Academic Editor: Roberto Bei
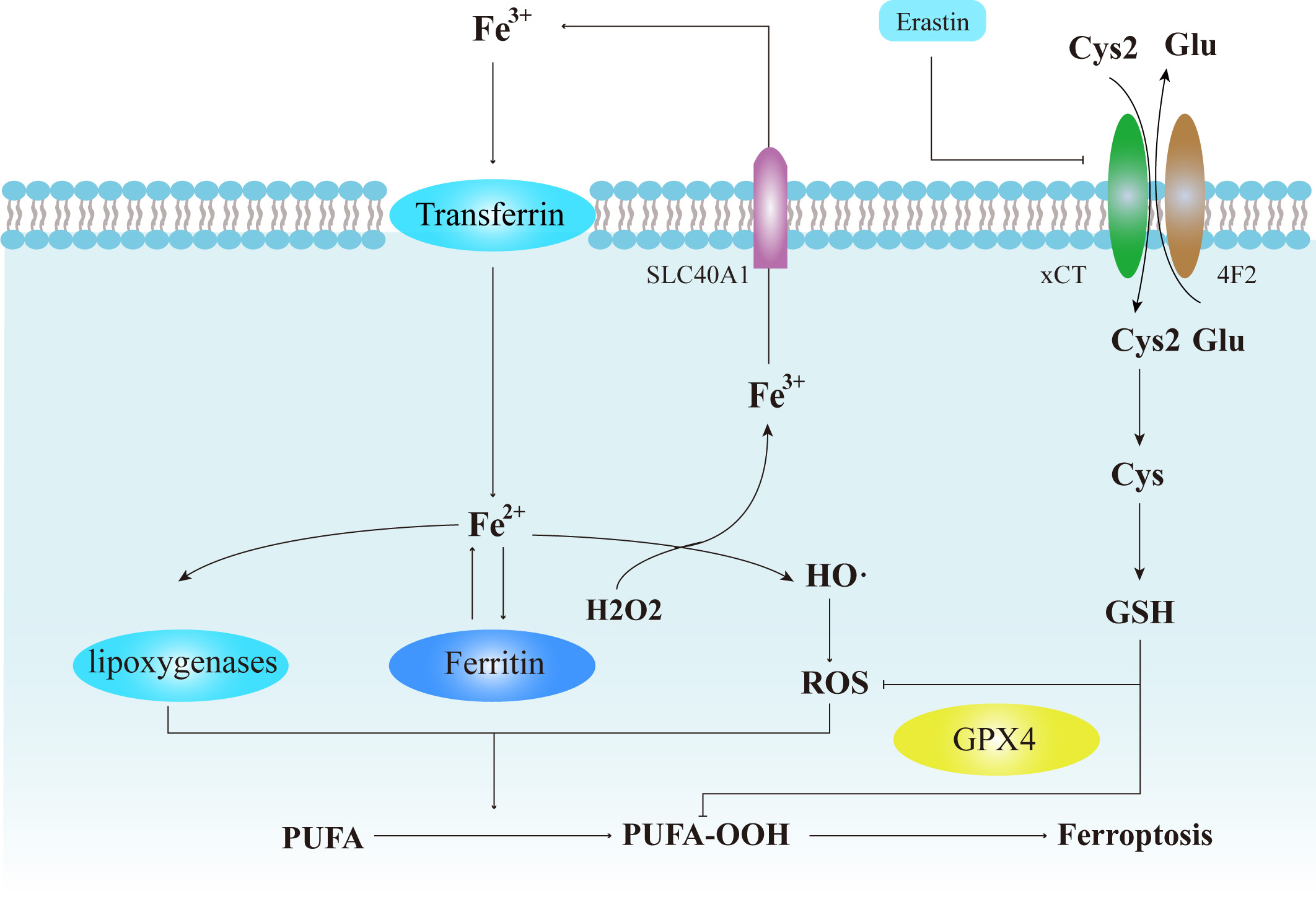
Ferroptosis is an emerging form of non-apoptotic, regulated cell death that is mechanistically dependent on aberrant iron accumulation and excessive lipid peroxidation. Further evidence indicates that ferroptosis plays a crucial role in the efficacy of tumor immunotherapy. Ferroptosis is often constrained by tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), and this poses a challenge to clinicians aiming to exploit the potency of immunotherapy to treat various forms of cancer. Current advances revealed a dual character to TAMs in regulating tumor ferroptosis. Specifically, some signaling molecules released from cells undergoing ferroptosis can exert effects on TAM polarization. In this review, we summarize the currently characterized mechanisms of macrophage-ferroptosis crosstalk, discuss how macrophage-ferroptosis crosstalk affects the outcome of tumor immunotherapy, and provide an overview of current advances that seek to leverage this crosstalk to improve cancer immunotherapy efficacy. Despite the fact that further efforts are still required to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms that control this signaling, targeting macrophage-ferroptosis crosstalk has clear potential for reversing immunotherapeutic resistance and may shed light on new therapeutic strategies to overcome some advanced and metastatic malignancies.