1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, 51472 Changwon, Republic of Korea
2 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, 52828 Jinju, Republic of Korea
3 Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University, 52828 Jinju, Republic of Korea
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to compare the maternal,
surgical, and neonatal outcomes in pregnant women with coronavirus disease 2019
(COVID-19) who underwent cesarean delivery at term and provide evidence for the
management of parturient with COVID-19. Methods: This case-control study
was conducted retrospectively and evaluated 67 cases of cesarean delivery
between February 1 and May 31 performed at the Gyeongsang National University
Changwon Hospital, Korea. Case group included women who had positive reverse
transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test within 7 days before
delivery. Control group was selected based on mode of delivery and gestational
age among women with negative RT-PCR result. Results: A total of 34
women with COVID-19 and 33 COVID-19-negative women and their neonate were
included in this study. Preoperative C-reactive protein was higher in case group
(6.4 mg/L vs 1.8 mg/L, p
Graphical Abstract

Keywords
- COVID-19
- cesarean delivery
- pregnancy
- neonate
- SARS-CoV-2
Since the first case of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) was identified in December, 2019, many investigations have been conducted to determine whether this new infectious disease is related to maternal and fetal complications in pregnant women [1, 2, 3, 4]. Maternal adaptation to pregnancy involves diverse anatomical and physiological changes, and in particular, immunological tolerance may increase maternal vulnerability to infectious diseases [5, 6]. Early case series on COVID-19 reported that the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in pregnant women and nonpregnant population were similar [7, 8, 9]. However, several subsequent studies have raised concerns about the severity of pregnancy-related COVID-19 infection [10, 11, 12, 13], and the World Health Organization’s classification of pregnant women as a vulnerable group is largely based on these findings.
Although available data suggest that pregnancy is a risk factor for severe COVID-19, there is lack of evidence regarding the impact of COVID-19 on cesarean section’s surgical aspects. COVID-19 alone is not an indication for cesarean section delivery (CD), and there is no consensus or rationale that supports performing CD for all parturients with COVID-19 [14, 15].
In brief, there is a need to develop guidelines that can guide or support the mode of delivery if pregnant women at term have COVID-19 disease. We conducted a case-control study to provide evidence of COVID-19-related surgical outcomes in parturients with COVID-19 quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) positive report who underwent CD. This study aimed to identify whether COVID-19 affects maternal, surgical, and neonatal outcomes and vertical transmission in pregnant women with COVID-19 who underwent CD at term.
We conducted a retrospective case-control study in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Republic of Korea. The case group was defined as pregnant women who underwent CD and had a COVID-19 qPCR positive report within 7 days before delivery (either by nasal or pharyngeal swab) between February 1 and May 31. Parturients with COVID-19 who delivered vaginally were excluded. We compared clinical characteristics of COVID-19-positive parturients whose infection was identified within 7 days before delivery with a control group of parturients who underwent CD and had a COVID-19 qPCR negative report before admission. The control group was made up of parturients who underwent either an elective or emergency CD in the same period. Pair-matching with 1:1 ratio was conducted based on gestational age and parity. All the parturients of the control group had confirmation of COVID-19 qPCR negative report within 3 days before admission to the labor unit.
Cesarean section was performed by 1 of the 3 maternal-fetal medicine specialists (author: JY, HCC, JEP) with at least 5 years of experience as an obstetrician. To prevent inadvertent spread of COVID-19, and in accordance with national guidelines, a specially designed negative-pressured stretcher car was used for the transportation of COVID-19 positive pregnant women through a designated passage. General anesthesia was administered to all parturients in the case group in the negative-pressured operating room, and the anesthesiologist equipped with D-level protection suit along with powered air-purifying respirator. In the control group, routine cesarean section care was applied and spinal anesthesia was performed when available. Both groups were subjected to critical pathway system, which included intravenous patient-controlled analgesia and single dose of antibiotics. Indications for CD other than COVID-19 reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) positive report at term included previous CD or uterine surgery, breech presentation, cephalon-pelvic disproportion, failure to progress, nonstress test evidence of fetal distress, and maternal request.
