estimated that 10%–20% of people over the age of 65 years are diagnosed with MCI [2]. Some researchers suggest that MCI tends to progress toward a clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), with an annual conversion incidence rate of approximately 30% [3], with a lifetime risk ranging from 60%–90% [4]. The main clinical manifestations of MCI include memory loss, along with diminished attention, executive function, language function, visuospatial ability, and numeracy [5]. Research indicates that attention deficits predict cognitive decline in the early stages of probable AD and MCI [6]. Attention deficits in MCI patients may result in severe daily activity dysfunction [7].
Research has identified various attention functions, such as alertness, selective attention, and divided attention, which overlap with the domain of executive functions [8]. Numerous tests exist for the evaluation of attention performance at a behavioral level [9]. Thus, the Alertness, Go/No-go, Incompatibility, and Divided Attention subtests from the Test of Attention Performance (TAP, version 2.3, Psytest, Herzogenrath, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany) appear to capture three essential and independent components of attention function in both healthy and disease states. On a neuroanatomical level, attention is linked to two primary networks, the dorsal attention network (DAN), which is involved in top-down selection of stimuli and responses, and the ventral attention network (VAN), which predominantly directs attention to salient events and might act as a “circuit breaker” for the DAN [10]. One study also considered the frontoparietal network (FPN) and cingulo-opercular network (CON) as extended components of the attention network, which are associated with executive attention [8]. The two executive attention networks act relatively independently in producing top-down control: the CON is hypothesized to maintain task-sets while the FPN is thought to facilitate rapid adjustments in adaptive control [11].
An analytic review [12] identified divided attention as a strong predictor for the progression from MCI to AD. Divided attention refers to the capacity to concentrate on multiple tasks or stimuli simultaneously, commonly termed multi-tasking or dual tasking [13]. Studies have shown that divided attention impacts multiple aspects of individuals with AD, including difficulties in simultaneity of focus on two or more related stimuli, impairments in motor tasks such as gait and postural stability, and increased risk of falls in daily activities [14, 15]. Rodda et al. [16] observed that divided attention might be the earliest aspect of attentional control impacted in early stage AD. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) [17] and positron emission tomography (PET) studies [18] have reported that individuals with amnestic MCI (aMCI) exhibit impaired performance and decreased activation in the left prefrontal cortex when compared with normal control (NC) subjects. Alertness, a non-selective attention component, denotes a general readiness state that enhances stimulus processing and response initiation [19], fundamental to all cognitive and attentional performances [20], with the alertness network relying on frontal and parietal regions as well as the thalamus.
Selective attention [21] is the capability to filter out irrelevant stimuli and concentrate on a specific stimulus or task. It broadly covers component processes such as spatial and object selection in visual search, along with switching and response inhibition. Selective attention deteriorates linearly with AD progression [22]. A previous study suggested that patients with aMCI have subtle deficiencies in visual search (orienting) task, but their conflict resolution is similar to that of NCs [23], suggesting a potential dysfunction in selective attention. Van Dam et al. [24] conducted an fMRI study on aMCI patients and found that behavioral deficits in executive control of attention (such as enhanced conflict effects) coexist with corresponding neural deficits (reduced activation in the prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex). Executive control of attention plays a role in complex mental tasks by monitoring and resolving conflicts, acting as a potential top-down influence on selective attention. Selective attention involves cortical networks spanning multiple regions, although their exact localization is unclear.
Although deficits in attention and executive control of attention are often among the first deficits observed following memory loss in prodromal AD, their neural underpinnings have not yet been fully elucidated. Combining behavioral studies of attention mechanisms with advanced technologies, such as functional neuroimaging, may aid in accurately identifying the pathophysiology underlying deficits linked to MCI. Resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI) [25] is highly sensitive in detecting abnormalities in neuronal activity and function in neurodegenerative diseases. rs-fMRI measures the amplitude of the blood-oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signal, reflecting the energy expenditure and intensity of neuronal activity. The amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) is a data-driven rs-fMRI-based indicator that measures the total power of the BOLD signal within the 0.01 Hz to 0.1 Hz range, revealing abnormalities in spontaneous neural activity in brain regions. The ALFF indicates changes in neural activity associated with AD spectrum disorders, aiding discrimination between healthy individuals, MCI, and AD patients [26].
Despite the growing body of research on attention in MCI, the greatest focus has been on a single aspect of attention, such as divided attention, selective attention, or alertness. To the authors’ knowledge, no study has simultaneously investigated all three aspects of attention in MCI patients. Moreover, previous conflicting results have highlighted the influence of task paradigms and condition severity, which has contributed to the current confusion of attention deficits in MCI patients. Thus, in the present study, we administered four standard paradigm subtasks of the TAP to measure aspects of attention in MCI patients. Finally, to explore neural alteration in MCI patients, we used z-scored ALFF (zALFF) to investigate changes in the attention network and aimed to address the following questions: (i) are all subtypes of attention equally impacted in MCI patients and which attention subtypes are most affected? (ii) how is the attention network altered in patients with MCI? and (iii) what is the correlation between attention deficit and the zALFF value?
