1 Hainan Provincial Key Laboratory for Human Reproductive Medicine and Genetic Research, Department of Reproductive Medicine, Hainan Provincial Clinical Research Center for Thalassemia, Key Laboratory of Reproductive Health Diseases Research and Translation (Hainan Medical University), Ministry of Education, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Hainan Medical University, Haikou 571101, Hainan, China
2 Institute of Microbiology, Guangdong Academy of Sciences, 510250 Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
3 Department of Laboratory Medicine, Guizhou Qiannan People's Hospital , 558099 Qiannan, Guizhou, China
4 School of Management, Hainan Medical University, 571199 Haikou, Hainan, China
†These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
Background: The primary objective was to investigate how Forkhead Box
A1 (FOXA1) contributes to late-onset preeclampsia (LOPE) and its impact on
trophoblast invasion and migration. Methods: The prospective cohort
study included 15 pregnant women with LOPE (gestational age of
Keywords
- FOXA1
- late-onset preeclampsia
- trophoblasts
- immunohistochemistry
- invasion
- migration
Preeclampsia (PE) is characterized by hypertension and proteinuria occurring at
20 weeks of gestation in women, and affects approximately 6% of pregnant women
worldwide [1, 2, 3, 4]. PE can result in maternal and neonatal mortality and morbidity
[5]. The detailed etiology of PE remains an area of intense research. Studies
have suggested that both the mother and fetus play a role in the development of
PE [6, 7]. PE can be categorized as mild, moderate, and severe. Chronologically,
PE can be classified as “early-onset” (occurring before 34
Forkhead Box A1 (FOXA1) is a forkhead box transcriptional factor primarily found
in mammary luminal epithelial cells. FOXA1 can facilitate the binding of estrogen
receptor alpha (ER
This study firslty investigated FOXA1 expression in placental tissues of patients with LOPE. Additionally, in vitro experiments explored the impact of FOXA1 overexpression on trophoblast proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and migration. Overall, these findings provide novel insights into understanding the role of FOXA1 in the pathophysiology of LOPE.
This was a prospective cohort study that included 15 pregnant women who developed LOPE after reaching a gestational age of 34 weeks or more, and 18 healthy pregnant women who delivered at full term (37 weeks or more), conducted between 2012 and 2018, at the First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical College. All participants were carrying single pregnancies, and placental samples were obtained through elective cesarean section. Ethical approval for the study was granted by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical College. All participants provided written informed consent.
After performing a cesarean section, placental tissues were collected and subsequently incubated in 10% formalin for 48 hours. Next, the tissues underwent a dehydration process using alcohol, and diaphanization using xylene before being embedded in paraffin.
The placental tissues were permeabilized for 5 minutes with phosphate buffered
saline (PBS) containing 0.2% Triton X-100 (#X100, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) and
10% goat serum (#50197Z, Thermo Fisher Scientific. Waltham, MA, USA). Subsequently,
they were incubated overnight at 4 °C with an anti-FOXA1 antibody
(Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA) or an anti-cytokeratin7 (CK7) antibody (Abcam,
Cambridge, MA, USA). Following PBS washes, the sections were incubated with a
fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated or Cy5-conjugated secondary antibody
(Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA) for 1 hour at 37 °C. After additional PBS
washes, the nuclei were counterstained with 4
The IHC analysis of FOXA1 was conducted following the methods described in a
previous study [22]. The IHC staining score for placental trophoblasts was
determined based on the intensity of staining and the percentage of positive
cells. Depending on the staining intensity, it was categorized as follows:
“intense staining” (dark brown), “moderate staining” (brown yellow), “weak
staining” (light yellow), or “non-staining” (no staining), corresponding to
scores of 3, 2, 1, and 0 points, respectively. Additionally, based on the
percentage of positive cells, it was divided into the following groups: 0,
Human HTR-8/SVneo cells were obtained from Shanghai Institute of Cell Biology (Shanghai, China) in 2017.
The cell lines were verified by CK7 immunofluorescent staining, and have been tested for mycoplasma contamination and the test outcome is negative. The cell lines were cultured in HERA CELL 150 medium (Thermo, Waltham, MA,
USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (#10099141; Thermo Fisher
Scientific). The cells were maintained in a humidified incubator (HERA CELL 150;
Thermo Fisher Scientific) with 5% CO
Total RNA from 1
Protein extraction from HTR-8/SVneo cells (1
Cell apoptosis was assessed using the FITC-Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI)
Apoptosis Detection kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The
transfected cells were collected, ensuring that suspension cells were also
included, and washed twice with cold PBS. Subsequently, the cells were
resuspended in 1
The Transwell invasion assay was used to assess cell invasion. In brief, the
transfected cells were seeded onto the top chamber of a Transwell (8 µm)
that was coated with Matrigel (Corning, New York, NY, USA). The upper chamber was
filled with Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) 1640 medium (#11875119;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) without FBS, while the lower chamber
contained RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS (#10099141; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). After an additional 24 hours of incubation, the
invaded cells were fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde (#158127; Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) for 30
minutes and then stained with Giemsa (#G4507; Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). Cells that
had invaded the lower membrane surface were counted in ten random fields
(10
Cell migration was evaluated using a wound healing assay [21]. Briefly, transfected HTR-8/SVneo cells were seeded in six-well plates (#140675; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and cultured for 24 hours. Subsequently, an artificial wound was created using a 200 µL pipette tip. The width of the wound was measured by ImageJ software at 0, 6, and 9 hours, respectively.
