Academic Editor: Michael H. Dahan
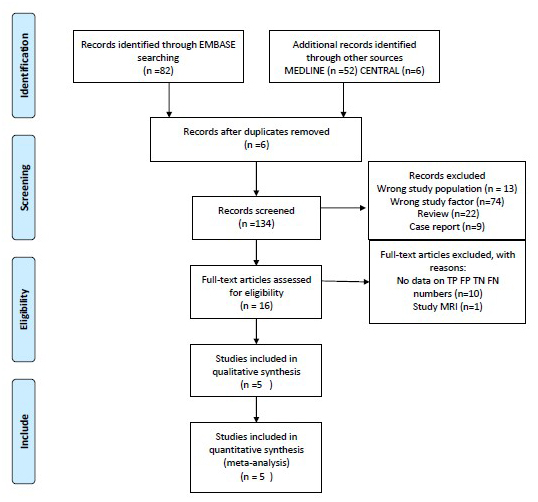
Objective: To assess the accuracy of ultrasound in diagnosing acute appendicitis in pregnant women. Mechanism: The National Library of Medicine (MEDLINE, 1990–2020), Excerpta Medica Database (EMBASE,1946–2020) and the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (CENTRAL) were used to extract articles that were published in English. A total of five studies involving 521 patients were selected. The DerSimonian and Laird random-effects model and Quality Assessment Tool for Diagnostic Accuracy (QUADAS-2) were used to analyze the data. Findings in brief: We identified 140 related articles and included 5 articles enrolling 521 patients. The values obtained using ultrasound for appendicitis during pregnancy were sensitivity of 0.62 (95% Confidence interval (CI): 0.43–0.78), the specificity of 0.91 (95% CI: 0.74–0.97), and the Positive Likelihood Ratio of 7.0 (95% CI: 2.5–19.7), the Negative Likelihood Ratio of 0.41 (95% CI: 0.27–0.63) and the Diagnostic Odds Ratio of 17 (95% CI : 6–49). Conclusion: Ultrasound had medium-level sensitivity and high specificity for the diagnosis of appendicitis in pregnant women.