1 Key Laboratory of Cognitive Science, Laboratory of Membrane Ion Channels and Medicine, College of Biomedical Engineering, South-Central Minzu University, 430079 Wuhan, Hubei, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a prominent cause of neonatal mortality and neurodevelopmental disorders; however, effective therapeutic interventions remain limited. During neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury events, increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and decreased antioxidant levels lead to the induction of oxidative stress, which plays a pivotal role in the pathological process of neonatal HIE. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a key endogenous antioxidant transcription factor that protects against oxidative stress by promoting the transcription of various antioxidant genes. It has been demonstrated that Nrf2 signaling pathway activation by different compounds may protect against neonatal HIE. This review outlines the role of oxidative stress in neonatal HIE and summarizes the impact of antioxidants on neonatal HIE via activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. In conclusion, Nrf2 signaling pathway potentially exerts antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic and antiferroptotic effects, thereby emerging as a focal point for future neonatal HIE treatment strategies.
Keywords
- neonatal brain
- Nrf2
- HIE
- oxidative stress
- inflammation
- apoptosis
- ferroptosis
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a neurological disorder
induced by the disturbance of blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain [1]. HIE
is considered a primary cause of disability and mortality in neonates [2, 3]. The
incidence of HIE is 1–8 per 1000 full-term infants in developed nations and
approximately 26 per 1000 full-term infants in low-income and middle-income
regions [4, 5]. As a result of the hypoxic-ischemic insult in the brain, infants
may have the acute clinical presentations of brain damage, such as abnormal fetal
heart rate tracings, low Apgar scores or poor umbilical cord gases (pH
One of the most broadly accepted pathophysiological mechanisms of neonatal HIE is oxidative stress [15]. Oxidative stress, which is involved in a variety of diseases, develops from overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and results in serious injury to cerebral tissue [16]. When ROS production exceeds the antioxidant capacity of molecules and enzymes, biological processes such as DNA and mitochondrial damage, protein carbonylation, lipid peroxidation and enzyme inactivation occur, resulting in inflammation, apoptosis, and ferroptosis and eventually brain damage [15, 17, 18, 19]. Thus, it is of great importance to analyze the role of oxidative stress in neonatal HIE.
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a crucial antioxidant
transcription factor that can regulate several cytoprotective factors to reduce
oxidative stress [20]. Under physiological conditions, Nrf2 remains at a low
level via directed degradation by ubiquitylation [21]. When cells are exposed to
oxidative stress, Nrf2 and Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) separate,
and Nrf2 binds with the antioxidant response element (ARE) in the nucleus and
then upregulates the levels of various antioxidant-encoding genes, such as heme
oxygenase-1 (HO-1), glutathione (GSH), and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
phosphate (NADPH) quinone oxidoreductase 1 [NQO1] [22]. By upregulating these
antioxidants, Nrf2 is able to decrease ROS-mediated cellular injury and keep a
dynamic redox balance [23]. A previous study revealed that genistein, which is a
bioactive isoflavone phytoestrogen found in soybeans, exerted a neuroprotective
effect against HIE in neonatal mice by reducing neuroinflammation and oxidative
stress via the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-
Here, we summarized the pathological mechanisms of oxidative stress in neonatal HIE and the modulation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Furthermore, we outlined a series of compounds that have been observed to provide neuroprotection in neonatal HIE models by reducing oxidative stress by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway.