For all statistical analyses, SPSS 22.0 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was
utilized. The normal distribution of the data were assessed by Kolmogorov-Smirnov
test. Student’s t-test was employed to compare measurement data of
normal distribution between two groups. The data were presented as means
To determine the FOXA1 expression in placental tissues of patients with LOPE, we
performed immunofluorescence double-staining of placental tissue, captured under
a laser confocal fluorescence microscope (Fig. 1). In the image from the normal
group, the placental villi appear well-matured, with a relatively uniform matrix
and a plump shape. Endothelial cells are intact, and the nuclei between
syncytiotrophoblasts are neatly arranged. Additionally, a few red blood cells can
be observed within the villi capillary lumens. In contrast, the LOPE group
exhibits disordered nuclei in the trophoblasts, along with vascular reduction,
lumen stenosis, and incomplete endothelial cells. The immunofluorescent staining
reveals a weaker fluorescence intensity of FOXA1 in LOPE placental tissue
compared to the normal group. CK7, a trophoblast-specific marker protein, is
expressed in both cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast cells. Under low
magnification, the study reveals FOXA1 expression in both syncytiotrophoblast and
cytotrophoblast cells within the villi. When observed at 60
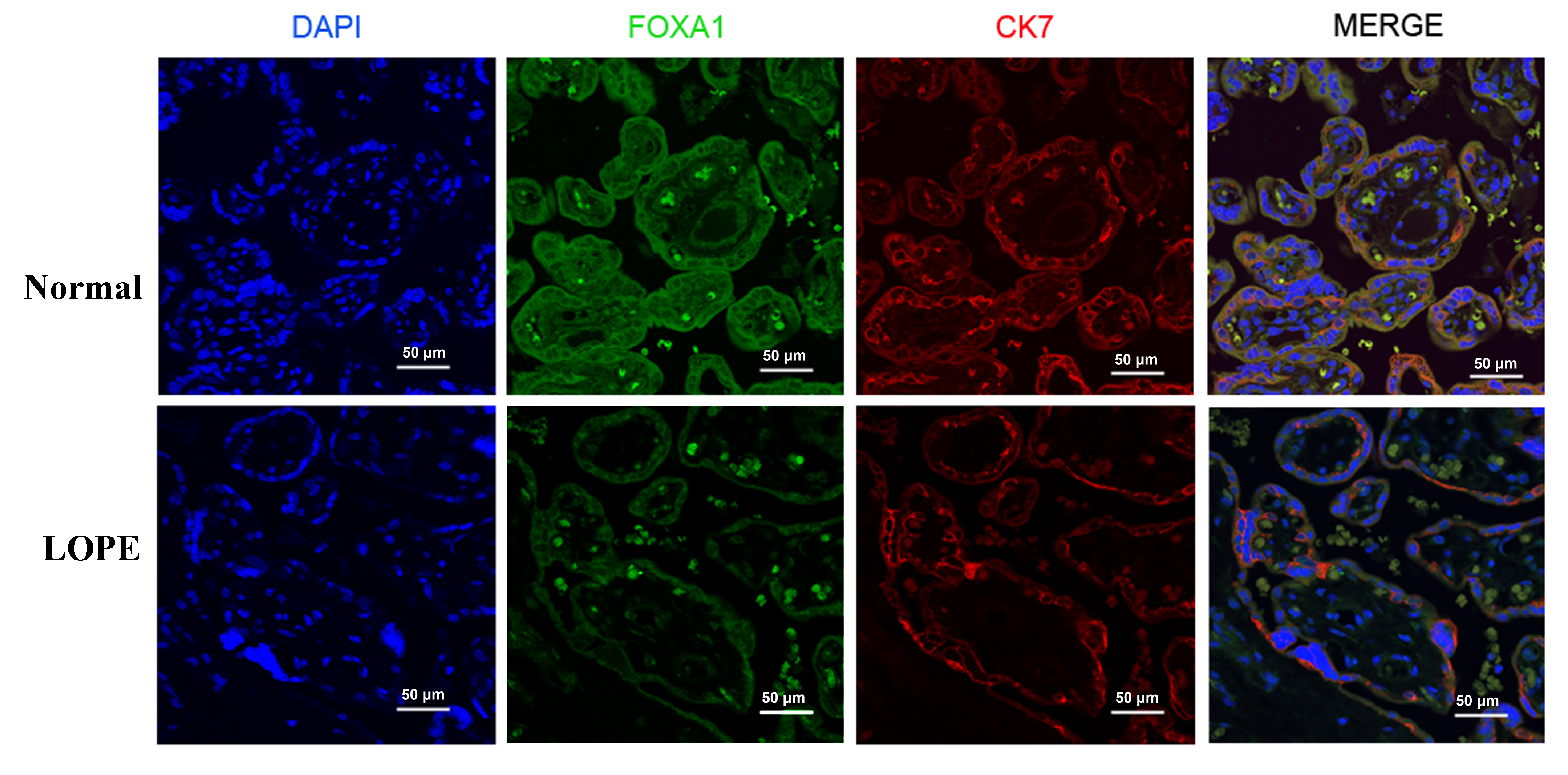 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.Immunofluorescent staining of the FOXA1 in the placental tissues from normal pregnant women and women with LOPE. DAPI, diamidino-2-phenylindole; FOXA1, Forkhead Box A1; LOPE, late-onset preeclampsia; CK7, cytokeratin7.