Patients’ clinical data were collected retrospectively by searching the electronic medical records. Patients’ age, height and weight, gestational age at delivery, parity, obstetric and other relevant medical history, indication for CD, length of hospital stay, weight of placenta, neonatal sex, and 1- and 5-min APGAR scores, C-reactive protein (CRP), admission battery, and chest radiograph were all part of preoperative work-up. On admission day, as well as postoperative days 1 and 3, all parturients had blood drawn for complete blood cell counts. The neonates’ cord blood gas analyses were routinely performed. If the parturient had COVID-19 qPCR positive report, all neonates were tested for SARS-CoV-2 test with airway swab and cord blood within 24 h of birth.
Continuous variables were presented as medians and interquartile ranges, while categorical variables were presented as count and percentage. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-test and Mann–Whitney U test for the continuous variables and chi-squared test and Fisher’s exact test for the categorical variables. Statistical significance was considered when p value was
The characteristics of the cohort are depicted in Table 1. The median maternal age was same in both the groups, and there was no difference between maternal body mass indices and gestational age at delivery. Each group consisted of approximately 40% of nulliparous women (44.1% in the case group and 36.4% in the control group). The case group had higher emergency setting, such as labor or premature rupture of membranes upon presentation, than the control group; this is because most parturients enrolled to the case group were referred because they tested positive for COVID-19 and had obstetric necessity for urgent delivery. Even though there were obstetric complications, some parturients were transferred for elective delivery because of the possibility of emergency development during the quarantine.
| Variable | Case group (n = 34) | Control group (n = 33) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 33 (31–37) | 33 (31–37) | 0.827 | |
| BMI | 27.7 (24.3–30.1) | 25.4 (24.1–28.1) | 0.322 | |
| Gestational age at delivery, week | 38.5 (38.3–39.2) | 38.3 (38.1–38.6) | 0.204 | |
| Nulliparity, n (%) | 15 (44.1) | 12 (36.4) | 0.204 | |
| Presentation, n (%) | ||||
| Labor pain | 19 (55.9) | 3 (9.1) | ||
| PROM | 6 (17.6) | 2 (6.1) | 0.259 | |
| Seizure | 1 (2.9) | - | 1 | |
| Term | 7 (20.6) | 28 (84.8) | ||
| Indications of CD | ||||
| Previous CD | 6 (17.6) | 10 (30.3) | 0.262 | |
| Breech presentation | 1 (2.9) | 1 (3.0) | 1 | |
| CPD | - | 2 | 0.425 | |
| FTP | - | 7 | ||
| NST evidence of fetal distress | - | 2 | ||
| MRCD | - | 11 | ||
| COVID-19 | 26 | - | ||
| Anesthesia | ||||
| General | 34 (100%) | 2 (6.1%) | ||
| Spinal | 0 (0%) | 31 (93.9%) | ||
| Comorbidities, n (%) | 7 (20.5) | 6 (18.2) | 1 | |
| Gestational hypertension | 4 | 1 | 0.356 | |
| Preeclampsia | 1 | - | 1 | |
| Hyperthyroidism | 1 | 2 | 0.614 | |
| Hypothyroidism | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Gestational Thrombocytopenia | - | 1 | 0.493 | |
| Anti-phospholipid syndrome | - | 2 | 0.239 | |
| GDM | - | 1 | 0.493 | |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%). BMI, body mass index; PROM, premature rupture of membranes; CD, cesarean delivery; CPD, cephalopelvic disproportion; FTP, failure to progress; NST, non-stress test; MRCD, maternal requested cesarean delivery; GDM, gestational diabetes.
Since COVID-19 RT-qPCR positive report was considered an indication for CD in the study groups, most parturients did not have choice of labor trial and this affected the indications of CD in the case and control groups. There was no statistical significance between the two groups when the intrapartum indications and maternal-requested CD of the control group were compared to positive COVID-19 in the case group. Some parturients had comorbidities during pregnancy, and there were no differences between the groups.
