1. Introduction
Immune thrombocytopenia is an autoimmune disease characterized by a platelet
count below 100 10/L [1]. According to foreign research, the
incidence of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) in adults ranges from 1.6 to 3.9/per
100,000, with a prevalence of about 1/10,000 [2]. Uncertainty surrounds the
etiology of ITP, which is closely linked to immune intolerance brought on by an
immune cell and immune factor imbalance in addition to autoantibody factors [3].
By controlling the differentiation and homeostasis of immune cells and immune
factors, it has been shown that the Notch-aromatic hydrocarbon receptor
(AhR)-interleukin-22 (IL-22) signaling pathway can be involved in the regulation
of various inflammatory responses and immune diseases, such as hepatitis B [4],
gastric cancer [5], and lung adenocarcinoma [6]. Recently, it has been proposed
that Notch signaling may help ITP develop by increasing the production of IL-22
in CD4T cells through AhR [7]. In this paper, we review the mechanisms of
the Notch-AhR-IL-22 signaling pathway to set the groundwork for understanding the
pathogenesis of the disease and to provide novel insights into ITP therapy.
2. Pathogenesis of Immune Thrombocytopenia
ITP is an autoimmune condition with a complicated etiology,
and anti-platelet autoantibodies may contribute to excessive platelet destruction
by the mononuclear macrophage system [8]. The pathogenesis of
ITP is related to the overproliferation of helper T cell (Th) subpopulations such
as Th1, Th2, Th17, Th22, and regulatory T cells (Treg), regulatory B cells
(Breg), bone marrow-derived suppressor cells and other immunosuppressive cells
decreased, and dysfunction of dendritic cells and natural killer
cells [9, 10, 11], where abnormal B and T cells are the main features of the disease.
Naive CD4T cells are stimulated to differentiate into Th1 cells by IL-12
and gamma interferon (IFN-), and Th1 cells produce cytokines like
IFN-, tumor necrosis factor- (TNF-), IL-2, and
IL-22 that encourage B cell differentiation and proliferation. Th2 cells are
induced by IL-4 and differentiated from naive CD4T cells, secreting
cytokines IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10 that can synergistically control B cells with Th1
cells [12]. Sun et al. [13] discovered increased serum
levels of Th1 cells and associated cytokines and decreased levels of Th2 cells
and associated cytokines in ITP patients, indicating that an imbalance in the
ratio of Th1/Th2 cells may exist be crucial in the pathogenesis of ITP.
Activation of AhR can greatly promote the differentiation of CD4T cells
into the Th22 cell population, a subpopulation of CD4T cells that mainly
secrete cytokines such as IL-22, IL-13, IL-26, and TNF-. In addition to
cooperating with Th17 and Th1 cells in ITP, Th22 cells can also contribute to the
pathophysiology of ITP by secreting IL-22 [14]. The findings from Jernas
et al. [15] showed that elevated plasma IL-22 levels in
children with ITP are associated with Th22 and Th1 cells, suggesting that Th22
cells and IL-22 may play a key role in the pathogenesis of ITP in children. Th17
cells are a subset of pro-inflammatory lymphocytes differentiated by CD4T
cells under the combined action of transforming growth factor-
(TGF-) and IL-6, which work together to mediate inflammatory responses
and autoimmune diseases by secreting IL-17, IL-21, IL-22, and other cytokines,
with IL-17 serving as a marker for pro-inflammatory factors [16]. An imbalance in
the expression of Th17 cells may work in concert with Th22 and Th1 cells to
mediate the pathogenesis of ITP, according to a research by Zhan et al.
[17] who discovered a significant increase in serum Th17, Th1, and Th22 cells in
ITP patients and a positive correlation between Th17 and Th1 and Th22 cells.