Next, in order to confirm if FOXA1 expression was altered in LOPE placental tissues, we performed IHC staining analysis of FOXA1 in placental tissues (Fig. 2). The findings reveal a significantly reduced FOXA1 protein expression in the LOPE group when compared to the normal group.
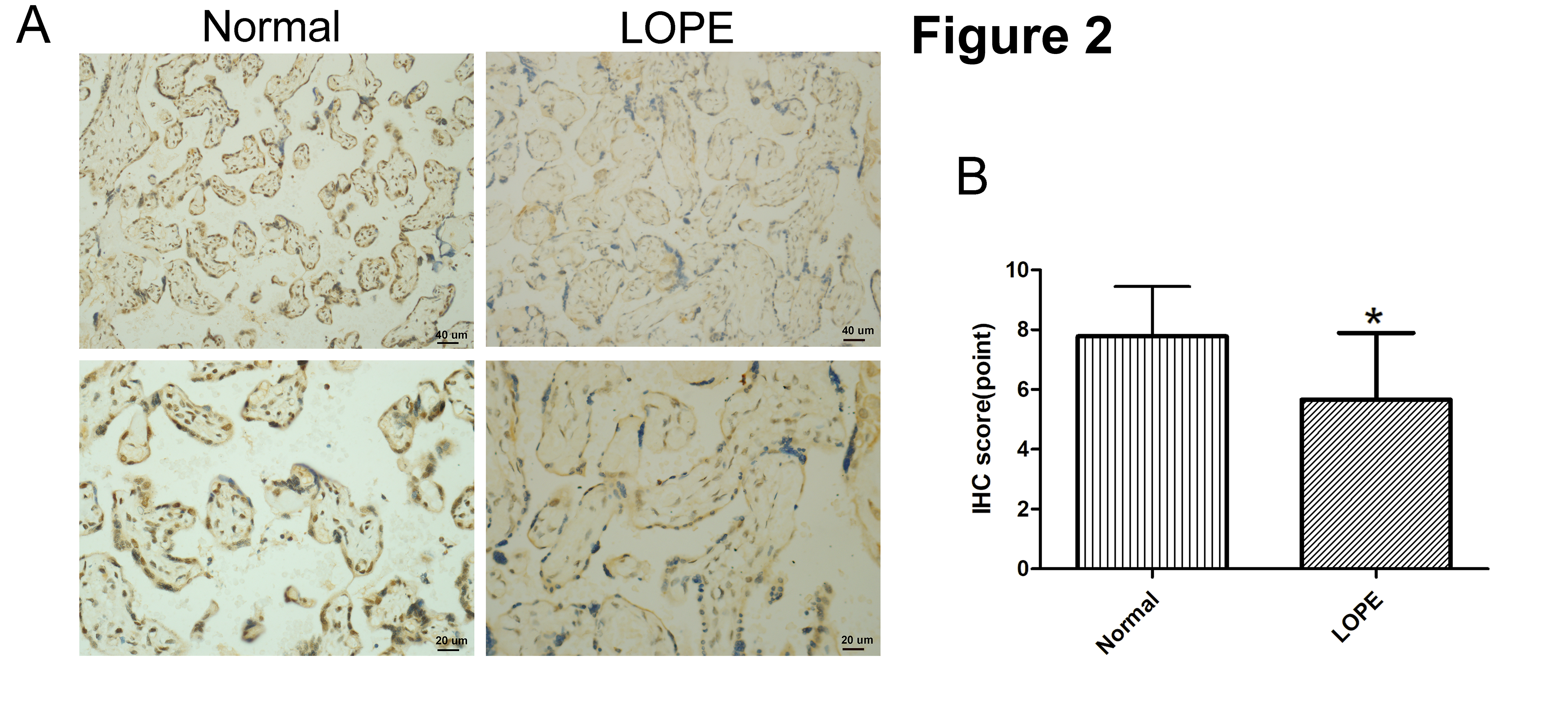 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of FOXA1. (A) IHC staining
of FOXA1 in the placental tissues from normal pregnant women and women with LOPE.