This cross-sectional study received approved
by the Ethics Committee of the Third People’s Hospital Affiliated to Fujian
University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Approval No. 2023-kl-017). A total of
25 NCs and 31 MCI patients were recruited from various communities in Fuzhou
between May and October, 2023. The inclusion criterion for MCI participants was
that they met the diagnostic criteria for MCI proposed by the international
working group [27]. Diagnostic criteria for MCI included: (1) cognitive decline
with a Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) score
All participants completed the Fuzhou version of the MoCA for global cognition, Geriatric Depression Scale, Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale for depression and anxiety, the Lawton-Brody Activity of Daily Living Assessment, and the Edinburgh Handedness Inventory to determine handedness. Furthermore, the TAP [9], which is a comprehensive battery of standard neuropsychological tests with subtests for alertness, divided attention, Go/No-go and incompatibility paradigms, was employed to assess attention domains including alertness, selective attention, and divided attention.
The alertness task assesses general response readiness and the capacity to enhance response readiness over a short period. The task was measured by simple reaction time tasks, performed under two different conditions: with (intrinsic alertness) and without (phasic alertness) a warning signal. Participants had to quickly respond by a button press whenever a cross appeared at the center of a screen.
The Go/No-go task (Test Form “2 of 5”) measured selective attention. Five squares, each featuring a unique pattern, were shown on a screen. Two of these squares were target stimuli and participants were required to respond as quickly as possible by pressing a button when they appeared. Additionally, no reaction was required for the other squares (see Fig. 1A,B). This test variant more closely resembled a choice reaction task.
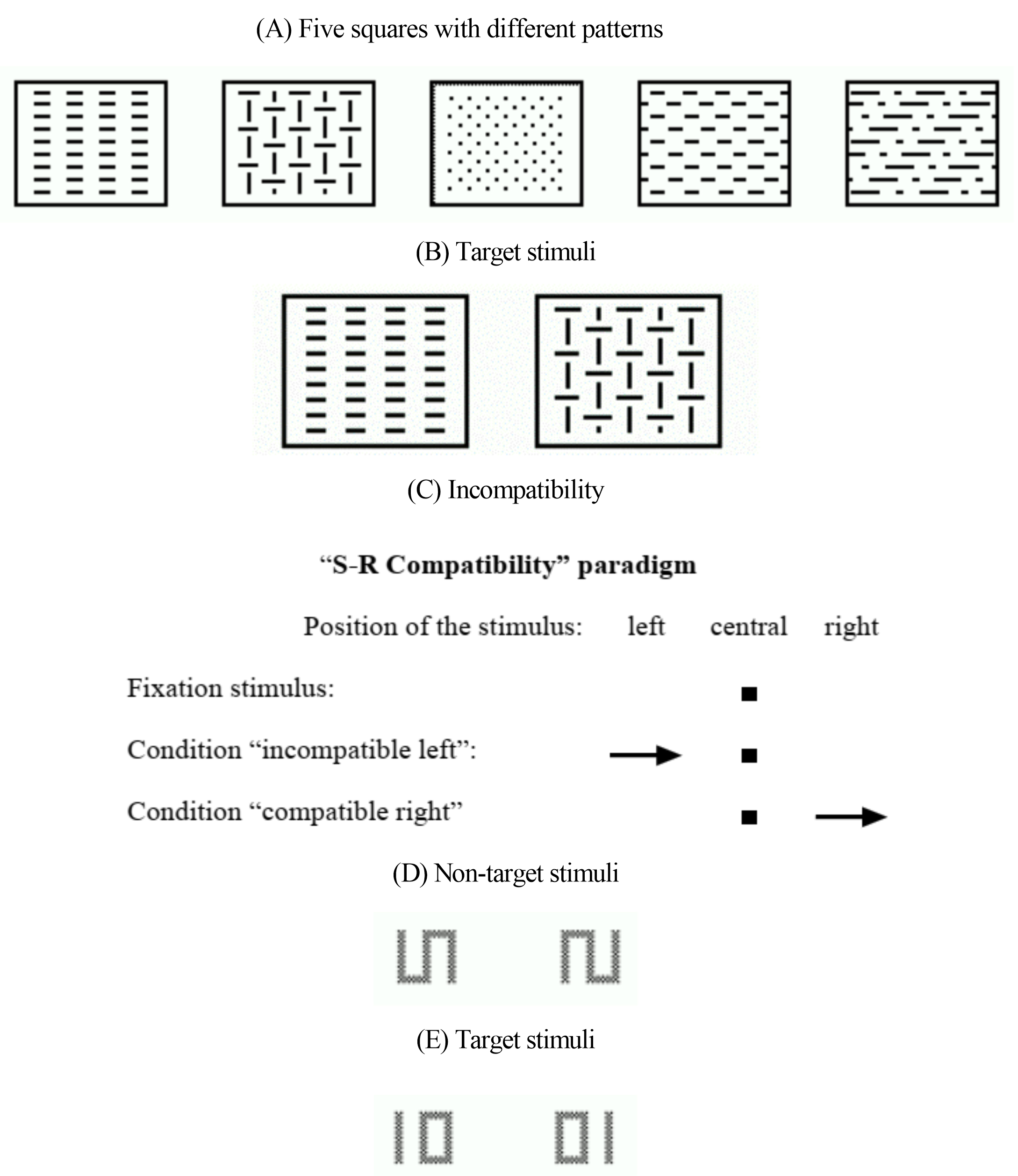 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
TAP Procedure. (A,B) Stimuli of the Go/No-go test. (C) S-R Compatibility paradigm in the incompatibility test. (D,E) Examples of non-target and target stimuli in the Divided Attention test. TAP, Test of Attention Performance; S-R, stimulus-reaction.
