1 Department of Scientific Research, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences Affiliated Zhoupu Hospital, 201318 Shanghai, China
2 Department of Physiology, Laboratory of Neurodegenerative Diseases, Changzhi Medical College, 046000 Changzhi, Shanxi, China
3 Traditional Chinese Vascular Surgery, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 201203 Shanghai, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a chronic neurodegenerative disease whose main
pathological features are the degeneration of dopamine neurons and deposition of
Keywords
- Parkinson's disease
- electroacupuncture
- dopamine
-synuclein
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that occurs in
middle-aged and older people. Studies have shown that the prevalence and
incidence of PD increase with age [1]. The main clinical manifestations of PD are
motor symptoms such as tremors, muscle rigidity, and bradykinesia. The main
pathological features include the degeneration of dopamine (DA) neurons and the
deposition of
At present, drug therapy is the main way for the treatment of PD. The most used drug is levodopa, which has represented the standard way to treat PD. It is an effective medical therapy for the symptomatic treatment of PD [6]. Nevertheless, long-term levodopa treatment is often related to motor fluctuations, such as discontinuous drug delivery, short half-life, poor bioavailability, and narrow therapeutic window [7]. These motor fluctuations have a serious impact on the quality of life of PD patients [7]. In addition to direct supplementation of exogenous DA precursors such as levodopa, other kinds of drugs treat PD clinically: DA receptor agonists such as pramipexole, monoamine oxidase B inhibitors (MAOBIs) such as selegiline, catechol-O-methyl transferase inhibitors such as entacapone, anticholinergics such as benztropine, and N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist such as amantadine [8, 9, 10]. However, although these treatments are initially effective, they present many problems, such as low tolerance and long-term effects. The management of PD has been transformed by surgical treatments. There are several therapeutic options available for managing PD motor complications, including deep brain stimulation (DBS), ablative or lesioning procedures (pallidotomy, thalamotomy, subthalamotomy), and dopaminergic medication infusion devices [11]. Typically, advanced treatment options are chosen based on factors such as the patient’s clinical characteristics, efficacy, ease of use, and risks of therapy [11]. PD treatment can be classified into early and advanced stages. Early PD refers to the initial stages of the condition. At this stage, the symptoms may not significantly impact daily activities. A cross-sectional evaluation of 15 years of experience with a large cohort suggests that the use of levodopa-sparing drugs should be considered more confidently [12]. Additionally, in appropriate clinical scenarios, combining substitution therapy with other antiparkinsonian medications should be considered to minimize levodopa dosage requirements [12]. Advanced PD refers to the later stages of the condition. Patients with advanced PD may experience severe motor complications and non-motor symptoms. Advanced PD treatment options encompass levodopa–carbidopa intestinal gel, continuous subcutaneous apomorphine infusion, DBS, radiofrequency ablation, stereotactic radiosurgery, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided focused ultrasound [13]. Among the invasive treatments, DBS demonstrates the most extensive evidence base, albeit carrying the highest individual per-patient risk [14]. However, currently, no therapy can efficiently curb the progression of PD [15]. All the while, various attempts are made to improve drug treatment for PD and avoid long-term complications. Good nursing, rehabilitation, and psychological therapy can improve symptoms to a certain extent, but the effect is limited. Therefore, it is particularly important to choose other treatment methods to slow down the progression of PD.
Acupuncture, used in China for over 2000 years, is a therapeutic method to treat
a wide range of chronic disorders. It has become popular all over the world.
Electroacupuncture is a modification of manual acupuncture, in which electrical
stimulation is administered through acupuncture needles. Compared with
traditional manual acupuncture, electroacupuncture has many advantages, such as
convenience, accuracy, objectivity, and repeatability, making it more suitable
for experimental research and clinical application. The effectiveness of
electroacupuncture depends on the choice of parameters, including acupoints,
current intensity, stimulation frequency, single treatment time, and treatment
times. Accumulating evidence indicates that electroacupuncture can be used to
treat various central nervous system diseases. The central nervous system
diseases include PD [16], stroke [17], pain [18], post-traumatic stress disorder
[19], spinal cord injury [20], and major depressive disorder [21]. According to
these studies, electroacupuncture is effective and has few side effects for the
treatment of various central nervous system diseases. Specifically,
electroacupuncture has obvious advantages in the non-drug treatment of PD [22].
