1. Introduction
Stroke is a prevalent cerebrovascular disorder characterized by significant
rates of disability and mortality. The two primary classifications of stroke
are hemorrhagic stroke and ischemic stroke. Ischemic strokes
account for approximately 80% of all stroke cases, with middle cerebral artery
thromboembolism as the principal etiology [1]. Patients who experience ischemic
stroke frequently exhibit significant neurological impairments. At present, the
sole interventions that have demonstrated efficacy during the acute phase of
ischemic stroke are the administration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and
mechanical thrombectomy [2]. Unfortunately, the therapeutic
window is narrow, and only a small proportion of patients are
eligible [3, 4, 5]. Therefore, potential drugs for ischemic stroke
treatment are urgently needed. The pathophysiology of ischemic
stroke involves complicated molecular mechanisms, such as
oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Available
pharmacological therapies targeting crucial stages in the pathophysiology of
ischemic stroke aim to promote optimal poststroke neurological recovery by
reducing neuronal apoptosis, inhibiting inflammation, promoting angiogenesis, and
removing free radicals [6, 7]. However, the performance of these therapies is not
clinically satisfactory. In recent years, promoting
neurogenesis from endogenous neural stem cells (NSCs)
has emerged as a promising therapeutic approach for treating
ischemic stroke [8].
Josef Altman was the first to present evidence of neurogenesis in the adult
brain when he identified newly formed neurons and glial cells through the use of
tritiated thymidine to label proliferating cells [9]. Since then, accumulating
evidence has revealed that neurogenesis persists in the adult
mammalian brain. Although research on adult neurogenesis in
humans is controversial, the occurrence of neurogenesis in the adult human brain
is widely acknowledged [10, 11]. Presently, two extensively
documented neurogenic niches housing adult NSCs exist within the adult brain: the
subventricular zone (SVZ) located in the lateral ventricle (LV)
and the subgranular zone (SGZ) situated in the dentate gyrus (DG) of the
hippocampus. Under normal physiological conditions, SVZ NSCs
are responsible for the production of transit-amplifying cells
(TACs), subsequently leading to the emergence of neuroblasts. These neuroblasts
undergo migration along the rostral migratory stream (RMS) to reach the olfactory
bulb (OB), where they differentiate into interneurons that play a crucial role in
the sense of smell. NSCs located in the SGZ are responsible for generating
excitatory glutamatergic neurons, which subsequently integrate into the granule
cell layer of the DG. These neurons play a crucial role in
spatial and temporal memory processing. During ischemic stroke,
SGZ NSCs proliferate and migrate toward the granule cell layer within the DG,
although their migration remains confined within the boundaries of the
hippocampus [12]. Simultaneously, ischemic
injury drastically increases neurogenesis in both rodent and human SVZs, and
neuroblasts deviate from the conventional pathway toward the
adjacent parenchyma and striatal ischemic penumbra. Within the
ischemic penumbra, a limited population of neuroblasts produces neurons,
potentially facilitating tissue restoration and the recovery of
locomotor function. However, a significant proportion of NSCs undergo
differentiation into astrocytes, which subsequently transform into reactive
astrocytes that play a crucial role in the process of glial scar formation. This
impedes the effective repair of nerve injuries [8, 13, 14]. A
prior investigation employed a genetic approach utilizing the herpes simplex
virus thymidine kinase/ganciclovir (HSV-TK/GCV) suicide system to eliminate
doublecortin (DCX) neuroblasts, which led to increased
infarct size and exacerbated neurological impairments in mice that underwent
middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) [15]. These findings indicate that
neurogenesis induced by ischemia appears to play a role in alleviating
histological and neurobehavioral impairments.
Taken together, these findings indicate that enhancing neurogenesis and
augmenting neuronal regeneration within the ischemic penumbra subsequent to
cerebral ischemia can potentially enhance the restoration of neurological
function. Multiple pathways are believed to be implicated in adult neurogenesis,
including the Notch signaling pathway [16], Sonic Hedgehog signaling (SHH)
pathway [17, 18], and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway [19, 20]. This review primarily concentrates on the role of the
Wnt/-catenin pathway in adult neurogenesis and its potential therapeutic
implications for the management of cerebral ischemia (Fig. 1).
