1 Department of Pain, Guizhou Provincial People's Hospital, 550002 Guiyang, Guizhou, China
2 Department of Anesthesiology, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, 563000 Zunyi, Guizhou, China
3 Department of Pain, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, 563000 Zunyi, Guizhou, China
4 Department of Pain, The Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, 550004 Guiyang, Guizhou, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to observe the clinical efficacy
of long-term spinal nerve posterior ramus pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) in treating
subacute herpes zoster neuralgia (HZN). Methods: A total of 120
patients with subacute HZN in the thoracolumbar region and back were equally
randomized to the conventional PRF group (P group, n = 60), with a pulse
of 180 s, or to the long-term PRF group (LP group, n = 60), with a pulse
of 600 s. The patients’ baseline characteristics, the incidence rate of
postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), and the dose of analgesics were compared between
the two groups. Results: Based on the pain-rating index (PRI),
the PRI-sensory, PRI-affective, visual analogue scale, and present pain intensity
scores in the two groups were lower at T
Keywords
- long-term pulsed radiofrequency
- postherpetic neuralgia
- pulsed radiofrequency
- subacute herpes zoster neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a chronic neuropathic pain persistent after the onset of herpes zoster but residual after recovery from herpes [1, 2]. Its incidence and prevalence gradually increase with age. About 65% of patients aged 60 years and older with herpes zoster develop neuralgia [3]. This severe neuralgia usually lasts for more than a few months and manifests as spontaneous pain in the damaged skin area. According to its duration, the pain is divided into acute herpes zoster neuralgia (HZN; pain lasts for less than 1 month), subacute HZN (pain lasts for 1–3 months), and PHN (pain lasts for more than 3 months). Studies showed that oral medication, nerve block, and pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) treatment had much better effects on acute HZN than on subacute HZN and PHN [4, 5]. No exact explanation exists for this phenomenon. Studies revealed that 15–30 days is the key conversion period of HZN, and during this period the changes in the function and plasticity of subcutaneous nerve fibers reach a peak and the pain changes from acute inflammatory pain to nerve injury pain [6, 7, 8, 9]. Therefore, controlling pain by adjusting the nerves through PRF during this period is more desirable. After a certain duration, the patient’s subcutaneous nerve fibers atrophy significantly, and plasticity changes in nerve fibers persist, which may lead to the poor analgesic effect of standard PRF.
The spinal nerve posterior ramus is a mixed nerve originating from the lumbar spinal nerve. It is located below the anterior branch, on the upper edge of the transverse process of the lower vertebral body, and about 60 degrees backward from the lateral side of the superior articular process. It is divided into medial and lateral branches. The lateral branch mainly controls the paravertebral muscles and the skin on the back of the body [10]. After the medial branch encircles the outer side of the superior articular process, it passes through the bony fiber tube formed by the accessory process of the upper joint and the intermastoid groove ligament of the lower joint to descend the three vertebral bodies. It then sends out fine branches to the facet joint and the nearby muscles. Recent clinical studies found spinal nerve posterior ramus PRF effective for treating lower-back PHN, thereby reducing the patient’s dose of morphine and untoward reactions [11].
Pain signals can be transmitted to the central dorsal horn of the spinal cord through the peripheral end of dorsal root ganglion nociceptor neurons [12]. Moreover, the dorsal horn of the spinal cord uploads the received pain information to the thalamus and brain through the corresponding interneurons, finally producing pain. Studies have revealed that the closer the dorsal root ganglion is treated, the better the effect [13, 14, 15, 16]. PRF is an improved version of radiofrequency thermocoagulation, which has been used for treating chronic pain [17]. PRF mainly emits pulses to act around the nerve tissue through the radiofrequency instrument and creates a high voltage so that the heat generated by the pulse current near the affected tissue can be diffused. The local temperature does not exceed 42 °C, avoiding the damage caused by high temperature to the nerve, and the nerve tissue does not degenerate and can play a protective role in integrating nerve functions to avoid postoperative sensory and motor nerve abnormalities caused by nerve injury [18, 19]. Kagan et al. [20] reported that the ultrastructural assessment of PRF lesions in rat lower extremity nerve showed that PRF treatment did not cause the unmyelinated nerve fibers to ultrastructurally impair. The efficacy of PRF treatment does not depend on the thermal injury to neurologic tissues [21]. PRF is widely used in various neuropathic pains, and clinicians have confirmed its effectiveness. A large number of researchers have confirmed that the conventional PRF mode adopts a temperature of 42 °C, a voltage of 40 V, and a time of 120 s, and its intensity is limited; thus, the patient does not get optimal treatment. Therefore, this study prolonged the duration of PRF to observe its long-term analgesic effect on subacute HZN and analyzed its possible mechanism to provide a theoretical basis for the clinical treatment of subacute HZN.
