1 Department of Pharmacy, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, 430060 Wuhan, Hubei, China
2 Department of Pharmacy, Wuhan Fourth Hospital, 430033 Wuhan, Hubei, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDs), such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD), are major health problems worldwide. To date, available remedies against NDs are limited. In fact, current treatment options include drug intervention and nutritional therapy, which mainly focus on the repair of neuronal damage and functional monitoring. However, these treatments do not completely alleviate disease symptoms. Recently, eliminating harmful molecules, such as reactive oxygen species, and inhibiting neuroinflammation have become potential strategies recommended by many researchers. Accordingly, remarkable interest has been generated in recent years regarding natural products, including polyphenols, that provide neuroprotective effects. In this review, we aimed to provide experimental evidence of the therapeutic potential of punicalagin (PUN), a prevailing compound in pomegranate polyphenols with antioxidant activity. Overall, the chemistry, methods of determination, characteristics of metabolism, transformation mechanisms of action, and neuroprotective effects of PUN on NDs are summarised to provide a scientific basis for elucidating the therapeutic mechanisms and targets of NDs.
Keywords
- punicalagin
- neurodegenerative disorders
- therapy
- evidence
Increased consumption of fruits or nuts has beneficial effects on human health and can prevent various diseases [1]. Pomegranate (Punica granatum) is an ancient fruit that has been used since biblical times and is considered to be of high nutritional value and a folkloric medicine mainly based on anecdotal evidence of its benefits in treating a number of ailments and diseases [2]. Pomegranate has been traditionally used as a blood tonic in Asian countries; however, it is also popular in South America and Europe owing to its broad-spectrum health-beneficial properties [3].
According to previous studies, pomegranate juice is associated with many
positive health functions, such as reducing inflammation, inhibiting and
preventing cancer development, alleviating diabetes, and promoting
neuroprotective actions via antioxidant activity [4]. These biological
effects are attributed to bio-polyphenols, which are primarily composed of
hydrolyzable tannins [5]. Based on extensive evidence, punicalagin (PUN) is the
most abundant component of pomegranate peels. It has been that [6] reported that
more than two-thirds of the antioxidant activity of pomegranate juice is
attributed to the high proportion of PUN and its hydrolyzed tannins. The
concentration of PUN in juice can reach approximately 2 g/L and is composed of
high levels of glucose, which is located in the center of PUN [7]. Glucose exists
in