(B) IHC scores of FOXA1 expression in the placental tissues were compared between
the normal group and LOPE group. Bar results represent the mean
No notable differences were detected in delivery times, pregnancy times, maternal age, 1- and 5-minute Apgar scores between the normal and LOPE group. However, the gestation week at delivery was notably shorter in LOPE group compared to normal group. Patients in the LOPE group exhibited higher systolic and diastolic blood pressure in comparison to the normal group. Furthermore, 24-hour proteinuria was detected in the LOPE group, but not in the normal group. Additionally, both placental weight and neonate birth weight were lower in the LOPE group, compared to the normal group (Table 1).
| Characteristics | Normal (n = 18) | LOPE (n = 15) | p-values |
| Maternal age (year) | 32.67 |
31.80 |
0.618 |
| Pregnancy times | 2.72 |
2.40 |
0.487 |
| Delivery times | 0.78 |
0.53 |
0.200 |
| Gestation weeks at delivery | 38.75 |
37.89 |
0.043 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 111.61 |
156.67 |
|
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 71.28 |
91.07 |
|
| 24 h proteinuria (g) | Not test | 1.87 |
|
| 1-minute Apgar score | 9.94 |
9.33 |
0.066 |
| 5-minute Apgar score | 10 | 10 | - |
| Neonate birthweight (g) | 3202.78 |
2684.60 |
0.003 |
| Placental weight (g) | 559.00 |
496.0 |
0.017 |
Significant differences between groups were determined by Student’s t-test. LOPE, late-onset preeclampsia.
To create trophoblasts overexpressing FOXA1, we introduced a retrovirus designed to overexpress FOXA1 into HTR-8/SVneo cells. This resulted in a significant elevation in FOXA1 expression levels compared to the negative control (NC) group (Fig. 3A,B), determined by qPCR and