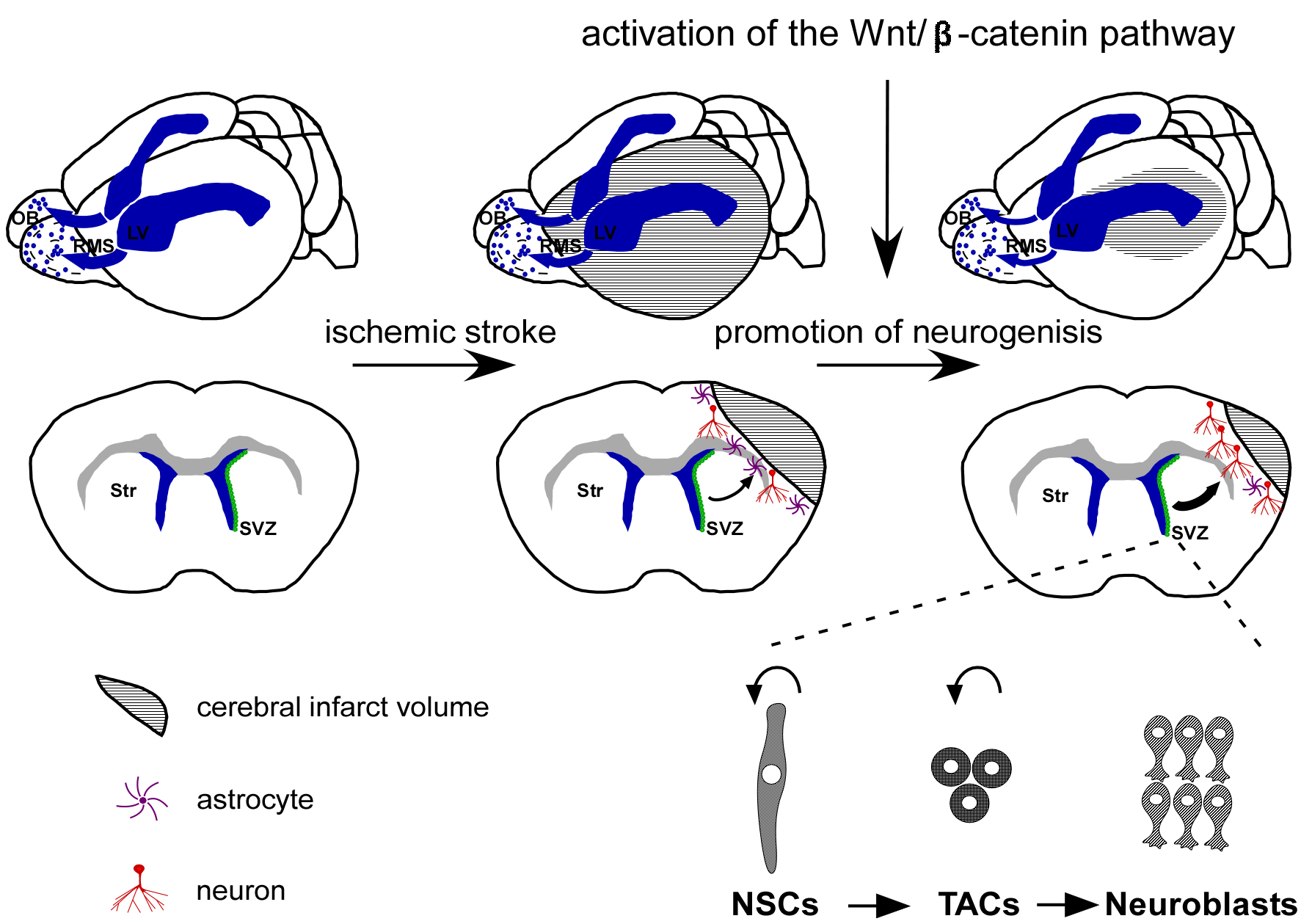 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
Activation of the Wnt/-catenin pathway offers a
promising therapeutic strategy for treating ischemic stroke by promoting
neurogenesis. Under typical physiological circumstances, SVZ NSCs are
responsible for producing TACs, which possess the capacity to generate
neuroblasts that subsequently migrate through the RMS toward the OB, where they
undergo differentiation into interneurons. However, in the event of ischemic
stroke, neuroblasts deviate from their conventional pathway toward the ischemic
penumbra. Within the ischemic penumbra, a limited population of neuroblasts
produces neurons. Activation of the Wnt/-catenin pathway has been shown
to facilitate neurogenesis and augment neuronal regeneration within the ischemic
penumbra following cerebral ischemia, leading to an improvement in nerve function
impairment. SVZ, subventricular zone; NSCs, neural stem cells; TACs,
transit-amplifying cells; RMS, rostral migratory stream; OB, olfactory bulb; LV, lateral ventricle; Str, Striatum.
2. The Wnt Signaling Pathway
The Wnt signaling pathway primarily consists of Wnt ligands, which are secreted
glycoproteins, and cell-surface receptors called Frizzled. The
mammalian genome harbors a total of 19 Wnt genes that
encode Wnt ligands. Wnt signaling pathways can be categorized into three
different types: the Wnt/-catenin pathway (also referred to as the
canonical Wnt signaling pathway), the planar cell polarity pathway (Wnt/PCP), and
the Wnt/Ca signaling pathway.
In the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, Wnt ligands bind to
the Frizzled receptor (Fzd) and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein
5/6 (LRP5/6). Then, the cytoplasmic protein Dishevelled (Dvl) is activated.