Treg is a subpopulation of T cells that specifically exerts immunosuppressive
effects and is distinguished by high levels of CD25 and the forkhead/winged helix
transcription factor (Foxp3) on CD4T cells [18]. Treg cells exert
immunosuppressive effects through the secretion of IL-10, TGF-, and
IL-35, and they can also inhibit T cell activity by expressing cytotoxic T
lymphocyte antigens on their surface [19]. Treg and Th17 cells are functionally
regulated by one another, and Zhou et al. [20] found
that in the peripheral blood of ITP patients, the levels of Treg cells and
TGF-, which play an inhibitory role, were significantly decreased, while
the levels of Th17 cells and IL-17, which play a pro-inflammatory role, were
significantly increased. This finding suggests that the imbalance of Th17/Treg
cells was one of the causes of ITP. Numerous studies have demonstrated that
immune dysregulation in ITP patients can be caused by a reduction in the amount
of Treg cells, a reduction in suppressive activity, or an imbalance between Th17
and Treg cells [8, 21].
B cell activating factor (BAFF) abnormalities are currently thought to be the
primary humoral immune mechanism in the pathogenesis of ITP. BAFF regulates T
cell activation and maturation as well as B cell differentiation, maturation, and
apoptosis [22]. In addition, Toll-like receptor7 (TLR7) may be
another pathogenic mechanism of ITP because it can stimulate dendritic cells to
generate large amounts of BAFF and increase the production of circulating
anti-platelet antibodies [23]. Breg cells have negative regulatory effects,
primarily through the production of TGF- and IL-10 to play an
immunomodulatory role, and ITP patients have fewer serum Breg cells, which
externally manifests as decreased IL-10 and TGF-, which can inhibit
monocyte TNF- expression and induce Treg cell differentiation and
diminish CD4T cell function [19, 24]. Breg cells may play
a role in the impaired immune cell suppression experienced by ITP patients,
according to research by Zhu et al. [10] that found significantly
lower levels of Breg cells, IL-10, and TGF- in patients with ITP. In
conclusion, abnormalities like a Th1/Th2 imbalance, an increased ratio of Th1,
Th17, and Th22 in T-cell subsets, a decrease in Treg cell numbers, an imbalance
between Th17/Treg cells, higher BAFF, and a decrease in Breg cell numbers are
linked to the pathogenesis of ITP.
3. Notch Signaling System Components and the Function of Immunity
Regulation
The Notch signaling pathway is an intercellular signaling pathway with great
evolutionary conservation that primarily regulates cell proliferation,
differentiation, migration, and apoptosis. It also plays an important role in
maintaining tissue homeostasis and the stability of the internal environment
[25]. Notch signaling in the mammalian immune system can
regulate various cells to direct early T and B cell lineage development, control
the differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells, and control the maturation of T
cells and their subpopulations [26, 27]. Four Notch receptors
(Notch-1, Notch-2, Notch-3, Notch-4) and five ligands, three Delta-like ligands
(DLL-1, DLL-3, DLL-4), and two Jagged family ligands
(Jagged-1, Jagged-2) have been identified [28], where the ligand binds
to the receptor, activating Notch signaling, which regulates the expression of
related genes in adjacent cells [29]. An increasing quantity of research
indicates that activating CD4T cells’ Notch receptors and ligands can cause
CD4T cells to differentiate into various Th-cell subsets that secrete a
range of inflammatory factors and cause a variety of immune disorders [25, 30].
It has been suggested that Notch signaling promotes Th1 and Th2 cell
differentiation, with greater expression of the Notch ligand DLL-1
causing Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) to differentiate toward Th1 cells,
whereas increased expression of Jagged-1 causes APCs to differentiate
toward Th2 cells [31]. Notch signaling regulates the differentiation of Th17
cells in addition to its effects on Th1 and Th2 cells. Unintervened ITP patients
had an imbalance of Th17/Treg cells that leaned greater toward Th17 cells,
according to Yu et al. [32], when Notch signaling activity was blocked,
Th17 cell and IL-17 expression decreased along with a decrease in the Th17/Treg
cells ratio, indicating that Notch signaling is necessary for maintaining
Th17/Treg cells homeostasis and that it can be used to restore it. Another
research discovered that by controlling the expression of FoxP3, the
DLL-1 ligand of Notch signaling induces the differentiation of
CD4T cells into Treg cells [33]. Many investigations have shown that Notch
signaling might influence the production of immune factors and the
differentiation of different immune cells, causing an imbalance that may
contribute to the onset of various autoimmune illnesses. For
example, Ma et al. [34] observed increased expression of Notch-1,
Notch-3, and the Notch ligand DLL-1 in blood samples from ITP patients,
while Notch-2 expression was comparatively lowered. Similar findings were made by
Wang et al. [35] who reported that patients with acute ITP had
significantly increased Notch-1 and Notch-3 expression. These findings suggest
that Notch signaling can be widely expressed on CD4T cell surfaces and can
regulate the immune function and differentiation of different immune cells like
Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg, which can contribute to the pathogenesis of ITP by
upsetting immune cells and immune factor homeostasis.
