1 School of Medicine, Taizhou University, 318000 Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
Abstract
Background: The relationship between serum calcium levels and
pregnancy-induced hypertension is controversial. This work aimed to evaluate the
relationship between serum calcium levels and the risk of pregnancy-induced
hypertension. Methods: The following database: Chinese National
Knowledge Infrastructure and PubMed, were searched to identify articles on the
relationship between serum calcium levels and pregnancy-induced hypertension. The
meta-analysis was conducted by using Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program]. Results: A total of
twenty one articles included in the present study. The meta-analysis revealed that
patients with pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) had lower calcium levels (standardized weighted mean difference (SMD)
= –0.68; 95% (–0.79, –0.56); p
Keywords
- calcium
- hypertension
- case-control study
- meta-analysis
Pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) is a significant cause of maternal morbidity [1, 2]. A previous study disclosed that 5.1% of pregnancies are affected by PIH [3]. Furthermore, approximately 15% of global maternal deaths (~30,000 deaths per year) are attributed to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy [4]. Consequently, the prevention and treatment of PIH in urgent in the present study.
Calcium plays a critical role in many vital processes, such as neuronal excitability, the release of neurotransmitters, muscle contraction, membrane integrity, and blood coagulation [5]. In addition, blood pressure is regulated by intracellular calcium in the vascular smooth muscle cell via vasoconstriction and variations in the vascular volume. Therefore, appropriate calcium intake for pregnant women can prevent future osteoporosis and reduces the risk of PIH [6]. However, results reported in previous studies were inconsistent for the relationship between serum calcium level and PIH [7]. Thus, this meta-analysis must confirm the relationship between serum calcium level and PIH.
Our meta-analysis aimed to determine whether or not serum calcium level levels are associated with the risk of PIH, which will offer the basis for the prevention and treatment of PIH.
This study protocol was followed PRISMA guidelines.
We searched related articles from the Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure and PubMed databases until July 12, 2022. The following terms: “calcium”; and “pregnancy hypertension”, was used for articles published. In addition, we also searched the references list of relevant studies selected from the electronic databases manually to find additional articles. The language of papers published is restricted to Chinese and English.
The retrieved articles met the following criteria: (1) the study involved humans; (2) the study focused on the relationship between PIH and serum calcium level; (3) data needed was easily extracted directly or indirectly from the article; (4) publication language was confined to English and Chinese.
Two authors evaluated the independently using Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) [8]. We used NOS to assess non- randomized controlled trial (RCT) studies. It includes three main domains (1) selection (cases and control definition, cases and controls selection) maximum of four stars, (2) comparability (are cases and controls comparable or not) maximum of two stars, (3) exposure (for what degree we are confident that our population exposed to the exposure) maximum three stars.
The meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program]
(Version 5.4. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020, London, UK). The standardized weighted mean
difference (SMD) with a corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) was used to
compare the mean serum calcium level between the two groups. Heterogeneity among
effect sizes was tested using a Q statistic and an I
A total of 21 potential articles were identified in this study (Table 1, Ref. [11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31] and Fig. 1). NOS was used to assess non-RCT studies (Table 1).
| First author | year | Total | Sample types | Country | NOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tong M [11] | 2010 | 90 | serum | China | 9 |
| Wei J [12] | 2008 | 187 | serum | China | 9 |
| Li Y [13] | 2010 | 100 | serum | China | 8 |
| Zhao Y [14] | 2008 | 160 | serum | China | 9 |
| Yu S [15] | 2009 | 142 | serum | China | 8 |
| Hao Y [16] | 2005 | 89 | serum | China | 9 |
| Guo L [17] | 2013 | 118 | serum | China | 9 |
| Zhao, F [18] | 1989 | 212 | serum | China | 9 |
| Kumar N [19] | 2019 | 220 | serum | India | 5 |
| Li YZ [20] | 2022 | 511 | serum | China | 9 |
| Li XJ [21] | 2020 | 166 | serum | China | 9 |
| Zhu SY [22] | 2019 | 290 | serum | China | 9 |
| Liu SQ [23] | 2012 | 80 | serum | China | 9 |
| Wu MZ [24] | 2006 | 218 | serum | China | 9 |
| Xu J [25] | 2011 | 120 | serum | China | 8 |
| Liang YB [26] | 2009 | 133 | serum | China | 9 |
| Gu LJ [27] | 2014 | 110 | serum | China | 9 |
| Wang LP [28] | 2008 | 100 | serum | China | 7 |
| Zheng Q [29] | 2015 | 220 | serum | China | 7 |
| Wen XG [30] | 2015 | 143 | serum | China | 9 |
| Xie F [31] | 2020 | 160 | serum | China | 9 |
Note: NOS, Newcastle-Ottawa Scale.