confirmed by western blot assay. Subsequently, we assessed cell apoptosis/cycle through flow cytometry. FOXA1 did not exert any significant effect on the cell apoptotic rate of trophoblasts when compared to the NC group (Fig. 4A). Furthermore, FOXA1 overexpression significantly increased S phase cell population while decreasing the G2/M phase population, without affecting G0/G1 phase population, compared to NC group (Fig. 4B).
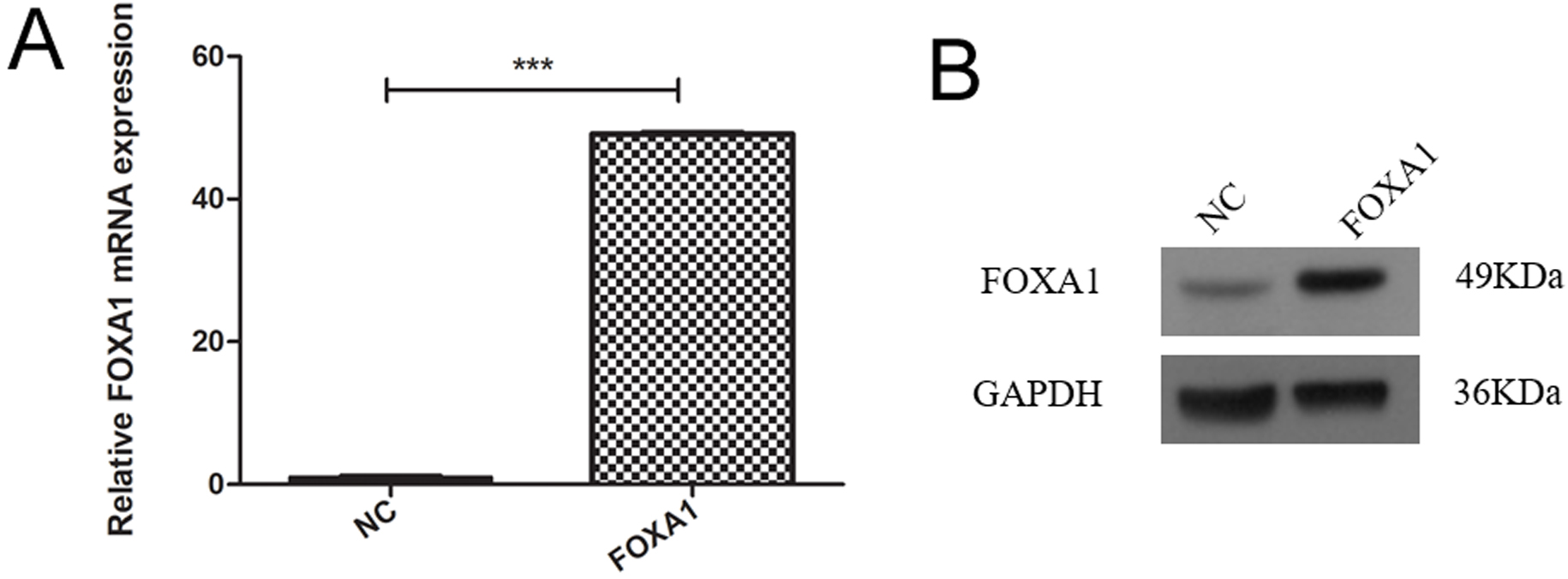 Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.Overexpression of FOXA1 in the trophoblast cells. (A) The mRNA
expression of FOXA1 in the HTR-8/SVneo cells from NC and FOXA1 group was
determined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). (B) The
expression of FOXA1 protein in the HTR-8/SVneo cells from NC and FOXA1 group was
determined by western blot assay. FOXA1, Forkhead Box A1; NC, negative control;
GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Bar results represent the mean
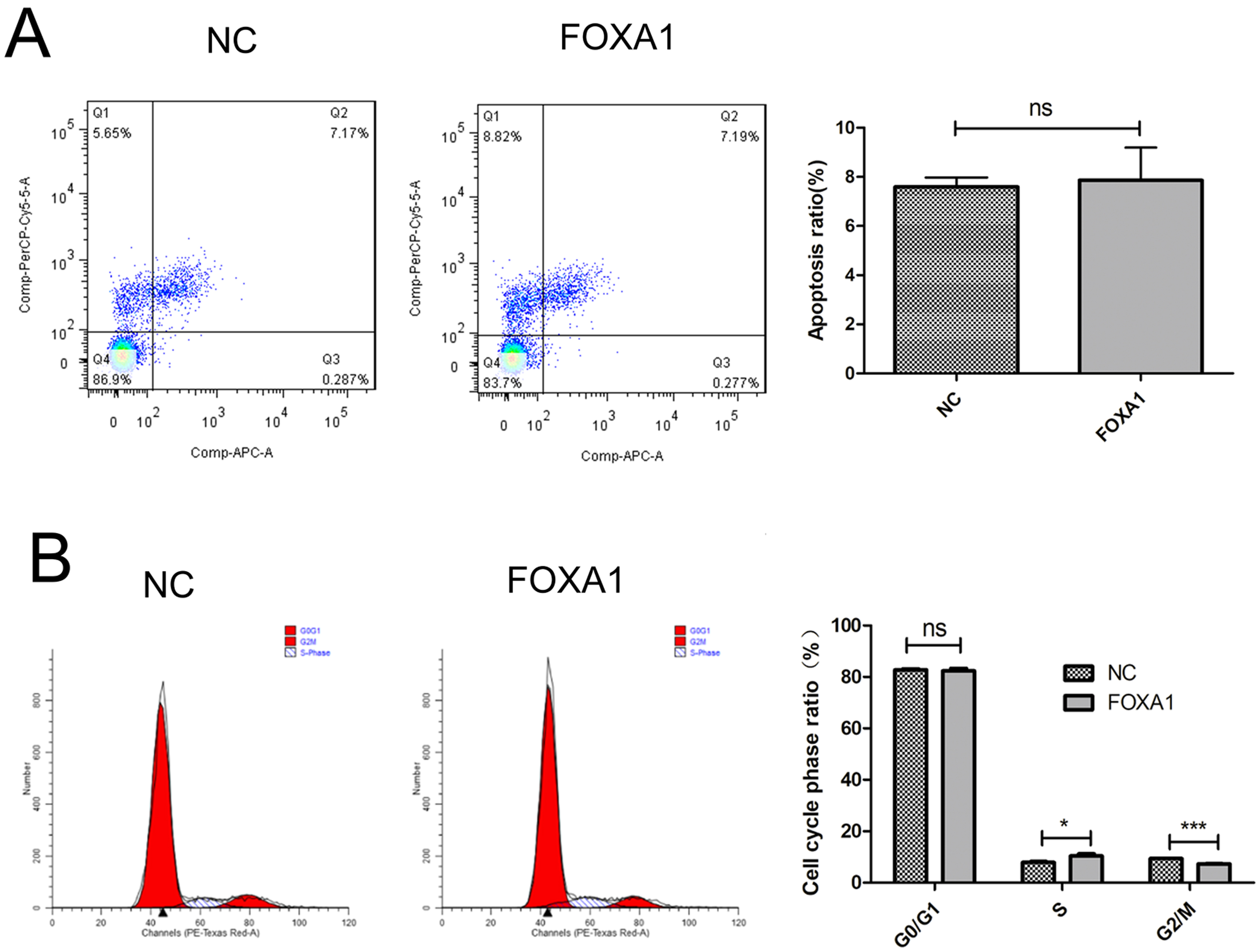 Fig. 4.
Fig. 4.Effects of FOXA1 overexpression on the cell apoptosis and cell
cycle of trophoblast cells. (A) The cell apoptosis of HTR-8/SVneo cells from NC
and FOXA1 group was determined by flow cytometry. (B) The cell cycle of
HTR-8/SVneo cells from NC and FOXA1 group was determined by flow cytometry.
FOXA1, Forkhead Box A1; NC, negative control. Bar results represent the mean
To further evaluate migration/invasion of trophoblasts, transwell invasion assay deciphered that FOXA1 overexpression enhanced invasive capacity of trophoblasts compared to NC group (Fig. 5). Wound healing assay revealed that FOXA1 overexpression significantly accelerated the closure of wounds in trophoblasts when compared to NC group (Fig. 6).