The incompatibility task assessed the tendency for interference in terms of stimulus-reaction incompatibility (Simon effect) [28], emphasizing the inhibition of selective attention [29]. In this task, arrows were displayed on either side of a fixation point, pointing left or right. Participants were required to respond with the right or left hand, depending on the direction of the arrow, regardless of the side on which the arrow appears. The compatible condition occurs when the side of the stimulus in the visual field and the direction of the response hand (corresponding to the direction of the arrow) align. The incompatible stimulus condition occurs when the arrow’s presentation side does not match its pointing direction (see Fig. 1C).
The divided attention task primarily assessed attention allocation and resource management (based on either shift or capacity theory). It required participants to simultaneously manage both visual and auditory tasks. For the visual task, stimuli such as a rotated “S” (90°), the mirror image of the rotated “S”, a “01”, or a “10” appeared in the center of the screen according to a predetermined rhythm (see Fig. 1D,E). Participants had to promptly press the button when the stimulus “01” or “10” was displayed. For the auditory task, a high and low pitched tone was alternately emitted at varying intervals, asynchronous to the appearance of the visual stimuli. Participants had to promptly press the button when high or low tones were emitted consecutively. In addition to this dual-task, a simple single task condition was also employed where only the visual or the auditory task was required to be processed.
MRI scans were performed using a 3T MRI scanner (SIGNA Architect, General
Electric Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) with a 16-channel head
coil. Gradient echo-planar images were obtained with the following parameters:
echo time (TE) = 30 ms, repetition time (TR) = 2000 ms, voxel size = 3.4
The preprocessing of rs-fMRI data and calculation of zALFF values were performed using the Data Processing & Analysis of the Brain Imaging toolbox [30] (http://rfmri.org/dpabi) within MATLAB R2018b (Mathworks Inc., Natick, MA, USA). The preprocessing involved removal of the initial 10 volumes of functional data. The remaining volumes underwent slice timing correction, spatial realignment within subjects, co-registration to each subject’s T1 images, and segmentation. Participants were excluded if head movement exceeded 3 mm in any direction or if head rotation was greater than 3°. The Friston 24-parameter model was employed for subject-level head motion correction. Images underwent normalization through structural image unified segmentation and were subsequently resampled to 3-mm cubic voxels. After applying a 4-mm3 FWHM Gaussian Kernel for smoothing, linear and quadratic trends were eliminated. Temporal filtering was not applied during preprocessing to allow for analysis of the entire frequency band.
A low-frequency band (0.01–0.1 Hz) was analyzed in this study. The ALFF
reflects the intensity of regional
spontaneous neural activity and may help to detect potential pathological
mechanisms in the AD spectrum [26, 31]. To minimize variability among different
participants, z-score standardization of the ALFF was used to measure
local functional activity. Consistent with prior research, results were deemed
significant at a voxel-wise threshold of p
Demographic and neuropsychological data of both groups were analyzed using SPSS version 26 (IMBL, Armonk, NY, USA). The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to assess normality. The independent sample t-test was applied to normally distributed continuous variables, the Mann-Whitney test was used for non-normally distributed variables, and categorical variables were analyzed using the Chi-squared test. A p-value threshold of 0.05 was assumed to determine statistical significance.
To investigate the association between the zALFF value and attention function, zALFF values were extracted from a 6-mm radius sphere centered at each peak label with significant differences between groups and a Pearson or Spearman’s Rank Correlation analysis was subsequently performed.