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital (approval No. KY2022-78), and all patients signed the informed consent form. A total of 120 patients with subacute HZN (men and women, aged 45–70 years, with disease duration ranging from 1 to 3 months) were hospitalized. They were equally randomized to the conventional PRF group (P group, n = 60), with a pulse of 180 s, and the long-term PRF group (LP group, n = 60), with a pulse of 600 s.
The inclusion criteria were as follows. (1) The pain of the patients was located in the chest, waist, and back, and the number of damaged segments was between 1 and 3, which met the diagnostic standard of the International Association for the Study of Pain. (2) All patients also had pigmentation or scars after local skin rashes, local scars had fallen off, no active exudation and bleeding were observed, and tenderness or hyperalgesia was noted. (3) The visual analogue scale (VAS) score was from 4 to 7. (4) No other acute or chronic pain, history of mental illness, and history of severe cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases were present.
The exclusion criteria were as follows. (1) VAS score was
The corresponding posterior branch of the spinal nerve PRF was selected based on
different pain sites. All patients with chest, waist, and back pain underwent
surgery in the prone position with the help of digital x-ray to ensure safety and
efficacy. Patients underwent the following treatment procedures: (1) Punch
surgery. This surgical method involved routine electrocardiogram monitoring,
adopting an appropriate position, using digital x-ray to locate the puncture
position according to the nerve distribution position, routine disinfection,
draping, and choosing a radiofrequency needle of appropriate length for puncture
based on the puncture site. (2) Radiofrequency pulse treatment: After the puncture
needle was put in place, the core of the radiofrequency needle was pulled out,
and an electrode was inserted. The treatment device showed an impedance of
100–500
The short form of the McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ) consists of a pain-rating index (PRI) having 15 descriptors of pain: 11 sensory (PRI-sensory, PRI-S) and 4 affective pains (PRI-affective, PRI-A). The SF-MPQ also includes VAS and present pain intensity (PPI) of the standard MPQ. In the PRI-S and PRI-A categories of PRI, all descriptors are assigned scores of 0–3 to represent “none”, “light”, “medium”, and “heavy”, respectively. The total PRI was calculated based on these scores. VAS scores allowed the patients to quantify the pain sensation between 0–10 points, with 0 representing no pain and 10 the maximum pain. In PPI, 0 represents no pain, 1 light pain, 2 discomfort, 3 pain, 4 terrible pain, and 5 extreme pain.
The incidence rate (IR) of PHN was calculated based on the number of cases
(N1) with persistent pain after treatment, the VAS score greater than 4,
and the number of cases (n) before PRF treatment: IR = (n –
N1)/n
Patients with subacute HZN were followed up for 2 months after PRF treatment, and the postoperative VAS scores were calculated based on the patient data. The treatment condition of patients was assessed during their visit to the clinic and on telephonic follow-up; the VAS scores and the dose of analgesics were recorded, and the efficacy 2 months after treatment was evaluated.