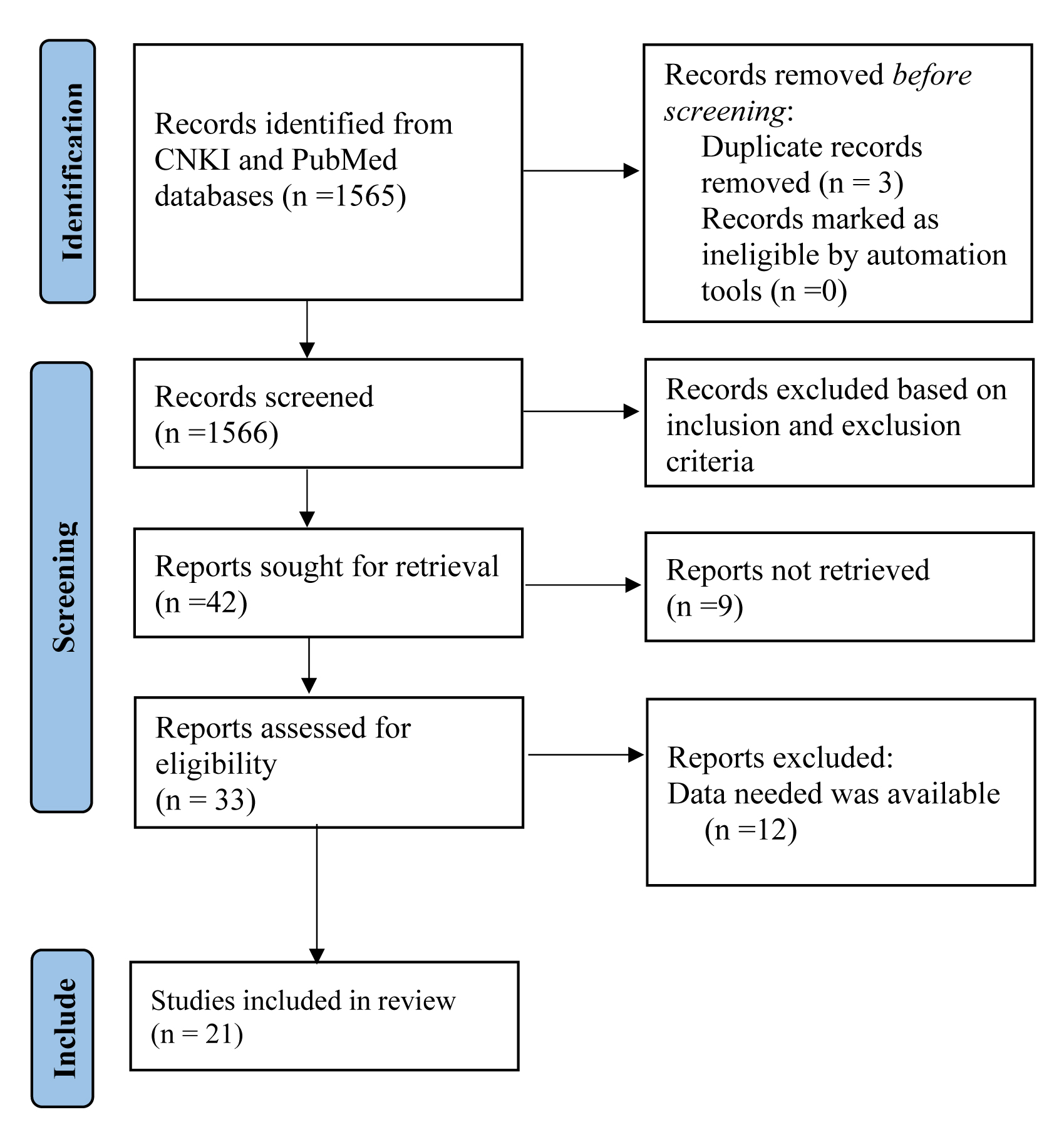 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.PRISMA diagram of the search strategy.
