1 Department of Food Science and Nutrition, Hallym University, 24252 Chuncheon, Gangwon, Republic of Korea
2 Department of Anatomy, College of Korean Medicine, Dongguk University, 38066 Gyeongju, Gyeongbuk, Republic of Korea
3 Department of Emergency Medicine, Kangwon National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, 24289 Chuncheon, Gangwon, Republic of Korea
4 Department of Physical Therapy, College of Health Science, Youngsan University, 50510 Yangsan, Gyeongnam, Republic of Korea
5 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and Research Institute of Oral Sciences, College of Dentistry, Gangnung-Wonju National University, 25457 Gangneung, Gangwon, Republic of Korea
6 Department of Neurobiology, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, 24341 Chuncheon, Gangwon, Republic of Korea
7 Department of Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, Dankook University, 31116 Cheonan, Chungnam, Republic of Korea
8 Department of Surgery, Kangwon National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, 24289 Chuncheon, Gangwon, Republic of Korea
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: A gerbil model of ischemia and reperfusion (IR) injury in
the forebrain has been developed for studies on mechanisms, prevention and
therapeutic strategies of IR injury in the forebrain.
Pycnogenol
Keywords
- immunoglobulin G
- neuroprotection
- proinflammatory cytokines
- pyramidal cell
- transient forebrain ischemia
A brief interruption of blood supply to brains brings ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury in the specifically vulnerable subregions of the brain including the hippocampus [1, 2]. Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus) have been developed for a model of transient forebrain ischemia to study neuronal damage and protection or therapy, their mechanisms in the forebrain induced by IR injury in the forebrain has been developed for studies on mechanisms, prevention and therapeutic strategies of IR injury in the forebrain [3, 4, 5]. The gerbil anatomically has an incomplete Willis’ circle which has no the posterior communicating arteries [6, 7]. This anatomical characteristic gives us to easily develop IR injury in the forebrain by ligation of two common carotid arteries (not two vertebral arteries) in gerbils which survive a long time without brainstem failure [8, 9]. It is known that, in gerbils, transient forebrain ischemia for five minutes leads to irreversible loss (death) of pyramidal cells (principal neurons) located in subfield Cornu Ammonis (CA) 1 of the hippocampus at four to five days after IR [10, 11]. Accumulating data have demonstrated diverse phenomena in IR-induced neural injury including blood-brain barrier (BBB) breakdown and neuroinflammatory response [12, 13, 14].
Extracts derived from plants have been considered as the potential materials of
multi-targeting agents for the remedy of neurological diseases such as cerebral
ischemia [15, 16]. For example, extract from pine bark has been reported to have
neuroprotective effects against experimental brain insults. As in vivo
experiments, extract from Korean red pine (Pinus densiflora) bark and
Pycnogenol
It has been demonstrated that PYC considerably protects hippocampal pyramidal neurons from IR injury in gerbils via its antioxidative efficacy [17]. However, the effects of PYC against IR-induced BBB leakage and neuroinflammation have not been examined yet. Therefore, the main purpose of the present study was to investigate whether PYC protected or attenuated IR injury-induced BBB leakage and neuroinflammation.
The protocol of all experimental procedures was approved (approval no., KW-2000113-1) on 7th Feb. 2020 by the Ethics Committee of Kangwon National University (Chuncheon, Gangwon, Korea). Animal handling stuck to the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” [20]. In addition, all efforts were made to reduce pain in the animals and minimize the numbers of the animals used.
Adult male gerbils at six months of age (body weight, 72–78 g) were used for
this study. The gerbils were obtained from the Experimental Animals Center of
Kangwon National University (Chuncheon, Republic of Korea). The gerbils were
housed in pathogen-free environment under standard laboratory conditions
(temperature, 23
A total of 126 gerbils were blindly and randomly divided into eight groups as follows: (1) sham IR plus (+) vehicle group (Sham+vehicle group; n = 14) was subjected to sham IR operation, treated with vehicle (saline), and sacrificed at zero and 5 days after sham IR operation; (2) IR+vehicle group (n = 21) was given IR operation, treated with vehicle, and sacrificed at two and five days after IR operation; (3), (4) and (5) sham+25, 50, and 100 mg/kg PYC group (n = 14, respectively) was subjected to sham IR operation, treated with 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg of PYC, respectively, and sacrificed at zero and five days after IR; (6) and (7) IR+25 and 50 mg/kg PYC group (n = 14 respectively) was given IR operation, treated with 25 and 50 mg/kg of PYC, respectively, and sacrificed at five days after IR operation and (8) IR+100 mg/kg PYC group (n = 21) was given IR operation, treated with 100 mg/kg PYC, and sacrificed at two and five days after IR operation.
IR injury was induced in the forebrain containing the hippocampus by occlusion
of bilateral common carotid arteries in accordance with previously described
method [15]. In brief, all gerbils were anesthetized with 2–2.5% isoflurane
(657801261, Hana Pharm. Co., Ltd., Gyeonggi-Do, Korea) using an inhaler. A middle
incision was made in the ventral surface of the neck, the common carotid arteries
were isolated from the carotid sheath and clamped with aneurysm clips for five
minutes, and the clips were removed for reperfusion. Complete blockage and
reperfusion of arterial blood was observed by observing blood flow in the central
retinal arteries using HEINE K180 ophthalmoscope (C-182.27.388, Heine
Optotechnik, Herrsching, Germany). For body temperature, normal temperature (37
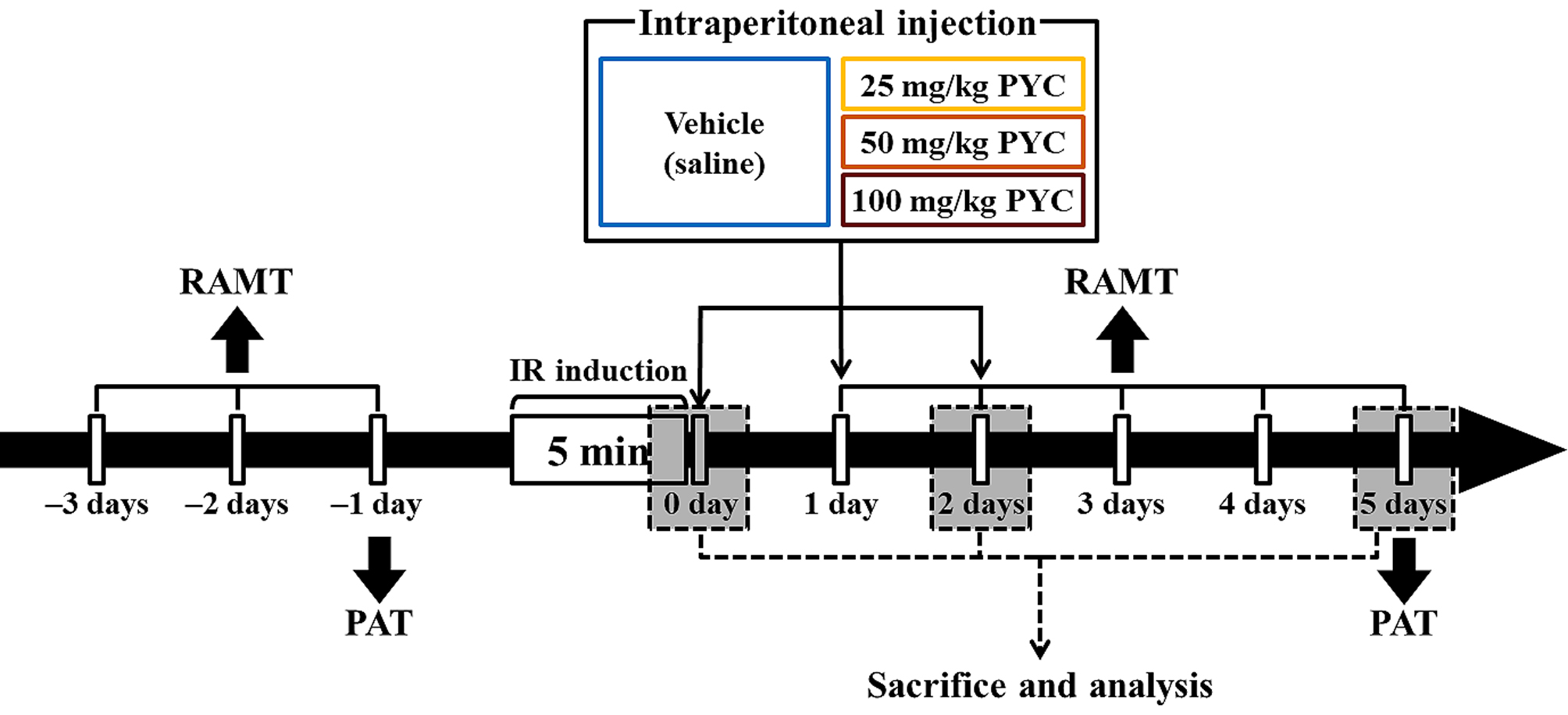
PYC was purchased from Horphag Research Ltd. (1049951, Horphag Research Ltd., Geneva, Switzerland), and PYC (25, 50, and 100 mg/kg in saline, respectively) or saline was intraperitoneally administrated immediately, at one day and two days after IR, respectively (Fig. 1).