The surgical and neonatal outcomes of CD according to maternal COVID-19 during peripartum period are summarized in Table 2. There was no difference in the length of hospital stay between the two groups; the median duration of hospital stays for CD was 5 days in both the groups. The laboratory evaluation showed no differences between the groups except in the preoperative level of CRP. Preoperative and postoperative day 1 and 3 hemoglobin levels did not differ based on COVID-19 status. The white blood cells count was slightly higher in the control group than in the case group; however, it was not statistically significant. CRP (mg/L), a serum marker of inflammation was higher in the case group than in the control group (6.4 mg/L vs 1.8 mg/L, p
| Variable | Case group (n = 34) | Control group (n = 33) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital stay, days | 5 (4–6) | 5 (5–5) | 1 | |
| Hb, preoperative (g/dL) | 12.1 (11.6–12.8) | 12.0 (11.1–12.5) | 0.243 | |
| Hb, postoperative day 1 (g/dL) | 10.9 (10.1–12.2) | 11.0 (10.2–11.8) | 0.951 | |
| Hb, postoperative day 3 (g/dL) | 10.2 (9.4–11.2) | 10.0 (9.4–10.6) | 0.318 | |
| WBC, preoperative ( | 7.54 (6.82–8.51) | 7.90 (7.29–9.24) | 0.217 | |
| CRP, preoperative (mg/L) | 6.4 (3.3–13.4) | 1.8 (1.2–3.8) | ||
| Postop complications, n (%) | 3 (8.8) | 6 (18.2) | 0.305 | |
| PPH | 1 | 3 | 0.356 | |
| Wound infection | - | 2 | 0.239 | |
| Fever | - | 1 | 0.493 | |
| Pleural effusion | 1 | - | 1 | |
| Atelectasis | 1 | - | 1 | |
| Neonatal gender, Female | 20 (58.8) | 17 (51.5) | 0.722 | |
| 1-minute APGAR score† | 7.3 (7–8) | 8.0 (7–9) | 0.006 | |
| 5-minute APGAR score† | 8.7 (8–9) | 9.2 (9–10) | 0.005 | |
| Cord blood pH | 7.30 (7.28–7.32) | 7.33 (7.31–7.35) | ||
| Cord blood base deficit (mEg/L) | 3.5 (1.3–4.1) | 4.0 (3.2–5.6) | 0.002 | |
| NICU admission, n (%) | 3 (8.8) | 3 (9.1) | 1 | |
| Neonatal COVID-19, n (%) | 0 | N/A | N/A | |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%). Hb, Hemoglobin; WBC, white blood cell; CRP, C-reactive protein; PPH, postpartum hemorrhage; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; N/A, not available.
†Values are presented as mean (interquartile range).
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.A boxplot of C-reactive protein between case and control group.
In neonatal outcomes, the case group had lower 1- and 5-min APGAR score than the control group (7.3 vs 8.0 and 8.7 vs 9.2, respectively) with statistical significance (p = 0.006 and p = 0.005, respectively). Cord blood analysis revealed significant differences between the groups, with the control group having a higher cord blood pH (7.33 vs 7.30, p
In our study population, not all the case group patients had COVID-19 symptoms. Table 3 shows subgroups according to symptoms and analyses of the variables. Of the 33 patients, 9 had fever or respiratory and non-respiratory symptoms. Severe COVID-19 was defined as COVID-19 related pneumonia that leads to intensive care unit admission, use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, or death, and there were 4 severe cases among the symptomatic groups. There was 1 severe case that presented with seizures, which was later confirmed to be caused by a hyperthyroidism storm. In our study, there were no cases of COVID-19-related maternal death.