4. Immunomodulatory Effects of AhR
AhR is a ligand-dependent transcriptional protein that forms protein complexes
with chaperone proteins to keep its cytoplasmic location [36]. When AhR binds to
ligands, it moves from the cytoplasm to the nucleus where it forms a heterodimer
with the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor nuclear transporter (ARNT) [37]. It has
been demonstrated that AhR plays a critical part in the development of embryonic
and adult tissues, reproduction, and endogenous metabolism in addition to
promoting chemical and microbial defenses [38]. AhR and its signaling networks
are connected to the secretion and production of some factors associated with
inflammation [39]. Additionally, AhR serves as an environmental sensor and is
crucial for both immune modulation and immune damage [40]. One of the key
transcription factors for the development of Th cell subpopulations, AhR
regulates the expression and differentiation of T and B cells, as well as the T
cell immune process. AhR can alter the number of immune cells in the body and
take part in the body’s immune response by activation by binding to various
ligands [36]. It has been shown that AhR signaling may affect the intercellular
homeostasis of Th17/Treg cells, with the exogenous ligand
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (2,3,7,8-TCDD) activating AhR and causing the
differentiation of Treg cells and the endogenous ligand 6-formylindolo
[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) promotes Th17 cell differentiation after AhR activation,
which causes dysregulation of the homeostasis of Th17/Treg cells and upregulation
of immune factors implicated in disease development, such as IL-17 and IL-22
[41]. The differentiation and homeostasis of Th17 and Treg cells may be dependent
on AhR ligands, and variations in AhR expression can disrupt the balance of these
two T-cell subpopulations, resulting in the onset of autoimmune diseases,
according to a study by Singh et al. [42]. One research discovered in a
mouse model that the coordinated function of the AhR and typical TGF-
signaling pathways in differentiation is crucial for the differentiation of
CD4T cells into Th17 cells [43]. It was also discovered
that AhR is required for the release of IL-22 and that AhR is a direct target of
miR15a/16-1 in CD4T cells, where IL-22 is inversely correlated with the
release of miR15a/16-1 [38]. It has been found that AhR is essential for IL-22
secretion, and AhR is a direct target of miR15a/16-1 in CD4T cells, and
IL-22 secretion is negatively correlated with miR15a/16-1, and this gene
overexpression can reduce the synthesis of IL-22 by inhibiting AhR [44].
Additionally, the connection between AhR and Notch signaling has been discovered
in mouse CD4T cells, and it can be utilized to regulate the cell cycle,
proliferation, and differentiation. Notch signaling boosts the release of IL-22
through AhR, and IL-22 expression is decreased by AhR
antagonists in reaction to Notch signaling activation, and TCDD activation of AhR
raises the levels of Notch-1 and Notch-2, tentatively revealing
a functional link between AhR and Notch pathway was revealed and the role of AhR as a bridge in the Notch-AhR-IL-22 signaling
pathway [45, 46].