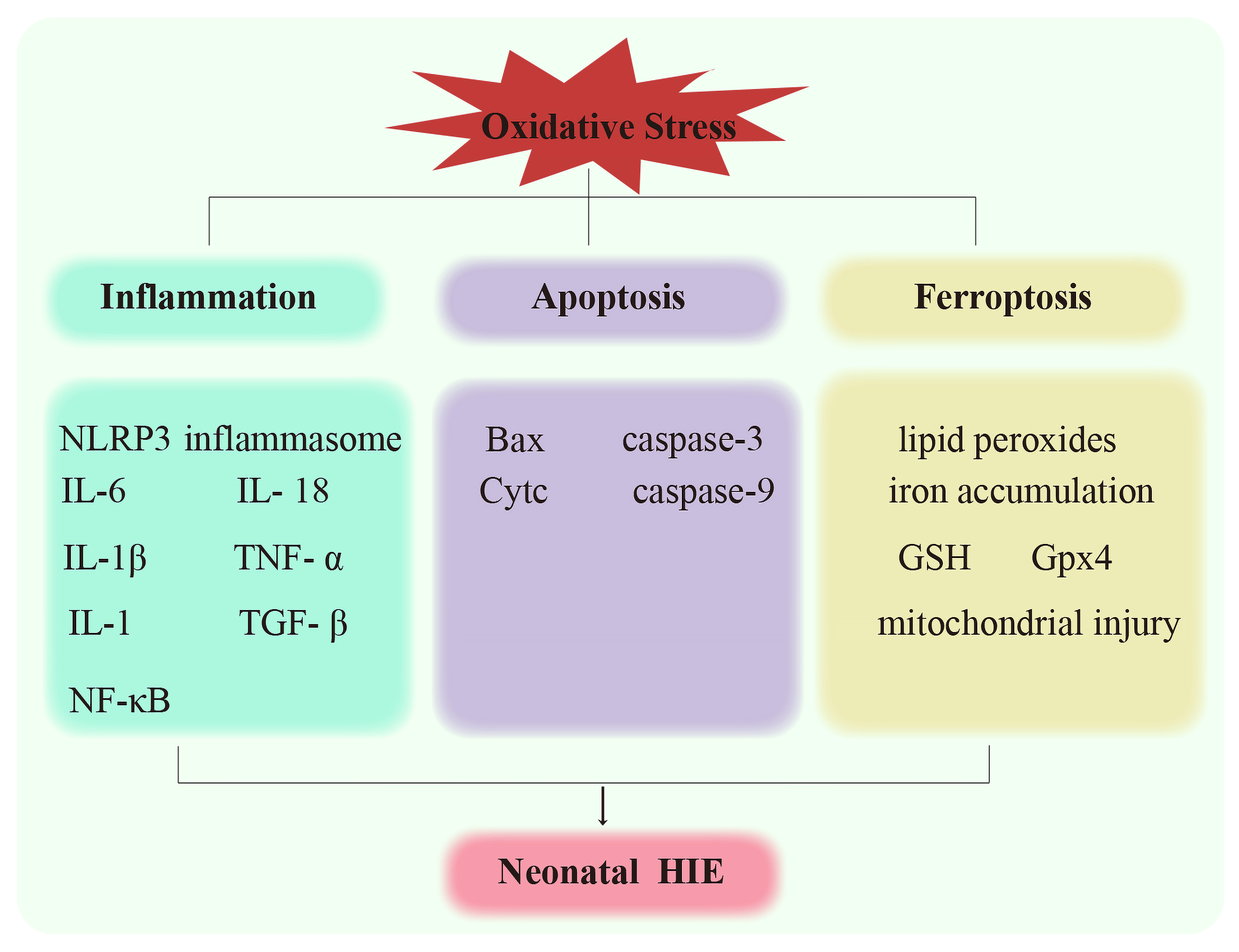
Following a hypoxic-ischemic event, large amounts of ROS are produced, which can lead to the induction of oxidative stress [15]. Oxidative stress is involved in a large number of pathophysiological processes, and in neonatal HIE, it induces inflammation, apoptosis and ferroptosis. In this section, we focus on the association between oxidative stress and neonatal HIE (Fig. 1).
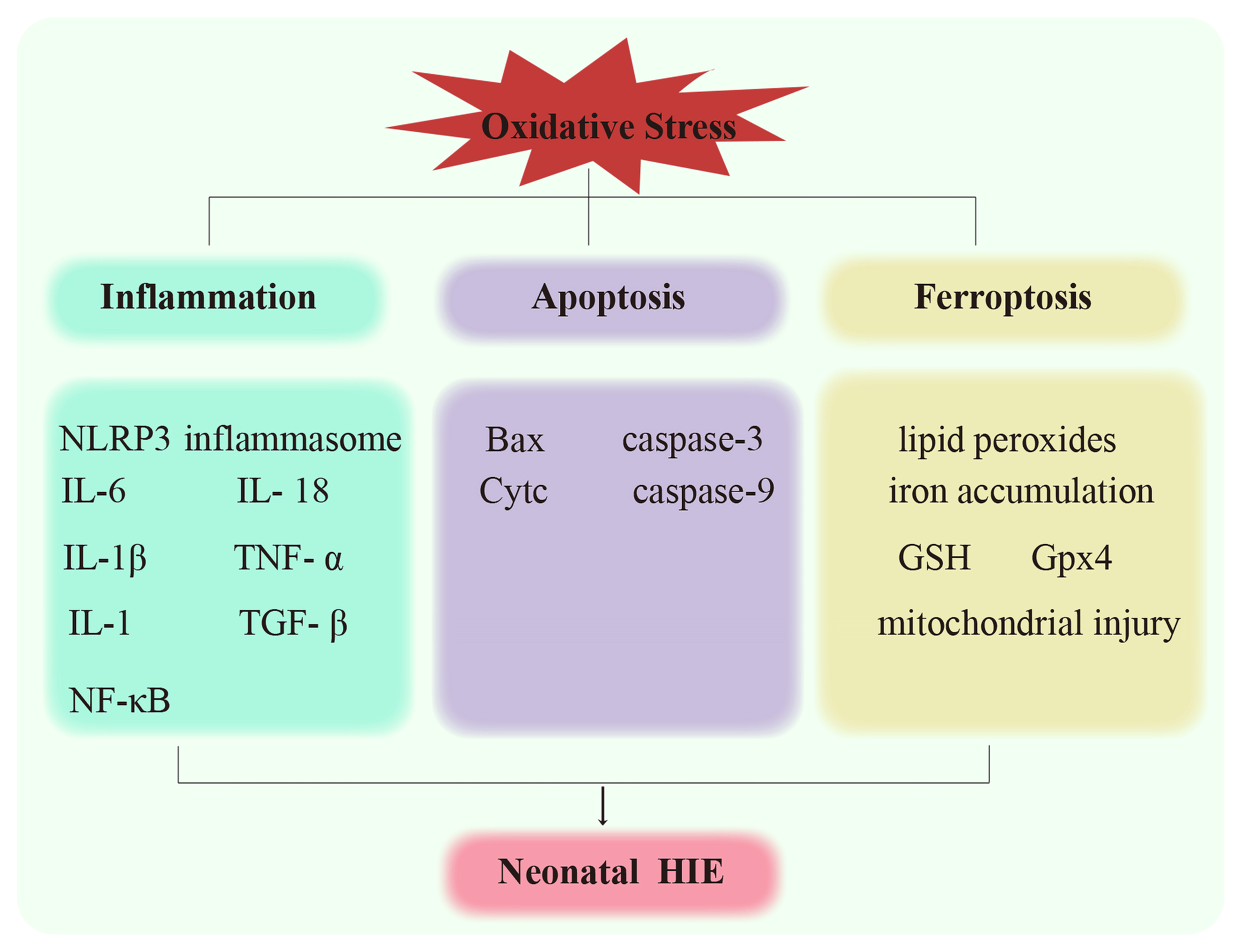 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Oxidative stress and neonatal HIE. Following a hypoxic-ischemic
event, large amounts of ROS are produced, which can lead to the induction of
oxidative stress. Additionally, ROS take part in the activation of the NLRP3
inflammasome, which can later increase the activity of caspase-1, pro-IL-1 and
pro-IL-18, and then proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-
Inflammation is a widespread cellular response associated with many neurological
diseases [26]. Following hypoxic-ischemic injury, ROS take part in the activation
of the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin
domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome [27], which can later increase the
activity of caspase-1, pro-interleukin-18 (pro-IL-18) and pro-IL-1 [28].
Following the activation of caspase-1, proinflammatory cytokines such as
interleukin-1
Apoptosis is a programmed cell death mode in mammals. The release of excessive ROS from mitochondria triggers the release of hydrolytic enzymes from lysosomes, which activates the B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2)-associated X protein (Bax), eventually increasing the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane and resulting in the release of cytochrome c (Cytc) from the mitochondria [15]. Once released into the cytoplasm, Cytc forms an apoptotic complex with the caspase-9 zymogen. Subsequently, activated caspase-9 initiates