Activation of Dvl leads to the degradation of a complex containing glycogen
synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3), adenomatous polyposis coli (APC),
the protein kinase casein kinase 1 (CK1), and Axin. In the
absence of Wnt pathway activation, the
GSK-3/APC/CK1/Axin complex phosphorylates cytosolic
-catenin, leading to its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation by
the proteasome. Conversely, upon activation of the Wnt pathway, the degradation
machinery of the GSK-3/APC/CK1/Axin complex is hindered,
resulting in the cytosolic accumulation of -catenin and its subsequent
transportation into the nucleus. Intranuclear -catenin participates in
interactions with T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor (TCF/LEF)
proteins, thereby promoting the transcription of downstream genes (Fig. 2)
[21, 22, 23]. In addition to the canonical pathway, Wnt ligands can
initiate various signaling cascades that do not rely on -catenin,
namely, the Wnt/PCP pathway and the Wnt/Ca signaling pathway. The Wnt/PCP
pathway begins with the interaction between a Wnt ligand and Fzd, subsequently
leading to the activation of Dvl. The activation of Dvl, in turn, initiates the
activation of small G proteins, including Rac and Rho, which subsequently
activate Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). This intricate series of events ultimately contributes to
the establishment of cellular polarity and the facilitation of cell migration
[24, 25]. The initiation of the Wnt/Ca pathway occurs
when a Wnt ligand interacts with Fzd, leading to the subsequent activation of
phospholipase C (PLC). This activation subsequently modulates the release of
calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby governing the regulation of
intracellular calcium concentrations [26].
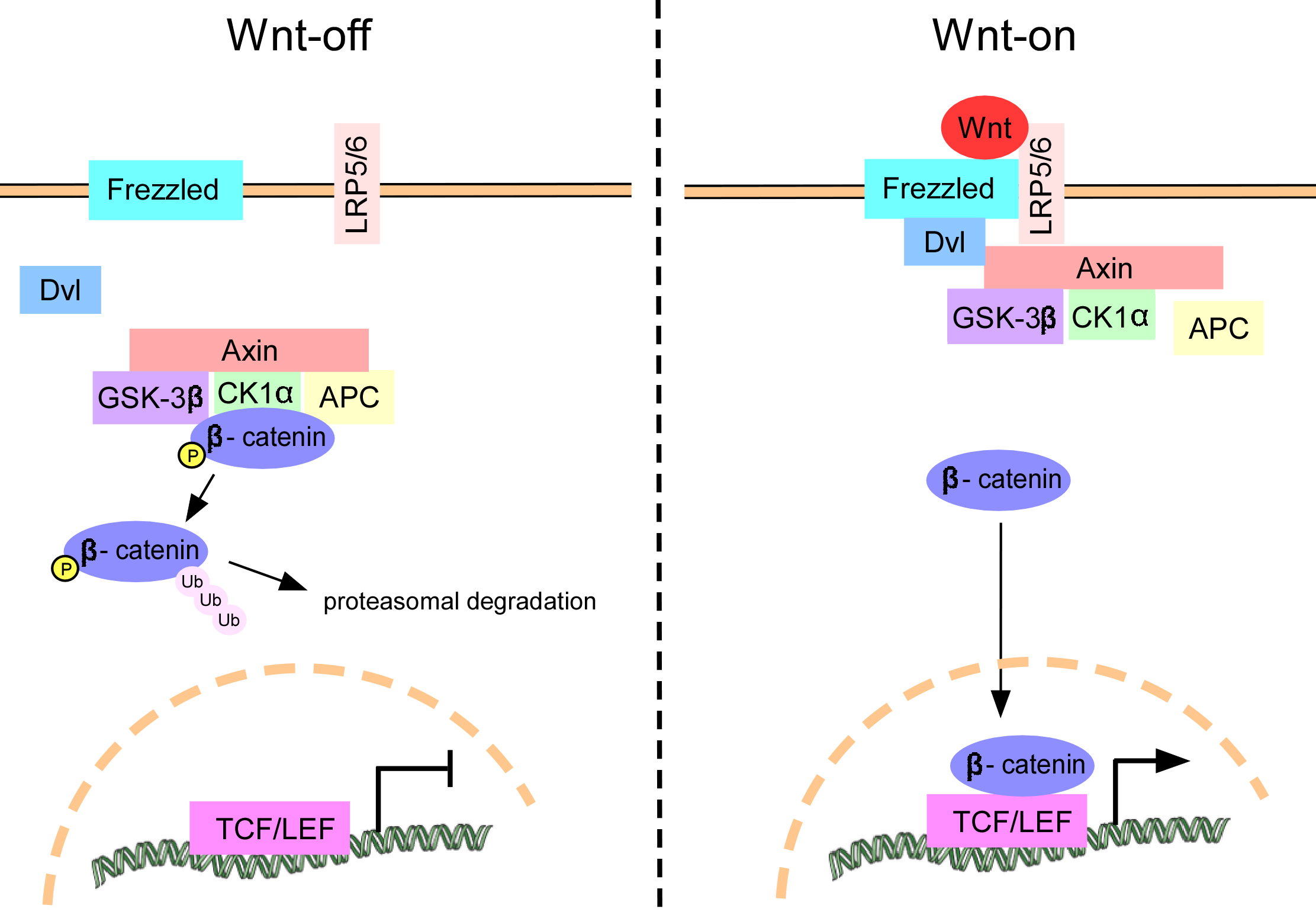 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
Schematic diagram of the Wnt/-catenin
pathway. In the absence of Wnt ligand stimulation,
-catenin undergoes phosphorylation by the
GSK-3/APC/CK1/Axin complex, leading to its ubiquitination and
subsequent removal via the proteasome (Wnt-off). Upon
activation of the Wnt/-catenin pathway, the Wnt ligand
binds to the Frizzled receptor and LRP5/6, resulting in
activation of the cytoplasmic protein Dvl. This activation of Dvl triggers the
degradation of the GSK-3/APC/CK1/Axin complex, leading to the
accumulation of -catenin in the cytosol and its subsequent translocation
into the nucleus. In the nuclear compartment, -catenin engages in
interactions with TCF/LEF proteins, thereby facilitating the transcription of
genes located downstream (Wnt-on). Dvl, Dishevelled; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; CK1, casein kinase 1; LRP5/6, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor.
Research has demonstrated that the Wnt signaling pathway, particularly the
Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway, is important for
neurogenesis. This review aimed to consolidate existing studies pertaining to the
role of the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway in neurogenesis throughout
developmental stages and in the adult brain. Additionally, we explored the
potential therapeutic implications of the Wnt/-catenin pathway in the
