1 Department of Neurology, Nantong Hospital to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nantong Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 226001 Nantong, Jiangsu, China
2 Department of Neurology, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, 210004 Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
3 Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Nantong University, 226001 Nantong, Jiangsu, China
4 Department of Acupuncture and Massage, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, 226001 Nantong, Jiangsu, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: Neuroinflammation triggered by chronic cerebral
ischemia-induced microglial pyroptosis is a significant contributor to vascular
cognitive impairment. It has been shown that emodin possesses anti-inflammatory
and neuroprotective properties, however, it’s potential molecular and signaling
transduction pathway remains to be illuminated. This study researched the
neuroprotective mechanisms of emodin focussing on emodin effects on
lipopolysaccharide/adenosine triphosphate (LPS/ATP)-caused pyroptosis in BV2
cells and HT-22 hippocampal neurons. Methods: To explore the
neuroprotective effect of emodin, Emodin was applied to BV2 cells, HT-22
hippocampal neurons, and BV2/HT-22 co-cultures stimulated with LPS/ATP to
evaluate the cell morphology, levels of inflammatory factors, NLRP3 inflammatory
inflammasome activity and focal pyroptosis-related protein expression, as same as
neuronal apoptosis. Results: Emodin alleviated LPS/ATP-induced
pyroptosis of BV2 cells by preventing the activity of the NLRP3 inflammasome and
the cleavage of pyroptosis executive protein Gasdermin D (GSDMD). Furthermore,
levels of interleukin (IL)-18, IL-1
Keywords
- emodin
- microglia
- neuroinflammation
- NLRP3 inflammasome
- pyroptosis
As a stroke or vascular brain injury, vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) is induced by cerebrovascular lesions as well as their risk factors, which includes a range of cognitive impairments, from vascular moderate cognitive impairment to vascular dementia [1]. Since there is now no effective therapy for VCI patients, VCI is becoming a major public health issue worldwide [2]. VCI is a progressive disease with the neuroinflammatory response playing an significant function in the pathological changes of the vascular-neural cascade [3].
Pyroptosis, known as cellular inflammatory necrosis, is a recently identified
pattern of cell demise related to inflammation [4]. NLRP3 inflammasome
(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein3 Inflammasome),
an important regulator of pyroptosis, is a multimeric protein complex composed of
the receptor protein NLRP3, apoptosis-associated speckle-like protein (ASC) and
cysteine aspartate-specific protease 1 precursor (pro-caspase-1), which is mainly
expressed in astrocytes or microglia [5, 6]. As innate immune cells of the
nervous system, microglia cells have a crucial function in the central nervous
system (CNS) homeostasis [7]. Following ischemic brain injury, cells sent
damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMPs) signals, which are recognized by
NOD-like receptor proteins of the NLRP3 inflammasome [8]. The NOD-like receptor
proteins NLRP3 recruits ASC to activate caspase-1, which in turn, activates
pro-IL-18 and pro-IL-1
Emodin (1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methylanthraquinone, Fig. 1a) is an anthraquinone compound extracted from natural plants, which has been confirmed to have many pharmacological functions like anti-cancer [12], anti-inflammation [13], anti-oxidation [14], anti-viral [15], anti-bacterial [16], immunosuppression [17], and regulation of lipid metabolism [18]. Emodin can ameliorate ischemic brain injury via its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions, however the exact mechanism and target remain unclear [19]. Previous studies about emodin mostly focus on microglial activation [20], while there are few reports on microglial pyroptosis.
