- Academic Editor
-
-
-
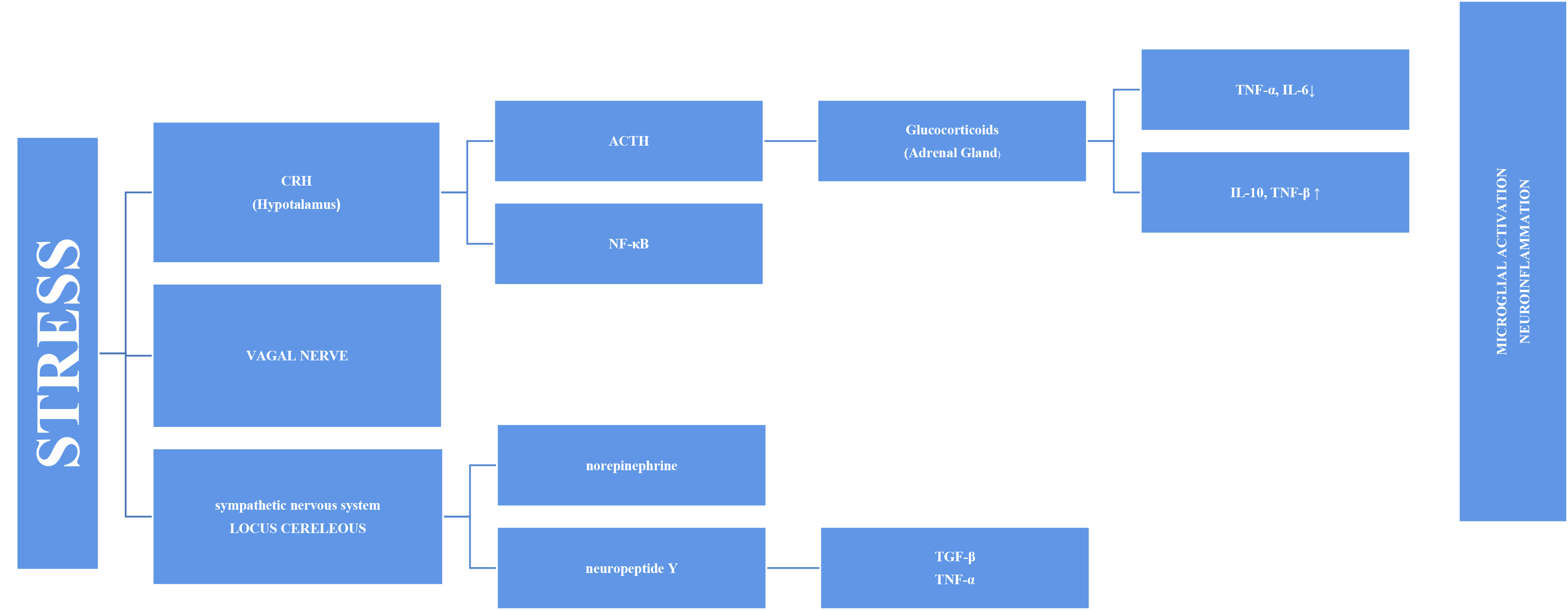
The feeling of emotional tension, restlessness, pressure, and inability to relax is referred to as psychological stress. Although it is unclear how psychological stress affects neurobiological processes, several factors are thought to be involved, including central and peripheral neuroinflammation, structural degeneration in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, alterations in fear neurocircuitry, and neuroplasticity. Aside from data relating cognitive impairment to chronic low-grade inflammatory stress, there is growing evidence linking mental stress, oxidative stress, and systemic inflammation to the development of psychological disorders. After chronic and acute illnesses, insomnia, depression, anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, and cognitive impairment were reported. Cognitive impairment is exacerbated by systemic and central inflammatory processes. There is uncertainty about the potential mechanisms causing these symptoms, although they are likely complex, with systemic inflammation playing a significant role. Therefore, this review aims to investigate the role of inflammation in stress-induced cognitive impairment. Depicting the inflammatory mechanisms of cognitive impairment is critical for understanding and treating illnesses, such as chronic stress exposure and anxiety disorders.