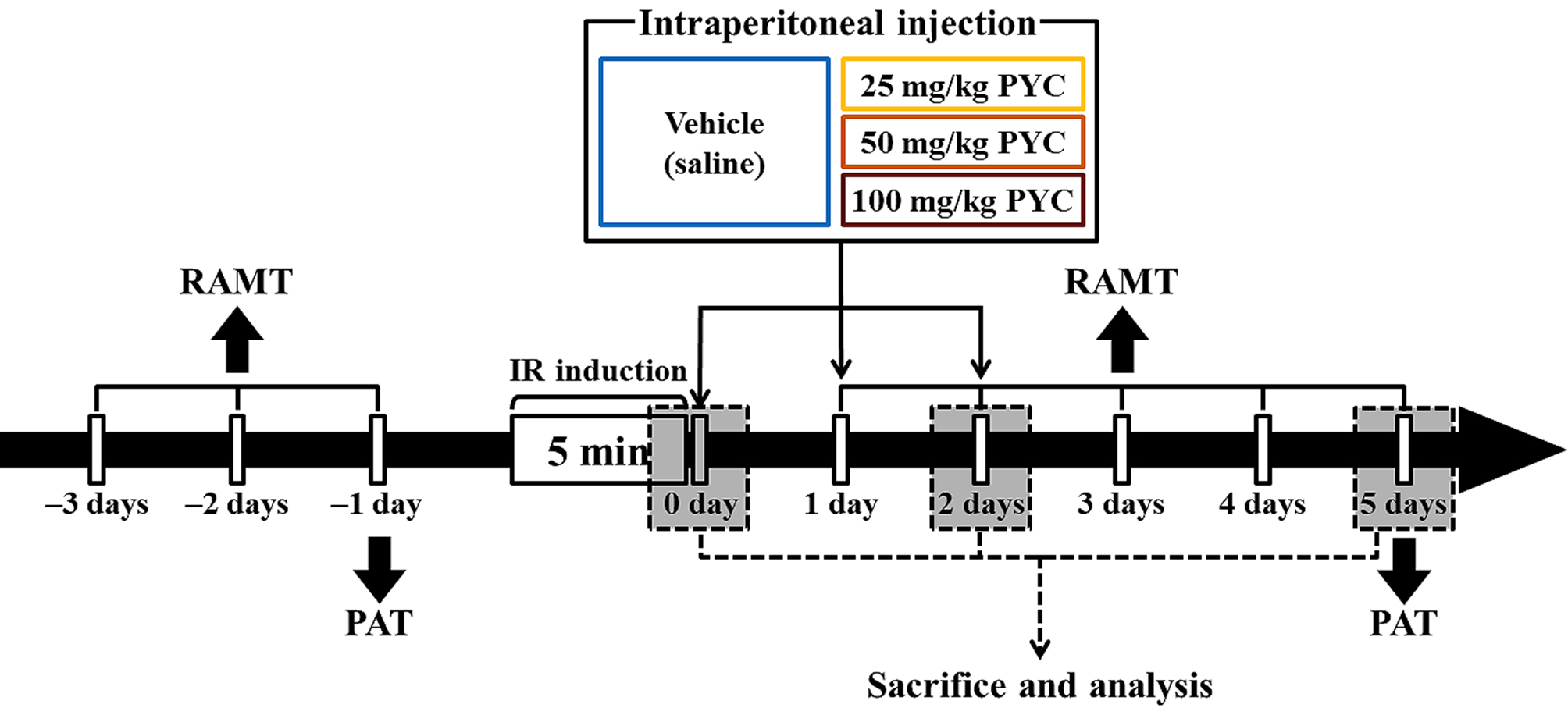 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Experimental timeline RAMT was daily conducted for three days before and for five days after IR induction. PAT was carried out at one day before and five days after sham and IR, respectively. Gerbils were given IR injury for five minutes and, thereafter, they were respectively treated with vehicle (saline), 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg PYC immediately, at one day and two days after sham and IR.
RAMT was conducted to examine change in spatial learning memory following IR injury at designated times (Fig. 1) according to published protocols [6, 21]. In short, a central octagonal plate consisting of a non-transparent acryl board (diameter, 20 cm) with eight radial arms (5 cm wide; 9 cm high, and 35 cm long) (60150, Stoelting Co., Wood Dale, IL, USA). The gerbils were trained three times for three days (once a day) prior to IR (Fig. 1). The substantive test was conducted once a day for five days from one day after IR (Fig. 1). In detail, Pellet feed (RodFeed, DBL Co Ltd., Chungbuk, Korea) was put at the end of each arm, and the gerbil was placed onto the central platform. The trial (test) was wrapped up when the gerbil consumed the feed. The numbers of errors were calculated for re-entering the arms that had already been entered.
To evaluate IR-induced change in short-term memory, PAT was performed at designated times (Fig. 1) according to previous methods [22, 23] with some modification. Gemini Avoidance System (GEM 392, San Diego Instruments Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) was used. This apparatus consists of dark and light rooms that were divided by vertical door. The test had two sessions (training and testing sessions). For training session, at one day before IR (Fig. 1), the gerbil was placed in the light room with its back towards the dark room, allowed to freely explore both rooms for three minutes, and the dark room was electrified for five minutes. If the mouse stepped into the dark compartment, it would receive a mild foot shock. Testing session was performed five days after IR (Fig. 1). The gerbil was placed to the light room and allowed to explore for five minutes, and the latency time (seconds) to enter the dark room was recorded within three minutes.
Histopathological sections were prepared at zero, two, and five days after IR.
In brief, as described in a published paper by [15], the gerbils were given deep
anesthesia by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital sodium (200 mg/kg;
644912121, JW pharm. Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea). The gerbils were rinsed
transcardially with 0.1 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) and fixed
immediately with 100 mL of 4% paraformaldehyde (in 0.1 M PB, pH 7.4). The
gerbils were decapitated and their brains were removed from the skulls. The
brains were then placed in the same fixative overnight and stored overnight in
0.1 M phosphate buffer (PB, pH 7.4) containing 25% sucrose and 0.002%
CaCl
CV staining was performed to evaluate change in cellular distribution and
morphology in the hippocampus after IR according to a previous study [15] with
some modification. In short, the sections intended for CV staining were first
mounted on gelatin-coated microscope slides, air dried at room temperature and
incubated overnight in 95% ethanol at 56
The images of the CV-stained cells were taken using BX53 microscope (BX53, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), and IR-induced change was examined.
To evaluate the therapeutic neuroprotection by PYC in the hippocampus after IR, NeuN (a marker for neurons) immunofluorescence and FJB (a fluorescent marker for the degeneration of neurons) histofluorescence were performed according to a published method [15] with some modification.
For NeuN immunofluorescence, the sections were incubated in mouse anti-NeuN
(diluted 1:1,100; MAB377; Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) overnight at 4
For FJB histofluorescence was carried out to investigate the therapeutic neuroprotection by PYC in the hippocampus after IR. FJB (AG325-30MG, EMD Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) solution was prepared by dissolving 0.0003% FJB in acetic acid. According to a published method [15] with some modification, the sections were incubated with 0.06% potassium permanganate for ten minutes at room temperature, washed with DW, and incubated in the FJB solution for 20 minutes at room temperature. After washing, the sections were warmed for the reaction and completely dried. Thereafter, the sections were cleared and coverslipped.
