†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: Michael H. Dahan
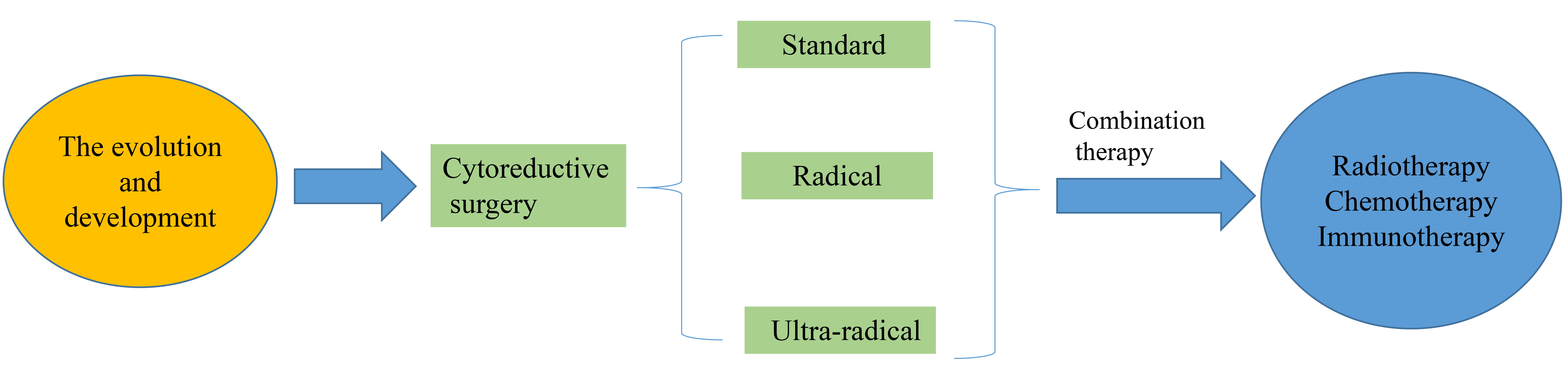
Objective: Ovarian carcinoma is a malignant tumor with the highest mortality of any cancer occurring in female reproductive system. Cytoreductive surgery is the main treatment for ovarian cancer and has markedly improved. Mechanism: This article discusses the evolution and development of ovarian cancer cytoreductive surgery (CRS), including classical standard tumor cell reduction, visceral-peritoneal debulking (VPD) and ultra-radical cytoreduction (URC). Findings in Brief: we reviewed CRS in combination with radiotherapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy for ovarian cancer (OC). Finally, we discussed the opportunity and challenges of ROC therapeutic. Conclusions: This study reveals that CRS and combination therapy can help clinicians to find the optimum treatment for ovarian cancer (OC).