Clinical studies have indicated that electroacupuncture treatment at acupoints
“Baihui” (GV20), “Dazhui” (GV14), “Zusanli” (ST36), “Hegu” (LI4), and
“Yanglingquan” (GB34), “Taichong” (LR3), “Taixi” (KI3), “Sanyinjiao” (SP6),
“Weizhong” (BL40) [23] may significantly enhance clinical symptoms reduction,
alleviate drug side-effects, delay disease progression as well as improve life
quality for patients with PD [24, 25, 26]. The pilot study demonstrated that following
electroacupuncture therapy, movement sway was reduced by 31%, and ankle/hip sway
increased by 46% in the intervention group [23]. Clinical ratings showed an
overall improvement in mental, behavioral, and mood functions as well as everyday
activities and motor skills (p
| Acupoints | Descriptions | Illustrations | References or Links |
| “Baihui” (GV20) | GV20 is the acupoint at the top of the head. It is located on the midline of the head in line with the apex of the ears, and it centers on the crown of the head. | 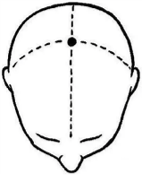 |
https://www.akupunkturatkm.com/post/akupunkturna-to%C4%8Dka-baihui-gv20-stotine-sre%C4%8Danj |
| “Dazhui” (GV14) | GV14 is located on the posterior aspect of the body, in the depression below the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebrae, approximately at the level of the shoulder. | 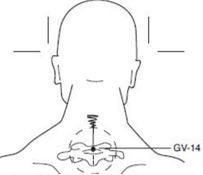 |
https://musculoskeletalkey.com/gv-14-da-zhui-big-vertebrae-central-reunion-point-2/ |
| “Fengfu” (GV16) | GV16 is located on the midline of the back of the neck in depression immediately below the occipital protuberance. | 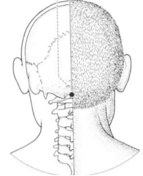 |
https://acumed.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/PL_GoverningVessel.pdf |
| “Guanyuan” (CV4) | CV4, the 4th meridian point of the conception vessel (CV), is located on the lower abdomen, at a point 3/5th down the ventral midline, which means on the lower 3/5th of the ventral midline connecting the umbilicus to the pubic tubercle. | 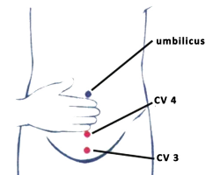 |
https://www.peakmassager.com/cv-4-acupuncture-point/ |
| “Hegu” (LI4) | LI4 is located on the dorsum of the hand, midway between the 1st and 2nd metacarpal bones, approximately in the middle of the 2nd metacarpal bone on the radial side. |  |
[29] |
| “Quchi” (LI11) | LI11 is at the lateral end of the transverse cubital crease midway between LU 5 and the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. |  |
https://www.peakmassager.com/li-11-acupuncture-point/ |
| “Sanyinjiao” (SP6) | SP6 is located medially 4-finger wide above the ankle. |  |
[30] |
| “Shangjuxu” (ST37) | ST37 may be found 6 cun below ST 35, at 1 finger width lateral from the anterior border of the tibia. |  |
[31] |
| “Taichong” (LR3) | LR3 is located on the dorsum of the foot, in the depression distal to the junction of the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones. |  |
https://acupuncturenepal.com/taichong-lr3.html |
| “Taixi” (KI3) | KI3 was located in the ankle area, at the midpoint between the prominence of the medial malleolus and the calcaneal tendon. |  |
https://acupuncturenepal.com/taixi-ki3-nomenclature-location-function-indication.html |
| “Taiyang” (EX-HN 5) | EX-HN 5 is located in the depression about 1 finger-breadth posterior to the midpoint between the lateral end of the eyebrow and the outer canthus. |  |
https://www.medicofisiatra.com.br/post/ex-hn5-taiyang |
| “Weizhong” (BL40) | BL40 is at the midpoint of the transverse crease of the popliteal fossa. |  |
[32] |
| “Yanglingquan” (GB34) | GB34 is located in the depression anterior and inferior to the fibula capitulum. |  |
[33] |
| “Zusanli” (ST36) | ST36 is located on the lateral surface of the leg, 3 cun distal to the lower border of the patella, 1 finger-breadth lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia, between the tibialis anterior muscle and the tendon of the extensor digitorum longus. |  |
[34] |
