Academic Editor: Peter A. McCullough
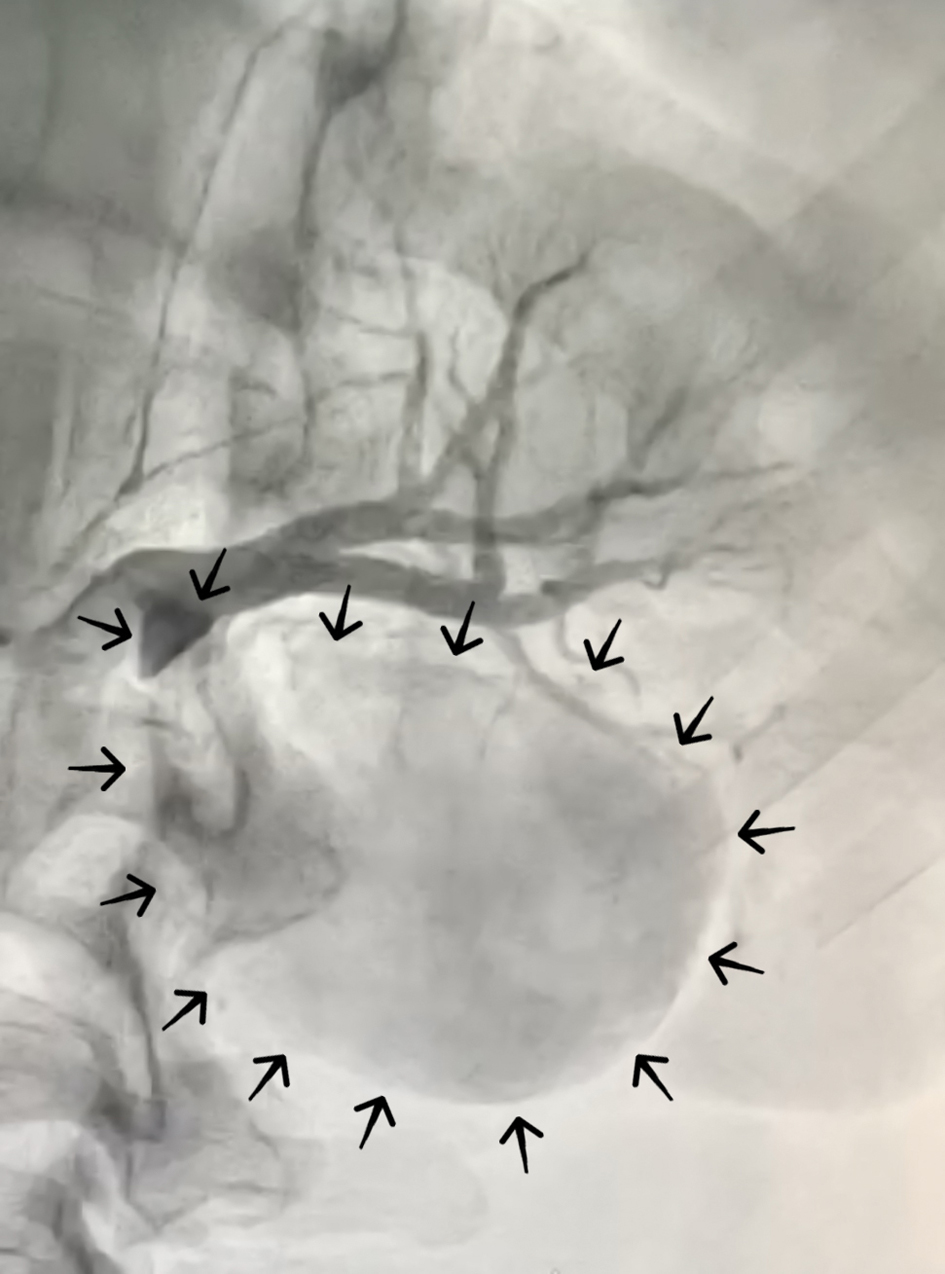
Renal artery aneurysms, although rare, may give rise to complications both per se (due to the risk of thrombosis and subsequent wall rupture) and by impairment of the renal function (due to extrinsic compression and high blood pressure). We describe a paucisymptomatic young patient with acute thrombosis of a massive dissecting renal artery aneurysm, for which the successful treatment was performed through ex-vivo vascular surgery followed by autotransplantation of the reconstructed kidney. The aneurysm was described through abdominal echography, computed tomography angiography, and transfemoral transcatheter arterial angiography. It originated from an atypical branch emerging at 90 degrees from the left renal artery. After a short branching off, it degenerated into a dissected aneurysmal sac as large as half a kidney (outer diameter of 60 mm), compressing the lower pole of the left kidney and delaying the lower half nephrogram. Ex-vivo surgical exclusion of the aneurysm was successfully performed. The kidney was reimplanted in the left iliac fossa (termino-lateral anastomosis between the renal artery and external left iliac artery, termino-terminal ureteric anastomosis) with excellent postoperative outcomes. For most asymptomatic aneurysms, expectant treatment is a reasonable approach. However, interventional or surgical repair is indicated in certain circumstances depending on the size of the aneurysm and its natural history, rupture risk, and interventional/surgical risks. The renovascular hypertension, dissecting and thrombotic events, its giant size, the young fertile age, and the presence of the flank pain were all indicative of the need for aneurysm exclusion in our case.