For the analysis of neuronal damage or death (loss), five sections were selected
with 140
IR-induced BBB leakage and interleukin-1
| Primary Antibodies | Dilutions | Suppliers |
|---|---|---|
| Rabbit anti-interleukin 1β (IL-1β) | 1:1,000 | Chemicon, Temecula, CA, USA |
| Rabbit anti-gerbil immunoglobulin G (IgG) | 1:200 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK |
| Secondary Antibodies | Dilutions | Suppliers |
| Biotinylated goat anti-rabbit IgG | 1:250 | Vector Laboratories Inc., Burlingame, CA, USA |
The density of IgG and IL-1
SPSS software (version 15.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for all
statistical analyses. In addition, Kolmogorov and Smirnov test was applied to
evaluate normal distributions, and Bartlett test was used to calculate identical
standard error of the mean (SEM). All presented data were taken for the normality
test. The statistical significances of the mean between all experimental groups
were determined by two-way analysis of variance followed by post hoc
Tukey’s test for all pairwise multiple comparisons. All presented data were
displayed as the mean
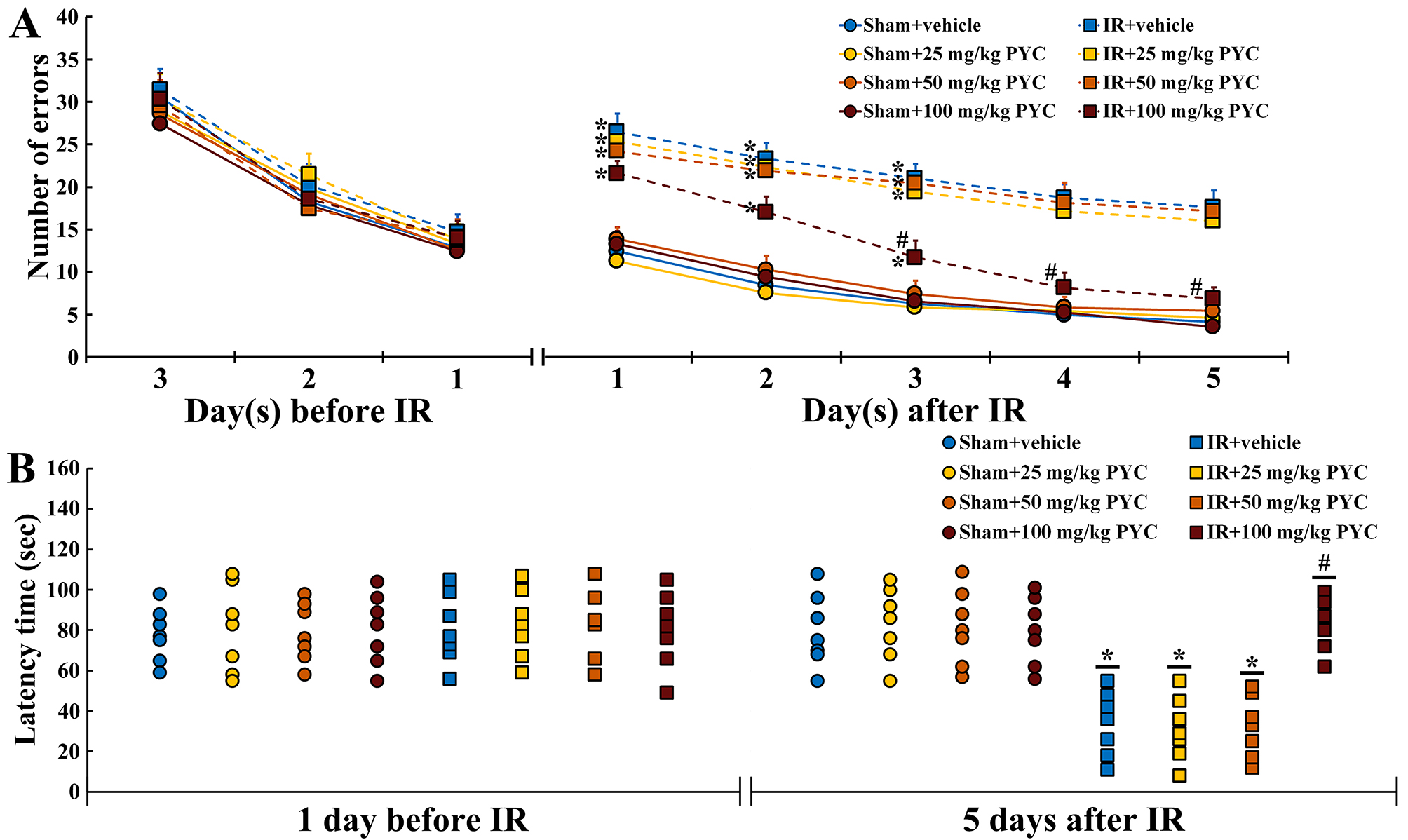
Before IR, changes in the numbers of errors were similar among all groups. This finding indicated that all gerbils had been pre-trained equally (Fig. 2A). In all of the sham groups, patterns in the numbers of errors were time-dependently decreased after sham IR and the numbers were not significantly different between the groups (Fig. 2A). In contrast, in the IR+vehicle, IR+25 mg/kg and IR+50 mg/kg PYC groups, the numbers of errors were significantly high after IR compared with those in the sham+vehicle group (Fig. 2A). However, in the IR+100 mg/kg PYC group, the numbers of errors were significantly low at three days after IR compared with that in the IR+vehicle group and became similar to those in the sham+vehicle group at four and five days after IR (Fig. 2A).
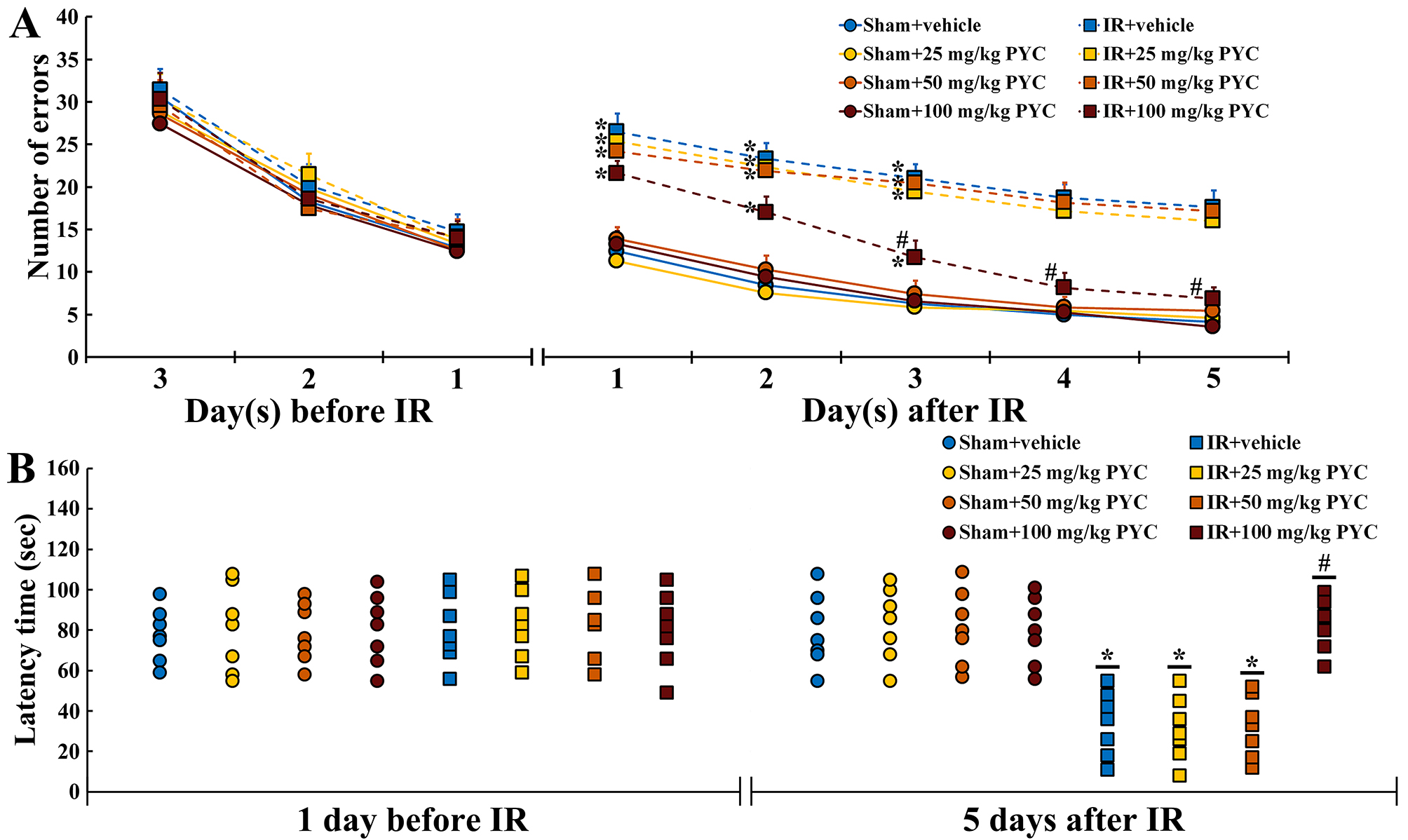 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Behavioral changes assessed by RAMT and PAT. (A,B)
Mean numbers of errors by RAMT (A) for three days before and five days after sham
and IR and mean latency time by PAT (B) at one day before and five days after
sham and IR of the sham+vehicle, sham+PYC (25, 50 and 100 mg/kg), IR+vehicle, and
IR+PYC (25, 50 and 100 mg/kg) groups. In the IR+100 mg/kg PYC group, the numbers
of errors are significantly reduced from three days after IR and similar to the
IR+vehicle group at four and five days after IR. The latency time in the IR+100
mg/kg group is similar to the sham+vehicle group at five days after IR. The bars
indicate the means
At one day before IR, latency time was similar among all groups. This finding indicated that all gerbils had undergone same training (Fig. 2B). In all of the sham groups, no significant differences in latency time were found at five days after sham IR (Fig. 2B). On the other hand, in the IR+vehicle, IR+25 mg/kg and IR+50 mg/kg PYC groups, the latency time was significantly shortened compared with the sham+vehicle group (Fig. 2B). However, in the IR+100 mg/kg group, the latency time was significantly lengthened at five days after IR compared with the IR+vehicle group (Fig. 2B).