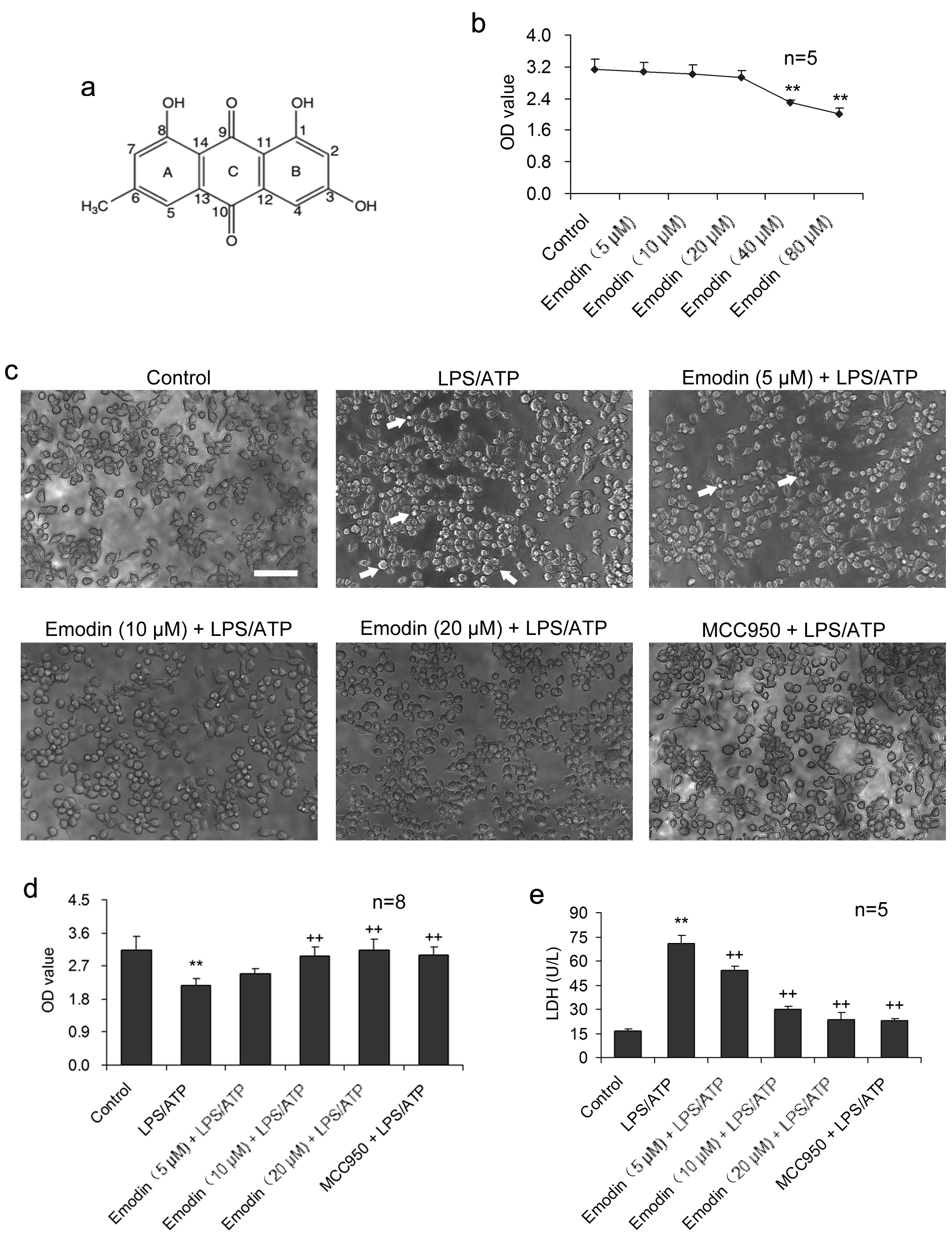 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Emodin suppresses LPS/ATP-caused injury in BV2 cells.
BV2 cells were stimulated with LPS and ATP in the presence or absence of emodin.
(a) The molecular structure of emodin. (b) BV2 cells were treated with emodin (0,
5, 10, 20, 40, 80
This study was designed from the perspective of microglial pyroptosis and neuronal injury. By establishing a co-culture model of BV2 microglial cells and HT-22 hippocampal neurons combined with LPS/ATP stimulation, we explored the potential effects of emodin in inhibiting neuroinflammation and exerting neuroprotection to achieve insight into the in vitro molecular and signaling mechanism of emodin.