the activation of caspase-3, which ultimately cleaves the DNA fragment of the substrate and leads to cell death [37]. Hypoxic-ischemic conditions lead to inadequate provision of nutrients and oxygen to cells, resulting in a considerable amount of neuronal apoptosis [38, 39, 40]. A previous study showed that lycopene (Lyc), which is a carotenoid compound isolated from tomatoes, reduced ROS-induced apoptosis in both in vivo and in vitro experiments [41]. Likewise, Chen et al. [42] indicated that myricetin exerted a neuroprotective effect on the neonatal rat brain by mitigating ROS-induced neuronal apoptosis and ameliorated long-term neurological prognosis and infarct volume in neonatal HIE models. Thus, ROS-related apoptosis plays an important role in brain damage associated with neonatal HIE.
Ferroptosis is a programmed cell death mode induced by the anomalous metabolism of iron, lipids and GSH and characterized by iron-regulated lipid peroxidative accumulation [43]. Hypoxic-ischemic conditions lead to the formation of ROS and lipid peroxidation, iron accumulation, reduced GSH and glutathione peroxidase 4 (Gpx4) activity, and mitochondrial injury, ultimately leading to the development of ferroptosis [44, 45, 46, 47]. Ferroptosis results in the accumulation of iron-regulated ROS, reduction in cellular antioxidant capacity, and subsequent cell death, which can increase central nervous system damage [43, 48]. Recent research has shown that exogenous melatonin (Mel) can alleviate hypoxic-ischemic brain injury by reducing ROS-induced ferroptosis and exert obvious neuroprotective effects on neonatal HIE models [49]. Furthermore, Cai et al. [50] found that treatment with vitamin D (VD) efficiently reduced ferroptosis by suppressing oxidative stress and provided neuroprotection in neonatal HIE models. Hence, ROS-induced ferroptosis is considered to be an important pathophysiological factor of neonatal HIE.
