-
- Academic Editor
-
-
-
†These authors contributed equally.
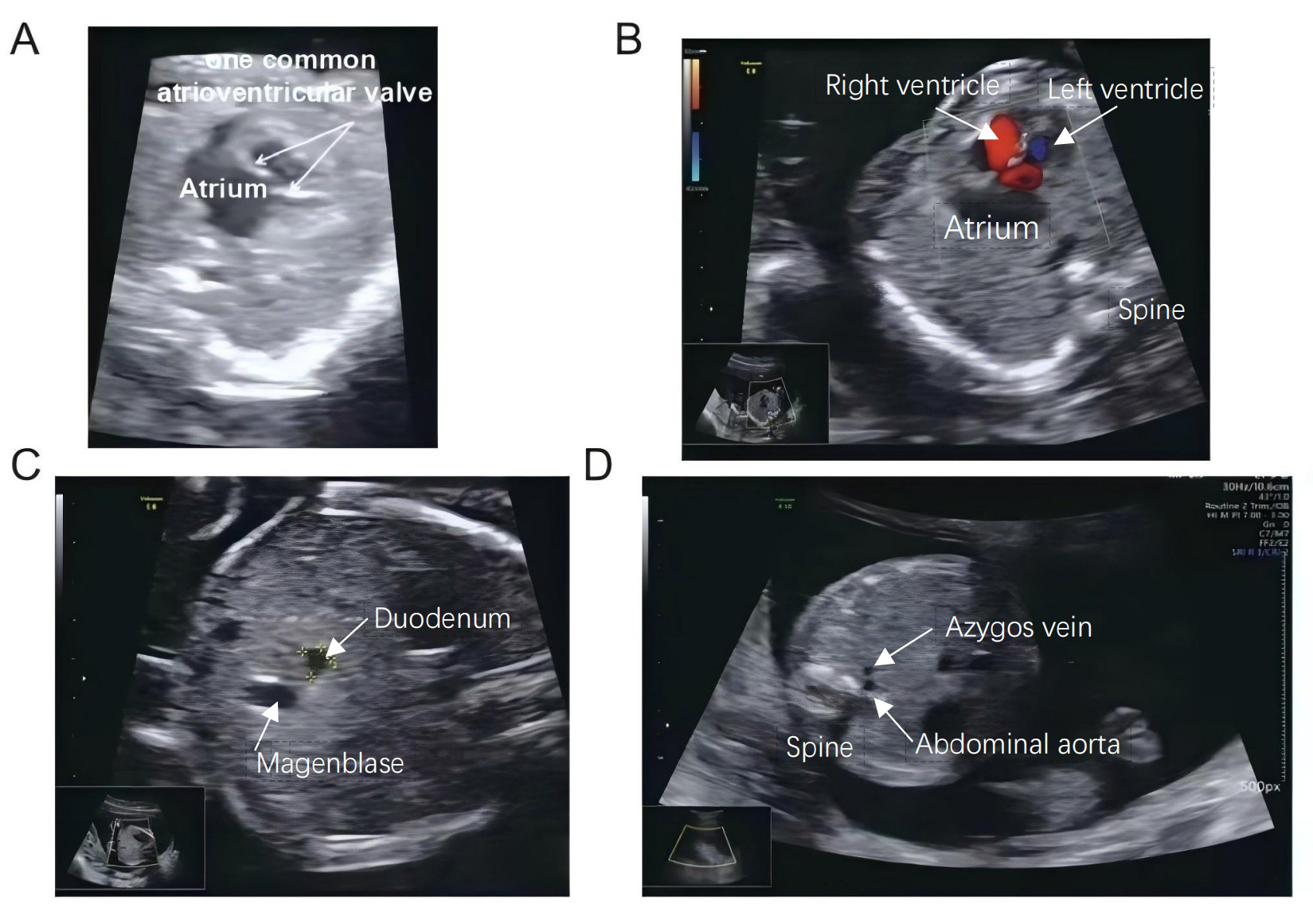
Heterotaxy syndrome is characterized by abnormal organ arrangement across the left-right (L-R) axis, often leading to complex congenital heart defects (CHDs). Genetic analysis via whole-exome sequencing revealed two novel compound heterozygous mutations in the polycystic kidney disease 1 like 1 (PKD1L1) gene (NM_138295.3: c.6659T>A and c.8104dup). These genetic alterations are implicated in the abnormal development of the L-R axis, contributing to the severe cardiac malformations observed.
This case report describes a Chinese fetus diagnosed with heterotaxy and severe cardiac anomalies identified through prenatal ultrasound.
Our results expand the known spectrum of PKD1L1 mutations and highlight the importance of genetic testing in prenatal diagnosis of heterotaxy. These findings emphasize the value of genetic testing in informing clinical decisions and guiding reproductive counseling.