BV2, a line of mouse microglial cells, was purchased from Guangzhou Jennio Biotech Co., Ltd (Guangzhou,
China) and cultured in DMEM at a density of 2
The cell line of mouse hippocampus neurons HT-22 (Jennio Biotech, Guangzhou,
China) was cultured in DMEM in a cell culture incubator. The cell cultures were treated with emodin (20
To detect the toxicity of emodin or LPS and ATP co-stimulation, 5
Proteins from cultured BV2 cells were extracted with lysis
buffer (2% SDS, 62.5 mM Tris-HCl pH 6.8, 10% glycerol, 4%
Following the manufacturer’s instructions, the levels of
TNF-
4% paraformaldehyde was used to fix the BV2 cells for 20 min at room temperature, followed with incubation in PBS with 0.3% Triton X-100 and 3% normal goat serum for 30 min. Then, cells were incubated with the primary antibody against ASC (1:100; ab307560, Abcam) overnight at 4 °C, followed by incubation with FITC-conjugated secondary antibody (1:400; ab6717, Abcam) for 18 h at 4 °C. To mark the nuclei, DAPI was used as a counterstain on BV2 cells, and the stained cells were quantified in five randomly selected visual areas on each coverslip under fluorescence microscopy (DMLB, Leica, Heidelberg, Germany). The ratio of DAPI-labeled cells to ASC-positive cells in each field of view was calculated for statistical analysis.
After fixation and permeability as above, the HT-22 cells were incubated with
primary antibody against NeuN (1:400; ab104224, Abcam) for 24 h at 4 °C.
Cells were immediately incubated with Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated secondary
antibody (1:400; ab150120, Abcam) for 18 h at 4 °C. To visualize
apoptotic cells, the Fluorescein in situ cell death detection kit (Cat.
no. 11684795910, Roche, Basel, Switzerland) was used in the TUNEL experiment as directed by the manufacturer. All images were
visualized by fluorescence microscopy (DMLB, Leica, Germany) at 200
LDH is an enzyme that is normally found in the cytoplasm and is released into the medium when the cell membrane is disrupted, thus, the quantification of LDH release can be used to evaluate the integrity of cell membranes. After LPS and ATP treatment, using an LDH Assay kit (Cat. no. K726, BioVision, Mountain View, CA, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, the cell supernatants were gathered for LDH measurement. LDH oxidizes lactate to produce NADH, reacting with WST, which can be measured at 450 nm optical density using an absorbance plate reader. Therefore, the volume of LDH that cells secreted was measured at 450 nm optical density with an absorbance plate reader (Model Synergy 2, BioTek, VT, USA), and then, the values were interpolated using the calibration curve and the LDH release finally was calculated and expressed as the value of U/L, which represents the degree of cell necrosis.
The vitality of the HT-22 cell was assessed using Syto-13/PI, two dyes with
various membrane permeabilities. Syto-13 is used to identify viable cells, whereas a non-permeant membrane red dye called PI is used to
spot cells that have changed membrane integrity and are either necrotic or in the
advanced stages of apoptosis. Briefly, cells were incubated with 0.1
Data are reported as mean
Emodin had no conspicuous cytotoxicity to BV2 cells during 24 h treatment at 20
The impact of emodin on LPS/ATP-induced BV2 cell pyroptosis was investigated
under the inverted phase-contrast microscope (Fig. 1c). LPS/ATP caused the
formation of abnormal cells, such as dysfunction of pores and cellular membrane
damage, as well as irregular shrinkage or
formation of closed-cell foams or bubbles. Necrosis was considerably increased.