5. Notch-AhR-IL-22 Signaling Pathway is Involved in
the Development of ITP
Immune thrombocytopenia is currently a diagnosis of exclusion, and the
condition’s pathogenesis is still a hot subject of study among experts and
scholars. It has recently been suggested that the Notch-AhR-IL-22 axis is one of
the mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of ITP, which has a
fine regulation of the immune and inflammatory responses and is made up primarily
of cis-acting components and trans-conduction systems, the cis-element consists
of members of the and Jagged gene families in Notch ligands, while the trans expression system
is composed of Notch receptors Notch1-4 bound to DLL and Jagged
proteins [25, 47]. In humans and mice, the Notch-AhR-IL-22 axis exists with
organ-specific gene expression profiles, and the Notch and IL-22 signaling
pathways are primarily linked hierarchical fashion via Notch-induced endogenous
AhR ligands [47]. IL-22 is a cytokine that has both pro-inflammatory and
anti-inflammatory effects, and it is primarily produced by CD4T cells, and
when IL-22 is secreted alongside other inflammatory factors such as IL-17,
IFN-, and TNF-, its pro-inflammatory properties are
increased, mediating a variety of inflammatory or autoimmune diseases [48, 49].
Furthermore, IL-22 raises the levels of cytokines like IL-1 and IL-18, which
regulate platelet apoptosis and cause thrombocytopenia [17]. Wang et al. [35] proposed that the Notch signaling
pathway might promote IL-22 expression in CD4T cells by activating AhR, and this research discovered that inhibiting the Notch signaling
pathway could significantly reduce IL-22 secretion by CD4T cells and
AhR-mRNA expression in ITP patients, however, CD4T cell differentiation to
Th17 cells was unaffected, indicating that Notch signaling was directed at the
IL-22 factor secreted by CD4T cells.
In the intricate network of inflammatory molecules involved in
ITP pathogenesis, Th22 cells are also important in the Notch-AhR-IL-22 signaling
cascade, and IL-22 is the main Th22 cell effector molecule [17]. Zeng et al. [50] showed that Notch signaling regulates
IL-22 transcript levels, and overexpression of the activated Notch- AhR pathway
induces CD4T cell differentiation into Th22 cells, which not only increases
circulating IL-22 secretion but also works synergistically with Th17 and Th1
cells to disrupt the body’s immune cell homeostasis. Previous research has shown
that the Notch signaling ligand jagged-1 can increase IL-22 secretion by
promoting Th22 cell expression, as well as raise AhR and IL-22 mRNA and protein