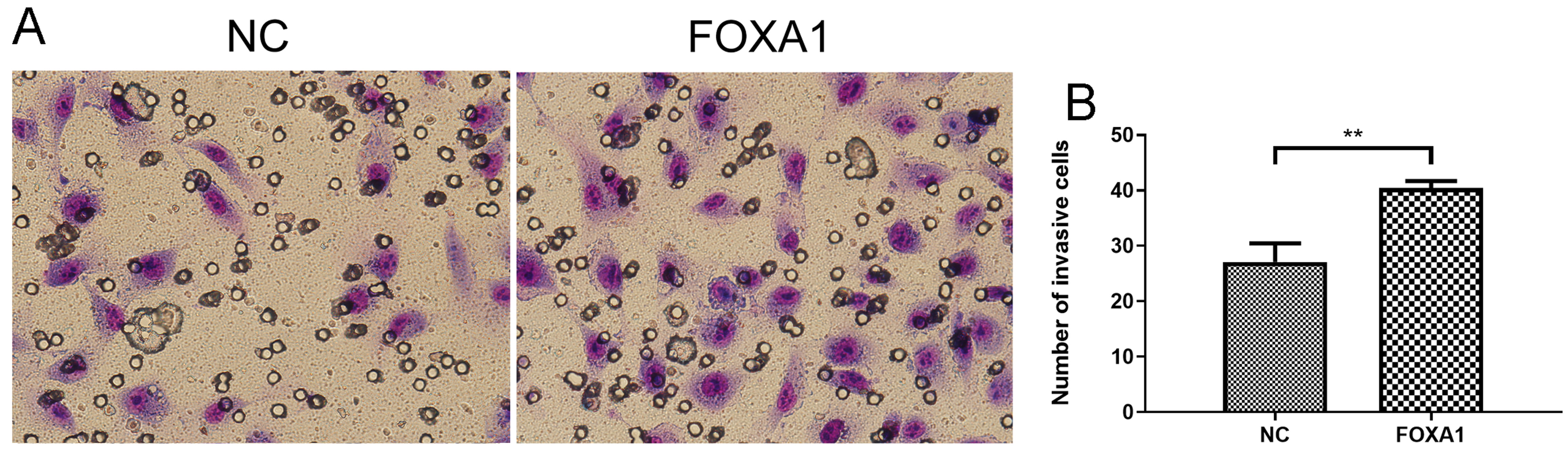 Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.Effects of FOXA1 overexpression on the cell invasion of
trophoblast cells. The cell invasion of HTR-8/SVneo cells from NC and FOXA1
group was determined by Transwell invasion assay. FOXA1, Forkhead Box A1; NC,
negative control. Bar results represent the mean
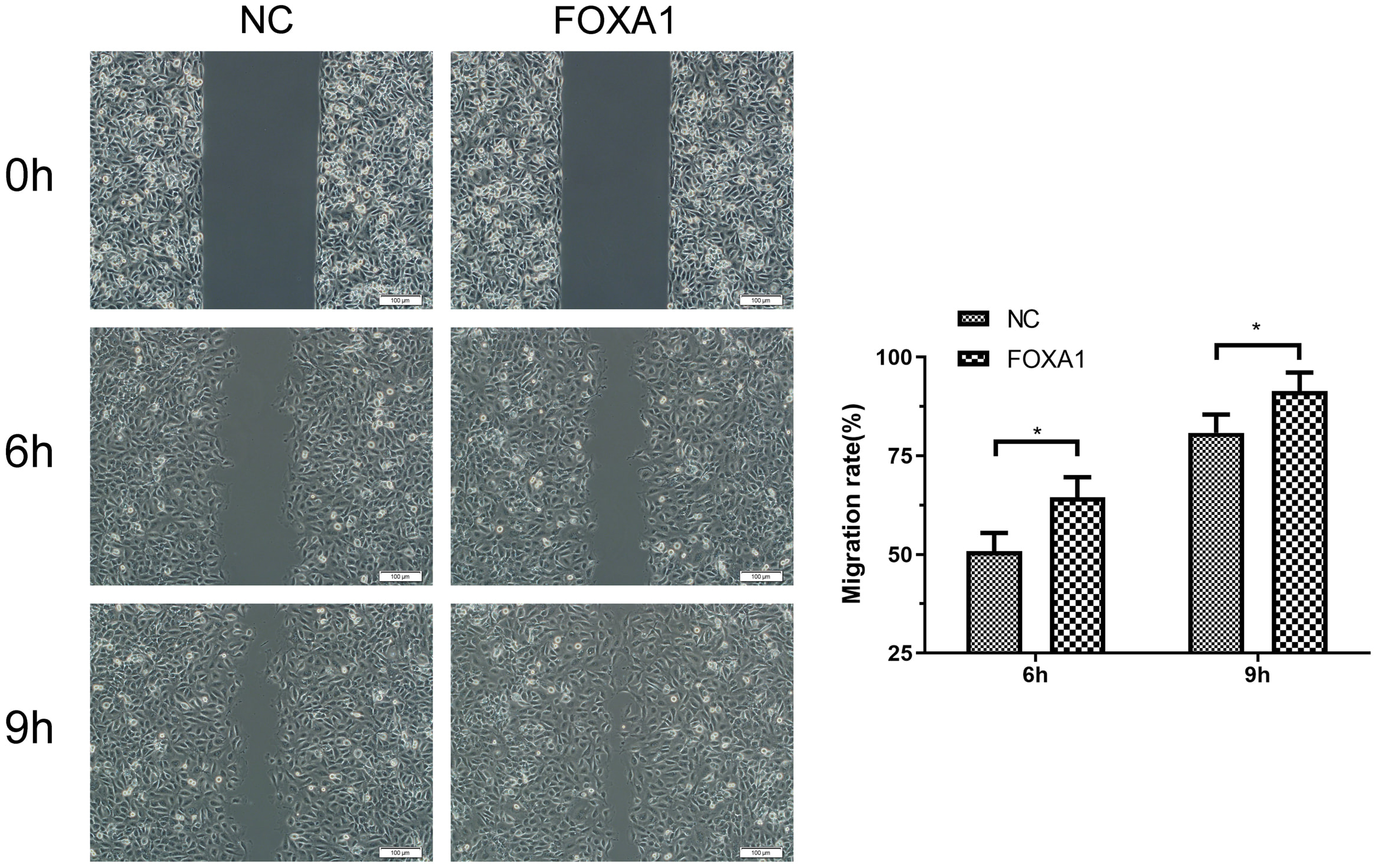 Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.Effects of FOXA1 overexpression on the cell migration of
trophoblast cells. The cell migration of HTR-8/SVneo cells from NC and FOXA1
group was determined by wound healing assay. Scale bar = 100 µm.
FOXA1, Forkhead Box A1; NC, negative control. Bar results represent the mean