Demographic characteristics, such as sex, age, height, weight, body mass index,
hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and diseases of the heart system, showed no
statistically significant differences (see Table 1). A statistically significant
difference in years of education was observed between the MCI and NC groups
(p
| MCI (n = 25) | NC (n = 31) | t/Z/Chi-squared | p-value | ||
| Sex (Female/Male) | 9/16 | 10/21 | 0.086 | 0.769a | |
| Age (years) | 66.00 (63.00, 69.50) | 66.00 (61.00, 72.00) | –0.107 | 0.914b | |
| Height | 1.60 |
1.61 |
–0.387 | 0.701c | |
| Weight | 60.22 |
63.20 |
–1.169 | 0.247c | |
| Body mass index | 23.03 (21.46, 25.30) | 24.61 (21.88, 26.06) | –1.236 | 0.216b | |
| Education (years) | 8.56 |
11.66 |
–4.448 | 0.001c,* | |
| MoCA | 23.00 (21.00, 24.50) | 27.00 (26.00, 28.00) | –6.428 | 0.001b,* | |
| Comorbidity (yes/no) | |||||
| Hypertension | 17/8 | 20/11 | 0.075 | 0.784a | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 24/1 | 26/5 | 1.049 | 0.306a | |
| Diseases of the heart system | 25/0 | 31/0 | - | - | |
p-value*, statistically significant.
a Chi-squared test.
b Mann-Whitney test.
c Independent t-test. -, indicates the data were not applicable.
MCI, mild cognitive impairment; NC, normal control; MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment.
The results of the TAP tests showed statistically significant differences in
omissions of alertness without warning tone, correction of divided
attention/visual dual task, omissions of divided attention/visual dual task, and
the total omissions of divided attention (p
| MCI (n = 25) | NC (n = 31) | t/Z | p-value | |
| Alertness without warning — correct (n) | 40.00 (40.00, 40.00) | 40.00 (40.00, 40.00) | 0.000 | 1.000b |
| Alertness without warning — omissions (n) | 0.00 (0.00, 2.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | –2.132 | 0.033b,* |
| Alertness without warning — median (ms) | 410.81 |
381.85 |
0.971 | 0.336c |
| Alertness with warning — correct (n) | 40.00 (40.00, 40.00) | 40.00 (40.00, 40.00) | –0.880 | 0.379b |
| Alertness with warning — omissions (n) | 0.00 (0.00, 0.75) | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | –1.942 | 0.052b |
| Alertness with warning — median (ms) | 374.00 (320.25, 405.25) | 346.00 (314.00, 376.00) | –0.993 | 0.321b |
| Alertness-index phasic | 0.03 (–0.01, 0.14) | 0.07 (–0.04, 0.14) | –0.119 | 0.905b |
| Go-No-go (2 of 5) — correct (n) | 24.00 (20.00, 24.00) | 24.00 (23.00, 24.00) | –0.694 | 0.488b |
| Go-No-go (2 of 5) — errors (n) | 1.00 (0.00, 4.50) | 0.00 (0.00, 2.00) | –1.094 | 0.274b |
| Go-No-go (2 of 5) — omissions (n) | 0.00 (0.00, 4.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 1.00) | –0.694 | 0.488b |
| Go-No-go (2 of 5) — median (ms) | 698.00 (647.25, 749.75) | 692.50 (617.50, 740.00) | –0.725 | 0.468b |
| Incompatible — correct (n) | 29.00 (27.00, 30.00) | 29.00 (27.00, 30.00) | –0.197 | 0.844b |
| Incompatible — errors (n) | 1.00 (0.00, 2.50) | 1.00 (0.00, 2.00) | –0.233 | 0.816b |
| Incompatible — omissions (n) | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 1.00) | –0.301 | 0.763b |
| Incompatible — median (ms) | 651.00 (535.50, 813.25) | 649.00 (577.00, 767.00) | –0.478 | 0.633b |
| Divided attention: auditory — correct (n) | 19.00 (14.50, 19.00) | 18.00 (16.00, 20.00) | –0.511 | 0.609b |
| Divided attention: auditory — omissions (n) | 1.00 (1.00, 5.00) | 2.00 (0.00, 4.00) | –0.461 | 0.645b |
| Divided attention: auditory — median (ms) | 688.00 (587.00, 845.00) | 647.00 (617.50, 768.00) | –0.096 | 0.923b |
| Divided attention: visual — correct (n) | 17.00 (7.50, 20.00) | 20.00 (19.00, 20.00) | –2.356 | 0.018b,* |
| Divided attention: visual — omissions (n) | 2.00 (0.00, 7.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 1.00) | –2.258 | 0.024b,* |
| Divided attention: visual — median (ms) | 663.00 (576.50, 783.50) | 608.00 (542.00, 675.38) | –1.920 | 0.055b |
| Divided attention: total — errors (n) | 2.00 (0.50, 6.50) | 1.00 (0.00, 2.00) | –0.927 | 0.354b |
| Divided attention: total — omissions (n) | 5.00 (2.50, 16.00) | 3.00 (1.00, 5.00) | –2.144 | 0.032b,* |
p-value*, statistically significant.
b Mann-Whitney test.
c Independent t-test.