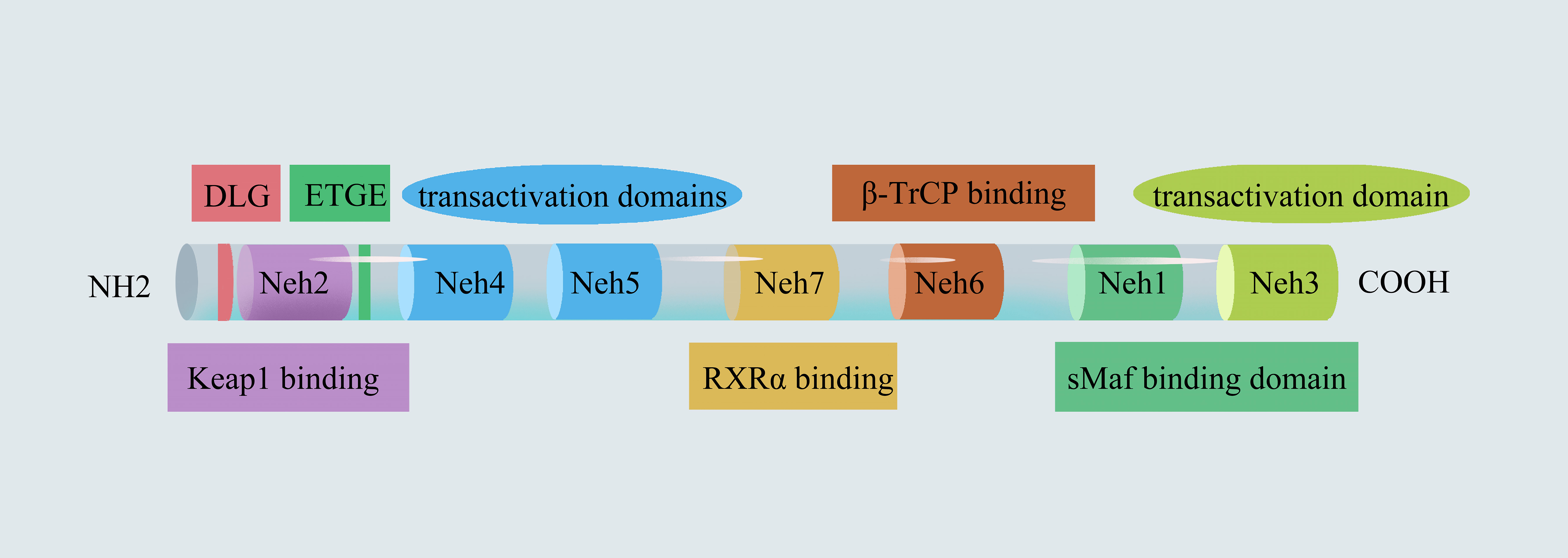
The Nrf2 protein is a member of the Cap-n-Collar family of transcription factors
and has 7 functional domains named Nrf2-ECH homology 1-7 (Neh1-7) [51, 52, 53] (Fig. 2). The Neh1 domain modulates small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma (sMaf)
proteins and DNA binding and is responsible for promoting Nrf2 nuclear
translocation [23]. The Neh2 region interacts with Keap1 via the high-affinity
Glu-Thr-Gly-Glu (ETGE) and low-affinity Asp-Leu-Gly (DLG) of the degenerate motif
of the Neh2 structure [54]. Keap1 is a cysteine-rich inhibitor of Nrf2 that
regulates the stability and ubiquitination of Nrf2 [55]. The interactions of Nrf2
with other coactivators are mediated by Neh3, Neh4, and Neh5 [56]. Neh6 is a
negatively regulated structural domain that leads to the ubiquitination of Nrf2
by binding to the
 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Region structures of Nrf2. The Nrf2 protein includes 7 Neh
regions: Neh1-Neh7. The Neh2 region interacts with Keap1 through the DLG and ETGE
motifs. The Neh4, Neh5 and Neh3 regions are vital for transactivation. The Neh7
region binds to RXR
Nrf2 is one of the vital regulators of endogenous antioxidant production and plays an important role in improving cerebral injury [60, 61]. Under physiological conditions, Nrf2 remains at a low level due to its direct degradation through ubiquitylation [21]. Following a hypoxic-ischemic event, Nrf2 is separated from Keap1 and subsequently migrates from the cytoplasm into the nucleus [62]. Then, Nrf2 can heterodimerize with the transcriptional regulator sMaf [63, 64], bind to ARE [65, 66, 67, 68, 69], and upregulate the expression of various enzymes involved in antioxidant protection, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (Gpx) and catalase (CAT) [70]. By upregulating these antioxidant enzymes, Nrf2 can reduce ROS production and inhibit oxidative stress-induced cellular damage and ultimately keep a dynamic redox balance [70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75]. Furthermore, Zhang et al. [76] found that Nrf2 knockout aggravated brain infarct after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic (HI) injury. Therefore, the Nrf2 signaling pathway plays a crucial part in the regulation of oxidative stress after neonatal HIE.