Basic researches have shown that electroacupuncture can effectively alleviate the motor dysfunction of PD model animals via a variety of acupoint combinations, including “Baihui” (GV20) and “Dazhui” (GV14) [35, 36, 37], “Yanglingquan” (GB34) and “Taichong” (LR3) [38, 39], “Zusanli” (ST36) and “Sanyinjiao” (SP6) [40], “Fengfu” (GV16) and “Taichong” (LR3) [41], “Baihui” (GV20) and “Taiyang” (EX-HN 5) [42, 43], “Hegu” (LI4) and “Taichong” (LR3) [44], “Baihui” (GV20) and “Sanyinjiao” (SP6) and “Taichong” (LR3) [45], “Fengfu” (GV16) and “Taichong” (LR3) and “Guanyuan” (CV4) and “Zusanli” (ST36) [46]. Specific electroacupuncture parameter settings can refer to the current intensity as 1mA, 2mA, 3mA step by step; each current intensity is maintained for 10 minutes; the stimulation frequency is 100Hz; each treatment lasts 30 minutes; 6 treatments a week; the treatment lasts for 4 weeks [35, 36, 37]. These studies provide potential insight into electroacupuncture in PD therapy. To better facilitate the application of electroacupuncture on PD, the neuroprotective effects and the underlying molecular mechanisms need to be illustrated.
At present, the research on the effects and the underlying mechanisms of
electroacupuncture in the treatment of PD is based on PD animal models, mainly
including the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP),
6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) and rotenone-induced PD animal models. The PD models
can simulate the pathogenesis of PD causing PD dyskinesia and can be used to
assess the effectiveness of treatment strategies. As shown below, accumulating
evidence indicates that electroacupuncture can rescue the main pathological
features of PD, including the degeneration of DA neurons and the deposition of
The degeneration of DA neurons, the reduction of DA transmitter production, and the imbalance of DA transmitters in the SN-striatum pathway is the main pathological change of PD, which in turn leads to a series of movements such as tremor, muscle rigidity, and slow movement. A study published in Nature Medicine showed that electroacupuncture on the sciatic nerve could induce the production of DA in the adrenal medulla [47]. As DA can cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB), electroacupuncture can promote the production of DA to replenish the brain. Besides, in a study using an MPTP-induced PD mouse model, electroacupuncture at the 2 acupoints “Zusanli” (ST36) and “Sanyinjiao” (SP6) with a frequency of 100 Hz could increase striatal tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) level [40] and then alleviated the motor deficits of PD mice. TH is an important enzyme in DA production, and its abundance reflects the increase in DA production. Another study showed the subcutaneous injection of rotenone induced a significant decrease in TH level in the SN of PD model rats, while the electroacupuncture treatment at the 2 acupoints “Fengfu” (GV16) and “Taichong” (LR3) also significantly increased TH level in PD rats [48]. Similarly, in the PD model rats established by injection of 6-OHDA into the left striatum, electroacupuncture treatment at “Baihui” (GV20) and “Taiyang” (EX-HN 5) could also increase the TH level in SN of PD rats [43]. Besides, in another study using 6-OHDA injected into the left striatum, both TH and DA transporters in the SN of PD rats were significantly down-regulated, while electroacupuncture at “Baihui” (GV20) and “Taiyang” (EX-HN 5) could up-regulate the contents of TH and DA transporters in the SN of PD rats [49]. In addition, electroacupuncture at “Baihui” (GV20) and “Taiyang” (EX-HN 5) could also increase the DA content in the striatum of 6-OHDA-induced PD rats [42]. What’s more, electroacupuncture at “Yanglingquan” (GB34) and “Taichong” (LR3) could reduce the degeneration of DA neurons in MPTP-induced PD mice [39]. Moreover, electroacupuncture at “Fengfu” (GV16), “Taichong” (LR3), and “Zusanli” (ST36) could increase the TH levels in serum and SN by up-regulating the activity of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway and alleviate the motor deficits of rotenone-induced PD mice [50]. Therefore, electroacupuncture can increase the content of DA and protect DA neurons, thus exerting neuroprotective effects on PD.