Intergroup comparison of zALFF values revealed that the MCI group exhibited significantly higher zALFF values in the left middle occipital gyrus (MOG), left superior frontal gyrus orbital part (ORBsup), and right inferior frontal gyrus orbital part (ORBinf) when compared with the NC group. Conversely, the left median cingulate and paracingulate gyri (MCC), left precuneus (PCUN), and right rolandic operculum (ROL) had significantly lower zALFF values. See Table 3 and Fig. 2 for details.
| Contrast | Brain region | MNI coordinates | t-value | Cluster | ||
| X | Y | Z | ||||
| MCI |
L_MOG | –36 | –69 | 24 | 4.62242 | 226 |
| L_ORBsup | –24 | 18 | –12 | 3.65016 | 90 | |
| R_ORBinf | 24 | 27 | –18 | 3.50226 | 77 | |
| NC |
L_MCC | –9 | 9 | 36 | –4.58538 | 195 |
| L_PCUN | –15 | –66 | 30 | –3.60058 | 106 | |
| R_ROL | 48 | –15 | 18 | –3.64084 | 77 | |
MOG, middle occipital gyrus; ORBsup, superior frontal gyrus orbital part; ORBinf, inferior frontal gyrus orbital part; MCC, median cingulate and paracingulate gyri; PCUN, precuneus; ROL, rolandic operculum; MNI, Montreal Neurological Institute; zALFF, z-scored amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation.
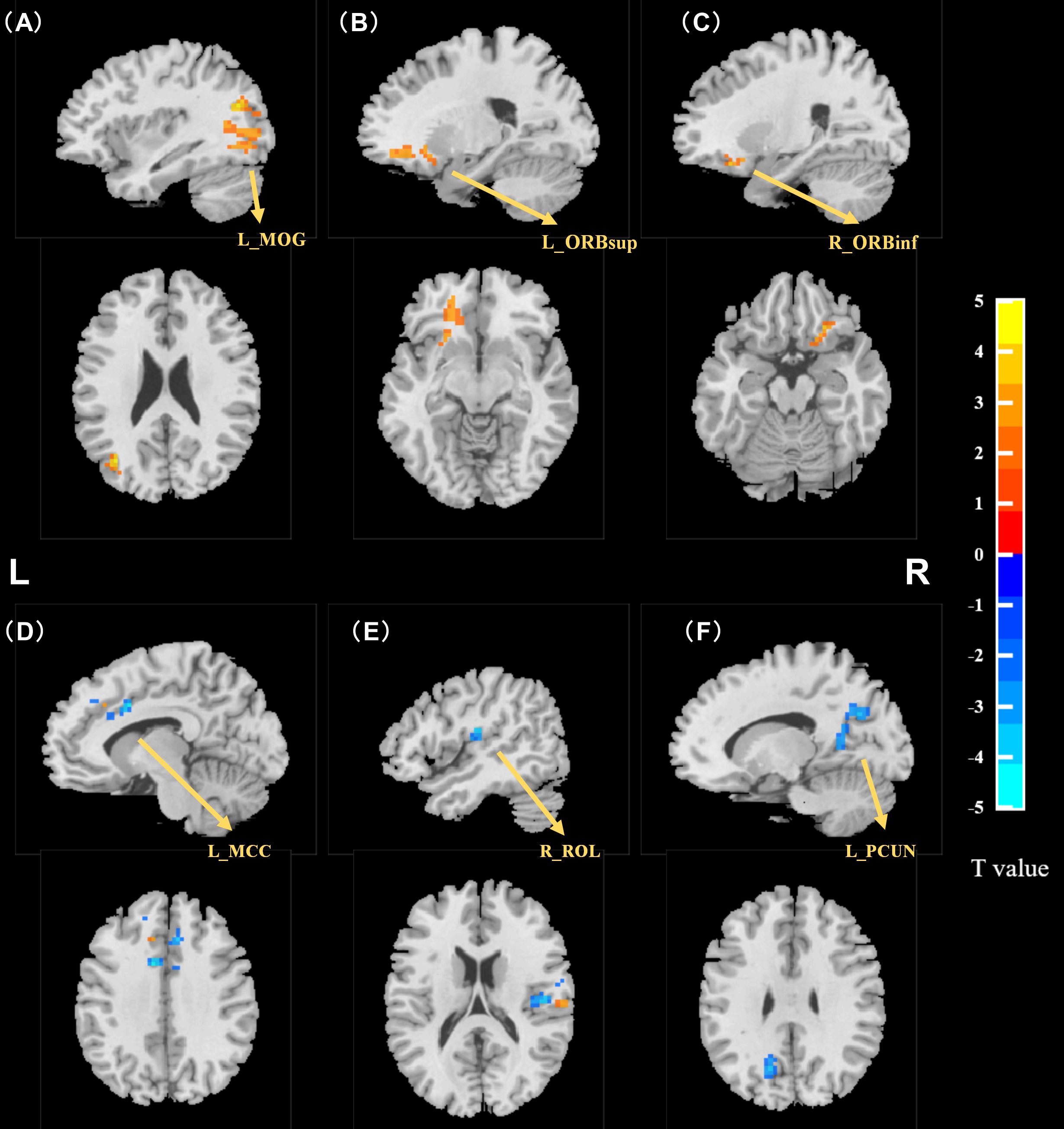 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
Independent sample t-test results for zALFF (MCI vs
NC). zALFF was higher in the MCI group than in the NC group in the (A) left
middle occipital gyrus, (B) left superior frontal gyrus orbital part, and (C)
right inferior frontal gyrus orbital part (two-tailed, voxel threshold p
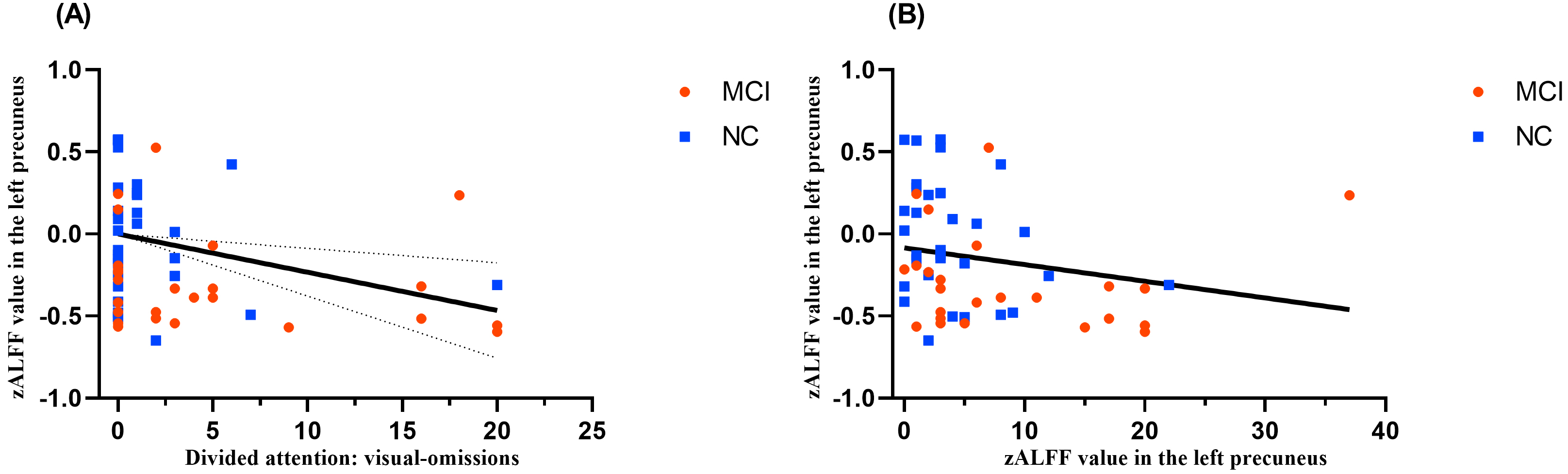
Partial correlation analysis revealed the following statistically significant findings: zALFF in L_PCUN was negatively correlated with omissions of divided attention/visual dual task (r = –0.275, p = 0.04, see Fig. 3A) and total omissions of divided attention (r = –0.342, p = 0.01, see Fig. 3B).
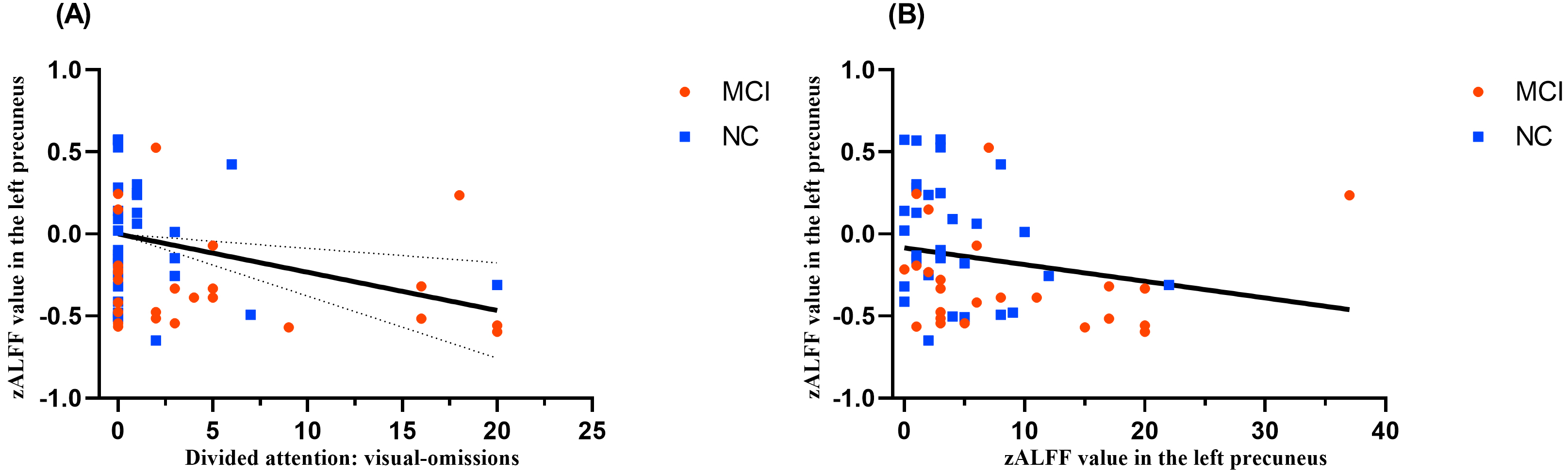 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.
