- Academic Editors
-
-
-
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is one of the most prominent diseases seen in pregnancy that adversely affects materno-fetal welfare. It is usually screened by an oral glucose tolerance test (GTT), which has some limitations. Adiponectin and triglyceride-glycemic (TyG) index were two biomarkers examined in the GDM context with inconclusive effectiveness. This study aimed to examine both markers' performance in screening for GDM among Iraqi women.
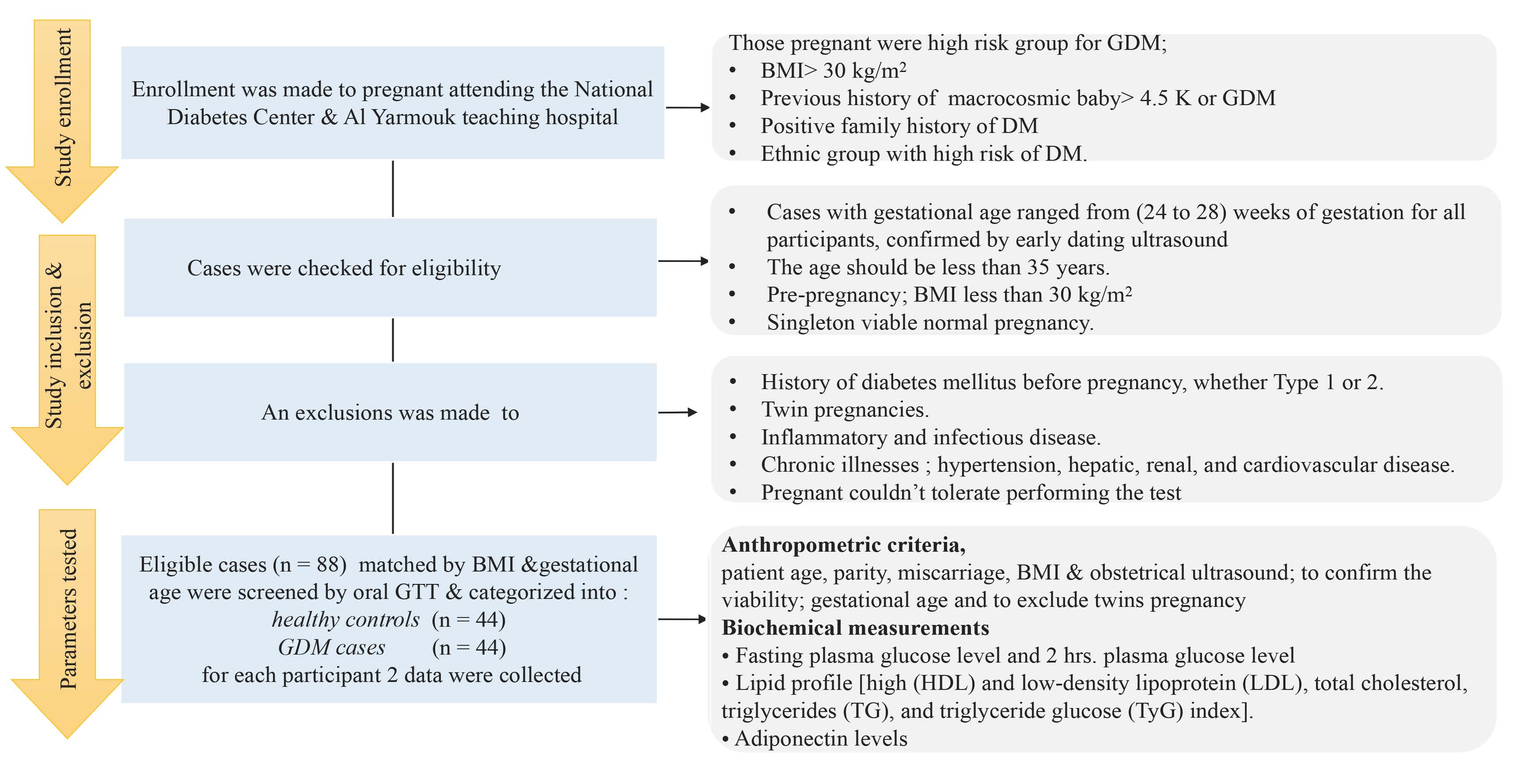
An observational cross-sectional study recruited gestational age and body mass index (BMI) matched pregnant at 26–28 weeks into two groups: healthy controls (n = 44/88) and GDM cases (n = 44/88). Participants' demographics, biochemical [FBS (fasting blood sugar), 2hr_GTT (2-hour glucose tolerance test), HDL (high-density lipoprotein), LDL (low-density lipoprotein), total cholesterol, TG (triglyceride), and TyG index], and hormonal (adiponectin) were recorded.
Serum adiponectin was significantly higher among healthy pregnant (8.44 ± 1.12 ng/mL vs. 5.28 ± 0.89 ng/mL); p < 0.0001. In contrast, the TyG index was significantly higher among GDM cases (4.02 ± 0.04 vs. 3.96 ± 0.02; p < 0.0001). Adiponectin showed strong inverse links with FBS, 2hr_GTT with r = (–0.76, –0.80); p < 0.0001, respectively. TyG index was moderately, inversely, and significantly linked to serum adiponectin as r = –0.58; p < 0.0001. Adiponectin and TyG index reliably predicted GDM with a high area under the curve of 0.83 vs. 0.88; p < 0.001, respectively.
Both biomarkers correlated well to GDM parameters and showed high sensitivity and specificity in screening for GDM. Their efficiency, easy integrations in practice, and promising therapeutic application suggested by researchers warrant further studies.