Lewy bodies are another typical pathological change of PD, and
As mentioned above, electroacupuncture can rescue the main pathological features
of PD, including the degeneration of DA neurons and the deposition of
Oxidative stress can cause the degeneration and loss of DA neurons and promote the apoptosis of DA neurons. It plays an important role in promoting the development of PD disease. Therefore, antioxidant therapy provides a new direction for the treatment of PD to some extent. A study explored the effect of electroacupuncture on MPTP-induced oxidation in mice. Researchers found that subacute administration of MPTP could enhance the oxidation of lipids and proteins in the striatum and reduce the expression of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase. MPTP also reduced the expression of the anti-oxidant transcription factor, nuclear factor-E2-related factor-2 (Nrf2), and Nrf2-regulated antioxidant enzymes such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate quinone oxidoreductase-1 and heme oxygenase-1 in the striatum and midbrain. In addition, Nrf2 also regulates human placental alkaline phosphatase (hPAP). And they also found that MPTP inhibited the expression of hPAP in the striatum and midbrain. Electroacupuncture at the 2 acupoints “Zusanli” (ST36) and “Sanyinjiao” (SP6) with a frequency of 100 Hz for half an hour a day (1 mA for 10 minutes, 1.2 mA for 10 minutes, and 1.4 mA for 10 minutes) could effectively reverse these changes caused by MPTP [40], thereby improving the motor function of PD mice. Another study constructed PD model rats by injecting 6-OHDA into the medial tract of the right forebrain. Results showed that neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) in the dentate gyrus of PD rats was increased, and electroacupuncture at “Hegu” (LI4) And “Taichong” (LR3) could down-regulate the nNOS content in PD rats [44]. In addition, electroacupuncture at the 3 acupoints “Baihui” (GV20), “Sanyinjiao” (SP6), and “Taichong” (LR3) could also alleviate the pathological changes in rotenone-induced PD rats, which might be related to the upregulation of SOD activity, glutathione peroxidase (GSH-px) activity, and glutathione (GSH) content, as well as down-regulation of malondialdehyde (MDA) content [45]. These results provide further evidence to support that electroacupuncture produces a series of antioxidant effects in PD.
In recent years, the role of neuroinflammation in PD has attracted much
attention. The degeneration and necrosis of DA neurons are closely related to
immune abnormalities. Neuroinflammation contributes to the onset and progression
of PD. It is of great significance to inhibit neuroinflammation in the treatment
of PD. In the MPTP-induced PD mouse model, electroacupuncture at the 2 acupoints
“Zusanli” (ST36) and “Sanyinjiao” (SP6) with a frequency of 100 Hz for half an
hour a day could reduce the microglia1 activation and astrocyte proliferation in
the striatum and midbrain [40], in turn, improved the motor capacity of PD mice.
Another study revealed that the expression of glial fiber acidic protein (GFAP)
and connexin (Connexin 43, Cx43) in the striatum of 6-OHDA-induced PD rats was
significant ascending, electroacupuncture at “Fengfu” (GV16) and “Taichong” (LR3)
could significantly down-regulate the GFAP and Cx43 contents in PD rats [52]. In
addition, in the PD rat model induced by subcutaneous injection of rotenone, the
expression level of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in the SN of PD rats was
significantly increased. At the same time, electroacupuncture at “Fengfu” (GV16)
And “Taichong” (LR3) could significantly down-regulate the expression of COX-2
[53], indicating that electroacupuncture can reduce the inflammatory mediator in
the SN of PD rats. Moreover, a study found that the expression of phosphorylated
extracellular regulated protein kinases (p-ERK1/2), tumor necrosis factor
(TNF-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a type of protein necessary for nerve cell survival and maintenance of phenotype. They are potential DA neuron protective factors, which protect catecholamine-containing cells from toxic damage. As the important neurotrophic factors in the SN-striatum system, the decline of BDNF and GDNF levels plays a key role in the pathogenesis of PD [57]. Studies have shown [41] that in the rotenone-induced PD rats, the mRNA expression of BDNF and GDNF in the SN remarkably decreased, while electroacupuncture at “Fengfu” (GV16) and “Taichong” (LR3) could up-regulate the expression of BDNF and GDNF in the SN, thereby improving the abnormal behavior of PD rats. Another study showed that [39], in the