| Characteristics | Symptomatic (n = 9) | Asymptomatic (n = 25) | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Fever, 5 (55.6) | 33 (31–37) | 0.827 | |
| Respiratory, 5 (55.6) | ||||
| Non-respiratory, 5 (55.6) | ||||
| Severe COVID-19 | 4 (44.4) | 0 | 0.003 | |
| Pneumonia | 3 | - | ||
| ICU admission | 2 | - | ||
| ECMO | 0 | - | ||
| Death | 0 | - | ||
| WBC, preoperative ( | 7.08 (6.67–7.49) | 8.24 (6.94–8.82) | 0.125 | |
| CRP, preoperative (mg/L) | 12.0 (6.5–15.7) | 5.0 (2.9–10.1) | 0.093 | |
| 1-minute APGAR score | 8 (7–8) | 8 (7–8) | 0.076 | |
| 5-minute APGAR score | 9 (9–9) | 9 (9–9) | 0.113 | |
| Cord blood pH | 7.30 (7.22–7.33) | 7.30 (7.28–7.32) | 0.585 | |
| Cord blood base deficit (mEg/L) | 3.7 (1.1–6.3) | 3.5 (1.8–4.1) | 0.815 | |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%). ICU, intensive care unit; ECMO, Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; WBC, white blood cell; CRP, C-reactive protein.
Although white blood cell count was lower (7.08 vs 8.24, p = 0.125) and CRP level was higher in the symptomatic groups (12.0 vs 5.0), it was not statistically significant (p = 0.093). APGAR scores at 1 and 5 min as well as cord blood analyses were similar between the symptomatic and asymptomatic groups. Fig. 2 shows box plot of log-scaled CRP of subgroup analysis of the case group.
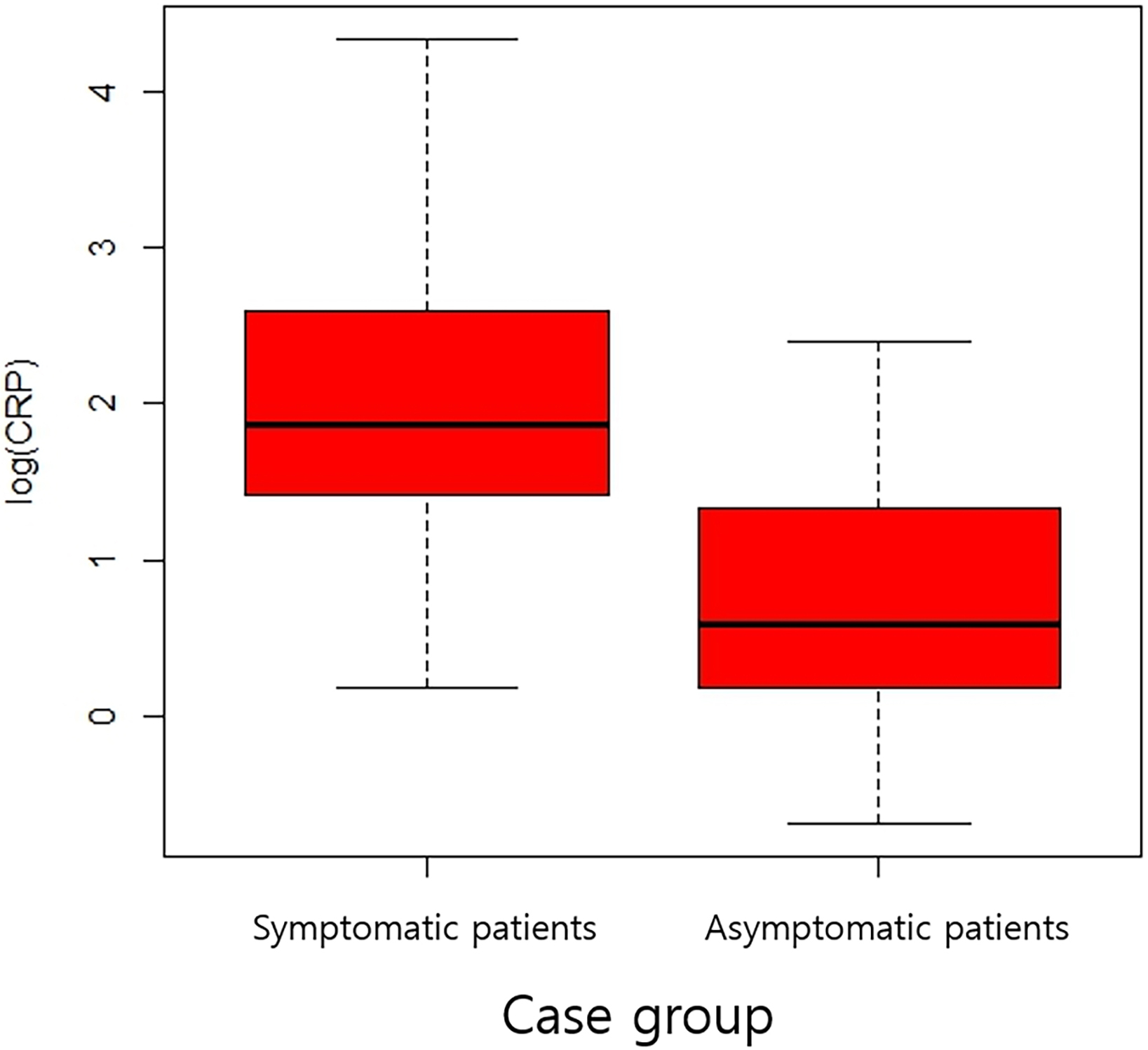 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.A boxplot of C-reactive protein in log scale between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients in case group.
