Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark (FBL) is published by IMR Press from Volume 26 Issue 5 (2021). Previous articles were published by another publisher on a subscription basis, and they are hosted by IMR Press on imrpress.com as a courtesy and upon agreement with Frontiers in Bioscience.
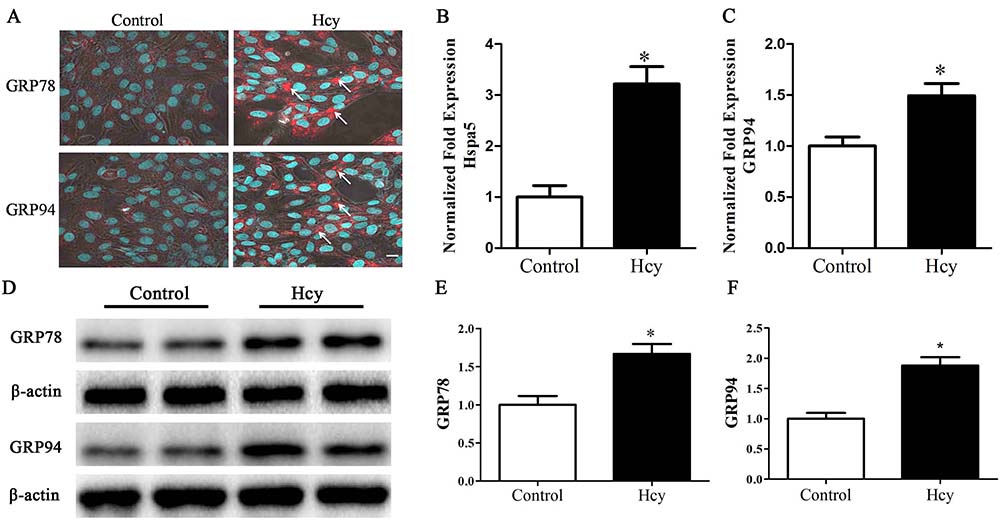
Hyperhomocysteinemia induces stress response in endoplasmic reticulum (ERS). Here, we tested whether blockage of homocysteine (Hcy) induced ERS and subsequent apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells can be inhibited by blockage of PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP signaling. Short-term exposure of vascular smooth muscle cells to Hcy led to the phosphorylation of PERK (pPERK), which in turn, phosphorylated eIF2 alpha (peIF2α) and inhibited the unfolded protein response. Long-term Hcy exposure, however, increased the expression of ATF-4 and CHOP and led to apoptosis. Treatment of cells with salubrinal, a specific inhibitor for eIF2α decreased the expression of ATF-4 and CHOP, and prevented apoptosis. Together, the results show that PERK pathway is involved in Hcy-induced vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis and that blocking the PERK pathway protects against this injury.