treatment of cerebral ischemia.
3. The Role of the Wnt/-catenin Pathway in Neurogenesis during
Brain Development
The Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway has diverse
functions throughout various stages of neural development. Overall, stimulation
of the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway promotes neurogenesis and
suppresses gliogenesis [27, 28].
Chenn et al. [29] employed transgenic mice to induce
excessive activation of -catenin in neural precursors, resulting in the
identification of enlarged brains characterized by augmented cerebral cortical
surface area and folds, in addition to enlarged lateral ventricles lined with
neuroepithelial precursor cells. This outcome can be attributed to an increased
population of proliferative precursor cells [29]. Machon et al. [30]
employed a D6-Cre mouse strain to conditionally inactivate
-catenin (Ctnnb1) within the murine cerebral cortex
and hippocampus after embryonic day (E) 10.5. The results showed that
-catenin is needed for hippocampal progenitor proliferation, cortical
neuronal migration, late-embryonic cortical proliferation, and cortical radial
glial cell maintenance [30]. Additionally, several other studies have
demonstrated the indispensability of the Wnt pathway in the development of the
hippocampus [31, 32]. Furthermore, the Wnt/-catenin pathway plays a
crucial role in the early stages of cerebellar development and assumes a pivotal
function in governing differentiation within the cerebellar ventricular zone in
the subsequent stages of embryonic development [33].
In vitro, the introduction of exogenous Wnt3a protein enhanced the
proliferation and differentiation of NSCs isolated from the forebrain of E14.5
mice [34]. The inhibition of GSK-3 or the overexpression of
-catenin in ventral midbrain (VM) precursors leads to an increase in
neuronal differentiation and the quantity of dopaminergic (DA) neurons [35].
Furthermore, Wnt1 and Wnt3a promoted the proliferation of VM precursors obtained
from E14.5 rats, and Wnt5a induced the differentiation of DA precursors (from
either the cortex or VM) into DA neurons [36, 37]. These findings indicate that
Wnts serve as pivotal regulators of neurogenesis in the VM.
As described above, the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway is known to play
a crucial role in brain development, particularly in neurogenesis. However, the
precise mechanism and downstream target genes involved in the promotion of
neurogenesis by Wnt/-catenin remain uncertain. Furthermore, the
complexity of the mechanism is further compounded by considerations of spatial
heterogeneity. A study revealed that -catenin plays a crucial role in
the proliferation and neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and luciferase reporter assays revealed that
-catenin binds directly to the promoter or proximal enhancer regions of
proneural genes, including neurogenin 1, neurogenin 2,
mash1, and myoD, resulting in their activation [38]. A separate
ChIP investigation revealed that the -catenin/T-cell factor 1 (TCF1) complex plays a
direct role in modulating the expression of Sox1, a marker of neural precursor
cells, in the context of neuronal differentiation in embryonic stem cells [39].