Extensive evidence shows that PUN has different biological activities, such as in cancer, cardiovascular diseases, liver diseases, and inflammation [8, 9, 10]. Recently, a pharmacological study found that this substance and its polyphenols had significant neuroprotective potential against Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), stroke, and stress [11, 12, 13, 14]. Neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) have common characteristics that are associated with oxidative stress (OS) and inflammation. Therefore, oral polyphenols, such as PUN, which have strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, may be feasible and effective as preventive and therapeutic strategies for NDs. In this review, the therapeutic potential and mechanisms of action of PUN in neurological diseases are systematically summarised to provide new insights into the treatment of NDs.
PUN (C
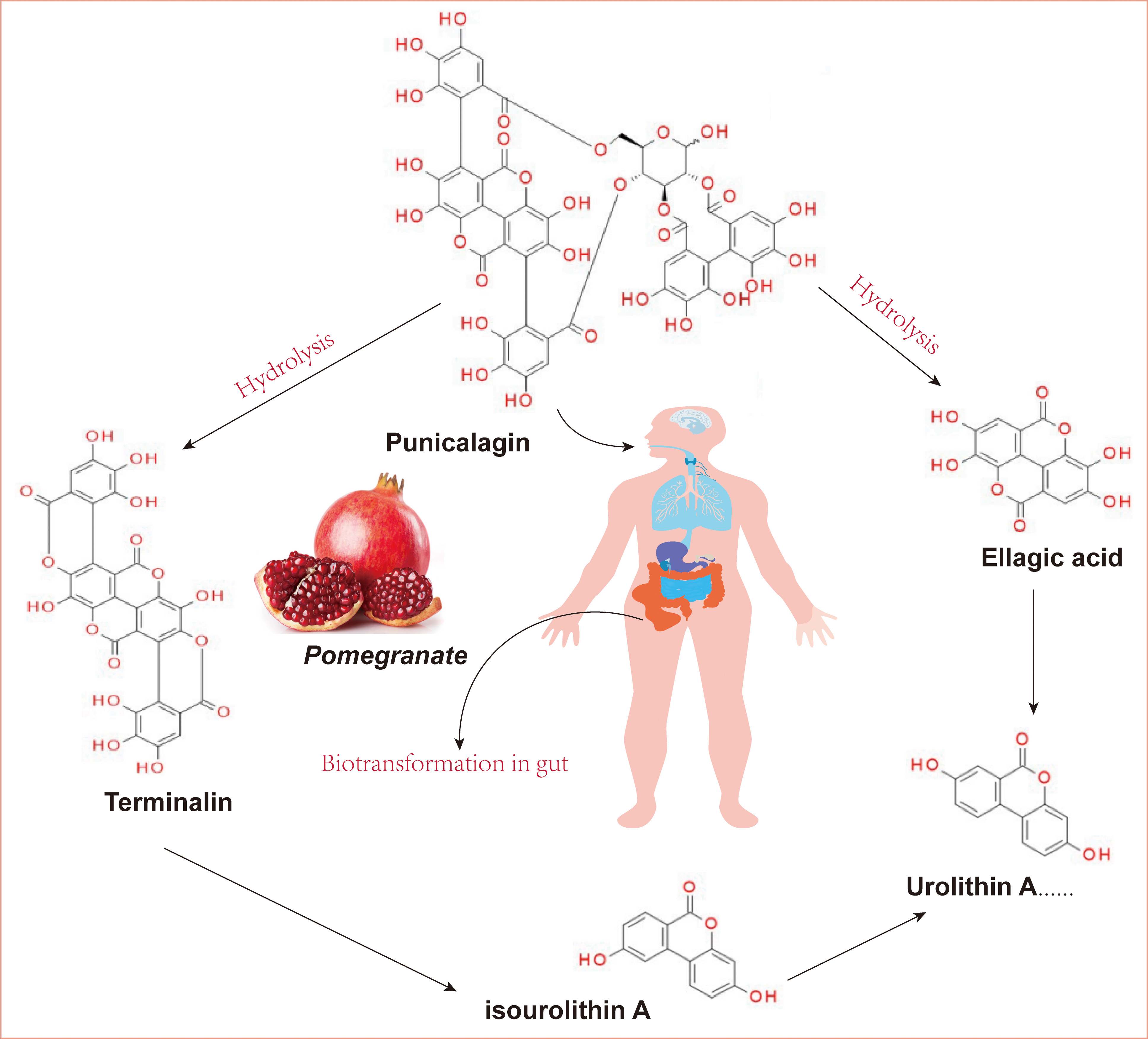 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.The structure of punicalagin and its derivatives. (Ellagic acid and terminalin were produced from PUN derived from pomegranate through hydrolysis and then metabolized into urolithins via biotransformation-gut microbiota). PUN, punicalagin.
PUN was isolated from the fruits and leaves of Elemia japonicae and Chekhoa. PUN is a specific component of pomegranate fruit [18]. It has been reported that the PUN content in pomegranate peel can reach 10–50 mg/g, which is the highest in common fruits. In addition, the concentration process was not found to affect the composition, properties, or content of PUN, indicating that concentrated pomegranate juice could provide health benefits to the body [19].
Currently, many mature chemical analysis methods, such as gas chromatography,
high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and ultra-performance liquid
chromatography-MS-MS (UPLC-MS
Qu et al. [21] developed an HPLC method for ellagic, gallic acid, and PUN determination. These results indicate that the HPLC method has good stability and reproducibility, a high recovery rate, and low limits of detection and quantification. In comparison to existing methods, this method significantly improves the permeability of the sample and can achieve content detection of four polyphenols, including pomegranate glycoside, pomegranate, ellagic acid (EA), and pyrogallic acid, in one operation. Other analytical methods, such as Raman spectrum and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, have been reported, which have certain advantages in the qualitative and isomeric analysis [6].
Oxidative stress in the body has now drawn much attention for its potential role in various diseases and is believed to be responsible for the increase in disease incidence in Western societies [22]. Numerous studies have shown that OS is a key link in cancer, inflammation, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, and aging [23, 24]. The toxicity of reactive oxygen species (ROS) depends on associated and sensitive biological substrates, such as nucleic acids, proteins, and membrane lipids. The biologically relevant ROS include superoxide anion radicals, lipid peroxides, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals [25]. Hence, the activated antioxidants have been demonstrated to be beneficial for health through scavenging these oxygen free radicals.