MPTP-induced PD mouse model, electroacupuncture at “Yanglingquan” (GB34) and “Taichong” (LR3) could activate protein kinase B (Akt) and BDNF in SN, thereby playing the neuroprotective role and reducing PD motor symptoms. Similarly, electroacupuncture at “Baihui” (GV20) and “Taiyang” (EX-HN 5) could also increase the expression of BDNF in the striatum and SN of 6-OHDA-induced PD rats [42, 43]. Moreover, another study found that electroacupuncture at the 2 acupoints “Fengfu” (GV16) and “Taichong” (LR3), or electroacupuncture at the 4 acupoints “Fengfu” (GV16), “Taichong” (LR3), “Guanyuan” (CV4) and “Zusanli” (ST36) both could up-regulate the expression of GDNF and its receptor Ret in 6-OHDA-induced PD rats. Besides, electroacupuncture at 4 acupoints causes higher GDNF content than at the 2 acupoints [46]. The above studies have shown that the increased content of neurotrophic factors participates in the effect of electroacupuncture in the treatment of PD. In addition to the lack of neurotrophic factors, nerve cell apoptosis may play an important role in the death of DA neurons in the SN. Reducing neuronal apoptosis may alleviate the onset and progression of PD. A study using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP) nick end labeling (TUNEL) method found that electroacupuncture at “Baihui” (GV20) and “Taiyang” (EX-HN 5) could reduce 6-OHDA-induced neuronal apoptosis in PD rats [42]. Another study using flow cytometry found that in 6-OHDA-induced PD model rats, electroacupuncture at “Fengfu” (GV16) and “Taichong” (LR3) could significantly reduce the apoptosis rate of neurons in SN of PD rats [58].
Evidence has shown that endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in the
pathogenesis of PD. A study demonstrated that electroacupuncture at “Fengfu”
(GV16) and “Taichong” (LR3) could improve the motor function of PD rats, which
was probably related to the down-regulation of the eukaryotic initiation factor
2alpha (eIF2
The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is an important pathway for protein
degradation in the body. The pathogenic genes of familial PD are closely related
to UPS, and the UPS function of the SN in patients with sporadic PD is also
selectively damaged. The studies indicate that UPS dysfunction plays an important
role in the onset and progression of PD. A study showed that ubiquitin, ubiquitin
C terminal hydrolase-L1 (UCH-L1), and ubiquitin-activating enzyme-1 (UBE1)
significantly decreased in SN of rotenone-induced PD rats, which were reversed by
electroacupuncture treatment at the 2 acupoints “Fengfu” (GV16) and “Taichong”
(LR3) [48]. In another study, the expression of 20s proteasome in the SN of
rotenone-induced PD rats also decreased, which was also reversed by
electroacupuncture treatment at “Fengfu” (GV16) and “Taichong” (LR3) [62]. In
addition, a similar study showed that the expression of 26s proteasome decreased
and the expression of NF-
A decrease in DA transmitter is the main cause of PD symptoms, but it is not the only neurotransmitter involved in the pathogenesis of PD. Excitatory amino acids and their receptors in the brain are also involved in the pathogenesis of PD, and their excitotoxicity is vital during PD progression. A study showed that the expression level of Cx43 protein and the content of excitatory amino acid glutamate significantly increased in the striatum of 6-OHDA-induced PD rats. Glutamate is a neurotoxic amino acid. When glutamatergic neurons release glutamate excessively, glutamate exerts excitotoxic effects. Electroacupuncture at the 2 acupoints “Fengfu” (GV16) and “Taichong” (LR3) could improve the motor function of PD rats, which may be related to the down-regulation of striatal Cx43 and glutamate levels [64], suggesting electroacupuncture could reduce the excitotoxicity in PD.
A number of studies have revealed a strong association between PD and autophagic defects. Enhancing autophagy to remove impaired mitochondria and toxic protein aggregation is a novel, promising therapeutic approach to treating PD. A study investigated the therapeutic mechanisms of electroacupuncture treatment in PD mice, and they reported that electroacupuncture at “Yanglingquan” (GB34) and “Taichong” (LR3) improved motor deficits and enhanced autophagy initiation (increased Beclin 1), autophagosome biogenesis (increased Atg5, Atg7, Atg9A, Atg12, Atg16L, Atg3, and LC3-II), autophagy flux/substrate degradation (decreased p62), and mitophagy (increased PINK1 and DJ1) in neurons of the SN, striatum, hippocampus, and cortex in PD mice [65]. This study indicated that electroacupuncture has exciting therapeutic potential in PD by regulating neuronal autophagy.