The primary finding of this study was that COVID-19-positive parturients who underwent CD had higher levels of preoperative CRP than those without COVID-19, and their neonates had higher 1- and 5-min APGAR scores and better composition of cord blood. However, these findings did not result in maternal or neonatal mortality and morbidity. There were no differences in the length of hospital stay, postoperative hemoglobin levels, and postoperative complications between the case and control groups. No vertical transmission of COVID-19 was identified in this study.
Since its first outbreak, COVID-19 has been the greatest threat not only in the medical aspects of high mortality rate in vulnerable populations and prevention of worldwide spread but also to the social standards, which eventually evoked contactless life. In South Korea alone, from January 20, 2020, there were over 25 million confirmed cases including reinfections, and COVID-19-related deaths have exceeded 28,000 as of October 10, 2022 [16]. In the early period of the pandemic, specifically between January, 2020 and February, 2021, the prevalence of COVID-19 in pregnant women was lower (0.02%) than in nonpregnant women in reproductive age (0.14%) [17, 18]. Furthermore, the disease severity in pregnant women was not significantly higher than in the general population [17, 19, 20, 21].
According to the labor and delivery guidance for COVID-19 published in 2020 [14], COVID-19 is not an indication for a CD, and the role of the obstetrician is advocated when choosing mode of delivery for COVID-19-positive parturients. According to the Royal College of Obstetricians, there is no evidence to favor 1 mode of delivery over another in women with COVID-19 in relation to the risks of vertical transmission [15]. Knight et al. [22] reported a higher rate of CD in a United Kingdom national population-based cohort study in 2018, with a CD rate of 49–59% than of 29% in the control group. They presumed that in COVID-19-positive pregnant women, there would be a higher rate of fetal compromise, maternal deterioration during labor, and clinician’s deliberation about the need for an expedited delivery as the reasons for decision favored for CD. In a recent national multicenter cohort study [18], the rate of CD was comparable (78.5%) to that of a systematic review (52.3–95.8%) conducted in 2021 [23].
In a randomized controlled trial conducted in 2019, there were no significant differences in the APGAR score and cord blood gas values between general anesthesia and combined spinal/epidural anesthesia [24]. However, a network meta-analysis by Kim et al. [25] which included 3689 women from 46 randomized trials concluded that spinal anesthesia had a better 1- and 5-min APGAR score than general anesthesia. They reported that epidural anesthesia had the highest rank for umbilical venous pH among 4 different anesthetic techniques. The reason why control group had better APGAR score and cord blood gas analyses should be interpreted in the context of differences in anesthesia between the case and control groups. Meanwhile, in our study, all COVID-19-positive patients received general anesthesia to protect the medical care giver while most of the control group patients received neuraxial anesthesia. The difference in APGAR scores and cord blood gas values between the groups should be attributed to anesthesia, rather than COVID-19 considering relatively milder presentation of COVID-19 in the case group.