In addition, some articles suggest that the Wnt/-catenin signaling
pathway facilitates the proliferation of NSCs while inhibiting their
differentiation, thereby playing a role in the preservation of stem cell
characteristics [40, 41]. This disparity could be attributed to variations in the
culture conditions of neural progenitor cells, specifically the presence or
absence of Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) [38].
Taken together, these findings highlight the involvement of
Wnt/-catenin signaling in NSCs during development and imply that this
pathway may also facilitate adult neurogenesis and contribute to nerve
regeneration following cerebral ischemia.
4. The Role of the Wnt/-catenin Pathway in Adult Brain
Neurogenesis
4.1 Inhibition of the Wnt/-catenin Pathway Blocks Adult
Brain Neurogenesis
Wnt/-catenin signaling is activated in adult NSCs [42, 43].
Numerous published studies have
shown that the ablation of
Wnt/-catenin signaling impedes the proliferation of adult NSCs and their
subsequent differentiation into neurons. The overexpression of mutant Wnt1
protein in the DG led to reduced proliferation of adult hippocampal NSCs and
impaired generation of new neurons by suppressing Wnt signaling, consequently
impacting spatial memory and object recognition memory [44, 45].
Knockout of Wnt7a led to a
substantial decrease in the abundance of NSCs and an increase in the rate of cell
cycle termination in neural progenitors located in the DG and SVZ of adult mice.
Furthermore, Wnt7a plays a pivotal role in the process of neuronal
differentiation and maturation. The absence of Wnt7a expression led to a
noteworthy decrease in the number of newly formed neurons in the DG region of the
hippocampus [46, 47]. Another study showed that the suppression
of Wnt signaling through the knockdown of the Frizzled-1 receptor in the
hippocampus resulted in reduced neuronal differentiation of NSCs and altered
migration patterns of newly generated neurons [48].
However, Austin et al. [42] reported that conditional deletion of
-catenin in adult Glast-positive NSCs did not have any impact
on their maintenance, activation, or differentiation. Interestingly, a separate
investigation indicated that conditional knockout of
-catenin in Sox2-positive NSCs in the DG inhibited newborn
neuron generation and the survival of neuronal progenitors [49].
4.2 Activation of the Wnt/-catenin
Pathway Promotes Adult Brain Neurogenesis
In contrast to knockout of -catenin, conditional stabilization
of -catenin in mice resulted in the displacement of NSCs from the SGZ.
Additionally, in an in vitro model of hippocampal NSCs, the activation
of the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway facilitated the differentiation of
active NSCs into neurons while also inducing the proliferation or differentiation
of quiescent NSCs in a dose-dependent manner [42]. Another
study indicated that the activation of the Wnt/-catenin signaling
pathway within the SVZ through the suppression of GSK-3 resulted in an
elevated quantity of nascent neurons within the olfactory bulb. This phenomenon
can be attributed to the increased proliferation of Mash1 progenitor cells
within the SVZ [50].
The observed phenotypes resulting from the activation of Wnt/-catenin
signaling in adult NSCs are consistent with other reports in
the literature. Activation of the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway leads
to increased expression of NeuroD1 and long interspersed nuclear element 1 (LINE-1), both of which are pivotal in the
process of neuronal differentiation [49]. Overexpression of
Wnt7a and stabilized -catenin promote NSC
self-renewal in vitro. The introduction of -catenin
through lentiviral transduction resulted in an increase in the population of type
B NSCs within the SVZ of adult brains [46]. The overexpression of Wnt3in NSCs in vitro or in the DG in vivo promoted neuroblast
proliferation and neuronal differentiation [44]. In another study, the
overexpression of Wnt3a or Wnt5a was found to enhance the
proliferation and neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells derived
from postnatal and adult mouse brains [51]. In addition, the augmentation of
neurogenesis in the hippocampus was also observed upon the removal of Wnt
inhibitors [52, 53]. Moreover, the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway plays
a significant role in the maturation of newborn neurons, as well as in the growth
of dendrites and the formation of dendritic spines in adult hippocampal neurons
[53, 54, 55].
In summary, the available evidence suggests that activation of the
Wnt/-catenin pathway in adult NSC niches promotes adult neurogenesis,
whereas the inhibition of this pathway hinders adult neurogenesis (Table 1, Ref.
[42, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55]).