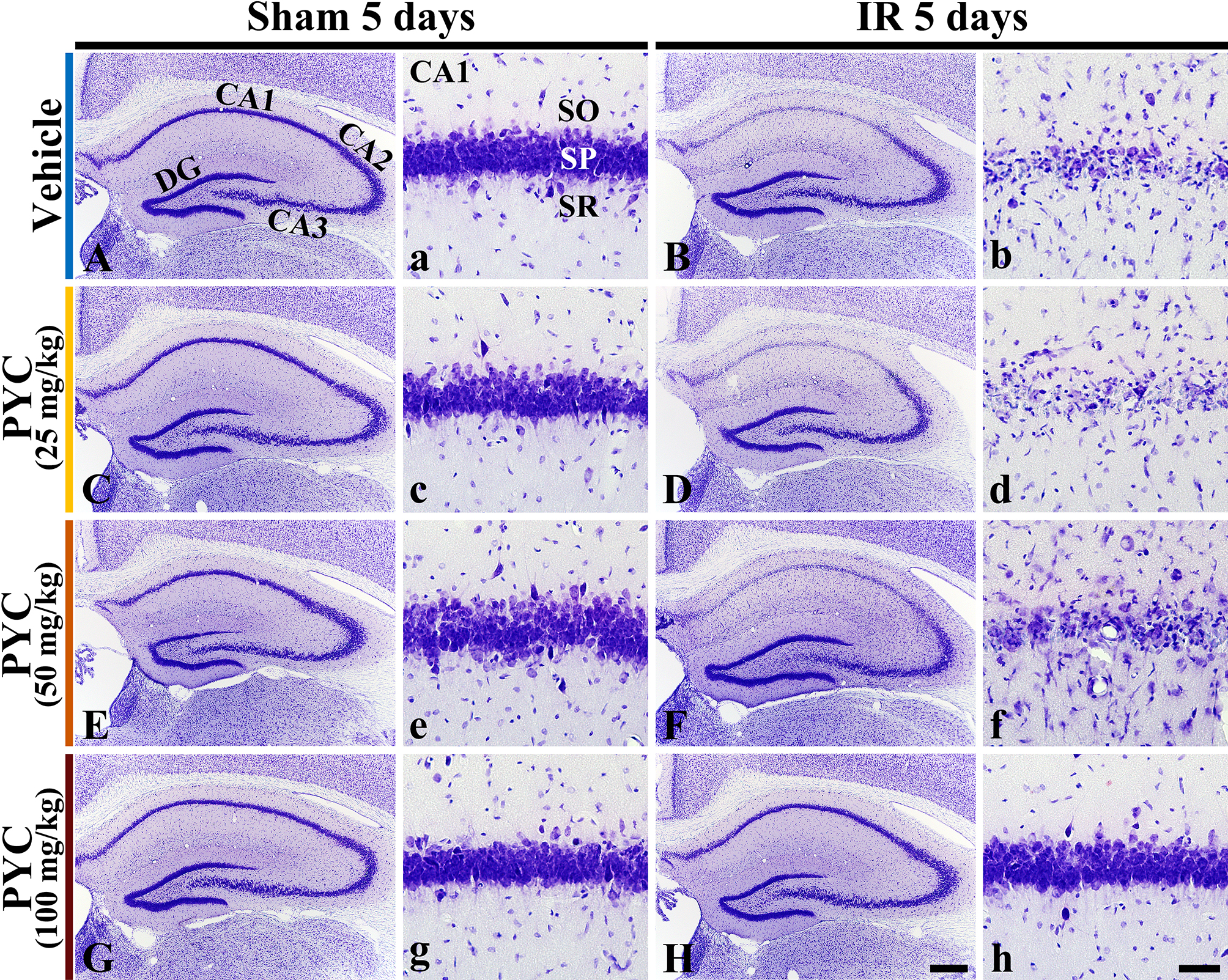
CV staining is used to stain Nissl substance in the cytoplasm of neurons. In all sham groups, CV-stained cells were distinguished in all subregions CA 1–3 of the hippocampus (Fig. 3A,C,E,G). In these groups, CV-stained cells were intensively distributed in the stratum pyramidale (SP) (Fig. 3a,c,e,g). On the other hand, in the IR+vehicle, IR+25 mg/kg and IR+50 mg/kg PYC groups, CV stainability was significantly weakened in SP of CA1, not in CA2/3, at five days after IR (Fig. 3B,D,F). When the SP of CA1 was examined in detail, CV-stained cells were apparently damaged (Fig. 3b,d,f). However, in the IR+100 mg/kg PYC group, CV-stained cells of CA1 were not different from those of the sham+vehicle group (Fig. 3H,h).