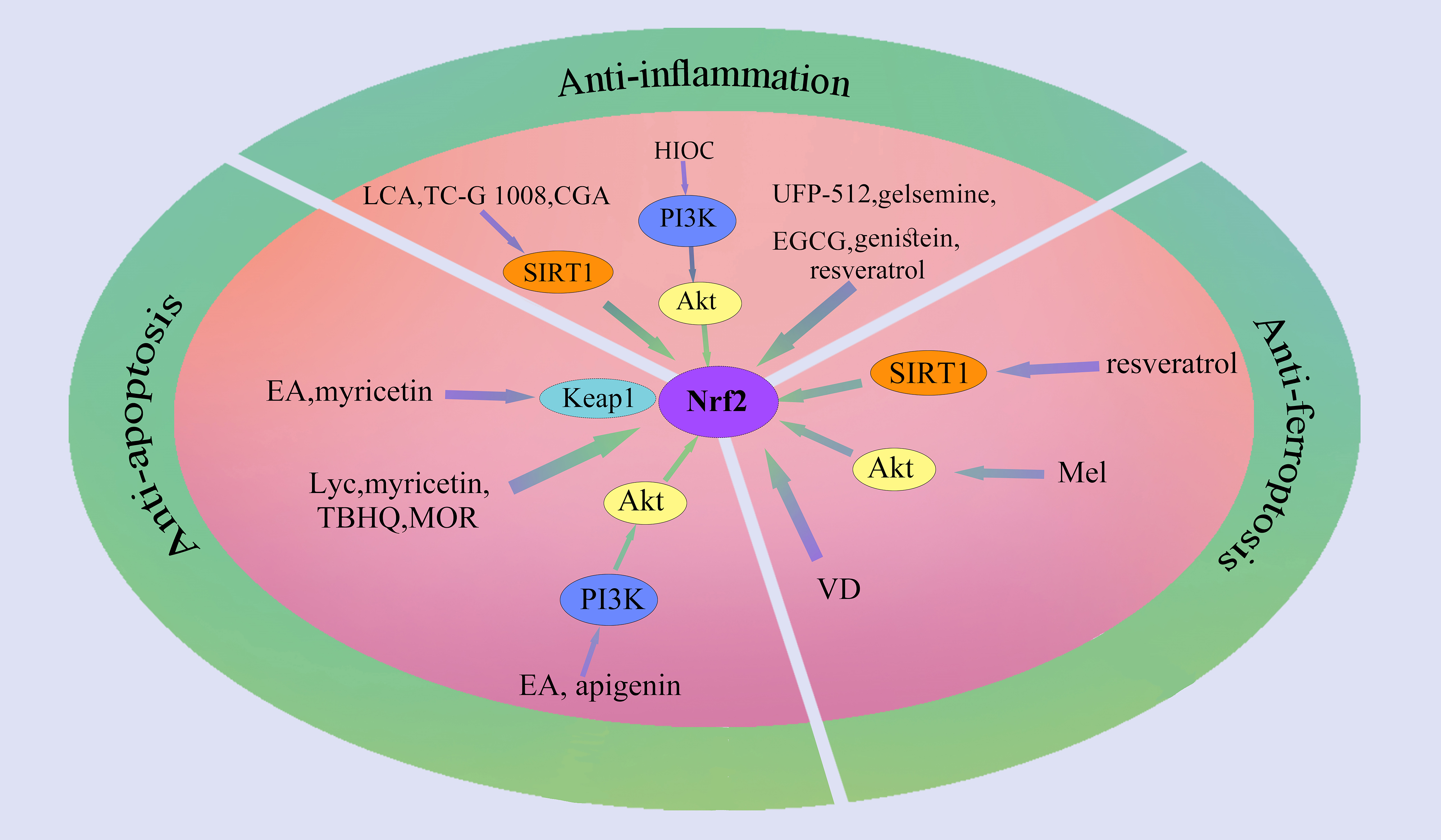
Different compounds have been shown to exert great neuroprotective effects on neonatal HIE by ameliorating oxidative damage through the activation of Nrf2 (Table 1, Ref. [24, 25, 35, 36, 41, 42, 44, 49, 50, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86]). These compounds can be divided into three types: against ROS-induced inflammation, against ROS-induced apoptosis, and against ROS-induced ferroptosis (Fig. 3). The terms Nrf2, oxidative stress and neonatal brain were searched in PubMed to find relevant studies.