Table 1.Evidence of the role of the
Wnt/-catenin pathway in adult brain neurogenesis.
| Signaling molecule |
Manipulation |
Effect on Wnt/β-catenin pathway |
In vivo/In vitro |
Phenotype |
Reference |
| Wnt1 |
overexpression of mutant Wnt1 |
inhibits |
in vivo |
inhibits hippocampal neurogenesis |
[44, 45] |
| Wnt7a |
knockout |
inhibits |
in vivo |
inhibits neurogenesis in DG and SVZ |
[46, 47] |
| Frizzled-1 |
knockdown |
inhibits |
in vivo |
inhibits hippocampal neurogenesis |
[48] |
| β-catenin |
knockout |
inhibits |
in vivo |
inhibits hippocampal neurogenesis |
[49] |
| Dickkopf-1 |
overexpression |
inhibits |
in vivo |
decreases proliferation of Mash1 progenitor cells within the SVZ |
[50] |
| β-catenin |
knockout |
inhibits |
in vivo |
inhibits dendritic development |
[55] |
| β-catenin |
stabilization |
activates |
in vivo |
promotes NSCs proliferation and their displacement from their correct SGZ location |
[42] |
| GSK-3β |
inhibition by CHIR99021 |
activates |
in vitro |
promotes neuronal differentiation of active NSCs and promotes the activation of quiescent NSCs |
[42] |
| β-catenin |
overexpression of stabilized β-catenin or inhibition of GSK-3β by Ro3303544 |
activates |
in vivo |
increases proliferation of Mash1 progenitor cells within the SVZ |
[50] |
| GSK-3β |
|
|
|
| Wnt7a |
overexpression of Wnt7a or stabilized β-catenin |
activates |
in vitro |
promotes NSCs self-renewal |
[46] |
| β-catenin |
| β-catenin |
overexpression of stabilized β-catenin |
activates |
in vivo |
increases numbers of type B NSCs in SVZ |
[46] |
| Wnt3 |
overexpression |
activates |
in vivo/in vitro |
promotes neuroblasts proliferation and neuronal differentiation |
[44] |
| Wnt3a |
overexpression |
activates |
in vitro |
enhances the proliferation and neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells |
[51] |
| Wnt5a |
| Dickkopf-1 |
knockout |
activates |
in vivo |
enhances hippocampal neurogenesis |
[52] |
| secreted frizzled-related protein 3 |
knockout |
activates |
in vivo |
promotes hippocampal neurogenesis, dendritic growth and spine formation |
[53] |
| β-catenin |
stabilization |
activates |
in vivo |
accelerates dendritic growth, but eventually causes dendritic defects and excessive spine numbers |
[54] |
DG, dentate gyrus; SGZ, subgranular zone.
5. The Role of the Wnt/-catenin Pathway in
Neurogenesis after Cerebral Ischemia
The occurrence of cerebral ischemia leads to the stimulation of NSCs in the SVZ,
resulting in their increased proliferation and subsequent asymmetric division
into migratory neuroblasts. These neuroblasts subsequently migrate toward
ischemic regions, where they undergo differentiation into
neurons, potentially facilitating functional recovery. Additionally, NSCs in the
SGZ can migrate to the granular cell layer and differentiate into new neurons,
potentially reversing the learning and memory deficits caused by ischemia.
However, it should be noted that this reparative mechanism is insufficient to
fully compensate for the extensive damage caused by severe cerebral ischemia [8, 13]. Studies have indicated that the Wnt/-catenin
pathway within adult NSC niches facilitates neurogenesis following cerebral
ischemia and contributes to the restoration of neurological function (Table 2,
Ref. [56, 57, 58, 59]).
Table 2.Evidence of the role of the Wnt/-catenin pathway in
neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia.
| Signaling molecule |
Manipulation |
Effect on Wnt/-catenin pathway |
In vivo/In vitro |
Phenotype |
Reference |
| -catenin |
knockdown |
inhibits |
in vivo |
inhibits neurogenesis in SVZ and increases infarct volume |
[56] |
| Dickkopf-1 |
overexpression |
inhibits |
in vitro |
inhibits neuronal differentiation of NSCs derived from the SVZ of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mice |
[57] |
| Wnt3a |
overexpression |
activates |
in vivo |
increases neurogenesis and promotes neurological function recovery |
[58] |
| Wnt3a |
overexpression |
activates |
in vivo |
promotes neurogenesis in SGZ and SVZ, decreases infarct volume, and enhances sensorimotor functions |
[59] |
5.1 Inhibition of the Wnt/-catenin Pathway Impedes
Neurogenesis Subsequent to Cerebral Ischemia
Lei et al. [56] administered -catenin Small interfering RNA (siRNA)
intracerebroventricularly to mice subjected to transient middle cerebral artery
occlusion (tMCAO) to deactivate -catenin, leading to an increase in
infarct volume and a decrease in neurogenesis within the SVZ. The administration
of -catenin siRNA resulted in a significant reduction in the
populations of 5-Bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU)/3-tubulin (Tuj1) cells, BrdU/Doublecortin (DCX) cells, and
BrdU/Microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) cells within the ischemic striatum, which serve as markers
for newborn immature neurons, proliferating progenitors, and newborn mature
neurons, respectively [56]. Furthermore, the use of a genetic
approach to induce the overexpression of the Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) in NSCs derived
from the SVZs of mice subjected to MCAO suppressed neuronal differentiation [57].