Emodin treatment (5, 10, and 20
IL-18 and IL-1
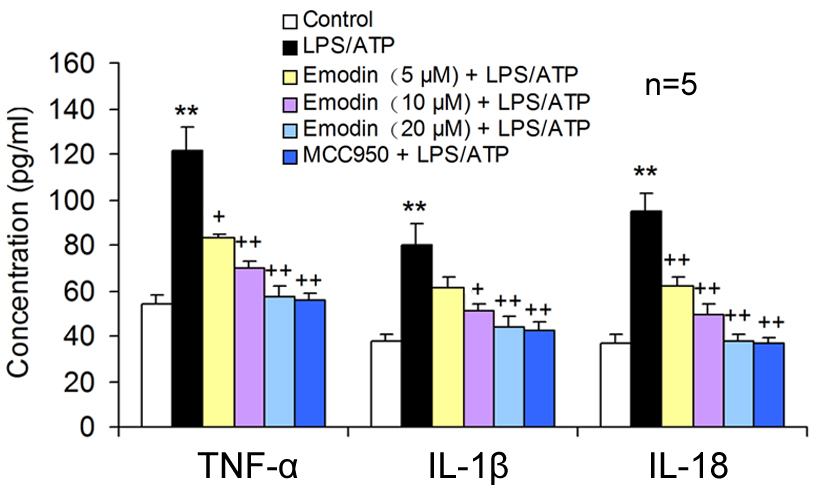 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Emodin decreased the pro-inflammatory cytokine release in
LPS/ATP-induced BV2 cells. BV2 cells were co-stimulated with LPS and ATP after
18 h pretreatment with emodin or MCC950. The TNF-
NLRP3 receptor protein does not possess pro-inflammatory activity. NLRP3 combines with caspase-1 and ASC to form the NLRP3 inflammatory body, which becomes proinflammatory. The activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome was examined using green fluorescence to label ASC and blue fluorescence to locate the nuclei in BV2 cells. Compared to the control group, a large number of NLRP3 inflammasomes were observed in the LPS/ATP stimulated cells, suggesting that LPS/ATP could activate NLRP3 inflammasomes. MCC950, the NLRP3 inflammatory body specific inhibitor, significantly inhibited the NLRP3 inflammatory body activation. Emodin also suppressed the formation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 3a,b), suggesting that emodin can suppress the NLRP3 inflammatory body activation.
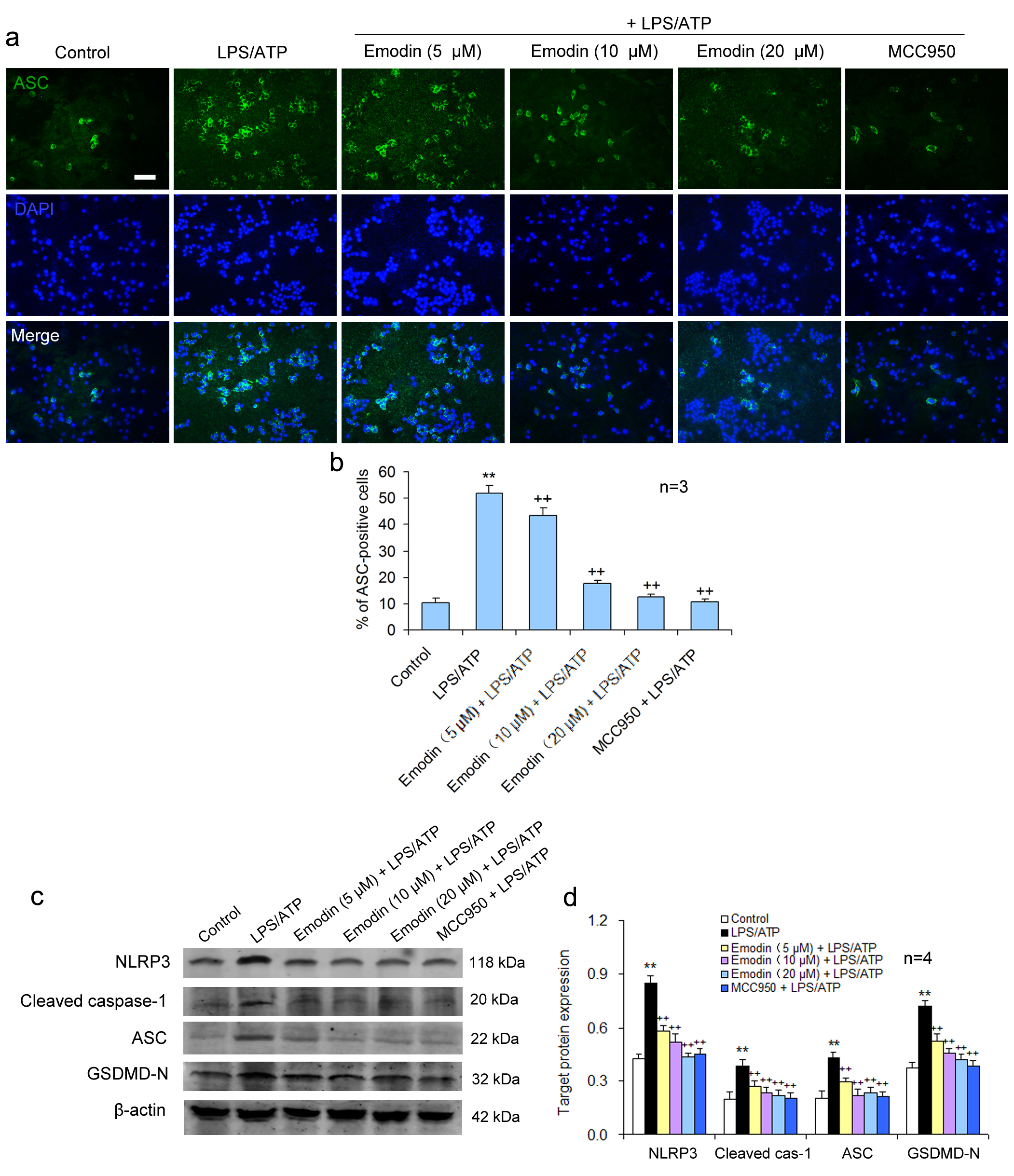 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Emodin suppresses pyroptosis via NLRP3/caspase-1 axis
inhibition in BV2 cells. BV2 cells were treated as above. (a) BV2 cells were
subjected to immunofluorescent staining for ASC and the nuclei were stained using
DAPI. Scale bar = 50
Pyroptosis is carried out by the pyroptosis-executing protein GSDMD and is triggered by NLRP3 activation. It was showed that emodin pretreatment significantly restrained the pyroptosis-related protein levels of NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1, and GSDMD-N in LPS/ATP-treated BV2 cells, similar to the effect of MCC950 (Fig. 3c,d). This suggests that emodin can prevent LPS/ATP-caused BV2 cell pyroptosis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Under normal conditions, there were no significant differences in LDH, optical density (OD) values measured by CCK8, and apoptotic rates between the HT-22 neuron group and the HT-22 neuron co-cultured group (Fig. 4). After LPS/ATP treatment, the release of LDH was significantly enhanced in the co-culture group (Fig. 4f), neuronal OD values were prominently decreased (Fig. 4e), and the neuronal apoptosis rate was improved (Fig. 4c,d), suggesting that microglial pyroptosis aggravates the degree of neuronal injury under LPS/ATP conditions.