 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Compounds that activated Nrf2 in neonatal HIE. Neuroprotective compounds showed anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic and anti-ferroptotic effects on neonatal HIE via activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway or Nrf2-related pathway. Akt, protein kinase B; CGA, chlorogenic acid; EA, echinocystic acid; EGCG, epigallocatechin gallate; HIOC, N-[2-(5-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl) ethyl]-2-oxopiperidine-3-carboxamide; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; LCA, licochalcone A; Lyc, lycopene; Mel, melatonin; MOR, morroniside; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SFN, sulforaphane; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; TBHQ, tertiary-butylhydroquinone; VD, vitamin D; UFP-512, H-Dmt-Tic-NH-CH(CH2–COOH)-Bid; TC-G 1008, G-protein-coupled receptor 39-C3.
| Compounds | Model | Dose and mode of administration of drugs | Efficacy | Results | Reference |
| LCA | OGD/R (primary cortical neurons) | In vitro: 0, 10, 20 and 40 µM during OGD/R (28 h) | SOD |
Reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory response | [35] |
| TC-G 1008 | HIBD model (SD) | In vivo: 15 mg/kg intranasally at 1, 25, 49, and 73 h after HIBD | Nrf2 |
Reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory response | [77] |
| HIOC | HIBD model (SD) and OGD/R model (primary cortical neurons) | In vivo: 10 mg/kg, intraperitoneally at 12, 24 and 48 h after HIBD; In vitro: 100, 250, 500 and 750 nM, pretreatment | Nrf2 |
Inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis | [78] |
| Resveratrol | HIBD model (SD) | In vivo: 20 and 40 mg/kg intraperitoneally after 7 days of pretreatment | Nrf2 |
Reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory response | [79] |
| UFP-512 | HIBD model (SD) | In vivo: 5 mg/kg intraperitoneally before HIBD | Nrf2 |
Reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory response | [80] |
| Gelsemine | HIBD model (C57BL/6) and OGD/R model (BV2) | In vivo: 10 µg/kg intraperitoneally at 20 min before HIBD; In vitro: 100 nM for 3h before OGD/R | SOD |
Reduces oxidative stress and inflammatory response | [36] |
| Myricetin | HIBD model (SD) and OGD/R model (PC12 cell) | In vivo: 25 mg/kg gavage starting 1 h after HI; In vitro: 200 µM, pretreatment for 2 h | Nrf2 |
Inhibits oxidative stress and apoptosis | [42] |
| TBHQ | HIBD model (SD) | In vivo: 20 mg/kg intraperitoneally after 1 h of HI and repeated once daily for 7 consecutive days | Nrf2 |
Inhibits apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress | [81] |
| MOR | OGD/R model (HT-22 cells) | In vitro: 5, 10 and 20 µM for 2 h and then exposed to OGD/R | SOD |
Inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis | [82] |
| EGCG | OGD/R model (BV2) | In vitro: 50, 100, 150, 200 and 250 µM, pretreatment for 1 h | HO-1 |
Inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis | [83] |
| CGA | HIBD model (SD) and OGD/R model (primary cortical neurons) | In vivo: 150, 300 and 600 mg/kg intraperitoneally for 3 days after HIBD; In vitro: 100, 200 and 300 µM after OGD | CAT |
Inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis | [84] |
| Genistein | HIBD model (C57BL/6) and OGD/R model (primary cortical neurons) | In vivo: 10 mg/kg, intraperitoneally once daily for 3 consecutive days before the operation; In vitro: 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5 and 15 µM for 24 h before OGD/R and during OGD/R | Bcl-2 |
Inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis | [24] |
| Lyc | HIBD model (SD) and OGD/R model (primary cortical neurons) | In vivo: 5, 10 and 20 mg/kg intragastrically after HIBD; In vitro: 2.5, 5 and 10 µM after OGD insult | Bcl-2 |
Inhibits apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress | [41] |
| EA | HIBD model (C57BL/6) and OGD/R model (primary cortical neurons) | In vivo: 50, 75 and 100 mg /kg intraperitoneally after HIBD; In vitro: 5, 10, 15 and 20 µM during OGD/R | Nrf2 |
Inhibits apoptosis and oxidative stress | [25] |
| Apigenin | HIBD model (SD) | In vivo: 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg intragastrically after HIBD | Nrf2 |
Inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis | [85] |
| VD | HIBD model (SD) and OGD/R model (SH-SY5Y cells) | In vivo: 0.1 µg/kg intraperitoneally for 2 weeks; In vitro: 20 ng/mL prior to OGD | SOD |
Suppresses ferroptosis | [50] |
| Mel | HIBD model (SD) | In vivo: 10 mg/kg intraperitoneally after HIBD | GSH |
Suppresses ferroptosis | [49] |
| Resveratrol | HIBD model (SD) | In vivo: 25 µg/3 µL intracerebroventricularly for 30 min before HIBD | Gpx4 |
Suppresses ferroptosis | [44] |
| SFN | HIBD model (SD) | In vivo: 5 mg/kg intraperitoneally for 30 min before HIBD | Nrf2 |
