†These authors contributed equally.
Academic Editor: Hsien-Yuan Lane
This is an open access article under the CC BY 4.0 license.
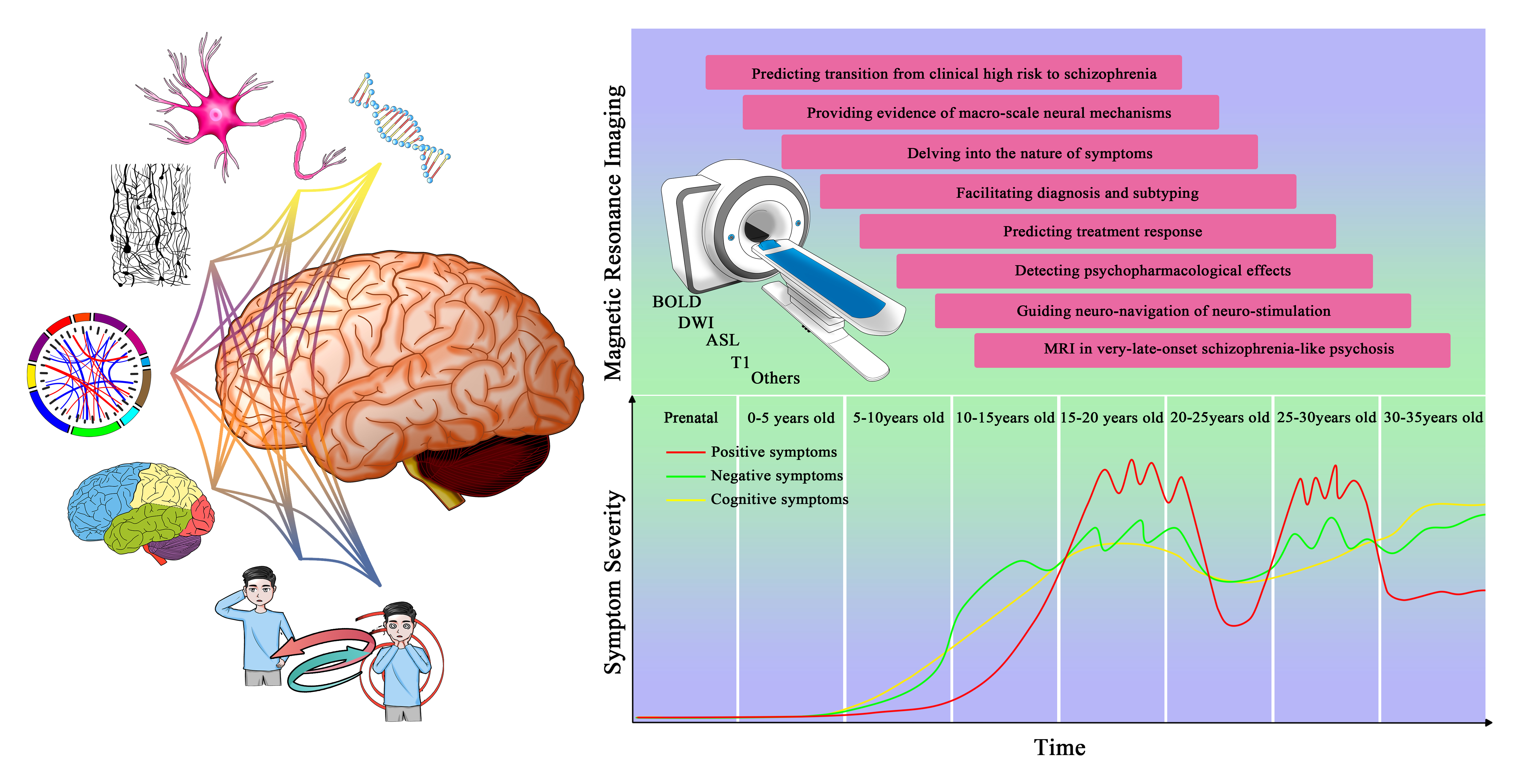
As a non-invasive detection method and an advanced imaging method, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been widely used in the research of schizophrenia. Although a large number of neuroimaging studies have confirmed that MRI can display abnormal brain phenotypes in patients with schizophrenia, no valid uniform standard has been established for its clinical application. On the basis of previous evidence, we argue that MRI is an important tool throughout the whole clinical course of schizophrenia. The purpose of this commentary is to systematically describe the role of MRI in schizophrenia and to provide references for its clinical application.