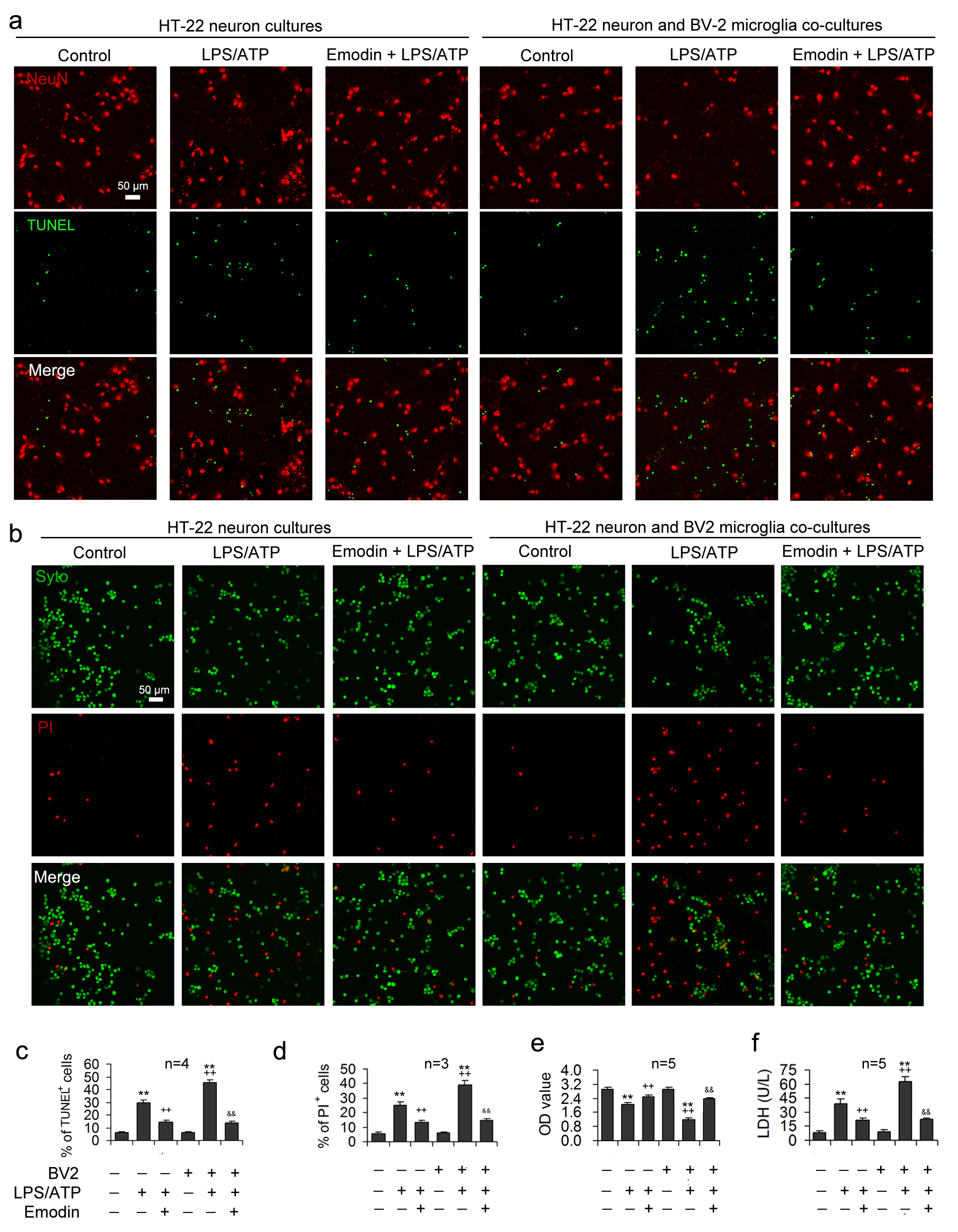 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Emodin alleviates LPS/ATP-induced neuronal toxicity by
inhibiting inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. LPS and ATP were applied to the
HT-22 neuronal mono-cultures or the transwell co-cultures of HT-22 neurons and
BV2 microglia after emodin pretreatment. NeuN and TUNEL double-staining was
performed in HT-22 cells to assess the neuroprotection influence of emodin.