According to Harman’s free radical theory of aging, age-related chronic NDs such as AD, PD and multiple sclerosis (MS), are the consequence of damage to macromolecules by ROS in the mitochondria [26]. The role of OS in neurodegeneration has gained momentum in recent years as excessive ROS generation has been implicated in several neurodegenerative pathologies [23]; this can be explained by the fact that the mammalian brain is one of the most metabolically active organs in the body. Despite a relatively small size (2% of total body weight) the brain requires 20% of the oxygen consumption and energy generation from oxidation of glucose in the human body [27]. More importantly, the enhanced neuronal vulnerability to OS aggravated such fuel overconsumption. Nervous degeneration is a progressive age-related process. As aging intensifies, the mitotic renewal potential of neurons is compromised by long-term pro-oxidative environment [28]. The accumulation of ROS-damaged macromolecules, such as lipid peroxidation, oxidatively modified proteins, and DNA, can result in a serious decline in cell viability.
According to previous studies, ROS disrupts
the blood-brain barrier (BBB) by destroying tight junction proteins [29].
Furthermore, studies have confirmed that OS is an important mechanism underlying
amyloid
PUN has potent anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic, and antioxidant properties [31]. PUN protects endogenous organs and cells from OS-induced damage by directly scavenging free radicals and inducting Nrf-2 expression and the hundreds of antioxidant response element-dependent genes it regulates to counter the physiological and pathophysiological outcomes of oxidant exposure. Table 1 (Ref. [32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39]) displays the protective effect of PUN as an antioxidant in NDs based on in vitro experimental data.
| No. | Cell line | Models | PUN dose | Duration (hrs) | Effects | Suggested mechanisms | References |
| 1 | PC12 cells | H |
0.5, 1, 5, 10, 20 µM | 24 | cell viability |
ROS |
[32] |
| 2 | HT22 cells | Glutamate-induced oxidative toxicity | 6.25 and 50 µM | 24 | cell viability |
ROS |
[33] |
| 3 | IMR-32 cells | A |
20 µM | 48 | cell viability |
ROS |
[34] |
| 4 | SH-SY5Y cells | 6-OHDA-induced 7-oxidative damage | 50, 100, 200 µM | 2 | cell viability |
ROS |
[35] |
| 5 | Primary microglia | LPS-induced neuroinflammation | 5–40 µM | 24 | cell viability |
COX-2 |
[36] |
| 6 | BV2 cell line | LPS-induced neuroinflammation | 25, 50, 75, 100 µM | 24 | cell viability |
IL-6 |
[37] |
| 7 | BV2 cell line | LPS-induced neuroinflammation | 10, 20, 50 µM | 24 | COX-2 and iNOS |
IL-1 |
[38] |
| 8 | Primary microglia | A |
10 µM | 24 | TNF- |
NFATc2 |
[39] |
ROS, Reactive oxygen species; SOD, Superoxide dismutase; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; PGE2, Prostaglandin E2; COX-2, Cyclooxygenase-2.
Clementi et al. [32] pretreated PC12 cells with PUN (0.5, 1, 5, 10, and
20 µM) for 24 h and then exposed them to H
Interestingly, PUN has been shown to be beneficial in cell models of PD. Chu and Han [35] treated human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells with 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), a synthetic organic compound, in vitro to mimic PD. Pretreatment of SH-SY5Y cells with PUN (50, 100, and 200 µM) for 2 h significantly alleviated the 6-OHDA-induced decline in cell viability and apoptosis. PUN treatment effectively restored the mitochondrial function and enhanced AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation. Thus, a theoretical basis may exist for the application of PUN in the clinical treatment of PD.
According to considerable evidence, neuroinflammation plays a significant role
in AD and other NDs. Olajide et al. [36] examined PUN’s effects on
activated microglia in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced model of neuroinflammation. Rat primary
microglia were pretreated with PUN (5–40 µM) before stimulation with LPS
(10 ng/mL) and it was found to result in significant reductions in
TNF-
Owing to preclinical evidence, the in vivo effects of PUN on the treatment of NDs were evaluated, and the results are displayed in Table 2 (Ref. [38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50]).