The effective rate of treatment of the posterior branch of the spinal cord in
the long-term PRF group was 87% during the preliminary observation by our study
group, whereas in the conventional PRF group it was 65%. We used the R software
package to analyze the sample size. The statistical test power (1 –
The SPSS 26.0 statistical (SPSS IBM Corporation, NY, USA) was used for data analysis. The data were expressed as mean
The two groups of patients were found to have no statistically significant
differences (p
| Variables | P group (n = 60) | LP group (n = 60) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year, |
64 |
65 |
0.361 |
| Sex ratio (male/female) | 32/28 | 30/30 | 0.452 |
| VAS score (points, |
6.2 |
6.3 |
0.674 |
| Underlying disease (n) | 0.426 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus (n) | 14 | 16 | |
| Hypertension (n) | 18 | 20 | |
| Diabetes mellitus & hypertension (n) | 10 | 8 | |
| None (n) | 18 | 16 | |
| Involved dermatome (n) | 0.126 | ||
| Thoracic (n) | 22 | 24 | |
| Lumbosacral (n) | 38 | 36 | |
| Analgesics at pre-PRF treatment stage (n) | 0.422 | ||
| Tramadol only (n) | 8 | 6 | |
| Tramadol with pregabalin (n) | 10 | 10 | |
| Opioid only (n) | 6 | 6 | |
| Opioid with pregabalin (n) | 8 | 14 | |
| Opioid with gabapentin (n) | 12 | 10 |
After PRF treatment, the PRI-S, PRI-A, VAS, and PPI scores were lower at
T
| Variable | Patient group | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRI-S | P | 13.1 |