Representative images are demonstrated in (a) and statistical data for the
proportion apoptotic cells expressed as the ratio of TUNEL-labeled cells to the
sum of NeuN
The supernatants obtained from the co-culture models were analyzed to confirm
the neuronal damage caused by excessive inflammatory mediator release, showing
that LPS/ATP stimulation resulted in markedly increased concentrations of
TNF-
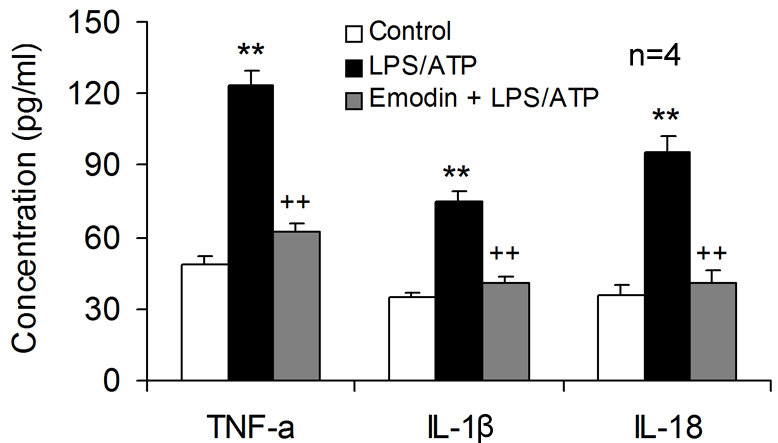 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Emodin is neuroprotective by inhibiting inflammatory mediator
release from microglia. Emodin was applied to the transwell co-cultures of HT-22
neurons with BV2 microglia, followed by LPS and ATP co-stimulation. Cell culture
supernatants in lower compartment were harvested to determine the concentration
of TNF-
This report describes the novel neuroprotective mechanism of emodin by
antagonizing the neuroinflammatory response mediated by microglia pyroptosis.
Emodin inhibited LPS/ATP-induced activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, preventing
pyroptosis executive protein gasdermin D (GSDMD) cleavage, and suppressing
LPS/ATP-caused pyroptosis in BV2 cells. Furthermore, emodin decreased levels of
the inflammatory mediators TNF-
The anti-inflammation effect of emodin has been reported recently but the
precise mechanism remains largely unknown. Park et al. [21] demonstrated that emodin surpressed microglia activity and decreased the
pro-inflammatory cytokine release. Liu et al. [22] reported that emodin
inhibited NLRP3 inflammasome activation and reduced IL-1
A increasing body of research has confirmed the existence of bidirectional
interactions between neurons and microglia [25]. Neuronal injury is associated
with neuroinflammation resulting from abnormal glial function. Under pathological
conditions, the pro-inflammatory cytokines produced by microglia have cytotoxic
effects on neurons [26] and conversely, DAMPs released by neurons are activation
signals of microglia [27]. An animal experiment successfully alleviated
stroke-induced progressive cognitive impairment by silencing microglia to
suppress neuroinflammation [28]. The present study showed that after LPS/ATP
treatment, the viability of HT-22 hippocampal neurons in the co-cultured group
was observably decreased comparison with that of the non-co-cultured group. The
severity of cell injury and the rapidity of neuronal apoptosis were markedly
increased in the co-culture group, suggesting the interaction between microglia
and neurons in pathological conditions. It has been demonstrated that emodin has
a protective impact on neurons [29]. Du et al. [30] reported that emodin
could exert a protective effect on HT-22 hippocampal cells by activating the PKC
pathway to reduce the inflammatory response in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. To
further elucidate the neuroprotective mechanism of emodin, we used emodin at a
concentration of 20
Emodin also reduced the release of pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-
In conclusion, emodin exerts neuroprotective effects on LPS/ATP-induced HT-22 hippocampal neurons, possibly by suppressing NLPR3 inflammasome-initiated pyroptosis in BV2 cells and antagonizing microglial neurotoxicity. This novel mechanism of emodin may be a potential treatment for neuroinflammation.
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
CC and XWY designed the research study. WJ and ZL performed the research. SW, LLX, and JFL provided help and advice on the TUNEL experiments. WJ and TM analyzed the data. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (approval number: 202112-012).
Not applicable.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 82201586), The Nantong Municipal Health and Family Planning Commission Science Foundation (Grant no. MB2021028), The Scientific Research Fund for Nantong social livelihood science and technology plan (Grant no. MS22022048), the Scientific Research Fund for Nantong TCM Medical Alliance (Grant no. TZYK202102), and Research and Practice Innovation Program of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (KYCX22_1893).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.