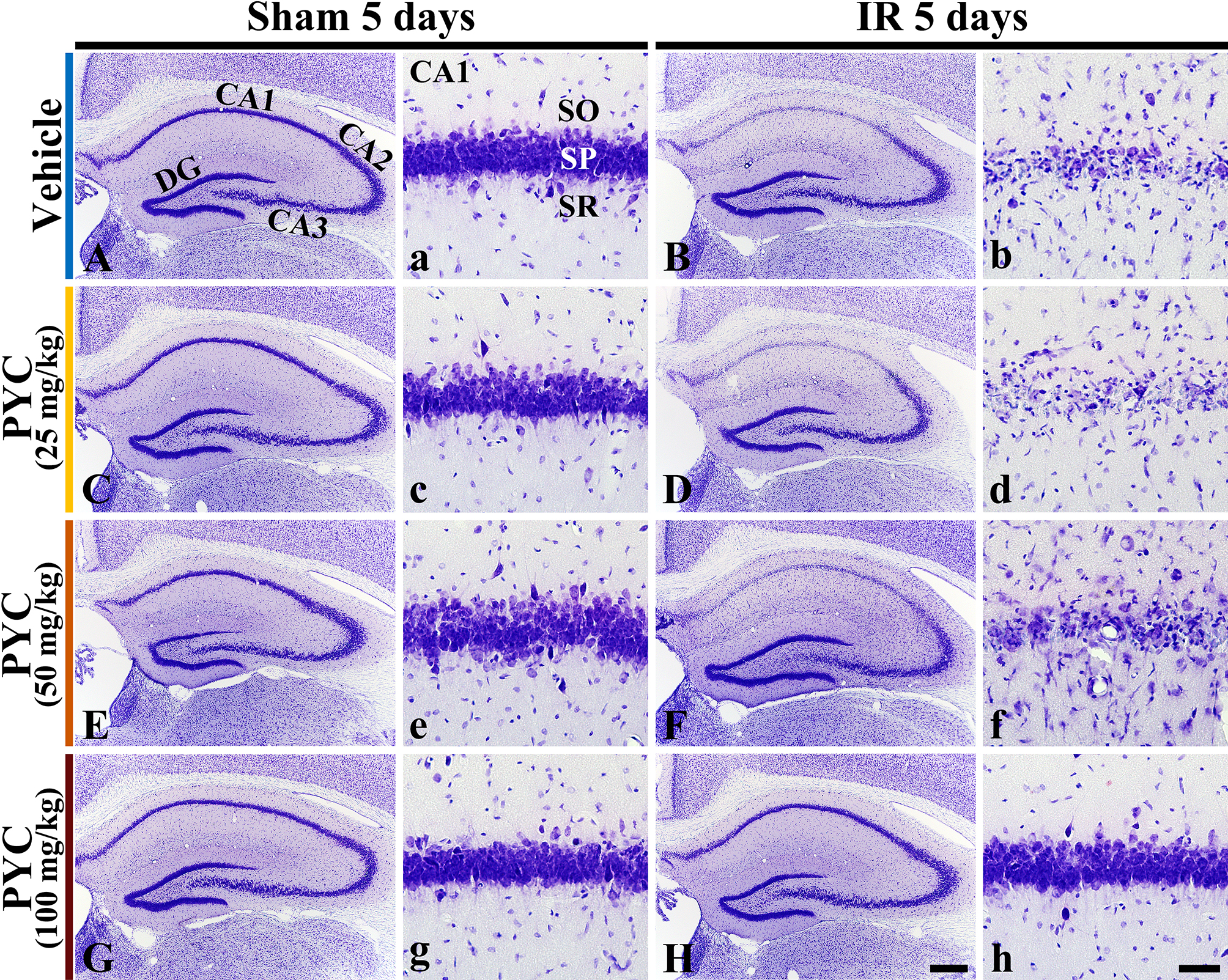 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Microphotograph of CV staining. Changes in CV staining in the
hippocampus and its CA1 of the sham or IR+vehicle group (A,a,B,b), sham or
IR+25 mg/kg PYC group (C,c,D,d), sham or IR+50 mg/kg PYC group (E,e,F,f), and sham or IR+100 mg/kg PYC group (G,g,H,h) at five days after sham
and IR. In the IR+vehicle, +25 mg/kg and +50 mg/kg PYC groups, CV-stained cells
are almost damaged in the stratum pyramidale (SP, arrows) of CA1. However, in the
IR+100 mg/kg PYC group, CV-stained cells of CA1 are not damaged. DG, dentate
gyrus; SO, stratum oriens; SR, stratum radiatum. Scale bars = 200
Based on the results of CV staining, we carried out following items in sham and IR+100 mg/kg PYC groups.
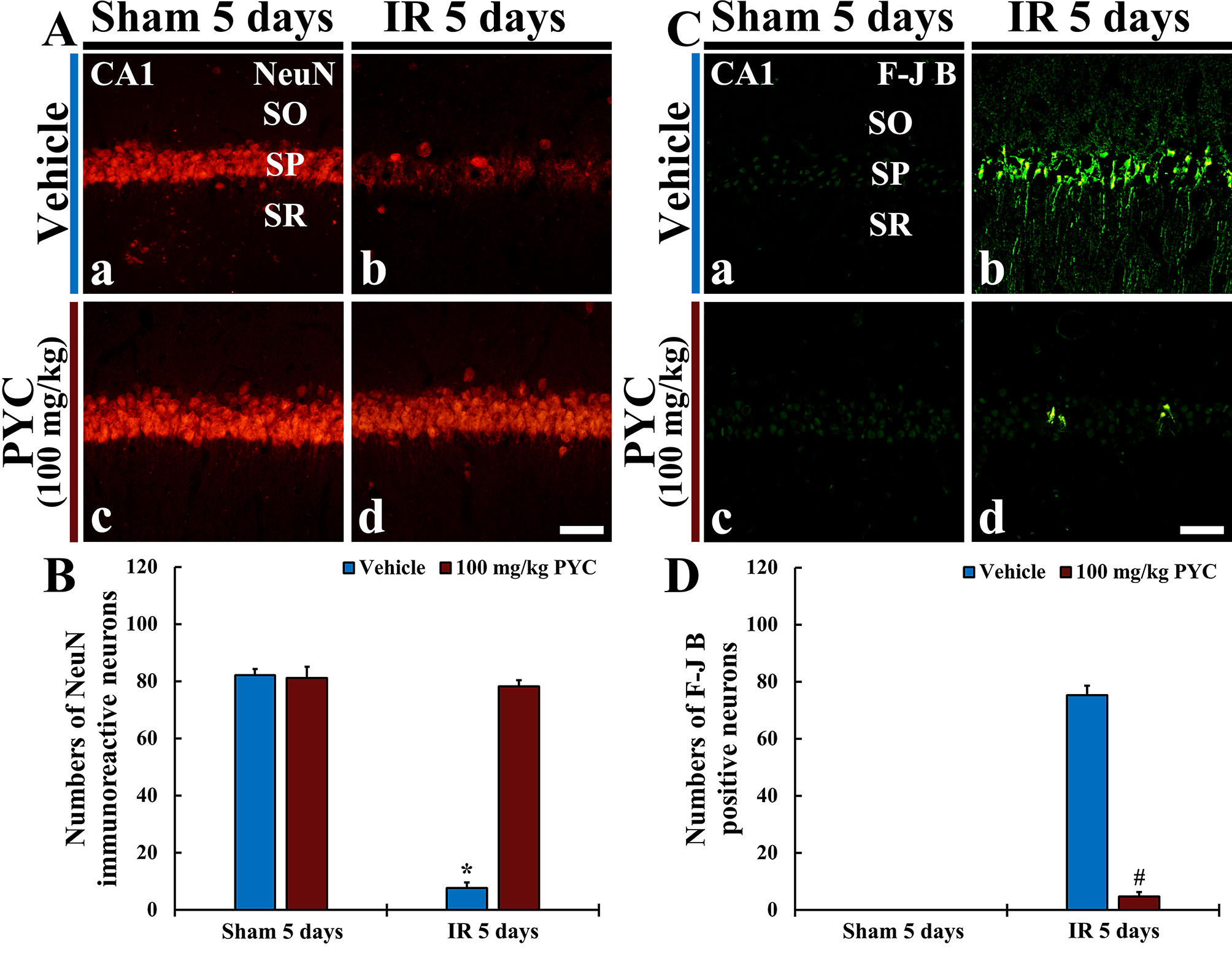
NeuN protein is localized in nuclei and perinuclear cytoplasm of most of the neurons in the central nervous system of mammals. FJB is known as a fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration during acute neuronal distress.