6.5 |
8.6 |
4.6 |
| LP | 13.4 |
4.3 |
6.9 |
3.6 | |
| PRI-A | P | 4.0 |
3.6 |
3.8 |
2.7 |
| LP | 4.5 |
3.1 |
2.3 |
2.5 | |
| VAS | P | 6.3 |
3.2 |
4.1 |
2.9 |
| LP | 6.2 |
3.0 |
2.5 |
2.3 | |
| PPI | P | 3.6 |
2.5 |
2.1 |
1.8 |
| LP | 4.0 |
2.5 |
2.0 |
1.3 |
T
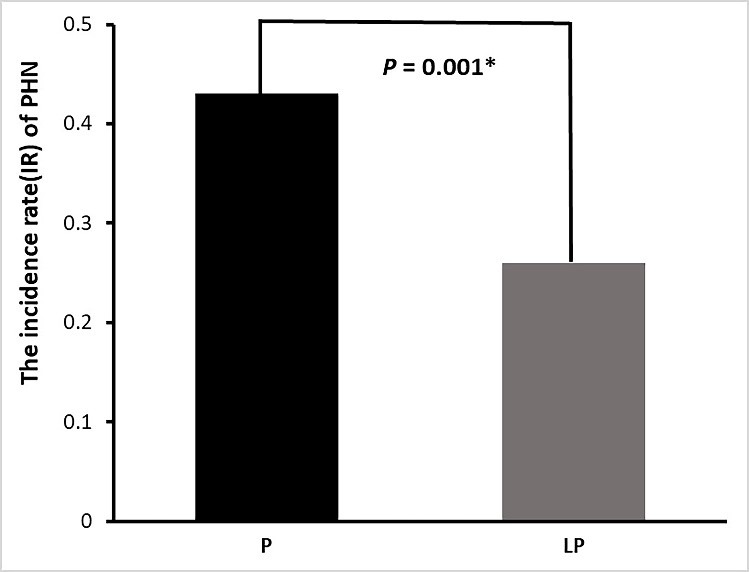
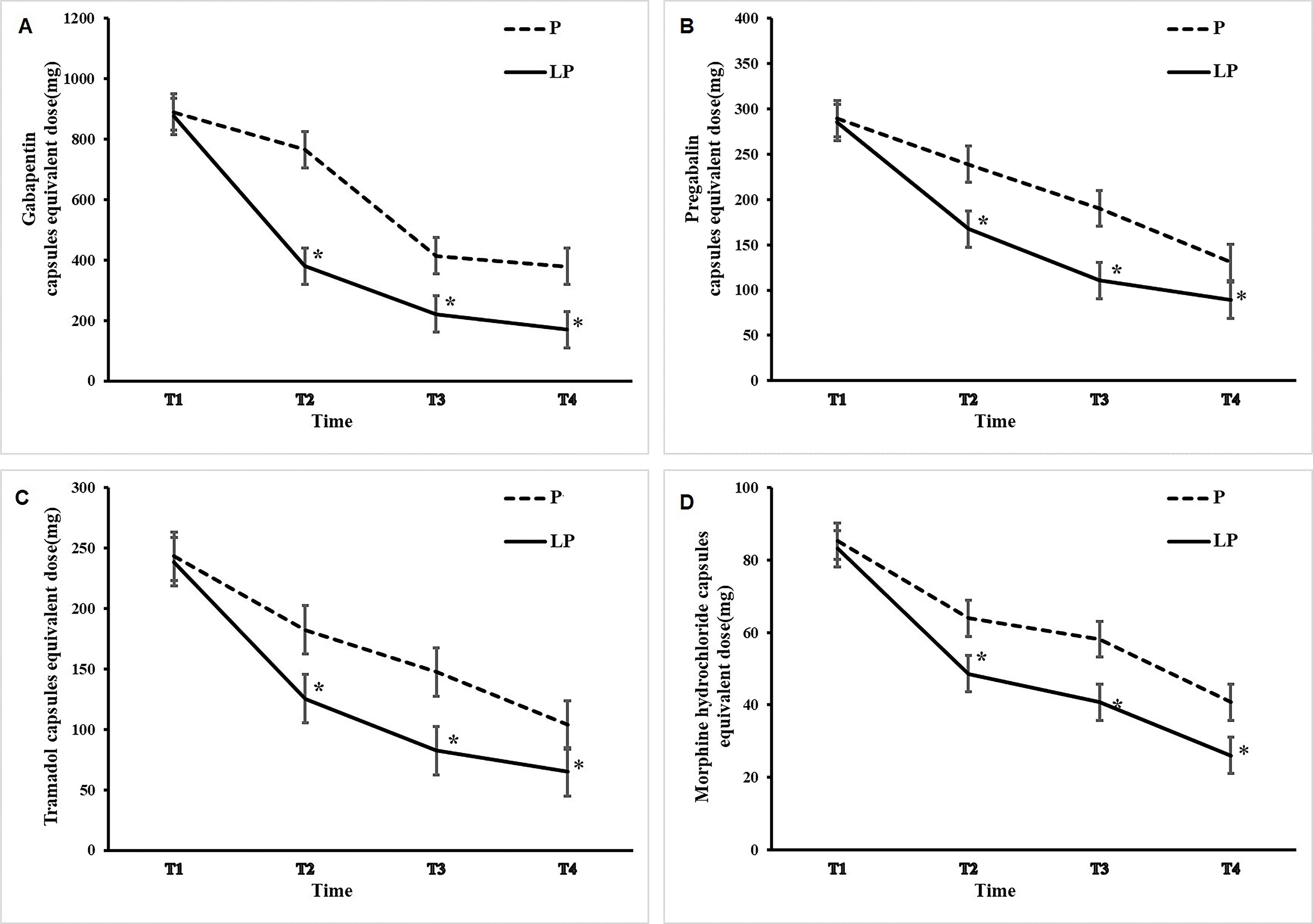
After 2 months of treatment, the patients’ analgesic intake and incidence of PHN were followed up (Figs. 1,2).
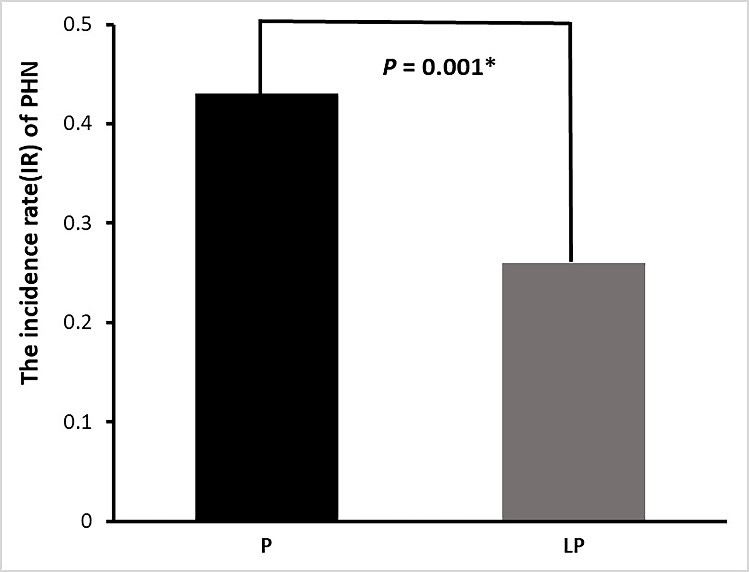 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Proportion of clinically significant PHN 2 months after PRF
treatment in the two patient groups. Gray and black bars show the incident rate
of PHN in the LP and P groups, respectively. *p
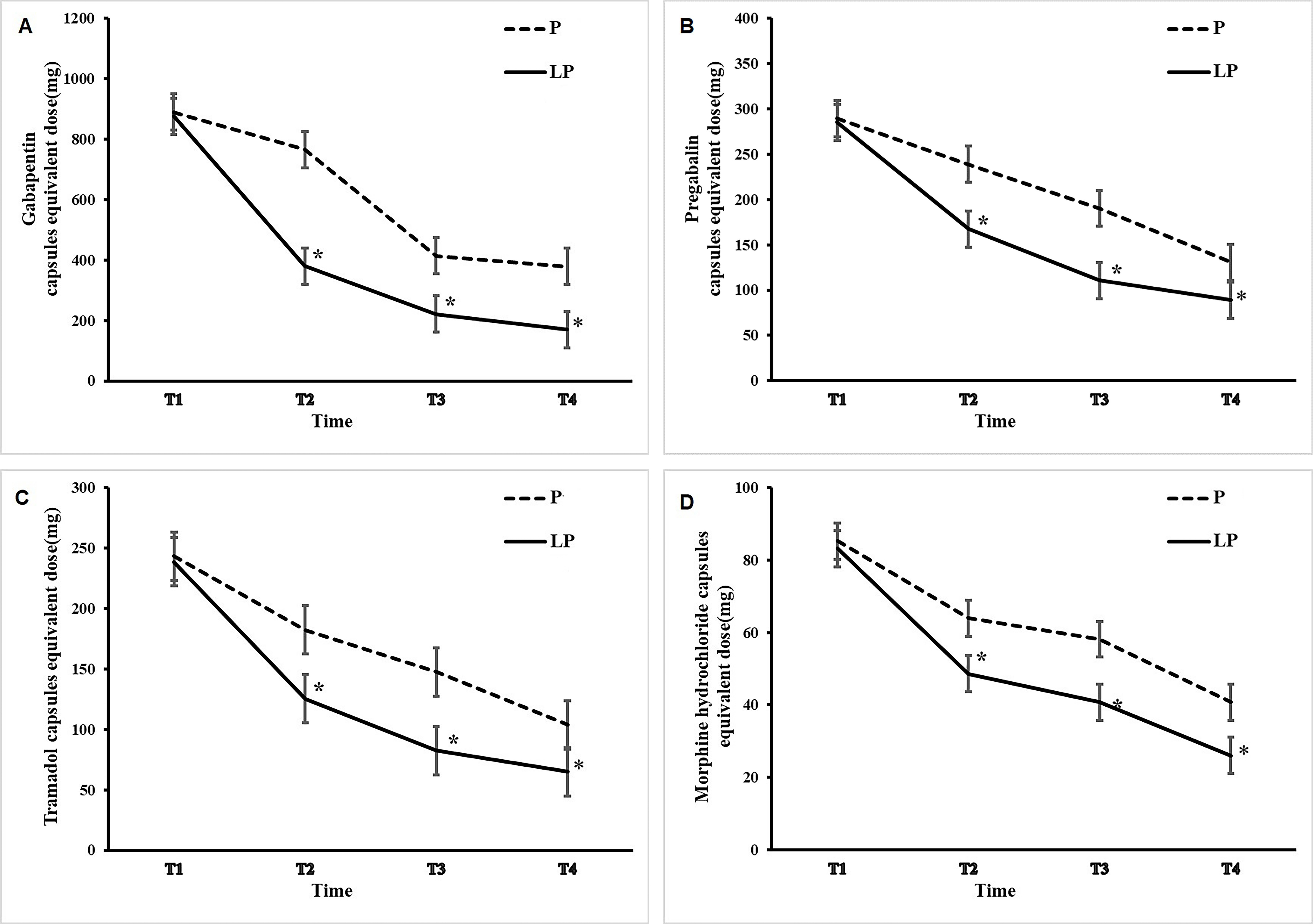 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Changes in dose of tramadol, morphine hydrochloride, pregabalin,
and gabapentin after PRF treatment. The solid curves and the dotted curves
depict the dose changes in the LP group and P group, respectively. The dose of
tramadol (A), morphine (B), pregabalin (C), and gabapentin (D) was generally
higher. *p
The study aimed to explore long-term spinal nerve posterior ramus PRF efficiency in patients with subacute HZN, and the results showed that increasing pulse treatment duration could improve pain relief and sleep quality in patients. As neuropathic pain, HZN is manifested as spontaneous allodynia and hyperalgesia in the damaged skin area, which persists for a long time. Its incidence is closely related to aging, and various analgesics (such as antiepileptics, tricyclic antidepressants, and opioids) have varying degrees of analgesic effects on HZN [22, 23, 24]. However, the neuropathic pain it produces cannot be completely controlled. Some patients still develop subacute HZN and PHN. The efficacy of analgesics is much lower in patients with subacute HZN than in those with acute HZN. Persistent pain can cause anxiety, insomnia, depression, and even loss of life and working ability in severe cases [25]. Some scholars believe that inflammation and degeneration of peripheral nerve fibers and endings are the main causes of HZN pain [6]. Some other scholars believe that the formation of this type of neuralgia is not only caused by peripheral nerve lesions but may also be related to pathological changes in the central nervous system (spine and brain) [26]. In persistent pain in HZN, neuronal cells are continuously stimulated by peripheral nerve afferent fibers; this leads to continuous activation of neuronal cells, release of some inflammatory factors, and triggering of the activation of glial cells so that the activation state of neurons is protected, producing central sensitization [27]. Therefore, the treatment of this neuropathic pain involves blocking or weakening of the pain afferent signal and avoiding continuous stimulation of the spinal center [28].