The heterogeneity test found heterogeneity exists (I
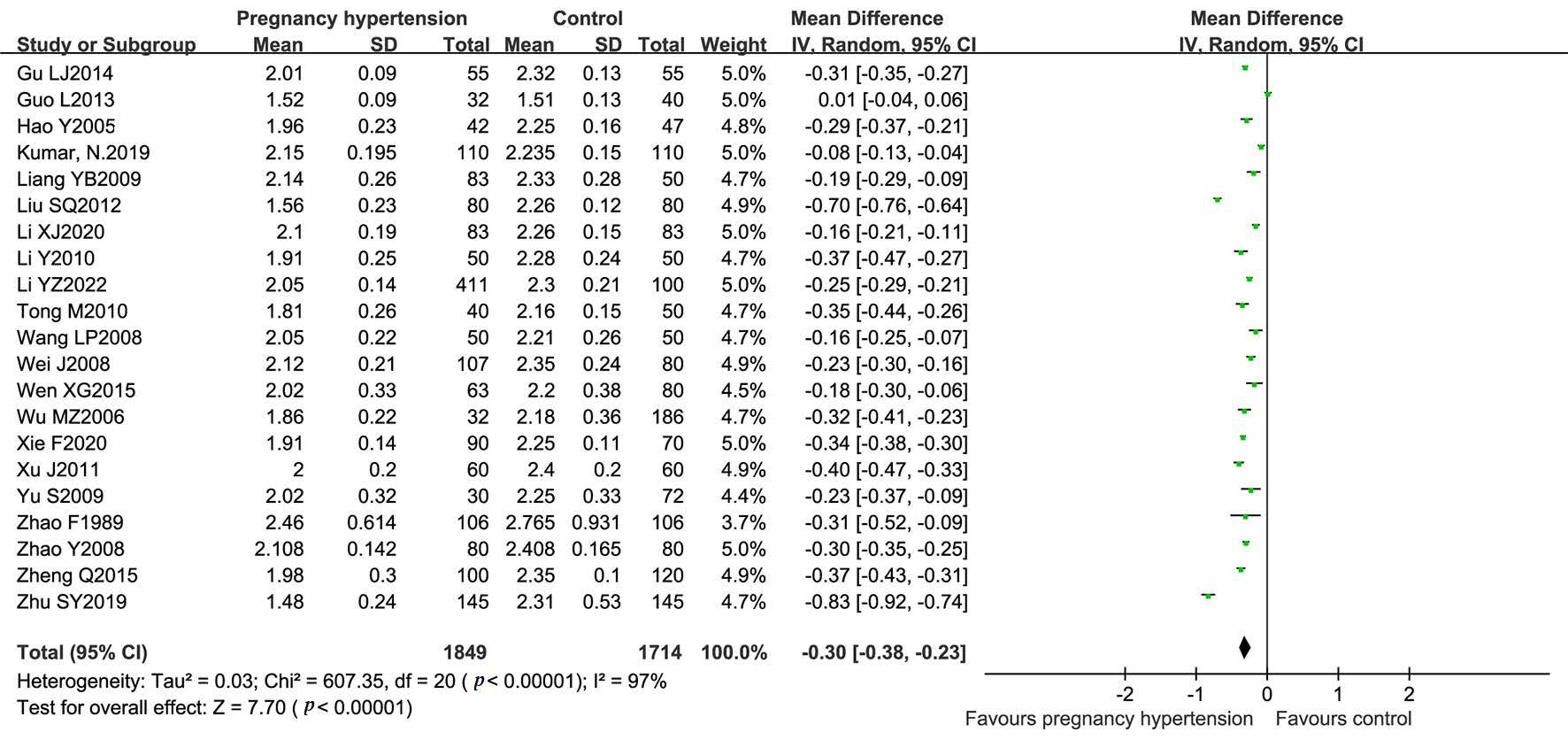 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Forest plot and the risk of bias among studies included.
Funnel plots determined publication bias. There was no evidence of publication bias (Fig. 3).
