- Academic Editor
-
-
-
Male infertility is a critical factor in the success of in vitro fertilization (IVF), yet a comprehensive predictive model for assessing its risk remains lacking. This study aimed to explore the factors affecting the high-quality embryo rate in male infertility patients, as well as to develop targeted intervention measures.
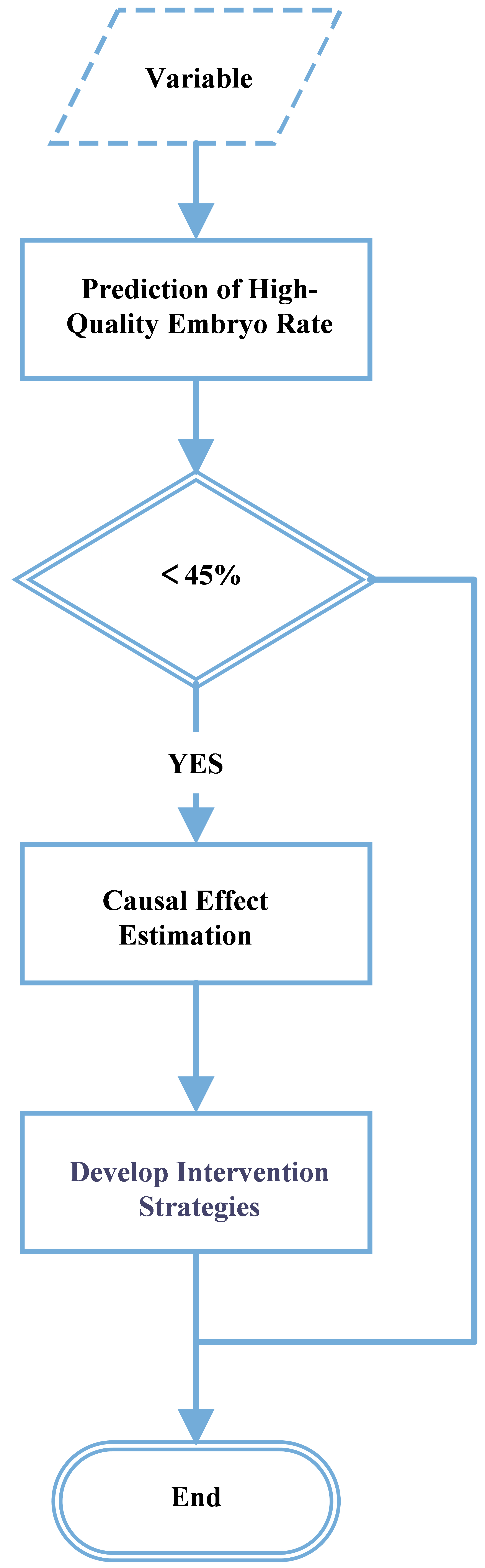
A retrospective analysis was performed using clinical data from 373 infertility couples who underwent IVF treatment, and the couples were grouped based on a high-quality embryo rate of ≥45% and <45% for statistical analysis. We developed an outcome prediction model and a causal effect estimation model to evaluate the impact of different intervention measures, based on the results of univariate logistic regression analysis.
The results demonstrated significant differences in Antral Follicle Count (AFC), sperm DNA fragmentation index (DFI), male height, male weight, and mycoplasma infection. Further univariate logistic regression analysis identified that AFC, basal luteinizing hormone (LH), sperm DFI, male height, male weight, and mycoplasma infection significantly affected the high-quality embryo rate, all showing negative correlations. The dataset was divided into a training set (80%) and a test set (20%) for the construction and validation of the outcome prediction model and the causal effect estimation model. The causal effect estimation model for mycoplasma infection demonstrated that treating mycoplasma infection could increase the high-quality embryo rate. The causal effect estimation model for sperm DFI revealed that reducing sperm DFI could increase the high-quality embryo rate. The causal effect estimation model for male weight demonstrated that being overweight can reduce the high-quality embryo rate.
Reducing sperm DFI levels, weight loss, and treating mycoplasma infection are effective methods for improving the high-quality embryo rate in male infertility.