PD is a chronic neurodegenerative disease involving non-motor symptoms, of which
gastrointestinal disorders are the most common. Considering recent results,
intestinal dysfunction may be involved in the pathogenesis of PD. In our previous
study, we found that electroacupuncture at “Baihui” (GV20) and “Zusanli” (ST36)
was able to alleviate the motor deficits and partially rescue the significant
loss of dopaminergic neurons in the SN of MPTP-induced PD mice. Moreover,
electroacupuncture could significantly reverse the decreased intestinal microbial
alpha diversity of PD mice. The abundance of Erysipelotrichaceae was
significantly increased in PD mice, and the alteration was also reversed by
electroacupuncture. In addition, the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and
TNF-
To sum up, as a traditional Chinese medicine treatment method with effective and
few side effects, electroacupuncture is considered a non-drug therapy and serves
as a novel, promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of PD. Accumulating
evidence indicates that electroacupuncture can rescue the main pathological
features of PD, including the degeneration of DA neurons and the deposition of
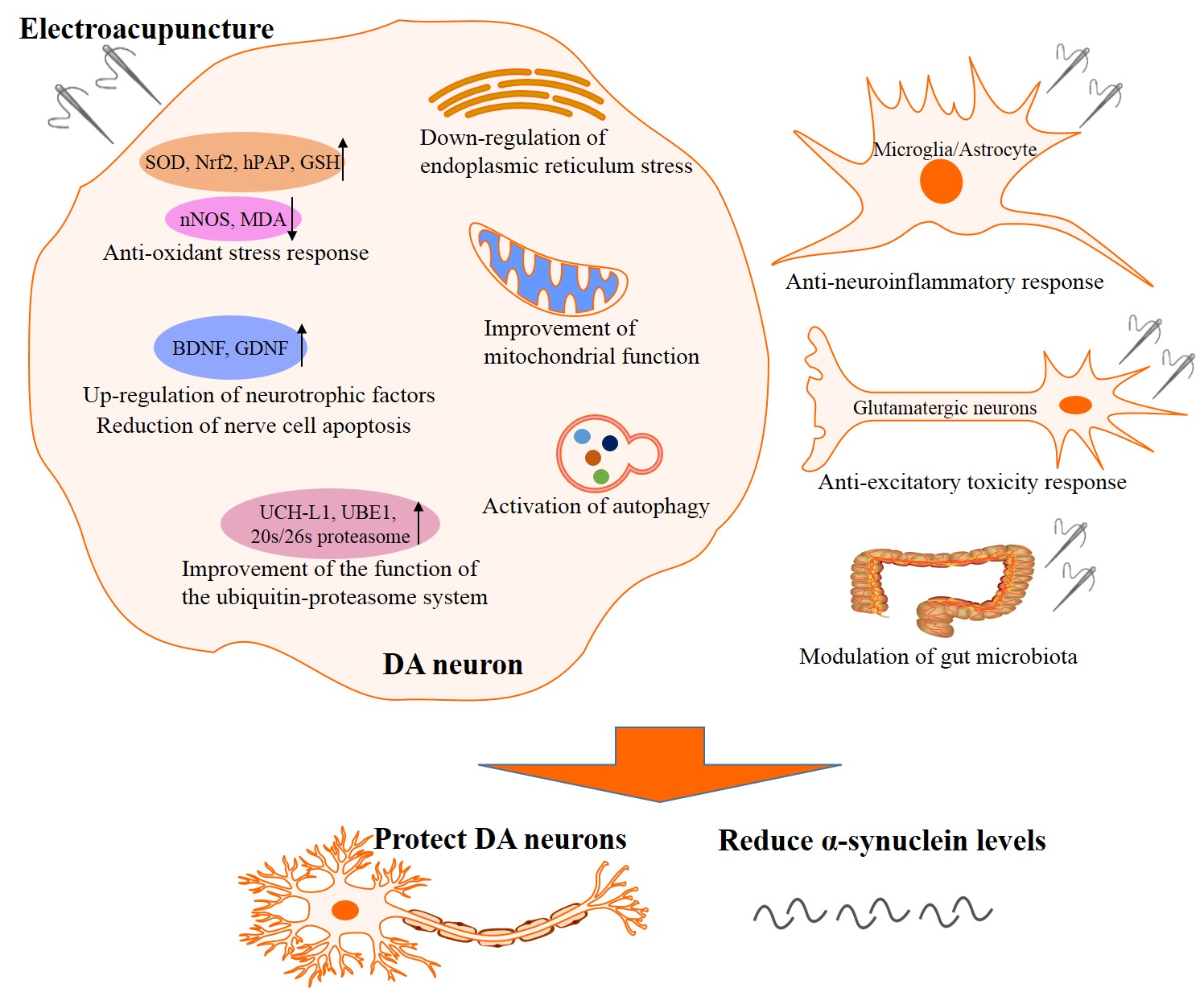 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.The underlying mechanisms of the neuroprotective effects of electroacupuncture on PD. The underlying mechanisms include ① anti-oxidant stress response, ② anti-neuroinflammatory response, ③ up-regulation of neurotrophic factors and reduction of nerve cell apoptosis, ④ down-regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and improvement of mitochondrial function, ⑤ improvement of the function of the ubiquitin-proteasome system, ⑥ anti-excitatory toxicity response, ⑦ activation of autophagy, and ⑧ modulation of gut microbiota. PD, Parkinson’s disease; DA, dopamine; SOD, superoxide dismutase; Nrf2, nuclear factor-E2-related factor-2; hPAP, human placental alkaline phosphatase; GSH, glutathione; nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; MDA, malondialdehyde; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GDNF, glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; UCH-L1, ubiquitin C terminal hydrolase-L1; UBE1, ubiquitin-activating enzyme-1.
However, the current research also has some shortcomings: ① The mechanisms of action of electroacupuncture in the treatment of PD are extensive and scattered, and the interaction between the molecular mechanisms cannot be explained clearly. ② The acupoints of electroacupuncture in different studies are not unified, and the therapeutic effects of different point combinations have not been compared. ③ The introduction or guidance on the application of electroacupuncture on PD in the clinic is lacking. Although clinical studies have shown that electroacupuncture treatment