| Condition | No. | Animal model | Dosage | Findings | Ref. |
| AD | 1 | APP/PS1 transgenic mice; 2-month-old | 50, 25 and 12.5 mg/kg daily; Oral administration for 45 days | Alleviated learning and memory impairment and ameliorated A |
[40] |
| 2 | Male APP/PS1 transgenic mice; 12-month-old | 1561 mg/L daily; Oral administration for 3 months | Improve cognitive deficits and reduced neuroinflammation | [41] | |
| 3 | Male Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) male mice; LPS-induced neuroinflammation model | 2.5 mg/kg daily; Oral administration for 4 weeks | Inhibited neuroinflammation, OS and memory impairment | [39] | |
| [38] | |||||
| PD | 4 | Male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats; Manganese-induced Parkinson’s disease; | 2.5 mg/kg daily; Oral administration for 35 days | Enhanced animal motor functions and decreased their catalepsy score | [42] |
| 5 | Male Wistar rats; ACR ip injection-induced d toxicity; | 10, 20, 40 mg/kg daily; Ip injection for 11 days | Recovered movement disorders, changed OS and reduced apoptosis | [43] | |
| Stroke | 6 | Male Wistar rats; Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)-induced ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury model | 15 and 30 mg/kg daily; Oral administration for 7 days | Presented a dose-dependent reduction in infarct volume and substantial improvement in behavioral deficits | [44] |
| 7 | Male Wistar rats; MCAO-I/R injury model | 15 and 30 mg/kg daily; Oral administration for 7 days | Improved neurologic deficits, brain water content (BWC), histopathology changes | [45] | |
| 8 | Male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats; Intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH)-induced brain inflammatory damage | 25, 50, 75 mg/kg daily; Oral administration for 2 weeks | Reduced inflammatory cell infiltration and cell damage, improved brain tissue architecture and BBB integrity | [46] | |
| Diabetes-induced neurology | 9 | C57BL/6 male mice; HFD (60% kcal fat content, D12492)-induced diabetes | 50 and 100 mg/kg daily; Oral administration for 8 weeks | Ameliorated the diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction and improved the neuronal apoptosis | [47] |
| 10 | C57BL/6J mice; Embryos were cultured for 24 or 36 hours with 100 mg/dL glucose | 0, 10 and 20 µmol/L; Whole-embryo cultured with 24 h | Protected against high Glucoseinduced cellular stress and neural tube defects | [48] | |
| 11 | Male Sprague-Dawley rats; Exposed to restraint stress on days 14–20 of pregnancy, three times each day | 50 and 100 mg/kg daily; Oral administration for 3 days | Protected the neurodevelopment and cognitive functions in vivo in rats offspring exposed to prenatal restraint stress | [49] | |
| Sleep deprivation memory deficits | 12 | Male Wistar rats; Lateral ventricular injection penicillin-G to induced neurotoxicity | 0.001, 0.01, or 0.1 µg/rat; Received a lateral ventricular injection | Alleviated total sleep deprivation and impaired memory processes | [50] |
AD, Alzheimer’s disease; PD, Parkinson’s disease; OS, Oxidative stress; BBB, Blood brain barrier.
AD is an age-related progressive neurodegenerative disorder and the most
prevalent cause of dementia [51]. Despite some pathological features, such as the
accumulation of A
Based on accumulating evidence, glia-mediated neuroinflammation is a
pathological hallmark of many central nervous system (CNS) disorders, including AD and brain aging [52].
Kim et al. [38] evaluated the anti-inflammatory activity of PUN in mice
co-treated with LPS. To examine the memory-improving effects of PUN in an
LPS-induced neuroinflammatory injury model, PUN (1.5 mg/kg) was continuously
administered to mice through drinking water for 4 weeks, followed by daily
injections of LPS for 1 week. PUN was found to ameliorate these memory-impaired
effects and reduce hippocampus levels of IL-1
PD is an incurable neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor and nonmotor deficits, which are caused by the death of dopaminergic (DA) neurons [54]. The hallmark of PD is related to the depletion of dopamine in the striatum, which leads to symptoms such as bradykinesia and resting tremors. Hence, the main goal of PD therapy is to prevent damage to dopaminergic neurons, despite the availability of few effective therapeutic agents for PD.
Environmental pollutants, such as manganese chloride (MnCl
As mentioned above, PUN has strong ability to mitigate PD progression, which is associated with its satisfactory activities in improving redox homeostasis and neuroinflammation.
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide, affecting millions of individuals each year [56]. Of these patients, 15% experience haemorrhagic, while 85% experience an ischaemic stroke. Cerebral ischaemia (CI) is considered one of the most disabling cerebral events. CI can cause motor, sensory, visual, speech, cognitive and other neurological dysfunction and forgetfulness, spatial learning, and memory disorders [57]. The conventional clinical drug such as alteplase can be applied for acute stroke; however, its therapeutic application is limited to the first 3 h of the occurrence of the stroke [58]. Owing to their limited therapeutic applications, remarkable research has focused on the evolution of traditional medicinal plants, nutritional supplements, and plant compounds.