Inhibits apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress | [86] |
Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; CAT, catalase; CGA,
chlorogenic acid; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; EA, echinocystic acid; EGCG,
epigallocatechin gallate; GSH, glutathione; Gpx, glutathione peroxidase; Gpx4,
glutathione peroxidase 4; h, hour; HI, hypoxic-ischemic; HIBD, hypoxic-ischemic
brain damage; HIF-1
Following HI conditions, the inflammatory response is triggered by ROS, and the activation of Nrf2 can suppress inflammation via ROS elimination [86, 87]. Next, we summarized some compounds that provided neuroprotection in neonatal HIE models by inhibiting ROS-induced inflammation by activating Nrf2-related pathways or the Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Licochalcone A (LCA) is the main phenolic component of licorice. A recent study
has found that LCA administration counteracts OGD/R-induced downregulation of
sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)/Nrf2 and exerts beneficial effects on rat primary cortical
neurons by ameliorating ROS-induced inflammation. LCA upregulated the expression
of SOD, Nrf2, SIRT1, HO-1 and Gpx and decreased ROS, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH),
malondialdehyde (MDA), TNF-
A previous study has shown that H-Dmt-Tic-NH-CH(CH2–COOH)-Bid (UFP-512), which is a potent
Collectively, these results indicate that these compounds may exert neuroprotective effects in neonatal HIE models by activating Nrf2-related pathways or the Nrf2 signaling pathway to relieve ROS-induced inflammation.
After hypoxic-ischemic injury, the accumulation of excess ROS can lead to apoptosis, and apoptosis can be inhibited by activating Nrf2 [88, 89, 90]. Subsequently, we outlined several compounds that provided neuroprotection by ameliorating ROS-induced apoptosis by activating Nrf2-related pathways or the Nrf2 signaling pathway in neonatal HIE models.
Our previous study has confirmed that echinocystic acid (EA), which is an herbal pentacyclic triterpene, increases the ratios of p-PI3K/PI3K and p-Akt/Akt and the expression level of Nrf2 and exerts a neuroprotective effect against hypoxia-induced ischemic brain damage and ROS-induced neural apoptosis in both in vivo and in vitro models. EA administration also upregulated the expression of Bcl-2, GSH, NQO1 and HO-1 and downregulated the expression of Bax, MDA, ROS, Keap1 and cleaved caspase-3. Moreover, EA could effectively alleviate neuronal injury and long-term neurobehavioral deficits and decrease cerebral infarction and brain atrophy after HI [25]. Similarly, apigenin is widely found in chamomile tea, vegetables and celery and has a variety of biological properties, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic properties. Treatment with apigenin provided neuroprotection in neonatal HIBD rats by inhibiting ROS-induced apoptosis through the activation of the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Apigenin especially decreased the expression of Bax and cleaved caspase-3 and upregulated the expression of Bcl-2, HO-1, Nrf2 and myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1). Moreover, apigenin administration also markedly decreased cerebral edema and inflammation and improved structural tissue damage following HI [85].
Lycopene (Lyc) is a carotenoid compound isolated from tomatoes. Fu et
al. [41] found that treatment with Lyc was able to significantly upregulate the
protein levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 and ameliorated ROS-mediated apoptosis and
hypoxia-induced ischemic brain damage in both in vivo and in
vitro HI models. Furthermore, Chen et al. [42] demonstrated that
myricetin, which is a naturally occurring flavonol compound, could attenuate
neonatal HI brain injury by alleviating ROS-induced apoptosis through activating
the Nrf2 signaling pathway in both in vivo and in vitro HI
models. Myricetin could increase the expression levels of NQO-1, Nrf2, Bcl-2 and
HO-1 and decrease the expression of MDA, ROS, Bax, Keap1 and cleaved caspase-3.
In addition, myricetin also effectively reduced glial activation and brain
infarction volume in HI injury. Similarly, Zhang et al. [81] indicated
that tertiary-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ), which is an Nrf2 activator, promoted the
nuclear transcription of Nrf2 and suppressed oxidative stress and apoptosis in
neonatal HIBD rats. TBHQ increased the expression of Nrf2, HO-1, NQO1, SOD2 and
IL-10 and downregulated the levels of ROS, MDA, caspase-3, caspase-9, ICAM-1 and
IL-1
In general, the instances summarized above indicate that these compounds could ameliorate ROS-induced apoptosis and hold great promise for the treatment of neonatal HIE by activating the Nrf2-related pathway or Nrf2 signaling pathway.