levels to participate in the development of ITP [51]. As was
stated earlier, Notch signaling and AhR individually regulate the immune cell
differentiation and homeostasis, which results in an imbalance in the number of
Th1, Th2, Th22, Th17, and Treg cells in vivo, and the
pathogenic process of ITP can also be mediated by several pathways, such as Notch
signaling that induces AhR to increase direct secretion of IL-22 from CD4T
cells or the Notch-AhR pathway that induces differentiation of CD4T cells
into Th22 cells to enhance IL-22 expression (see Fig. 1 for details).
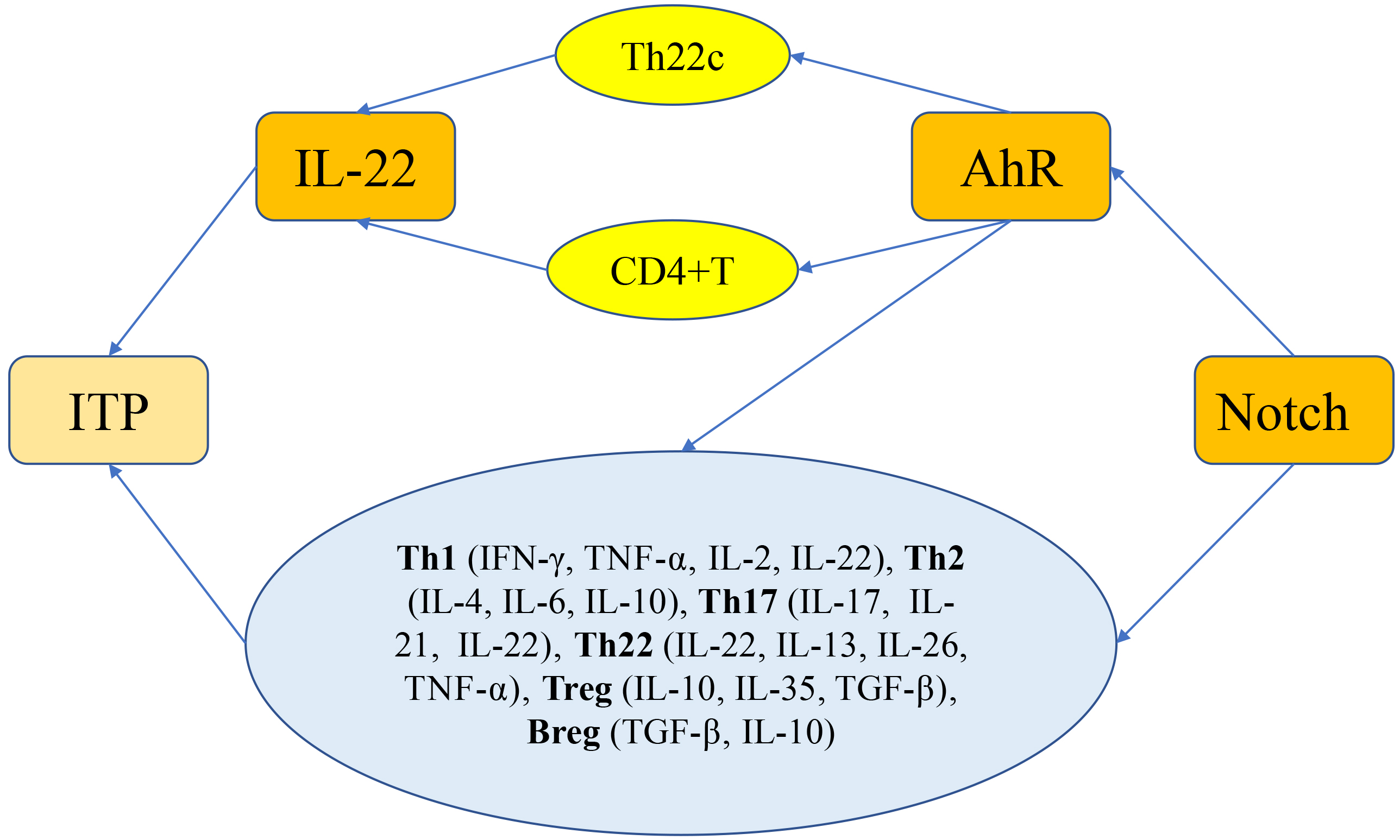 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
Notch-induced AhR regulation of IL-22 secretion signaling
pathway in ITP. Notch signaling and AhR individually regulate the immune cell
differentiation and homeostasis, which results in an imbalance in the number of
Th1, Th2, Th22, Th17, and Treg cells in vivo, and the pathogenic process
of ITP can also be mediated by several pathways, such as Notch signaling that
induces AhR to increase direct secretion of IL-22 from CD4T cells or the
Notch-AhR pathway that induces differentiation of CD4T cells into Th22
cells to enhance IL-22 expression. Abnormalities like a Th1/Th2 imbalance, an
increased ratio of Th1, Th17, and Th22 in T-cell subsets, a decrease in Treg cell
numbers, an imbalance between Th17/Treg cells, and a decrease in Breg cell
numbers are linked to the pathogenesis of ITP.
Given the regulatory role of the Notch-AhR-IL-22 signaling pathway in ITP, some
studies have suggested that decreasing IL-22 levels by blocking the
Notch-AhR-IL-22 axis could be used to treat or mitigate the progression of ITP.
According to a study by Cao et al. [52] untreated ITP
patients had a significantly higher percentage of serum Th22 cells than did treat
ITP patients, but after high-dose dexamethasone treatment the levels of Th22
cells and IL-22 significantly decreased, and the platelet levels in the ITP
patients quickly recovered. According to recent research, resveratrol, an AhR
antagonist, inhibited Notch-AhR signaling, markedly decreased IL-22 levels, and
slowed the pathogenesis of ITP [7]. All of the aforementioned results suggest
that inhibiting the Notch-AhR-IL-22 signaling pathway’s expression can reduce the
amount of IL-22 secreted, which in turn suppresses the immune inflammatory
response and returns ITP’s immune system to normal, and
perhaps blocks any link of the Notch-AhR-IL-22 axis is expected to be a potential
target for immunotherapy of ITP.