In the sham+vehicle and sham+100 mg/kg PYC groups, pyramidal neurons located in
SP of CA1 were well immunostained with NeuN (about 82 and 83 cells/250
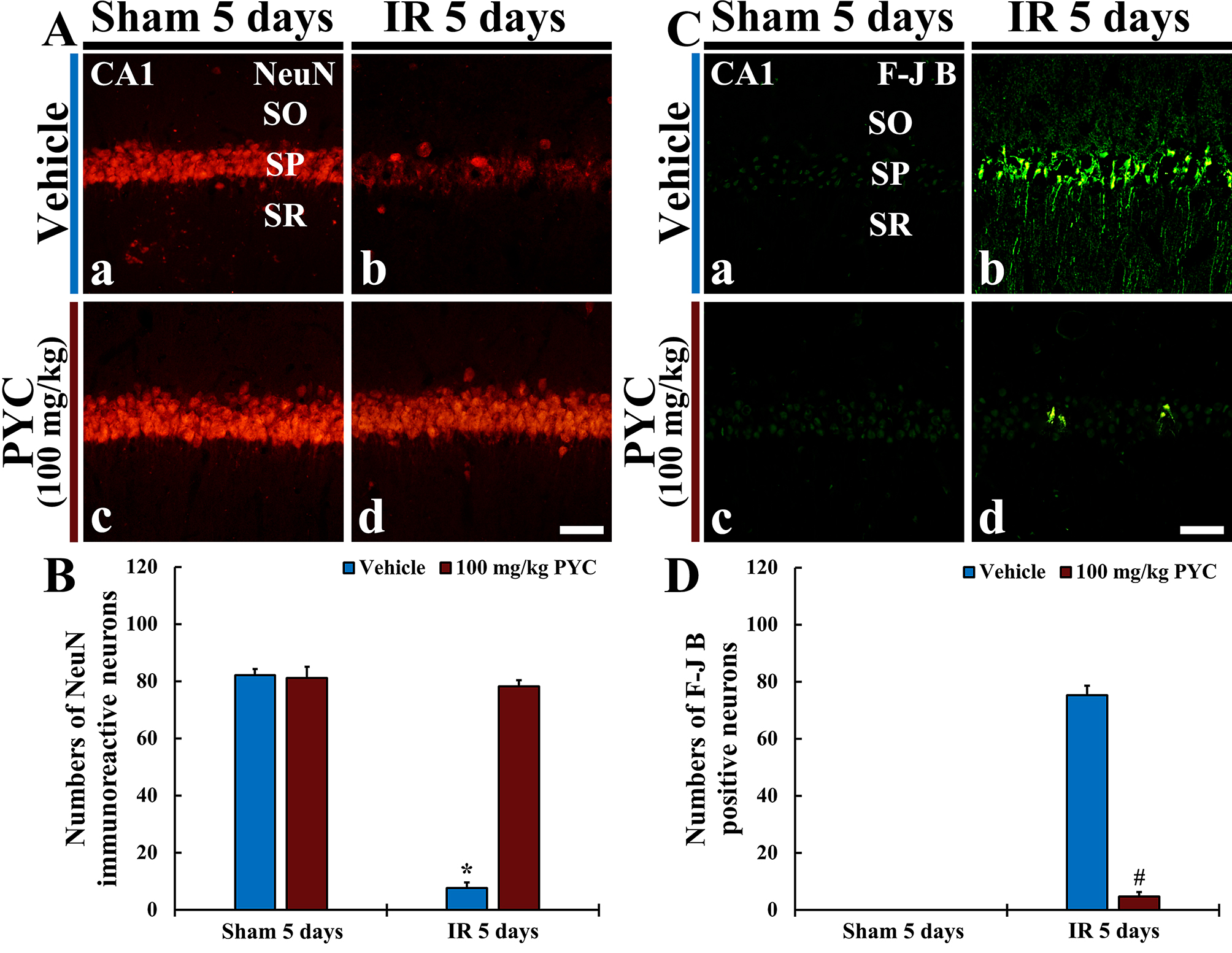 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.NeuN immunofluorescence and FJB histofluorescence. (A,C)
NeuN immunofluorescence (A) and FJB histofluorescence (C) in CA1 of the
sham+vehicle (Aa,Ca) and sham+100 mg/kg PYC (Ac,Cc), IR+vehicle (Ab,Cb), and IR+100 mg/kg PYC (Ad,Cd) groups at five days after sham or IR
operation. In the IR+vehicle group, NeuN-immunostained cells are rarely detected
and many FJB-stained cells are shown in SP. However, in the IR+100 mg/kg PYC
group, many NeuN-immunostained cells and a few FJB-stained cells are found in the
SP. (B,D) Mean numbers of NeuN-immunostained (B) and FJB-stained (D) cells
in SP. The bars indicate the means
In the IR+vehicle group, NeuN-immunostained cells were rarely observed (about 7
cells/250
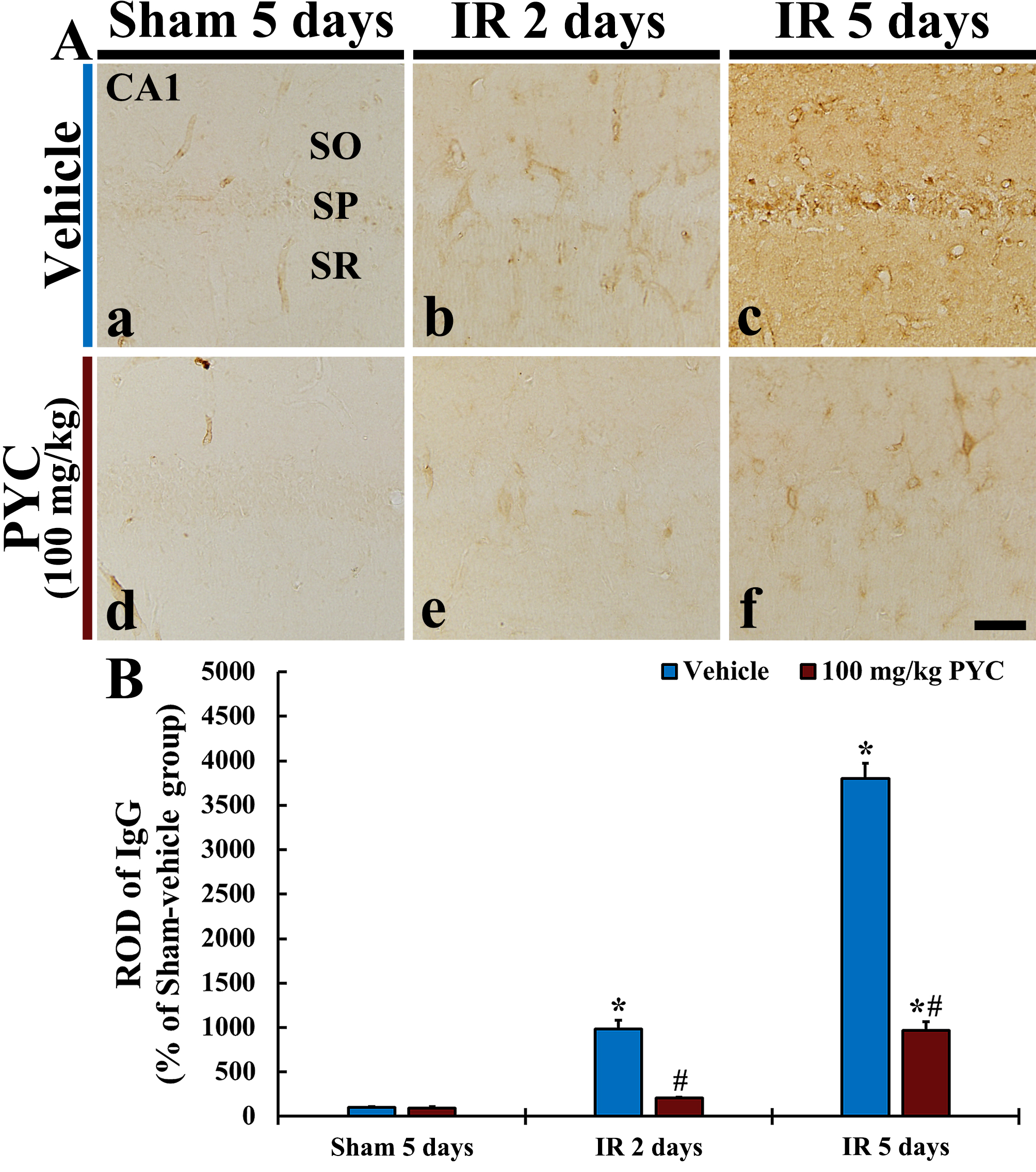
In this study, we examined IgG immunoreactivity for BBB leakage in CA1 after IR operation. In all sham groups, IgG immunoreactivity was mainly detected in blood vessels in CA1; it was hardly found in CA1 parenchyma (Fig. 5Aa,Ad). In the IR+vehicle group, IgG immunoreactivity at two days after IR was in blood vessels (ROD: about 980% versus sham+vehicle group) in CA1, and, at five days after IR, a significantly increased IgG immunoreactivity was dominantly found in CA1 parenchyma (ROD: about 3800% versus sham+vehicle group) (Fig. 5Ab,B). On the other hand, in the IR+100 mg/kg PYC group, IgG immunoreactivity at two days after IR was significantly attenuated (ROD: about 21% versus IR+vehicle group) as compared with that at the corresponding time point of the IR+vehicle group (Fig. 5Ae,B). At five days after IR, IgG immunoreactivity was also significantly lower (ROD: about 25% versus IR+vehicle group) than that at the corresponding time point of the IR+vehicle group (Fig. 5Af,B).