Correlation analysis between attention and zALFF values. (A) Correlation of zALFF values in the left precuneus and omissions of divided attention/visual dual task. (B) Correlation of zALFF values in the left precuneus and total omissions of divided attention.
Divided attention is an early detectable deficit in aMCI that can be correlated with fMRI changes [17]. This is the first study to detect a divided attention deficit in MCI that is significantly associated with the left precuneus.
Normal aging leads to decreased efficiency in intrinsic and phasic alertness, causing older adults to perform more poorly than younger individuals on related tasks [33]. Alertness deficits can substantially impact behavioral and cognitive impairments associated with MCI [34]. The current study identified a significant difference in the omissions of alertness without a warning tone between the groups, suggesting that individuals with MCI showed a reduced intrinsic alertness response compared with healthy elderly individuals. Specifically, MCI individuals were unable to maintain a preparatory response over an extended period of time. In contrast, no significant difference in phasic alertness was found (i.e., briefly focusing attention on an anticipated event) between the groups. Although there was no significant difference in reaction time for alertness, the MCI group exhibited diminished intrinsic and phasic alertness when compared with the NC group. This study supports the conclusion that reduced information processing speed is a key cognitive deficit in MCI. In the Go/No-go test, the “2 out of 5” task addresses response selection problems. This task was selected to emphasize higher memory demands, which resulted in significantly increased response latency, thereby suppressing immediate impulsive response [35]. The findings indicate that there was no significant difference in response selection between the two groups. However, whether patients with MCI exhibit more inhibitory control problems, another important aspect of selective attention, requires further investigation. The incompatibility task results align with the results of previous studies [23], indicating that inhibition control was not impaired in the MCI group when compared with the NC group. However, a study by Perry et al. [21] observed that patients with mild AD (mean MMSE = 20.4) exhibited deficits in sustained, divided, and selective attention tasks. In the early stages of the disease (mean MMSE = 26.1), patients performed relatively well on sustained and divided attention tasks, but showed deficits in selective attention tasks including response selection and inhibition, auditory target selection, and attentional switching speed. The differing findings may be related to disease severity and assessment paradigms, and further research is required to determine whether selective attention is affected in patients with MCI. Divided attention, an increasingly important clinical aspect of attention in MCI, refers to the ability to allocate cognitive resources simultaneously across multiple targets or processes. According to the capacity model, the simultaneous performance of two tasks requires a division of resources and performance can be improved by exerting a higher level of effort. The key criterion for the successful division of attention in this procedure is the omissions, as reaction times are of secondary importance. The number of visual omissions and the total number of omissions were statistically different between the two groups, suggesting a considerable limitation in attention capacity. Consistent with previous studies [17, 36], the present study confirmed that individuals with MCI have a significant deficit in divided attention. It is noteworthy that visual stimuli were most frequently omitted. Further clarification is needed to determine whether the high rate of visual omissions is entirely attributable to reduced capacity or whether it also reflects an impairment of visual processing.
Neuroimaging studies indicate that the frontal and parietal cortices play a
crucial role in producing attention-related regulatory signals that feed back to
the visual cortex. The attention network comprises two primary
components: higher-order nodes, such as the frontal and parietal cortices, which
regulate spatial attention and lower-order nodes, such as the sensory cortex,
where attention-related sensory processing changes are implemented [37]. Current
literature indicates that the brain regions containing pathological Tau
accumulation overlap significantly with areas of the visual network (VIN) [38],
particularly the occipital and lingual gyri, which are stable brain regions
within the VIN [39]. The occipital lobe is the primary processing area for visual
stimuli in the brain and mainly responsible for object recognition, including the
functional properties of objects. The middle occipital gyrus is related to
spatial perception around the human body [40]. In MCI patients, reduced
activation has been mainly observed in the FPN, whereas AD patients exhibit more
hypoactivation in the VIN, and inefficient VIN activation may disrupt higher
cognitive processing in AD patients [41]. The current study observed increased
zALFF values in the left middle occipital gyrus in the MCI group when compared
with the NC group. A meta-analysis [31] revealed that patients with aMCI
exhibited higher ALFFs in the right lingual gyrus, left middle occipital gyrus,
left hippocampus, and left inferior temporal gyrus when compared with NC groups.
