-
- Academic Editor
-
-
-
Intrinsic factor (IF) is a glycoprotein crucial for cobalamin (vitamin B12) absorption in the human body. This study aimed to evaluate the binding affinity of nitrosylcobalamin (NO-Cbl), a cobalamin analog, to recombinant human IF derived from plants, using hydroxocobalamin (OH-Cbl) as a comparative standard.
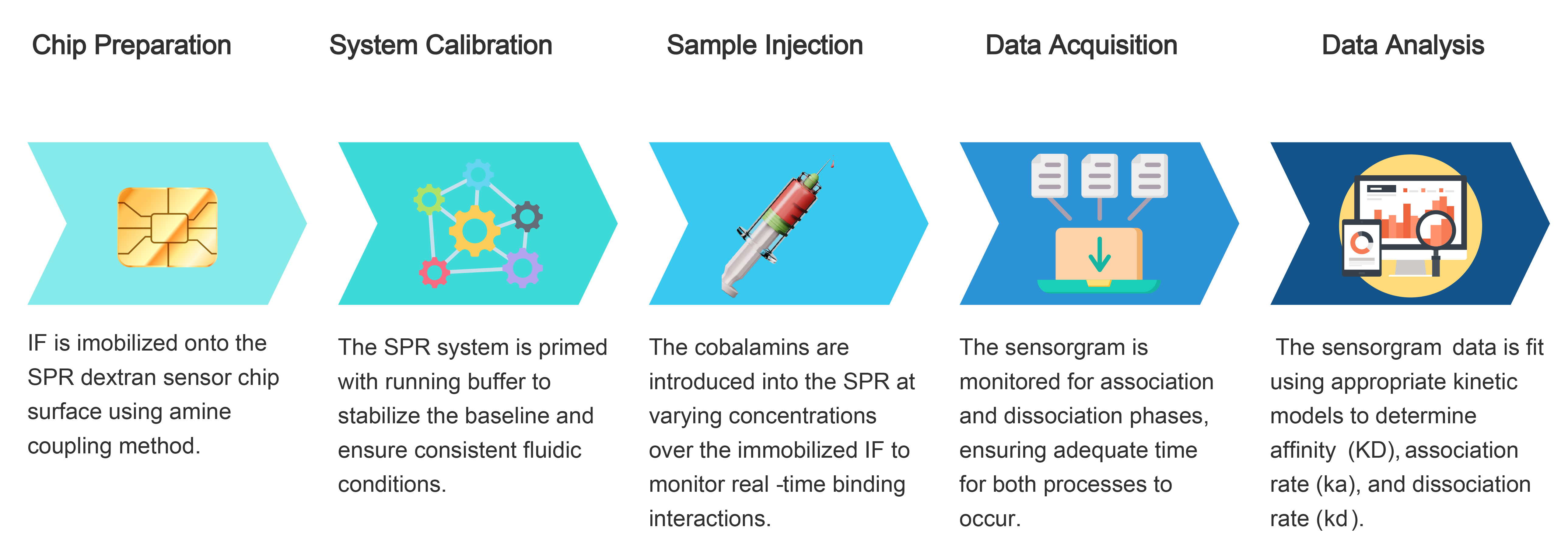
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was employed to assess the kinetic parameters of NO-Cbl and OH-Cbl interactions with plant- derived IF across various concentrations.
SPR analysis demonstrated that NO-Cbl and OH-Cbl exhibited high binding affinities to IF, with equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) values in the picomolar range. OH-Cbl showed a slightly stronger binding affinity (KD = 4.79 × 10-11 M) than NO-Cbl (KD = 8.58 × 10-11 M). Despite NO-Cbl and OH-Cbl both being bound to IF, differences in binding affinity and stability were observed, particularly at higher concentrations.
Variations in IF binding between NO-Cbl and OH-Cbl may be attributed to the saturation of binding sites or recognition issues specific to plant-derived IF. This study underscores the potential of NO-Cbl as a targeted therapeutic agent capable of leveraging natural cobalamin uptake pathways. These results also highlight the suitability of using recombinant plant-derived IF as a model for predicting the biological activity of cobalamin analogs despite the nuanced differences from native human IF.