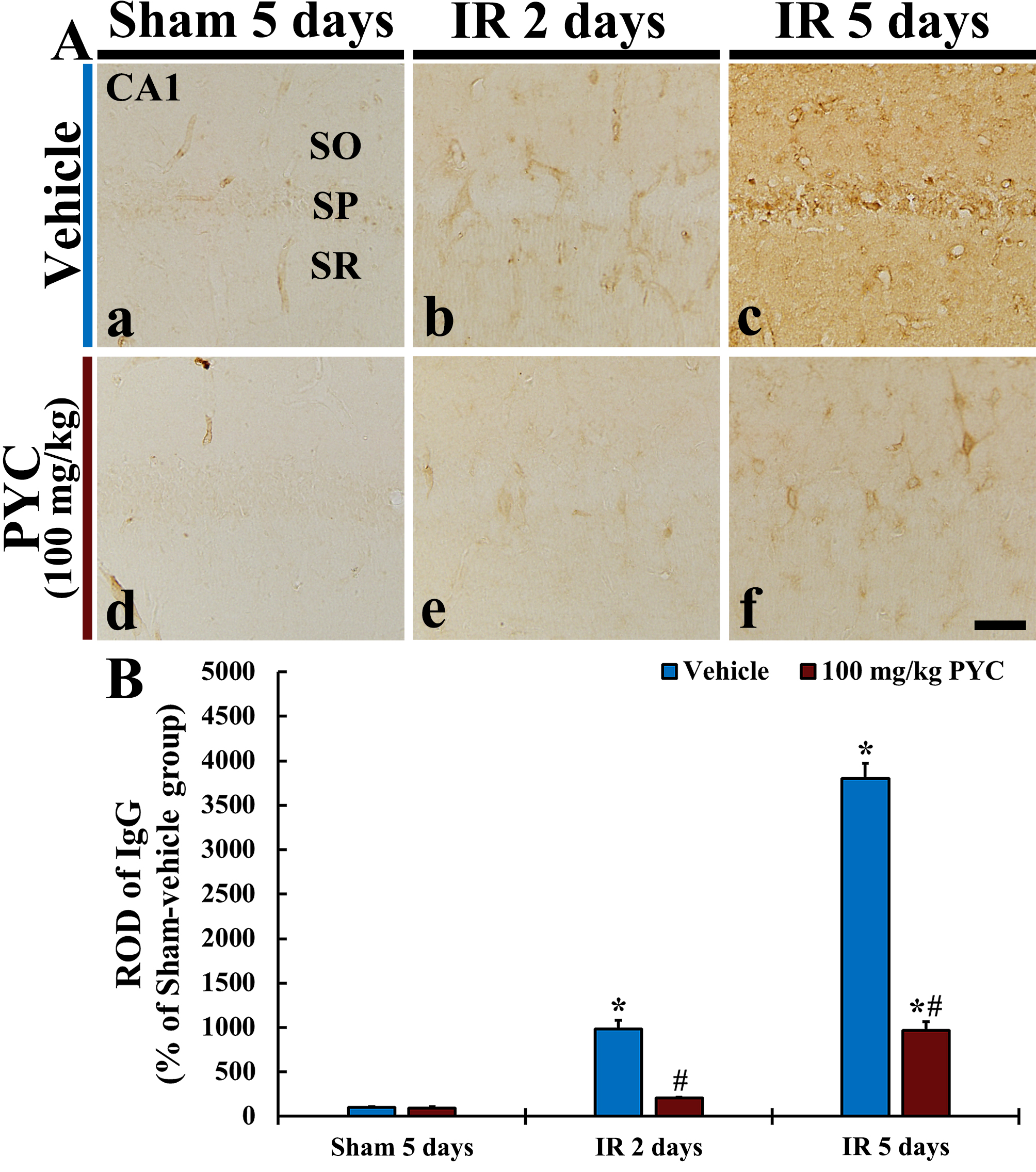 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.IgG immunohistochemistry. (A) IgG Immunohistochemistry in CA1
of the sham+vehicle (a), IR+vehicle (b,c), sham+100 mg/kg PYC (d), IR+100
mg/kg PYC (e,f) at two and five days after sham or IR operation. In the
IR+vehicle group, IgG immunoreactivity is significantly increased in parenchyma
at five days after IR, however, in the IR+100 mg/kg PYC group, IgG
immunoreactivity is significantly low when compared with the IR+vehicle group.
(B) ROD of IgG immunoreactive structure. The bars indicate the means
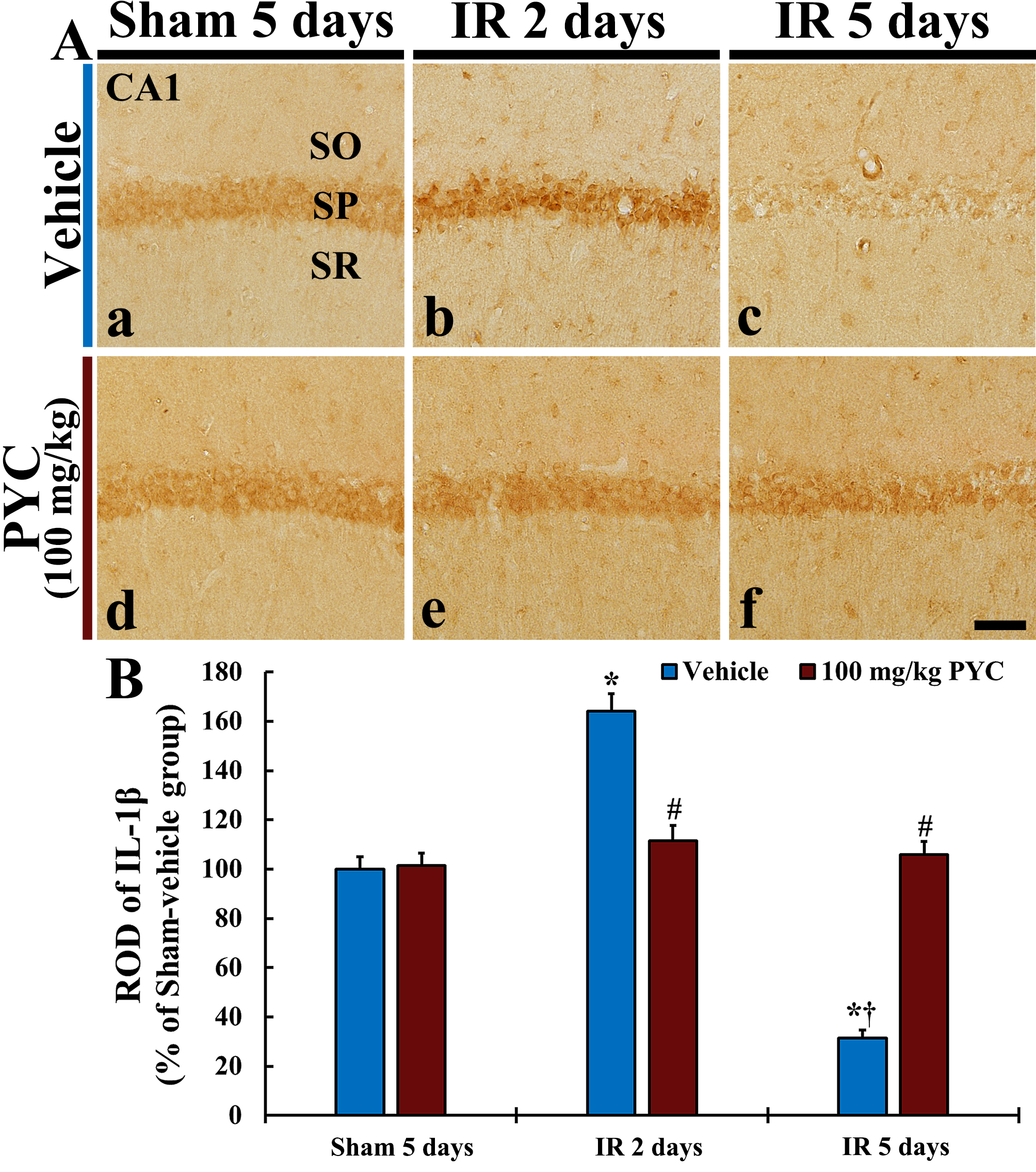
In this study, we examined IL-1
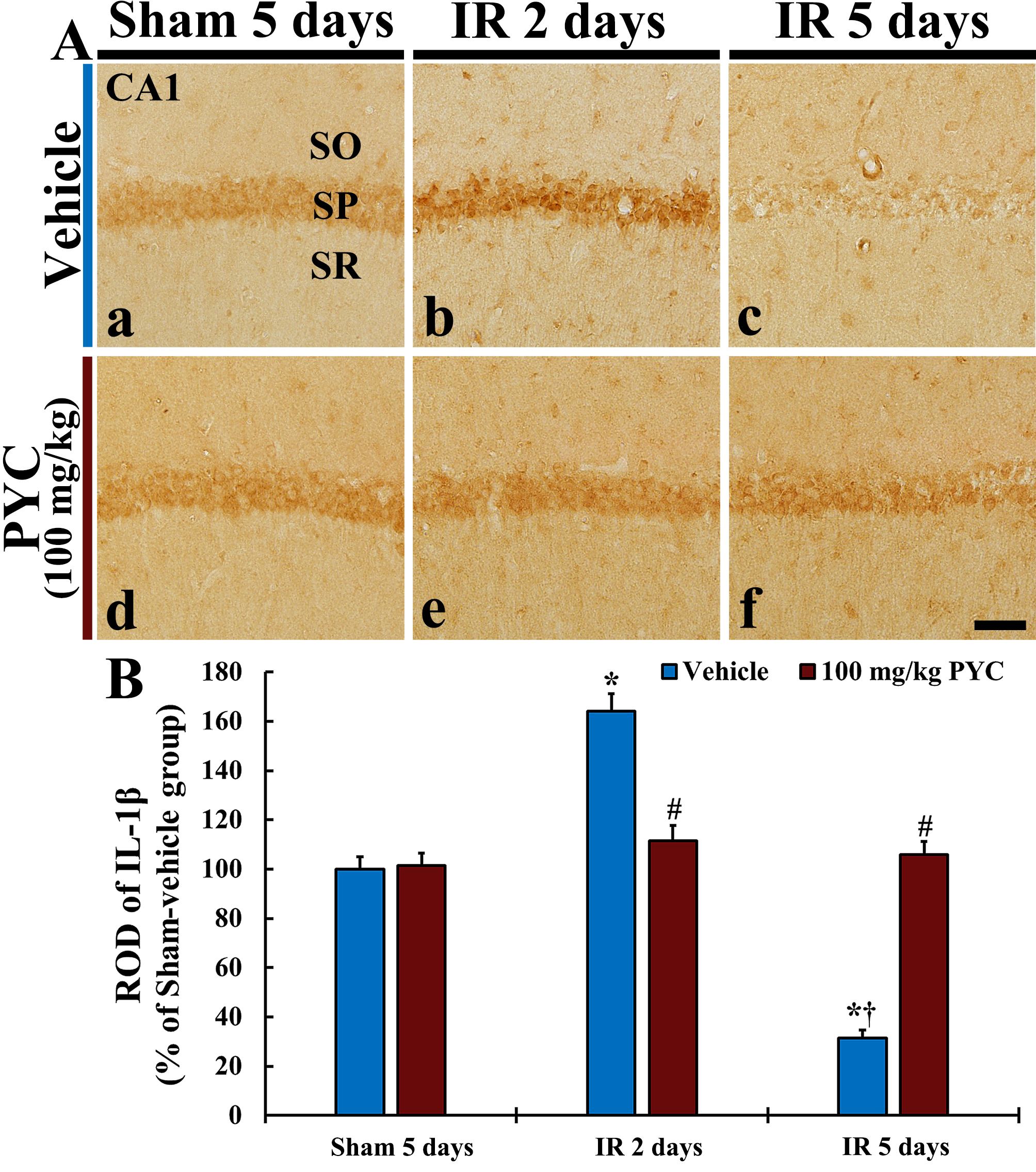 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.IL-1
It is well acknowledged that the hippocampus plays pivotal roles in spatial navigation and short-term memory, and these functional roles of the hippocampus are accomplished by trisynaptic circuitry of the principal neurons in the dentate gyrus (granule cells), CA3 and CA1 (pyramidal cells) [25, 26, 27, 28]. In this sense, it has been reported that IR injury in gerbil hippocampus brings loss/death of pyramidal cells and functional deficits of spatial and learning memory are induced [29, 30, 31, 32]. In addition, accumulated data have demonstrated that neuroprotective materials ameliorate memory deficits in gerbils with IR injury in the forebrain including the hippocampus. For instance, therapeutic treatment with extract from the root of Angelica gigas Nakai (Umbelliferae family) containing decursin, which is a coumarin derivative compound and regarded as a major ingredient of Angelica gigas Nakai root extract, after cerebral IR injury in gerbils improved the IR-induced cognitive deficits via tests of spatial memory (by 8-arm radial maze test) and learning memory (by passive avoidance test) [22]. In our current experiment, the results of the behavioral tests showed that treatment with 100 mg/kg PYC following IR remarkably reduced the number of errors in Radial Arm Maze Test (RAMT) (test for spatial memory function) and shortened the latency time in Passive Avoidance Test (PAT) (test for learning memory function) when compared with those in the ischemic gerbils treated with vehicle.
Extracts from pine bark have been reported that they have protective potential
in experimental models of neurological diseases [15, 17, 18, 33]. For example, a
bark extract derived from Korean red pine (Pinus densiflora) protects
neuronal PC-12 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death via reducing
oxidative stresses and inhibiting enzymatic activities of cholinesterases [18].
In a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease induced by 6-hydroxydopamine, PYC
administration alleviates catalepsy and increased expression of anti-inflammatory
gene which is related with nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 [33]. In
particular, in a gerbil model of IR, pretreatment with PYC displays an excellent
antioxidative efficacy and protects hippocampal pyramidal neurons from IR injury
[17]. It has been evidenced that bark extracts from pine trees contain diverse
phenolic compounds (17, 18). Namely, Korean red pine bark extract contains a
great amount of flavonoid, gallic acid and catechin [18], and PYC is consisted of
70