Caspases are cysteine proteases that mediate apoptotic death in various cellular systems, including neurons [59]. Yaidikar et al. [44] demonstrated a high expression of activated caspase-3 after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in rat brains. In addition, the relative expression of caspase-3 was found to be significantly downregulated, thereby alleviating apoptosis in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model rats treated with PUN. In neurological disorders, the BBB plays a central role in the homeostatic regulation of the brain microenvironment in the case of ischaemia, irreversible tissue damage, and BBB breakdown, leading to the extravasation of serum proteins and development of vasogenic brain oedema. In another study performed by this group, it was found that there was a significant reduction in neurological deficit scores as well as brain water content (BWC), an indicator used to evaluate altered BBB permeability was observed in MCAO rats after treating with 15 and 30 mg/kg PUN [45]. Interestingly, inflammatory cell infiltration and neuronal damage were reported to be markedly reduced, and antioxidant enzyme activities, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), were increased through activation of the Nrf-2/ARE/HO-1 signaling pathway in rats with spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) after PUN intragastric therapy [46]. Taken together, PUN supplementation can effectively improve the neuronal damage caused by cerebral I/R, and its main mechanism may involve enhanced antioxidant function.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, PUN has been widely reported to ameliorate diabetes. Notably, PUN has been found to prevent diabetes-related cognition dysfunction in recent years. He et al. [47] reported that PUN effectively promotes the expression of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and attenuates neuronal apoptosis induced by a high-fat diet (mouse). The potential mechanism of action of PUN is related to AMPK activation and Krebs homeostasis. These findings further confirm the neuroprotective effect of PUN and provide new ideas for further elucidation of the mechanisms underlying diabetes-related nervous lesions and drug development.
Maternal diabetes-induced birth defects occur in 6–10% of babies born to mothers with pregestational diabetes, representing an important genetic issue. Exploring the effects of natural polyphenols with significant antioxidant properties and low toxicity on diabetic embryonic diseases can promote the development of new and safe dietary supplements [60]. Zhong et al. [48] determined whether PUN could reduce high glucose-induced neural tube defects (NTDs) in embryonic day 8.5 (E8.5) mouse embryos and whether this rescue occurs through the blockage of cellular stress and caspase activation. Surprisingly, 20 mM PUN significantly inhibited high-glucose-induced NTD formation. Moreover, experimental evidence revealed that PUN supplementation could abrogate endoplasmic reticulum stress and suppress the high glucose-induced caspase 3 and caspase 8 cleavage. These observations suggest that PUN supplementation protects against the teratogenicity of hyperglycemia in developing embryos and may prevent diabetes-induced NDs.
Dementia and cognitive impairment are leading causes of disability and death worldwide and pose a global health challenge as the population ages. An abnormal increase in mitochondrial homeostasis is considered the main cause of cognitive impairment. Cao et al. [49] evaluated the effects of PUN on the expression of AMPK in the offspring of rats subjected to prenatal restrictive stress. Based on the results, PUN protected neurodevelopment and cognitive function in mice by inducing mitochondrial biogenesis and phase II enzymes. Furthermore, PUN can protect mice from memory impairment induced by 24 h of total sleep deprivation (TSD) in the passive avoidance test [50]. Considering the beneficial effects of PUN reported in these studies, the possible mechanism of action of PUN on memory alteration should be further explored.
Currently, most existing studies have opted to explore the potential of PUN to protect neurons using in vitro cell line models. Notably, an extensive amount of time will be required to translate the obtained data into an in vivo model. For the application of PUN in neurotherapy, it is important to consider its processing in the human body. First, PUN passes through the intestinal tract after being taken orally and is easily affected by low stomach pH. Notably, digestive hydrolases are active [31].
PUN is a phenolic compound that is a hydrolyzable tannin that forms the same
subgroup as gallotannins [61]. Although the water solubility of hydrolyzed
tannins is satisfactory, their high molecular weight (generally
EA, a precursor compound of urolithins, can be released from ellagitannins, and the gut microbiota can convert these large structures into metabolites that are more bioavailable than the precursor compounds [65]. There are different metabolisms of hydrolyzable tannins in different individuals owing to different microorganisms in the gut [66]. According to the differences in metabolic phenotypes, urolithins can be divided into the following metabolic phenotypes: Uro-A (producing only uro-A conjugates), Uro-B (producing uro-A, isouro-A, and/or uro-B), and Uro-0 (no urolithins) [67]. Based on numerous studies, pomegranate fruit preparations intake can generate urolithin A, isourolithin A, and urolithin B in the body, and these substances are most likely responsible for the neuroprotective activity of pomegranate in the brain [68, 69, 70].