To further determine the mechanism responsible for FOXA1-mediated invasion and migration in trophoblast cells, qPCR was performed to determine the mRNA expression levels of N-cadherin, vimentin and fibronectin. As shown in Fig. 7, FOXA1 had no effect on the mRNA expression levels of N-cadherin, vimentin or fibronectin comparing to the NC group.
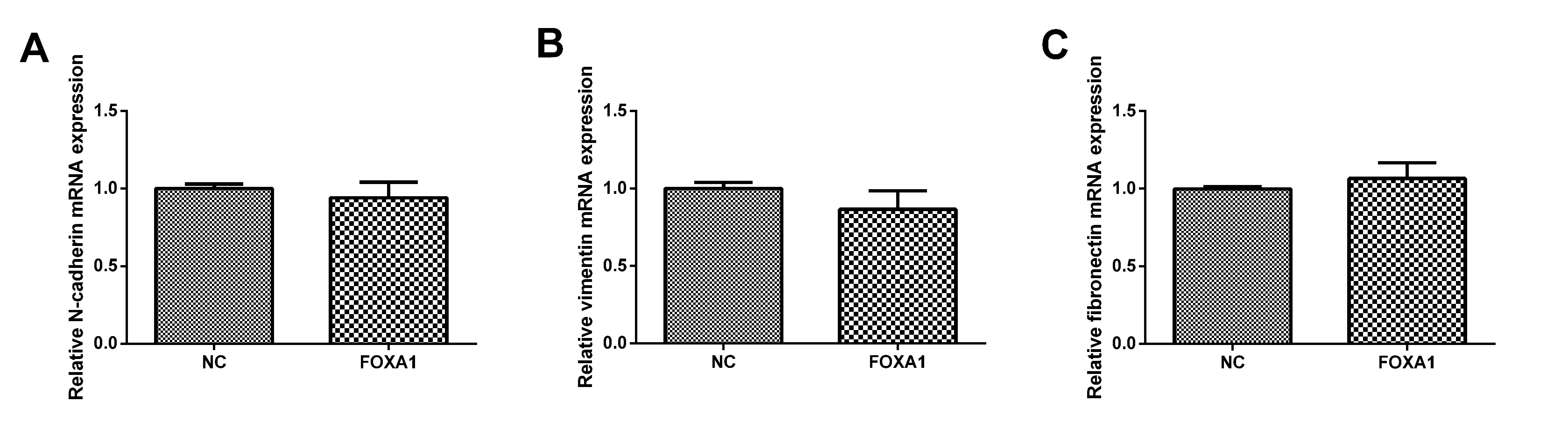 Fig. 7.
Fig. 7.Effects of FOXA1 overexpression on the mRNA expression of
N-cadherin, vimentin and fibronectin in trophoblast cells. The mRNA expressin
levels of N-cadherin, vimentin and fibronectin in HTR-8/SVneo cells from NC and
FOXA1 group was determined by qPCR. GAPDH was used as the internal control.
GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; FOXA1, Forkhead Box A1; NC, negative control.