at “Baihui” (GV20), “Dazhui” (GV14), “Zusanli” (ST36), “Hegu” (LI4), and “Yanglingquan” (GB34), “Taichong” (LR3), “Taixi” (KI3), “Sanyinjiao” (SP6), “Weizhong” (BL40) [23] can effectively improve the clinical symptoms, relieve side effects of drugs, delay the progression of the disease, and improve the life quality of PD patients [24, 25, 26], clinical application of electroacupuncture in human individuals with PD is still limited and that guidelines and definitive evidence about efficacy are still lacking. ④ The data on mechanisms presented in the review are primarily derived from animal studies. However, it should be noted that there may be variations in acupuncture points between animals and humans, which could potentially result in distinct effects and molecular changes. Therefore, caution should be exercised when extrapolating these findings to humans. ⑤ PD is a chronic disorder, and as such, it is crucial to investigate the long-term effects of electroacupuncture in human individuals to accurately predict its therapeutic efficacy. However, it is worth noting that current research in this area is limited, and long-term studies involving human participants are currently lacking. Hence, it is imperative that future research endeavors focus on evaluating the therapeutic effects of electroacupuncture for PD, particularly in terms of long-term therapy. These future investigations will provide valuable insights into the efficacy, safety, and sustained benefits of electroacupuncture, ultimately enhancing our understanding of its potential as a treatment modality for PD. Taken together, the application and underlying mechanisms of electroacupuncture in the treatment of PD still need to be further studied.
QQH, XRC, and GBL conceptualized and designed the study, designed the figures, drafted and edited the manuscript. WHL, PQC, LJW, and RYH collected and analyzed the literature. XRC, GBL, and RYH revised this manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This work was supported by Health Commission of Pudong New Area Health and Family Planning Scientific Research Project (PW2020E-4), Siming Youth Fund Project of Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (SGKJ-202119), Medical Innovation Research Special Project of 2021 “Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan” of Shanghai (21Y21920200), Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (2021L350) and the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (20210302124194), and was Sponsored by Shanghai Rising-Star Program and Sponsored by Shanghai Sailing Program (23YF1418200), Shanghai Municipal Health Commission Foundation grant (20234Y0294) and the Hundred Teacher Talent Program of Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences (A1-2601-23-311007-21).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