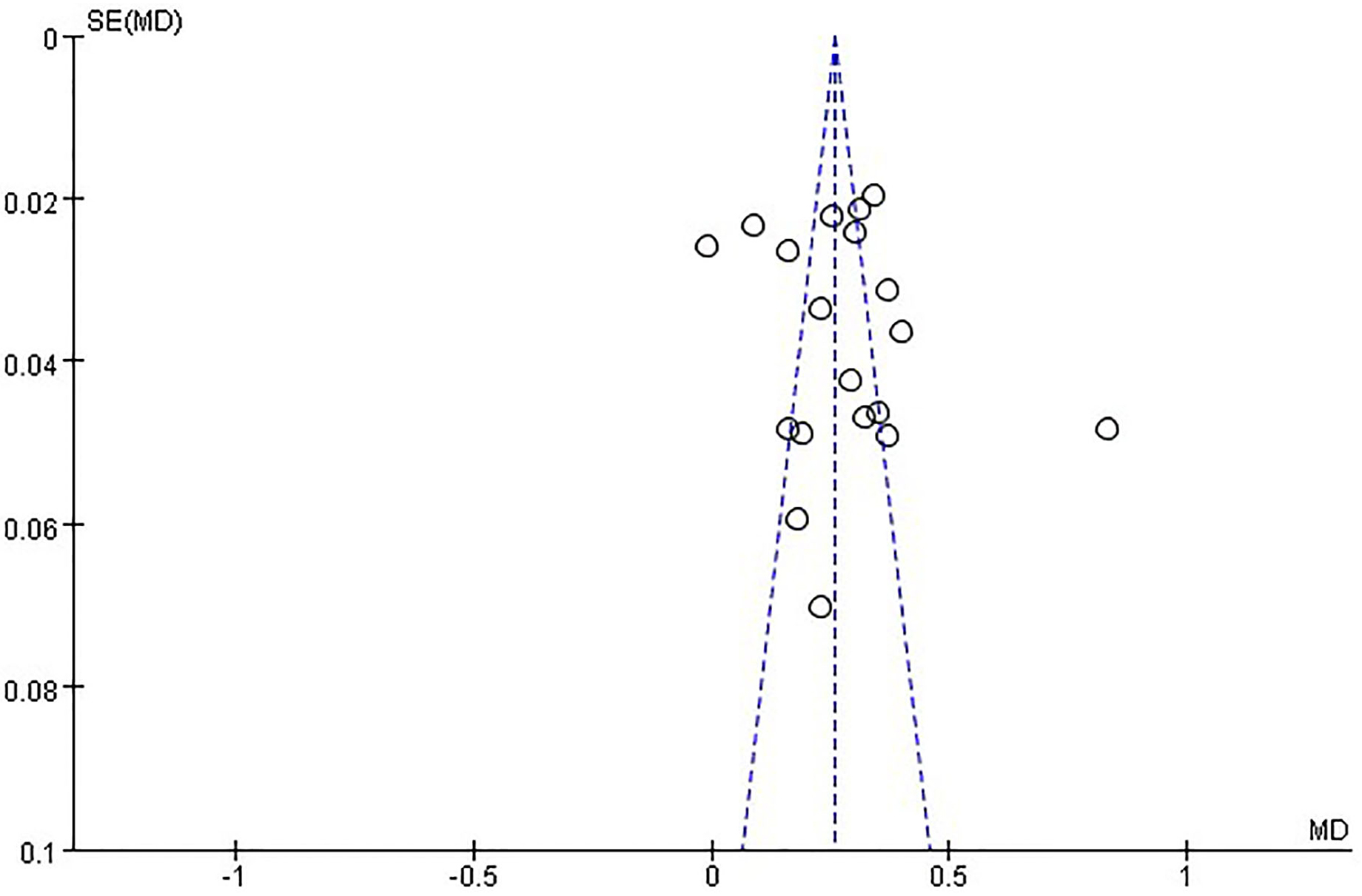 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Funnel plot and the risk of bias among studies included.
In this meta-analysis, we discovered that the mean serum calcium level in the PIH group was lower than in the control group. The results are consistent with previous results of meta-analysis [32]. Specifically, the serum calcium levels decreased in patients with PIH according to random effects, consistent with an earlier study [5, 33]. A recent study also confirmed that calcium supplementation could effectively reduce the risk of PIH [34, 35].
In recent years, studies have been carried out on serum trace elements levels during pregnancy. PIH is a pregnancy-specific condition that augments maternal and infant mortality and morbidity [36]. Vitamin D can facilitate the absorption of calcium. Thus, vitamin D supplementation also reduces the risk of PIH. Furthermore, a meta-analysis suggested that vitamin D supplementation also works well in preventing PIH [37]. Therefore, measuring serum calcium levels may be a novel way to monitor the risk of PIH.
The strengths of this study include a comprehensive literature search for all relevant No-RCTs, including the content of ordinary pregnant women and pregnancy hypertension women. In addition, we considered effect moderation by trial location and maternal and intervention characteristics. Finally, we reported a broad range of outcomes and considered core outcomes for pregnancy hypertension.
There are some limitations in our meta-analysis. First, this study included only published articles, and some unpublished articles may need to recruit in the present study. Second, this meta-analysis only searched the articles published in Chinese and English. Therefore, language bias also is not avoided. Third, a subanalysis of different phenotypes of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy should be performed [38]. However, this subanalysis is not possible due to a lack of data.
Our research suggests that the reduction in serum calcium concentration may be closely related to PIH. Pregnancy can easily lead to maternal calcium deficiency, increasing blood pressure. Future research should focus on ensuring calcium supplements maintain serum calcium balance and target women with low serum calcium for personalized PIH prevention.
CPL and LPH made contributions to study conception and design; YXS and LPH participated in data collection; LPH and YXS dedicated to data analysis and interpretation; CPL and YXS involved in the drafting of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
Thanks to all the peer reviewers for their opinions and suggestions.
This study was supported by the 2022 Taizhou University Higher Education Teaching Reform Project (No. 105 and No. 114).
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.



