- Academic Editor
-
-
-
Announcements
Open Access
Opinion
Beyond Passive Bystander: Glioblastoma-Educated Astrocyte Suppressing T Cell
Yuan-Yuan Wang1,2, Wei-Lin Jin1,*
Show Less
Affiliation
1
Institute of Cancer Neuroscience, Medical Frontier Innovation Research Center, The First Hospital of Lanzhou University, The First Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University, 730000 Lanzhou, Gansu, China
2
School of Life Science, Lanzhou University, 730000 Lanzhou, Gansu, China
*Correspondence:
ldyy_jinwl@lzu.edu.cn (Wei-Lin Jin)
Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2025, 30(10),
44810;
https://doi.org/10.31083/FBL44810
Submitted:
11 July 2025 |
Revised:
4 September 2025 |
Accepted:
11 September 2025 |
Published:
31 October 2025
Copyright: © 2025 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
This is an open access article under the
CC BY 4.0 license.
Abstract
Faust Akl et al. revealed in Nature a paradigm-shifting mechanism distinct from myeloid-driven immunosuppression, whereby glioblastoma induces T-cell apoptosis via tumor-derived IL-11, prompting astrocytes to reprogram into immunosuppressive tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)+ effectors, thereby establishing astrocytes as active immunomodulators. Therapeutically, herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) (anti-TRAIL) achieves a dual therapeutic effect, offering novel strategies to overcome glioblastoma (GBM)’s evasion tactics.
Keywords
astrocyte
IL-11
glioblastoma
oncolytic virus
STAT3
immune-suppressive TME
Funding
High Level Talent Introduction Funds from the First Hospital of Lanzhou University
Figures
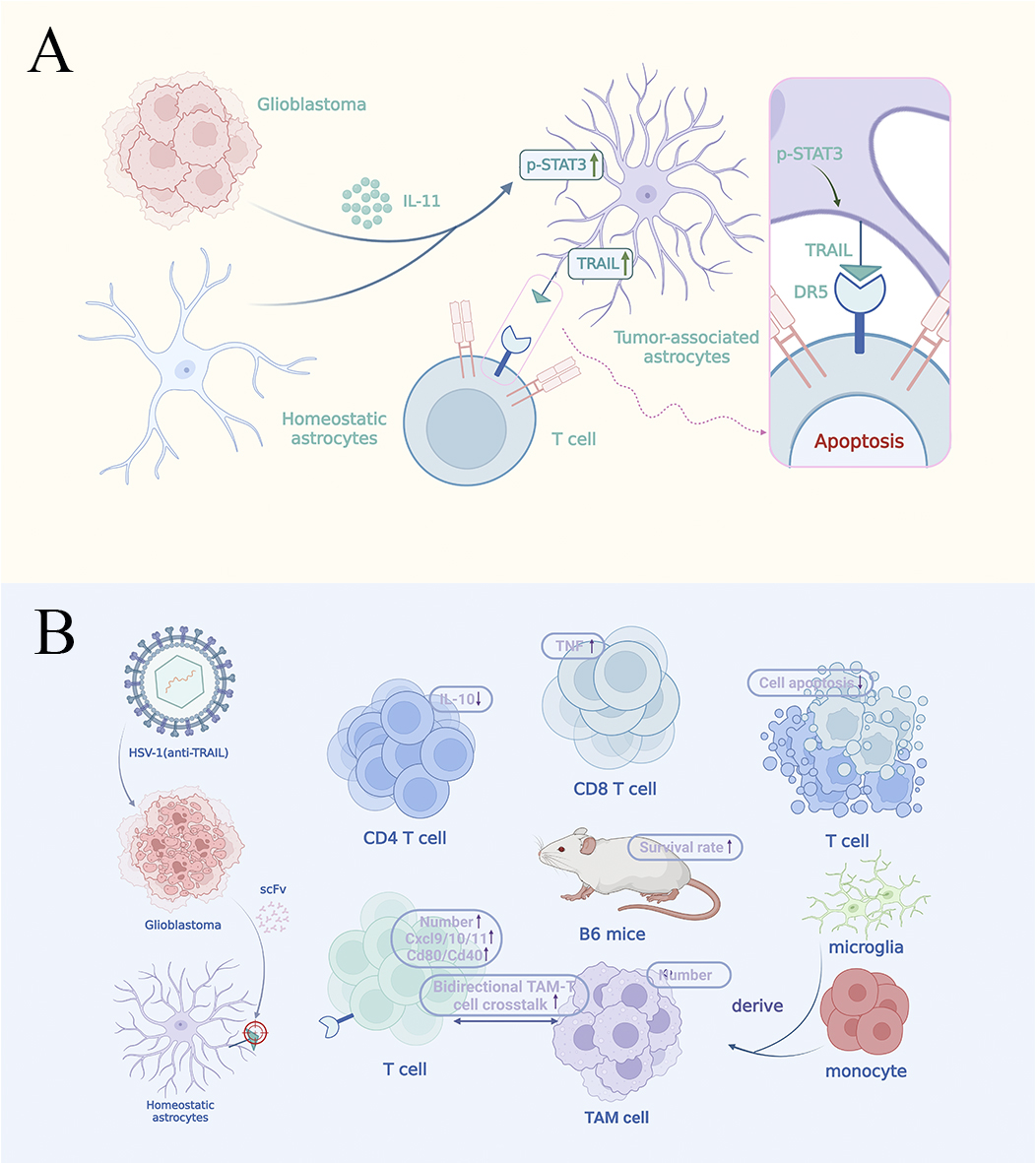
Fig. 1.