Similar to other ellagitannins, PUN has been confirmed to undergo analogical transformations in the human body. When PUN is hydrolyzed and degraded in the stomach, the products are processed into dibenzopyranone-type urolithin and isourolithin by the intestinal microflora [71, 72]. Compared to PUN, these released life-active molecules are not convergent but have many health benefits, including neuroprotective activity [73]. Iglesias-Aguirre et al. [74] summarised the neuroprotective functions of ellagitannin derivatives and discussed the neuroprotective effects of various urolithin types on brain health and their associated molecular mechanism. For instance, urolithin A has been demonstrated to cross the BBB and attenuate D-galactose-induced brain aging and cognitive function in mice via the activation of the miR-34a-Mediated SIRT1/mTOR signaling pathway [75]. Urolithin B has been demonstrated to have anti-apoptotic effects during brain aging, with an improvement in cognitive deficits by inhibiting Cyt C-mediated apoptosis and promoting the survival of neurons through the PI3K pathway in aging mice [76]. In summary, urolithins might be the main substances responsible for the neuroprotective activity of PUN in vivo.
Clinical trials are beginning to be undertaken using urolithin A, or elligatannin rich foods such as raspberry, walnuts or pomegranate [77, 78, 79]. These studies have demonstrated improved mitochondrial and endothelial cell function, muscle strength and endurance countering the decline in these components with aging. Urolithin A is a natural dietary metabolite that improves muscle health in old animals and in preclinical models of aging. Urolithin A induces beneficial alterations in fatty acid metabolism and intestinal cellular tight junctions which regulate intestinal permeability, improvement in gut bacterial biodiversity has also been observed. Urolithin A intake alters the gut microbiota, improving bacterial diversity and also improves endothelial cell function (UMIN-CTR, trial number: UMIN000042014) [80], improves fatty acid metabolism and increases the proliferation of the beneficial symbionts Clostridiales including, Ruminococcus lactaris, and Gemmiger formicilis in the microbiome [81]. R lactaris is an acetate producer, G formicilis is a carbohydrate fermenting Gram-ve anaerobic bacterium; both of these bacteria improve gut health. The Clostridiales is a key bacterial group that restricts gut colonization by potentially damaging Enterobacteriaceae pathogens thus ensuring a healthy gut environment is maintained for beneficial symbionts. Urolithin A also results in improvement in mitochondrial function with aging [82] and improved muscle performance suggesting urolithin A may counteract age-associated muscle decline and reduces age-related inflammation [83, 84, 85]. A double-blind randomized controlled trial [ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02734901] has shown that consumption of dietary achievable amounts of red raspberries which are rich in Urolithin A acutely improves endothelial function suggesting that punicalagin metabolites could also induce similar effects if therapeutic levels can be achieved [86].
According to available data, PUN might be a promising neuro prophylaxis for AD, PD, stroke, and other types of neurological diseases, regardless of the actual pharmacodynamic material basis [87]. Administering PUN with other components of pomegranate preparations as well as hydrolyzed conversion to EA, urolithins, and other components may prevent neurological defects [88]. In addition to the well-known antioxidant activity of PUN, the observed neuroprotective effects might be closely related to improvements in neuroinflammation in AD and PD. However, as most of the reported results are from animal and cell model studies, they must be considered in-depth before translation to practical applications. For example, to overcome the low bioavailability of PUN after oral administration, other routes of administration should be designed, such as the application of nanotechnology, sustained and controlled-release preparations, liposomes, and targeted therapy [89]. Finally, PUN might be a necessary factor in these neuroprotective effects; however, more research is needed to investigate the optimal therapeutic dose, timing of administration, and optimal PUN-containing substrates (purified compounds, extracts, juices, or fruits) for PUN to exert neuroprotective effects [90]. Moreover, whether PUN is responsible for its direct neuroprotective activity remains unclear, as increasing evidence suggests that derivatives of urolithins, produced by the intestinal metabolism of ellagitannins, may be the ultimate bioactive neuroprotective metabolites.
PC, ZLG and BHZ conceptualized and designed the study, analyzed and interpreted data. PC wrote the manuscript. PC and ZLG designed the figure. PC and ZLG acquired the data. PC and BHZ reviewed the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770381) and the Open Project of Hubei Key Laboratory of Wudang Local Chinese Medicine Research (Hubei University of Medicine) (WDCM2022006).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