6. Research Progress on the Notch-AhR-IL-22 Signaling Pathway and ITP
in Pregnancy
Pregnant women, as a special group, have a considerably higher incidence of ITP
than non-pregnant women due to changes in various systems and organs during
pregnancy, in addition to adult women and children who are susceptible to the
development of ITP [53]. ITP is the most common cause of serious thrombocytopenia
before pregnancy, in the first or second trimester of pregnancy, and accounts for
1%–4% of all causes of thrombocytopenia in pregnancy [54]. Existing research
suggests that the same factors that cause ITP in non-pregnant people also cause
it in pregnant people. These factors include defective T-cell gene expression,
specific anti-platelet antibody binding to antigens in pregnant women’s plasma,
impaired megakaryocyte maturation, increased platelet destruction, and
insufficient platelet production [9]. Although the precise pathogenesis of ITP is
still unknown, pregnancy may speed up the disease’s development [55]. The special
immune tolerance and immune homeostasis that occur during pregnancy may also play
a role in the disease’s pathogenesis [56]. Additionally, the timing of ITP can
have an impact on how a pregnancy develops, increasing the risk of clinical
problems like postpartum hemorrhage, neonatal thrombocytopenia, and even
intracranial hemorrhage [57]. In recent years, some researchers discovered that
the Notch-IL-22 pathway plays a role in the pathogenesis of ITP in pregnant mice
by controlling the immune response, subsequent research confirmed that blocking
the Notch-IL-22 pathway with recombinant human thrombopoietin can improve the
prognosis of pregnant mice with ITP and raise the platelet levels [58].
Additionally, research on the human placenta found that early gestation Notch
receptor expression levels were greater and Jagged-1 expression levels
were lower, as evidenced by the fact that Jagged-1 expression levels
were higher and Notch-1 and Notch-4 expression levels were reduced in late
gestation, the Notch signaling pathway may be differentially regulated during
pregnancy [59]. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that patients with ITP in
pregnancy have significantly higher serum levels of TNF-, IL-22, IL-5,
and IL-6 while significantly lower serum levels of IL-12 and IL-16, indicating
that the development of ITP in pregnancy is linked to an imbalance of related
immune cells and immune factors [60]. According to the research mentioned above,
IL-22 factors and Notch signaling may contribute to the pathogenesis of ITP
during pregnancy. Despite the rarity of reports on this pathway in ITP during
pregnancy, the Notch-AhR-IL-22 signaling pathway is more commonly studied in
non-pregnant ITP. This can serve as an experimental basis for future studies on
the Notch-AhR-IL-22 signaling pathway in ITP during pregnancy, and the mechanism
of this signaling pathway in ITP during pregnancy can also be further
investigated. Given that the pathogenesis and management of patients with ITP
during pregnancy are similar to those during non-pregnancy, immunotherapy
regarding ITP in pregnancy might start with blocking the Notch-AhR-IL-22
signaling pathway. To thoroughly investigate the Notch-AhR-IL-22 signaling
pathway’s role in ITP to generate fresh concepts for immunotherapy of ITP in
pregnancy.
7. Conclusions
In summary, the pathogenesis of ITP is defined by a complex
immune imbalance and immune intolerance condition caused by multiple factors,
pathways, and channels, and Notch signaling is involved in the development of ITP
by inducing AhR expression to promote the differentiation of CD4T cells to
Th22 cells and by increasing IL-22 secretion, which together disrupts the immune
homeostasis in vivo. Understanding the pathogenic role of the
Notch-AhR-IL-22 axis in ITP may set the experimental groundwork for further
research into the pathogenesis of ITP in pregnancy and may also open up new
possibilities for immunotherapy of ITP in pregnancy.
Author Contributions
Q-qF participated in the manuscript conception and design, participated in the drafting of the manuscript.
R-xH participated in the conception and design of the manuscript, revised the important contents of the manuscript, and approved the publication. Both authors have
participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all
aspects of the work. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Acknowledgment
Not applicable.
Funding
The Second Hospital of Lanzhou University’s “Science and Technology Innovation”
program (No: CY2019-MS11).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