Bar results represent the mean
PE is a complex disorder observed in pregnant women, yet its underlying pathophysiology remains to be fully understood. Mounting evidence suggests that abnormal trophoblast invasion plays a significant function in PE development [23, 24, 25]. Therefore, gaining insights into the molecular mechanisms governing trophoblast invasion is crucial to identify potential treatments for PE.
Our immunostaining results demonstrated a down-regulation of FOXA1 in placental tissues from women with LOPE in comparison to normal controls. In vitro studies further revealed that FOXA1 overexpression mitigated trophoblast apoptosis. Transwell invasion assay indicated that FOXA1 overexpression enhanced trophoblast invasive ability, while the wound healing assay showed that it also potentiated trophoblast migration. Taken together, our findings indicate that FOXA1 is down-regulated in LOPE placental tissues, and its overexpression not only affects cell cycle but also enhances trophoblast invasion and migration.
Numerous studies have explored the role of the forkhead box protein family in
the pathophysiology of PE [26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31]. FOXM1 was down-regulated in PE placental
tissues [26], and silencing FOXM1 was found to suppress trophoblast
proliferation, increase G0/G1 phase cell population, and induce apoptosis [26].
Mechanistically, FOXM1 silencing also reduced the expression of BCL-2 and
vascular endothelial growth factor in trophoblasts [26]. Another study revealed
that reduced FOXM1 expression limited trophoblast migration and angiogenesis, and
was associated with PE [27]. Zhang et al. [28] showed that FOXC2 could
promote trophoblast invasive ability through the Hedgehog signaling. Chen
et al. [29] demonstrated that FOXO1 enhanced trophoblast integrin
FOXA1, belonging to forkhead box protein family, has been extensively studied for its role in regulating cellular functions in various cancer types [16, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37]. However, its specific role in the context of PE has not been fully elucidated. Previous research by Wang et al. [21] revealed that miR-20a-mediated repression of FOXA1 could hinder proliferative/invasive capabilities of JEG-3 cells. In our study, we observed that FOXA1 expression was downregulated in LOPE placental tissues. Further functional investigations demonstrated that FOXA1 overexpression could promote trophoblast proliferation, invasion, and migration, while having no significant effect on trophoblast apoptosis. These findings shed light on underlying function of FOXA1 in LOPE pathophysiology, suggesting its involvement in regulating trophoblast behaviors and warranting further exploration.
In early pregnancy, the invasion of EVTs is a crucial process for the development of the placenta [38]. The precise mechanism responsible for trophoblast invasion remains not entirely clear. Various factors such as hormones, cytokines, growth factors, and proteinases have been implicated in this process [38]. Notably, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) are essential for facilitating trophoblast invasion by breaking down the extracellular matrix [39]. For instance, MMP9 and MMP2 are two well-known enzymes that play a pivotal role in trophoblast invasion [40]. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during development and the differentiation of cytotrophoblasts into EVT share similarities [41]. During normal placental formation, EVTs undergo a transformation from an organized epithelial phenotype to a migratory and invasive mesenchymal phenotype, which allows them to infiltrate the maternal decidual stroma and blood vessels [42]. However, the disruption of EMT hinders the trophoblasts’ ability to migrate and invade effectively. These findings underscore the importance of regulating EMT during the growth of trophoblast cells [42]. In the present study, we found that the expression of EMT-related markers, including N-cadherin, vimentin and fibronectin was not affected by FOXA1 overexpression in the trophoblast cells. These results indicate that the enhanced trophoblast cell invasion and migration mediated by FOXA1 overexpression could involve other mediators, such as MMPs and TIMPs, which still require further examination.
Our study has several limitations. First, the sample size in the current study is relatively small, and future studies should include larger clinical samples to validate our findings. Second, we only examined the effects of FOXA1 overexpression on trophoblast cell apoptosis, invasion, and migration in the HTR-8/SVneo cell line. As HTR-8/SVneo belongs to a type of first trimester cell line, utilizing primary trophoblast cells, BeWo, or JEG3 cells for similar investigations would bolster our findings. Third, the mechanisms responsible for FOXA1-mediated invasion and migration in trophoblast cells have not been elucidated, and future studies are needed to fully understand these underlying mechanisms.
In summary, our findings reveal a reduction in FOXA1 expression in the placentas of patients with LOPE. Furthermore, we observed that the overexpression of FOXA1 enhances the migratory and invasive abilities of trophoblast cells. These results suggest that FOXA1 could potentially be a therapeutic target for managing LOPE.
Data are available upon request.
YM, ZY and JZ conceived/designed the study. JZ, YW, ZW and QJ performed experiments. QJ, PL, HY and HK contributed to analysis. JZ, QJ and ZY analyzed the data. JZ wrote the manuscript. YM and ZY reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Ethical approval for study was granted by Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical College (approval number: 2022-50). All subjects provided written informed consent.
Not applicable.
This work was supported by Hainan Province Science and Technology Special Fund (No. ZDYF2020121), Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 822RC836, No. 821RC702), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81960283), the specific research fund of The Innovation Platform for Academicians of Hainan Province, Hainan Province Clinical Medical Center.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Publisher’s Note: IMR Press stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.