In this study, we found that treatment with 100 mg/kg PYC after IR considerably inhibited leakage of IgG in the hippocampal CA1 following IR. It is well accepted that BBB separates the central nervous system (CNS) from blood vessels by providing a highly selective semi-permeability and maintains homeostasis in the CNS [21, 22, 38, 39]. It has been demonstrated that neural damages in the CNS following IR might be caused by BBB breakdown which is closely associated with increase of BBB permeability and that blockage of such IR-induced BBB leakage can contribute to exert neuroprotective effects [22, 38]. For example, a precedent study has reported that, in infarct lesion in the brain of a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia, an extravasation of Evans blue dye was shown in the parenchyma of infarct lesion after the ischemia and that a reduction of the leakage of Evans blue dye and an attenuation of the volume of the infarct lesion following the ischemia were achieved by administration of Sac-1004, a pseudo-sugar derivative of cholesterol [40]. Additionally, it has been reported that invasion of IgG from blood vessels into hippocampal parenchyma following IR in gerbils and that post-treatments of extract from Angelica gigas Nakai or decursin decreased the IR-induced IgG leakage and protected CA1 pyramidal neurons from IR injury [22].
Neuroinflammation is one of the well-known mechanisms of neuronal death
following IR injury [15, 33, 41]. In general, inflammatory responses are
triggered when immune cells identify the antigen determinants of pathogens [42].
Especially, in brains, inflammatory responses are induced by resident microglia
and/or immunocytes which immigrate from blood vessels through increased BBB
permeability following pathological conditions such as IR [13, 41]. However, the
CNS is well known as an aseptic organ, and IR-induced neuroinflammatory response
does not involve pathogens, thus this response is termed as “sterile
inflammation” [43, 44]. In the sterile inflammation, detrimental inflammatory
processes are advanced by pro-inflammatory cytokines [45]. Among the
pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-1
In conclusion, our behavioral tests showed that post-treatment with 100 mg/kg
PYC after IR significantly attenuated IR-induced memory deficits. In
histopathological examination, post-treatment 100 mg/kg PYC protected hippocampal
CA1 pyramidal cells from IR injury. Furthermore, PYC treatment significantly
prevented BBB leakage and suppressed IL-1
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
TKL, MCS, JHA and DWK conducted experiments and data analysis. JHP, JHC, JCL, CHL, SH, MHW and IJK performed data curation and validation. TKL and JHP wrote the manuscript (original draft). MHW wrote the manuscript (review and editing). MHW and IJK supervised and administrated the project. TKL, MCS and IJK carried out funding aquisition.
The protocol of all experimental procedures was approved (approval no., KW-2000113-1) on 7th Feb. 2020 by the Ethics Committee of Kangwon National University (Chuncheon, Gangwon, Korea). Animal handling stuck to the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals”.
The authors would like to thank Seung Uk Lee and Hyun Sook Kim for their technical help in this work.
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2020R1F1A1071973, NRF-2020R1I1A3068251 and NRF-2020R1I1A1A01070897), and by BK21 FOUR (Fostering Outstanding Universities for Research; 4220200913807) funded by NRF of Korea.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.