Concordant with prior findings, we identified that there were functional
impairments and compensatory mechanisms in the left middle occipital gyrus. We
also found that zALFF values increased in the left superior orbitofrontal gyrus
and right orbitofrontal inferior gyrus in the MCI group. These two brain regions
are key parts of the prefrontal cortex and are typically involved in cognitive
functions including attention, inhibitory control, habit formation and working,
and spatial or long-term memory [42]. A previous rs-fMRI study in AD has
identified abnormal functional connectivity in the prefrontal cortex, a region
believed to exert top-down control by connecting various brain regions to
facilitate complex cognitive processes [43]. According to prior research [44],
increased zALFF values in these brain regions might reflect neuronal compensation
and/or amyloid-
Another important finding of this study was that zALFF values were reduced in the left middle cingulate gyrus (Brodmann Area 24) and left precuneus, which are key brain regions of the FPN. An imaging study has implicated broad areas of the FPN as contributors to attentional control across various forms of top-down selection [45]. The cingulate cortex is involved in inhibition control, behavioral correction, and emotional processing regulation. Increased functional connectivity between the hippocampus and cingulate gyrus has been detected prior to MCI [46]. The middle cingulate cortex is associated with higher-order functions including attention allocation, reward, decision-making, morality and ethics, impulse control (e.g., error detection and correction), and emotion processing. The middle cingulate cortex is connected to the prefrontal cortex, parietal lobe, and motor system, serving as a hub for “top-down and bottom-up attention” primarily for response selection and feedback-driven decision making. A study on ALFF and fractional ALFF within the Alzheimer Spectrum [26] revealed a significant decreasing trend of values across several brain regions, including the right MCC, bilateral inferior cerebellum lobe, and bilateral precuneus in ALFF/fALFF. Cera et al. [47] discovered that cognitive decline in MCI impacts the global functional connectivity of the cingulate cortex, particularly the dorsal posterior MCC, with a significant difference in the functional connectivity pattern when compared with healthy elderly individuals. A neuroimaging study [48] indicates that the MCC is crucial for cognition and attention, becoming active during cognitively demanding tasks that require stimulus response selection in the presence of competing streams of information such as divided attention and work-memory tasks. The precuneus, located in the posterior parietal cortex, is involved in a wide range of highly integrated tasks such as visuo-spatial imagery, episodic memory retrieval, and self-processing operations [49]. Lower functional connectivity has been observed between the precuneus and retrosplenial cortex in patients with subjective cognitive decline [50]. A meta-regression analysis has shown that the increased severity of cognitive impairment in aMCI patients was associated with greater decreases in ALFFs in the cuneus/precuneus cortices [31]. Teipel et al. [51] reported reduced cortical activation in cerebellar and posterior cortical areas, such as the parietal cortex, precuneus, posterior lateral temporal cortex, and parahippocampal gyrus, during working memory performance in AD/MCI patients when compared with healthy older adults. Brain activation patterns in healthy older adults have also revealed that divided attention is associated with substantial activation within the precuneus and posterior parietal regions [52]. Functional neuroimaging studies have shown that episodic memory processes not only require medial temporal lobe activity, but also attention functions [53]. This is consistent with the results reported here, suggesting that attention is crucial in episodic memory processes. Additionally, decreased zALFF values in the left precuneus were significantly negatively correlated with divided attention. These findings suggest that divided attention might be significantly enhanced in patients with MCI by modulating the function of the left precuneus. Further, we found decreased zALFF values in the right rolandic operculum of the MCI group. The rolandic operculum, situated at the junction of the frontal-parietal lobes, potentially acts as a key hub for information transfer between the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes in bottom-up attention modulation. These changes may directly imply reduced spontaneous neural activity in these regions, which may be due to neurophysiological processes, indicating a functional deficit or downregulation of excitability.
This study had several limitations. First, the sample size was relatively small and future research should aim to collect a larger sample to better substantiate more reliable conclusions and broaden the generalizability of these findings. Second, as a cross-sectional study, it does not provide insights into the temporal changes in spontaneous brain activity and its relationship to potential attention deficits over time. Longitudinal studies are necessary to better understand these processes. Longitudinal studies can repeatedly measure the same group at multiple time points, thereby clarifying the temporal trajectory of zALFF. Simultaneously, it allows better control of confounding factors and reduces bias in causal inference, enhancing focus on the interaction of zALFF and attention. Finally, the study focused only on the ALFF as an analytical method. Future studies could explore the attention alteration and attention network characteristics in MCI patients using multimodal brain imaging techniques.
The findings suggest that patients with MCI exhibit relatively normal performance on selective attention and phasic alertness tasks, but show a reduced capacity for divided attention and intrinsic alertness tasks. The decrement in capacity for divided attention in MCI patients might be associated with abnormalities in spontaneous neural activity in the left precuneus. This study offers novel insights into the neural basis of divided attention in MCI patients, offering a valuable reference for understanding attention alteration and alterations in the attention network, which might contribute to the early diagnosis and prevention of MCI.
The datasets used and/or analyzed for this study are available on request to the corresponding authors.
JL, YZ, YWY designed the research study and wrote the manuscript. JJZ, WLC, HYX collected data. YPX and QRX analyzed data. SXL and JH conceptualized and designed the study and give final approval of the version to be published. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
The studies involving human participants was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Third People’s Hospital Affiliated to Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Ethic Approval Number: 2023-kl-017). The study was carried out in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and all participants had signed informed consent.
We thank all participants and their families who participated in this study.
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2020J01754) and School Management Project of Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Program Number: X2024004 and X2024003.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.