5.2 Activation of the Wnt/-catenin Pathway Promotes
Neurogenesis after Cerebral Ischemia and is Beneficial for Ameliorating Nerve
Function Injury following Cerebral Ischemia
The increase in Wnt3a levels within the SVZ or striatum of mice afflicted with
focal ischemic injury was found to play a significant role in facilitating
functional recovery subsequent to the ischemic event. This was achieved through
the promotion of neurogenesis or the enhancement of neuronal viability [58]. A
separate study demonstrated that the intranasal administration of
Wnt3a subsequent to focal ischemic stroke in mice reduced
infarct volume, augmented sensorimotor functions, stimulated neurogenesis in the
SVZ and SGZ, increased the number of DCX/BrdU colocalized cells
migrating from the SVZ toward the peri-infarct area, and increased the quantity
of newly formed neurons (BrdU/NeuN cells) in the peri-infarct zone.
Conversely, intranasal administration of a Wnt inhibitor hindered neurogenesis
and decreased the quantity of newly generated neurons in the peri-infarct area
[59].
In addition, studies have revealed that some treatments and mechanisms can
further upregulate the Wnt/-catenin pathway after cerebral ischemia,
thereby promoting neurogenesis and contributing to the reinstatement of
neurological function [60, 61, 62, 63, 64]. Taken together, these findings indicate that the
activation of the Wnt/-catenin pathway subsequent to cerebral ischemia
has the potential to stimulate neurogenesis and ameliorate nerve function
impairment, making this pathway a viable therapeutic target for the management of
cerebral ischemia.
6. Limitations in the Available Studies on the Role
of the Wnt/-catenin Pathway in Postischemic Neurogenesis
As stated above, considerable advancements
have been made in the field of research pertaining to genetic or pharmacological
interventions in the Wnt/-catenin pathway aimed at increasing
neurogenesis following cerebral ischemia.
However, most studies lack a
quality study design. Many published studies utilized immunofluorescence
colocalization of BrdU with neuronal markers or neuroblastic markers to evaluate
neurogenesis and the de novo generation of neurons.
However, it is unclear whether these proliferative cells were derived from NSCs.
Previous studies have reported that astrocytes can transdifferentiate into
morphologically mature and functional neurons after cerebral ischemia [65].
Therefore, it is recommended that researchers employ lineage tracing techniques
in future studies to track the fate of NSCs to elucidate their
potential contributions to brain neurogenesis and postischemic stroke recovery.
Lineage tracing serves as a valuable tool for investigating the origin of new
neurons in ischemic regions, specifically whether they originate from NSCs within
the adult NSC niche. Additionally, it enables the examination of the impact of
the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway on the cellular fate of different NSC
populations. Currently, numerous techniques are available for lineage tracing
(for review, see [66]), with one of the most prevalent approaches involving the
integration of the Cre mouse line in combination with the
Rosa26-CAG-reporter mouse line. For adult NSC lineage
tracing, researchers can cross inducible NSC-specific Cyclization recombination enzyme (Cre) lines, such as
Nestin-CreERT2 mice [67] and Ascll-CreERT2 mice [68], with
Rosa26-CAG-reporter lines, such as Rosa26-CAG-tdTomato mice
[69], to generate
Nestin;
Rosa26 mice or Ascll;
Rosa26 mice. With tamoxifen administration, the NSCs in
lineage-traced mice exhibit stable expression of tdTomato, enabling the tracking
of the fate of cells originating from the NSC niche (Fig. 3).
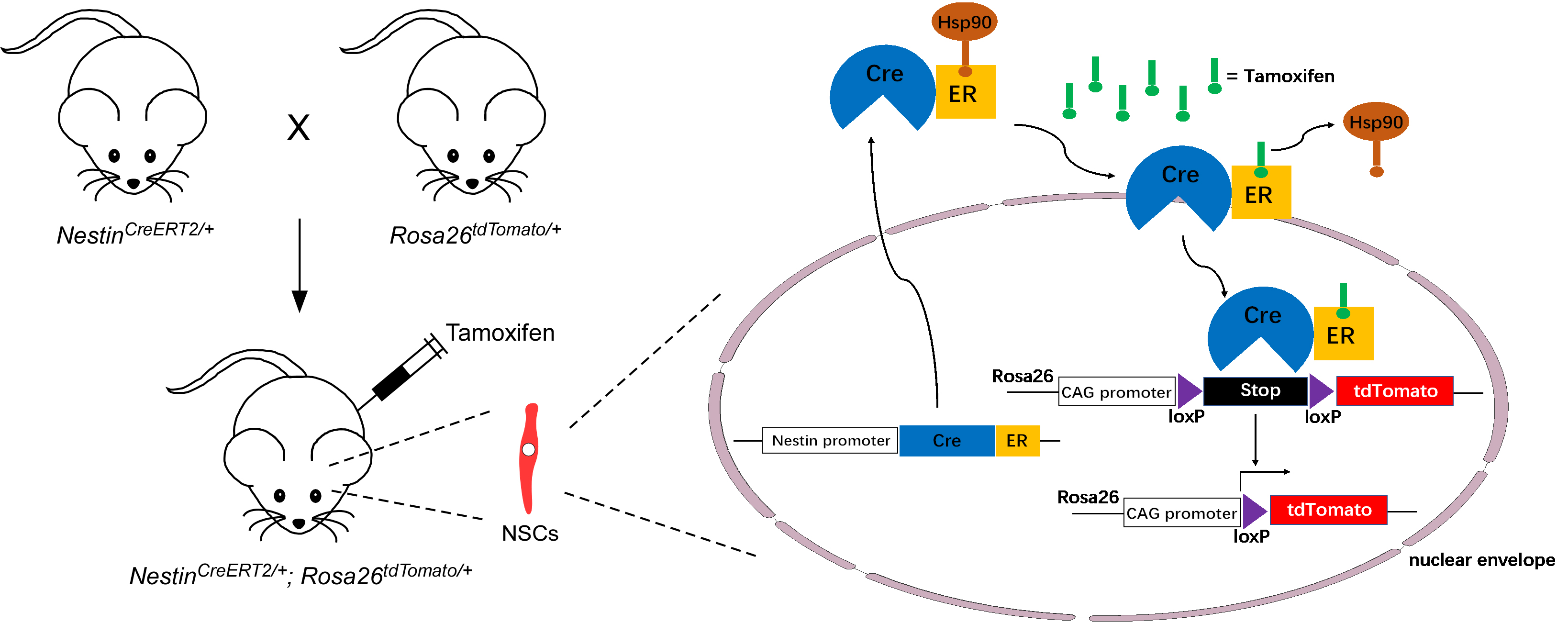 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.