PRF is an improved radiofrequency treatment. Its main advantage lies in using low control current and low control voltage; the temperature can be controlled. Studies have shown that temperatures lower than 45 °C do not cause significant nerve fiber damage and have a good effect on neuropathic pain [29, 30]. The mechanism of action of PRF current on neuropathic pain involves the neuromodulation induced by pulse current. Electric fields can reversibly block neurotransmission in unmyelinated C fibers, resulting in analgesia [31, 32]. However, traditional PRF has a poor analgesic effect on patients with a long course of acute herpetic neuralgia, especially patients with pain lasting more than 3 months. PRF has a short analgesic time and poor clinical efficacy in treating subacute HZN and PHN pain. Although PRF avoids the adverse reactions caused by nerve injury, the effect is not as good as continuous radiofrequency thermocoagulation [33]. This may be related to factors such as the operator’s skill level, PRF parameter settings, local tissue resistance, and target neural properties. At present, no gold standard is in place for PRF parameter setting. Frequency, voltage, time, and duration are key factors affecting postoperative efficacy. The same effect cannot be obtained using uniform parameters due to structural differences in different individuals and tissues. Therefore, the effective rate of PRF at this stage is improved, and the pain relief time of PRF is prolonged.
The results of this study indicated that the SF-MPQ scores in patients of both P and LP groups were lower after PRF treatment than before treatment. The SF-MPQ scores in patients were significantly lower in the long-term PRF group than in the conventional PRF group. After 2 months of PRF treatment, the dose of analgesics and IR in patients with PHN were significantly lower in the long-term PRF group than in the conventional PRF group. The analgesic effect of long-term PRF for treating subacute HZN was found to be better than that of the conventional PRF group. Studies reported that these changes might be related to the long-term enhancement in inhibition of primary afferent fibers induced by long-term high-frequency electrical stimulation. In recent years, studies on animal models of neuropathic pain have shown that the microglia are activated in the spinal cord during the induction period of neuropathic pain, and the astrocytes are activated during the transition and maintenance period of neuropathic pain [34, 35]. Sakakiyama et al. [36] reported that tramadol could reduce pain by inhibiting spinal astrocytes. Hidaka et al. [37]. reported that long-term PRF treatment in mice triggered the recovery of resinoid-induced mechanical pain by inhibiting extracellular signal–regulated kinase (ERK). Ren Yu et al. [38]. observed that PRF alleviated persistent neuropathic pain by selectively inhibiting the generation of long-term depression, inhibiting the activation of ERK in neurons and astrocytes in the superficial dorsal horn, and selectively and continuously regulating C fiber–mediated spinal cord nociceptive hypersensitivity. Lulin et al. [39]. revealed that intravenous lidocaine could alleviate PHN by inhibiting the activation of microglia and astrocytes in the spinal dorsal horn. They reported that the analgesic effect of PRF administered immediately after surgery could be attributed to its inhibition of ERK activation in dorsal horn cells. Therefore, we hypothesized that prolonging PRF time might control pain by inhibiting the activation of astrocytes in the spinal dorsal horn.
This study concluded that the analgesic effect of long-term PRF in treating subacute HZN (continuous pain for 1–3 months) was better than that of conventional PRF, and the number of cases of PHN was significantly reduced. This study recommends long-term PRF in patients with HZN with pain lasting more than 2 months based on patients’ clinical conditions.
The article already contains all relevant data. If necessary, the corresponding author can be contacted for further information.
QS and JY—Conception and design. QS, JLY, and JFZ—Study materials provision, data collection, and analysis. QS, JLY, and JY—Manuscript writing. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital (approval No. KY2022-78), and all patients signed the informed consent form.
The authors would also like to thank all patients for permitting us to use their clinical information and follow-up outcomes for this study.
The present study was supported by the Guizhou Provincial Health Commission (approval gzwkj2021-284), Basic Research Program of Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Department (202042940112211125).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.