Background: Dexmedetomidine (DEX) reportedly protects against
ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury and associated damage to the kidneys, but the
underlying mechanisms have yet to be established. Methods: Unilateral
nephrectomy was performed in Wistar rats, and the remaining kidney was clamped
for 1 h prior to reperfusion to establish an experimental model system. These
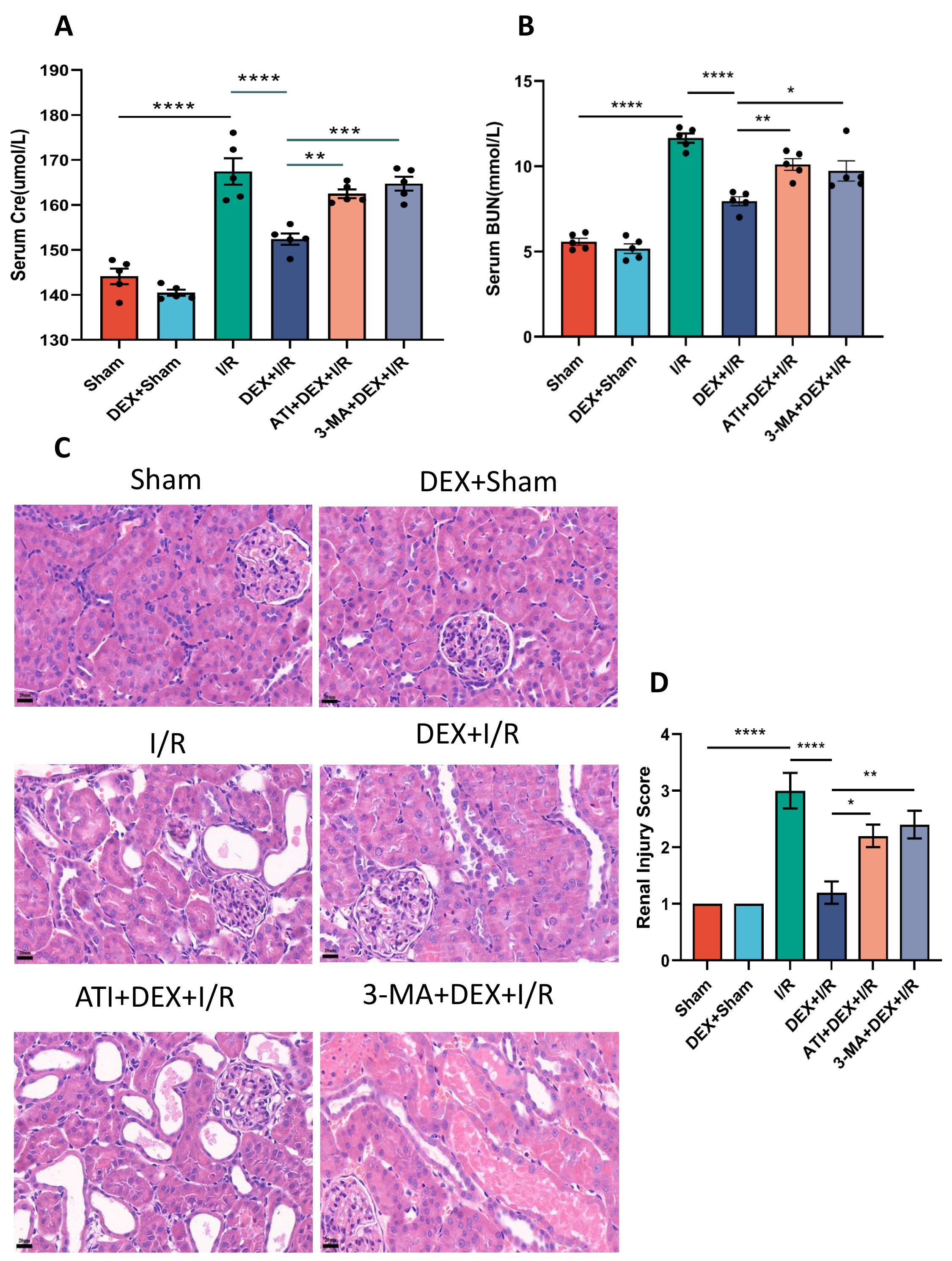
animals were then randomized into Sham, DEX + Sham, DEX + I/R, ATI (Altepamizole,
2-adrenergic receptor inhibitor) + DEX + I/R, and 3-MA
(3-methyladenine, autophagy inhibitor) + DEX + I/R groups. Serum renal function
biomarkers, acute kidney injury (AKI) histopathological scores, serum
inflammatory factors, redox biomarkers, markers of autophagic flux, and
autophagosome numbers were assessed. Levels of proteins related to the autophagic
pathway, including mTOR and AMPK, were also analyzed. Results: Serum
creatinine and urea nitrogen levels in the I/R group were significantly elevated
over those in sham control rats, as were AKI scores, serum inflammatory cytokine
concentrations (IL-6, IL-1, and TNF-), and serum levels of the
oxidative stress biomarker malondialdehyde (MDA). All of these parameters were
significantly reduced in the DEX + I/R group relative to I/R model rats. I/R
group rats also exhibited significant decreases in renal levels of autophagic
flux-related biomarkers and autophagosome numbers relative to sham controls,
while DEX administration partially restored normal autophagic flux in these rats.
Acute I/R also suppress the expression of AMPK in the kidney while increasing
mTOR expression, and DEX reversed these effects. The beneficial impact of DEX on
I/R-associated AKI was ablated by ATI or 3-MA administration.
Conclusions: These analyses provide strong evidence for the ability of
DEX to protect against I/R-associated AKI via the
2-AR/AMPK/mTOR pathway-mediated enhancement of autophagic activity.