After the occurrence of neonatal HIE, the accumulation of excess ROS could result in ferroptosis. However, activation of Nrf2 can ameliorate ferroptosis by eliminating ROS [44, 45, 91, 92, 93, 94]. Then, we identified various compounds that provide neuroprotection in neonatal HIE models by ameliorating oxidative stress and ferroptosis by activating Nrf2-related pathways or the Nrf2 signaling pathway.
A recent study has shown that resveratrol, which is a nonflavonoid polyphenol compound, can exert a neuroprotective effect against ROS-induced ferroptosis in the brain tissue of neonatal rats after HI via the SIRT1/Nrf2/Gpx4 signaling pathway. Intraperitoneal administration of resveratrol upregulated the expression of Gpx4 and Nrf2 and reduced the iron levels and MDA concentration. Furthermore, resveratrol attenuated brain atrophy, memory impairment and cognitive impairments [44]. In addition, it has been demonstrated that exogenous melatonin (Mel), which is secreted by the pineal gland, upregulates the transcription of p-Akt, Nrf2 and Gpx4 and exerts neuroprotective effects by attenuating ROS-induced ferroptosis in the cerebral tissue of neonatal rats post-HI. Exogenous Mel (10 mg/kg) increased the GSH expression level and decreased the 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) level. Additionally, treatment with exogenous Mel improved memory and long-term learning abilities in neonatal rats following HI [49].
Cai et al. [50] found that vitamin D (VD), which is a pleiotropic
steroid hormone, could obviously suppress oxidative damage and ferroptosis via
the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in both in vivo and in vitro HI
models. VD significantly reduced the levels of MDA & ROS and the levels of
inflammatory factors, including IL-1
Overall, these compounds significantly inhibited ROS-induced ferroptosis via activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway or Nrf2-related pathways and are promising neuroprotective drugs for neonatal HIE.
The reviewed literature in this study demonstrates that there is an important
relationship between oxidative stress and the pathophysiology of neonatal HIE,
and the Nrf2 signaling pathway plays an important part in cellular antioxidant
defense. Moreover, compounds targeting oxidative stress via activation of the
Nrf2 signaling pathway or Nrf2-related pathways exert great neuroprotective
effects against neonatal HIE. However, there are crucial issues that should not
be ignored. First, Nrf2 mRNA was significantly upregulated post-injury in the
cortex at 48 and 72 h and in the hippocampus at 48 and 72 h and 1 week in a mouse
model of focal traumatic brain injury [95]. So, it will be better to confirm the
optimal time to administer a possible Nrf2 activating compound via determining
the spatial and temporal distribution of the Nrf2 signaling pathway in neonatal
HIE. Furthermore, clinical and systematic preclinical studies are needed to
support the safety of these compounds in the treatment of neonatal HIE. Second, a
previous study has shown that due to the aggravation of oxidative stress,
mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) expression is markedly higher in healthy controls
than in patients with ischemic stroke [96]. Therefore, the relationship between
neonatal HIE and ROS-induced mtDNA damage is worth exploring. Third, Liu
et al. [97] reported that arachidonyl-2-chloroethylamide (ACEA)
attenuated neurological dysfunction and oxidative stress by promoting
mitochondrial autophagy (mitophagy) in an subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) model. Therefore, ROS-induced
abnormal mitophagy may be an important factor in neonatal HIE. At last, ketogenic
diet (KD) is one of treatments for neonatal HIE [98]. And a recent study has
shown that KD upregulates the expression of
Akt, protein kinase B; ACEA, arachidonyl-2-chloroethylamide; ARE, antioxidant
response element; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein;
COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; Cytc, Cytochrome c; CAT, catalase; CGA, chlorogenic
acid; DLG, Asp-Leu-Gly; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; ETGE,
Glu-Thr-Gly-Glu; EA, echinocystic acid; EGCG, epigallocatechin gallate; GPR39,
G-protein-coupled receptor 39; Gpx, glutathione peroxidase; GSH, glutathione;
Gpx4, glutathione peroxidase 4; h, hour; HIE, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy;
HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; HIBD, hypoxic-ischemic brain damage; HIOC,
N-[2-(5-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl) ethyl]-2-oxopiperidine-3-carboxamide; HI,
hypoxic-ischemic; HIF-1
J-WM conceptualized and designed the study. J-XL and DZ wrote the manuscript. J-XL, DZ, LC, SC and J-WM designed the figures. J-WM revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
We would like to thank American Journal Experts (AJE) for English language editing.
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82301574) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. CZQ23030 and CZZ23001) and the Fundamental Research Funds of the South-Central Minzu University (Grant No. YZZ19018).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.