Although leukocytosis was uncommon in the case group, the median white blood cell count was higher in the control group than in the case group, and CRP was significantly higher in the case group than in the control group. A large portion of patients in the case group did not have significant clinical symptoms upon admission, and even asymptomatic COVID-19-positive women had higher serum marker for inflammation [26] than COVID-19 pregnant women. Higher level of CRP in the case group shows the consistency and reliability of our study. Furthermore, the subgroup analysis demonstrated the relation between clinical symptoms and inflammatory response.
There were no cases of vertical transmission of COVID-19 during CD in our study. Recently Allotey et al. [27] reported that as high as 1.8% of COVID-19 pregnant women had RT-PCR positive newborns. They evaluated data from 472 studies, including 206 cohort studies and 266 case series on 28,952 mothers and 18,237 neonates. There were 592 neonates with COVID-19. There were 2 cases of intrapartum exposure identified among 18 cases assessed. They concluded that vertical transmission of COVID-19 was possible, although this is likely to be rare. According to a recent national cohort study reported in 2022 [18], there was no evidence of intrapartum transmission of COVID-19. These findings suggest that the vertical transmission of COVID-19 is rare, especially when the infection has occurred late in pregnancy or within 7 days before delivery.
In this study, the interpretation of COVID-19-indicated CD was important. Previous CD and the breech presentation did not differ between the groups. Assuming the same proportion of patients required CD by themselves, other intrapartum indications of CD, such as failure to progress and evidence of fetal distress showed no differences between groups. As previously stated, COVID-19 alone should not be considered an indication of CD, and the management of pregnant women in active labor or with premature rupture of membranes needs conventional management as COVID-19 negative parturient [14, 15]. However, our findings showed that there were no significant differences in maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality, so obstetrician should be aware of this when making decision on the mode of delivery of COVID-19 positive parturient. Despite the nonsubtle differences in APGAR score and cord blood gas composition because of anesthetic choice, and because the neonatal intensive care unit admission rate per group was not significantly different, the deliberate use of CD to control disease contamination and prevent inadvertent spread of disease during labor should also be considered.
This study had several limitations. First, we conducted a single-centered case-control study with 34 patients in the case group, resulting in a relatively small sample size. Second, there were limited variables in regards to disease severity and outcomes. For example, we were unable to evaluate the placental pathology report of COVID-19 positive and negative pregnancies at term. Only a small portion of patients in the case group had clinical symptoms of COVID-19. The inclusion of asymptomatic COVID-19 pregnant women might make interpretation and clinical application more difficult. Another limitation is that COVID-19 vaccination of pregnant women was not assessed in both groups. Finally, the cohort of this study consists mainly on outbreak of omicron variant. According to the findings of this study, the wild type, the alpha, the delta and other variant of SARS-CoV-2 may have different effects on pregnancy and CD.
To the best of our knowledge, this study was the first study focusing on COVID-19-positive pregnant women at term with regard to the obstetric and neonatal outcomes in the setting of urgent needs for delivery. Our study found that CD conducted on COVID-19-positive pregnant women showed comparable surgical and neonatal outcomes compared to COVID-19-negative controls. There is imperative necessity for the development of guidelines on how to manage parturient with COVID-19 considering the high disease prevalence. The current study may help support the evidence-based delivery on COVID-19-positive pregnant women.
Pregnant women with coronavirus disease 2019 at term who underwent urgent cesarean delivery showed comparable surgical and neonatal outcomes except for higher preoperative C-reactive protein levels compared to COVID-19-negative women. The results should be confirmed in a larger study.
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conceptualization: JY, HCJ. Data curation: JY, IK. Formal analysis: JY, IK, JCB. Investigation: JEP, JCB. Methodology: HCJ, JEP, JCB. Resources: JY, HCJ, JEP. Software: JY. Supervision: HCJ, JEP, JCB. Visualization: JY. Writing–original draft: JY, JEP, IK. Writing–review & editing: JY, JCB, HCJ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
The Institutional Review Board of Gyeongsang National University Hospital approved this study with a waiver of informed consent due to the retrospective nature of the study (IRB No. GNUH-2022-05-009).
We would like to present our special thanks to all medical care givers of Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital who stood firm against the huge tide of COVID-19 throughout the pandemic.
This research received no external funding.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.