Schematic protocol for lineage tracing of Nestin-positive adult NSCs. Nestin;
Rosa26 mice are generated by crossing
Nestin-CreERT2 mice with Rosa26-CAG-tdTomato mice. Upon the
administration of tamoxifen to Nestin;
Rosa26 mice, Hsp90 is displaced from CreER, allowing Cre
recombinase to enter the nucleus of Nestin-positive adult NSCs. Subsequently, the
Cre recombinase removes the loxP-Stop-loxP cassette, resulting in
permanent tdTomato expression in adult NSCs. ER, Estrogen receptor; CAG, cytomegalovirus enhancer plus chicken beta-actin promotor.
There are additional limitations in studies on the role of the
Wnt/-catenin pathway in postischemic neurogenesis. All current studies
on the Wnt/-catenin pathway in postischemic neurogenesis have been
conducted using animal models. Given the ongoing debate surrounding human adult
neurogenesis, the transition from preclinical research to clinical trials for the
treatment of ischemic stroke through the activation of the Wnt/-catenin
pathway presents significant obstacles. In addition, the potential of agonists of
Wnt/-catenin signaling to enhance neurogenesis following cerebral
ischemia remains uncertain. The preclinical exploration of Wnt/-catenin
signaling agonists holds significance for their eventual clinical utility.
7. Conclusion
Ischemic stroke is characterized by
increased morbidity, disability, recurrence, and mortality. Intravenous
thrombolysis and thrombectomy are approved medical treatments for acute stroke.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the limited timeframe within which these
therapies can be administered, as well as the potential for intracerebral
hemorrhage and other bleeding complications that may arise from the utilization
of intravenous thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy. Thus, there is a need
for the development of new treatments. Researchers have focused
on endogenous NSC-induced neurogenesis following ischemic stroke
due to the demonstrated positive impact of
NSCs on neural repair. According to existing studies, the
modulation of numerous signaling pathways has been found to facilitate NSC
proliferation and differentiation while also
augmenting angiogenesis and synaptic plasticity. These mechanisms collectively
contribute to the process of neural repair subsequent to ischemic brain injury.
Based on the existing evidence, the Wnt/-catenin pathway is a promising
therapeutic target for alleviating the consequences of ischemic stroke. The
activation of this pathway facilitates neurogenesis, leading to the generation of
newly formed neurons that can replace deceased neural cells within the ischemic
core. Future studies should further investigate whether the newly generated
neurons are functional in vivo and whether they can integrate with
existing neural circuits. Furthermore, additional in-depth lineage tracing
experiments should be conducted.
Author Contributions
JDX and LSC designed the study. JDX wrote the manuscript and draw Figures and
Tables; LSC revised the manuscript; SYL, LXX, YNZ, and WRJ collected and sorted
references, as well as provided comments to improve the manuscript. All authors
contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved
the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and
agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Acknowledgment
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was funded by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of
China (Grant No. LQ23H280003 and LQ23H280006) and Research Project of Zhejiang
Chinese Medical University (Grant No. 2021RCZXZK08 and 2021RCZXZK06).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Fig. 2.
Fig. 2. Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.


